Whole-Body 3D Pose Estimation Based on Body Mass Distribution and Center of Gravity Constraints
Abstract
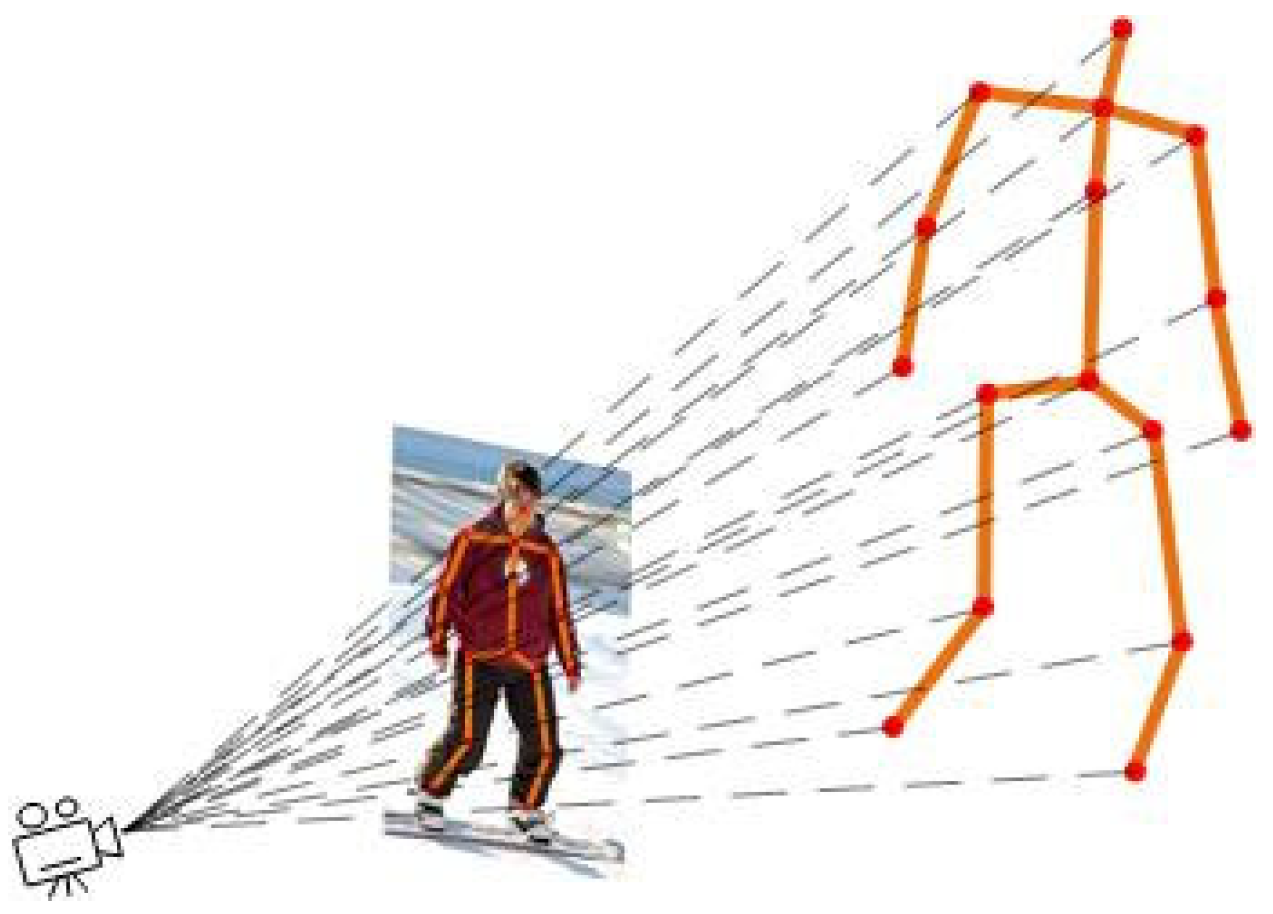
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Challenges
1.2. Related Work
1.2.1. Transformer Structure
1.2.2. Whole-Body 3D Pose Estimation
1.3. Research Gap and Our Contributions
- We propose a new method for whole-body 3D pose estimation on the basis of the body mass distribution and center of gravity position constraints, and our method achieves the SOTAs on a widely used dataset.
- Based on the observation of different postures and weight changes in the human body and the research of existing methods, the changing rules of the center of gravity of the human body under different postures are fully considered, and the prior information in the process of estimating the human body posture is increased in the network, which effectively solves the problem of the inaccurate estimation of keypoint positions due to occlusion in the posture estimation process.
- On the basis of the mass distribution relationship of human body segments, we add body mass distribution constraints when the network is used to estimate the whole-body poses, establish a mapping relationship between the center of gravity position and the human body pose, and use two different methods to encode the keypoint position information, thereby improving the accuracy of pose estimation.
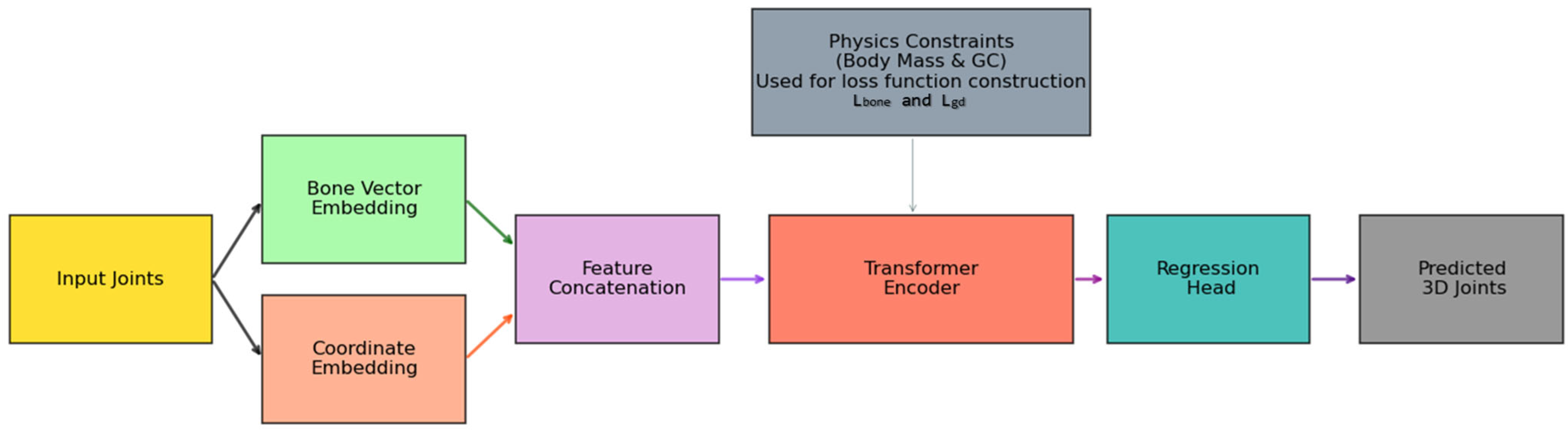
2. Methodology
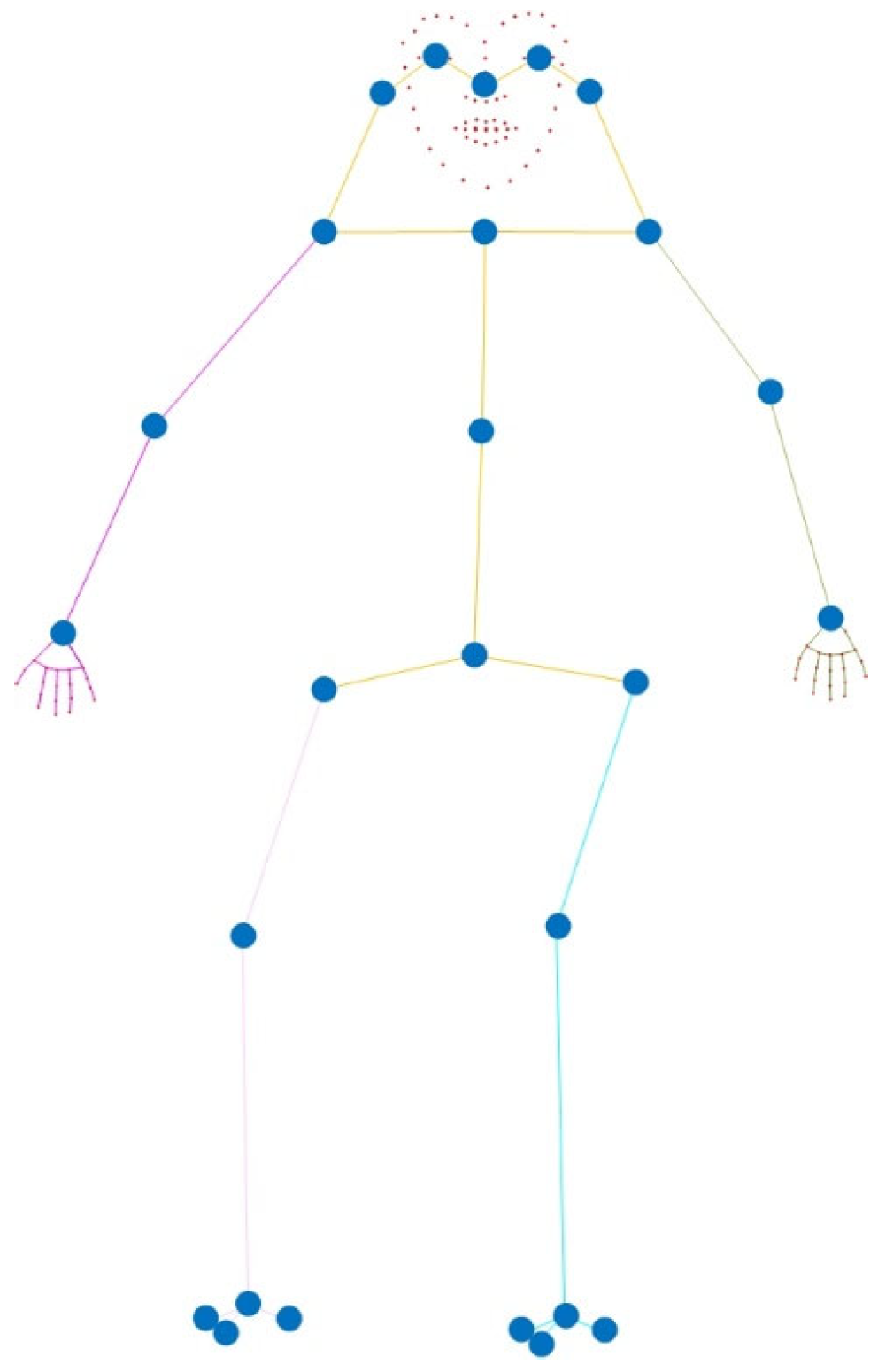
2.1. Keypoint Position Encoding Based on the Human Body Structure
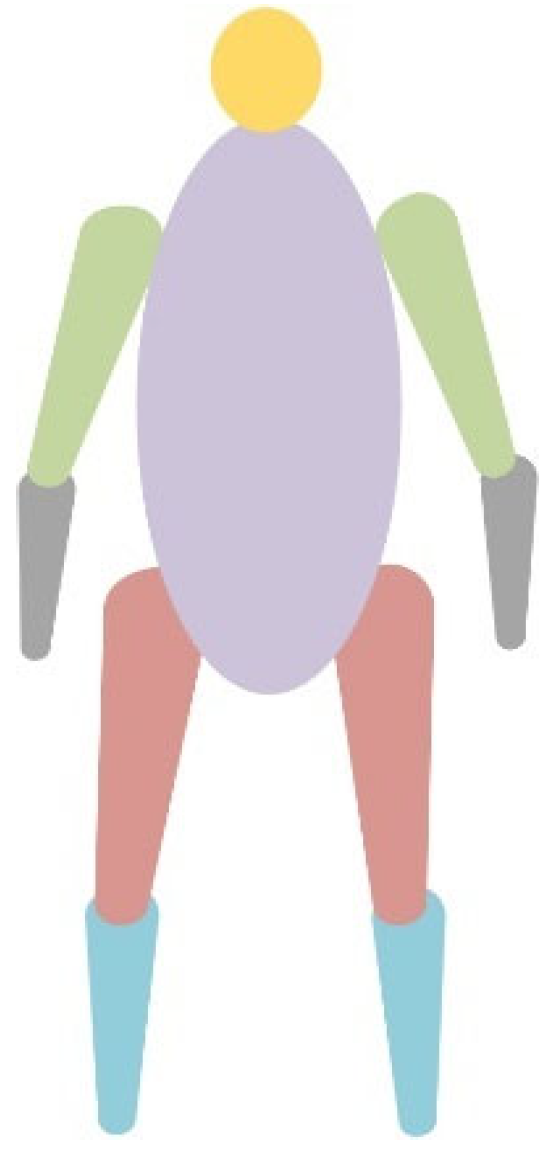
2.2. Body Mass Distribution and Center of Gravity Constraints
2.3. Loss Function
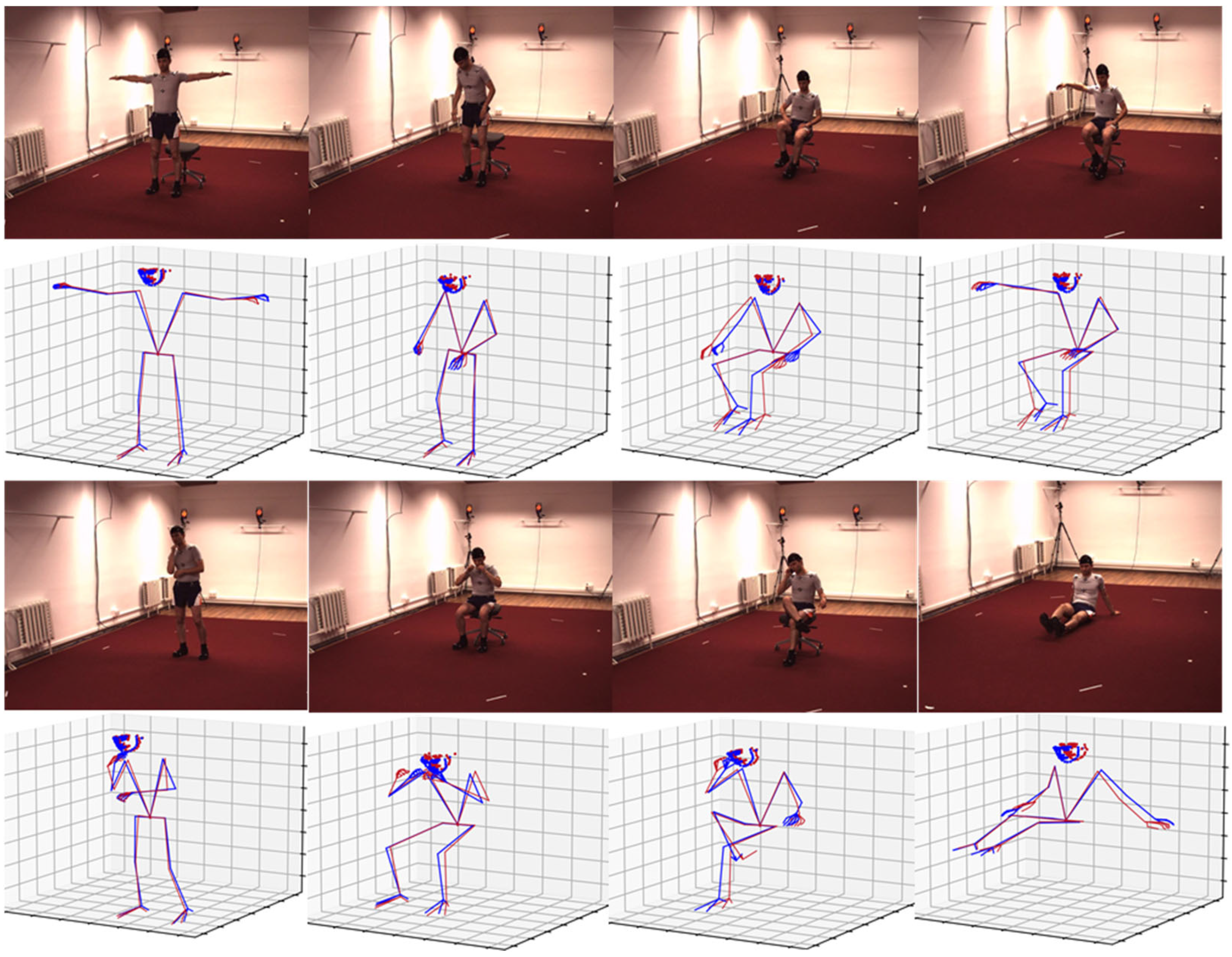
3. Experiments
3.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
3.2. Implementation Details
3.3. Performance Comparison
3.4. Ablation Study
3.4.1. Effects of the Body Mass Distribution and Center of Gravity Position Constraints
3.4.2. Impact of the Loss Function
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huo, R.; Gao, Q.; Qi, J.; Ju, Z. 3d human pose estimation in video for human-computer/robot interaction. In International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 176–187. [Google Scholar]
- Grabner, A.; Roth, P.M.; Lepetit, V. 3d pose estimation and 3d model retrieval for objects in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3022–3031. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Diao, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, G. The reliability and validity of gait analysis system using 3D markerless pose estimation algorithms. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 857975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Divya, R.; Peter, J.D. Smart healthcare system-a brain-like computing approach for analyzing the performance of detectron2 and PoseNet models for anomalous action detection in aged people with movement impairments. Complex Intell. Syst. 2022, 8, 3021–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-Y.; Ting, P.-W.; Tang, Y.-H.; Chou, E.-T.; Fu, L.-C. Hand pose estimation in object-interaction based on deep learning for virtual reality applications. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2020, 70, 102802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Dong, W.; Fan, B. A survey on depth ambiguity of 3D human pose estimation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Hwang, J.; Kwak, N. 3D human pose estimation using convolutional neural networks with 2D pose information. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2016 Workshops: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, October 8–10 and 15–16, 2016, Proceedings, Part III 14; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2016; pp. 156–169. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.-J.; Lundeen, K.M.; McGee, W.; Menassa, C.C.; Lee, S.; Kamat, V.R. A vision-based marker-less pose estimation system for articulated construction robots. Autom. Constr. 2019, 104, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.; Gavrila, D.M. Multi-view 3D human pose estimation in complex environment. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 96, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Roy-Chowdhury, A. Inverse compositional estimation of 3d pose and lighting in dynamic scenes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Savarese, S.; Fei-Fei, L. 3D generic object categorization, localization and pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 14–21 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Trivedi, M.M. A two-stage head pose estimation framework and evaluation. Pattern Recognit. 2008, 41, 1138–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessanha Santos, N.; Lobo, V.; Bernardino, A. Two-stage 3D model-based UAV pose estimation: A comparison of methods for optimization. J. Field Robot. 2020, 37, 580–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-K.; Cheng, K.-Y. 3D Human pose estimation by an annealed two-stage inference method. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; pp. 535–538. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Long, P. 3D human pose estimation in motion based on multi-stage regression. Displays 2021, 69, 102067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Bao, Q.; Sun, Y.; Mei, T. Recent advances of monocular 2D and 3D human pose estimation: A deep learning perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cao, W.; Zheng, B.; Wu, M.; Pedrycz, W.; Hirota, K. Two-Stage Representation Refinement Based on Convex Combination for 3D Human Poses Estimation. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2024, 5, 6500–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-K.; Cheng, K.-Y. A two-stage Bayesian network method for 3D human pose estimation from monocular image sequences. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2010, 2010, 761460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo-Serra, E.; Quattoni, A.; Torras, C.; Moreno-Noguer, F. A joint model for 2d and 3d pose estimation from a single image. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 3634–3641. [Google Scholar]
- Rogez, G.; Weinzaepfel, P.; Schmid, C. Lcr-net++: Multi-person 2d and 3d pose detection in natural images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 42, 1146–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.; Hossain, R.; Romero, J.; Little, J.J. A simple yet effective baseline for 3d human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2640–2649. [Google Scholar]
- Andriluka, M.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. Monocular 3d pose estimation and tracking by detection. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 623–630. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrizi, R.; Peng, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, K. A Deep Neural Network-based method for estimation of 3D lifting motions. J. Biomech. 2019, 84, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehraban, S.; Qin, Y.; Taati, B. Evaluating Recent 2D Human Pose Estimators for 2D-3D Pose Lifting. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 18th International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG), Istanbul, Turkiye, 27–31 May 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Liu, H.; Ding, R.; Liu, M.; Wang, P. Lifting transformer for 3d human pose estimation in video. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.14304. [Google Scholar]
- Grinciunaite, A.; Gudi, A.; Tasli, E.; Den Uyl, M. Human pose estimation in space and time using 3d cnn. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2016; pp. 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ghezelghieh, M.F.; Kasturi, R.; Sarkar, S. Learning camera viewpoint using CNN to improve 3D body pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 685–693. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, D. A CNN-based 3D human pose estimation based on projection of depth and ridge data. Pattern Recognit. 2020, 106, 107462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendran, S.; Ali, H.; Vidal, R. 3d pose regression using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2174–2182. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, L.; Liang, H.; Yuan, J.; Thalmann, D. 3d convolutional neural networks for efficient and robust hand pose estimation from single depth images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1991–2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, D.; Rhodin, H.; Casas, D.; Fua, P.; Sotnychenko, O.; Xu, W.; Theobalt, C. Monocular 3d human pose estimation in the wild using improved cnn supervision. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Qingdao, China, 10–12 October 2017; pp. 506–516. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Liu, H.; Tang, H.; Wang, P.; Van Gool, L. Mhformer: Multi-hypothesis transformer for 3d human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 13147–13156. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Wang, W.; Tian, Y. Graformer: Graph-oriented transformer for 3d pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 20438–20447. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Tu, Z.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, J. Mixste: Seq2seq mixed spatio-temporal encoder for 3d human pose estimation in video. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 13232–13242. [Google Scholar]
- Shuai, H.; Wu, L.; Liu, Q. Adaptive multi-view and temporal fusing transformer for 3d human pose estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 4122–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampali, S.; Sarkar, S.D.; Rad, M.; Lepetit, V. Keypoint transformer: Solving joint identification in challenging hands and object interactions for accurate 3d pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11090–11100. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Zhu, S.; Mendieta, M.; Yang, T.; Chen, C.; Ding, Z. 3d human pose estimation with spatial and temporal transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 11656–11665. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanin, M.; Khamiss, A.; Bennamoun, M.; Boussaid, F.; Radwan, I. Crossformer: Cross spatio-temporal transformer for 3d human pose estimation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.13387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, H.; Ding, R.; Liu, M.; Wang, P.; Yang, W. Exploiting temporal contexts with strided transformer for 3d human pose estimation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, S.; Blythman, R.; Ghosal, K.; Moynihan, M.; Simms, C.; Smolic, A. Jointformer: Single-frame lifting transformer with error prediction and refinement for 3d human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; pp. 1156–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, S.; Zhu, X.; Tan, Z. 3D WholeBody Pose Estimation based on Semantic Graph Attention Network and Distance Information. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.01196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Samet, N.; Picard, D. H3wb: Human3. In 6m 3d wholebody dataset and benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 20166–20177. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zeng, A.; Yuan, C.; Li, Y. Effective whole-body pose estimation with two-stages distillation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 4210–4220. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Xie, X.; Li, Y. RTMW: Real-time multi-person 2D and 3D whole-body pose estimation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.08634. [Google Scholar]
- Samet, N.; Rommel, C.; Picard, D.; Valle, E. PAFUSE: Part-based Diffusion for 3D Whole-Body Pose Estimation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.10220. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, D. Vitpose++: Vision transformer for generic body pose estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 46, 1212–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Shiratori, T.; Joo, H. Frankmocap: Fast monocular 3d hand and body motion capture by regression and integration. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.08324. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, G.; Choi, H.; Lee, K.M. Accurate 3D hand pose estimation for whole-body 3D human mesh estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2308–2317. [Google Scholar]
- Weinzaepfel, P.; Brégier, R.; Combaluzier, H.; Leroy, V.; Rogez, G. Dope: Distillation of part experts for whole-body 3d pose estimation in the wild. In Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part XXVI 16; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2020; pp. 380–397. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, H.; Simon, T.; Sheikh, Y. Total capture: A 3d deformation model for tracking faces, hands, and bodies. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8320–8329. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, J.; Tzionas, D.; Black, M.J. Embodied hands: Modeling and capturing hands and bodies together. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.02610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Joo, H.; Sheikh, Y. Monocular total capture: Posing face, body, and hands in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 10965–10974. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Gao, Q.; Lai, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Ju, Z. HR-GCN: 2D-3D Whole-body Pose Estimation with High-Resolution Graph Convolutional Network From a Monocular Camera. IEEE Sens. J. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, L.R.; Izumi, N.; Khan, S.; Kyrala, G.; Landen, O.; Ma, T.; Nagel, S.; Pak, A. Simplified model of pinhole imaging for quantifying systematic errors in image shape. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 8719–8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Fang, C.; Shen, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Luo, J. Anatomy-aware 3d human pose estimation with bone-based pose decomposition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17245-2004; Inertial Parameters of Adult Human Body. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Ionescu, C.; Papava, D.; Olaru, V.; Sminchisescu, C. Human3. 6m: Large scale datasets and predictive methods for 3d human sensing in natural environments. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 36, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Qian, C.; Ouyang, W.; Luo, P. Whole-body human pose estimation in the wild. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2020; pp. 196–214. [Google Scholar]
- Dabhi, M.; Jeni, L.A.; Lucey, S. 3d-lfm: Lifting foundation model. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 10466–10475. [Google Scholar]

| Body Segment | Gender | Relative Quality/% | Body Segment | Gender | Relative Quality/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neck | M | 8.62 | Upper Arm | M | 2.43 |
| F | 8.20 | F | 2.66 | ||
| Upper Torso | M | 16.82 | Forearm | M | 1.25 |
| F | 16.35 | F | 1.14 | ||
| Lower Torso | M | 27.23 | Hand | M | 0.64 |
| F | 27.48 | F | 0.42 | ||
| Thigh | M | 14.19 | Foot | M | 1.48 |
| F | 14.10 | F | 1.24 | ||
| Calf | M | 3.67 | |||
| F | 4.43 | ||||
| Body Segment | Gender | Body Segment | Gender | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neck | M | 46.9 | 53.1 | Upper Arm | M | 47.8 | 52.2 |
| F | 47.3 | 52.7 | F | 46.7 | 53.3 | ||
| Upper Torso | M | 53.6 | 46.4 | Forearm | M | 42.4 | 57.6 |
| F | 49.3 | 50.7 | F | 45.3 | 54.7 | ||
| Lower Torso | M | 40.3 | 59.7 | Hand | M | 36.6 | 63.4 |
| F | 44.6 | 55.4 | F | 34.9 | 65.1 | ||
| Thigh | M | 45.3 | 54.7 | Foot | M | 48.6 | 51.4 |
| F | 44.2 | 55.8 | F | 45.1 | 54.9 | ||
| Calf | M | 39.3 | 60.7 | Overall Centroid | M | 43.8 | 56.2 |
| F | 42.5 | 57.5 | F | 44.5 | 55.5 |
| Method | WholeBody | Body | Face | Hands |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Baseline [42] | 125.4 | 125.7 | 24.6 | 42.5 |
| Large Simple Baseline [21] | 112.3 | 112.6 | 14.6 | 31.7 |
| JointFormer [40] | 88.3 | 84.9 | 17.8 | 43.7 |
| 3D-LFM [59] | 64.13 | 60.83 | 10.44 | 28.22 |
| SemGAN [41] | 47.87 | 45.39 | 15.95 | 27.77 |
| Ours | 44.49 | 40.41 | 6.09 | 22.07 |
| Constraints | WholeBody | Body | Face | Hands |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| body mass distribution constraints | 67.50 | 59.24 | 10.10 | 29.41 |
| center of gravity position constraints | 58.34 | 50.76 | 8.32 | 25.73 |
| body mass distribution and center of gravity constraints | 44.49 | 40.41 | 6.09 | 22.07 |
| Loss Function | WholeBody | Body | Face | Hands |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 59.71 | 47.69 | 15.35 | 31.93 | |
| 51.75 | 44.21 | 13.29 | 25.61 | |
| 49.29 | 45.57 | 9.90 | 26.61 | |
| 44.49 | 40.41 | 6.09 | 22.07 |
| Methods | Dir. | Disc. | Eat. | Greet | Phone | Photo | Pose | Purch. | Sit | SitD. | Smoke | Wait | WalkD. | Walk | WalkT. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PoseFormer [37] | 41.5 | 44.8 | 39.8 | 42.5 | 46.5 | 51.6 | 42.1 | 42.0 | 53.3 | 60.7 | 45.5 | 43.3 | 46.1 | 31.8 | 32.2 |
| JointFormer [40] | 45.0 | 48.8 | 46.6 | 49.4 | 53.2 | 60.1 | 47.0 | 46.7 | 59.6 | 67.1 | 51.2 | 47.1 | 53.8 | 39.4 | 42.4 |
| Ours | 41.4 | 38.1 | 33.6 | 41.7 | 42.6 | 50.2 | 42.3 | 40.9 | 57.0 | 61.2 | 43.5 | 46.6 | 43.4 | 27.9 | 30.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, F.; Xu, G.; Wu, Q.; Qin, P.; Pan, L.; Zhao, Y. Whole-Body 3D Pose Estimation Based on Body Mass Distribution and Center of Gravity Constraints. Sensors 2025, 25, 3944. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133944
Wei F, Xu G, Wu Q, Qin P, Pan L, Zhao Y. Whole-Body 3D Pose Estimation Based on Body Mass Distribution and Center of Gravity Constraints. Sensors. 2025; 25(13):3944. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133944
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Fan, Guanghua Xu, Qingqiang Wu, Penglin Qin, Leijun Pan, and Yihua Zhao. 2025. "Whole-Body 3D Pose Estimation Based on Body Mass Distribution and Center of Gravity Constraints" Sensors 25, no. 13: 3944. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133944
APA StyleWei, F., Xu, G., Wu, Q., Qin, P., Pan, L., & Zhao, Y. (2025). Whole-Body 3D Pose Estimation Based on Body Mass Distribution and Center of Gravity Constraints. Sensors, 25(13), 3944. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25133944








