Detection-Driven Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Multi-Target Tracker for Airborne Infrared Platforms
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The development of a multi-object tracker for infrared weak-texture targets integrates a YOLOv10-based target detection model with the GM-PHD tracking algorithm. This integration provides high inference speed and detection accuracy, making it suitable for real-time tracking tasks on airborne infrared platforms.
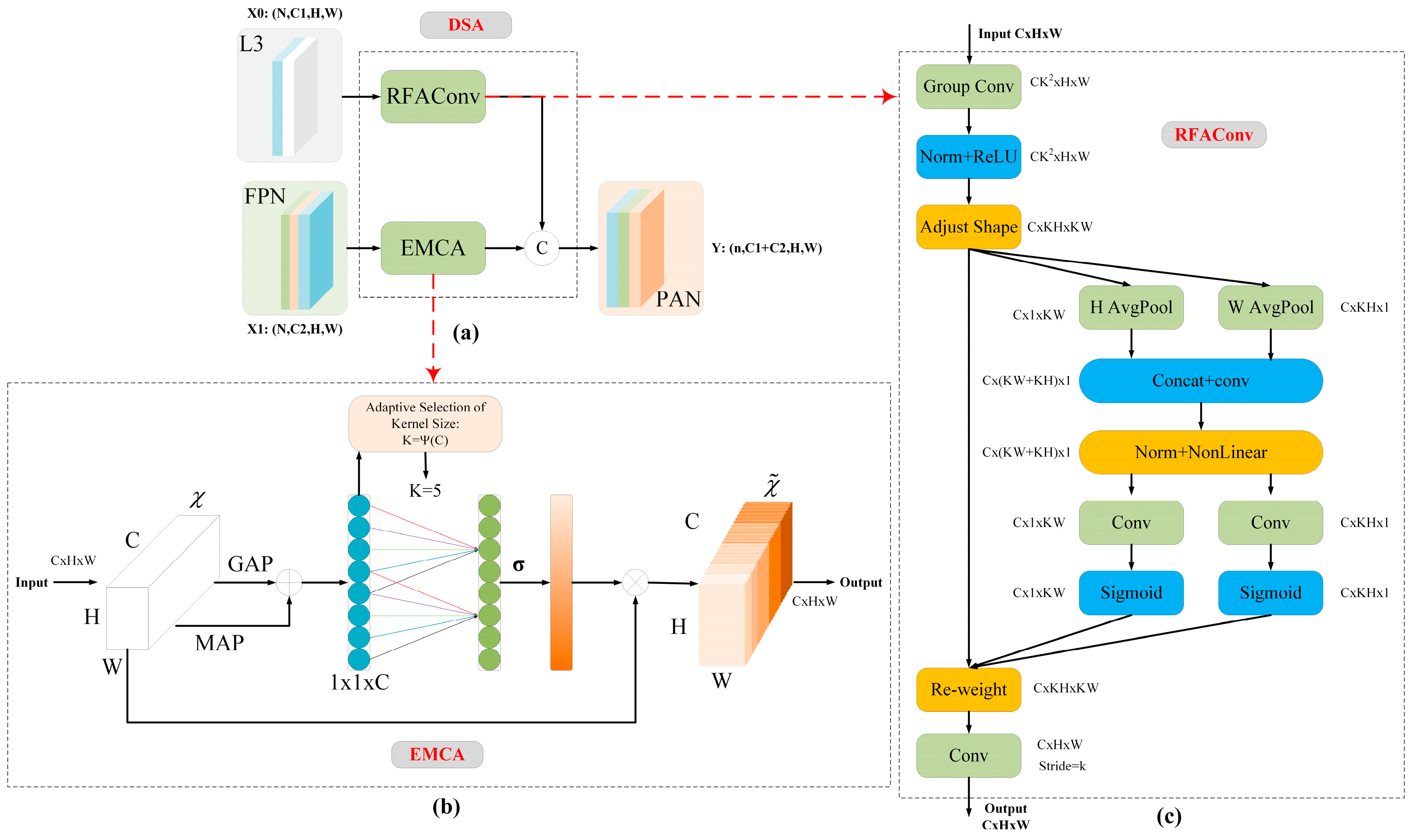
- The integration of a novel deep and shallow attention module within the neck network of the WTI-YOLO model employs the RFA module to prioritize detailed features from the shallow network, while simultaneously extracting high-level semantic information from the deep network through the EMCA module. This approach significantly improves the detection accuracy for targets with weak textures.
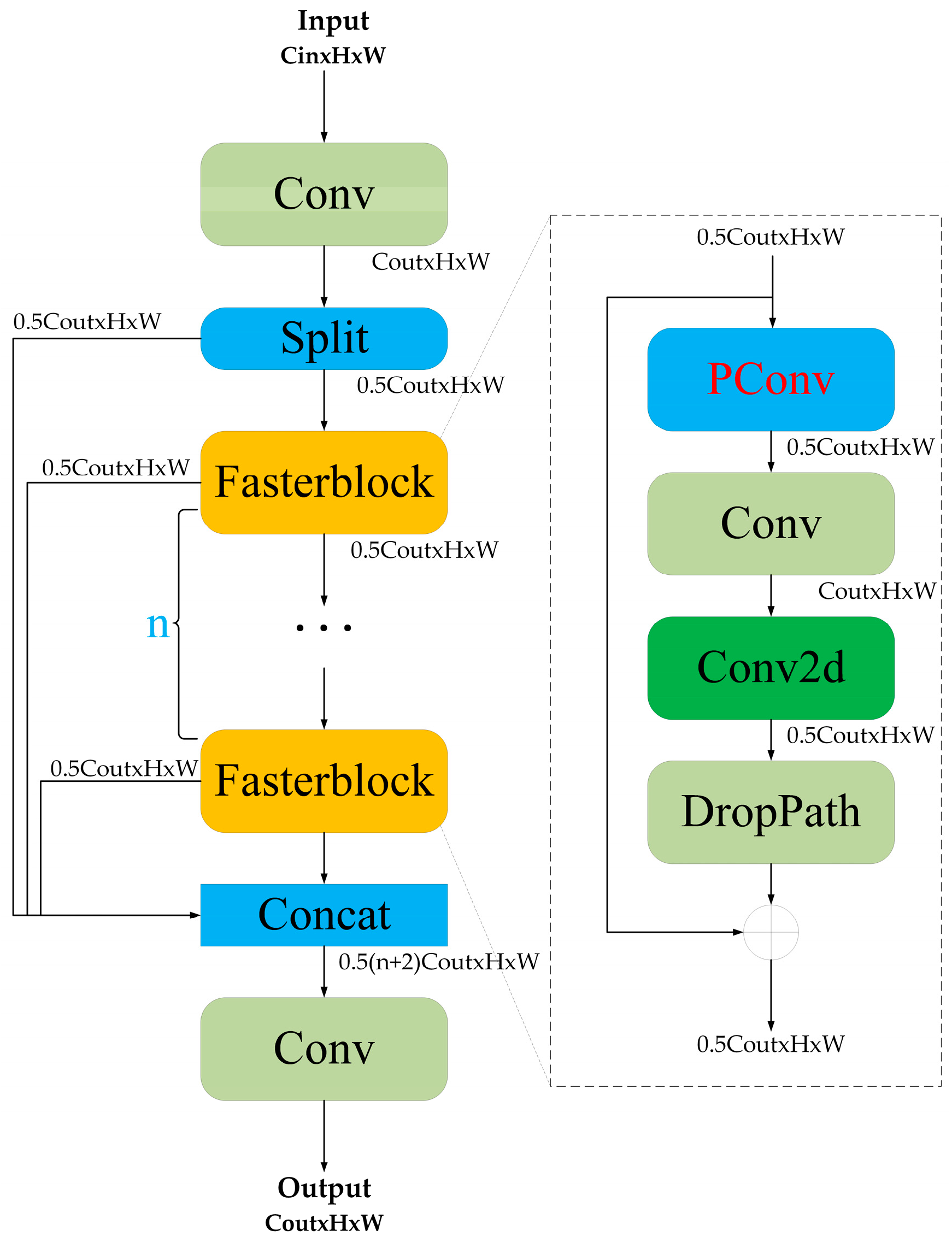
- The incorporation of the C2f_FasterBlock module serves to optimize WTI-YOLO, resulting in a substantial reduction in model parameters and computational complexity. This enhancement facilitates the model’s operation at speeds that align with the practical task requirements of airborne devices.
- The selection of the GM-PHD filter for multi-object tracking is informed by recent advancements in detection tasks. Additionally, the integration of the SSIM module facilitates data association, thereby enhancing the stability of target tracking while simultaneously reducing computational complexity and increasing the speed of target association.
2. Related Works
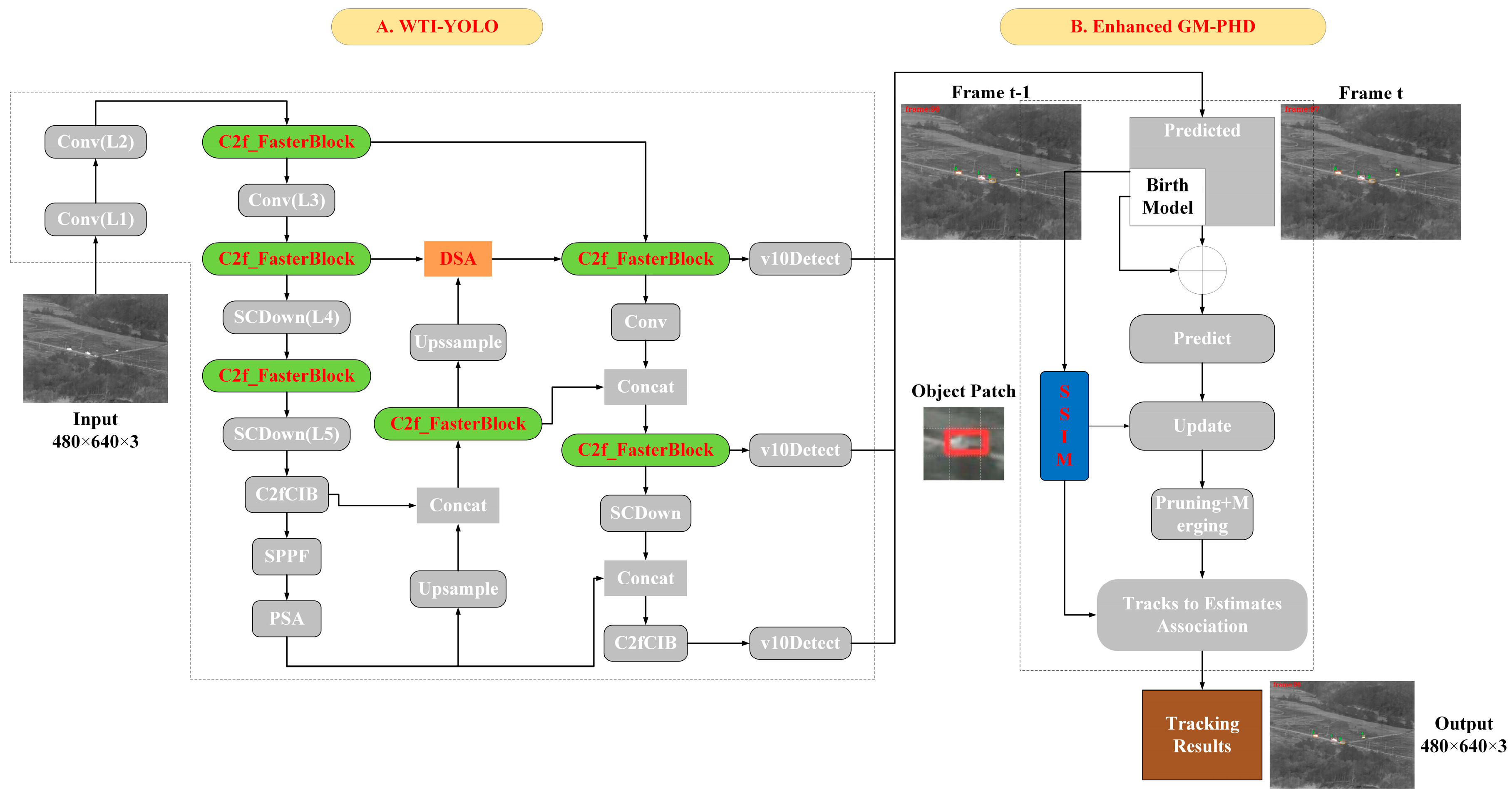
3. Proposed Method
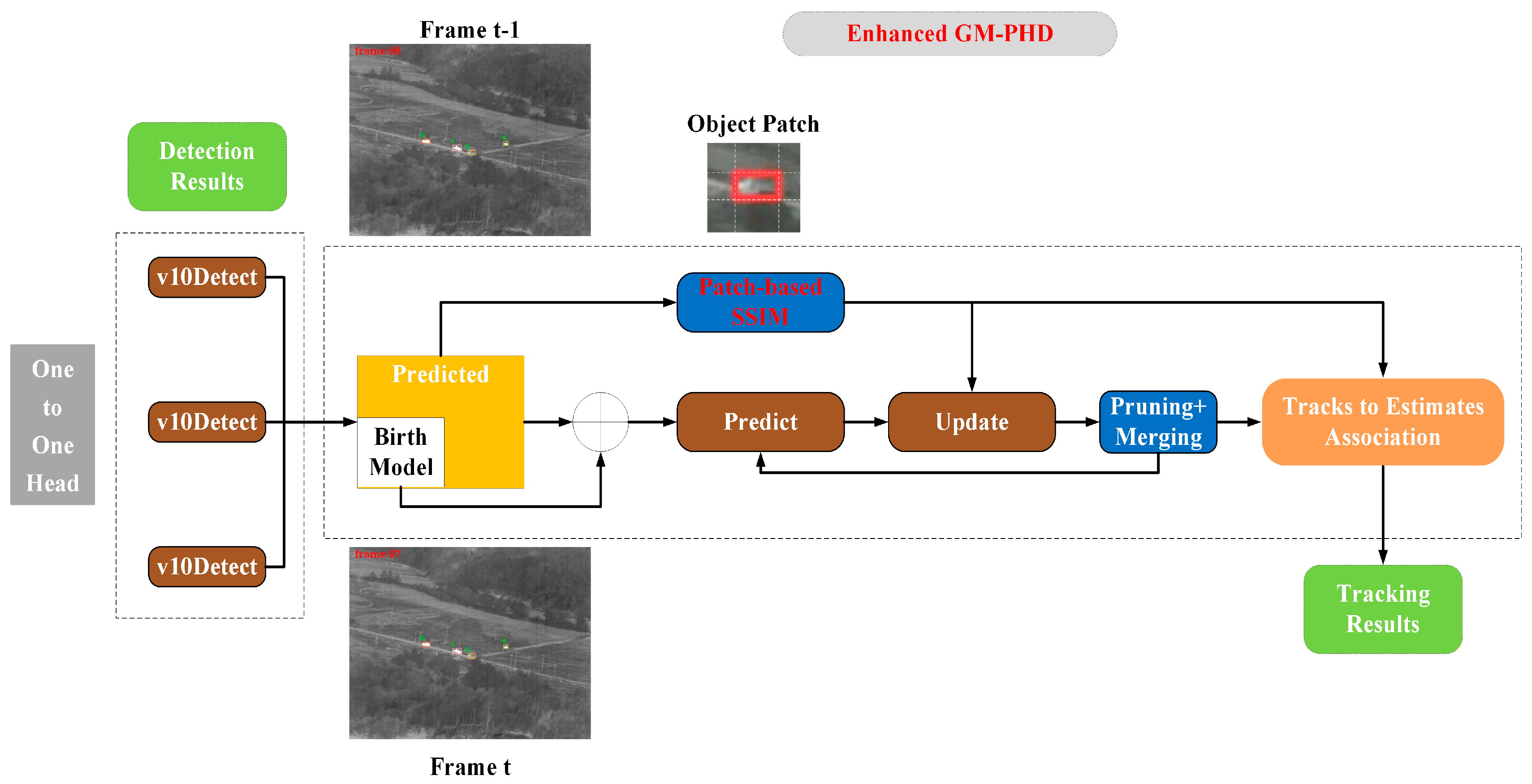
3.1. Overview of Our Method
3.2. Target Detection Improvements
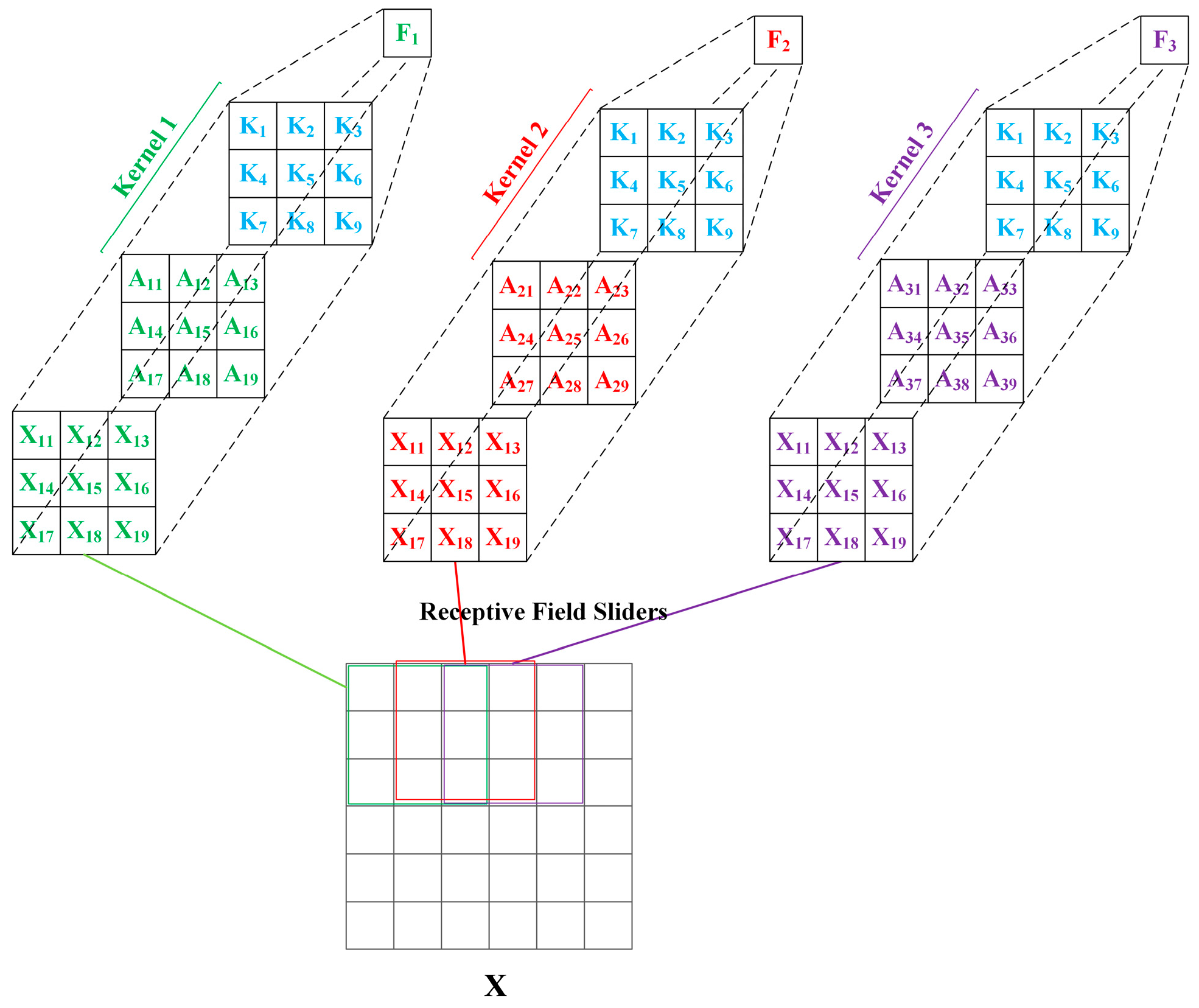
3.2.1. DSA Module
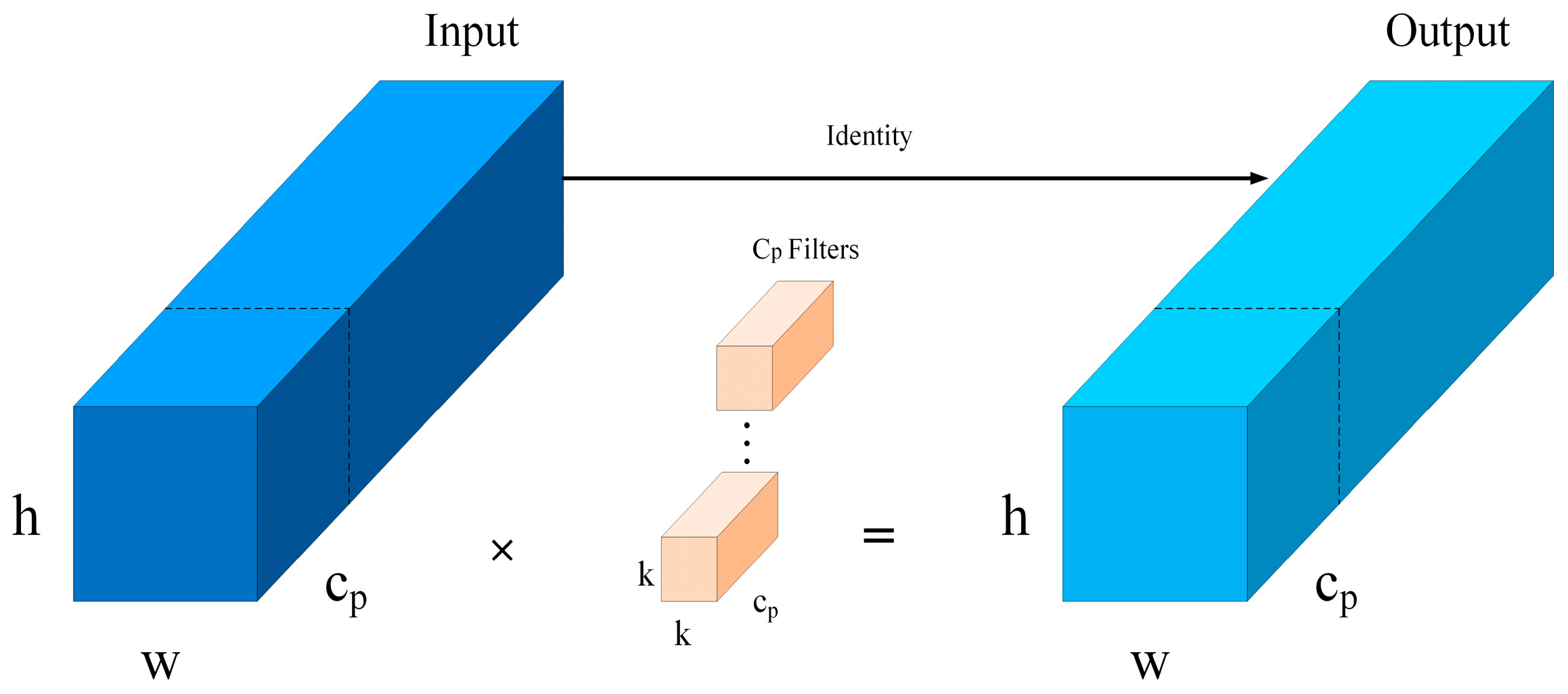
3.2.2. C2f_Fasterblock Module
3.3. GM-PHD Tracking Improvements
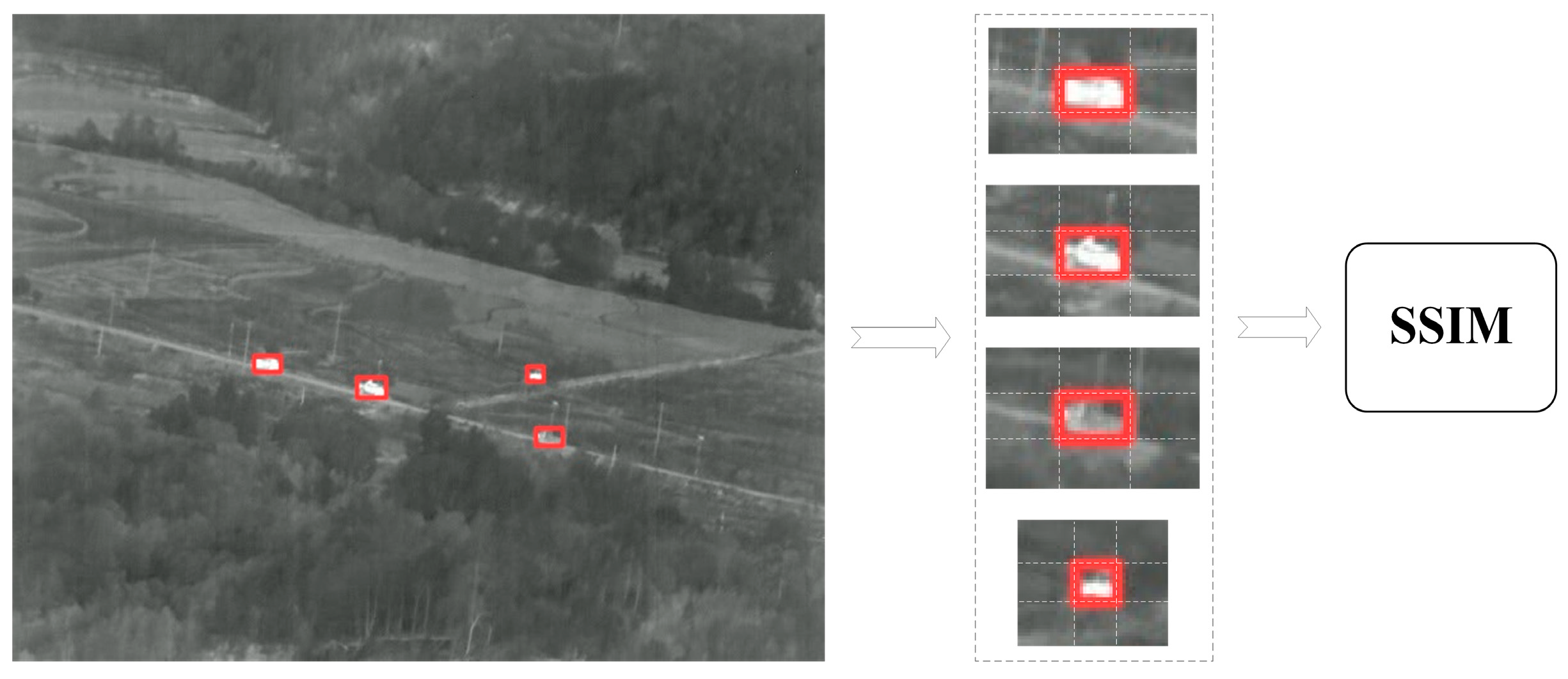
3.3.1. The SSIM Module
3.3.2. Tracking Strategy
4. Experiment
4.1. Dataset and Implementation
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
- ●
- Object detection evaluation: Mean average precision () is defined as the average of the average precision () across various categories, where is calculated as the area under the precision–recall () curve, a higher signifies that the model not only maintains high precision but also exhibits robust recall performance.where is given bywhere (True Positive) and (False Positive) denote the number of samples that the model accurately and inaccurately predicted as positive, respectively. Conversely, (False Negative) refers to the number of samples that the model incorrectly classified as negative.
- ●
- Multi-object tracking evaluation: is one of the CLEAR [49] metrics employed to assess the overall accuracy of multi-object tracking algorithms. This metric considers three primary types of errors: switches, , and . The calculation of is performed using the following formula:where denotes the number of identity switches per frame, while signifies the total number of ground truth targets per frame.
4.3. Evaluation of Experimental Results
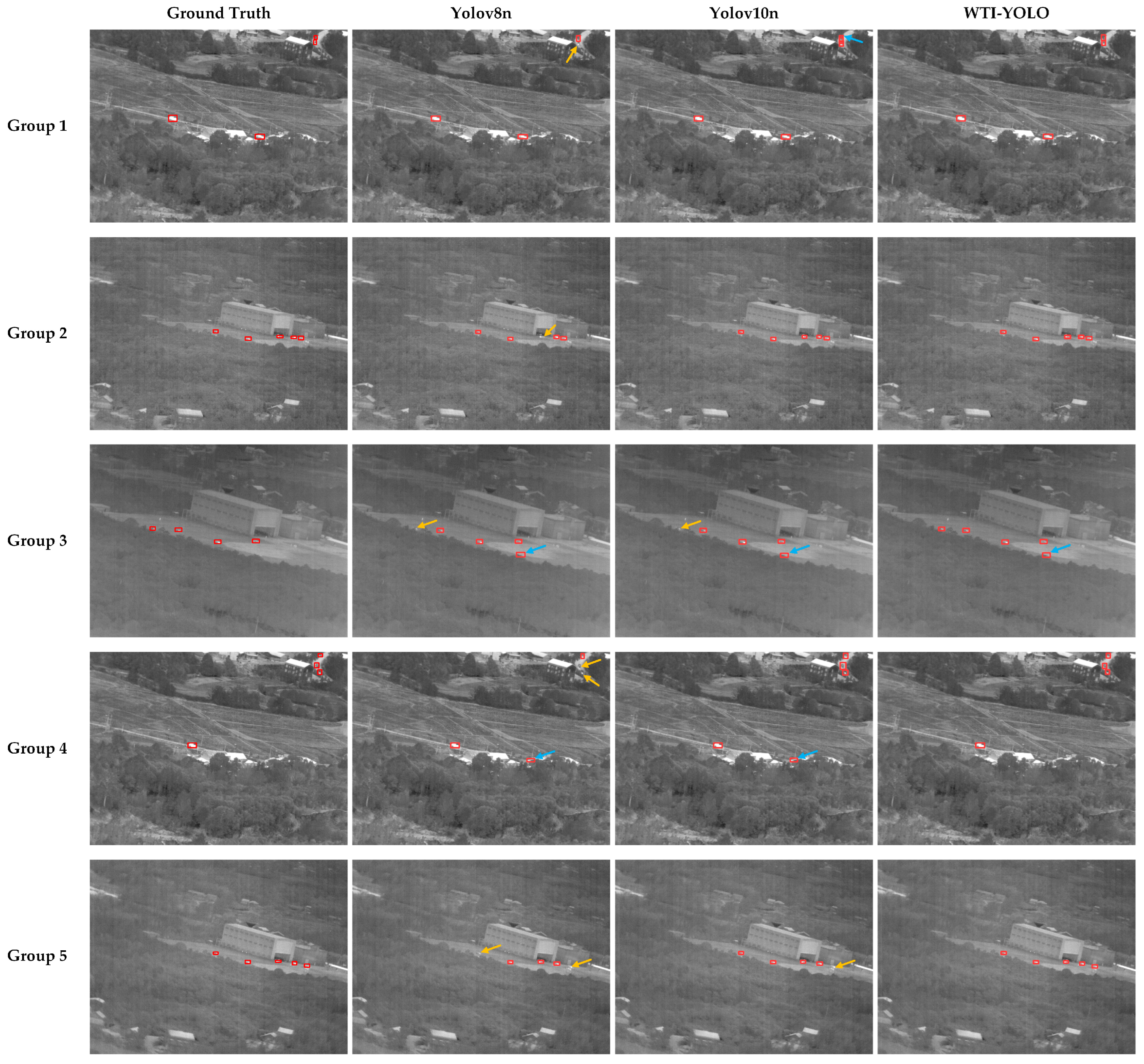
4.3.1. Detection Experiment
Ablation Experiment
Robustness Testing in Different Environments
Comparison of Advanced Detection Models
4.3.2. Tracking Experiment
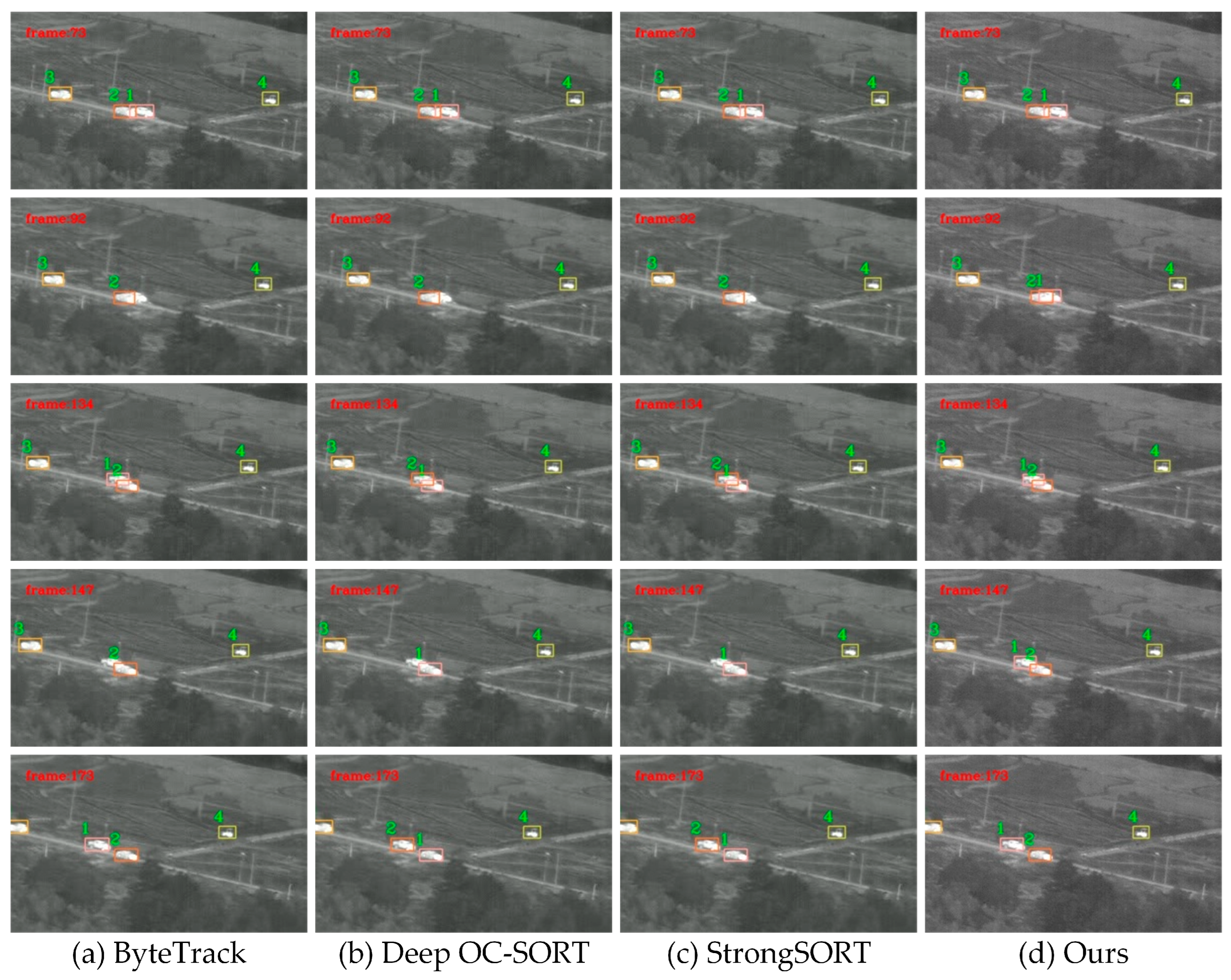
Comparison to MOT Methods
Testing Tracking Performance in Different Environments
Qualitative Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanglin, G.; Mei, D.; Wei, C. A Small Target Detection Algorithm Based on Immune Computation and Infrared Background Suppression. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Natural Computation (ICNC 2007), Haikou, China, 24–27 August 2007; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 630–634. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Niu, C.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y. Infrared small target detection algorithm for UAV detection system. Laser Technol. 2024, 48, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Sha, Z.; Nie, H.; Zhu, M.; Nie, Y. Lightweight Neural Network for Centroid Detection of Weak, Small Infrared Targets via Background Matching in Complex Scenes. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Sun, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cao, S.; Liu, S. UCDnet: Double U-Shaped Segmentation Network Cascade Centroid Map Prediction for Infrared Weak Small Target Detection. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Sun, Y.; Cai, S.; Wu, C.; Du, Q. Object Tracking in Satellite Videos by Fusing the Kernel Correlation Filter and the Three-Frame-Difference Algorithm. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, S.; Li, S.; Han, M.; Wan, X.; Xia, G.-S. Object Tracking in Satellite Videos by Improved Correlation Filters with Motion Estimations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Niu, W.; Zheng, W. A Weak Moving Point Target Detection Method Based on High Frame Rate Image Sequences. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 7066–7069. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Yang, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, Y. Small Target Detection Utilizing Robust Methods of the Human Visual System for IRST. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2009, 30, 994–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, B.; Fan, F.; Liang, K.; Fang, Y. A Robust Infrared Small Target Detection Algorithm Based on Human Visual System. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 2168–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.; Qu, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Deng, L. An Infrared Small Target Detection Method Based on Multiscale Local Homogeneity Measure. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2018, 90, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojke, N.; Bewley, A.; Paulus, D. Simple Online and Realtime Tracking with a Deep Association Metric. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 3645–3649. [Google Scholar]
- Maggiolino, G.; Ahmad, A.; Cao, J.; Kitani, K. Deep OC-SORT: Multi-Pedestrian Tracking by Adaptive Re-Identification. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 8–11 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Pang, J.; Weng, X.; Khirodkar, R.; Kitani, K. Observation-Centric SORT: Rethinking SORT for Robust Multi-Object Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 9686–9696. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, P.; Jiang, Y.; Yu, D.; Weng, F.; Yuan, Z.; Luo, P.; Liu, W.; Wang, X. ByteTrack: Multi-Object Tracking by Associating Every Detection Box. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2022, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Su, F.; Gong, T.; Meng, H. StrongSORT: Make DeepSORT Great Again. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 25, 8725–8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. Trans. ASME–J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, W.; Fu, Y.; Hou, X.; Xu, F. Needles in a Haystack: Tracking City-Scale Moving Vehicles From Continuously Moving Satellite. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 1944–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Cao, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Xie, E.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, C.; Luo, P. Transtrack: Multiple object tracking with transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.15460. [Google Scholar]
- Meinhardt, T.; Kirillov, A.; Leal-Taixe, L.; Feichtenhofer, C. Trackformer: Multi-object tracking with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 8844–8854. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Tian, X.; Yu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Elhanashi, A.; Saponara, S.; Kpalma, K. MobileRaT: A Lightweight Radio Transformer Method for Automatic Modulation Classification in Drone Communication Systems. Drones 2023, 7, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. YOLOv10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, B.-N.; Ma, W.-K. The Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 4091–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hore, A.; Ziou, D. Image Quality Metrics: PSNR vs. SSIM. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 2366–2369. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, R.; Fan, H.; Zhu, Y.; Hui, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, P.; Li, D.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G.; Wang, L. A dataset for infrared time-sensitive target detection and tracking for air-ground application. China Sci. Data 2022, 7, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich Feature Hierarchies for Accurate Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation; IEEE Computer Society: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot Multibox Detector; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1506.02640v5. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.; Gao, C.; Feng, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, J. Small UAV Detection in Videos from a Single Moving Camera. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision: Second CCF Chinese Conference, CCCV 2017, Tianjin, China, 11–14 October 2017; Springer: Singapore, 2017; Volume 773, pp. 187–197. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, L.; Schumann, A.; Muller, T.; Schuchert, T.; Beyerer, J. Flying Object Detection for Automatic UAV Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2017 14th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), Lecce, Italy, 29 August–1 September 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Xu, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhai, G.; Yang, F.; Qian, L. Detection and tracking of infrared small target by jointly using SSD and pipeline filter. Digit. Signal Process. 2021, 110, 102949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Yan, Z.; Ren, M.; Wu, J.; Tian, L.; Guo, X.; Li, J. Improved YOLOv5 Infrared Tank Target Detection Method under Ground Background. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, X. YOLO-FIRI: Improved YOLOv5 for Infrared Image Object Detection. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 141861–141875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.; Mo, M.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, C.; Li, W.; Gao, X. Pareto Refocusing for Drone-View Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 1320–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaur, B.; Mishra, K.K. Small-Object Detection Based on YOLOv5 in Autonomous Driving Systems. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2023, 168, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, T.; He, W.; Zhang, Z. YOLOv7-UAV: An Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Image Object Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLOv7. Electronics 2023, 12, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, A.; Leal-Taixé, L.; Reid, L.; Roth, S.; Schindler, K. Mot16: A benchmark for multi-object tracking. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.00831. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, H.W.; Yaw, B. The Hungarian method for the assignment problem. Nav. Res. Logist. Q. 1955, 2, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, D.; Song, T.; Ye, Y.; Li, K.; Song, Y. RFAConv: Innovating Spatial Attention and Standard Convolutional Operation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2304.03198. [Google Scholar]
- Bakr, E.M.; El-Sallab, A.; Rashwan, M. EMCA: Efficient Multiscale Channel Attention Module. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 103447–103461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, S. A Lightweight Real-Time Infrared Object Detection Model Based on YOLOv8 for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Drones 2024, 8, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kao, S.; He, H.; Zhuo, W.; Wen, S.; Lee, C.-H.; Chan, S.-H.G. Run, Don’t Walk: Chasing Higher FLOPS for Faster Neural Networks. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.03667. [Google Scholar]
- Mahler, R.P.S. Multitarget Bayes Filtering via First-Order Multitarget Moments. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 1152–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, M. Stochastic Models and Methods for Multi-Object Tracking. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Sciences et Technologies—Bordeaux I, Talence, France, July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois, F.; Lassalle, J.-C. An Extension of the Munkres Algorithm for the Assignment Problem to Rectangular Matrices. Commun. ACM 1971, 14, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardin, K.; Stiefelhagen, R. Evaluating Multiple Object Tracking Performance: The CLEAR MOT Metrics. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2008, 2008, 246309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristani, E.; Solera, F.; Zou, R.S.; Cucchiara, R.; Tomasi, C. Performance Measures and a Data Set for Multi-Target, Multi-Camera Tracking. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016 Workshops, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 8–10 and 15–16 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. Part II. pp. 17–35. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.; Yang, W.; Ran, M.; Wang, S. FD-SSD: An improved SSD object detection algorithm based on feature fusion and dilated convolution. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2021, 98, 116402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Shang, D.; Wang, S.; Dong, S. DF-SSD: An improved SSD object detection algorithm based on DenseNet and feature fusion. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 24344–24357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wei, J.; Huang, H.; Zhang, D.; Chen, C. IRSDT: A Framework for Infrared Small Target Tracking with Enhanced Detection. Sensors 2023, 23, 4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, D.; Kupec, J.; Hong, J.; Daoudi, A. Real-Time Flying Object Detection with YOLOv8. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2305.09972. [Google Scholar]



| Yolov10n | DSA | C2f_Fasterblock | P (%) | R (%) | mAP0.5 (%) | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMCA | RFAConv | |||||||
| √ | 93.8 | 93.7 | 95.9 | 2.69 | 8.2 | |||
| √ | √ | 94.5 | 94.3 | 96.6 | 2.74 | 8.2 | ||
| √ | √ | 94.5 | 96.6 | 98.2 | 2.74 | 8.8 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 94.5 | 96.8 | 98.1 | 2.74 | 8.8 | |
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 96.0 | 97.3 | 98.5 | 2.25 | 7.3 |
| Road Scenarios | Lighting Conditions | Video Sequences | TP | FN | FP | P (%) | R (%) | mAP0.5 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| structured road | daytime | 78–80 | 2275 | 55 | 65 | 97.2 | 97.6 | 98.1 |
| unstructured road | daytime | 81–83 | 3627 | 121 | 83 | 97.8 | 96.8 | 98.5 |
| evening | 84–86 | 3590 | 95 | 291 | 92.5 | 97.4 | 98.1 |
| No. | Models | TP | FN | FP | P (%) | R (%) | Params (M) | FLOPs (G) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SSD-ST [34] | 33,512 | 11,531 | 895 | 97.4 | 74.4 | 2.8 | 24.8 |
| 2 | FD-SSD [51] | 29,683 | 15,360 | 1013 | 96.7 | 65.9 | 5.8 | 30.1 |
| 3 | DF-SSD [52] | 29,404 | 15,639 | 1007 | 96.7 | 65.3 | 10.0 | 31.6 |
| 4 | IRSDet [53] | 40,539 | 4504 | 1383 | 96.7 | 90.0 | 7.7 | 19.8 |
| 5 | Yolov8n [54] | 39,654 | 5389 | 2201 | 94.7 | 88.0 | 3.0 | 8.1 |
| 6 | Yolov10n [22] | 39,335 | 5708 | 2029 | 95.1 | 87.3 | 2.7 | 8.2 |
| 7 | WTI-YOLO (ours) | 470,916 | 4127 | 1141 | 97.3 | 90.8 | 2.2 | 7.3 |
| Tracker | IDs↓ | MOTA↑ | Frag↓ | FP↓ | FN↓ | IDR↑ | IDP↑ | IDF1↑ | FPS↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepSort [11] | 113 | 80.2 | 300 | 491 | 1513 | 71.4 | 79.0 | 75.0 | 90 |
| OC-SORT [13] | 32 | 79.1 | 163 | 345 | 1851 | 77.3 | 87.1 | 81.9 | 95 |
| Deep OC-SORT [12] | 17 | 80.5 | 175 | 380 | 1693 | 79.7 | 90.8 | 84.9 | 82 |
| ByteTrack [14] | 35 | 81.0 | 193 | 413 | 1584 | 76.1 | 85.4 | 80.5 | 80 |
| StrongSORT [15] | 74 | 82.0 | 190 | 399 | 1457 | 78.5 | 87.6 | 82.6 | 79 |
| Ours | 2 | 90.7 | 173 | 670 | 328 | 96.1 | 93.2 | 94.6 | 102 |
| Road Scenarios | Lighting Conditions | Video Sequences | IDs↓ | MOTA↑ | Frag↓ | FP↓ | FN↓ | IDR↑ | IDP↑ | IDF1↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| structured road | daytime | 78–80 | 0 | 87.7 | 59 | 174 | 112 | 95.9 | 92.3 | 94.0 |
| unstructured road | daytime | 81–83 | 1 | 90.1 | 61 | 170 | 130 | 95.9 | 93.7 | 94.8 |
| evening | 84–86 | 1 | 88.3 | 31 | 295 | 56 | 96.2 | 90.0 | 92.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, M.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Cao, S.; Nie, H.; Xu, X. Detection-Driven Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Multi-Target Tracker for Airborne Infrared Platforms. Sensors 2025, 25, 3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113491
Hong M, Wang J, Zhu M, Cao S, Nie H, Xu X. Detection-Driven Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Multi-Target Tracker for Airborne Infrared Platforms. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113491
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Mingyu, Jiarong Wang, Ming Zhu, Shenyi Cao, Haitao Nie, and Xiangdong Xu. 2025. "Detection-Driven Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Multi-Target Tracker for Airborne Infrared Platforms" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113491
APA StyleHong, M., Wang, J., Zhu, M., Cao, S., Nie, H., & Xu, X. (2025). Detection-Driven Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Multi-Target Tracker for Airborne Infrared Platforms. Sensors, 25(11), 3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113491





