A Computationally Efficient MUSIC Algorithm with an Enhanced DOA Estimation Performance for a Crossed-Dipole Array
Abstract
1. Introduction
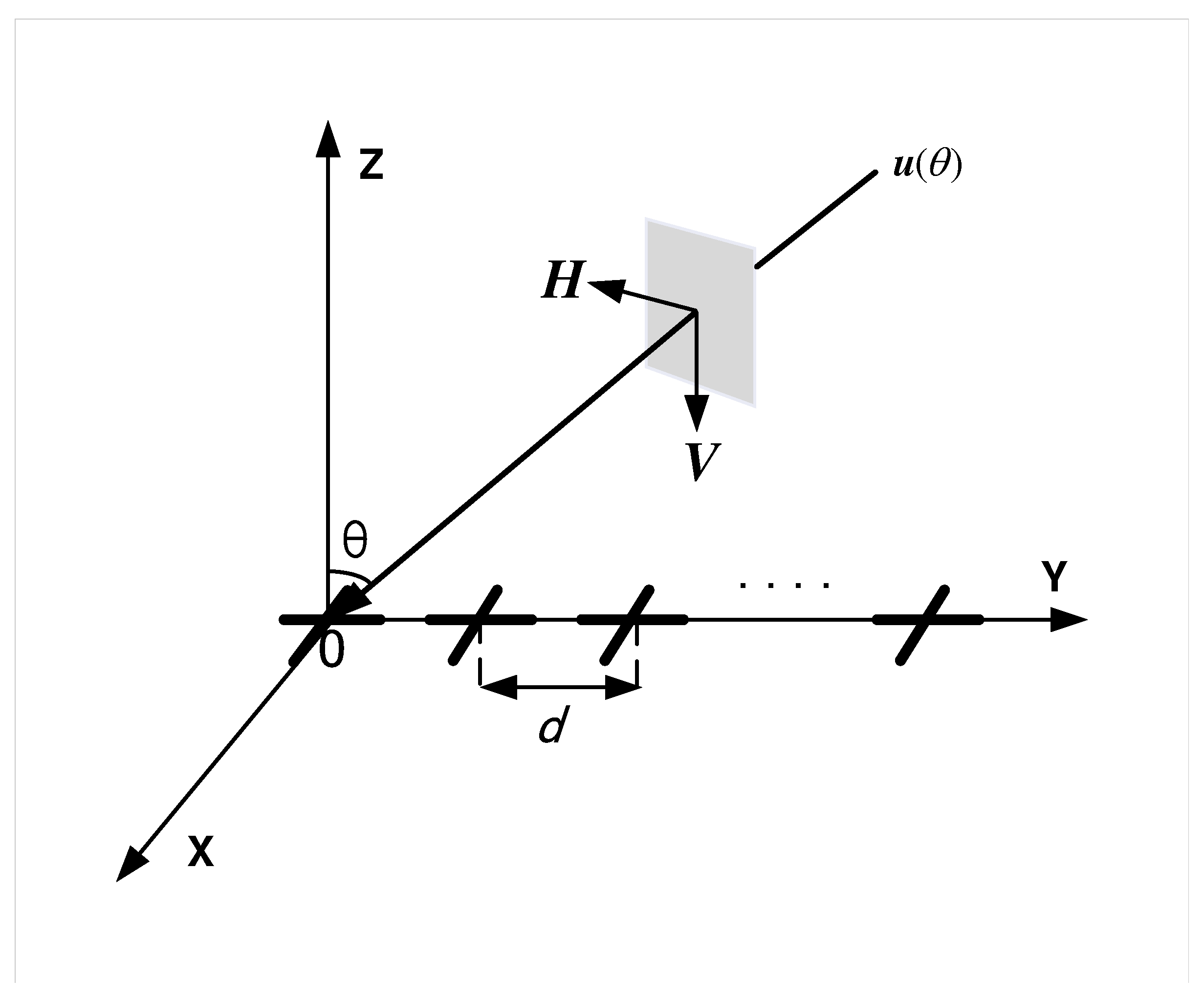
2. Model Construction and CRB
3. Proposed Algorithm
3.1. DR-MUSIC Algorithm
3.2. IRDR-MUSIC Algorithm
3.2.1. 1-D DOA Estimation
| Algorithm 1 The proposed IRDR-MUSIC algorithm for 1-D DOA estimation |
| Input: The LCDA received signal vector with L snapshots. Steps:
|
3.2.2. 2-D DOA Estimation
| Algorithm 2 The proposed IRDR-MUSIC algorithm for 2-D DOA estimation |
| Input: The PCDA received signal vector with L snapshots. Steps:
|
3.3. Computational Complexity Analysis
4. Simulations Results and Discussion
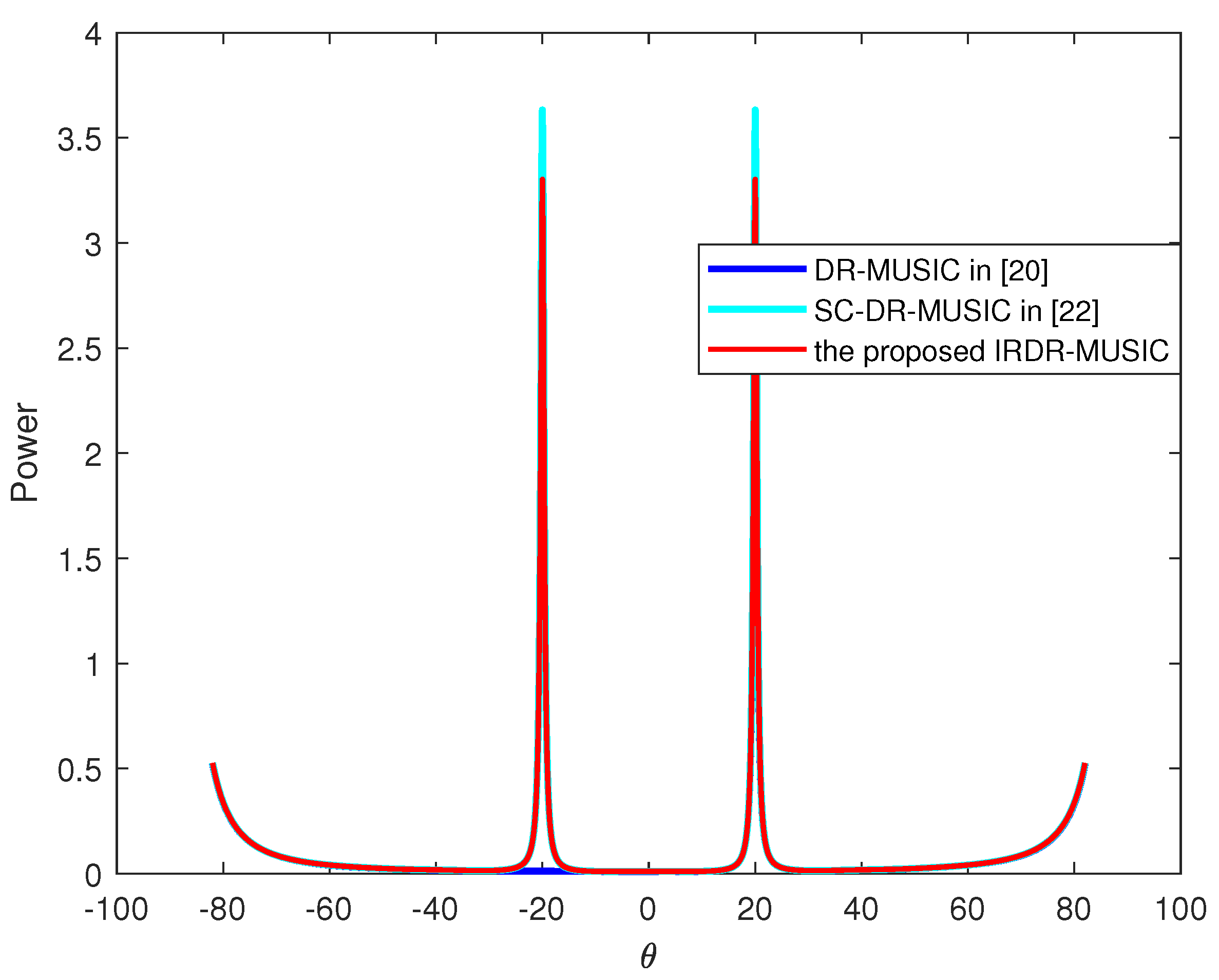
4.1. Spatial Spectrum Estimation
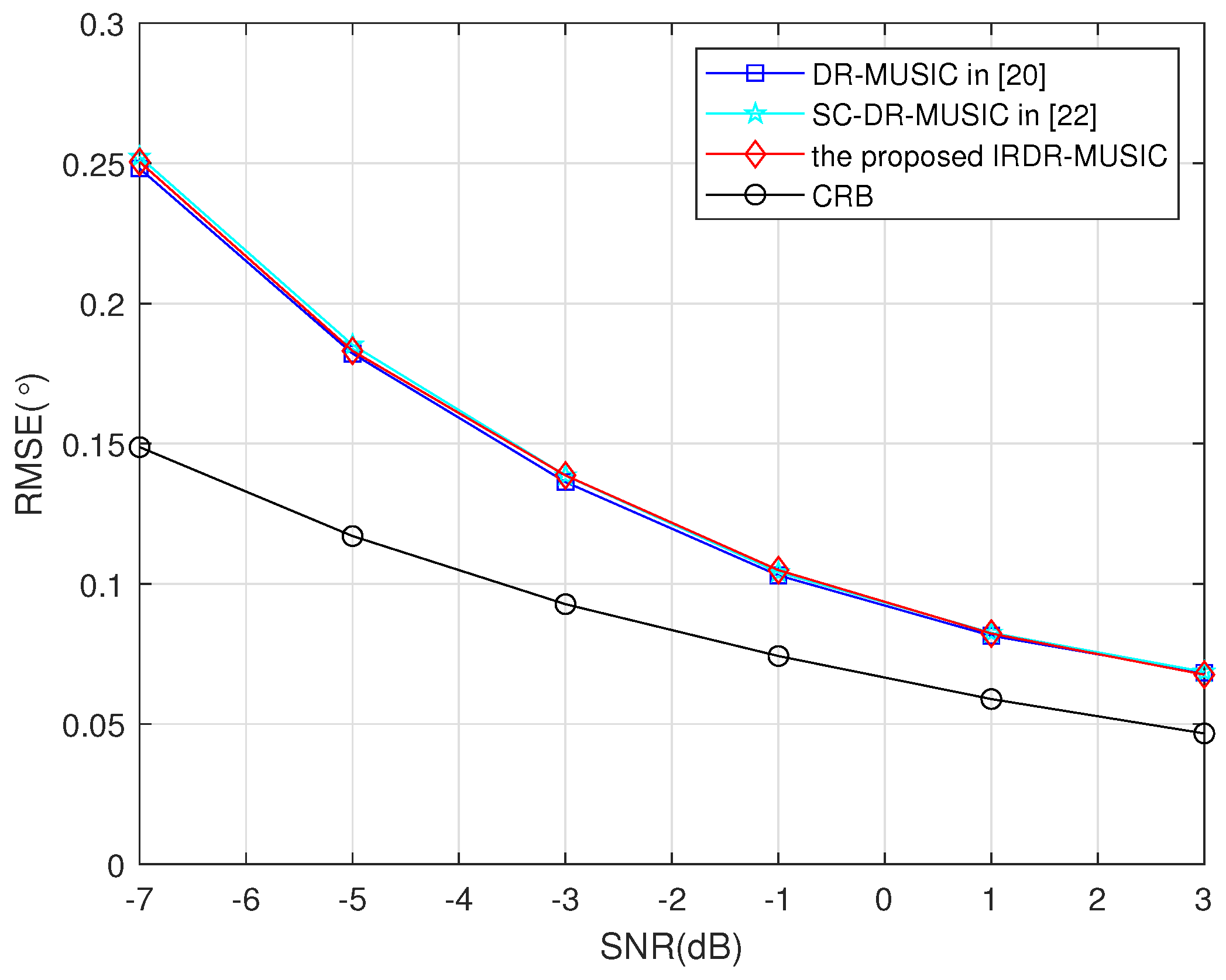
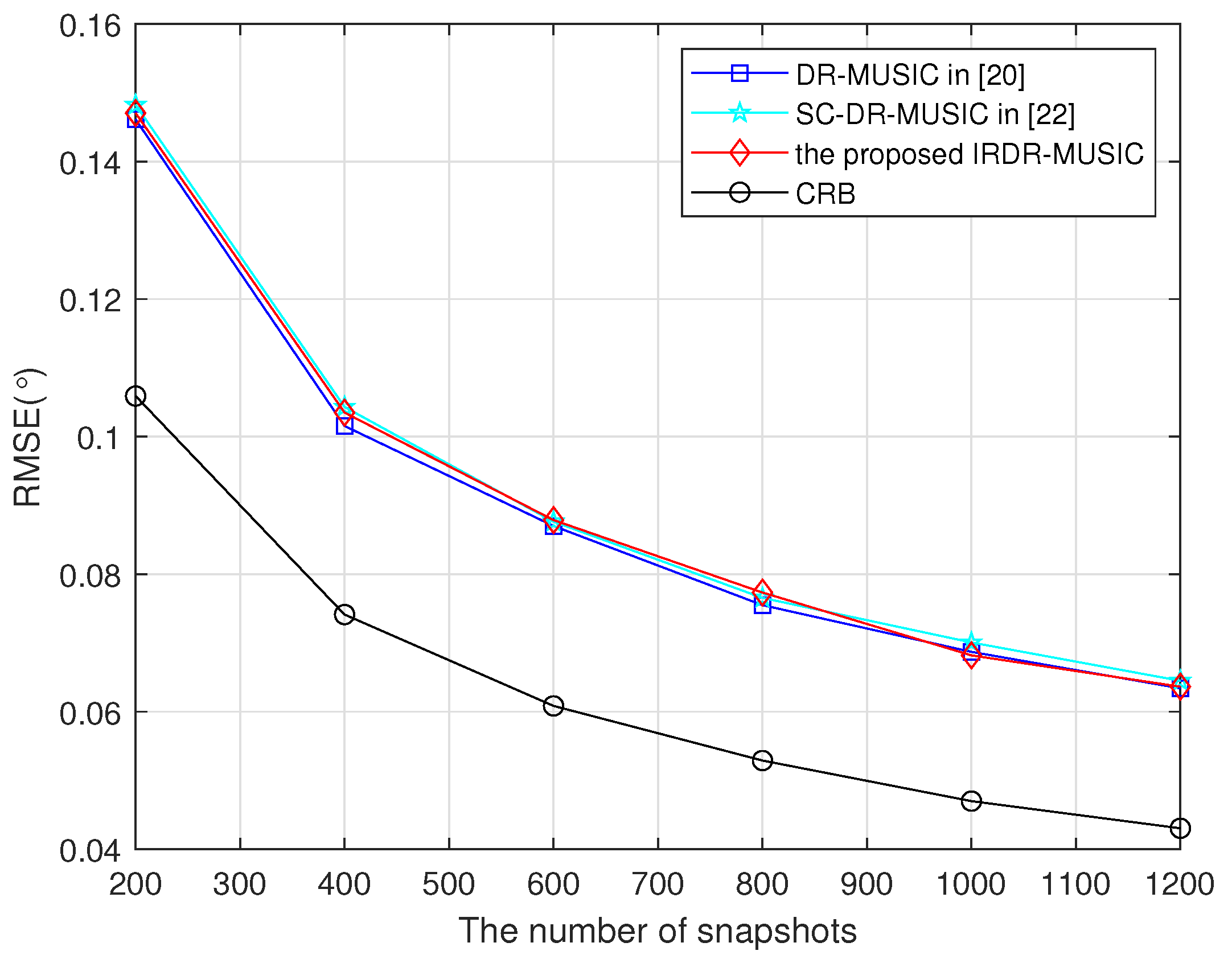
4.2. Estimation Accuracy
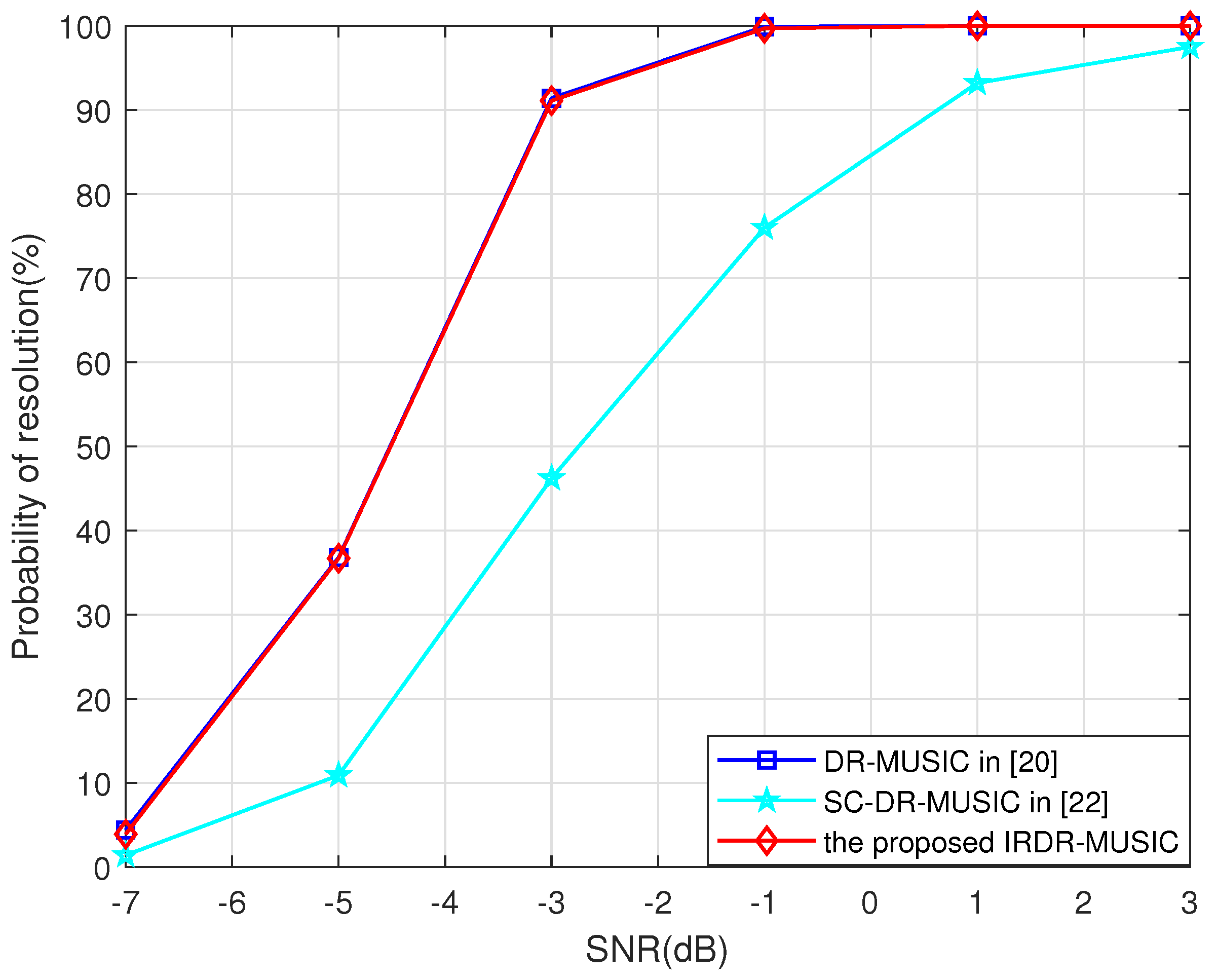
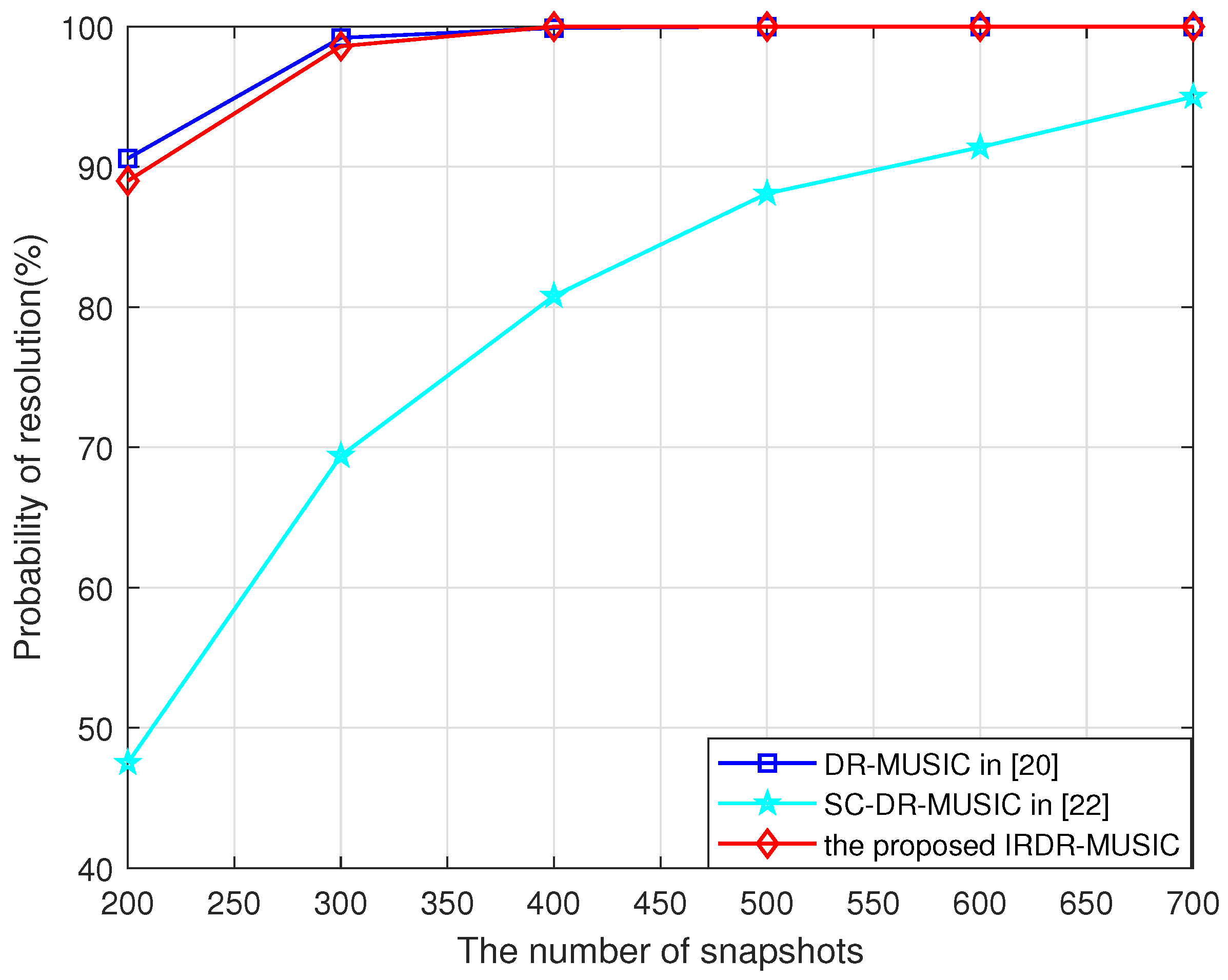
4.3. Multi-Target Resolution
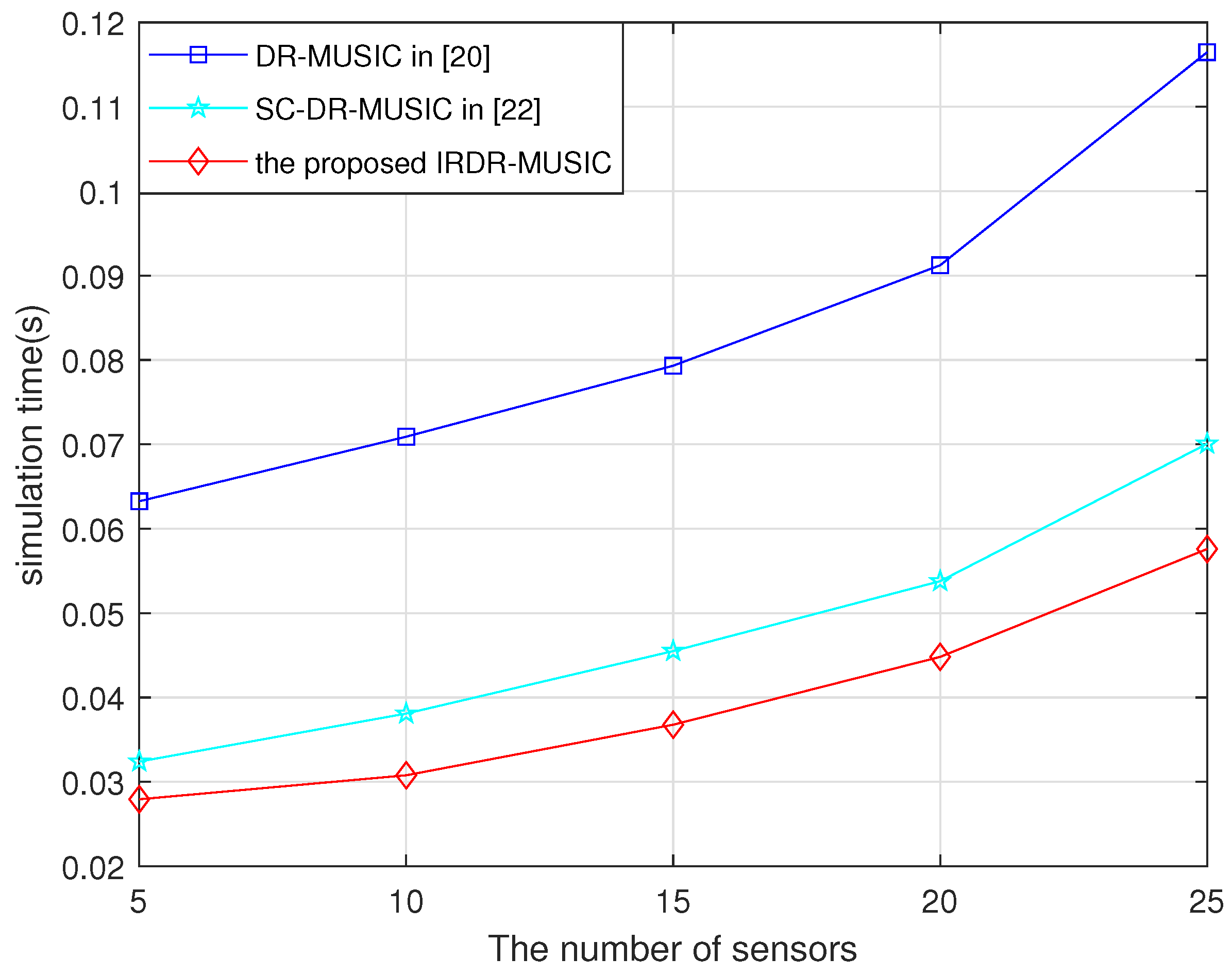
4.4. Running Time
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOA | direction-of-arrival |
| SVD | singular value decomposition |
| EMVSA | electromagnetic vector sensor array |
| FOV | field of view |
| LCDA | linear crossed-dipole array |
| PCDA | planar crossed-dipole array |
| MUSIC | multiple signal classification |
| DR-MUSIC | dimension-reduction MUSIC |
| SC-DR-MUSIC | symmetry-compressed dimension-reduction MUSIC |
| IRDR-MUSIC | improved real-valued dimension-reduction MUSIC |
References
- Andrews, M.R.; Mitra, P.P.; deCarvalho, R. Tripling the capacity of wireless communications using electromagnetic polarization. Nature 2001, 409, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W. Channel equalization and beamforming for quaternion-valued wireless communication systems. J. Frankl. Inst. 2017, 354, 8721–8733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhai, W.; Wang, X.; Amin, M.; Zoubir, A. Wideband Near-Field Integrated Sensing and Communications: A hybrid precoding perspective. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2025, 42, 88–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ren, J.; Liu, Y.; Pedersen, G.F.; Shen, M. Robust DOA Estimation in Satellite Systems in Presence of Coherent Signals Subject to Low SNR. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 109983–109993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Ma, X.; Sheng, W.; Han, Y. Sparsity-based direction-of-arrival and polarization estimation for mirrored linear vector sensor arrays. Signal Process. 2022, 192, 108369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, F.; Qi, B.; Meng, Z. DOA Estimation under GNSS Spoofing Attacks Using a Coprime Array: From a Sparse Reconstruction Viewpoint. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, Z.; Fu, H. A high resolution random linear sonar array based MUSIC method for underwater DOA estimation. In Proceedings of the 32nd Chinese Control Conference, Xi’an, China, 26–28 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, R.; Han, Y.; Sheng, W. A dual-resolution unitary ESPRIT method for DOA estimation based on sparse co-prime MIMO radar. Signal Process. 2023, 202, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Sheng, W.; Ma, X.; Kirubarajan, T. A maximum likelihood method for joint doa and polarization estimation based on manifold separation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2021, 57, 2481–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, T.; He, H.; Yang, J. Polarization estimation with vector sensor array in the underdetermined case. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5120913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Gao, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B. Gridless DOA Estimation with Extended Array Aperture in Automotive Radar Applications. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, A.; Avitabile, G.; Coviello, G. Multiple Source Angle of Arrival Estimation Through Phase Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, A.; Avitabile, G.; Talarico, C.; Coviello, G. A Reconfigurable Full-Digital Architecture for Angle of Arrival Estimation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2024, 71, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R. Multiple emitter location and signal parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulraj, A.; Roy, R.; Kailath, T. A subspace rotation approach to signal parameter estimation. Proc. IEEE 2005, 74, 1044–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swindlehurst, A.; Viberg, M. Subspace fitting with diversely polarized antenna arrays. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1993, 41, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Liu, W.; Ngan, H.Y. Joint doa and polarization estimation with crossed-dipole and tripole sensor arrays. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2020, 56, 4965–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Wan, Q.; Fan, R.; Wei, H. Improved music algorithm for multiple noncoherent subarrays. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2014, 21, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xin, J.; Zheng, N.; Sano, A. Computationally efficient subspace-based method for two-dimensional direction estimation with L-shaped array. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 3197–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Liu, W.; Ngan, H.Y. Joint 4-D doa and polarization estimation based on linear tripole arrays. In Proceedings of the 2017 22nd International Conference on Digital Signal Processing (DSP), London, UK, 23–25 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, F.; Jin, M.; Qiao, X. Low-complexity doa estimation based on compressed music and its performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 61, 1915–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, H.; Nan, H.; Ma, X.; Dai, M.; Qiu, S.; Han, Y. Ambiguity-free 2D doa and polarization estimation for mirrored linear crossed-dipole arrays. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2024, 60, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkar, S.; Harabi, F.; Gharsallah, A. Improved reactance domain unitary propagator algorithms for electronically steerable parasitic array radiator antennas. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2013, 7, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, Z. Extended Aperture 2-D Direction Finding with a Two-Parallel-Shape-Array Using Propagator Method. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2009, 8, 323–327. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Kailath, T. Fast subspace decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 539–551. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, Y. A DCT-based fast signal subspace technique for robust speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 2000, 8, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huarng, K.-C.; Yeh, C.C. A unitary transformation method for angle of arrival estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1991, 39, 975–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haardt, M.; Nossek, J.A. Unitary esprit: How to obtain increased estimation accuracy with a reduced computational burden. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1995, 43, 1232–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, M.; Gershman, A.B.; Haardt, M. Unitary root-music with a real-valued eigendecomposition: A theoretical and experimental performance study. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2000, 48, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.-G.; Jin, M.; Liu, S.; Qiao, X.L. Real-valued music for efficient direction estimation with arbitrary array geometries. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 1548–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Nehorai, A. Optimal polarized beampattern synthesis using a vector antenna array. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 576–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G. Two-Dimensional DOA Estimation for Polarization Sensitive Array Consisted of Spatially Spread Crossed-Dipole. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 5014–5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nan, H.; Ma, X.; Han, Y.; Sheng, W. A Computationally Efficient MUSIC Algorithm with an Enhanced DOA Estimation Performance for a Crossed-Dipole Array. Sensors 2025, 25, 3469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113469
Nan H, Ma X, Han Y, Sheng W. A Computationally Efficient MUSIC Algorithm with an Enhanced DOA Estimation Performance for a Crossed-Dipole Array. Sensors. 2025; 25(11):3469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113469
Chicago/Turabian StyleNan, Hao, Xiaofeng Ma, Yubing Han, and Weixing Sheng. 2025. "A Computationally Efficient MUSIC Algorithm with an Enhanced DOA Estimation Performance for a Crossed-Dipole Array" Sensors 25, no. 11: 3469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113469
APA StyleNan, H., Ma, X., Han, Y., & Sheng, W. (2025). A Computationally Efficient MUSIC Algorithm with an Enhanced DOA Estimation Performance for a Crossed-Dipole Array. Sensors, 25(11), 3469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25113469





