Prediction of Influence of Environmental Factors on the Toxicity of Pentachlorophenol on E. coli-Based Bioassays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain
2.2. Growth Conditions
2.3. Toxic Solutions
2.4. Bioassays
2.5. Data Acquisition
2.6. Data Processing
2.6.1. Raw Data Pre-Processing
2.6.2. EC50 Determination
2.6.3. Development of Exploratory Neural Network Models
2.6.4. Complementary Statistical Analyses
3. Results
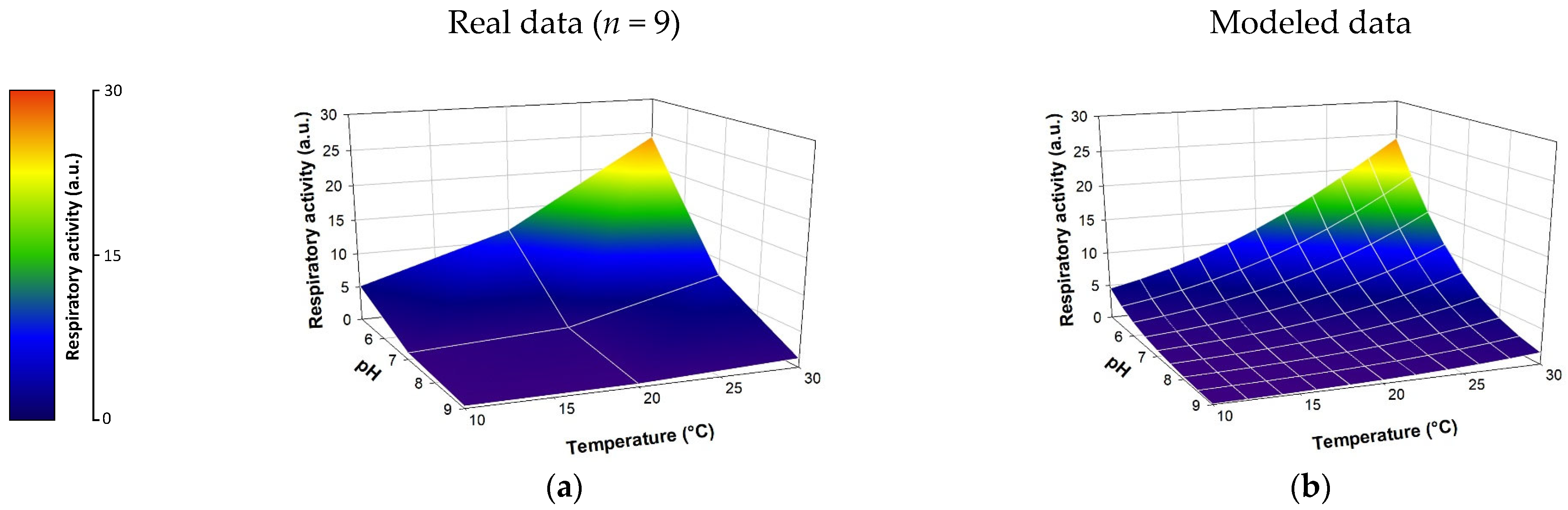
3.1. Effect of Abiotic Parameters (Temperature, pH, Conductivity) on the Respiratory Activity of the E. coli Strain
3.2. Modeling of Toxic Effects Induced by PCP as a Function of Abiotic Parameter Levels
3.2.1. Combined Effects of Abiotic Parameters (Temperature, pH, Conductivity) on the Inhibition of E. coli Respiratory Activity Induced by PCP
3.2.2. Development and Validation of Predictive Models
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kokkali, V.; van Delft, W. Overview of commercially available bioassays for assessing chemical toxicity in aqueous samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 61, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Gao, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhi, J. Redox Mediator-Based Microbial Biosensors for Acute Water Toxicity Assessment: A Critical Review. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 2513–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Renugopalakrishnan, V.; Liepmann, D.; Paulmurugan, R.; Malhotra, B.D. Cell-based biosensors: Recent trends, challenges and future perspectives. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.H.A.; Van Ginkel, S.W.; Hussein, M.A.M.; Abskharon, R.; Oh, S.-E. Toxicity assessment using different bioassays and microbial biosensors. Environ. Int. 2016, 92–93, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouanneau, S.; Durand-Thouand, M.-J.; Thouand, G. Design of a toxicity biosensor based on Aliivibrio fischeri entrapped in a disposable card. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 4340–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Han, H.; Liu, P.; Xiong, J.; Tian, F.; Li, X. Microbial Fuels Cell-Based Biosensor for Toxicity Detection: A Review. Sens. 2017, 17, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Jia, W.; Hou, C.; Lei, Y. Microbial biosensors: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 1788–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, F.; Turkewitz, A.P.; Martín-González, A.; Gutiérrez, J. Whole-cell biosensors for detection of heavy metal ions in environmental samples based on metallothionein promoters from Tetrahymena thermophila. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasseur, P.; Bois, F.; Ferard, J.F.; Rast, C. Influence of physicochemical parameters on the microtox test response. Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual. 1986, 1, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, S.; Zhou, X. Analyses of Factors to Affect the Bioassay System Using Luminescent Bacterium Vibrio fischeri. J. Health Sci. 2006, 52, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryabin, D.; Aleshina, E. Effect of salts on luminescence of natural and recombinant luminescent bacterial biosensors. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2008, 44, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 11348-2:2007(En); Water Quality—Determination of the Inhibitory Effect of Water Samples on the Light Emission of Vibrio Fischeri (Luminescent Bacteria Test)—Part 2: Method Using Liquid-Dried Bacteria. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Toro, D.M.D.; Allen, H.E.; Bergman, H.L.; Meyer, J.S.; Paquin, P.R.; Santore, R.C. Biotic ligand model of the acute toxicity of metals. 1. Technical Basis. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 2383–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyogi, S.; Wood, C.M. Biotic Ligand Model, a Flexible Tool for Developing Site-Specific Water Quality Guidelines for Metals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6177–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santore, R.C.; Ryan, A.C.; Kroglund, F.; Rodriguez, P.H.; Stubblefield, W.A.; Cardwell, A.S.; Adams, W.J.; Nordheim, E. Development and application of a biotic ligand model for predicting the chronic toxicity of dissolved and precipitated aluminum to aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamo, M.; Nagai, T. An application of the biotic ligand model to predict the toxic effects of metal mixtures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.S.; Balistrieri, L.S.; Todd, A.S. Using biotic ligand models to predict metal toxicity in mineralized systems. Appl. Geochem. 2015, 57, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, M.T.D.; Basiri, H.; Chrysochoou, G.; Enoch, S.J.; Firman, J.W.; Spînu, N.; Madden, J.C. The predictivity of QSARs for toxicity: Recommendations for improving model performance. Comput. Toxicol. 2025, 33, 100338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombelli, E.; Ringeissen, S. The computational prediction of toxicological effects in regulatory contexts: Current use and future potential of (Q)SAR tools. L’Actualité Chim. 2009, 335, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, K.; Kar, S.; Das, R.N. Chapter 1—Background of QSAR and Historical Developments. In Understanding the Basics of QSAR for Applications in Pharmaceutical Sciences and Risk Assessment; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-12-801505-6. [Google Scholar]
- Phull, B. 2.18—Marine Corrosion. In Shreir’s Corrosion; Cottis, B., Graham, M., Lindsay, R., Lyon, S., Richardson, T., Scantlebury, D., Stott, H., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 1107–1148. ISBN 978-0-444-52787-5. [Google Scholar]
- Chapter 11—Relevant applications. In Membrane Science and Technology; Drioli, E., Criscuoli, A., Curcio, E., Eds.; Membrane Contactors: Fundamentals, Applications and Potentialities; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; Volume 11, pp. 375–450. [Google Scholar]
- Office Francais de la Biodiversité Bienvenue sur Naïades|Naïades. Available online: https://naiades.eaufrance.fr (accessed on 24 July 2020).
- Tizzard, A.C.; Bergsma, J.H.; Lloyd-Jones, G. A resazurin-based biosensor for organic pollutants. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fai, P.B.; Grant, A. A rapid resazurin bioassay for assessing the toxicity of fungicides. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Wilson, I.; Orton, T.; Pognan, F. Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5421–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byth, H.-A.; Mchunu, B.I.; Dubery, I.A.; Bornman, L. Assessment of a simple, non-toxic Alamar Blue cell survival assay to monitor tomato cell viability. Phytochem. Anal. 2001, 12, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, K.J.; Brown, P.L.; Byrne, R.H.; Gajda, T.; Hefter, G.; Sjöberg, S.; Wanner, H. Chemical speciation of environmentally significant heavy metals with inorganic ligands. Part 1: The Hg2+– Cl–, OH–, CO32–, SO42–, and PO43– aqueous systems (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2005, 77, 739–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindimian, E.; Robaut, C.; Fillion, G. A method for cooperative or noncooperative binding studies using nonlinear regression analysis on a microcomputer. J. Appl. Biochem. 1983, 5, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Garric, J.; Migeon, B.; Vindimian, E. Lethal effects of draining on brown trout. A predictive model based on field and laboratory studies. Water Res. 1990, 24, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, K.J. On the use and utility of the Weibull model in the analysis of survival data. Control. Clin. Trials 2003, 24, 682–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutgers, M.; van Bommel, S.; Breure, A.M.; van Andel, J.G.; Duetz, W.A. Effect of pH on the toxicity and biodegradation of pentachlorophenol by Sphingomonas sp strain P5 in nutristat culture. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1998, 17, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcand, Y.; Hawari, J.; Guiot, S.R. Solubility of pentachlorophenol in aqueous solutions: The pH effect. Water Res. 1995, 29, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orser, C.S.; Lange, C.C. Molecular analysis of pentachlorophenol degradation. Biodegradation 1994, 5, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatout, S.; Leys, N.; Hendrickx, L.; Dams, A.; Mergeay, M. Physiological changes induced in bacteria following pH stress as a model for space research. Acta Astronaut. 2007, 60, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.M. Bacterial responses to osmotic challenges. J. Gen. Physiol. 2015, 145, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, A.; Shah, N.P. Effect of salt stress on morphology and membrane composition of Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus casei, and Bifidobacterium bifidum, and their adhesion to human intestinal epithelial-like Caco-2 cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 2594–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S.; Nikaido, H. High Salt Concentrations Increase Permeability through OmpC Channels of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 26464–26473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murínová, S.; Dercová, K. Response Mechanisms of Bacterial Degraders to Environmental Contaminants on the Level of Cell Walls and Cytoplasmic Membrane. Int. J. Microbiol. 2014, 2014, 873081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedwell, D.B. Effect of low temperature on microbial growth: Lowered affinity for substrates limits growth at low temperature. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 30, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, R.W.; Chapman, J.C.; Lim, R.P.; Gehrke, P.C.; Sunderam, R.M. Interactions between water temperature and contaminant toxicity to freshwater fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 34, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, D.J.; Alloway, B.J. Influence of Dissolved Organic Matter on the Solubility of Heavy Metals in Sewage-Sludge-Amended Soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2008, 39, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritash, A.K.; Kaushik, C.P. Biodegradation aspects of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turschwell, M.P.; Connolly, S.R.; Schäfer, R.B.; De Laender, F.; Campbell, M.D.; Mantyka-Pringle, C.; Jackson, M.C.; Kattwinkel, M.; Sievers, M.; Ashauer, R.; et al. Interactive effects of multiple stressors vary with consumer interactions, stressor dynamics and magnitude. Ecol. Lett. 2022, 25, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nin, C.J.; Rodgher, S. Effect of a temperature rise on metal toxicity for the aquatic biota: A systematic review. Rev. Bras. Ciências Ambient. 2021, 56, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman, A.D.; Parkerton, T.F.; Letinski, D.J.; Sutherland, C.A.; Butler, J.D.; Toro, D.M.D. Modeling Time-Dependent Aquatic Toxicity of Hydrocarbons: Role of Organism Weight, Temperature, and Substance Hydrophobicity. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryabin, D.G.; Efremova, L.V.; Karimov, I.F.; Manukhov, I.V.; Gnuchikh, E.Y.; Miroshnikov, S.A. Comparative sensitivity of the luminescent Photobacterium phosphoreum, Escherichia coli, and Bacillus subtilis strains to toxic effects of carbon-based nanomaterials and metal nanoparticles. Microbiology 2016, 85, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Wang, X.C.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Wu, M.N.; Wang, N. Bioassay based luminescent bacteria: Interferences, improvements, and applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminot, A.; Kérouel, R. Hydrologie des Écosystèmes Marins: Paramètres et Analyses; Editions Quae: Versailles, France, 2004; ISBN 978-2-84433-133-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Tao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qu, W. Global Trends and Diversity in Pentachlorophenol Levels in the Environment and in Humans: A Meta-Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4668–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. California Environmental Protection Agency. Public Health Goal for Pentachlorophenol in Drinking Water; Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment: Sacramento, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Commission Regulation (EC) No 552/2009 of 22 June 2009 Amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as Regards Annex XVII (Text with EEA Relevance); European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2009; Volume 164. [Google Scholar]



| pH = 5 | pH = 6 | pH = 7 | pH = 8 | pH = 9 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solution A | 98.8% | 86.8% | 38.5% | 6% | 0.3% |
| Solution B | 1.2% | 13.2% | 61.5% | 88% | 99.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jouanneau, S.; Thouand, G. Prediction of Influence of Environmental Factors on the Toxicity of Pentachlorophenol on E. coli-Based Bioassays. Sensors 2025, 25, 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103215
Jouanneau S, Thouand G. Prediction of Influence of Environmental Factors on the Toxicity of Pentachlorophenol on E. coli-Based Bioassays. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103215
Chicago/Turabian StyleJouanneau, Sulivan, and Gerald Thouand. 2025. "Prediction of Influence of Environmental Factors on the Toxicity of Pentachlorophenol on E. coli-Based Bioassays" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103215
APA StyleJouanneau, S., & Thouand, G. (2025). Prediction of Influence of Environmental Factors on the Toxicity of Pentachlorophenol on E. coli-Based Bioassays. Sensors, 25(10), 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103215










