Laboratory Cross-Sensitivity Evaluation of Low-Cost Electrochemical Formaldehyde Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laboratory Evaluation System
2.2. Interference Gas Selection
2.3. Methods for Concentration-Only Tests
2.4. Methods for Cross-Sensitivity Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentration-Only Tests
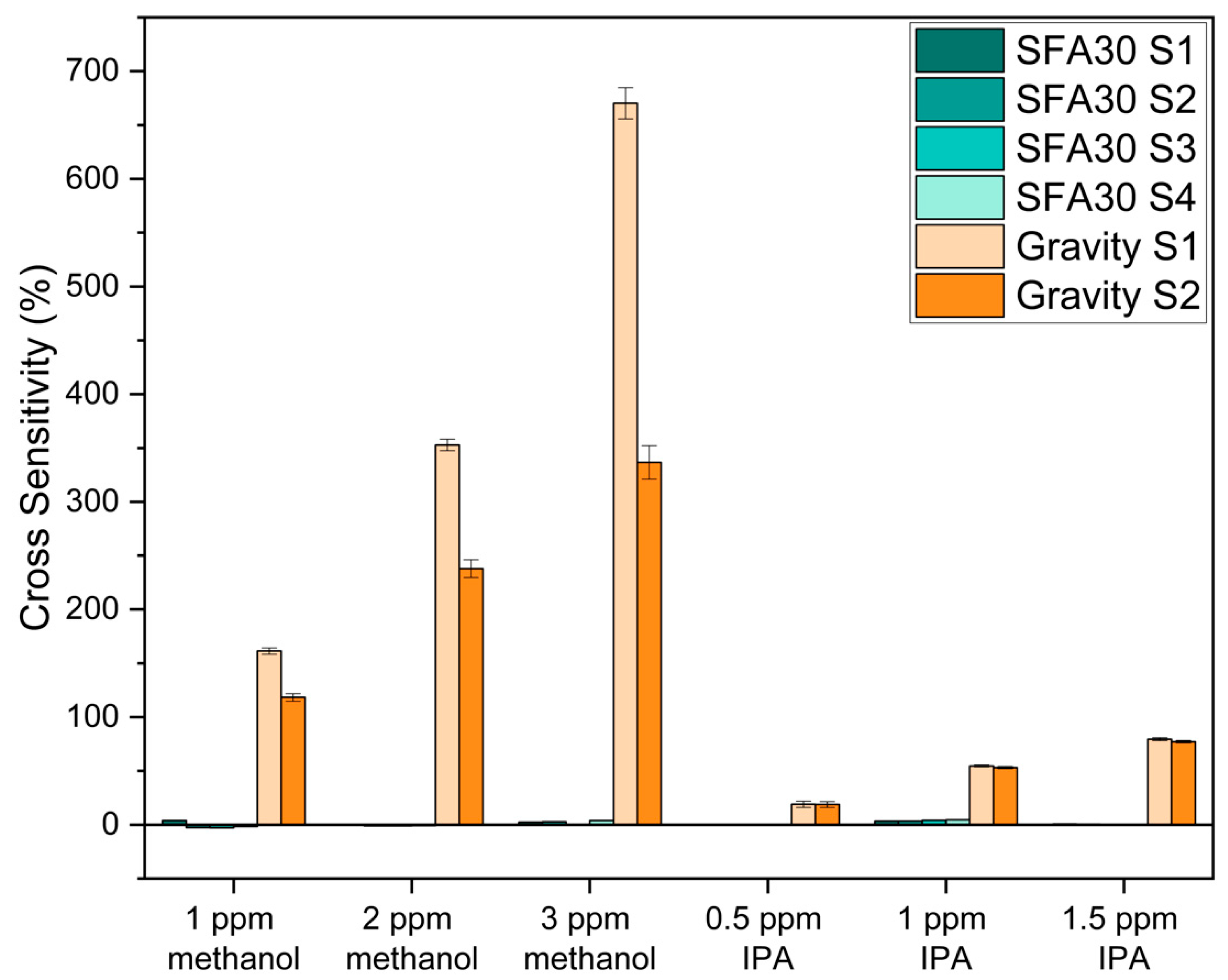
3.2. Cross-Sensitivity Evaluation
3.3. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kelsch, A.; Eatough, D.J.; Thalman, R.; Daher, N.; Kelly, K.; Jaramillo, I.C.; Hansen, J.C. Sources of Formaldehyde in Bountiful, Utah. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, J.K. Formaldehyde and Cancer: A Critical Review. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1994, 66, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, G.D.; Wolkoff, P. Cancer Effects of Formaldehyde: A Proposal for an Indoor Air Guideline Value. Arch. Toxicol. 2010, 84, 423–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Summary of Results for the 2005 National-Scale Assessment; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Jacob, D.J.; Keutsch, F.N.; Mickley, L.J.; Scheffe, R.; Strum, M.; González Abad, G.; Chance, K.; Yang, K.; Rappenglück, B.; et al. Formaldehyde (HCHO) As a Hazardous Air Pollutant: Mapping Surface Air Concentrations from Satellite and Inferring Cancer Risks in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5650–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, S.; Czerwinski, J.; Comte, P.; Popovicheva, O.; Kireeva, E.; Müller, L.; Heeb, N.; Mayer, A.; Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Comparison of the Toxicity of Diesel Exhaust Produced by Bio- and Fossil Diesel Combustion in Human Lung Cells Invitro. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, J.H.; Seinfeld, J.H. Chemistry of Secondary Organic Aerosol: Formation and Evolution of Low-Volatility Organics in the Atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3593–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Holloway, T.; Bindl, M.; Harkey, M.; De Smedt, I. Ambient Formaldehyde over the United States from Ground-Based (AQS) and Satellite (OMI) Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. United States Environmental Protection Agency Technical Note—Guidance for Developing Enhanced Monitoring Plans. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2019-11/documents/pams_emp_guidance.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2024).
- Pei, Z.; Balitskiy, M.; Thalman, R.; Kelly, K.E. Laboratory Performance Evaluation of a Low-Cost Electrochemical Formaldehyde Sensor. Sensors 2023, 23, 7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkey, M.; Holloway, T.; Kim, E.J.; Baker, K.R.; Henderson, B. Satellite Formaldehyde to Support Model Evaluation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD032881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giarracca, L.; Tran, L.S.; Gosselin, S.; Hanoune, B.; Gasnot, L. Quantitative Measurement of Formaldehyde Formed in Combustion Processes Using Gas Chromatography Analytical Approach. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2023, 195, 2716–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillett, K.W.; Kreibich, H.; Ayers, G.P. Measurement of Indoor Formaldehyde Concentrations with a Passive Sampler. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2051–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckel, A.; Richter, A.; Tarsu, T.; Wittrock, F.; Hak, C.; Pundt, I.; Junkermann, W.; Burrows, J.P. MAX-DOAS Measurements of Formaldehyde in the Po-Valley. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, R.; Guo, Y.; Yan, Y.; Ding, Z.; Zhou, B. Investigating the Sources of Formaldehyde and Corresponding Photochemical Indications at a Suburb Site in Shanghai From MAX-DOAS Measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brienza, S.; Galli, A.; Anastasi, G.; Bruschi, P. A Low-Cost Sensing System for Cooperative Air Quality Monitoring in Urban Areas. Sensors 2015, 15, 12242–12259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauerová, P.; Šindelářová, A.; Rychlík, Š.; Novák, Z.; Keder, J. Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors: One-Year Field Comparative Measurement of Different Gas Sensors and Particle Counters with Reference Monitors at Tusimice Observatory. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, P.; Gómez-Suárez, J.; Suárez, J.I.; Lozano, J. Low-Cost Air Quality Measurement System Based on Electrochemical and PM Sensors with Cloud Connection. Sensors 2021, 21, 6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Viciano-Tudela, S.; Parra, L.; Lacuesta, R.; Lloret, J. Evaluation of Suitability of Low-Cost Gas Sensors for Monitoring Indoor and Outdoor Urban Areas. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 20968–20975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jayaratne, R.; Thai, P.; Kuhn, T.; Zing, I.; Christensen, B.; Lamont, R.; Dunbabin, M.; Zhu, S.; Gao, J.; et al. Low-Cost Sensors as an Alternative for Long-Term Air Quality Monitoring. Environ. Res. 2020, 185, 109438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Aye, L.; Ngo, T.D.; Zhou, J. Performance Evaluation of Low-Cost Air Quality Sensors: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriano, D.; Prato, M.; Pfister, V.; Cassano, G.; Camporeale, G.; Dipinto, S.; Penza, M. 15—Stationary and Mobile Low-Cost Gas Sensor-Systems for Air Quality Monitoring Applications. In Proceedings of the Fourth Scientific Meeting EuNetAir, Linkoping, Sweden, 3–5 June 2015; pp. 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagulian, F.; Barbiere, M.; Kotsev, A.; Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Lagler, F.; Redon, N.; Crunaire, S.; Borowiak, A. Review of the Performance of Low-Cost Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hun, D.E.; Corsi, R.L.; Morandi, M.T.; Siegel, J.A. Formaldehyde in Residences: Long-Term Indoor Concentrations and Influencing Factors. Indoor Air 2010, 20, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisel, C.P.; Zhang, J.; Turpin, B.J.; Morandi, M.T.; Colome, S.; Stock, T.H.; Spektor, D.M.; Korn, L.; Winer, A.; Alimokhtari, S.; et al. Relationship of Indoor, Outdoor and Personal Air (RIOPA) Study: Study Design, Methods and Quality Assurance/Control Results. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 2005, 15, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo Alonso, M.; Madsen, H.; Liu, P.; Jørgensen, R.B.; Jørgensen, T.B.; Christiansen, E.J.; Myrvang, O.A.; Bastien, D.; Mathisen, H.M. Evaluation of Low-Cost Formaldehyde Sensors Calibration. Build. Environ. 2022, 222, 109380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Huertas, A.; Rebeiro-Hargrave, A.; Fung, P.L.; Varjonen, S.; Hieta, T.; Tarkoma, S.; Petaja, T. Low-Cost Formaldehyde Sensor Evaluation and Calibration in a Controlled Environment. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 11791–11802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, V.; Kumar, A.; Nagpal, S.; Jain, V.K. Ultrasensitive Detection of Formaldehyde at Room Temperature Using Si-Chip Assisted MOS/SiNWs Nanocomposite Based Sensor. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 919, 165840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. Batch Fabrication of Formaldehyde Sensors Based on LaFeO3 Thin Film with Ppb-Level Detection Limit. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 349, 130738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Li, H.; Wang, F.; Yuan, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, P.; Xie, L.; Sun, Y.; Chang, F. A High Sensitive and Low Detection Limit of Formaldehyde Gas Sensor Based on Hierarchical Flower-like CuO Nanostructure Fabricated by Sol–Gel Method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 27, 6766–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispi, S.; Neri, G. Development of a Conductometric Sensor Based on Al,Ca-Doped ZnO for the Detection of Formaldehyde. Sensors 2022, 22, 7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descamps, M.N.; Bordy, T.; Hue, J.; Mariano, S.; Nonglaton, G.; Schultz, E.; Tran-Thi, T.H.; Vignoud-Despond, S. Real-Time Detection of Formaldehyde by a Sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 170, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, N.; Deng, D.; Xing, X.; Xiao, X.; Wang, Y. Formaldehyde Detection: SnO2 Microspheres for Formaldehyde Gas Sensor with High Sensitivity, Fast Response/Recovery and Good Selectivity. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 238, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Lin, S. Highly Sensitive and Selective Room-Temperature Formaldehyde Sensors Using Hollow TiO2 Microspheres. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 219, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D.; Zi, B.; Zeng, J.; Lu, Q.; Xiong, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Q. Ultrasensitive Formaldehyde Sensor Based on SnO2with Rich Adsorbed Oxygen Derived from a Metal Organic Framework. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 2577–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, M.; Ren, J.; Liu, C.; Tan, J. Visible Light-Assisted Formaldehyde Sensor Based on HoFeO3 Nanoparticles with Sub-Ppm Detection Limit. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 16337–16344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washenfelder, R.A.; Attwood, A.R.; Flores, J.M.; Zarzana, K.J.; Rudich, Y.; Brown, S.S. Broadband Cavity-Enhanced Absorption Spectroscopy in the Ultraviolet Spectral Region for Measurements of Nitrogen Dioxide and Formaldehyde. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Leathey, L.A.; Anghelita, P.; Constantin, A.I.; Circiumaru, G.; Chihaia, R.A. System for Indoor Comfort and Health Monitoring Tested in Office Building Environment. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fissore, V.I.; Arcamone, G.; Astolfi, A.; Barbaro, A.; Carullo, A.; Chiavassa, P.; Clerico, M.; Fantucci, S.; Fiori, F.; Gallione, D.; et al. Multi-Sensor Device for Traceable Monitoring of Indoor Environmental Quality. Sensors 2024, 24, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bapat, K.P.; Im, O.; Wu, C.; Kim, K. An Air-Depolluting System for Indoor VOC Reduction. In Proceedings of the ARCC-EAAE 2022 International Conference, Resilient City: Physical, Social, and Economic Perspectives, Miami, FL, USA, 2–5 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Marques, G.; Pitarma, R. MHealth: Indoor Environmental Quality Measuring System for Enhanced Health and Well-Being Based on Internet of Things. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2019, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, J.; Tondini, S.; Gallichi Nottiani, D.; Scilla, R.; Gambaro, A.; Pasut, W.; Babich, F.; Lollini, R. Environmental Quality BOX (EQ-OX): A Portable Device Embedding Low-Cost Sensors Tailored for Comprehensive Indoor Environmental Quality Monitoring. Sensors 2024, 24, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, S.Q.; Goodell, B. Formaldehyde Emission from Wood Promoted by Lignin in the Presence of Iron Residues. Green. Chem. 2022, 24, 6631–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignau-Laulhere, J.; Plaisance, H.; Mocho, P.; Raulin, K.; Bigay, Y.; Desauziers, V. Performance of the Radiello® Diffusive Sampler for Formaldehyde Measurement: The Influence of Exposure Conditions and Ozone Interference. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 5497–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardo, M.T.; Cipolla, M.; Izzotti, A.; Canepa, P.; Fontana, V. A Comparison of Airborne Formaldehyde Field Measurements Collected in an Anatomic Pathology Laboratory. J. Environ. Prot. 2024, 15, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turlybekuly, A.; Shynybekov, Y.; Soltabayev, B.; Yergaliuly, G.; Mentbayeva, A. The Cross-Sensitivity of Chemiresistive Gas Sensors: Nature, Methods, and Peculiarities: A Systematic Review. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 6358–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvall, R.M.; Clements, A.L.; Hagler, G.; Kamal, A.; Kilaru, V.; Goodman, L.; Frederick, S.; Barkjohn, K.K.; VonWald, I.; Greene, D.; et al. Performance Testing Protocols, Metrics, and Target Values for Fine Particulate Matter Air Sensors: Use in Ambient, Outdoor, Fixed Site, Non-Regulatory Supplemental and Informational Monitoring Applications. EPA/600/R-20/280; U.S. EPA Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Cao, W.; Peng, C.; Wang, T.; Li, B.; Ma, H.; Su, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, J.; Zeng, M. Construction, Application and Verification of a Novel Formaldehyde Gas Sensor System Based on Ni-Doped SnO2Nanoparticles. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 11023–11030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alolaywi, H.Y.; Duanghathaipornsuk, S.; Kim, S.S.; Li, C.-H.; Jinschek, J.R.; Kim, D.-S.; Alba-Rubio, A.C. Electrochemical MoOx/Carbon Nanocomposite-Based Gas Sensor for Formaldehyde Detection at Room Temperature. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 067525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, G.E.; Nagaoka, M. Environmental Protection Agency EPA Hazard Summary: Formaldehyde; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Parrish, D.D.; Ryerson, T.B.; Mellqvist, J.; Johansson, J.; Fried, A.; Richter, D.; Walega, J.G.; Washenfelder, R.A.; De Gouw, J.A.; Peischl, J.; et al. Primary and Secondary Sources of Formaldehyde in Urban Atmospheres: Houston Texas Region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 3273–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvall, R.M.; Clements, A.L.; Hagler, G.; Kamal, A.; Kilaru, V.; Goodman, L.; Frederick, S.; Barkjohn, K.K.; VonWald, I.; Greene, D.; et al. Performance Testing Protocols, Metrics, and Target Values for Ozone Air Sensors. EPA/600/R-20/279; U.S. EPA Office of Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mead, M.I.; Popoola, O.A.M.; Stewart, G.B.; Landshoff, P.; Calleja, M.; Hayes, M.; Baldovi, J.J.; McLeod, M.W.; Hodgson, T.F.; Dicks, J.; et al. The Use of Electrochemical Sensors for Monitoring Urban Air Quality in Low-Cost, High-Density Networks. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 186–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.C.; Lee, J.D.; Edwards, P.M.; Shaw, M.D.; Evans, M.J.; Moller, S.J.; Smith, K.R.; Buckley, J.W.; Ellis, M.; Gillot, S.R.; et al. Evaluating the Performance of Low Cost Chemical Sensors for Air Pollution Research. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 189, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, T.; Grammatikos, S.; Cheffena, M. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticle-Carbon Nanotube Composite Electrochemical Gas Sensor for Highly Selective and Sensitive Detection of Methanol Vapour. Analyst 2024, 149, 2428–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, J.F.; Essalik, A.; Marusic, J.C. Micromachined Thin Film Solid State Electrochemical CO2, NO2 and SO2 Gas Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 59, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaiyan, K.P.; Mukundan, R. Electrochemical Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring. Electrochem. Soc. Interface 2019, 28, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.S.; Kim, J.W.; Jung, S.J.; Park, C.O. Suppression of NO and SO2 Cross-Sensitivity in Electrochemical CO2 Sensors with Filter Layers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 113, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wusiman, M.; Taghipour, F. Methods and Mechanisms of Gas Sensor Selectivity. Crit. Rev. Solid. State Mater. Sci. 2022, 47, 416–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijling, B.; Jiang, Q.; De Jonge, D.; Bocconi, S. Field Calibration of Electrochemical NO2 Sensors in a Citizen Science Context. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 1297–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
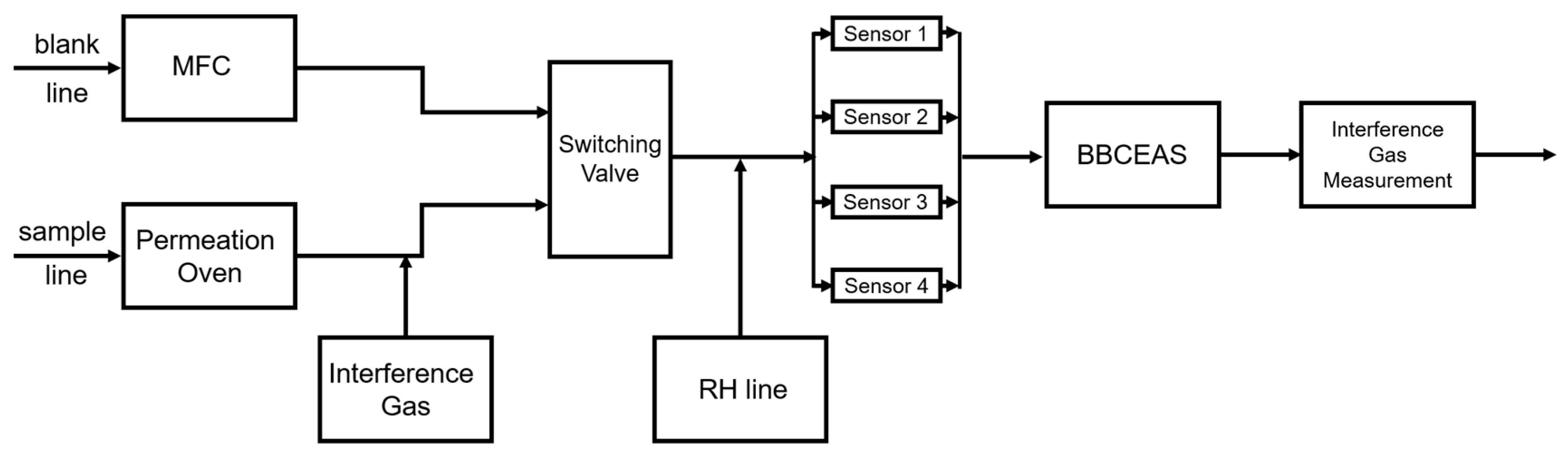
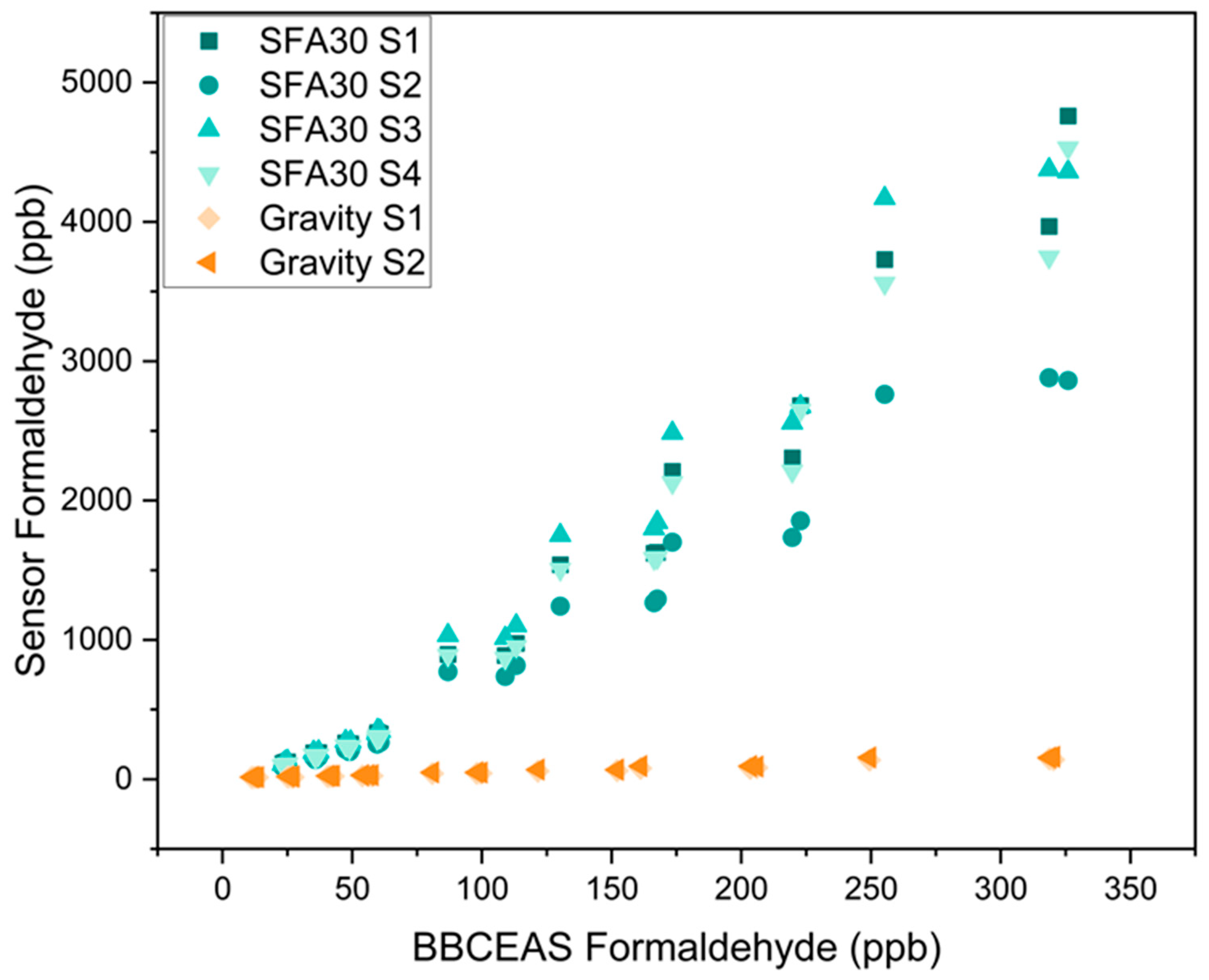
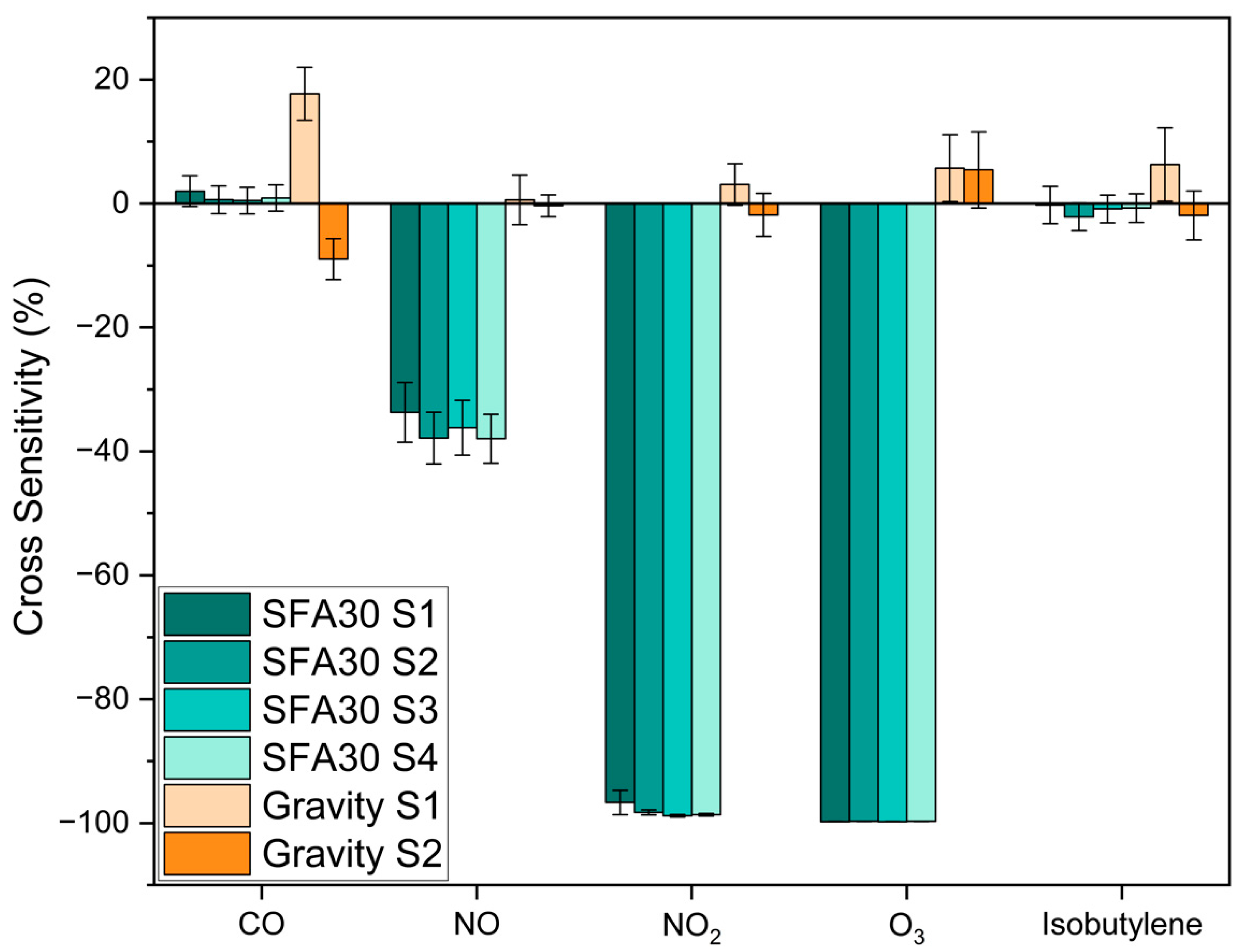
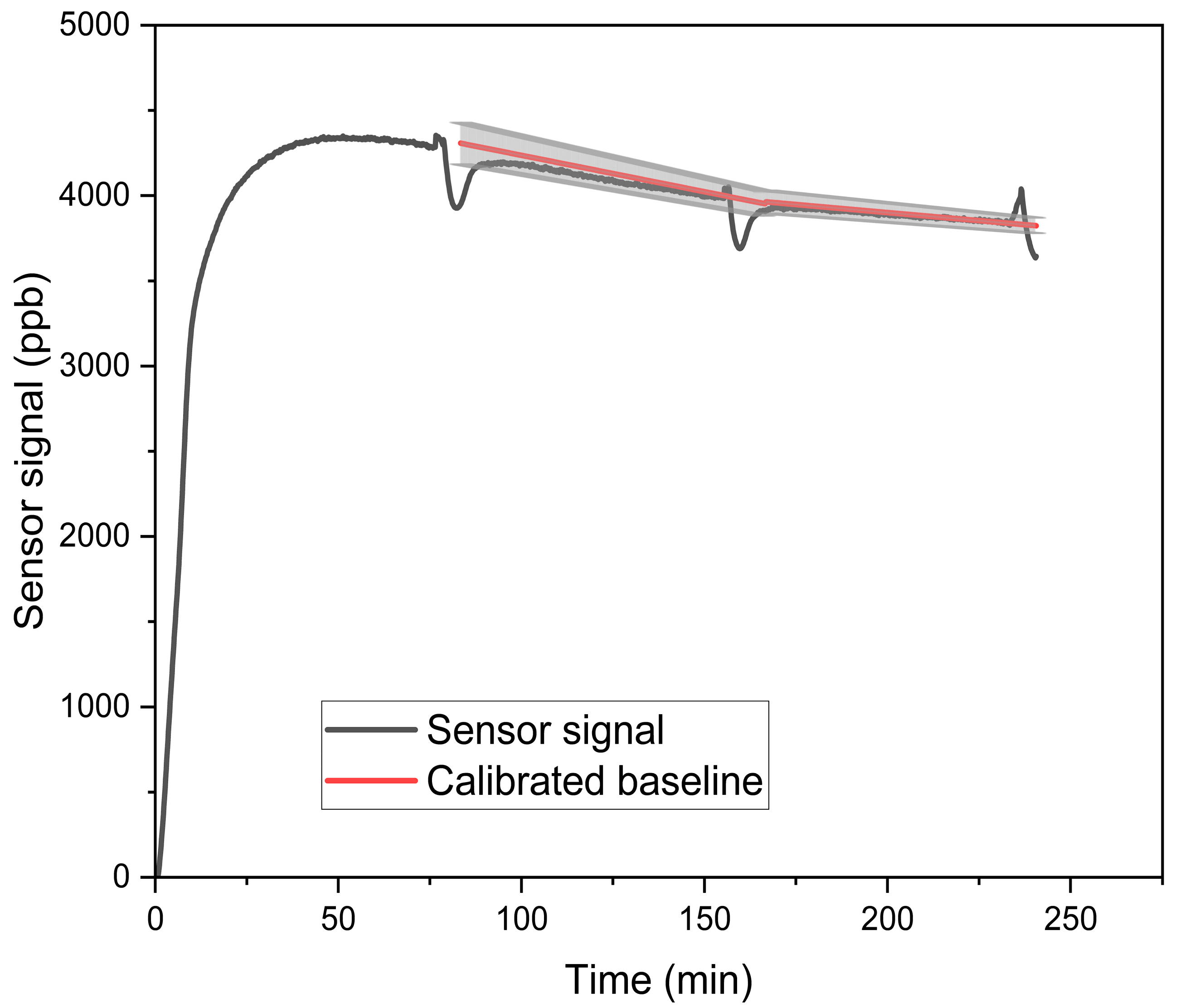
| Reference | Sensor Type | Concentration (ppb) | Temperature (°C) | RH (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pei et al. [10] | EC | 0–76 | 0–40 | 0–75 |
| Alonso et al. [26] | Micro fuel cell | 17.3–477 | 19.9–27.7 | 26.8–72.6 |
| Chattopadhyay et al. [27] | EC/MO | 0–800 | 22–50 | 8–85 |
| Gautam et al. [28] | MO | 10–1,000,000 | Room temperature | 49 ± 5 |
| Hu et al. [29] | MO | 50–1000 | 90–150 | N/A |
| Deng et al. [30] | MO | 50–1000 | 160–320 | 25 |
| Crispi and Neri [31] | MO | 125–4000 | 100–400 | N/A |
| Descamps et al. [32] | Fluorescence-based | 0–192 | 15–35 | 0–72.5 |
| Li et al. [33] | MO | 1000–500,000 | 200 | 25–30 |
| Li et al. [34] | MO | 124–5000 | Room temperature | 40–50 |
| Deng et al. [35] | MO | 1000–100,000 | 30–200 | 20–90 |
| Song et al. [36] | MO | 80–5000 | 140–180 | 11–75 |
| Sensor | SFA30 | Gravity | PS1-HCHO-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Sensirion AG | DFRobot | SGX Sensortech |
| Sensor type | Electrochemical | Electrochemical | Electrochemical |
| Price | USD 45 | USD 50 | USD 150 |
| LOD * | <20 ppb | Not reported | 10 ppb |
| Publications that used/evaluated the sensor | Pei et al. [10] El-Leathey et al. [38] Crispi and Neri [31] Fissore et al. [39] | Bapat et al. [40] Marques and Pitarma [41] Corona et al. [42] Fu et al. [43] | Not reported |
| Gas | Concentration * | |
|---|---|---|
| Outdoor trace gas (ppb) | CO | 547 ± 129 |
| Isobutylene | 108 ± 4.06 | |
| NO | 33.4 ± 0.587 | |
| NO2 | 38.5 ± 0.891 | |
| O3 | 68.6 ± 0.877 | |
| Indoor VOCs (ppm) | Methanol | 1, 2, or 3 |
| IPA | 0.5, 1, or 1.5 |
| Target Gas | Reference/Research-Grade Instruments |
|---|---|
| CO | Q-Trak 7575, TSI, Shoreview, MN, USA |
| Isobutylene | |
| NO | Model 42i NO-NO2-NOx Analyzer, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA |
| NO2 | |
| O3 | Model 106-L ozone monitor, 2B Technologies |
| Metrics | SFA30 | Gravity |
|---|---|---|
| Slope * | 13.2 ± 0.356 | 0.462 ± 0.0141 |
| Intercept * | −369 ± 52.9 | 3.86 ± 1.99 |
| R2 | 0.936 | 0.959 |
| RMSE (ppb) | 24.1 | 19.1 |
| NRMSE (%) | 7.95 | 6.18 |
| CV (%) | 4.50 | 1.13 |
| LOD (ppb) | 13.7 | 21.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pei, Z.; Kelly, K.E. Laboratory Cross-Sensitivity Evaluation of Low-Cost Electrochemical Formaldehyde Sensors. Sensors 2025, 25, 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103096
Pei Z, Kelly KE. Laboratory Cross-Sensitivity Evaluation of Low-Cost Electrochemical Formaldehyde Sensors. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103096
Chicago/Turabian StylePei, Zheyuan, and Kerry E. Kelly. 2025. "Laboratory Cross-Sensitivity Evaluation of Low-Cost Electrochemical Formaldehyde Sensors" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103096
APA StylePei, Z., & Kelly, K. E. (2025). Laboratory Cross-Sensitivity Evaluation of Low-Cost Electrochemical Formaldehyde Sensors. Sensors, 25(10), 3096. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103096







