Hybrid Mode Sensor Fusion for Accurate Robot Positioning
Abstract
Highlights
- Sensor data fusion works—simpler sensors have higher accuracy.
- There is an increase in performance with sensor fusion in a hybrid mode compared to a single-level fusion process.
- Robotic positions can be rectified using sensor data fusion.
- Typically, a sensor fusion level is focused at the third level of fusion according to the provided classification.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Titles;
- Research results;
- Methodology;
- Applications.
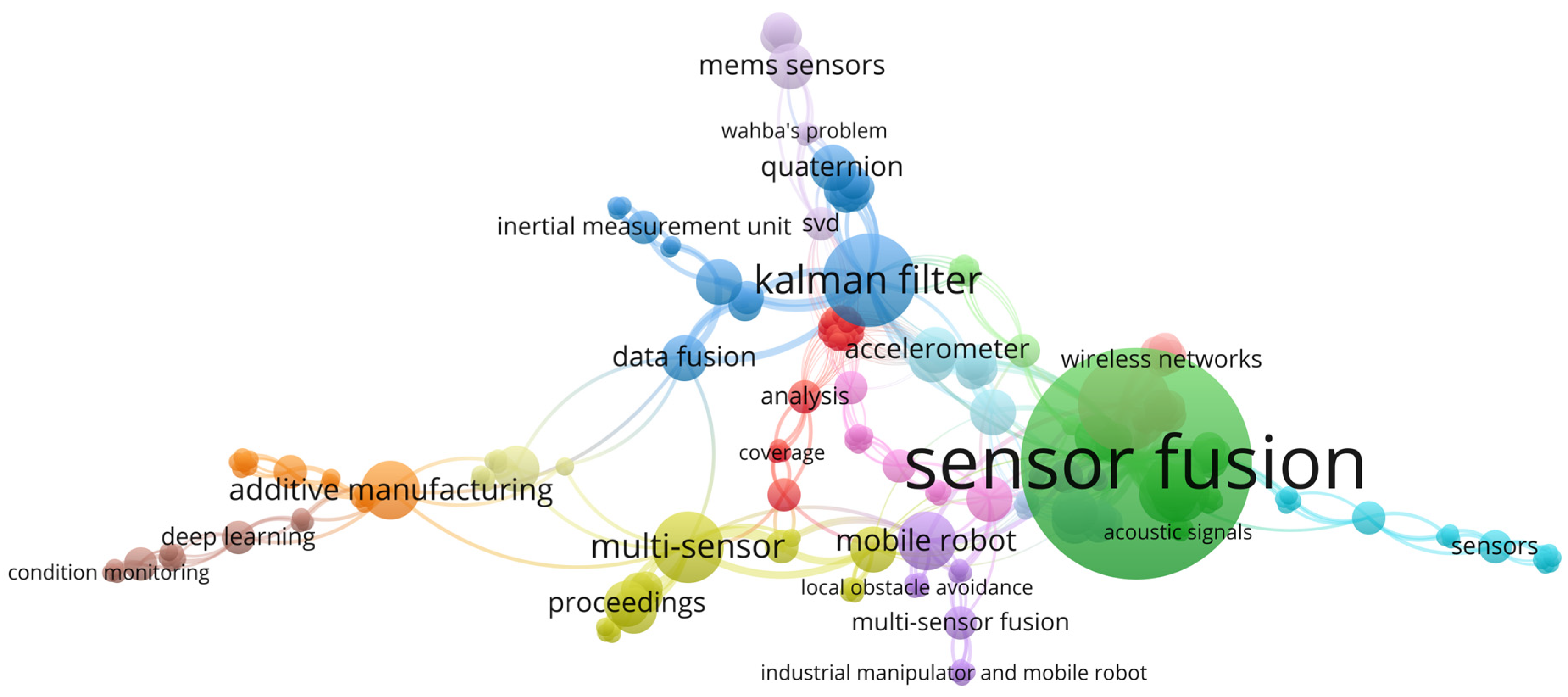
3. Technology of Sensor Fusion
3.1. Levels of Sensor Fusion
| Methods of Sensor Data Fusion | Application | Achievement | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fuzzy logic-based data fusion method | Robotics and automation | Introduced a novel fuzzy logic-based sensor data fusion method | [37] |
| Sensor data fusion for microrobot navigation | Microrobot navigation | Proposed a method for improving navigation in microrobots through sensor data fusion | [34] |
| MEMS sensor data fusion algorithms | Micro-electro-mechanical systems | Developed data fusion algorithms for MEMS sensors | [35] |
| Kalman filters | Navigation and tracking systems | Demonstrated effectiveness of Kalman filters in sensor data fusion | [38] |
| Deep learning-based sensor data fusion | Environmental monitoring | Introduced a deep learning approach to sensor data fusion for environmental data | [39] |
| Machine learning-based data fusion | Environmental monitoring | Proposed a multi-sensor data fusion method that uses machine learning | [40] |
| Deep learning-based multi-sensor data fusion | Autonomous vehicles | Improved sensor data fusion in autonomous vehicles using deep learning | [36] |
| Survey of sensor data fusion methods | Autonomous driving | Performed comprehensive survey on sensor data fusion methods in autonomous driving | [41] |
| Sensor data fusion techniques for IoT | Industrial Internet of Things | Discussed sensor data fusion methods that are applicable to IoT environments | [42] |
3.2. Sensor Fusion Software
4. Sensor Data Fusion in Technical Applications
4.1. Sensor Fusion in Mobile Robotics
4.2. Sensor Fusion in Production Processes
4.3. Sensor Fusion Algorithm in Robotics
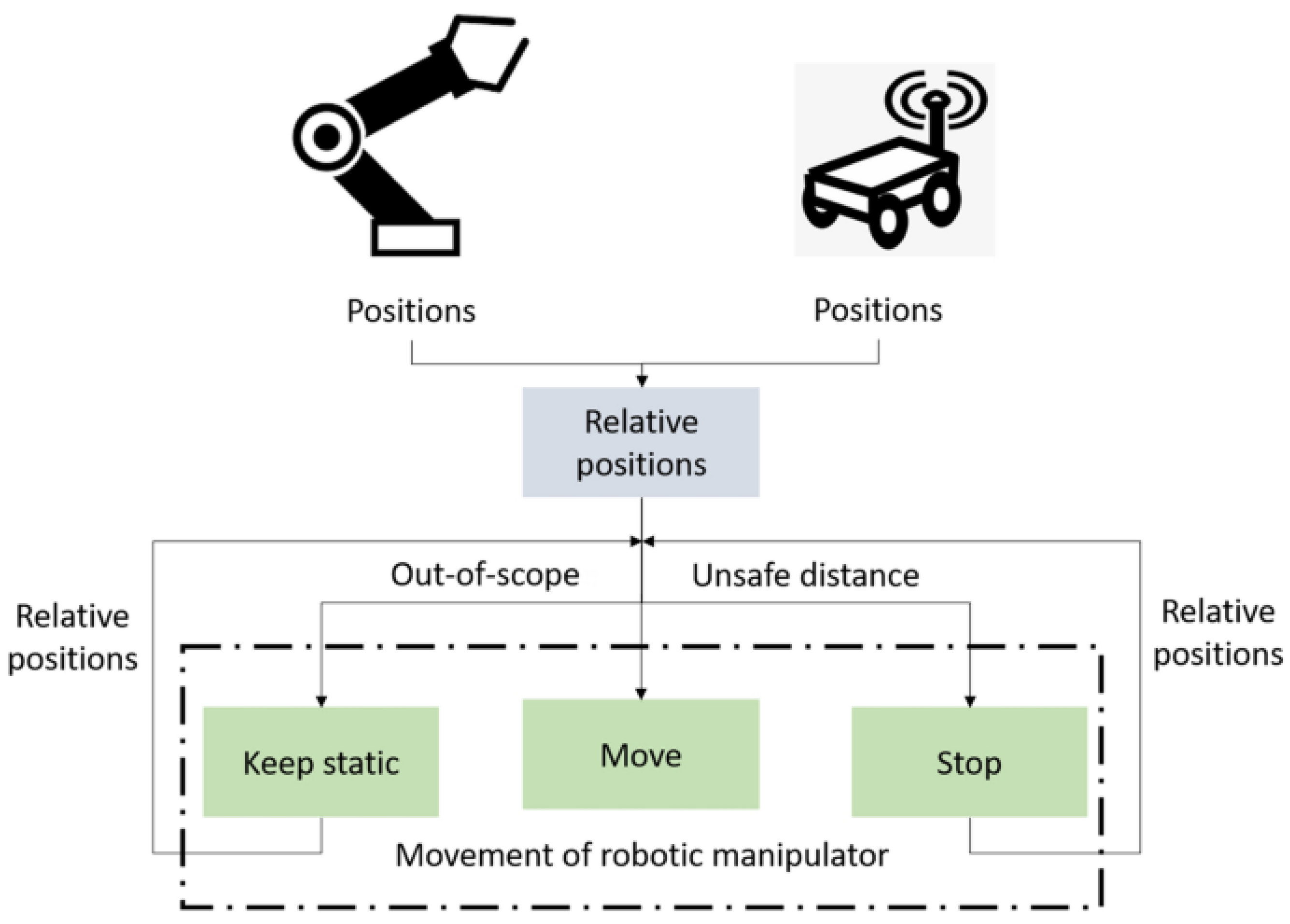
4.4. Sensor Fusion Technique for Localization and Position Detection
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- The widespread adoption of multi-sensory fusion as a key approach to overcome the limitations of individual sensors;
- A movement towards more complex and adaptive fusion algorithms that can effectively operate in real time and dynamically respond to environmental changes;
- The integration of machine learning and deep learning methods to improve the quality of data fusion and decision making;
- The creation of highly autonomous robotic systems capable of performing complex tasks under uncertain and changing conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHRS | Attitude and Heading Reference System |
| AMRs | Autonomous mobile robots |
| ANFIS | Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Interface |
| CNC | Computer numerical control |
| DKF | Decentralized Kalman filter |
| EKF | Extended Kalman filter |
| GTA | Gas tungsten arc |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| IoT | Industrial Internet of Things |
| IMUs | Inertial measurement units |
| IR | Infra-red |
| KF | Kalman filter |
| LiDAR | Light detection and ranging |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory |
| MIMUs | Magnetic and inertial measurement units |
| µSCM | Micro search-coil magnetometer |
| MEMS | Microelectromechanical system |
| HES | Micro-Hall-effect sensor |
| MDS | Multidimensional Scaling |
| PDR | Pedestrian dead reckoning |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| RF | Radio frequency |
| ROS | Robot Operating System |
| SFAs | Sensor fusion algorithms |
| SLAM | Simultaneous localization and mapping |
| UWB | Ultra-Wideband Positioning |
| UKF | Unscented Kalman filter |
| UFO | Untethered Floating Object |
| VFHs | Vector field maps |
| WMR | Wheeled mobile robot |
References
- Li, S.; Xu, J. Multi-Axis Force/Torque Sensor Technologies: Design Principles and Robotic Force Control Applications: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 4055–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, F.; Bernardino, J.; Durães, J.; Cunha, J. A Survey on Sensor Failures in Autonomous Vehicles: Challenges and Solutions. Sensors 2024, 24, 5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.K.; Huang, H.C.; Feng, T.C. Prediction of Thermal Deformation and Real-Time Error Compensation of a CNC Milling Machine in Cutting Processes. Machines 2023, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deilamsalehy, H.; Havens, T.C. Sensor Fused Three-Dimensional Localization Using IMU, Camera and LiDAR. Proc. IEEE Sens. 2016, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, N.; Arif, S.; Qadeer, N.; Khan, Z.H. Development of a Low Cost Wireless IMU Using MEMS Sensors for Pedestrian Navigation. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Communication, Computing and Digital Systems, C-CODE, Islamabad, Pakistan, 8–9 March 2017; pp. 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilev, M.; Macleod, C.N.; Loukas, C.; Javadi, Y.; Vithanage, R.K.W.; Lines, D.; Mohseni, E.; Pierce, S.G.; Gachagan, A. Sensor-Enabled Multi-Robot System for Automated Welding and In-Process Ultrasonic NDE. Sensors 2021, 21, 5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafadar, A.; Hayward, K.; Tolouei-Rad, M. Drilling Reconfigurable Machine Tool Selection and Process Parameters Optimization as a Function of Product Demand. J. Manuf. Syst. 2017, 45, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Ghosh, S.; Aravindan, S. Influence of Dry Micro Abrasive Blasting on the Physical and Mechanical Characteristics of Hybrid PVD-AlTiN Coated Tools. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 37, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Fang, H.; Relton, S.D.; Wong, D.C.; Alam, T.; Alty, J.E. Accuracy of Smartphone Video for Contactless Measurement of Hand Tremor Frequency. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2021, 8, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.K.; Hol, J.D.; Luinge, H. Tightly-Coupled Joint User Self-Calibration of Accelerometers, Gyroscopes, and Magnetometers. Drones 2018, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalec, P.; Faller, L.M. 3-D-Printing and Reliability Evaluation of an Easy-to-Fabricate Position Sensing System for Printed Functional Wearable Assistive Devices. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 4137–4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Liu, F.L.; Zhang, M.N.; Zhou, M.X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, X. A Combination of Vision- and Sensor-Based Defect Classifications in Extrusion-Based Additive Manufacturing. J. Sens. 2023, 2023, 1441936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidegger, T.; Speidel, S.; Stoyanov, D.; Satava, R.M. Robot-Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery—Surgical Robotics in the Data Age. Proc. IEEE 2022, 110, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Li, Y.; Su, Y.H.; Xu, D.; Hannaford, B. Surgical Instrument Segmentation for Endoscopic Vision with Data Fusion of Rediction and Kinematic Pose. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom. 2019, 2019, 9821–9827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimova, N.; Ochilov, U.; Yakhshiev, S.; Egamberdiev, I. Predictive Maintenance of Cutting Tools Using Artificial Neural Networks. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 471, 02021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, H.; Tah, J.H.M.; Mosavi, A. Deep Learning for Detecting Building Defects Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors 2019, 19, 3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zahid, A.; Taha, A.; Taylor, W.; Le Kernec, J.; Heidari, H.; Imran, M.A.; Abbasi, Q.H. An Intelligent Implementation of Multi-Sensing Data Fusion with Neuromorphic Computing for Human Activity Recognition. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, M.A.; Yousuf, M.A.; Ahmed, S.; Uddin, M.Z.; Alyami, S.A.; Al-Ashhab, S.; Akhdar, H.F.; Khan, A.; Azad, A.; Moni, M.A. Deep CNN-LSTM With Self-Attention Model for Human Activity Recognition Using Wearable Sensor. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2022, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratasich, D.; Khalid, F.; Geissler, F.; Grosu, R.; Shafique, M.; Bartocci, E. A Roadmap Toward the Resilient Internet of Things for Cyber-Physical Systems. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 13260–13283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsisi, M.; Tran, M.Q.; Mahmoud, K.; Mansour, D.-E.A.; Lehtonen, M.; Darwish, M.M.F. Towards Secured Online Monitoring for Digitalized GIS against Cyber-Attacks Based on IoT and Machine Learning. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 78415–78427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, Z.K.; Saguna, S.; Ahlund, C. Multiarmed Bandits for Sleep Recognition of Elderly Living in Single-Resident Smart Homes. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 4414–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanyam, A.; Ramesh, R.; Sudheer, R.; Honnavalli, P.B. Revolutionizing Healthcare: A Review Unveiling the Transformative Power of Digital Twins. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 69652–69676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.J.; Dorr, F.; Mejia, J.A.G.; Martínez-Ferrer, L.; Jungbluth, A.; Kalaitzis, F.; Ramos-Pollán, R. M3LEO: A Multi-Modal, Multi-Label Earth Observation Dataset Integrating Interferometric SAR and Multispectral Data. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.04230. [Google Scholar]
- Mouli, K.V.V.N.R.C.; Prasad, B.S.; Sridhar, A.V.; Alanka, S. A Review on Multi Sensor Data Fusion Technique in CNC Machining of Tailor-Made Nanocomposites. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulose, A.; Kim, J.; Han, D.S. A Sensor Fusion Framework for Indoor Localization Using Smartphone Sensors and Wi-Fi RSSI Measurements. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemec, D.; Janota, A.; Hrubos, M.; Simak, V. Intelligent Real-Time MEMS Sensor Fusion and Calibration. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 7150–7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Wang, Z.; Alsaadi, F.E.; Alharbi, K.H.; Cheng, Y. Federated Tobit Kalman Filtering Fusion with Dead-Zone-Like Censoring and Dynamical Bias under the Round-Robin Protocol. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Process. Over Networks 2020, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Sun, X.; Jia, F.; Rushworth, A.; Dong, X.; Zhang, S.; Fang, Z.; Yang, G.; Liu, B. Sensors and Sensor Fusion Methodologies for Indoor Odometry: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Cardiff, B.; John, D. A Review on Multisensor Data Fusion for Wearable Health Monitoring. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.05895. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Z.; Sekine, M.; Tamura, T.; Tanaka, N.; Yoshida, M.; Chen, W. Measurement and Estimation of 3D Orientation Using Magnetic and Inertial Sensors. Adv. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 4, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basti, A.; Obikawa, T.; Shinozuka, J. Tools with Built-in Thin Film Thermocouple Sensors for Monitoring Cutting Temperature. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Anwar, S. Paradox Elimination in Dempster–Shafer Combination Rule with Novel Entropy Function: Application in Decision-Level Multi-Sensor Fusion. Sensors 2019, 19, 4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasch, E.P.; Plano, S. JDL Level 5 Fusion Model: User Refinement Issues and Applications in Group Tracking. Signal Process. Sens. Fusion Target Recognit. XI 2002, 4729, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Liu, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y. MEMS Inertial Sensors Based Gait Analysis for Rehabilitation Assessment via Multi-Sensor Fusion. Micromachines 2018, 9, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakkoli, H.; Izhar; Duan, M.; Zhao, X.; Waikho, R.; Yang, L.J.; Lee, Y.K. Dual-Mode Arduino-Based CMOS-MEMS Magnetic Sensor System with Self-Calibration for Smart Buildings’ Energy Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, NEMS 2022, Taoyuan, Taiwan, 14–17 April 2022; pp. 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.H.; Kao, L.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Lin, T.C.; Song, Y.L.; Chang, L.M. A Sensor Fusion Based Nonholonomic Wheeled Mobile Robot for Tracking Control. Sensors 2020, 20, 7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adarsh, S.; Ramachandran, K.I. Design of Sensor Data Fusion Algorithm for Mobile Robot Navigation Using ANFIS and Its Analysis Across the Membership Functions. Autom. Control Comput. Sci. 2018, 52, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, L.; Angelova, D.; Bull, D.R.; Canagarajah, N. Localization of Mobile Nodes in Wireless Networks with Correlated in Time Measurement Noise. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2011, 10, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Martínez-Sánchez, J.; Arias-Sánchez, P.; Rashdi, R. External Multi-Modal Imaging Sensor Calibration for Sensor Fusion: A Review. Inf. Fusion 2023, 97, 101806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Yang, B.; Wang, X.; Shan, B.; Gao, J.; Chang, H.; Yao, Y. Design of Optimal Estimation Algorithm for Multi-Sensor Fusion of a Redundant MEMS Gyro System. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 4577–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H. Research on the Application of Multi-Scale & Multi-Sensor Fusion Algorithm in MEMS Gyroscope Data Processing. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2023, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthi, R.; Kumar, A.; Gopinathan, D.; Nayyar, A.; Qureshi, B. An Overview of IoT Sensor Data Processing, Fusion, and Analysis Techniques. Sensors 2020, 20, 6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ROS: Home. Available online: https://www.ros.org/ (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Sensor Fusion and Tracking Toolbox. Available online: https://uk.mathworks.com/products/sensor-fusion-and-tracking.html (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- OpenCV—Open Computer Vision Library. Available online: https://opencv.org/ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- RTMaps—DSPACE. Available online: https://www.dspace.com/en/pub/home/products/sw/impsw/rtmaps.cfm (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Home Page—Autoware. Available online: https://autoware.org/ (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Apollo. Available online: https://developer.apollo.auto/ (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Open Source Autopilot for Drones—PX4 Autopilot. Available online: https://px4.io/ (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- LidarView—Visualize and Process Live Captured 3D LiDAR Data in Real-Time. Available online: https://lidarview.kitware.com/ (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Sensor Fusion Software | Bosch Sensortec. Available online: https://www.bosch-sensortec.com/software-tools/software/sensor-fusion-software-bsx/ (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- GitHub—Simondlevy/TinyEKF: Lightweight C/C++ Extended Kalman Filter with Python for Prototyping. Available online: https://github.com/simondlevy/TinyEKF (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- FusionLib | FusionLib. Available online: https://fusionlib.com/ (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Das, A.K.; Kumar, K.; Majumdar, A.; Sahu, S.; Chandra, M.G. Multi-Sensor Fusion Framework Using Discriminative Autoencoders. Eur. Signal Process. Conf. 2021, 2021, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, D.; Patil, J.; Herkal, S.; Nagarajaiah, S.; Duenas-Osorio, L. CNN and Convolutional Autoencoder (CAE) Based Real-Time Sensor Fault Detection, Localization, and Correction. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 169, 108723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-G. Vocabulary standard for robotics in ISO. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Robot Ethics and Standards, Seoul, South Korea, 18–19 July 2022; pp. 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duro, J.A.; Bowen, J.A.; Kim, C.R.; Nassehi, H.A.; Duro, J.A.; Padget, J.A.; Bowen, C.R.; Kim, H.A.; Nassehi, A. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Framework for CNC Machining Monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2016, 66–67, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, X.; Kong, L.; Dong, G.; Remani, A.; Leach, R. Defect Inspection Technologies for Additive Manufacturing. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2021, 3, 022002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabot, A.; Rauch, M.; Hascoët, J.Y. Towards a Multi-Sensor Monitoring Methodology for AM Metallic Processes. Weld. World 2019, 63, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Liu, G.; Pi, Y. Increasing Stability in Robotic GTA-Based Additive Manufacturing through Optical Measurement and Feedback Control. Robot Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2019, 59, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bono, P.; Allen, C.; D’Angelo, G.; Cisi, A. Investigation of Optical Sensor Approaches for Real-Time Monitoring during Fibre Laser Welding. J. Laser Appl. 2017, 29, 022417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Yu, R.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.M. Machine Learning of Weld Joint Penetration from Weld Pool Surface Using Support Vector Regression. J. Manuf. Process 2019, 41, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Gao, X.; Katayama, S. Detection of Imperfection Formation in Disk Laser Welding Using Multiple On-Line Measurements. J. Mater. Process Technol. 2015, 219, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xue, W. Review of Tool Condition Monitoring Methods in Milling Processes. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 2509–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touret, T.; Changenet, C.; Ville, F.; Lalmi, M.; Becquerelle, S. On the Use of Temperature for Online Condition Monitoring of Geared Systems—A Review. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 2018, 101, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yang, E. Two-Stage Multi-Sensor Fusion Positioning System with Seamless Switching for Cooperative Mobile Robot and Manipulator System. Int. J. Intell. Robot Appl. 2023, 7, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. An Adaptive Compensation Algorithm for Temperature Drift of Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems Gyroscopes Using a Strong Tracking Kalman Filter. Sensors 2015, 15, 11222–11238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhong, S.; Luo, H.; Kuang, N. Drift Error Calibration Method Based on Multi-MEMS Gyroscope Data Fusion. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2023, 24, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hong, H. Research on Filtering Algorithm of MEMS Gyroscope Based on Information Fusion. Sensors 2019, 19, 3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.G.; Gudipalli, A.; Phang, S.K.; Jaganatha Pandian, B. Design and Development of an Inexpensive Inertial Measurement Unit in the Arduino Environment. In Proceedings of the Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies, i-PACT 2023, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 8–10 December 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfani, S.; Jafari, A.; Hajiahmad, A. Comparison of Two Data Fusion Methods for Localization of Wheeled Mobile Robot in Farm Conditions. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2019, 1, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Kuang, L.; He, W. Simulation of Gymnastics Performance Based on MEMS Sensor. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2021, 2021, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjepkema, D.; Van Dijk, J.; Soemers, H.M.J.R. Sensor Fusion for Active Vibration Isolation in Precision Equipment. J. Sound Vib. 2012, 331, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Arai, F. Microrobot with Passive Diamagnetic Levitation for Microparticle Manipulations. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 122, 243901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Leung, K.Y.; Liu, R.; Song, S.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, J.; Meng, M.Q.H.; Liu, J. Dynamic Tracking for Microrobot with Active Magnetic Sensor Array. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom. 2021, 2021, 7288–7294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.V.; Apuroop, K.G.S.; Konduri, S.; Do, H.; Elara, M.R.; Xi, R.C.C.; Wen, R.Y.W.; Vu, M.B.; Phan, V.D.; Tran, M. Multirobot Formation with Sensor Fusion-Based Localization in Unknown Environment. Symmetry 2021, 13, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbot, A.; Tan, H.; Power, M.; Seichepine, F.; Yang, G.Z. Floating Magnetic Microrobots for Fiber Functionalization. Sci. Robot 2019, 4, eaax8336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- York, P.A.; Peña, R.; Kent, D.; Wood, R.J. Microrobotic Laser Steering for Minimally Invasive Surgery. Sci. Robot 2021, 6, eabd5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Fang, J.; Xu, S.; Yang, D. Indoor Robot SLAM with Multi-Sensor Fusion. Int. J. Adv. Netw. Monit. Control. 2024, 9, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Seo, M.; Kim, H.S.; Seo, T. UKF-Based Sensor Fusion Method for Position Estimation of a 2-DOF Rope Driven Robot. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 12301–12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Gorostiza, E.; García-Garrido, M.A.; Pizarro, D.; Salido-Monzú, D.; Torres, P. An Indoor Positioning Approach Based on Fusion of Cameras and Infrared Sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Hu, T.; Ouyang, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X. Tightly Coupled LIDAR/IMU/UWB Fusion via Resilient Factor Graph for Quadruped Robot Positioning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Luo, J.; Xu, S.; Zhang, S.; Meng, S.; Xiang, K. An EKF-Based Multiple Data Fusion for Mobile Robot Indoor Localization. Assem. Autom. 2021, 41, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; He, Y.; Ma, X.; Xu, H.; Hao, J.; Feng, J. SLAM Method Based on Multi-Sensor Information Fusion. In Proceedings of the Proceedings—2021 International Conference on Computer Network, Electronic and Automation, ICCNEA 2021, Xi’an, China, 24–26 September 2021; pp. 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Queralta, J.P.; Gia, T.N.; Zou, Z.; Westerlund, T. Multi-Sensor Fusion for Navigation and Mapping in Autonomous Vehicles: Accurate Localization in Urban Environments. Unmanned Syst. 2020, 8, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandhasamy, S.; Kuppusamy, V.B.; Krishnan, S. Scalable Decentralized Multi-Robot Trajectory Optimization in Continuous-Time. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 173308–173322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y. A Comprehensive Introduction of Visual-Inertial Navigation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.11758. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Z.; Liu, J.; Chi, W.; Zhang, B. A Low-Cost and Robust Multi-Sensor Data Fusion Scheme for Heterogeneous Multi-Robot Cooperative Positioning in Indoor Environments. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Localization of Mobile Robot Based on Multi-Sensor Fusion. In Proceedings of the 32nd Chinese Control and Decision Conference, CCDC 2020, Hefei, China, 22–24 August 2020; pp. 4367–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Ngo, D.H.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Tran, D.T.; Dang, X.B. Indoor Mobile Robot Positioning Using Sensor Fusion. In Proceedings of the 2022 6th International Conference on Green Technology and Sustainable Development, GTSD, Nha Trang City, Vietnam, 29–30 July 2022; pp. 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cao, J.; Dobie, G.; MacLeod, C. A Framework of Using Customized LIDAR to Localize Robot for Nuclear Reactor Inspections. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 5352–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaiskos, K.; Lampousis, C.; Vlachos, K.; Papadopoulos, E. Implementation and Motion Control of a Microrobot Using Laser Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2022 30th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, MED 2022, Vouliagmeni, Greece, 28 June–1 July 2022; pp. 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uvet, H.; Demircali, A.A.; Kahraman, Y.; Varol, R.; Kose, T.; Erkan, K. Micro-UFO (Untethered Floating Object): A Highly Accurate Microrobot Manipulation Technique. Micromachines 2018, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, H.; Yasa, I.C.; Kilic, U.; Hu, W.; Sitti, M. Translational Prospects of Untethered Medical Microrobots. Prog. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 1, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Tiemerding, T.; Haenssler, O.C.; Fatikow, S. Automated Robotic Manipulation of Individual Sub-Micro Particles Using a Dual Probe Setup inside the Scanning Electron Microscope. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May; Volume 2015, pp. 950–955. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, A.; Sun, Y.; Jing, S. Fusion of Binocular Vision, 2D Lidar and IMU for Outdoor Localization and Indoor Planar Mapping. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 34, 025203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jiang, Z. Design of the Navigation System through the Fusion of IMU and Wheeled Encoders. Comput. Commun. 2020, 160, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudar, A.; Zhao, W.; Schoellig, A.P. Range-Visual-Inertial Sensor Fusion for Micro Aerial Vehicle Localization and Navigation. IEEE Robot Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.-S.; Ge, D.-Y.; Song, J.; Xiang, W.-J. Outdoor Scene Understanding of Mobile Robot via Multi-Sensor Information Fusion. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2022, 30, 100392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocato, S.; Daffara, C. A Method for Spatially Registered Microprofilometry Combining Intensity-Height Datasets from Interferometric Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.X.; Xie, C.X.; Xie, M.; Mao, J. Mobile Robot Positioning Method Based on Multi-Sensor Information Fusion Laser SLAM. Clust. Comput. 2019, 22, 5055–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, O.A.; Joerger, M.; Spenko, M. How Safe Is Particle Filtering-Based Localization for Mobile Robots? An Integrity Monitoring Approach. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2024, 40, 3372–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatise, M.B.; Hancke, G.P. A Review on Challenges of Autonomous Mobile Robot and Sensor Fusion Methods. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 39830–39846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Levels of Fusion | Description | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Level 0: Sub-Object Data Assessment | Removal of noise and unwanted signals. Correction of systematic measurement errors. Finding key characteristics from data. | [33] |
| Level 1: Object Assessment | Determination of the presence of objects in data. Determination of the type or category of an object. Monitoring of the position and state of an object over time. | [29] |
| Level 2: Situation Assessment | Identification of patterns and anomalies in object actions. Assessment of the environment and conditions. Combining the data to create an overall picture of the situation. | [33] |
| Level 3: Impact Assessment | The system predicts possible consequences of the current situation and assesses risks | [33] |
| Level 4: Process Refinement | Adaptation and optimization of the data collection and processing based on the results obtained. | [29] |
| Level 5: User Refinement | Interaction between the data fusion system and the user to improve the system’s understanding and decision making. | [33] |
| Software | OS | Features | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| ROS (Robot Operating System) and ROS 2 (all distrbutions) | Linux macOS Windows | Open platform for robotics Many packages for data fusion (robot_localization, sensor_msgs, etc.) Wide support for sensors and algorithms Large community and active development | [43] |
| MATLAB Sensor Fusion and Tracking Toolbox R2024b | Windows macOS Linux | Tools and algorithms for multi-sensor fusion Support for object tracking and localization Simulation and scenario testing Used in academic and industrial research | [44] |
| OpenCV 4.11.0 | Linux macOS Windows Android iOS | Computer vision library Offers functions for processing and merging data from cameras and sensors Widely used in image and video processing Large community and extensive documentation | [45] |
| RTMaps (Real-Time Multi-Sensor applications) | Linux Windows | Platform for real-time and multi-sensor applications Synchronous data acquisition and processing Used in the automotive and robotics industries Graphical development environment | [46] |
| Autoware (all versions) | Linux | Open-source software for autonomous driving Performs fusion of data from LiDAR, cameras, and radar Based on ROS Used in autonomous vehicle projects | [47] |
| Apollo (Baidu Autonomous Driving Platform) (all versions) | Linux | Open platform for autonomous driving Performs fusion of data from various sensors Modular architecture Support from major company Baidu | [48] |
| PX4 Autopilot v1.16.0 | NuttX (RTOS) Linux | Open platform for drones and UAV autopilot Offers data fusion algorithms for navigation Large developer community Used in research and commercial UAVs | [49] |
| LidarView v4.4.0 (by Kitware, Clifton Park, NY, USA) | Windows macOS Linux | Visualization and processing of LiDAR data Provides support for fusion of LiDAR data with data from other sensors Based on VTK and ParaView technologies Used in research and industry | [50] |
| Bosch Sensor Fusion SDK v3.4.0 | Android iOS | Designed for mobile applications Provides data fusion algorithms for motion tracking Used in smartphones and wearables Commercial SDK (by Bosch Sensortec, Reutlingen, Germany) | [51] |
| Kalman Filter Libraries (TinyEKF, etc.) (all versions) | Any OS (C/C++, Python) | Offers Kalman filter implementations for data fusion Used in embedded systems Provides support for extended and non-linear Kalman filters Lightweight and suitable for systems with limited resources | [52] |
| FusionLib (all versions) | Windows Linux | Data fusion library for C++ Supports various fusion algorithms Modular architecture for easy integration Has documentation and examples for quick start | [53] |
| Multi-Sensor Fusion Framework (by ETH Zurich’s) (all versions) | Linux | Unified platform for data fusion Provides support for various types of sensors Modular and extensible Developed at a leading research university | [54] |
| Methodology | Application | Sensors | Fusion Technique | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal level fusion for vibration reduction | Micro assembly | Diverse sensors | Signal-level fusion | [73] |
| Passive diamagnetic levitation | Microrobot manipulation in fluid environments | Magnetic fields | Magnetic control | [74] |
| Movable sensor array with dynamic tracking | Medical microrobotics | Magnetic sensors | Multi-point locating algorithm | [75] |
| Algorithm for multirobot formation | Multirobot formation | Ultrawideband system, IMUs, wheel encoders | Sensor fusion system | [76] |
| Magnetic control for patterning | Fiber functionalization | Magnetic sensors | Magnetic control | [77] |
| Laser sensors with feedback and control | Microrobotic motion control | Laser sensors | Closed-loop motion control | [78] |
| PL-ICP and extended Kalman filter (EKF) | Indoor Robot SLAM | LiDAR, cameras, IMUs, odometers | EKF, Bayesian | [79] |
| UKF-based sensor fusion | Mobile robot localization | IMUs, angle sensors | UKF algorithm | [80] |
| Maximum Likelihood Estimator | Indoor positioning | Cameras, infrared sensors | Fusion estimation | [81] |
| Resilient Factor Graph | Robot navigation | UWB, IMUs, LiDAR | Factor Graph Optimization | [82] |
| EKF with sensor fusion | Indoor localization of mobile robots | IMUs, odometers, laser radar | EKF | [83] |
| RBPF-SLAM with Maximum Posterior Estimation | Mobile robot navigation | Laser radar, ultrasonic sensors, monocular cameras | RBPF | [84] |
| Sensor Fusion with SLAM and LiDAR Scan | Mobile robots | LiDAR, GNSS, IMUs, wheel encoders | Sensor Redundancy Strategy | [85] |
| Fusion Level | Description | Examples | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-level fusion | Directly combines raw data from sensors, focusing on signal-level information. | IMU + GPS for raw positioning; LiDAR + camera for depth estimation. | Basic localization, rough mapping, and obstacle detection. |
| Intermediate-level fusion | Processes and combines features extracted from raw data for more significant ideas. | Feature-based fusion like parameter detection and object segmentation. | Object tracking, pattern recognition, and enhanced localization. |
| High-level fusion | Combines high-level decisions made by each sensor, focusing on interpreted or classified data. | Decision fusion for obstacle avoidance or object recognition. | Advanced navigation, autonomous decision making, and robotic manipulation. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masalskyi, V.; Dzedzickis, A.; Korobiichuk, I.; Bučinskas, V. Hybrid Mode Sensor Fusion for Accurate Robot Positioning. Sensors 2025, 25, 3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103008
Masalskyi V, Dzedzickis A, Korobiichuk I, Bučinskas V. Hybrid Mode Sensor Fusion for Accurate Robot Positioning. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103008
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasalskyi, Viktor, Andrius Dzedzickis, Igor Korobiichuk, and Vytautas Bučinskas. 2025. "Hybrid Mode Sensor Fusion for Accurate Robot Positioning" Sensors 25, no. 10: 3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103008
APA StyleMasalskyi, V., Dzedzickis, A., Korobiichuk, I., & Bučinskas, V. (2025). Hybrid Mode Sensor Fusion for Accurate Robot Positioning. Sensors, 25(10), 3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25103008









