Cross-Modal Weakly Supervised RGB-D Salient Object Detection with a Focus on Filamentary Structures
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a cross-modal weakly supervised method for the RGB-D SOD task, in which the text and point annotations are used to provide rich semantic information and position information, respectively. By fully integrating the advantages of weak labels from different modalities, the method effectively enhances the detection performance of salient objects in complex scenes, especially in highlighting filamentary structures.
- A cross-modal pseudo-label generation network (CPGN) is designed to provide stronger supervision for model training, which first leverages the multimodal alignment capability of CLIP to activate semantic priors from text labels, obtaining coarse annotations, and then point labels progressively enhance the richness and accuracy of these annotations to generate high-quality pseudo-labels.
- An asymmetric salient-region prediction network (ASPN) is proposed to extract and integrate the contextual information of RGB images and the geometric information of depth images. In ASPN, an edge constraint module is introduced to sharpen the edges of salient objects. Meanwhile, we construct a cross-modal weakly supervised saliency detection dataset (CWS) for the weakly supervised RGB-D SOD task.
2. Related Work
2.1. Weakly Supervised Salient Object Detection
2.2. Weakly Supervised RGB-D Salient Object Detection
2.3. Contrastive Language–Image Pre-Training
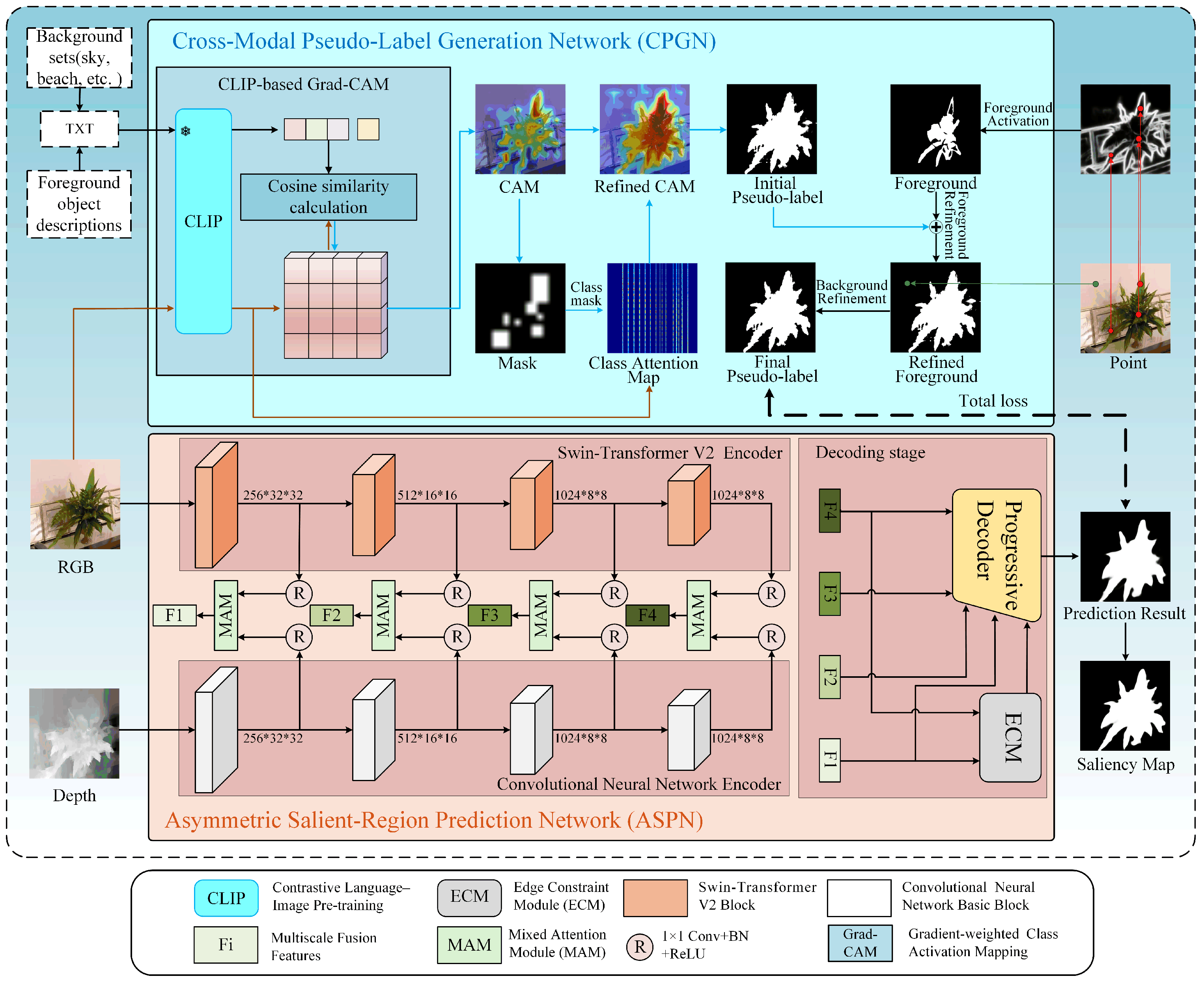
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Overview
3.2. Cross-Modal Pseudo-Label Generation Network
3.2.1. CLIP-Based Grad-CAM
3.2.2. Point Label Activation and Pseudo-Label Improvement
3.3. Asymmetric Salient-Region Prediction Network
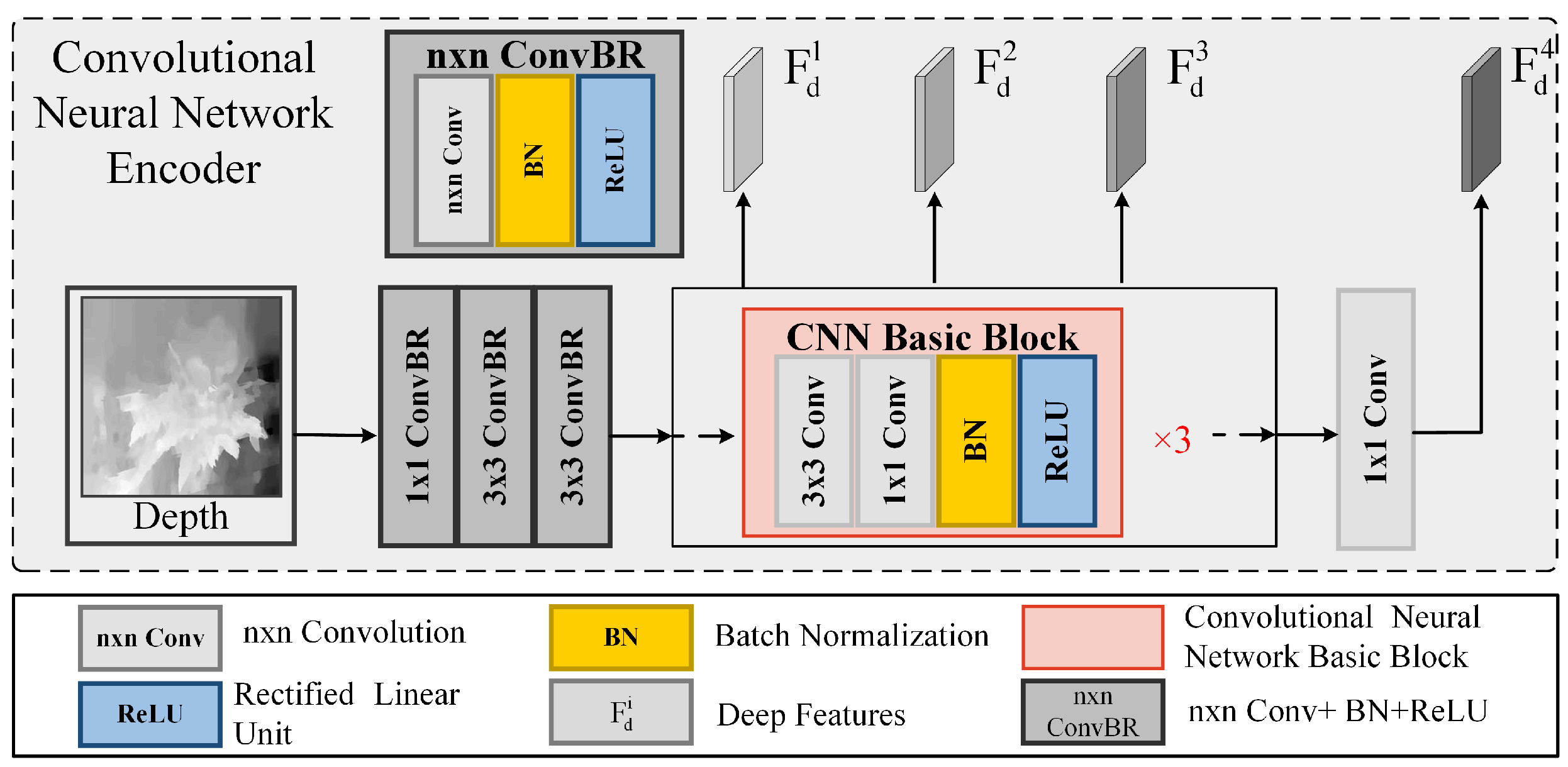
3.3.1. Asymmetric Encoder
- (a)
- Performing multi-head self-attention operations on each patch:Here, refers to the window-based multi-head self-attention operation, is the input feature at layer , and is the feature after the window-based multi-head self-attention operation.
- (b)
- To better capture the contextual relationships, multi-head self-attention operations are performed between windows:Here, refers to the cross-window multi-head self-attention operation. By stacking multiple layers of such operations, contextual features are gradually extracted. The final output is the contextual features after hierarchical feature extraction. Depth features are typically used to supplement the spatial positional information of the RGB features. Networks trained from scratch tend to achieve better performance in tasks related to depth maps. Therefore, we adopted a CNN-based backbone to extract depth features in the simplest way possible. As shown in Figure 2, the depth map is converted into a higher-dimensional embedding feature space through convolution layers with different receptive fields. Then, the learned depth features are transformed into multi-scale features with three different resolutions via three identical CNN-based blocks.
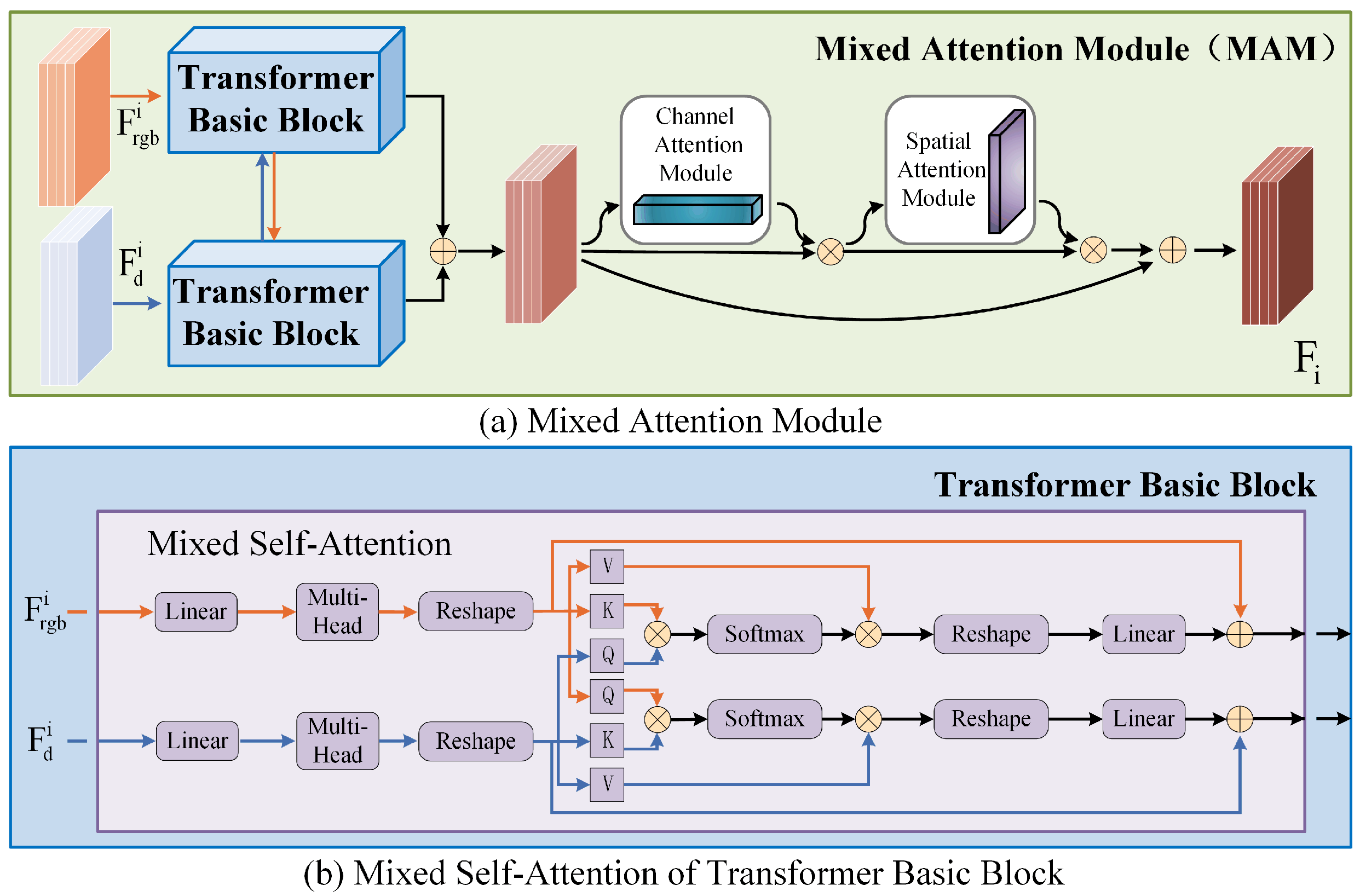
3.3.2. Mixed Attention Module (MAM)
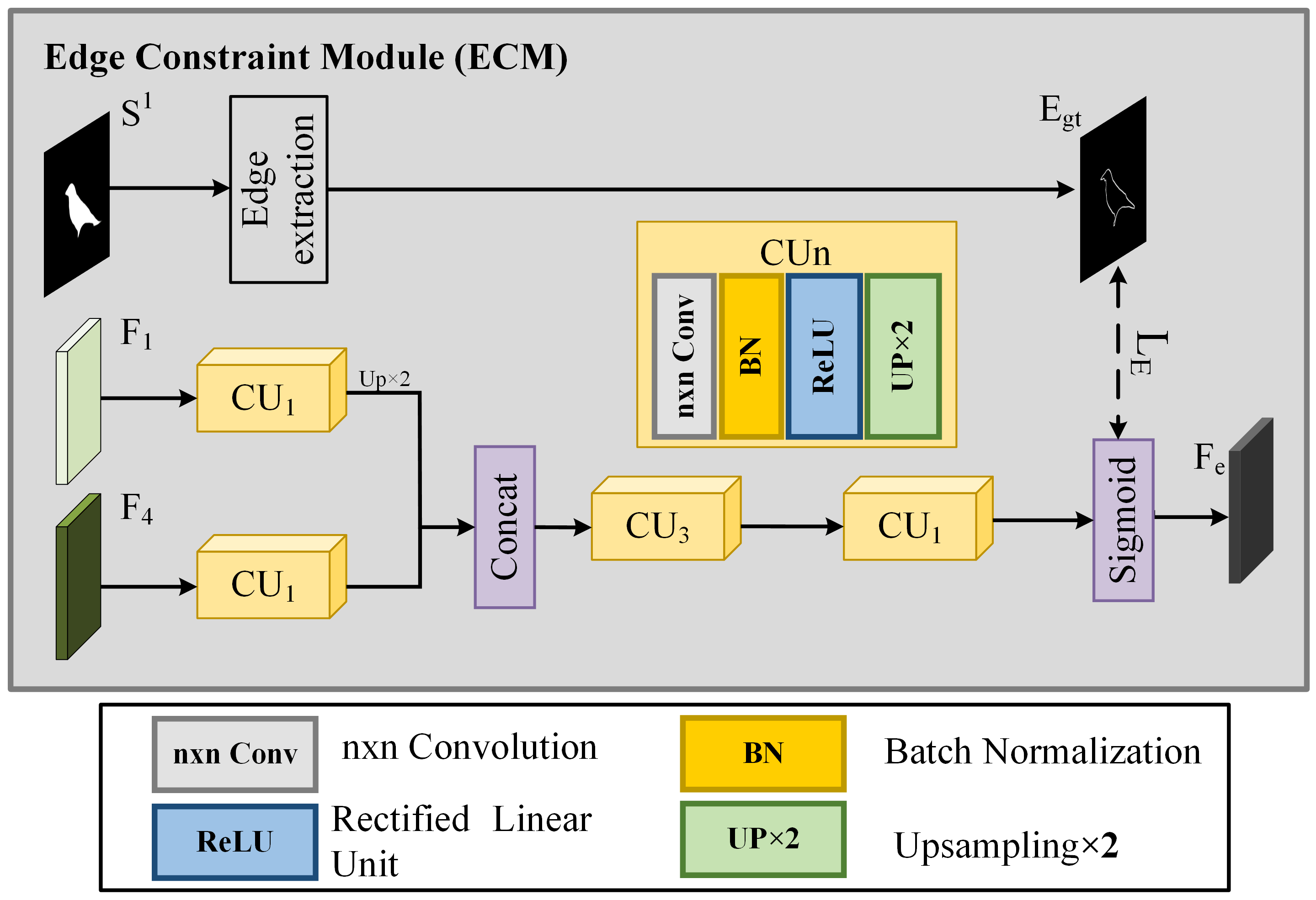
3.3.3. Edge Constraint Module (ECM)
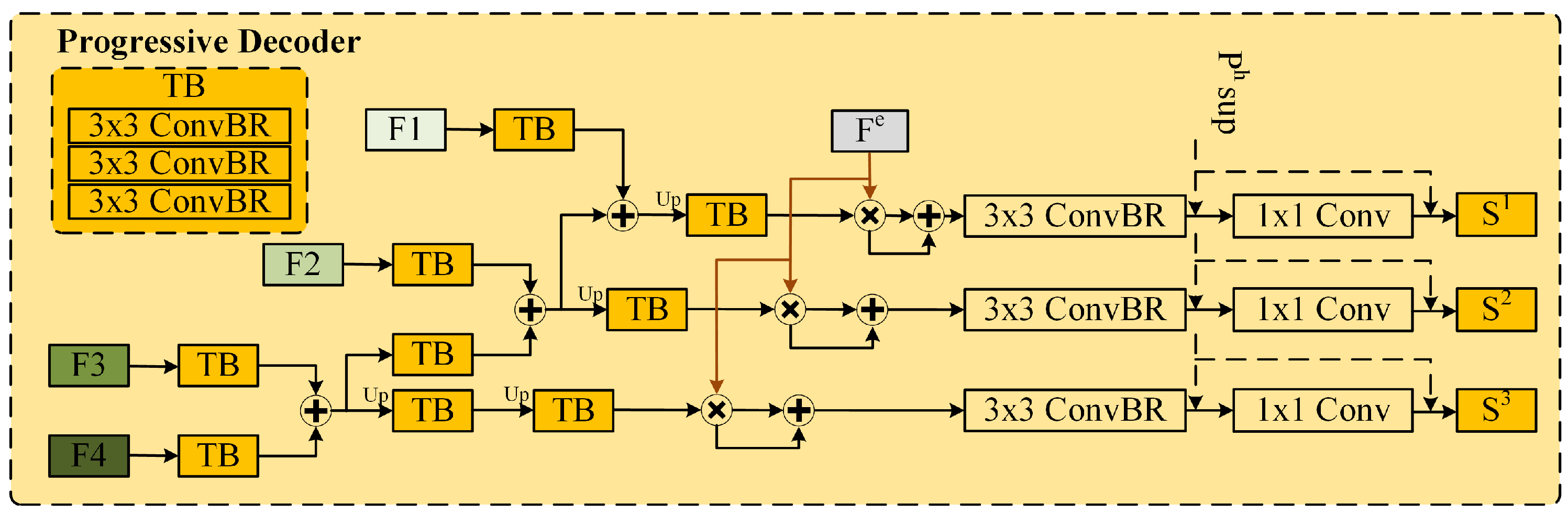
3.3.4. Progressive Decoder
3.4. Hybrid Loss Function
4. Experiment and Result Analysis
4.1. Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Performance Comparison with the State of the Art
4.3.1. Quantitative Evaluation
4.3.2. Qualitative Evaluation
4.3.3. Complexity Comparisons
4.4. Ablation Studies
4.4.1. Effectiveness of Cross-Modal Weak Labels
4.4.2. Effectiveness of Asymmetric Encoder and ECM
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, L.; Luo, X.; Shi, Y.; Meng, F.; Wu, Q.; Hong, H. Optimal Transport Quantization Based on Cross-X Semantic Hypergraph Learning for Fine-grained Image Retrieval. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Hong, H.; Meng, F.; Wu, Q.; Wu, J. Deep progressive asymmetric quantization based on causal intervention for fine-grained image retrieval. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 26, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Luo, X.; Hong, H.; Meng, F.; Wu, Q. Logit variated product quantization based on parts interaction and metric learning with knowledge distillation for fine-grained image retrieval. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 10406–10419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lin, J.; Zhong, G.; Yao, Y.; Li, Z. Multi-granularity Localization Transformer with Collaborative Understanding for Referring Multi-Object Tracking. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2025, 74, 5004613. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wan, L.; Liu, D.; Zhou, X.; An, P.; Shan, C. Saliency-Guided No-Reference Omnidirectional Image Quality Assessment via Scene Content Perceiving. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 5039115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itti, L.; Koch, C.; Niebur, E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 20, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Ma, L.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Yang, Z. Reliable metrics-based linear regression model for multilevel privacy measurement of face instances. IET Image Process. 2022, 16, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, B.; Pan, L. SMCNet: State-Space Model for Enhanced Corruption Robustness in 3D Classification. Sensors 2024, 24, 7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunair, H.; Khan, S.; Hamza, A.B. RSUD20K: A dataset for road scene understanding in autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 27–30 October 2024; pp. 708–714. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Shen, F.; Ding, D.; Deng, Y.; Li, C. Disentangled cross-modal transformer for RGB-D salient object detection and beyond. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 1699–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Ren, P.; Yin, B.; Wang, F.; Li, H. CATNet: A cascaded and aggregated transformer network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 2249–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Pu, Z.; Chen, J.; Gao, X. DGFNet: Depth-guided cross-modality fusion network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 26, 2648–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hao, F.; Liang, W.; Xu, J. Transformer fusion and pixel-level contrastive learning for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2023, 26, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhao, F.; Hong, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y. Complementary parts contrastive learning for fine-grained weakly supervised object co-localization. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 6635–6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Y. Mutual information regularization for weakly-supervised RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hayat, M.; Yang, H.; Peng, D.; Lei, Y. Deep hypersphere feature regularization for weakly supervised RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 5423–5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, D. Weakly supervised RGB-D salient object detection with prediction consistency training and active scribble boosting. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 2148–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y.; Feng, M.; Wang, D.; Yin, B.; Ruan, X. Learning to detect salient objects with image-level supervision. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 136–145. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Ma, L.; Huang, Z.; Yuan, H. Progressive attention-based feature recovery with scribble supervision for saliency detection in optical remote sensing image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5631212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, R.; Deng, S.; Zhou, L.; Qin, H.; Liang, Q. MCS-ResNet: A Generative Robot Grasping Network Based on RGB-D Fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 74, 3504012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; Xu, K.; Ding, X. MSSD-SLAM: Multi-feature Semantic RGB-D Inertial SLAM with Structural Regularity for Dynamic Environments. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 74, 5003517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Tao, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, J.; Xie, S.; Peng, Q. Depth of Interaction in PET Detector Design: Performance Optimization with Light-Sharing Window. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 74, 4000910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Shao, F.; Xie, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Mu, B.; Jiang, Q. HFMDNet: Hierarchical fusion and multi-level decoder network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 5012115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.X.; Liu, J.J.; Fan, D.P.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J.; Cheng, M.M. EGNet: Edge guidance network for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8779–8788. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Deng, L.; Chen, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhu, L.; Dong, M.; Lu, X.; Guo, C. SFCFusion: Spatial-frequency collaborative infrared and visible image fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 5011615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, R.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Zhou, H.; Ma, J. CASPFuse: An Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Method based on Dual-cycle Crosswise Awareness and Global Structure-tensor Preservation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 74, 5002515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Cheng, L. Bidirectional feedback network for high-level task-directed infrared and visible image fusion. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2025, 147, 105751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xie, Y.; Lin, L. Weakly supervised salient object detection using image labels. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, K.J.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chuang, Y.Y. Weakly supervised salient object detection by learning a classifier-driven map generator. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 5435–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Li, A.; Song, P.; Liu, B.; Dai, Y. Weakly-supervised salient object detection via scribble annotations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 12546–12555. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, J.; Lim, E.G. Structure-consistent weakly supervised salient object detection with local saliency coherence. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 19–21 May 2021; Volume 35, pp. 3234–3242. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Han, J.; Liu, N.; Khan, S.; Cholakkal, H.; Anwer, R.M.; Khan, F.S. Robust perception and precise segmentation for scribble-supervised RGB-D saliency detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 46, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Cao, Y.; Liang, Z.; Lau, R.W. Weakly-supervised salient object detection with saliency bounding boxes. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 4423–4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Zhang, W. Weakly-Supervised Salient Object Detection Using Point Supervision. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhuge, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhang, L.; Qian, M.; Yu, Y. Multi-source weak supervision for saliency detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 6074–6083. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Yu, R.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J. Semantically-Enhanced Feature Extraction with CLIP and Transformer Networks for Driver Fatigue Detection. Sensors 2024, 24, 7948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asperti, A.; Naldi, L.; Fiorilla, S. An Investigation of the Domain Gap in CLIP-Based Person Re-Identification. Sensors 2025, 25, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ji, W.; Bi, Q.; Yan, C.; Zhang, M.; Piao, Y.; Lu, H. Joint semantic mining for weakly supervised RGB-D salient object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 11945–11959. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, X.; Wang, K.; Bai, X. Richer convolutional features for edge detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3000–3009. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Lu, H. Hierarchical dynamic filtering network for RGB-D salient object detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XXV 16; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 235–252. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, H.; Li, B.; Xiong, W.; Hu, W.; Ji, R. RGBD salient object detection: A benchmark and algorithms. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part III 13; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 92–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, R.; Ge, L.; Geng, W.; Ren, T.; Wu, G. Depth saliency based on anisotropic center-surround difference. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 1115–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Ye, J.; Ji, Y.; Ling, H.; Yu, J. Saliency detection on light field. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 2806–2813. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Fu, H.; Wei, X.; Xiao, J.; Cao, X. Depth enhanced saliency detection method. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service, Xiamen, China, 10–12 July 2014; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.P.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Cheng, M.M. Rethinking RGB-D salient object detection: Models, data sets, and large-scale benchmarks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 2075–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, Y.; Ji, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Lu, H. Depth-induced multi-scale recurrent attention network for saliency detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 7254–7263. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Geng, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, F. Leveraging stereopsis for saliency analysis. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 454–461. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 4 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Ma, L.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Hong, H.; Tian, J. Multi-source weakly supervised salient object detection via boosting weak-annotation source and constraining object structure. Digit. Signal Process. 2022, 126, 103461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Sun, F.; Sun, J.; Wang, F.; Li, H. Cross-modal fusion and progressive decoding network for RGB-D salient object detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2024, 132, 3067–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Su, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, H. Heterogeneous fusion and integrity learning network for RGB-D salient object detection. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2024, 20, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yao, S.; Hu, B.; Piao, Y.; Ji, W. C2DFNet: Criss-Cross Dynamic Filter Network for RGB-D Salient Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 5142–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
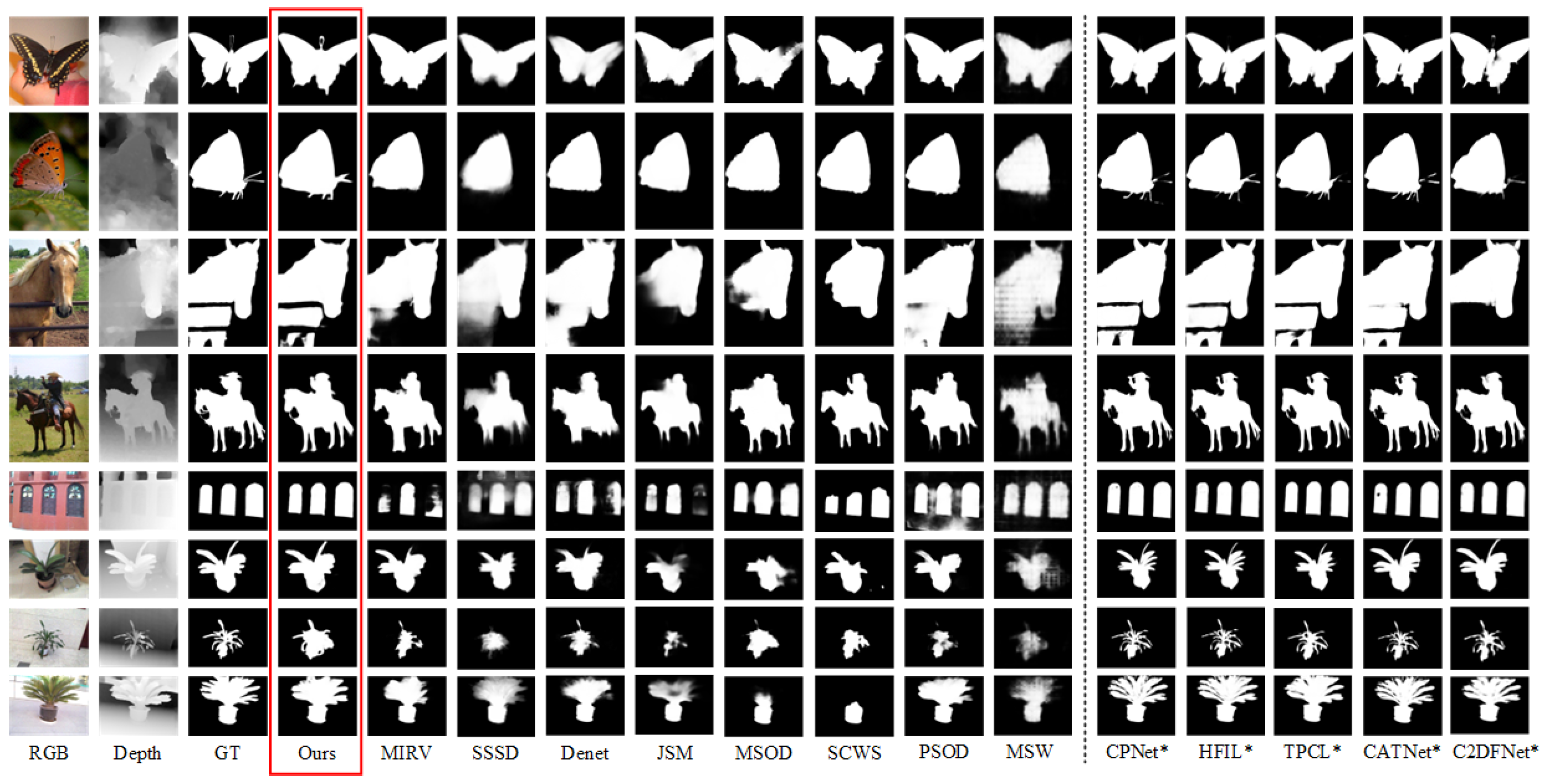

| Sup. | Weakly Sup. | Fully Sup. | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple Weak Labels Sup. | Single Weak Label Sup. | ||||||||||||||
| DATASET | Mtric | Our | MSOD | JSM | MSW | MIRV | SSSD | Denet | SCWS | PSOD | CPNet * | HFIL * | TPCL * | CATNet * | C2DFNet * |
| [49] | [38] | [35] | [15] | [32] | [17] | [31] | [34] | [50] | [51] | [28] | [11] | [52] | |||
| DUT-RGBD [46] | 0.887 | 0.828 | 0.791 | 0.825 | 0.876 | 0.877 | 0.845 | 0.857 | 0.887 | 0.951 | 0.950 | 0.935 | 0.953 | 0.930 | |
| 0.881 | 0.824 | 0.802 | 0.777 | 0.881 | 0.876 | 0.830 | 0.865 | 0.885 | 0.956 | 0.953 | 0.940 | 0.951 | 0.934 | ||
| 0.937 | 0.885 | 0.870 | 0.877 | 0.919 | 0.922 | 0.894 | 0.902 | 0.937 | 0.976 | 0.975 | 0.966 | 0.971 | 0.958 | ||
| 0.049 | 0.078 | 0.093 | 0.104 | 0.054 | 0.067 | 0.071 | 0.060 | 0.054 | 0.019 | 0.019 | 0.024 | 0.020 | 0.025 | ||
| SIP [45] | 0.870 | 0.735 | 0.707 | 0.781 | 0.876 | 0.876 | 0.852 | 0.833 | 0.870 | 0.907 | 0.908 | 0.900 | 0.913 | 0.872 | |
| 0.893 | 0.708 | 0.691 | 0.709 | 0.872 | 0.872 | 0.840 | 0.830 | 0.865 | 0.925 | 0.923 | 0.914 | 0.918 | 0.867 | ||
| 0.926 | 0.812 | 0.787 | 0.836 | 0.925 | 0.925 | 0.904 | 0.900 | 0.926 | 0.944 | 0.946 | 0.941 | 0.944 | 0.915 | ||
| 0.049 | 0.125 | 0.141 | 0.127 | 0.049 | 0.060 | 0.063 | 0.065 | 0.050 | 0.035 | 0.034 | 0.037 | 0.034 | 0.054 | ||
| NJU2K [42] | 0.891 | 0.802 | 0.723 | 0.784 | 0.890 | 0.902 | 0.883 | 0.853 | 0.884 | 0.934 | 0.936 | 0.925 | 0.937 | 0.912 | |
| 0.891 | 0.805 | 0.744 | 0.740 | 0.888 | 0.904 | 0.870 | 0.870 | 0.882 | 0.936 | 0.936 | 0.924 | 0.929 | 0.912 | ||
| 0.939 | 0.856 | 0.793 | 0.840 | 0.929 | 0.950 | 0.915 | 0.900 | 0.921 | 0.960 | 0.959 | 0.955 | 0.933 | 0.919 | ||
| 0.040 | 0.091 | 0.129 | 0.119 | 0.045 | 0.048 | 0.050 | 0.059 | 0.048 | 0.024 | 0.025 | 0.028 | 0.025 | 0.038 | ||
| DES [44] | 0.909 | 0.859 | 0.826 | 0.835 | 0.928 | 0.918 | 0.900 | 0.854 | 0.895 | 0.949 | 0.946 | 0.935 | 0.945 | 0.914 | |
| 0.878 | 0.831 | 0.827 | 0.777 | 0.927 | 0.909 | 0.890 | 0.877 | 0.897 | 0.937 | 0.935 | 0.923 | 0.914 | 0.896 | ||
| 0.957 | 0.927 | 0.890 | 0.890 | 0.972 | 0.967 | 0.957 | 0.886 | 0.944 | 0.984 | 0.980 | 0.971 | 0.979 | 0.955 | ||
| 0.022 | 0.042 | 0.056 | 0.065 | 0.018 | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.037 | 0.028 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.021 | ||
| NLPR [41] | 0.903 | 0.844 | 0.810 | 0.825 | 0.913 | 0.899 | 0.902 | 0.867 | 0.885 | 0.940 | 0.942 | 0.935 | 0.939 | 0.928 | |
| 0.866 | 0.792 | 0.789 | 0.728 | 0.902 | 0.884 | 0.874 | 0.842 | 0.857 | 0.929 | 0.927 | 0.920 | 0.916 | 0.899 | ||
| 0.948 | 0.879 | 0.890 | 0.840 | 0.954 | 0.947 | 0.943 | 0.913 | 0.921 | 0.972 | 0.972 | 0.968 | 0.968 | 0.958 | ||
| 0.023 | 0.050 | 0.058 | 0.075 | 0.025 | 0.035 | 0.031 | 0.039 | 0.038 | 0.016 | 0.016 | 0.017 | 0.018 | 0.021 | ||
| LFSD [43] | 0.862 | 0.803 | 0.766 | 0.808 | 0.854 | 0.835 | 0.832 | 0.806 | 0.848 | 0.892 | 0.885 | 0.885 | 0.898 | 0.863 | |
| 0.874 | 0.811 | 0.799 | 0.780 | 0.861 | 0.837 | 0.827 | 0.825 | 0.845 | 0.897 | 0.887 | 0.883 | 0.900 | 0.863 | ||
| 0.905 | 0.859 | 0.823 | 0.840 | 0.901 | 0.879 | 0.868 | 0.849 | 0.903 | 0.925 | 0.917 | 0.918 | 0.933 | 0.883 | ||
| 0.069 | 0.102 | 0.128 | 0.129 | 0.070 | 0.095 | 0.089 | 0.098 | 0.087 | 0.049 | 0.058 | 0.058 | 0.040 | 0.065 | ||
| STERE [47] | 0.895 | 0.842 | 0.858 | 0.838 | 0.890 | 0.881 | 0.879 | 0.876 | 0.899 | 0.920 | 0.922 | 0.916 | 0.925 | 0.902 | |
| 0.877 | 0.831 | 0.796 | 0.785 | 0.880 | 0.870 | 0.855 | 0.885 | 0.892 | 0.909 | 0.910 | 0.902 | 0.902 | 0.892 | ||
| 0.943 | 0.892 | 0.858 | 0.880 | 0.936 | 0.929 | 0.921 | 0.930 | 0.940 | 0.954 | 0.953 | 0.951 | 0.935 | 0.927 | ||
| 0.035 | 0.065 | 0.092 | 0.089 | 0.041 | 0.059 | 0.051 | 0.044 | 0.039 | 0.029 | 0.030 | 0.031 | 0.030 | 0.038 | ||
| Method | FLOPs (G) | Params (M) |
|---|---|---|
| Ours | 274.19 | 112.66 |
| SSSD [32] | 44.28 | 130.78 |
| JSM [38] | 17.94 | 47.85 |
| DeNet [17] | 179.71 | 18.57 |
| MIRV [15] | 37.14 | 63.58 |
| NJU2K | NLPR | |||||||
| Sup. | ||||||||
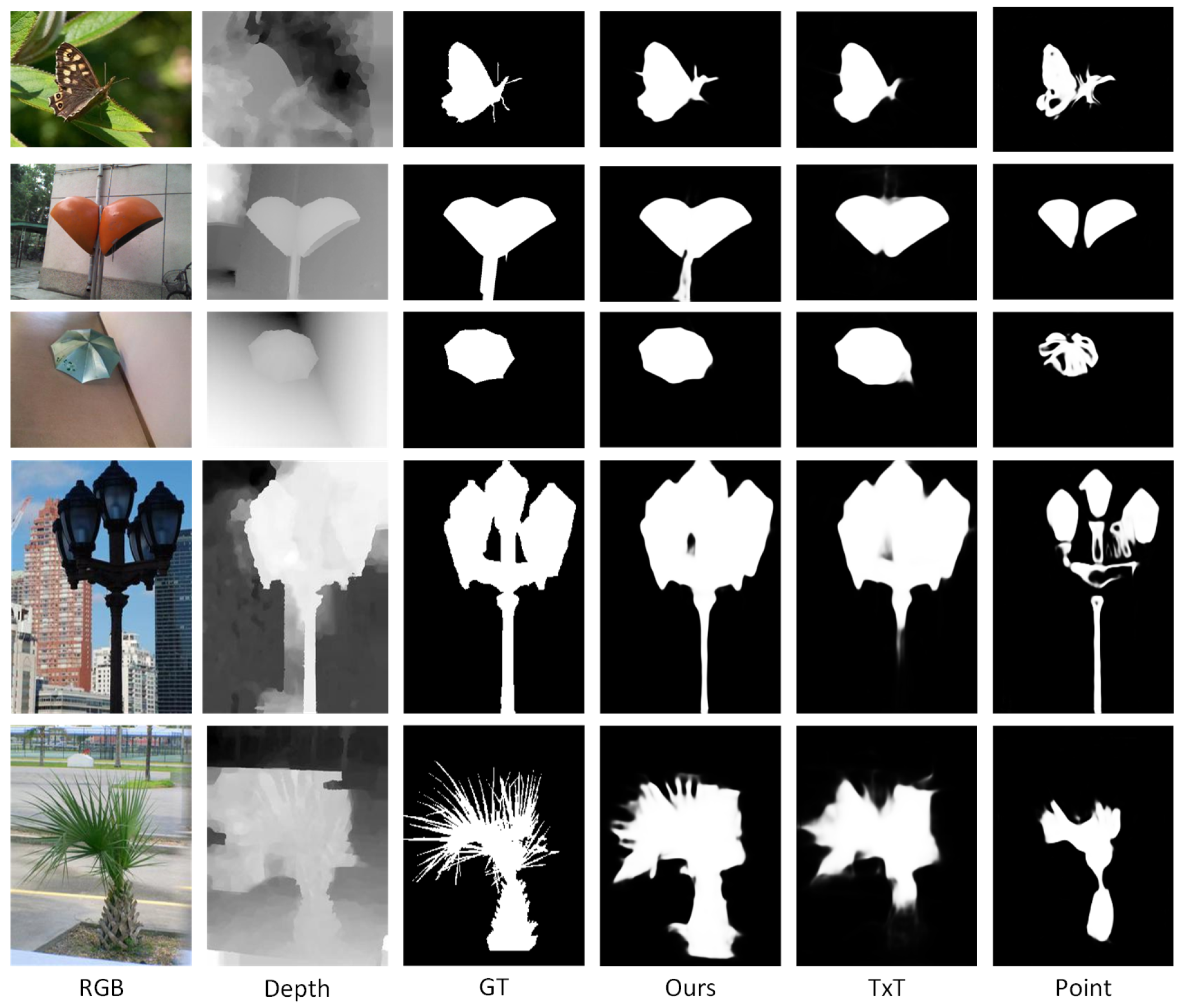
| TXT | 0.814 | 0.807 | 0.875 | 0.081 | 0.875 | 0.886 | 0.921 | 0.037 |
| Point | 0.672 | 0.747 | 0.744 | 0.134 | 0.724 | 0.785 | 0.804 | 0.067 |
| Ours | 0.891 | 0.891 | 0.939 | 0.040 | 0.903 | 0.866 | 0.948 | 0.023 |
| DUT-RGBD | DES | |||||||
| Sup. | ||||||||
| TXT | 0.818 | 0.811 | 0.889 | 0.088 | 0.879 | 0.835 | 0.920 | 0.038 |
| Point | 0.705 | 0.793 | 0.777 | 0.110 | 0.684 | 0.749 | 0.750 | 0.072 |
| Ours | 0.887 | 0.881 | 0.937 | 0.049 | 0.909 | 0.878 | 0.957 | 0.022 |
| NJU2K | NLPR | DUT-RGBD | DES | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | ||||||||||||||||
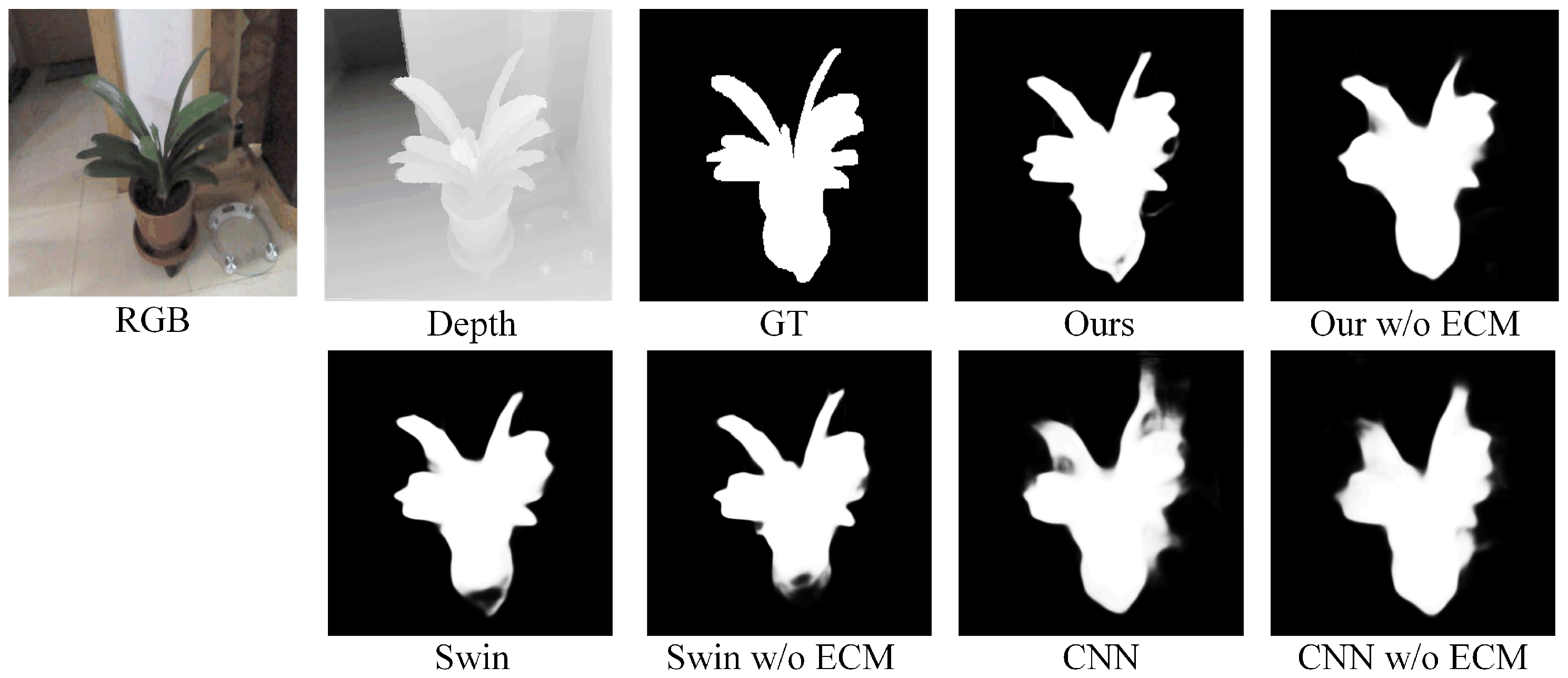
| CNN + CNN w/o ECM | 0.807 | 0.821 | 0.846 | 0.097 | 0.796 | 0.814 | 0.833 | 0.069 | 0.783 | 0.794 | 0.835 | 0.110 | 0.832 | 0.748 | 0.870 | 0.054 |
| CNN + CNN | 0.832 | 0.841 | 0.866 | 0.089 | 0.828 | 0.825 | 0.864 | 0.060 | 0.791 | 0.812 | 0.844 | 0.098 | 0.891 | 0.787 | 0.891 | 0.045 |
| Swin-Transformer + Swin-Transformer w/o ECM | 0.847 | 0.856 | 0.886 | 0.068 | 0.869 | 0.830 | 0.903 | 0.043 | 0.857 | 0.830 | 0.903 | 0.065 | 0.869 | 0.841 | 0.914 | 0.033 |
| Swin-Transformer + Swin-Transformer | 0.858 | 0.882 | 0.904 | 0.059 | 0.879 | 0.833 | 0.919 | 0.033 | 0.869 | 0.845 | 0.928 | 0.054 | 0.888 | 0.848 | 0.936 | 0.029 |
| Ours w/o ECM | 0.853 | 0.860 | 0.896 | 0.063 | 0.873 | 0.820 | 0.914 | 0.036 | 0.86 | 0.849 | 0.919 | 0.066 | 0.879 | 0.835 | 0.925 | 0.032 |
| Ours | 0.891 | 0.891 | 0.939 | 0.040 | 0.903 | 0.866 | 0.948 | 0.023 | 0.887 | 0.881 | 0.937 | 0.049 | 0.909 | 0.878 | 0.957 | 0.022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, G.; Feng, Z.; Li, X. Cross-Modal Weakly Supervised RGB-D Salient Object Detection with a Focus on Filamentary Structures. Sensors 2025, 25, 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25102990
Ding Y, Chen W, Zhang G, Feng Z, Li X. Cross-Modal Weakly Supervised RGB-D Salient Object Detection with a Focus on Filamentary Structures. Sensors. 2025; 25(10):2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25102990
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Yifan, Weiwei Chen, Guomin Zhang, Zhaoming Feng, and Xuan Li. 2025. "Cross-Modal Weakly Supervised RGB-D Salient Object Detection with a Focus on Filamentary Structures" Sensors 25, no. 10: 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25102990
APA StyleDing, Y., Chen, W., Zhang, G., Feng, Z., & Li, X. (2025). Cross-Modal Weakly Supervised RGB-D Salient Object Detection with a Focus on Filamentary Structures. Sensors, 25(10), 2990. https://doi.org/10.3390/s25102990





