An Improved Initial Alignment Method Based on SE2(3)/EKF for SINS/GNSS Integrated Navigation System with Large Misalignment Angles
Abstract
1. Introduction
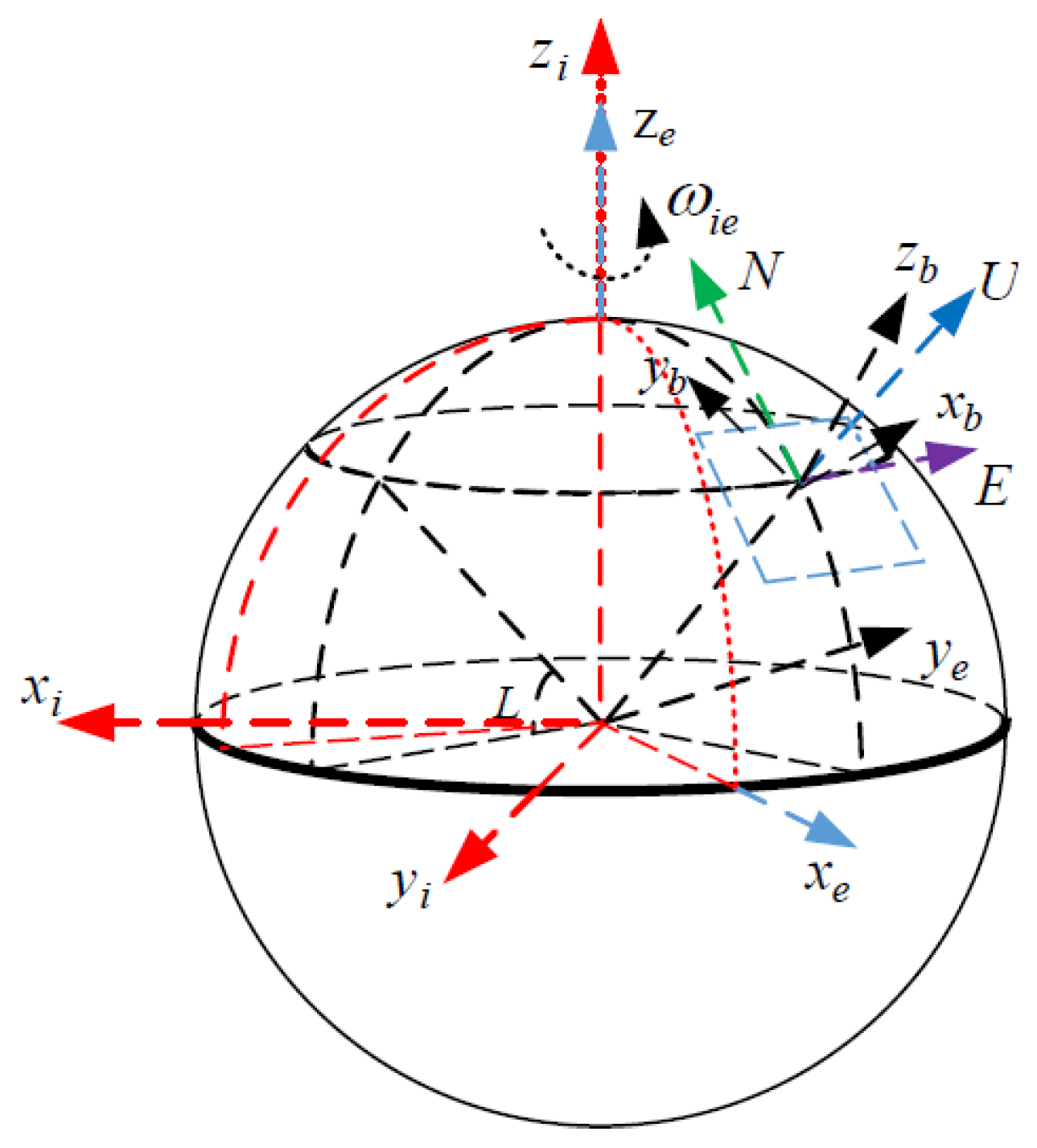
2. Inertial Navigation Error Equation under the Lie Group Framework
- (1)
- b-frame: Body coordinate system, with its three axes pointing to the right–front–up (R-F-U) of the carrier, respectively, denoted as ;
- (2)
- n-frame: It indicates the navigation frame and it is the frame used by the SINS to calculate the navigation parameters, denoted as Eastward–Northward–Upward (E-N-U);
- (3)
- e-frame: Earth coordinate system, with its origin at the geocenter. The x-axis is the intersection of the geocenter pointing to the prime meridian and the equator, the z-axis is the geocenter pointing to the north pole, and the y-axis forms a right-handed coordinate system with the x-axis and z-axis, denoted as ;
- (4)
- i-frame: Inertial coordinate system. It is a non-rotating coordinate system in inertial space, denoted as .
2.1. SINS Navigation Differential and Error Equations
2.2. Left Invariant Error Equation of Inertial Navigation in the Lie Group Framework
3. Filtering Model Based on SE2(3)/EKF
3.1. State Equation Based on SE2(3)
3.2. Measurement Equation Based on SE2(3)
3.3. SE2(3)/EKF Algorithm
- (1)
- One-step state prediction
- (2)
- State estimation
- (3)
- State estimation error
- (4)
- Filter gain
- (5)
- One-step prediction mean square error
- (6)
- Estimating mean square errorwhere is the state one-step prediction matrix, is the one-step transition matrix from time to time , and . is the state estimation matrix at time , is the state estimation error matrix at time , is the filtering gain matrix at time , is the measurement matrix at time , is the one step prediction mean square error matrix, is the measurement noise variance matrix, is the system noise variance matrix at time , , is the discretized system noise allocation matrix at time , and is the variance intensity matrix corresponding to the system noise matrix . is the estimated mean square error matrix.
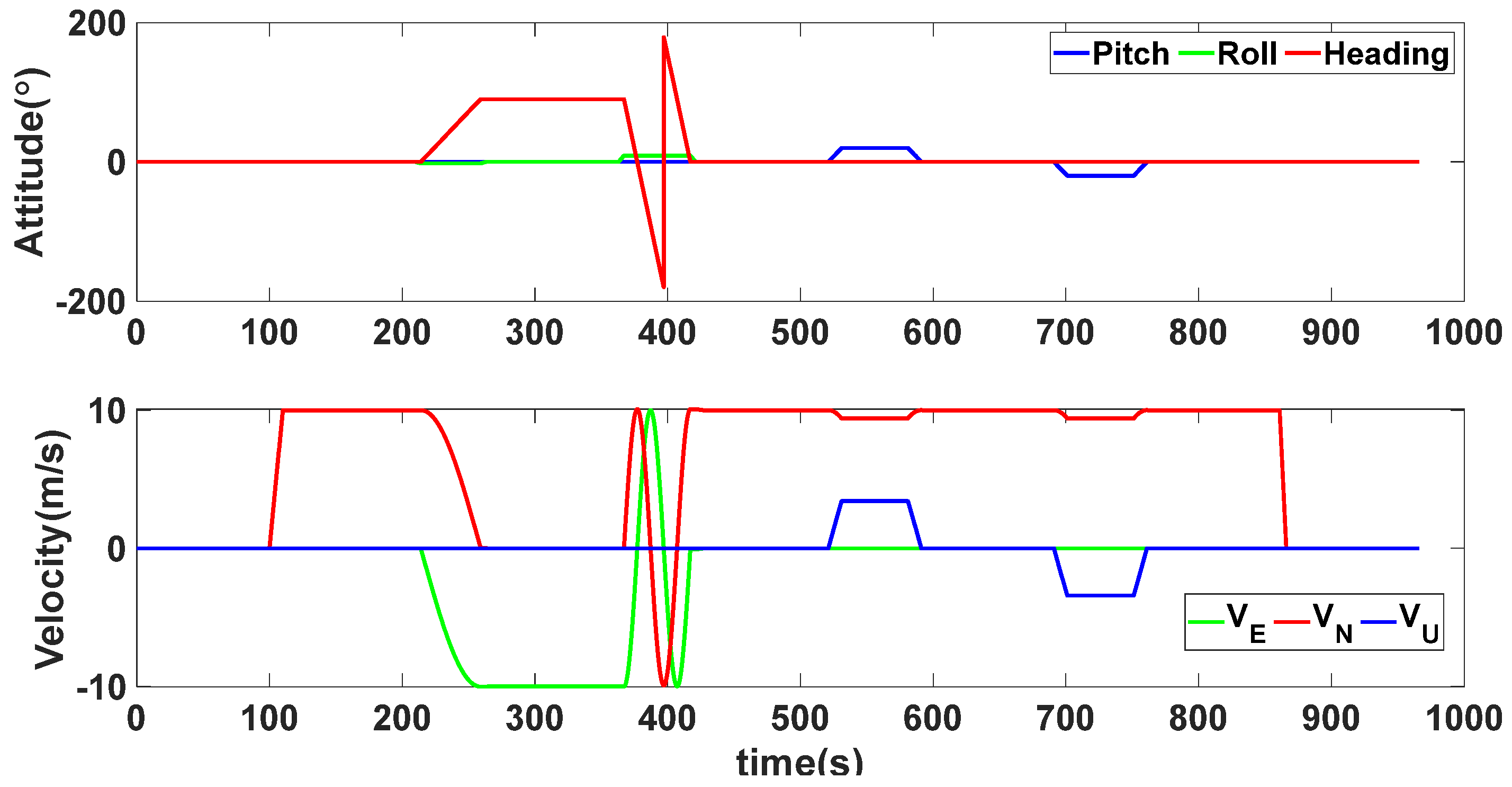
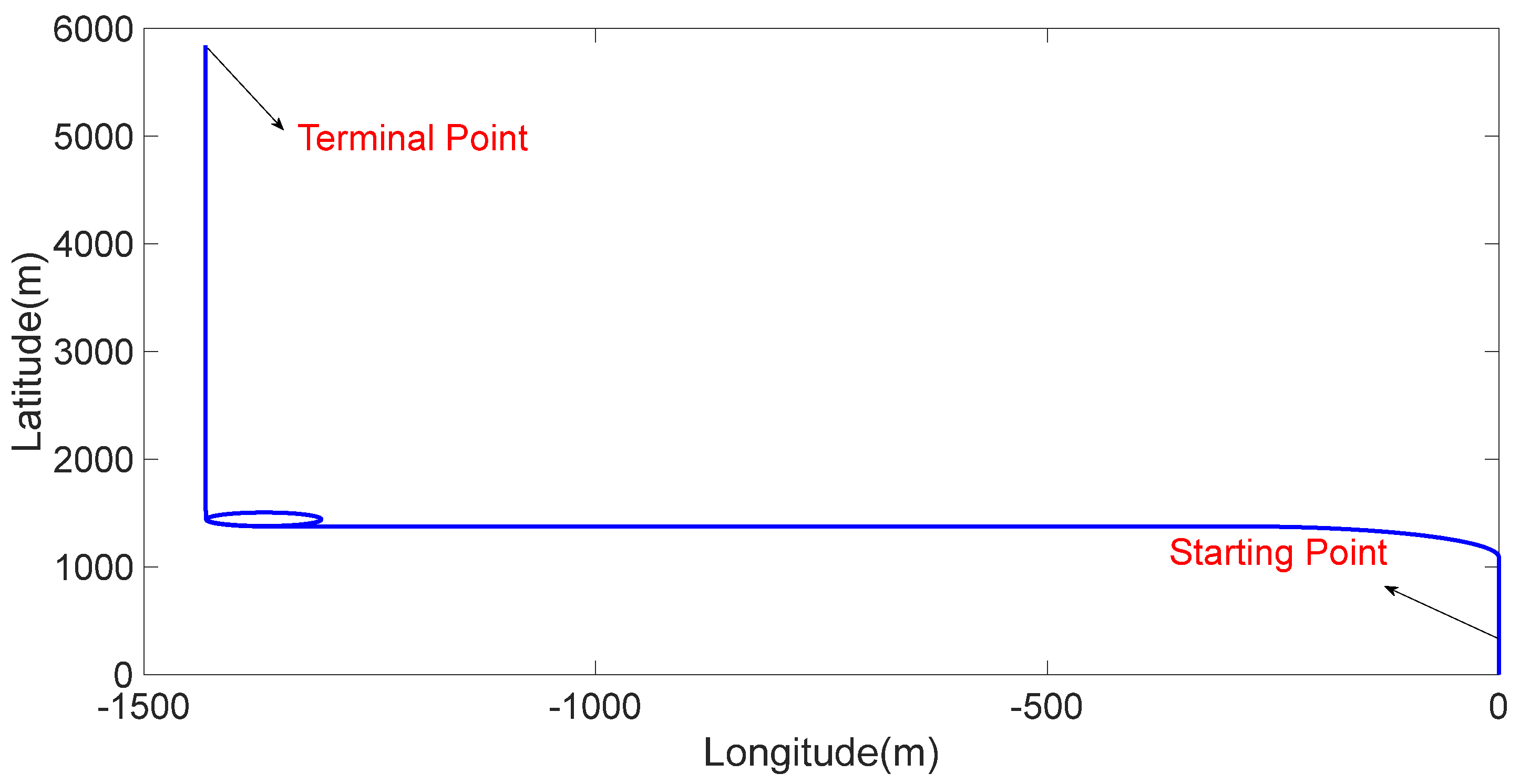
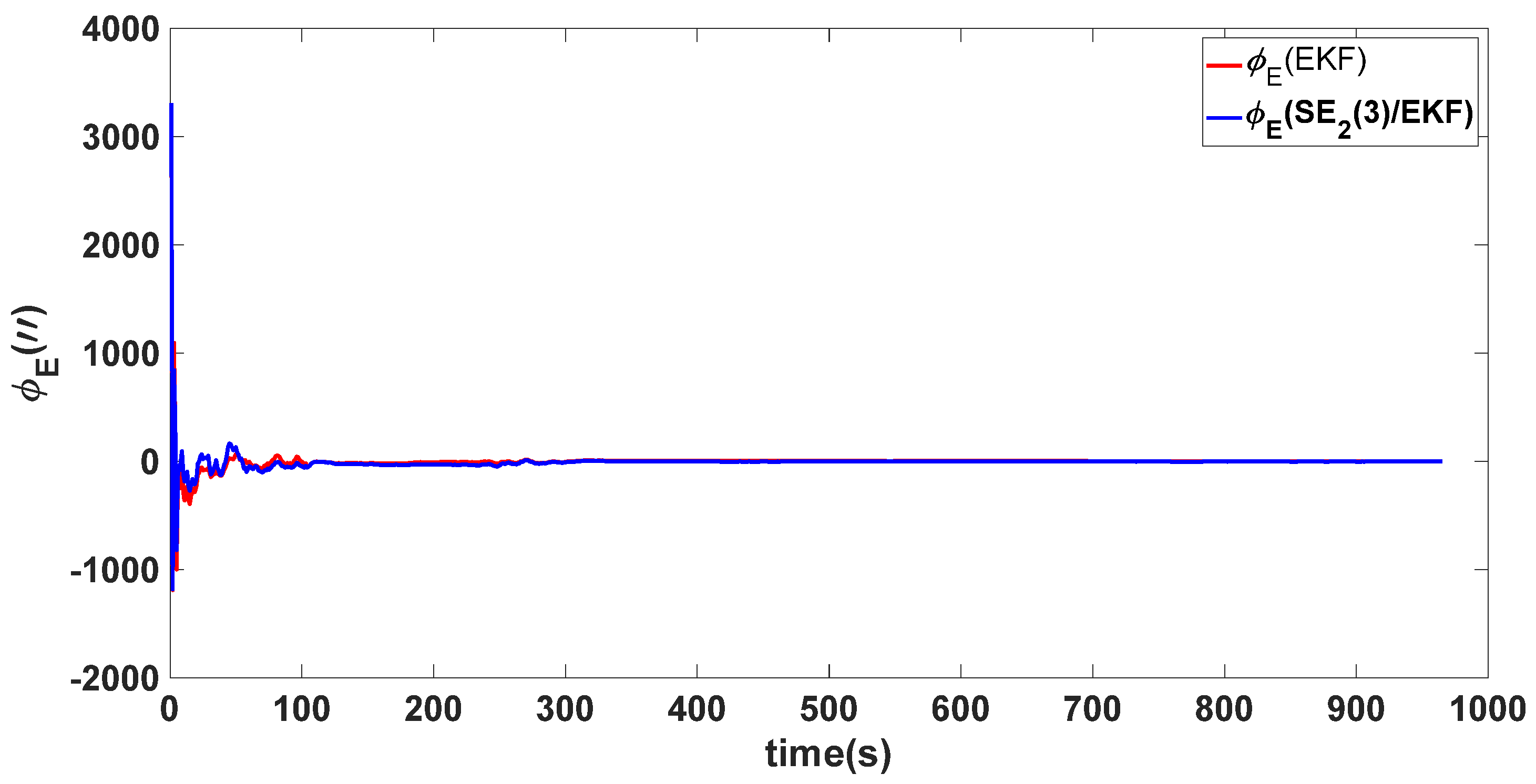
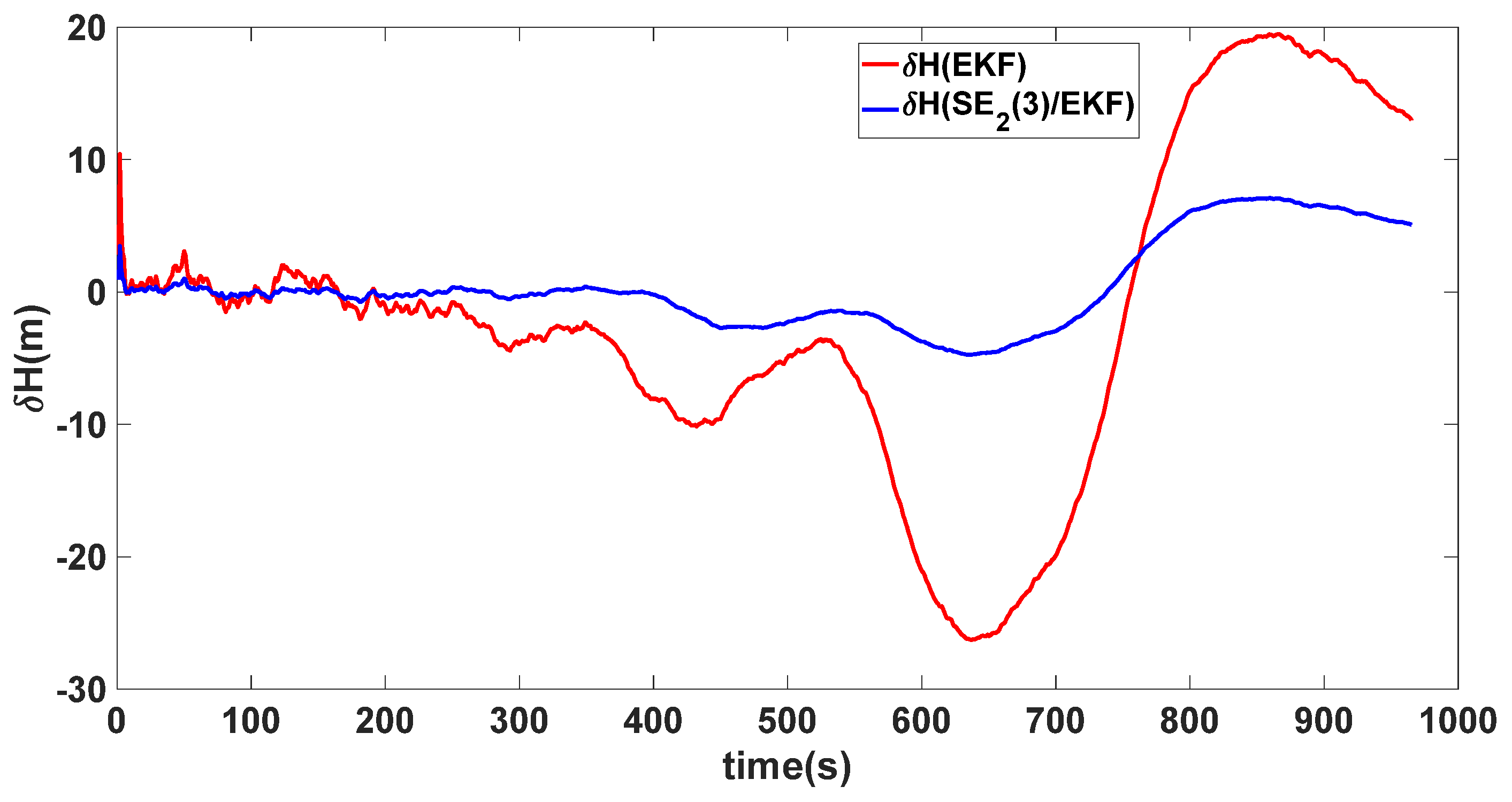
4. Simulation Results
4.1. Experiment 1
4.2. Experiment 2
4.3. Experiment 3
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SINS | Strap-down Inertial Navigation System |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| SE | Set Euclidean |
| EKF | Extended Kalman Filter |
| UKF | Unscented Kalman Filter |
| PF | Particle Filter |
| CKF | Cubature Kalman Filter |
| UPF | Unscented Particle Filter |
References
- Fang, J.C.; Wan, D.J. A Fast Initial Alignment Method for Strap-down Inertial Navigation System on Stationary Base. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1996, 32, 1501–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.C. Gradient Descent Optimization-based Self-alignment Method for Stationary SINS. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 68, 3278–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, X.D.; Lu, H.; Hao, Z.J.; Gu, C.C. Application of Adaptive Robust CKF in SINS/GPS Initial Alignment with Large Azimuth Misalignment Angles. Math. Prob. Eng. 2021, 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.F. Improvement to classical coning algorithms in maneuver performance based on a match correction structure. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 2019, 233, 2478–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y. Non-initial attitude error analysis of SINS by error closed-loop and energy-level constructing. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 106149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Cai, Y.F.; Li, Z.; Feng, S.Z.; Wang, H.; Sotelo, M.A. Map-based localization for intelligent vehicles from bi-sensor data fusion. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 203, 117586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Chen, H.L.; Tian, X. Automatic cruise system for water quality monitoring. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.Z.; Zhao, D.; Sun, Y.P.; Hong, J.Q.; Ding, S.H.; Luo, J. Design and testing of a control system associated with the automatic feeding boat for farming Chinese river crabs. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 150, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Chen, W.; Weng, D.; Wei, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Observability-Constrained Resampling-Free Cubature Kalman Filter for GNSS/INS with Measurement Outliers. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.L.; Qin, Y.Y.; Mei, C.B. Application of EKF and SUKF in SINS Alignment on Great-Swing Base. Meas. Control Technol. 2013, 32, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, X.S. Nonlinear Initial Alignment of INS based on Simplified UKF. J. Chin. Inerti. Technol. 2011, 19, 537–542. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.Y.; Gao, H.L.; You, J. In-Flight Alignment of Integrated SINS/GPS/Polarization/Geomagnetic Navigation System Based on Federal UKF. Sensors 2022, 22, 5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.S.; Liu, X.Y. Improved Particle Filter Algorithm in SINS Initial Alignment. J. Chin. Inerti. Technol. 2016, 24, 299–305. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Tang, L.J. Initial Alignment of Large Azimuth Misalignment Angles in SINS Based on CKF. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 33, 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Xu, X.S.; Liu, Y.T.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y. Initial Alignment of Large Azimuth Misalignment Angles in SINS Based on Adaptive UPF. Sensors 2015, 15, 21807–21823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Cao, J.; Shmaliy, Y.S.; Zhuang, Y. Distributed Kalman Filter for UWB/INS Integrated Pedestrian Localization under Colored Measurement Noise. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.L.; You, J.; Cao, S.Y. In-Flight Alignment Method of Integrated SINS/GPS Navigation System Based on Combined PF-UKF Filter. J. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. 2022, 56, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Tong, J.W.; Yan, Y.X. Application of KF/UPF in Initial Alignment of Large Azimuth Misalignment of SINS. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2018, 40, 2775–2781. [Google Scholar]
- Laan, N.; Cohen, M.; Arsenault, J.; Forbes, R. The Invariant Rauch-Tung-Striebel Smoother. IEEE Robot. Automat. Lett. 2020, 5, 5067–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potokar, E.; Norman, K.; Mangelson, J. Invariant extended kalman filtering for underwater navigation. IEEE Robot. Automat. Lett. 2021, 6, 5792–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titterton, D.; Weston, J. Strap-down inertial navigation technology-2nd edition—[book review]. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2005, 20, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, D.; Shmaliy, Y.S.; Chen, X.Y.; Shen, T.; Bi, S.H. Dual Free-Size LS-SVM Assisted Maximum Correntropy Kalman Filtering for Seamless INS-Based Integrated Drone Localization. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 71, 9845–9854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Shao, Q.; Wang, Z. Virtual Metrology Filter-Based Algorithms for Estimating Constant Ocean Current Velocity. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmann, W. Lie Groups: An Introduction through Linear Groups; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, B.C. Lie Groups, Lie Algebras, and Representations; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, G.W. Smooth Functions Invariant under the Action of a Compact Lie Group. Topology 1975, 14, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lageman, C.; Trumpf, J.; Mahony, R. Gradient-like Observers for Invariant Dynamics on a Lie Group. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2008, 55, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.B.; Wei, X.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, J.Y.; Li, L. On Sigma-Point Update of Cubature Kalman Filter for GNSS/INS under GNSS-Challenged Environment. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 8671–8682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.C.; Xu, X.S.; Yao, Y.Q.; Tong, J.W. A Novel BPNN-based Method to Overcome the GPS Outages for INS/GPS System. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 82134–82143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, S. Bayesian Filtering and Smoothing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
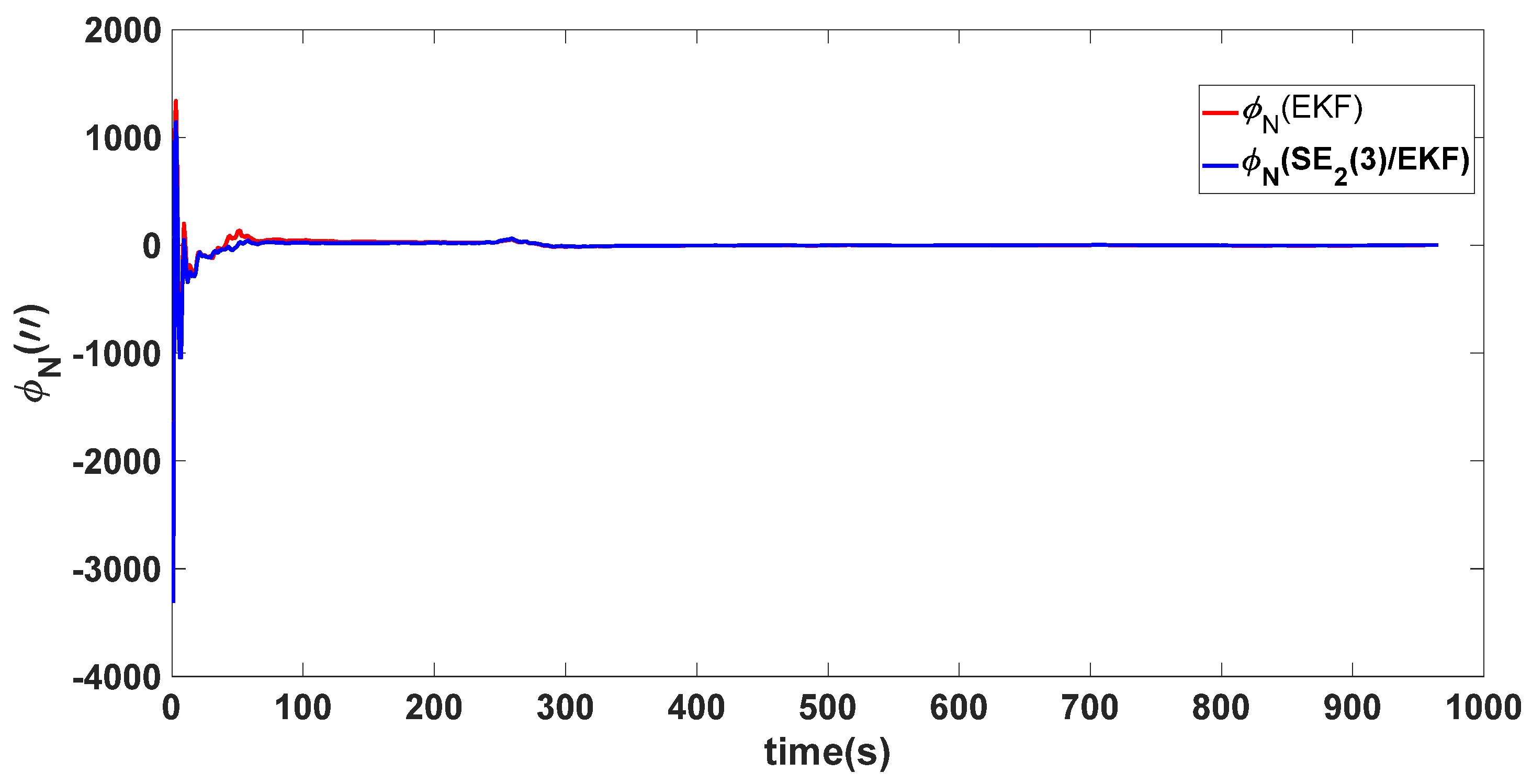
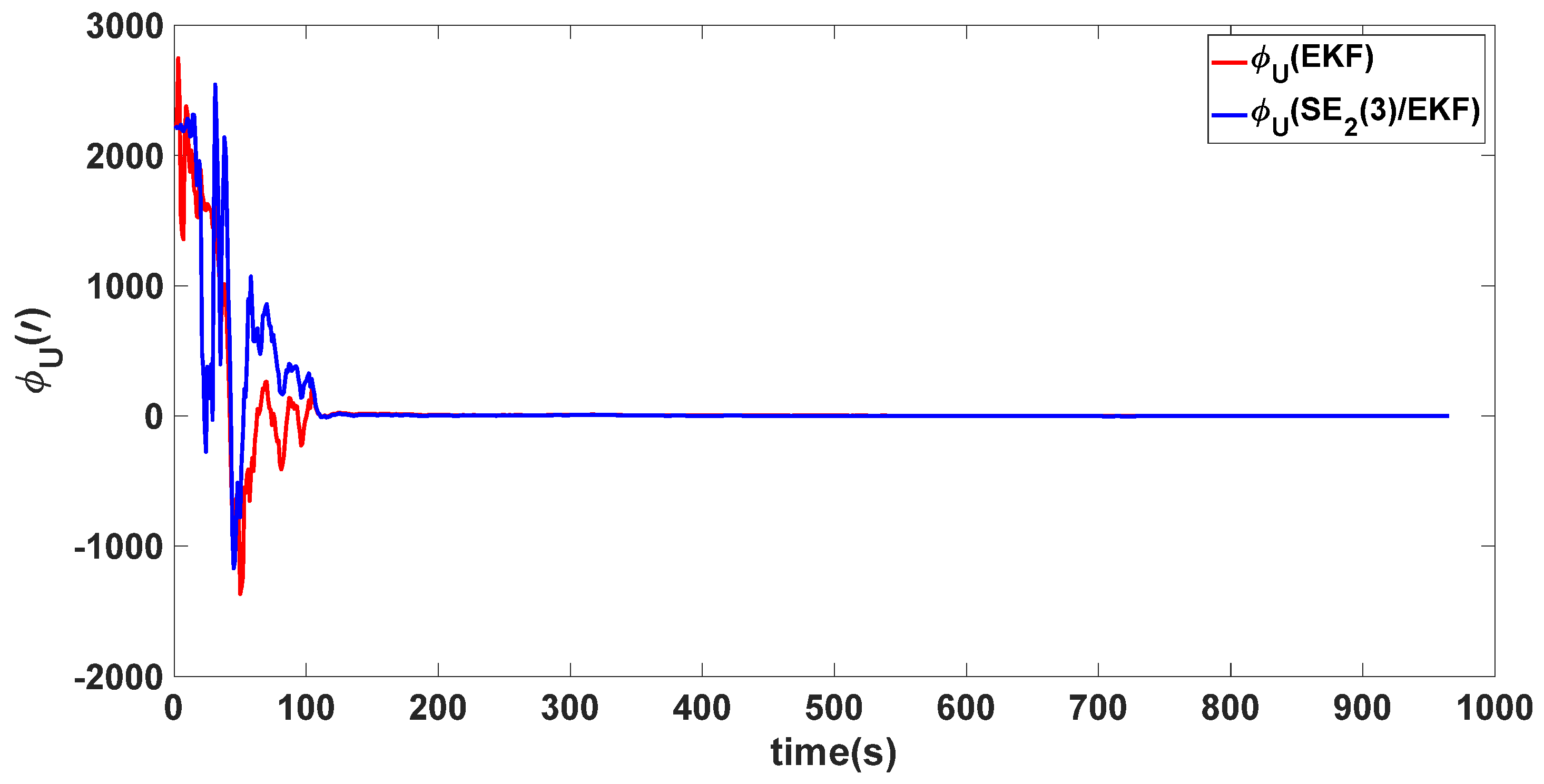
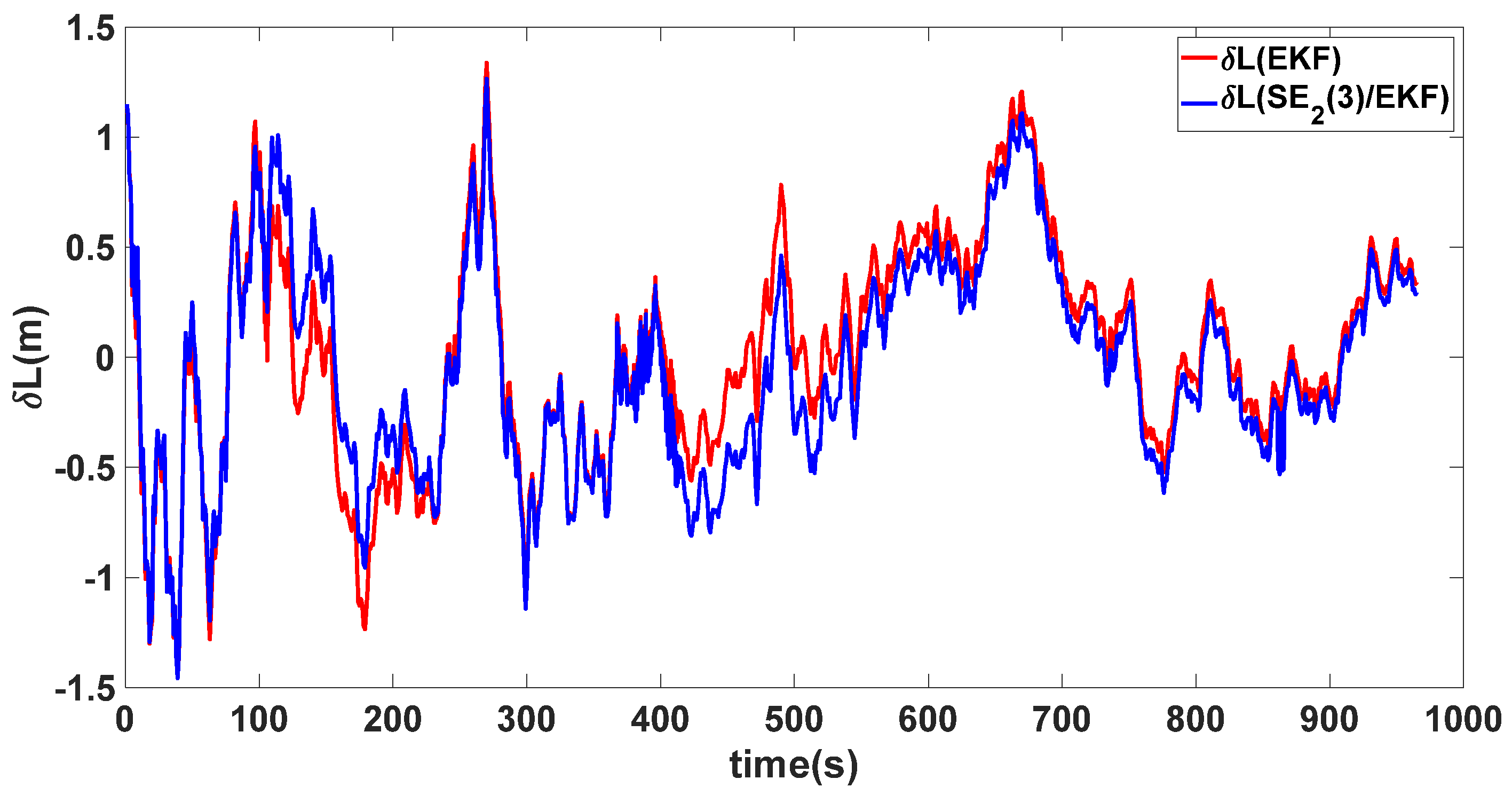
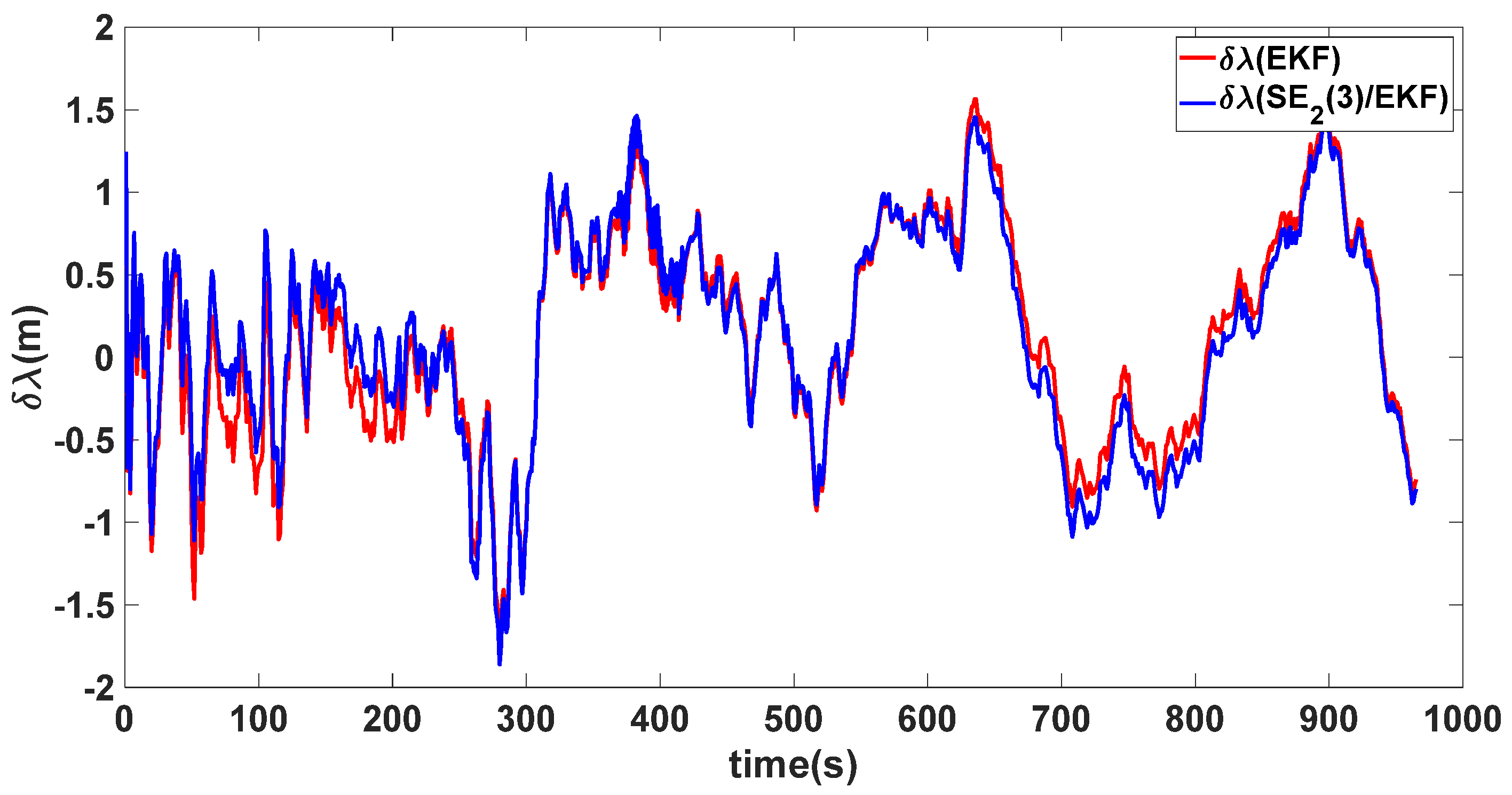
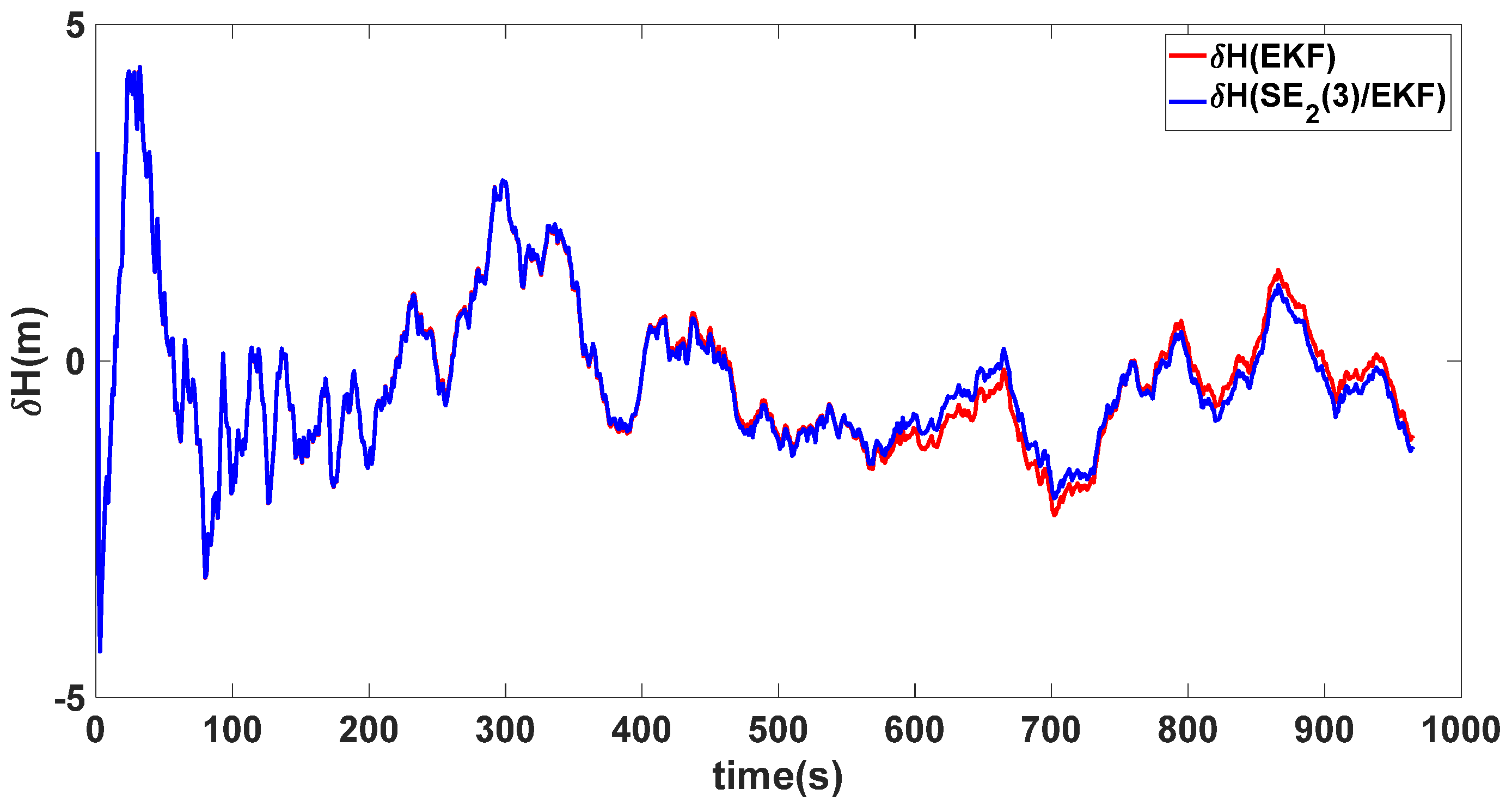
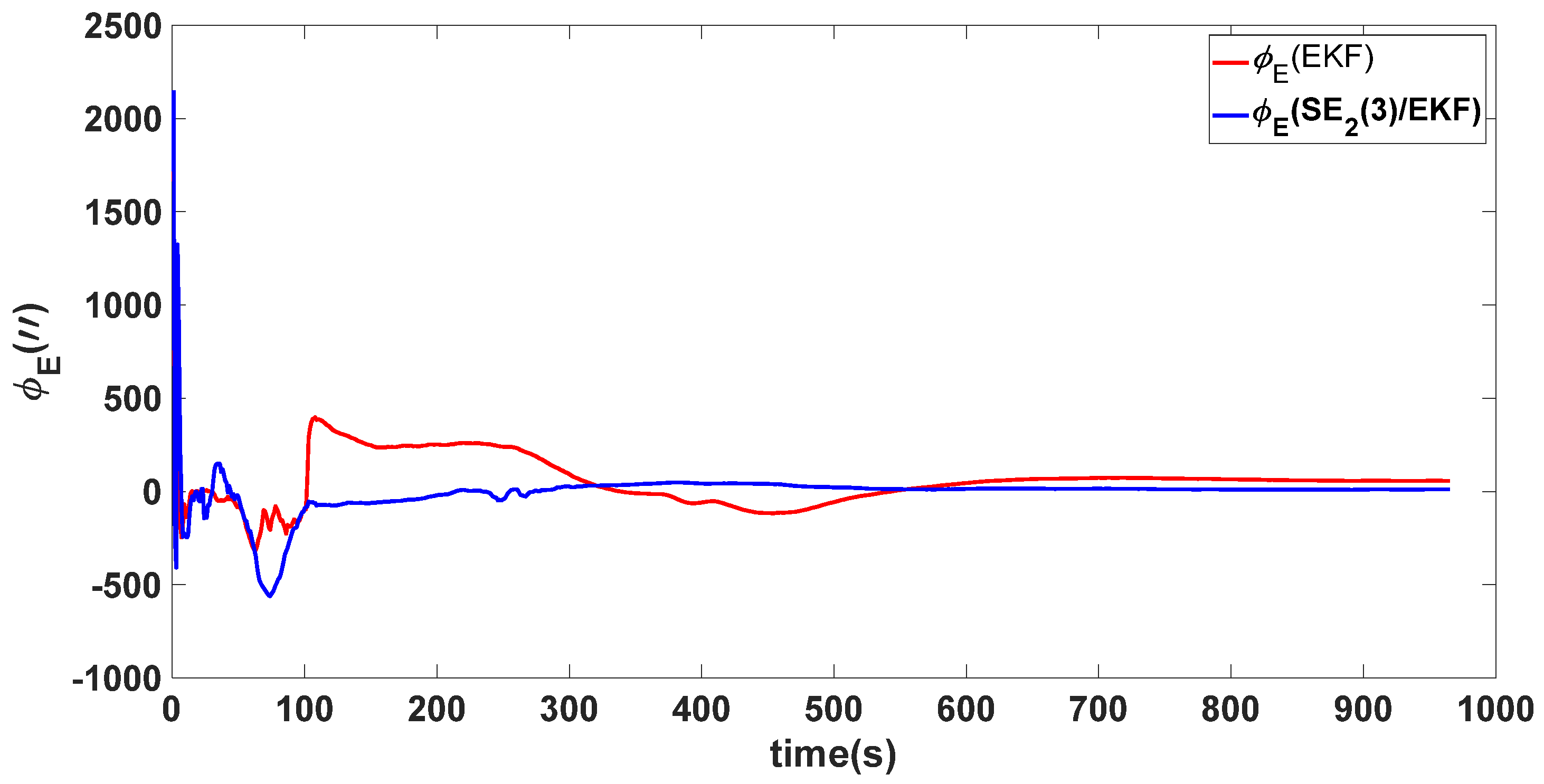
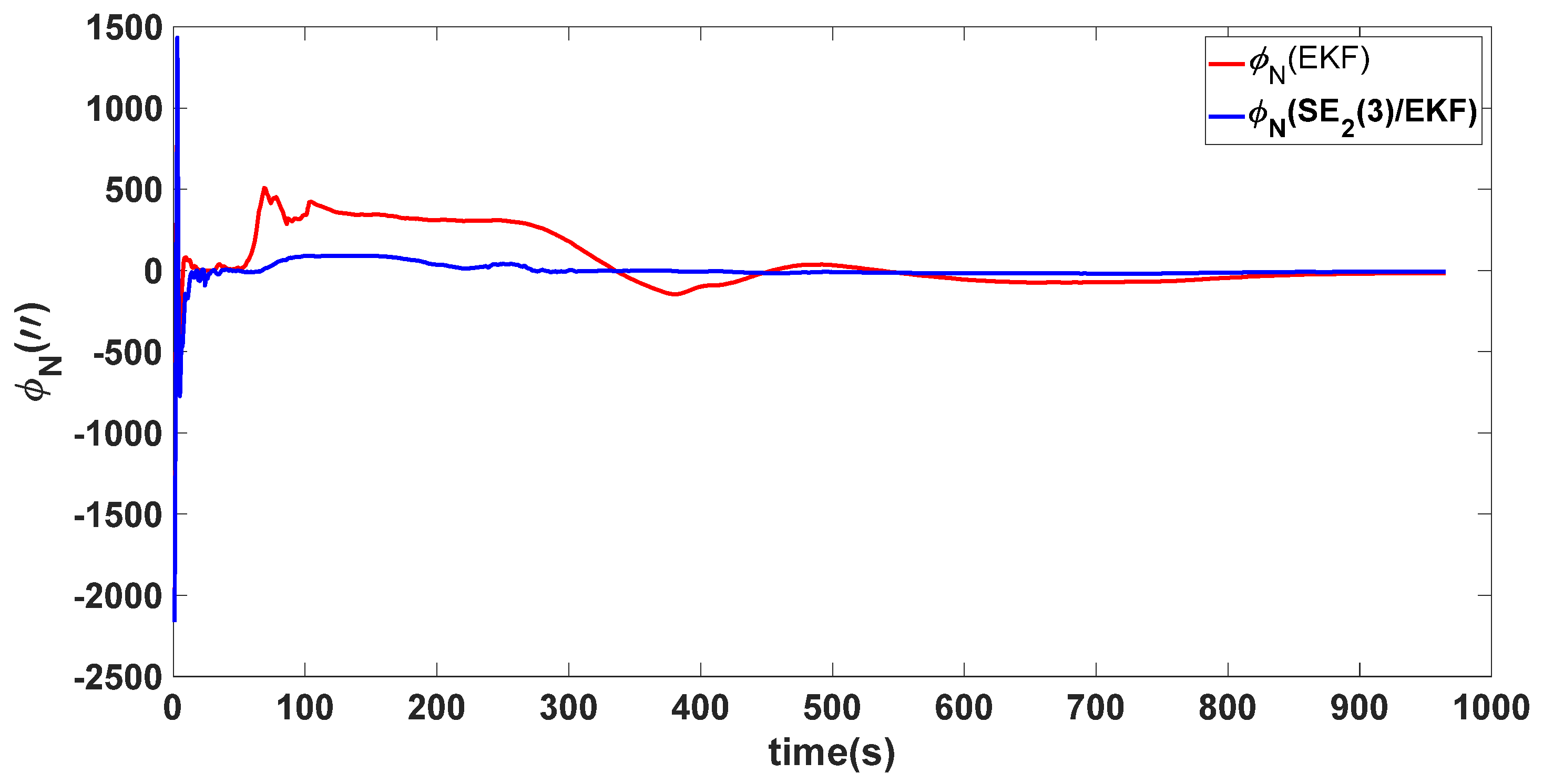
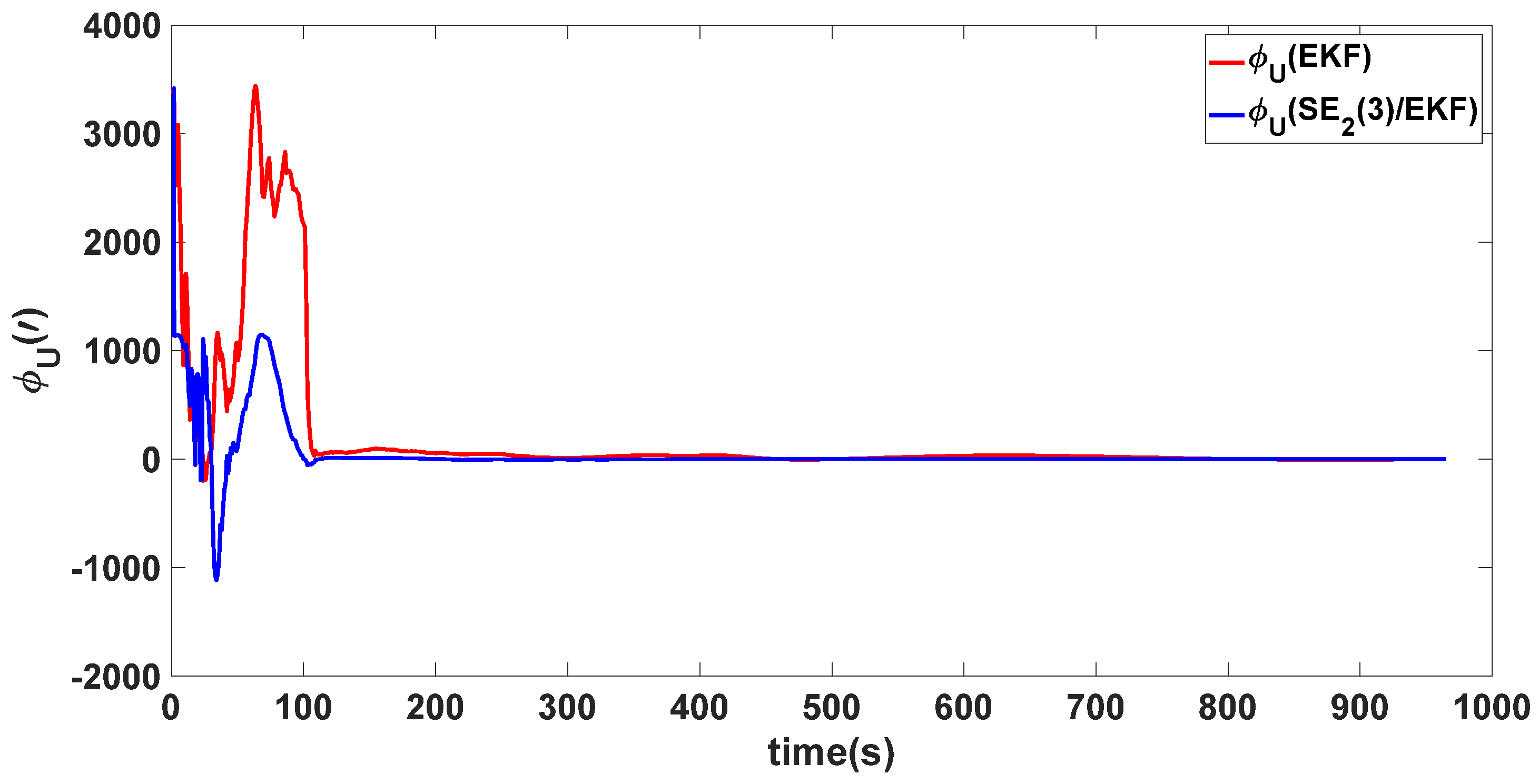
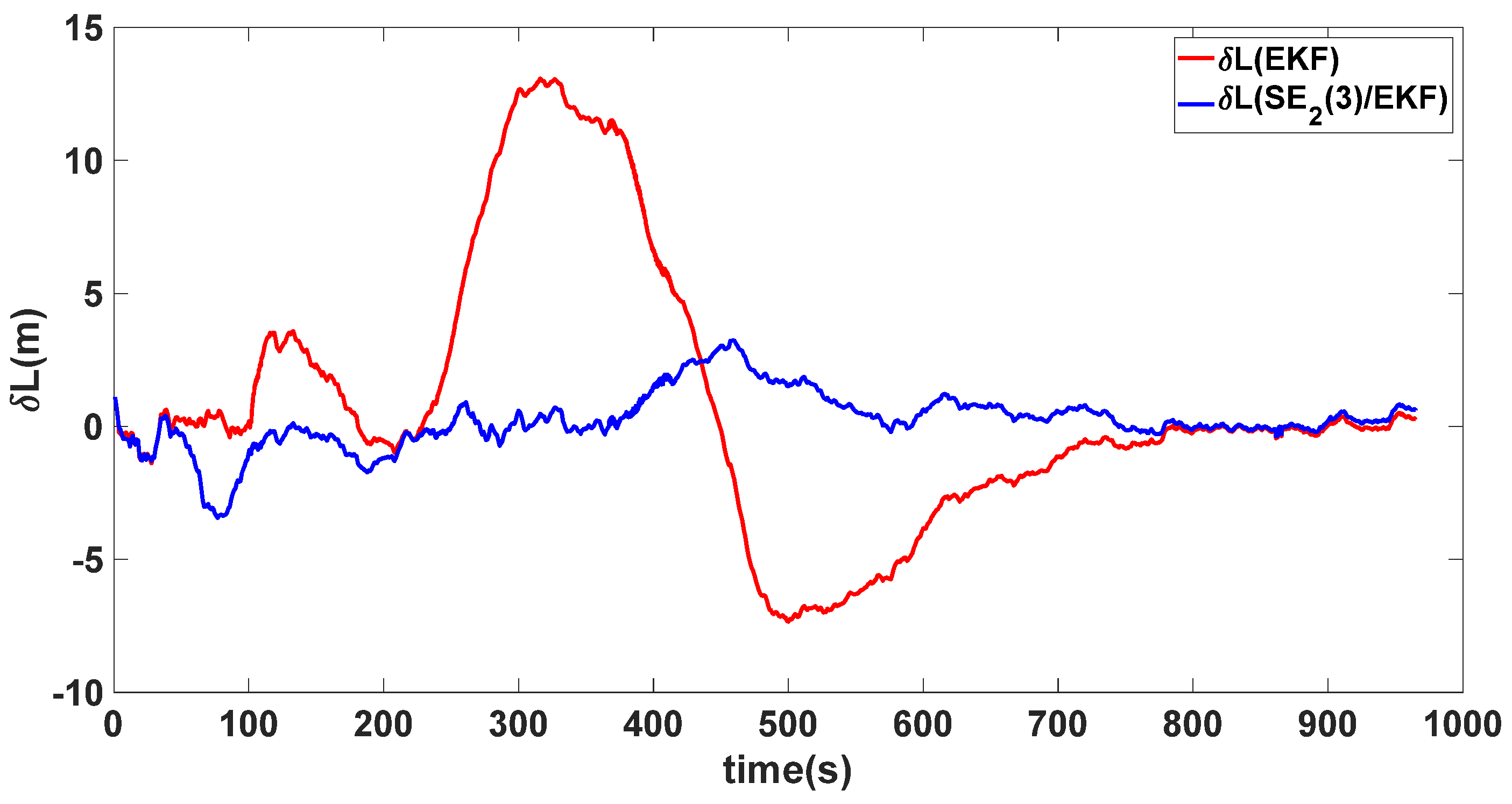
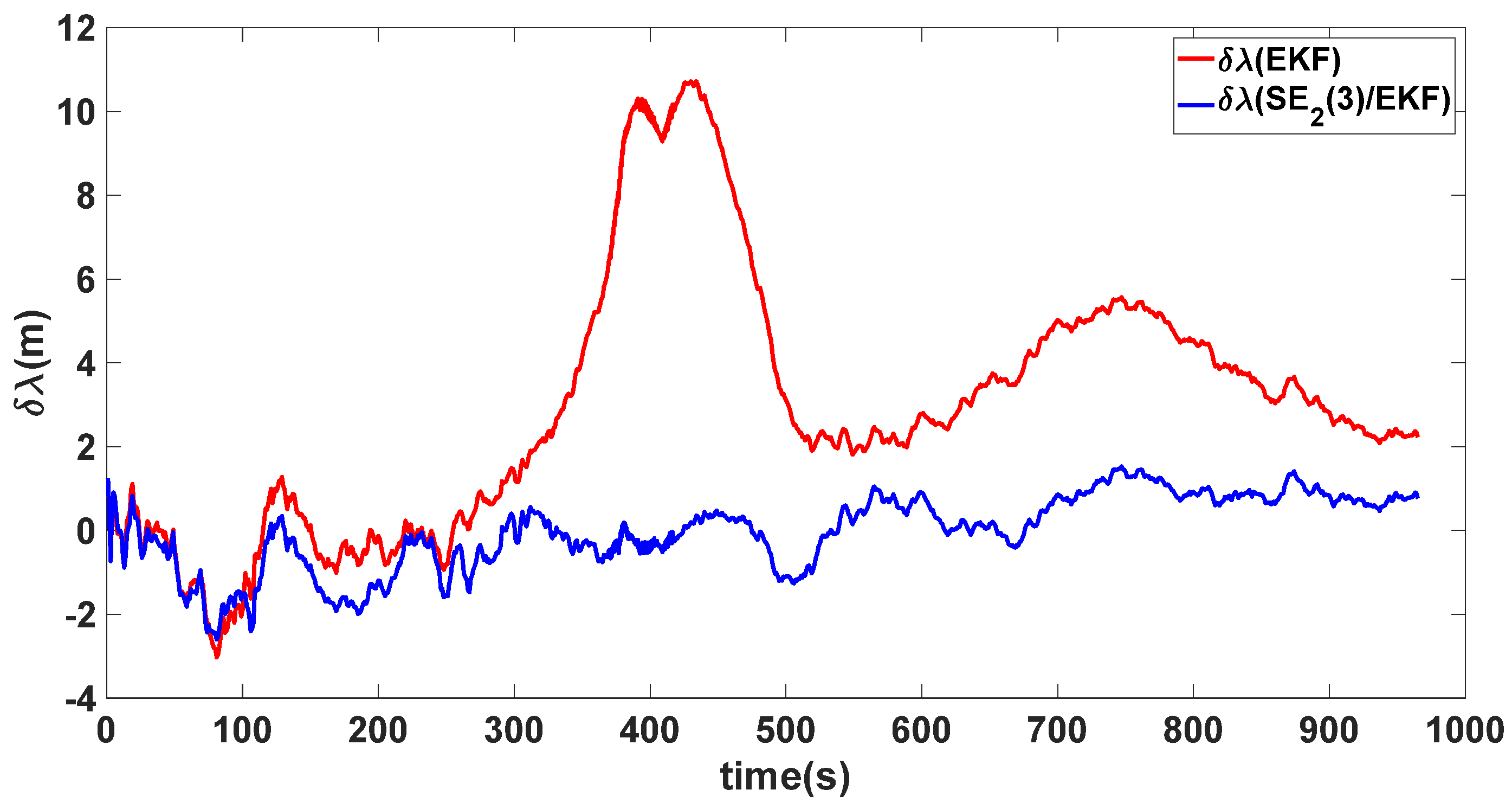
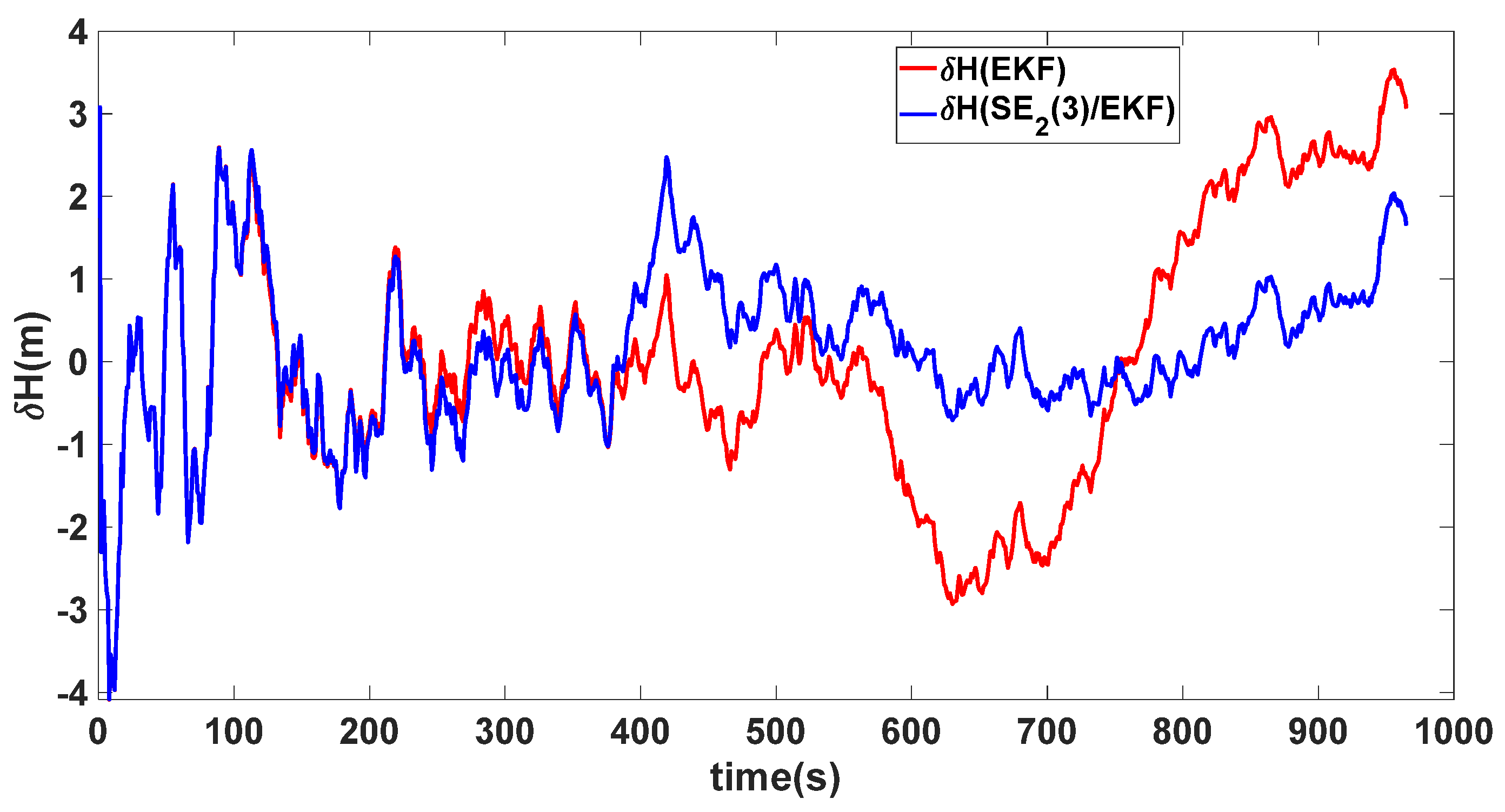
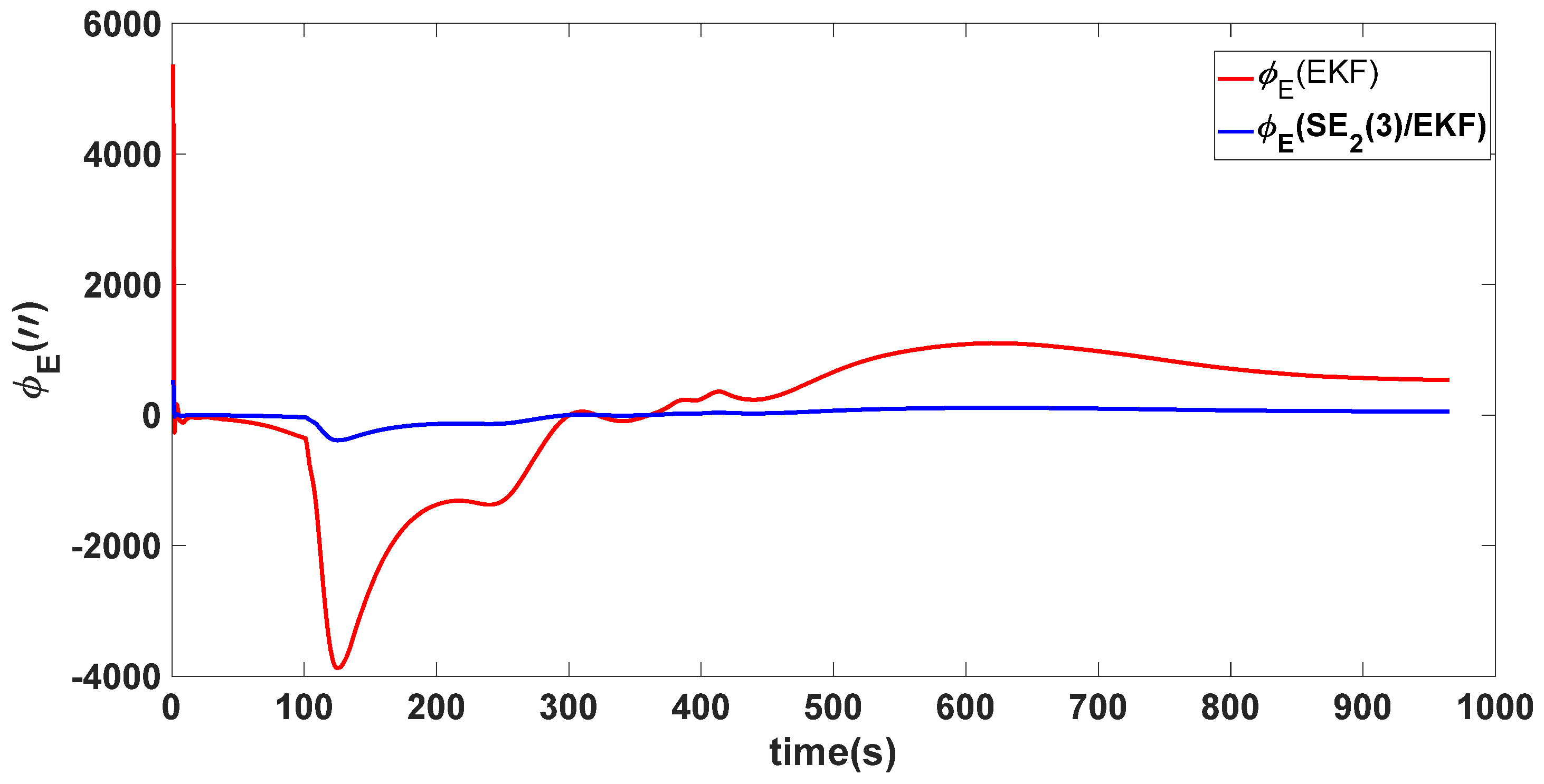
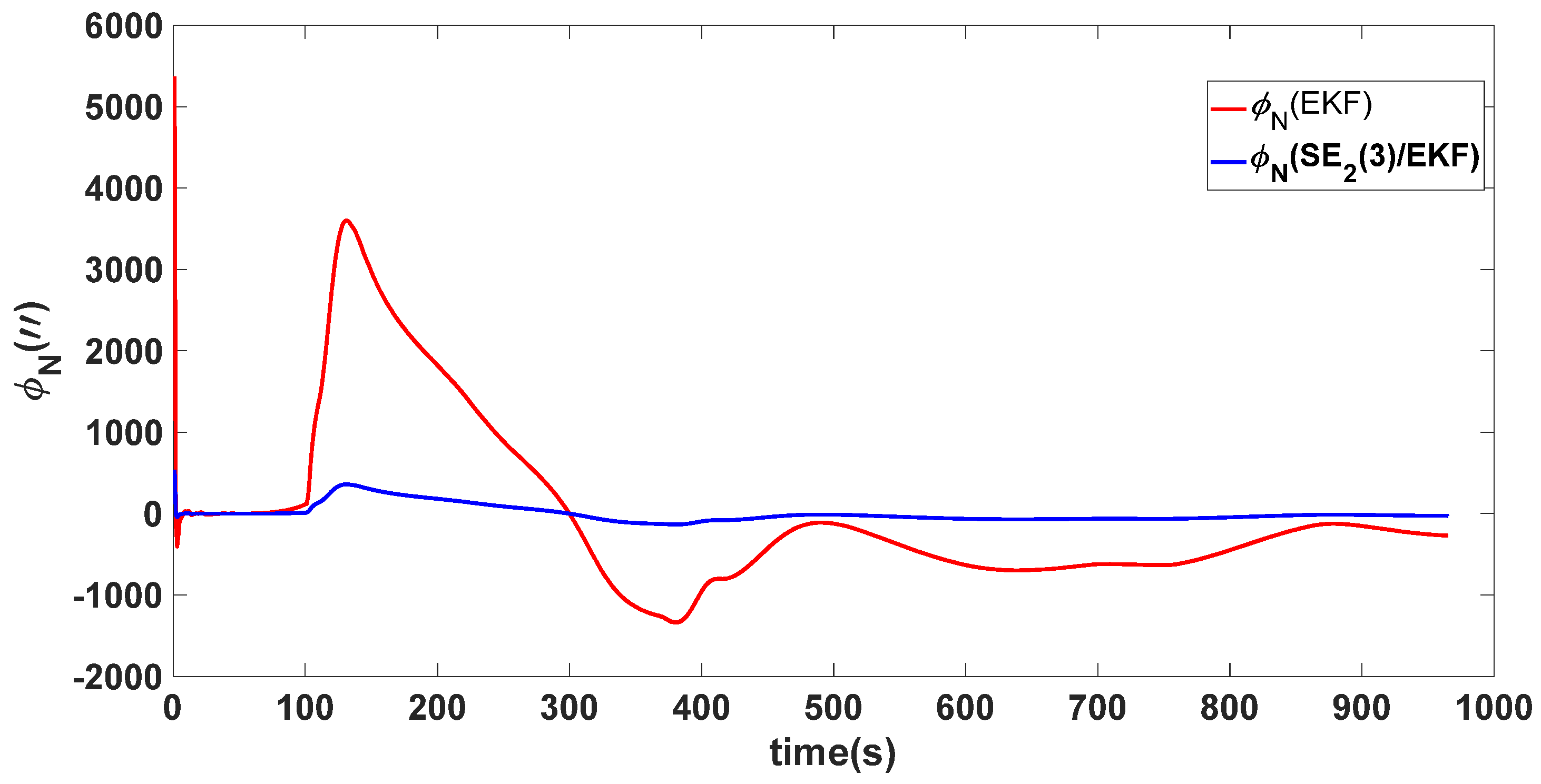
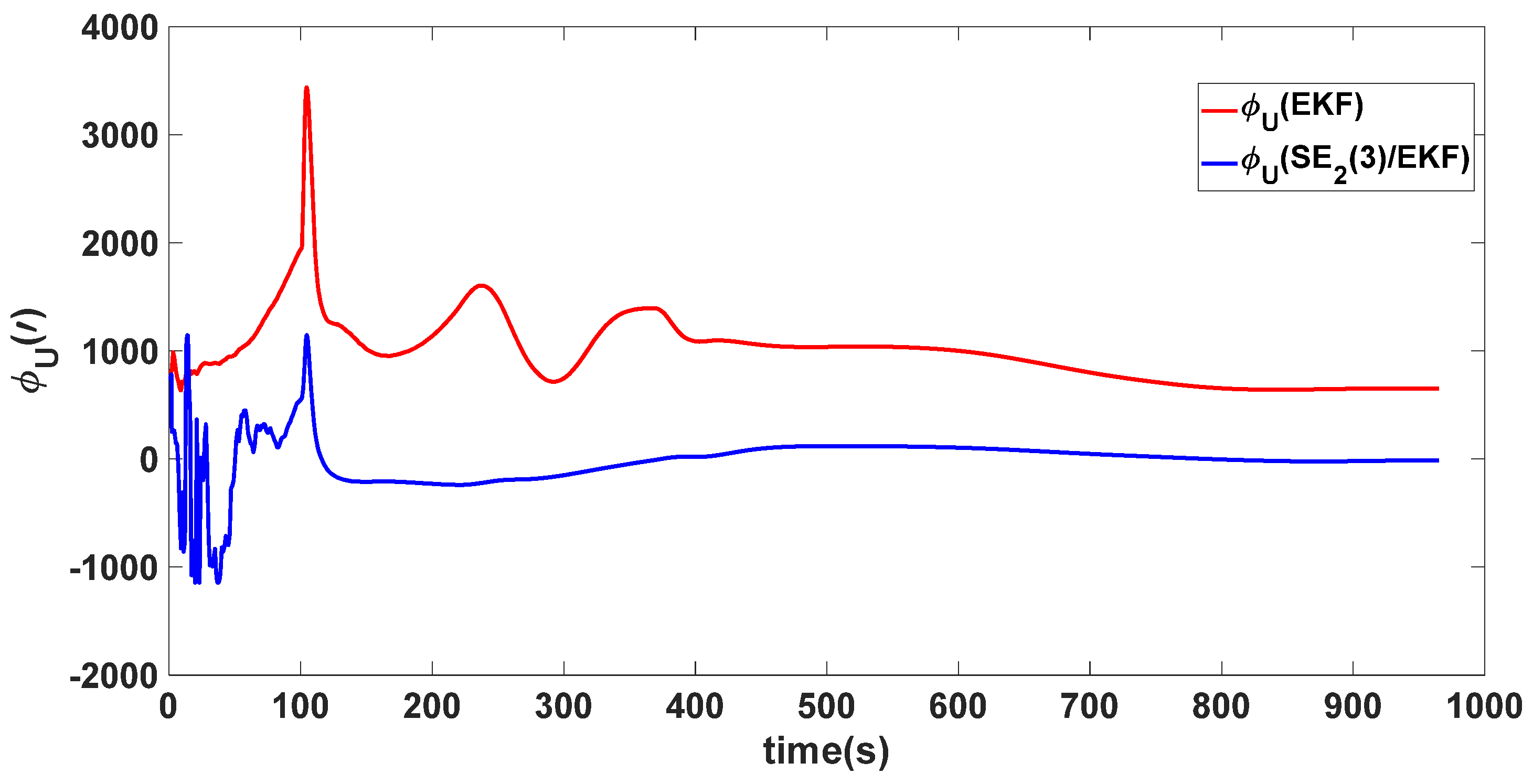
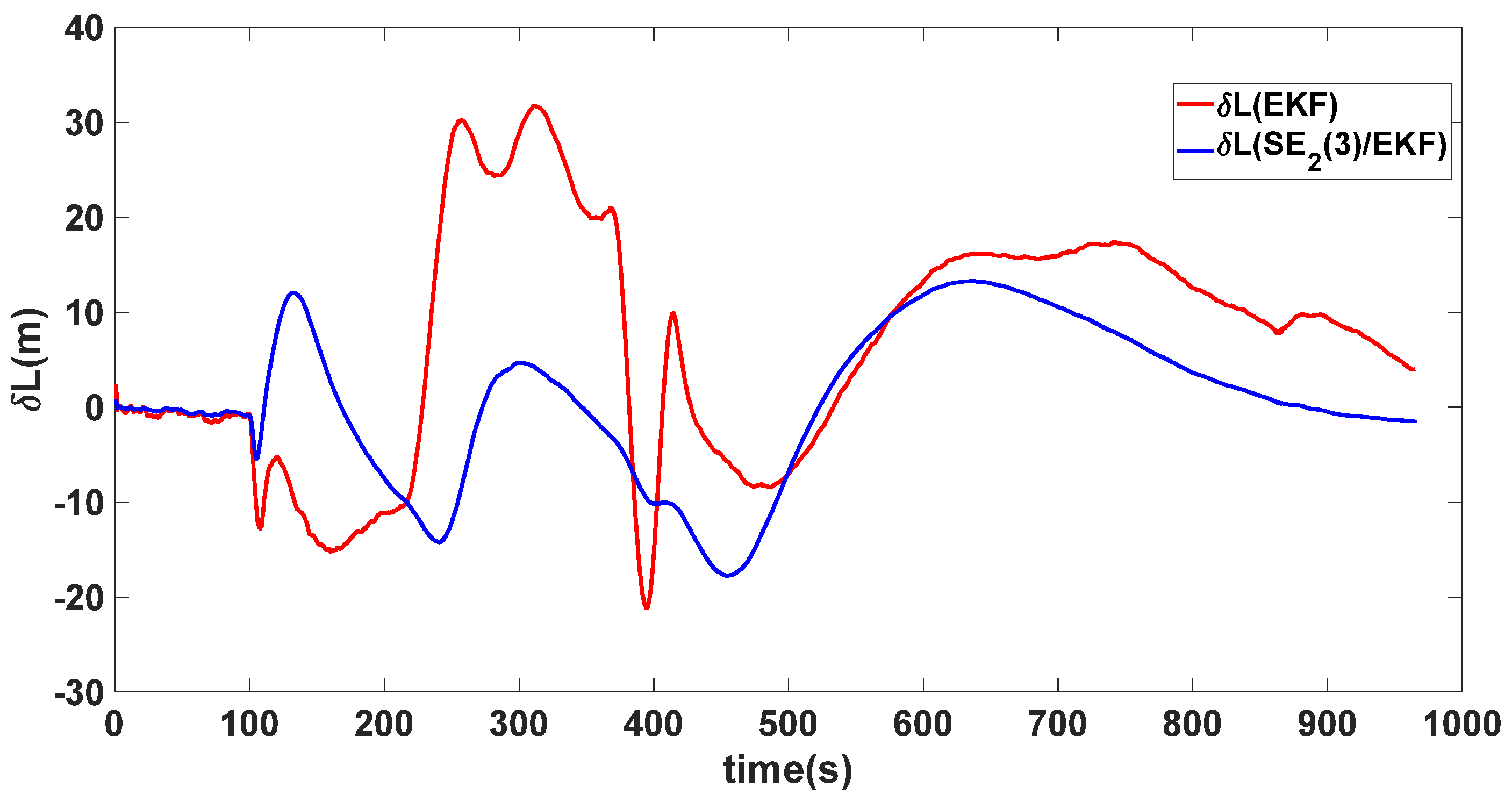
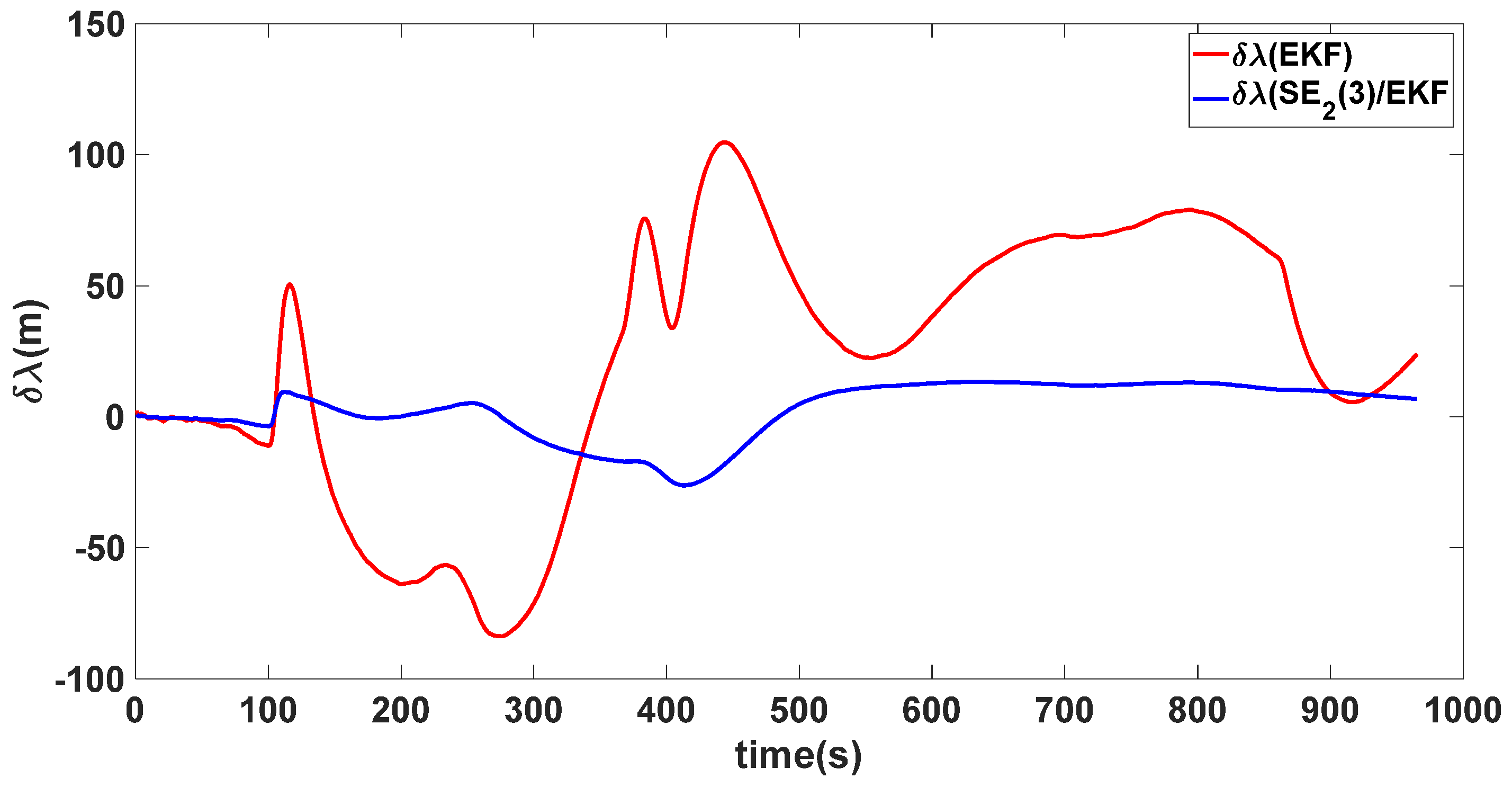
| Algorithm | Attitude and Position Error | Mean | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|
| SE2(3)/EKF | Pitch Error | −0.7871″ | 0.1214 |
| Roll Error | 1.2537″ | 0.0926 | |
| Heading Error | 0.0595′ | 0.0087 | |
| Latitude Error | 0.4381 m | 0.0412 | |
| Longitude Error | −0.2522 m | 0.0201 | |
| Height Error | −0.3418 m | 0.0603 | |
| EKF | Pitch Error | 0.9947″ | 0.1216 |
| Roll Error | 1.9856″ | 0.0945 | |
| Heading Error | −0.3037′ | 0.0107 | |
| Latitude Error | 0.4882 m | 0.0415 | |
| Longitude Error | −0.3065 m | 0.0203 | |
| Height Error | −0.5243 m | 0.0616 |
| Algorithm | Attitude and Position Error | Mean | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|
| SE2(3)/EKF | Pitch Error | 11.0881″ | 0.2950 |
| Roll Error | −7.7115″ | 0.1303 | |
| Heading Error | −1.0848′ | 0.0259 | |
| Latitude Error | 0.2507 m | 0.1201 | |
| Longitude Error | 0.8113 m | 0.0552 | |
| Height Error | 1.6058 m | 0.1191 | |
| EKF | Pitch Error | 57.2824″ | 0.3147 |
| Roll Error | −17.7575″ | 0.1366 | |
| Heading Error | −2.5052′ | 0.0445 | |
| Latitude Error | 0.5569 m | 0.1238 | |
| Longitude Error | 2.3491 m | 0.0612 | |
| Height Error | 3.1618 m | 0.1307 |
| Algorithm | Attitude and Position Error | Mean | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|
| SE2(3)/EKF | Pitch Error | ″ | 0.4387 |
| Roll Error | ″ | 1.2976 | |
| Heading Error | ′ | 0.2122 | |
| Latitude Error | −1.8307 m | 0.0204 | |
| Longitude Error | 2.2376 m | 0.1855 | |
| Height Error | 4.1076 m | 0.1372 | |
| EKF | Pitch Error | ″ | 0.4905 |
| Roll Error | ″ | 2.2026 | |
| Heading Error | ′ | 0.1851 | |
| Latitude Error | 5.3826 m | 0.1123 | |
| Longitude Error | 22.3550 m | 0.6989 | |
| Height Error | 16.1874 m | 0.1525 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Cui, B. An Improved Initial Alignment Method Based on SE2(3)/EKF for SINS/GNSS Integrated Navigation System with Large Misalignment Angles. Sensors 2024, 24, 2945. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24092945
Sun J, Chen Y, Cui B. An Improved Initial Alignment Method Based on SE2(3)/EKF for SINS/GNSS Integrated Navigation System with Large Misalignment Angles. Sensors. 2024; 24(9):2945. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24092945
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jin, Yuxin Chen, and Bingbo Cui. 2024. "An Improved Initial Alignment Method Based on SE2(3)/EKF for SINS/GNSS Integrated Navigation System with Large Misalignment Angles" Sensors 24, no. 9: 2945. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24092945
APA StyleSun, J., Chen, Y., & Cui, B. (2024). An Improved Initial Alignment Method Based on SE2(3)/EKF for SINS/GNSS Integrated Navigation System with Large Misalignment Angles. Sensors, 24(9), 2945. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24092945






