Development of Wafer-Type Plasma Monitoring Sensor with Automated Robot Arm Transfer Capability for Two-Dimensional In Situ Processing Plasma Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
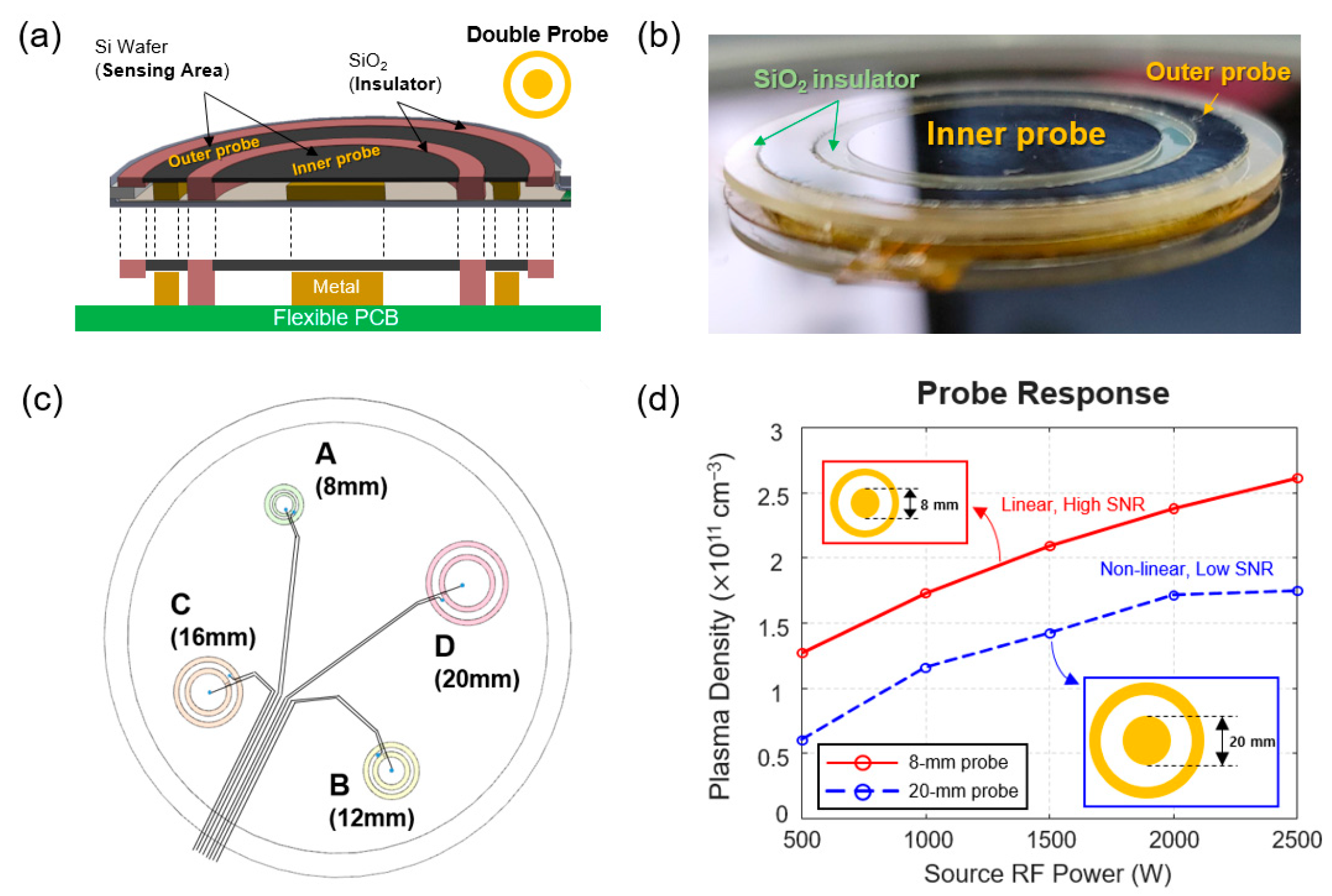
2.1. Double Probe Based on Floating Harmonic Method
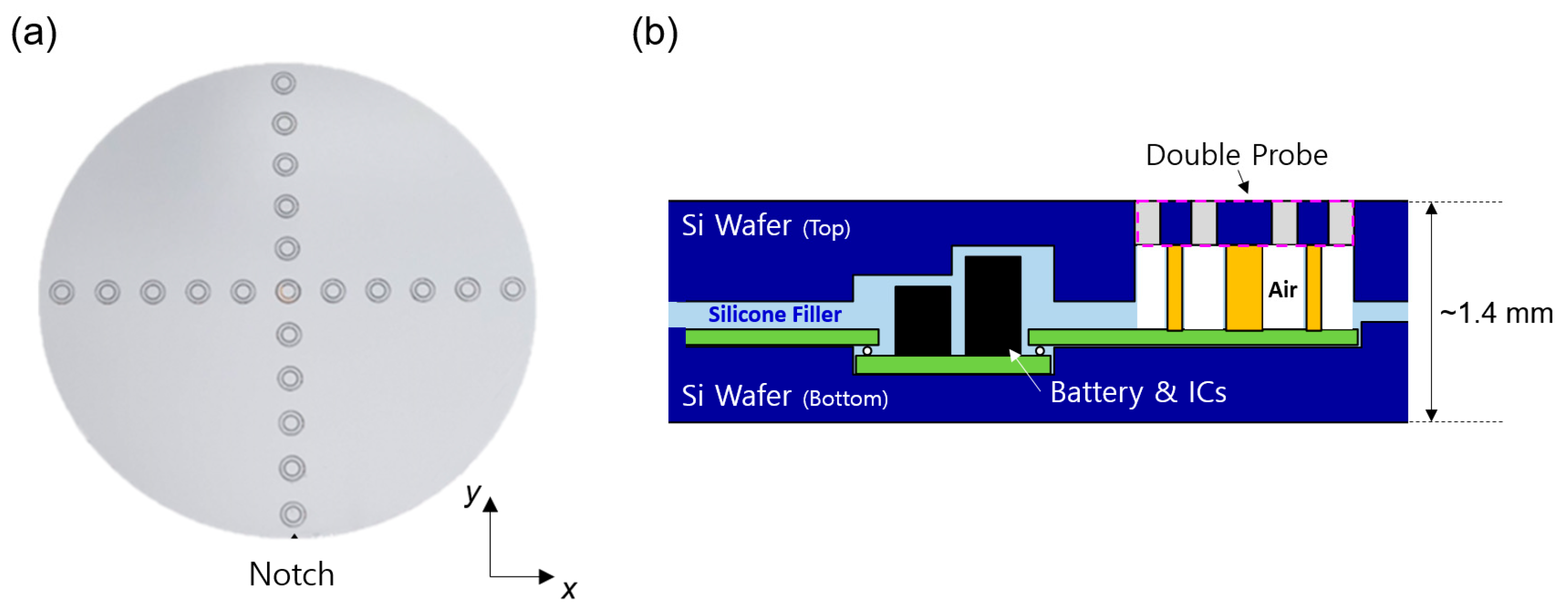
2.2. Wafer-Type Plasma Monitoring Sensor
2.2.1. System Characteristics
- Twelve-inch processing chamber compatibility;
- Floating-type double probe-based plasma diagnosis tool;
- Automated robot arm transfer capability via CTC software;
- Si- and SiO2-based materials with ultra-thin system design (i.e., thickness ~1.4 mm, weight ~210 g);
- Microprocessor unit (MCU)-based embedded system;
- Rule-based data acquisition using in-house designed software;
- Rechargeable Li-ion battery-based wireless system;
- Vacuum resistance ≤1 mTorr;
- Operation temperature −20 °C to 70 °C;
- Bias RF ≤500 W, Source RF ≤2500 W @ ICP chamber.
2.2.2. Probe Design
2.2.3. Operation Circuit for Plasma Diagnosis
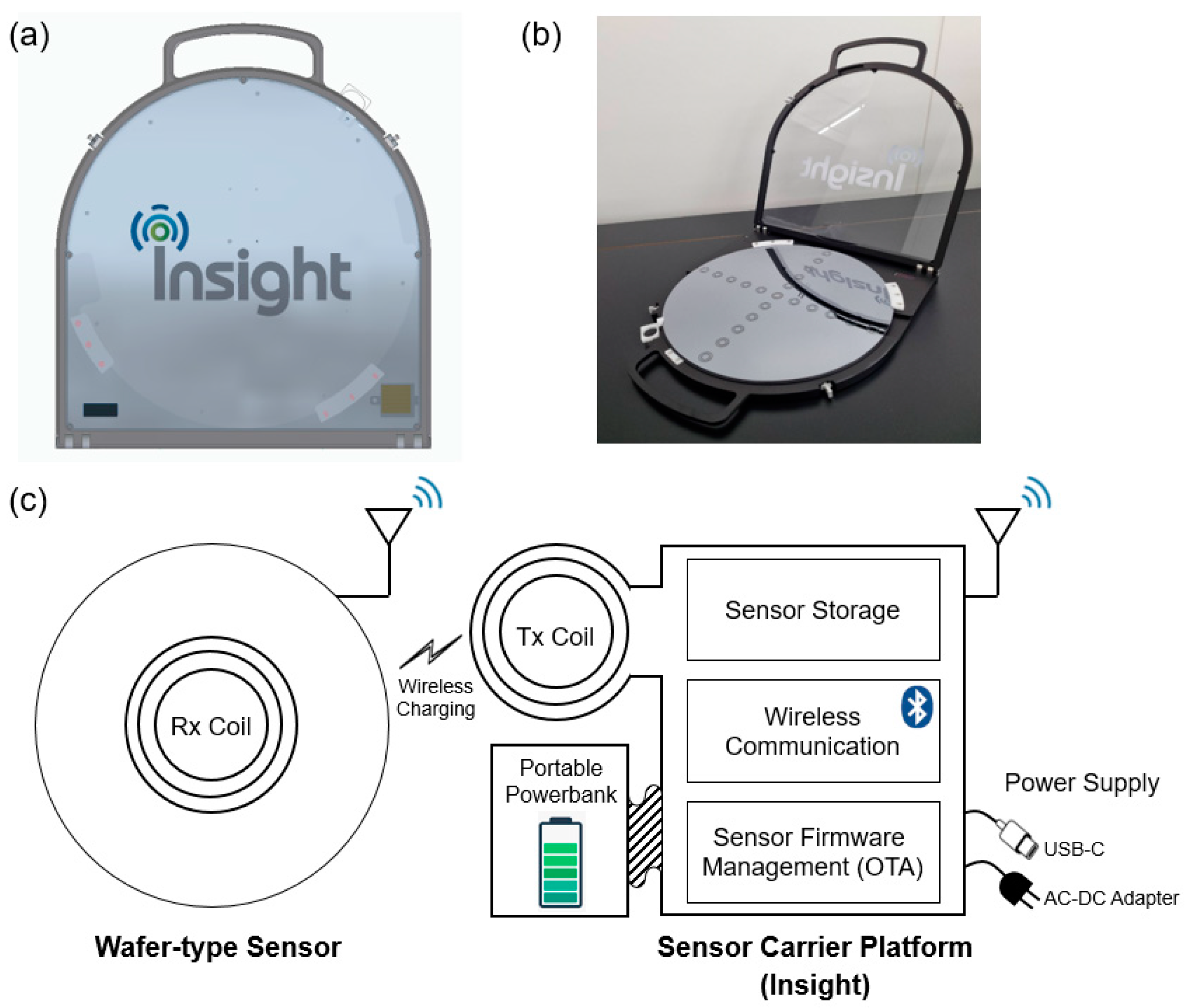
2.2.4. Sensor Carrier Platform
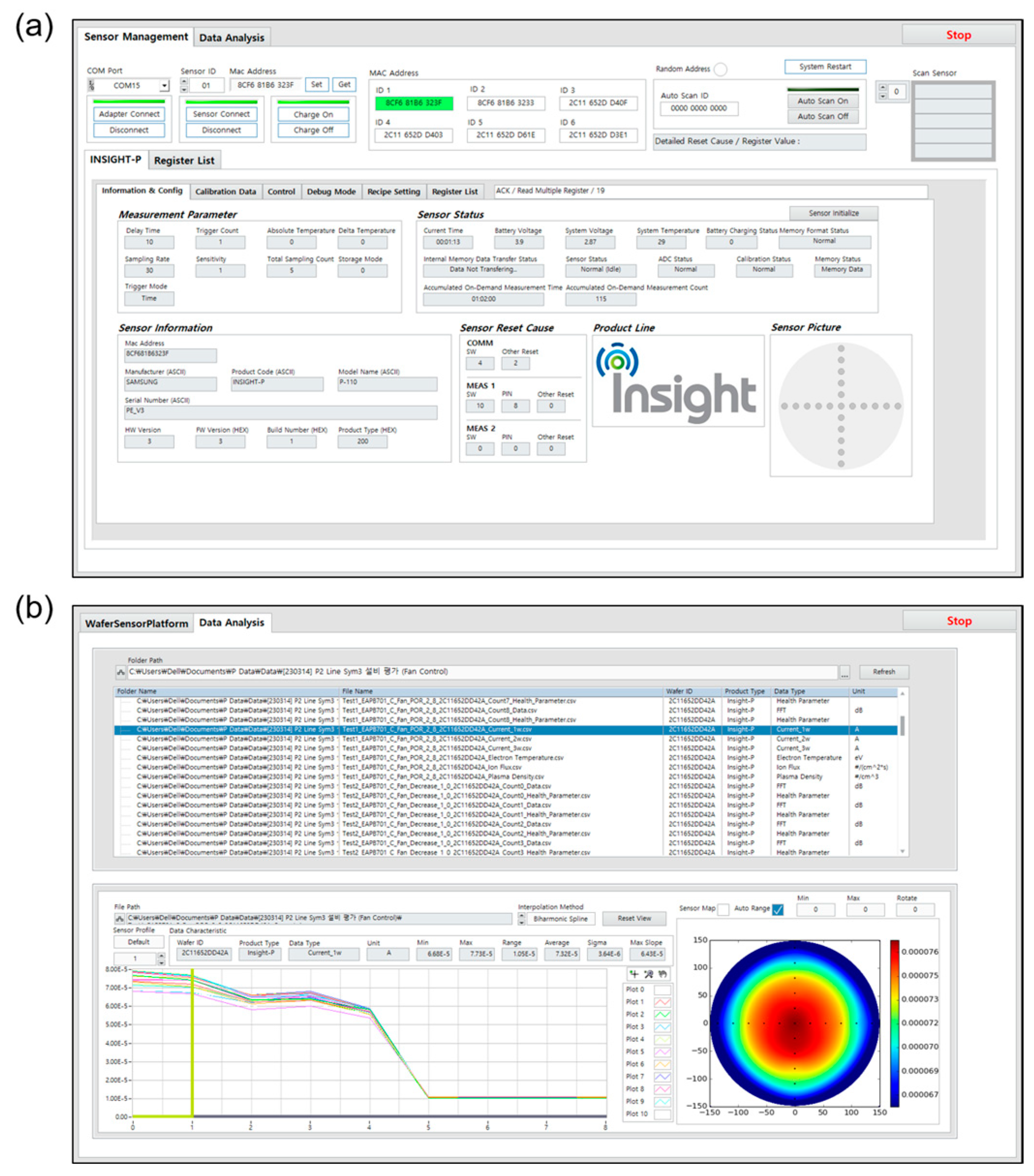
2.2.5. Data Acquisition Software
- (1)
- Sensor Management tab (Figure 8a): it is a console window that features several functions for sensor management, including sensor identification (i.e., version and type of a wafer-type sensor), sensor status alarm (i.e., normal or abnormal status), sensor parameter setup (i.e., number of FFT samples, DAC amplitude, etc.), operation mode selection (i.e., self-test mode, plasma diagnosis mode, calibration mode, etc.), and data storage (i.e., setup a file name and its save path).
- (2)
- Data Analysis tab (Figure 8b): it is a display window for data analysis after the plasma diagnosis. Users can freely access the plasma information that includes raw signals, FFT data, and calculated plasma parameters (i.e., electron temperature, plasma density, and ion flux) on an event-by-event basis. For users’ convenience, it also provides a wafer-shaped 2D plot, and the users can adjust a data range, color bar setting, and interpolation options for the 2D display of plasma distribution. Especially, it enables users to create of a pop-up window and is, thus, suitable for comparatively analyzing multiple data at a glance.
3. Experimental Results
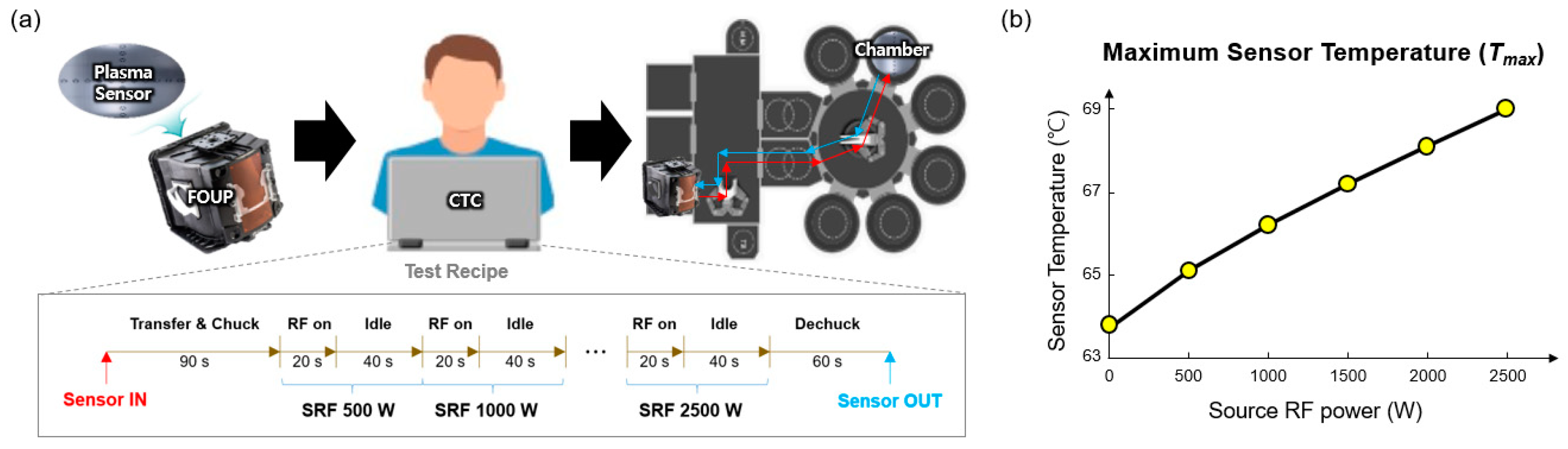
3.1. Robot Arm Transfer Capability
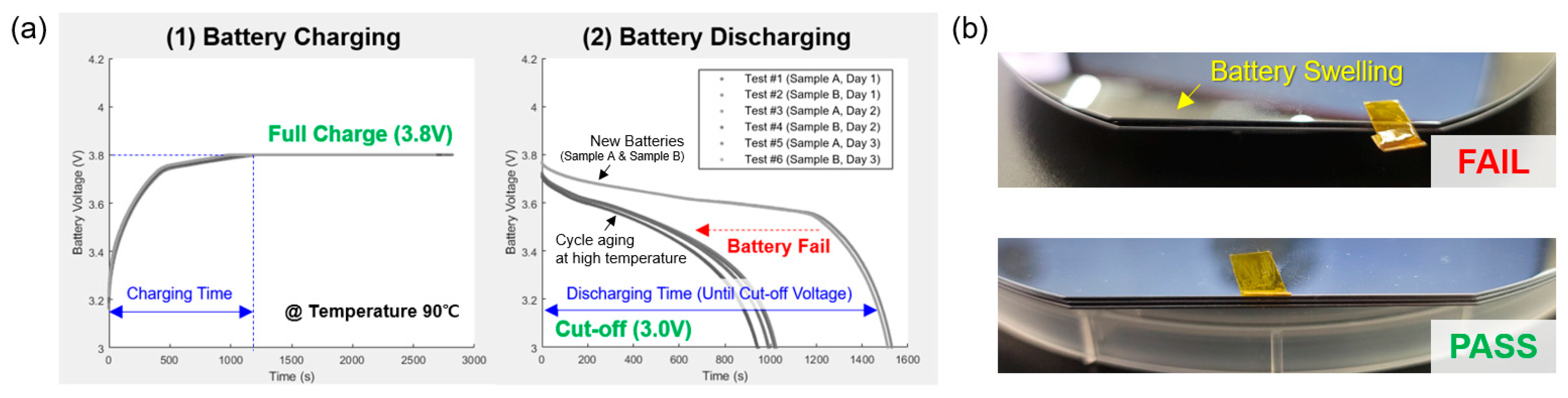
3.2. Thermal Stress Durability
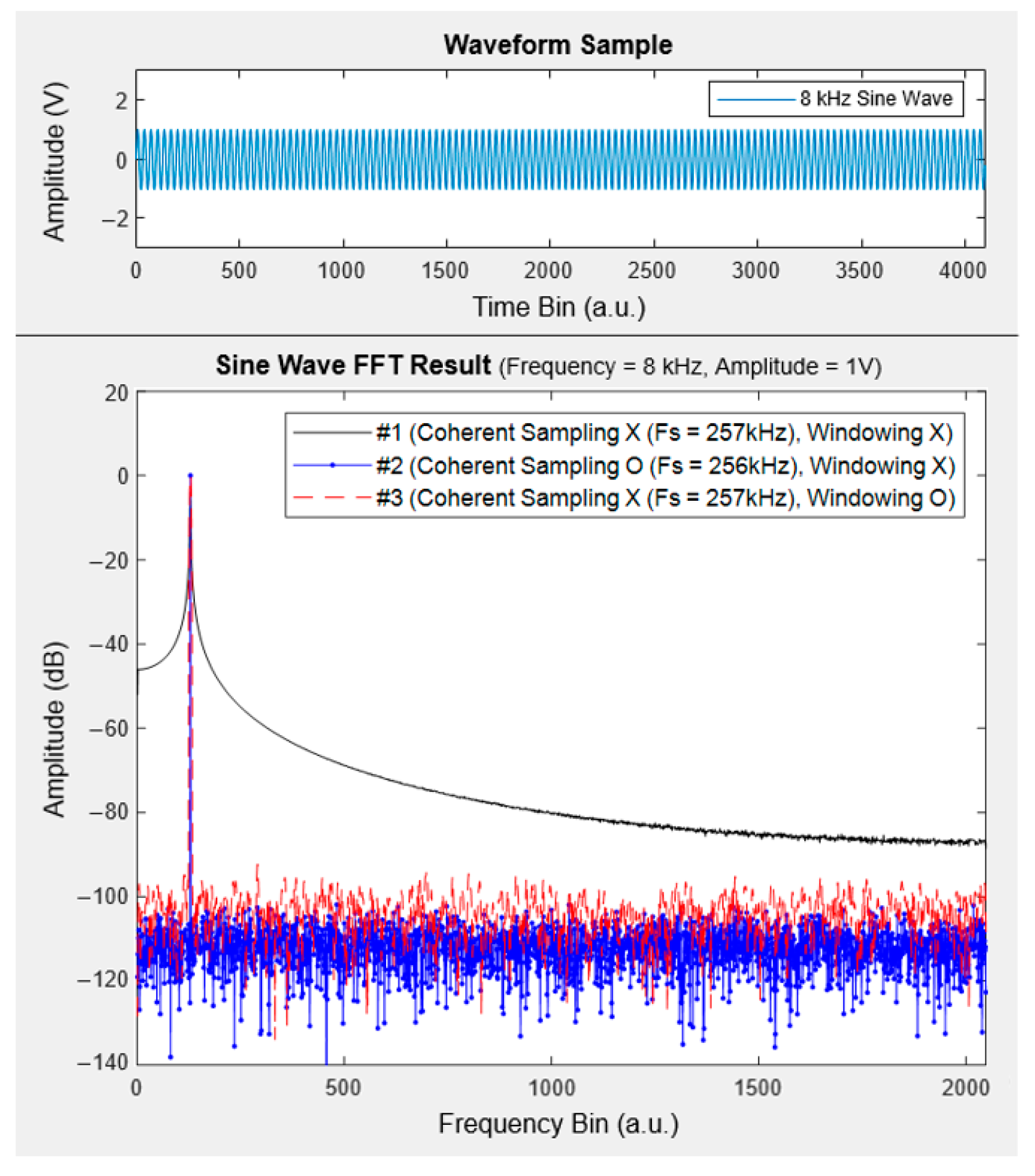
3.3. Data Integrity and Reproducibility
4. Summary and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weltmann, K.D. Future trends in plasma science. Plasma Process. Polym. 2019, 16, 1890001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroussi, M. Cold plasma in medicine and healthcare: The new frontier in low temperature plasma applications. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Jefimovs, K.; La Magna, A.; Stampanoni, M.; Romano, L. High aspect ratio tilted gratings through local electric field modulation in plasma etching. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 588, 152938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Pu, Y.; Miao, D.; Ning, X. Fabrication of durably superhydrophobic cotton fabrics by atmospheric pressure plasma treatment with a siloxane precursor. Polymers 2018, 10, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regodón Harkness, G.F.; Díaz Cabrera, J.M.; Fernández Palop, J.I.; Ballesteros, J. Low Electron Temperature Plasma Diagnosis: Revisiting Langmuir Electrostatic Probes. Coatings 2021, 11, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, I.H. Principles of Plasma Diagnostics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Godyak, V.A.; Piejak, R.B.; Alexandrovich, B.M. Measurement of electron energy distribution in low-pressure RF discharges. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 1992, 1, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, M.A.; Lichtenberg, A.J. Principles of Plasma Discharges and Materials Processing, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.F. Industrial applications of low-temperature plasma physics. Phys. Plasma 1995, 2, 2164–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crintea, D.L.; Czarnetzki, U.; Iordanova, S.; Koleva, I.; Luggenhölscher, D. Plasma diagnostics by optical emission spectroscopy on argon and comparison with Thomson scattering. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 045208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackus, A.J.M.; Heil, S.B.S.; Langereis, E.; Knoops, H.C.M.; Van de Sanden, M.C.M.; Kessels, W.M.M. Optical emission spectroscopy as a tool for studying, optimizing, and monitoring plasma-assisted atomic layer deposition processes. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2010, 28, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachdi, L.; Sushkov, V.; Hofmann, M. Optical emission spectroscopy diagnostics for plasma parameters investigation in a Duo-Plasmaline surface-wave sustained discharge. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2022, 194, 106432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.H.; You, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, Y.H. Plasma density measurements by phase resolved cutoff. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 081502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, D.H.; Choi, E.S.; Yoon, M.Y.; Seong, D.J.; You, S.J.; Lee, H.-C. Flat cutoff probe for real-time electron density measurement in industrial plasma processing. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2020, 29, 035016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I.; Mott-Smith, H.M. Studies of electric discharges in gas at low pressures. Gen. Electr. Rev. 1924, 27, 810. [Google Scholar]
- Godyak, V.A.; Demidov, V.I. Probe measurements of electron-energy distributions in plasmas: What can we measure and how can we achieve reliable results? J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 233011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.-M.; Eo, H.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, M.-Y.; Chung, C.-W. A wafer-like apparatus for two-dimensional measurement of plasma parameters and temperature distribution in low-temperature plasmas. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2021, 92, 053531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Koo, Y.; Kim, J.; Choi, K.; Hong, S. Wafer Type Ion Energy Monitoring Sensor for Plasma Diagnosis. Sensors 2023, 23, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Oh, S.-J.; Kim, Y.-C.; Choi, I.-J.; Chung, C.-W. Wireless wafer-type probe system for measurement of two-dimensional plasma parameters and spatial uniformity. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2013, 24, 095102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-C.; Jang, S.-H.; Oh, S.-J.; Lee, H.-C.; Chung, C.-W. Two-dimensional-spatial distribution measurement of electron temperature and plasma density in low temperature plasmas. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 053505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.O.; Malter, L. A floating double probe method for measurements in gas discharges. Phys. Rev. 1950, 80, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Jang, S.-H.; Chung, C.-W. Floating probe for electron temperature and ion density measurement applicable to processing plasmas. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 033305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-J.; Choi, I.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Chung, C.-W. Double probe based on harmonic current detection for electron temperature and electropositive ion flux measurement in RF plasmas. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2012, 23, 085001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabert, P.; Braithwaite, N. Physics of Radio-Frequency Plasmas; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Yao, J.; Saifutdinov, A.I.; Kudryavtsev, A.A.; Yuan, C.; Zhou, Z. Use of plasma electron spectroscopy method to detect hydrocarbons, alcohols, and ammonia in nonlocal plasma of short glow discharge. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2021, 30, 117001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demidov, V.I.; Ratynskaia, S.V.; Rypdal, K. Electric probes for plasmas: The link between theory and instrument. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2002, 73, 3409–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, M.B. Langmuir probe measurements in the gaseous electronics conference RF reference cell. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 1995, 100, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.hidenanalytical.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/ESPion-pdf.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2024).
- Gahan, D.; Dolinaj, B.; Hopkins, M.B. Retarding field analyzer for ion energy distribution measurements at a radio-frequency biased electrode. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2008, 79, 033502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.ccrprocessproducts.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/03/semion_rfea_datasheet_2018.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2024).
- Saifutdinov, A.I.; Sysoev, S.S. Development of a probe system for measuring the plasma parameters and the high-energy part of the electron-energy distribution function. Instrum. Exp. Tech. 2022, 65, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifutdinov, A.I.; Sysoev, S.S.; Gushchin, D.D. Development of a probe system for measuring plasma parameters under conditions of plasma polymerization and synthesis of nanostructures. High Energy Chem. 2023, 57 (Suppl. S1), S172–S177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.; Kim, J.; Cho, S.; Kim, K.; Jang, S.; Choi, Y.; Lee, H. Development of Wafer-Type Plasma Monitoring Sensor with Automated Robot Arm Transfer Capability for Two-Dimensional In Situ Processing Plasma Diagnosis. Sensors 2024, 24, 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24061786
Park H, Kim J, Cho S, Kim K, Jang S, Choi Y, Lee H. Development of Wafer-Type Plasma Monitoring Sensor with Automated Robot Arm Transfer Capability for Two-Dimensional In Situ Processing Plasma Diagnosis. Sensors. 2024; 24(6):1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24061786
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Haewook, Juhyun Kim, Sungwon Cho, Kyunghyun Kim, Sungho Jang, Younsok Choi, and Hohyun Lee. 2024. "Development of Wafer-Type Plasma Monitoring Sensor with Automated Robot Arm Transfer Capability for Two-Dimensional In Situ Processing Plasma Diagnosis" Sensors 24, no. 6: 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24061786
APA StylePark, H., Kim, J., Cho, S., Kim, K., Jang, S., Choi, Y., & Lee, H. (2024). Development of Wafer-Type Plasma Monitoring Sensor with Automated Robot Arm Transfer Capability for Two-Dimensional In Situ Processing Plasma Diagnosis. Sensors, 24(6), 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24061786





