A Novel Joint Denoising Method for Hydrophone Signal Based on Improved SGMD and WT
Abstract
1. Introduction
- This paper is the first to optimize the termination conditions in SGMD to improve its ability to remove noise signals.
- For SGMD generating excessive symplectic geometry components (SGCs), this paper uses spectral clustering to categorize the SGC and efficiently aggregate the noisy signals.
- The mixed signals are denoised by WT and the clusters are reconstructed to get the ideal denoised signal.
2. Algorithms and Models
2.1. Improved Symplectic Geometry Model Decomposition
2.1.1. Symplectic Geometry Model Decomposition
- Phase space reconstruction
- 2.
- Symplectic geometry similarity transformation
- 3.
- Diagonal averaging
- 4.
- Component reconstruction
2.1.2. Improved Component Reconstruction
2.2. Spectral Clustering
2.3. Spectral Entropy
2.4. Wavelet Threshold Denoising
2.4.1. Wavelet Decomposition
2.4.2. Threshold for Wavelet Coefficients
2.4.3. Wavelet Reconstruction
- (1)
- Obtain the absolute value of each element in the signal and arrange them in ascending order to obtain a new signal sequence as Equation (20):
- (2)
- If the threshold () uses the square root of the elements in the sequence , the corresponding risk accompanying this threshold is as Equations (21) and (22):
- (3)
- Find the point on the risk curve where the risky value is minimized and mark it as . Thus, the minimum threshold is noted as Equation (23):
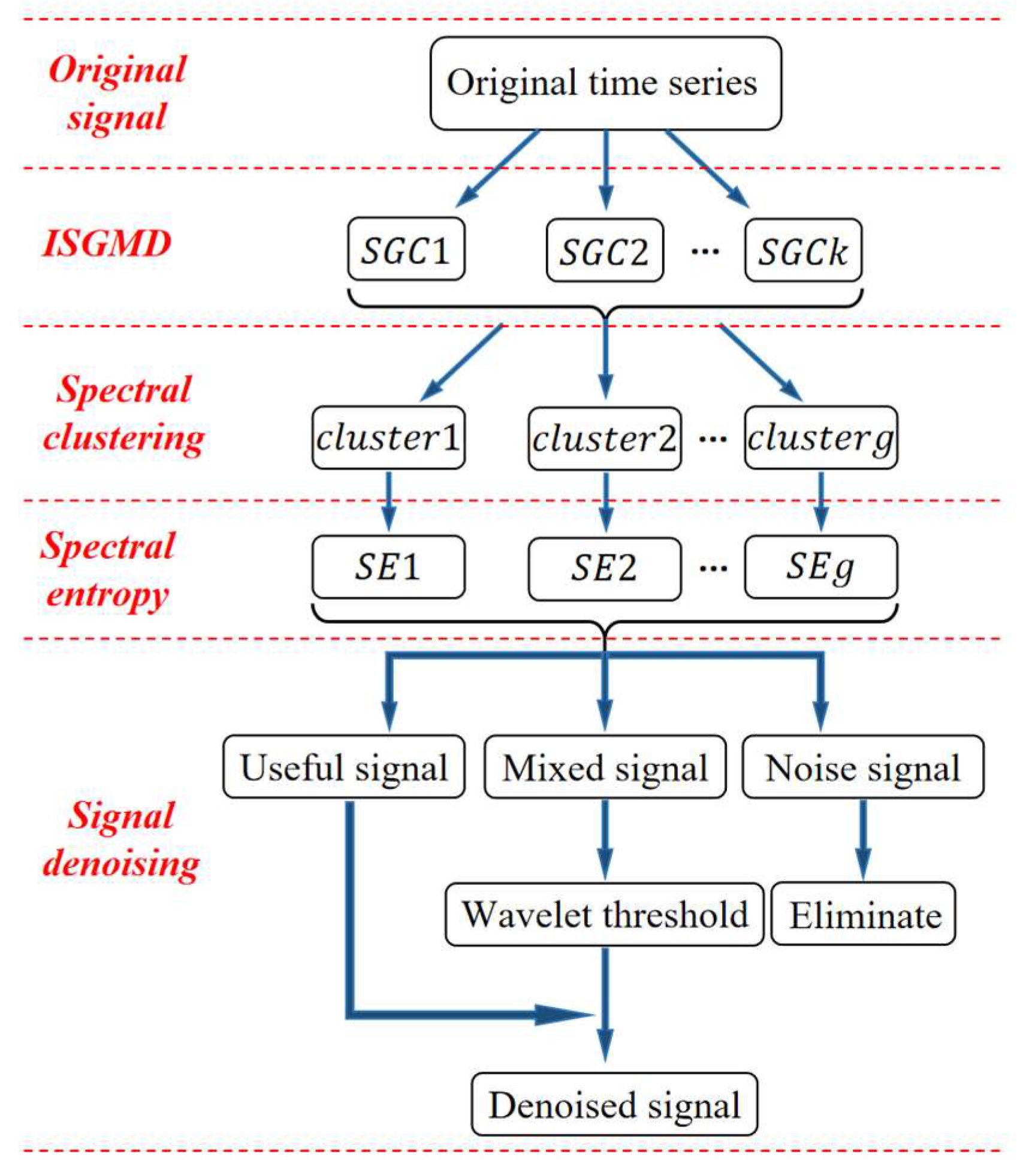
2.5. The Proposed Joint Denoising Algorithm (ISGMD-WT)
- Step 1: Optimize the SGMD
- Step 2: Symplectic geometry model decomposition
- Step 3: Cluster
- Step 4: Calculate and classify
- Step 5: Denoise and Reconstruct
3. Simulation and Application
3.1. Simulation 1
3.2. Simulation 2
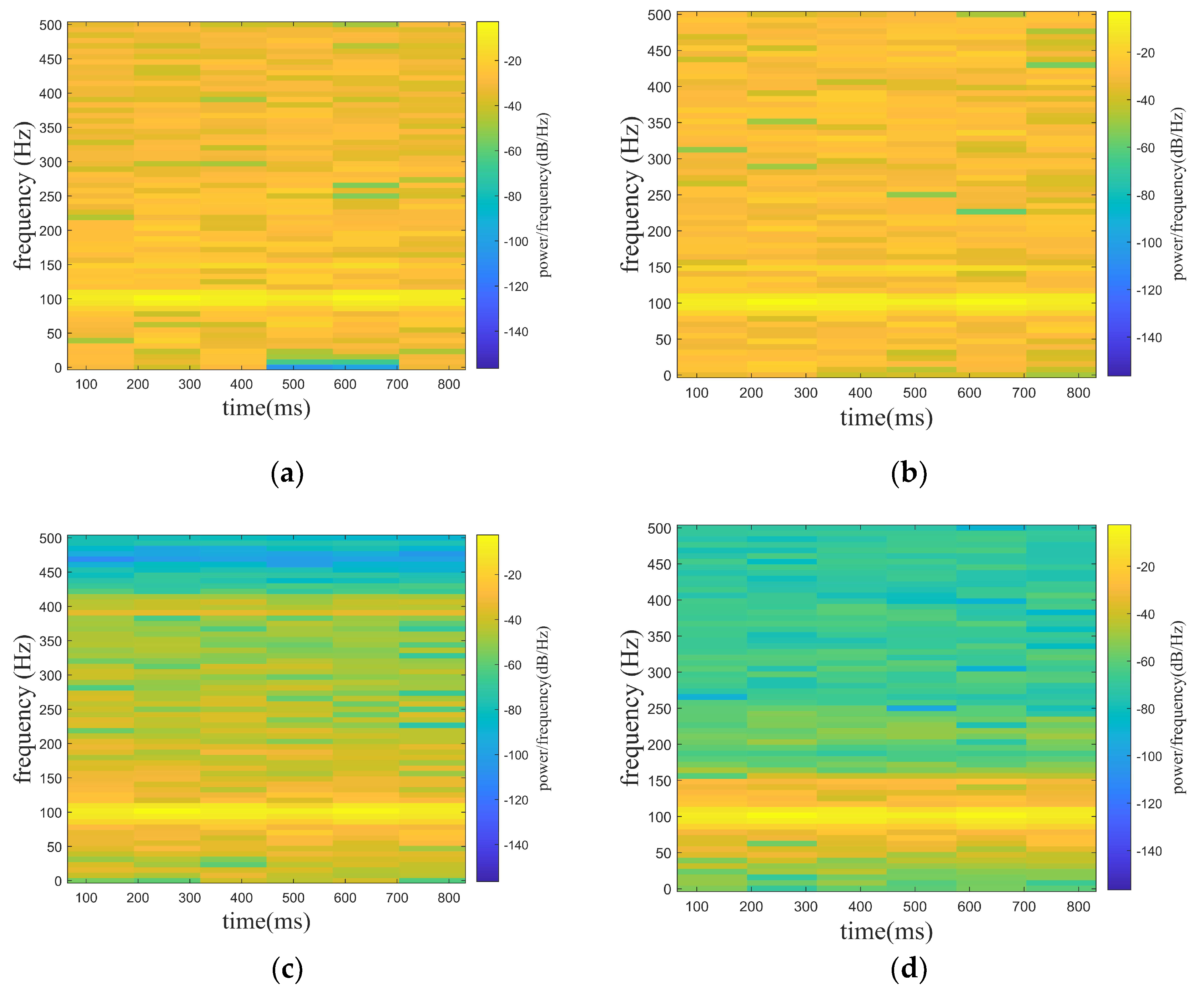
3.3. Application in Hydrophone Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hammar, L.; Molander, S.; Pålsson, J.; Crona, J.S.; Carneiro, G.; Johansson, T.; Hume, D.; Kågesten, G.; Mattsson, D.; Törnqvist, O. Cumulative impact assessment for ecosystem-based marine spatial planning. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatore, L.; Gallo, N.; Natali, M.L.; Campa, L.; Lunetti, P.; Madaghiele, M.; Blasi, F.S.; Corallo, A.; Capobianco, L.; Sannino, A. Marine collagen and its derivatives: Versatile and sustainable bio-resources for healthcare. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 113, 110963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Jin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T. A survey of underwater magnetic induction communications: Fundamental issues, recent advances, and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2466–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.-K.; Jiang, Y.-Y. Development of noise reduction algorithm for underwater signals. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Symposium on Underwater Technology (IEEE Cat. No. 04EX869), Taipei, Taiwan, 20–23 April 2004; pp. 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Baskar, V.V.; Rajendran, V.; Logashanmugam, E. Study of different denoising methods for underwater acoustic signal. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2015, 23, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, J.; Zhao, R.; Cao, H. Calibration analysis of high-G MEMS accelerometer sensor based on wavelet and wavelet packet denoising. Sensors 2021, 21, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peesapati, R.; Sabat, S.L.; Karthik, K.; Nayak, J.; Giribabu, N. Efficient hybrid Kalman filter for denoising fiber optic gyroscope signal. Optik 2013, 124, 4549–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Liu, N.; Sun, F.; Jiang, X. Random noise suppression of seismic data by time–frequency peak filtering with variational mode decomposition. Explor. Geophys. 2019, 50, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Ao, Y.; Yan, H.; Bai, Y.; Shi, N. Signal denoising based on wavelet threshold denoising and optimized variational mode decomposition. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 5599096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Pang, L.; Huang, H.; Shen, C.; Cao, H.; Shi, Y.; Liu, J. High-G calibration denoising method for high-G MEMS accelerometer based on EMD and wavelet threshold. Micromachines 2019, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liang, Y.; He, P.; Yang, J. Adaptive motion artifact reduction based on empirical wavelet transform and wavelet thresholding for the non-contact ECG monitoring systems. Sensors 2019, 19, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, L.; Yan, H.; Bai, Y.; Wang, P. Denoising and baseline drift removal method of MEMS hydrophone signal based on VMD and wavelet threshold processing. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 59913–59922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L.; Johnstone, I.M. Adapting to unknown smoothness via wavelet shrinkage. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 1200–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Fei, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, D. A novel fault diagnosis method based on EMD, cyclostationary, SK and TPTSR. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 1925–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Shan, H. Parkinson disease detection using energy direction features based on EMD from voice signal. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 41, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-R.; Shieh, J.-S.; Huang, N.E. Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A novel noise enhanced data analysis method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2010, 2, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, L. A new underwater acoustic signal denoising technique based on CEEMDAN, mutual information, permutation entropy, and wavelet threshold denoising. Entropy 2018, 20, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomiretskiy, K.; Zosso, D. Variational mode decomposition. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2013, 62, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Lin, J. Identification of mechanical compound-fault based on the improved parameter-adaptive variational mode decomposition. ISA Trans. 2019, 84, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Khazhina, S.; Du, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. Joint decision-making of parallel machine scheduling restricted in job-machine release time and preventive maintenance with remaining useful life constraints. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2022, 222, 108429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L. A parameter-adaptive VMD method based on grasshopper optimization algorithm to analyze vibration signals from rotating machinery. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 108, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Du, W.; Lei, Y.; Wang, J. Bearing fault diagnosis method based on adaptive maximum cyclostationarity blind deconvolution. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 162, 108018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Xu, T.; Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Hu, H.; Bai, Y. MEMS hydrophone signal denoising and baseline drift removal algorithm based on parameter-optimized variational mode decomposition and correlation coefficient. Sensors 2019, 19, 4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y. A Denoising Method for Mining Cable PD Signal Based on Genetic Algorithm Optimization of VMD and Wavelet Threshold. Sensors 2022, 22, 9386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cao, H.; Guo, T. A hybrid algorithm for noise suppression of MEMS accelerometer based on the improved VMD and TFPF. Micromachines 2022, 13, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.-B.; Dokos, S. A symplectic geometry-based method for nonlinear time series decomposition and prediction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 054103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, J. Symplectic geometry mode decomposition and its application to rotating machinery compound fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 114, 189–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Yang, Y.; Hu, N.; Cheng, Z.; Cheng, J. A noise reduction method based on adaptive weighted symplectic geometry decomposition and its application in early gear fault diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 149, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Cao, N.; Zhang, T. A novel signature extracting approach for inductive oil debris sensors based on symplectic geometry mode decomposition. Measurement 2021, 185, 110056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.-B.; Guo, T.; Sivakumar, B.; Liew, A.W.-C.; Dokos, S. Symplectic geometry spectrum analysis of nonlinear time series. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2014, 470, 20140409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J. Gearbox compound fault diagnosis based on a combined MSGMD–MOMEDA method. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 065102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Z. A method of embedding dimension estimation based on symplectic geometry. Phys. Lett. A 2002, 303, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Tan, B.; Wang, Q. Multi-step wind speed forecasting based on secondary decomposition algorithm and optimized back propagation neural network. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 113, 107894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, L.; Dandapat, S.; Mahanta, A. ECG signal denoising using higher order statistics in Wavelet subbands. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2010, 5, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Guo, P.; Zhang, W. Research on fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on the MCKD-SSD-TEO with optimal parameters. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2023, 37, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Ma, J.; Cao, J. A gyroscope signal denoising method based on empirical mode decomposition and signal reconstruction. Sensors 2019, 19, 5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Malik, J. Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2000, 22, 888–905. [Google Scholar]
- Von Luxburg, U. A tutorial on spectral clustering. Stat. Comput. 2007, 17, 395–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeti, M.; Katebi, S.; Boostani, R. Entropy and complexity measures for EEG signal classification of schizophrenic and control participants. Artif. Intell. Med. 2009, 47, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniczenko, P.P.; Lee, C.F.; Jones, N.S. Rapidly detecting disorder in rhythmic biological signals: A spectral entropy measure to identify cardiac arrhythmias. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 011915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooley, J.W.; Tukey, J.W. An algorithm for the machine calculation of complex Fourier series. Math. Comput. 1965, 19, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Li, F. Gamma spectrum denoising method based on improved wavelet threshold. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2020, 52, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. A modified artificial bee colony algorithm for image denoising using parametric wavelet thresholding method. Pattern Recognit. Image Anal. 2018, 28, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhao, R.; Shi, Y.; Chou, X. A new joint denoising algorithm for high-G calibration of MEMS accelerometer based on VMD-PE-wavelet threshold. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 8855878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, J.; Li, L.; Tuo, X.; Qu, K.; Rong, W. Novel wavelet threshold denoising method to highlight the first break of noisy microseismic recordings. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5910110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

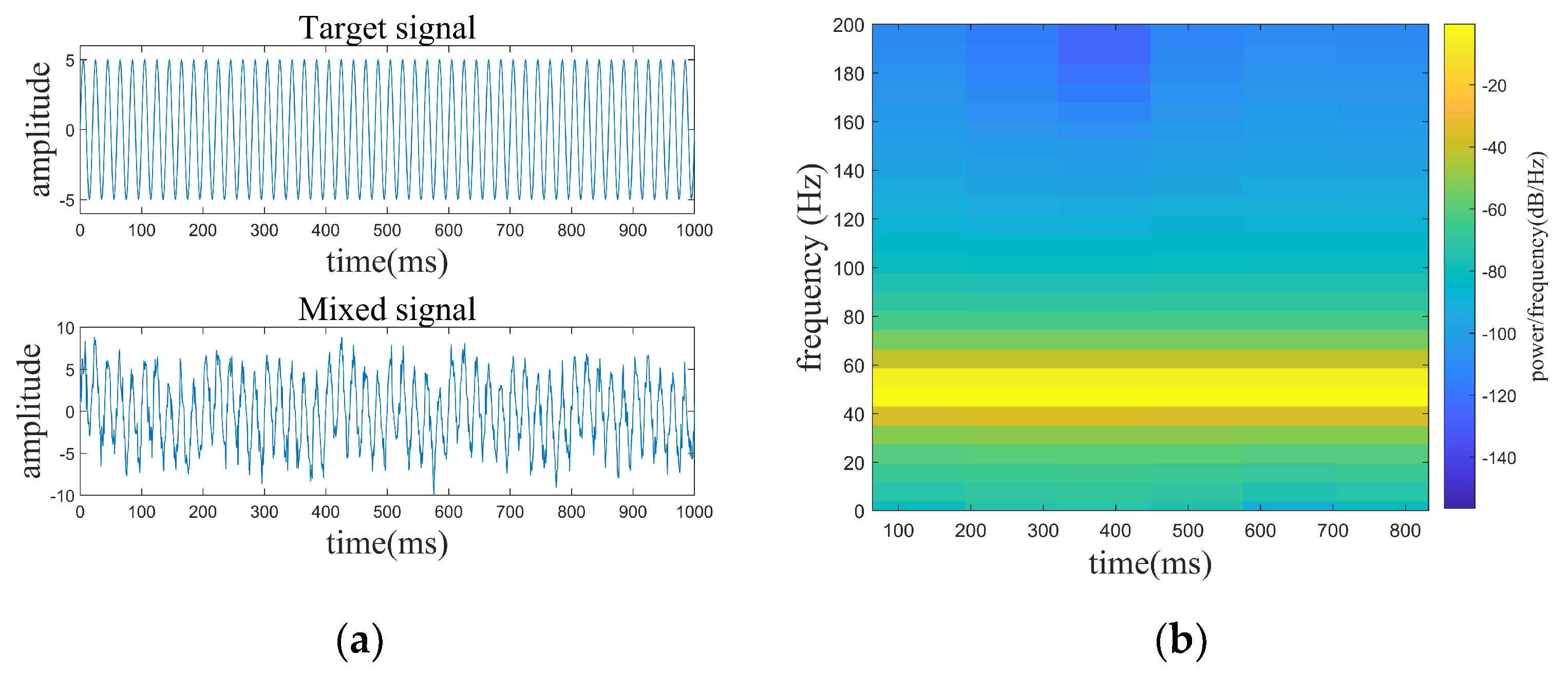
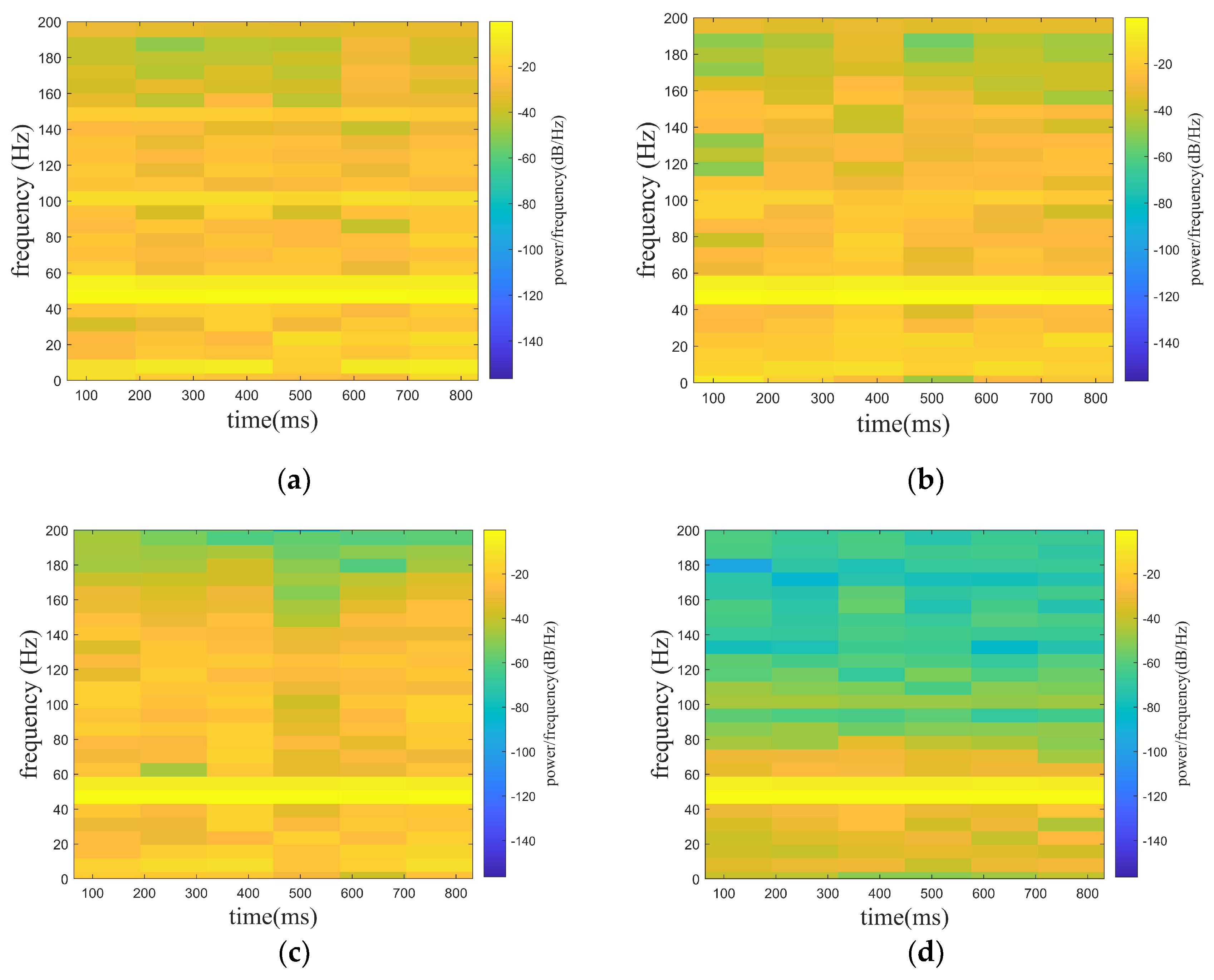
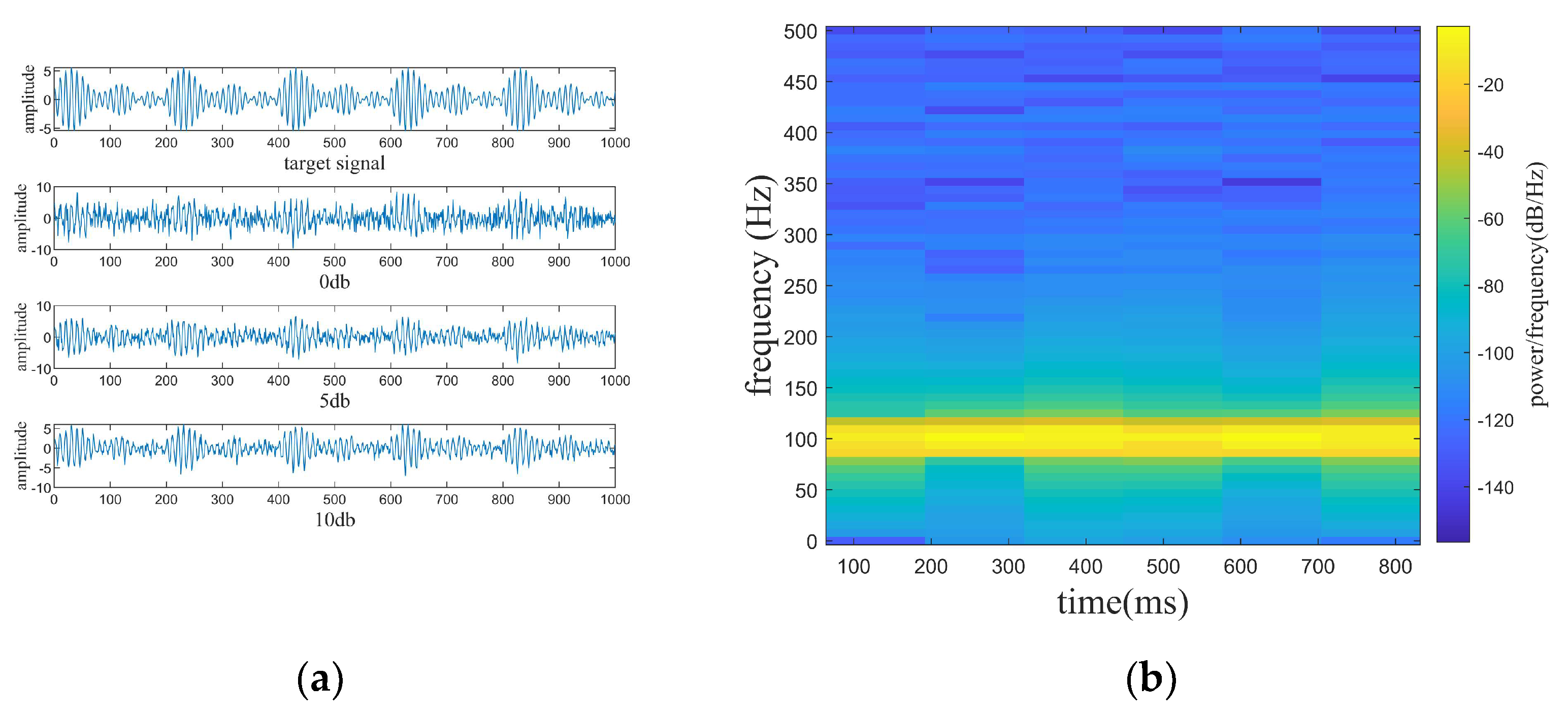








| Index | Original Signal | WT | EMD-WT | VMD-WT | ISGMD-WT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | 5.63 | 6.45 | 8.45 | 10.09 | 21.34 |
| RMSE | 1.8716 | 1.6826 | 1.3364 | 1.1067 | 0.3031 |
| White Noise | Index | Original Signal | WT | EMD-WT | VMD-WT | ISGMD-WT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 db | SNR | −2.64 | 0.96 | 4.90 | 8.58 | 9.23 |
| RMSE | 1.9360 | 1.7912 | 1.1375 | 0.9415 | 0.6909 | |
| 5 db | SNR | −1.28 | 6.04 | 5.08 | 10.19 | 13.43 |
| RMSE | 1.1888 | 0.9981 | 1.1139 | 0.6380 | 0.4261 | |
| 10 db | SNR | −0.33 | 8.10 | 8.64 | 9.37 | 17.87 |
| RMSE | 0.7059 | 0.7867 | 0.7393 | 0.6800 | 0.2557 |
| Index | WT | EMD-WT | VMD-WT | ISGMD-WT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNR | 23.96 | 29.31 | 36.07 | 42.18 |
| RMSE | 0.008401 | 0.005637 | 0.001555 | 0.001041 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, T.; Wang, X.; Ni, K.; Zhou, Q. A Novel Joint Denoising Method for Hydrophone Signal Based on Improved SGMD and WT. Sensors 2024, 24, 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24041340
Xing T, Wang X, Ni K, Zhou Q. A Novel Joint Denoising Method for Hydrophone Signal Based on Improved SGMD and WT. Sensors. 2024; 24(4):1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24041340
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Tianyu, Xiaohao Wang, Kai Ni, and Qian Zhou. 2024. "A Novel Joint Denoising Method for Hydrophone Signal Based on Improved SGMD and WT" Sensors 24, no. 4: 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24041340
APA StyleXing, T., Wang, X., Ni, K., & Zhou, Q. (2024). A Novel Joint Denoising Method for Hydrophone Signal Based on Improved SGMD and WT. Sensors, 24(4), 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24041340







