Tunable Characteristics of Optical Frequency Combs from InGaAs/GaAs Two-Section Mode-Locked Lasers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- Wavelength
- (2)
- Pulse width
- (3)
- Peak power
- (4)
- Repetition rate
2. Material Epitaxy and Two-Section Laser Structures
3. Process Flow and Experimental Setup
4. Experiment Results and Discussion
4.1. Laser Gain Analysis
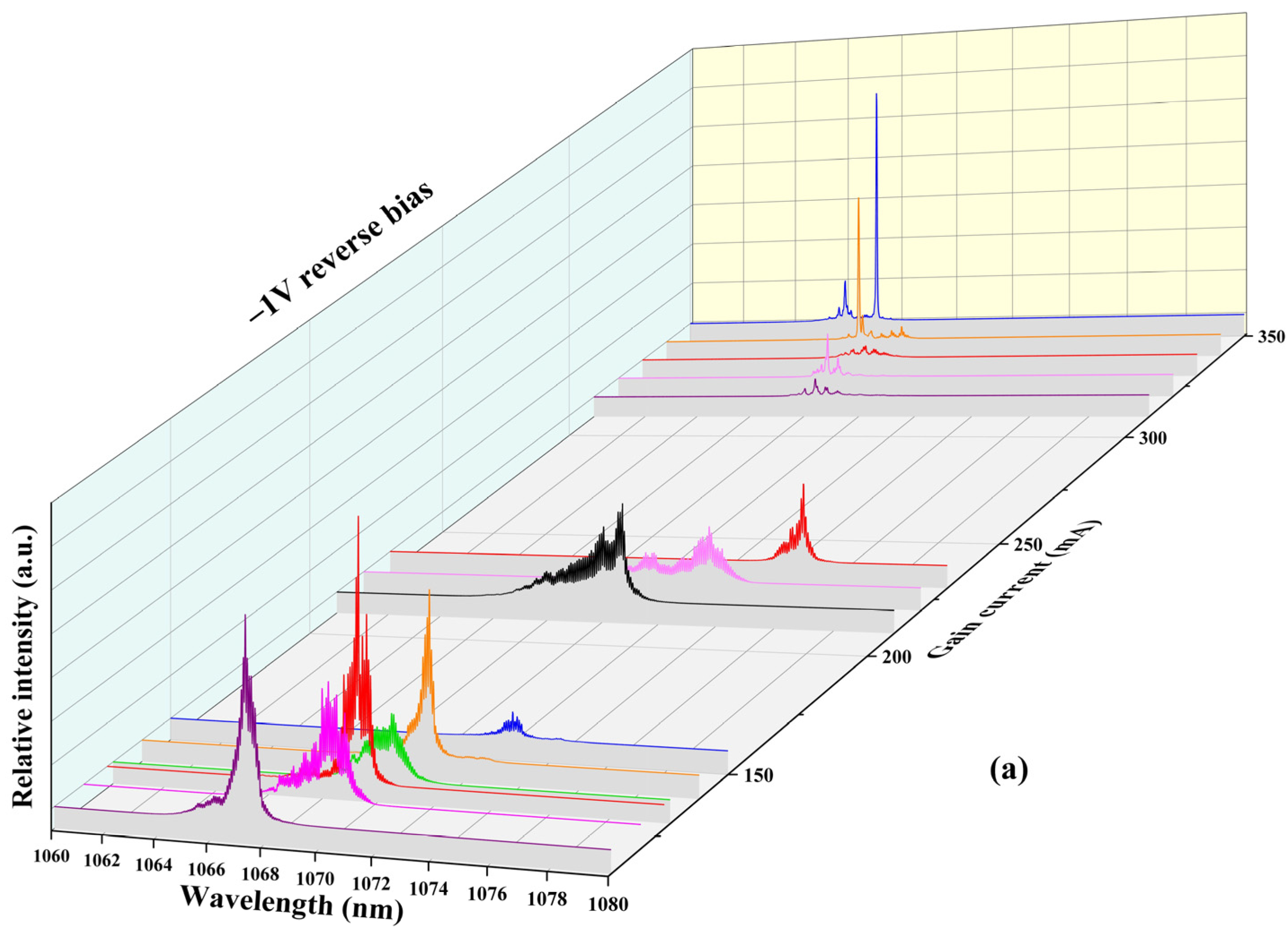
4.2. Laser Spectral Characteristic Analysis
4.3. PI Characteristic Analysis
4.4. Time-Frequency Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fortier, T.; Baumann, E. 20 years of developments in optical frequency comb technology and applications. Commun. Phys. 2019, 2, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chen, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T. Advances of semiconductor mode-locked laser for optical frequency comb generation. Natl. Sci. Open. 2022, 1, 20220026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Marsh, J.H. Frequency comb with 100 GHz spacing generated by an asymmetric MQW passively mode-locked laser. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 2760–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, A.; Van Gasse, K.; Kuyken, B. On-chip optical comb sources. APL Photonics 2022, 7, 100901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.G.; Rae, A.R.; Xia, M.; Penty, R.V.; White, I.H. InGaAs Quantum-Dot Mode-Locked Laser Diodes. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2009, 15, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haus, H.A. Mode-locking of lasers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2000, 6, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, P.A.; Bowers, J.E.; Koszi, L.A.; Soler, M.; Lopata, J.; Wilt, D.P. Monolithic hybrid mode-locked 1.3 μm semiconductor lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 56, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.C.; Chen, Y.K.; Tanbun-Ek, T.; Logan, R.A.; Chin, M.A.; Raybon, G. Transform-limited 1.4 ps optical pulses from a monolithic colliding-pulse mode-locked quantum well laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 57, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinecke, S.; Drzewietzki, L.; Weber, C.; Lingnau, B.; Breuer, S.; Lüdge, K. Ultra-Short Pulse Generation in a Three Section Tapered Passively Mode-Locked Quantum-Dot Semiconductor Laser. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auth, D.; Liu, S.; Norman, J.; Edward Bowers, J.; Breuer, S. Passively mode-locked semiconductor quantum dot on silicon laser with 400 Hz RF line width. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 27256–27266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Allford, C.P.; Shutts, S.; Forrest, A.F.; Alharbi, R.; Krysa, A.B.; Smowton, P.M. Smowton. Monolithic InP Quantum Dot Mode-Locked Lasers Emitting at 730 nm. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2020, 32, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akahane, K.; Matsumoto, A.; Umezawa, T.; Yamamoto, N. High-frequency short-pulse generation with a highly stacked InAs quantum dot mode-locked laser diode. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 60, SBBH02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, M.; Zali, A.R.; Gildeh, R.E.; Farmani, A. 80 GHz Bandwidth, 1.3μ m InAs/InGaAs CW-PW Quantum Dot Passively Colliding-Pulse Mode-Locked (CPM) Lasers for IR Sensing Application. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 6528–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, S.; Rossetti, M.; Elsässer, W.; Drzewietzki, L.; Bardella, P.; Montrosset, I.; Hopkinson, M. Reverse-emission-state-transition mode locking of a two-section InAs/InGaAs quantum dot laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 071118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataluna, M.A.; Nikitichev, D.I.; Mikroulis, S.; Simos, H.; Simos, C.; Mesaritakis, C.; Rafailov, E.U. Dual-wavelength mode-locked quantum-dot laser, via ground and excited state transitions: Experimental and theoretical investigation. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 12832–12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmeckebier, H.; Fiol, G.; Meuer, C.; Arsenijević, D.; Bimberg, D. Complete pulse characterization of quantum-dot mode-locked lasers suitable for optical communication up to 160 Gbit/s. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 3415–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.G.; Liu, J.R.; Poole, P.J.; Jiao, Z.J.; Barrios, P.J.; Poitras, D.; Zhang, X.P. Ultra-high repetition rate InAs/InP quantum dot mode-locked lasers. Opt. Commun. 2011, 284, 2323–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yvind, K. Semiconductor Mode-Locked Lasers for Optical Communication Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Denmark, Kongens Lyngby, Denmark, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nikitichev, D.I.; Ding, Y.; Cataluna, M.A.; Rafailov, E.U.; Drzewietzki, L.; Breuer, S.; Krakowski, M. High peak power and sub-picosecond Fourier-limited pulse generation from passively mode-locked monolithic two-section gain-guided tapered InGaAs quantum-dot lasers. Laser Phys. 2012, 22, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, C.; Schmeckebier, H.; Merghem, K.; Rosales, R.; Lelarge, F.; Martinez, A.; Ramdane, A. Frequency resolved optical gating characterization of sub-ps pulses from single-section InAs/InP quantum dash based mode-locked lasers. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 1742–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitichev, D.I.; Cataluna, M.A.; Fedorova, K.A.; Ding, Y.; Mikhrin, S.S.; Krestnikov, I.L.; Rafailov, E.U. High-Power Wavelength Bistability and Tunability in Passively Mode-Locked Quantum-Dot Laser. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2013, 19, 1100907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Luo, S.; Ji, H.M.; Liu, S.T.; Lu, D.; Ji, C.; Yang, T. Single-section mode-locked 1.55-μm InAs/InP quantum dot lasers grown by MOVPE. Opt. Commun. 2016, 370, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.J.; Bryce, A.C.; Jagadish, C. Advances in Semiconductor Lasers; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, J.H.; Hou, L. Mode-locked laser diodes and their monolithic integration. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2017, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merghem, K.; Calò, C.; Rosales, R.; Lafosse, X.; Aubin, G.; Martinez, A.; Ramdane, A. Stability of Optical Frequency Comb Generated With InAs/InP Quantum-Dash-Based Passive Mode-Locked Lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2014, 50, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Luo, S.; Ji, H.M.; Liu, S.T.; Xu, F.; Lv, Z.R.; Yang, T. Ultrashort Pulse and High Power Mode-Locked Laser With Chirped InAs/InP Quantum Dot Active Layers. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2016, 28, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.G.; Liu, J.R.; Poole, P.J.; Song, C.Y.; Chang, S.D. Ultra-narrow linewidth quantum dot coherent comb lasers with self-injection feedback locking. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 11909–11914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrutin, E.A.; Marsh, J.H.; Portnoi, E.L. Monolithic and multi-gigahertz mode-locked semiconductor lasers: Constructions, experiments, models and applications. IEE Proc.-Optoelectron. 2000, 147, 251–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Li, T.; Gao, X.; Qu, Y.; Liu, C. High-performance 1.06-μm InGaAs/GaAs double-quantum-well semiconductor lasers with asymmetric heterostructure layers. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34, 055013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Li, X.; Sia, J.X.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Liu, C. Stable mode-locked operation with high temperature characteristics of a two-section InGaAs/GaAs double quantum wells laser. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 16608–16614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Li, X.; Sia, J.X.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Liu, C. Mode-locked operation characteristics of a monolithic integrated two-section InGaAs/GaAs double quantum wells laser with asymmetric waveguide. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 147, 107702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakki, B.W.; Paoli, T.L. Gain spectra in GaAs double−heterostructure injection lasers. J. Appl. Phys. 1975, 46, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Liu, A.; Zheng, W. 80 GHz AlGaInAs/InP colliding-pulse mode-locked laser with high pulse power. Appl. Phys. Express 2016, 9, 122701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Li, X.; Sia, J.X.B.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, C. Modal gain characteristics of a two-section InGaAs/GaAs double quantum well passively mode-locked laser with asymmetric waveguide. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.A.; Chemla, D.S.; Damen, T.C.; Gossard, A.C.; Wiegmann, W.; Wood, T.H.; Burrus, C.A. Band-edge electroabsorption in quantum well structures: The quantum-confined Stark effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 53, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.; Chemla, D.; Damen, T.; Wood, T.; Burrus, C.; Gossard, A.; Wiegmann, W. The quantum well self-electrooptic effect device: Optoelectronic bistability and oscillation, and self-linearized modulation. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1985, 21, 1462–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Joseph, I.; Klingshirn, C.; Miller, D.A.B.; Chemla, D.S.; Koren, U.; Miller, B.I. Quantum-confined Stark effect in InGaAs/InP quantum wells grown by organometallic vapor phase epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1987, 50, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamuda, G.P. Design and Development of an External Cavity Diode Laser for Laser Cooling and Spectroscopy Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Stellenbosch, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, Y.Y. Improved Confinement Structure and Quantum-Well Designs for Long Wavelength InGaAlAs/InP Lasers. Master’s Thesis, Multimedia University, Cyberjaya, Malaysia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Arafin, S.; Simsek, A.; Kim, S.K.; Liang, W.; Eliyahu, D.; Morrison, G.; Coldren, L.A. Power1Vefficient Kerr frequency comb based tunable optical source. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
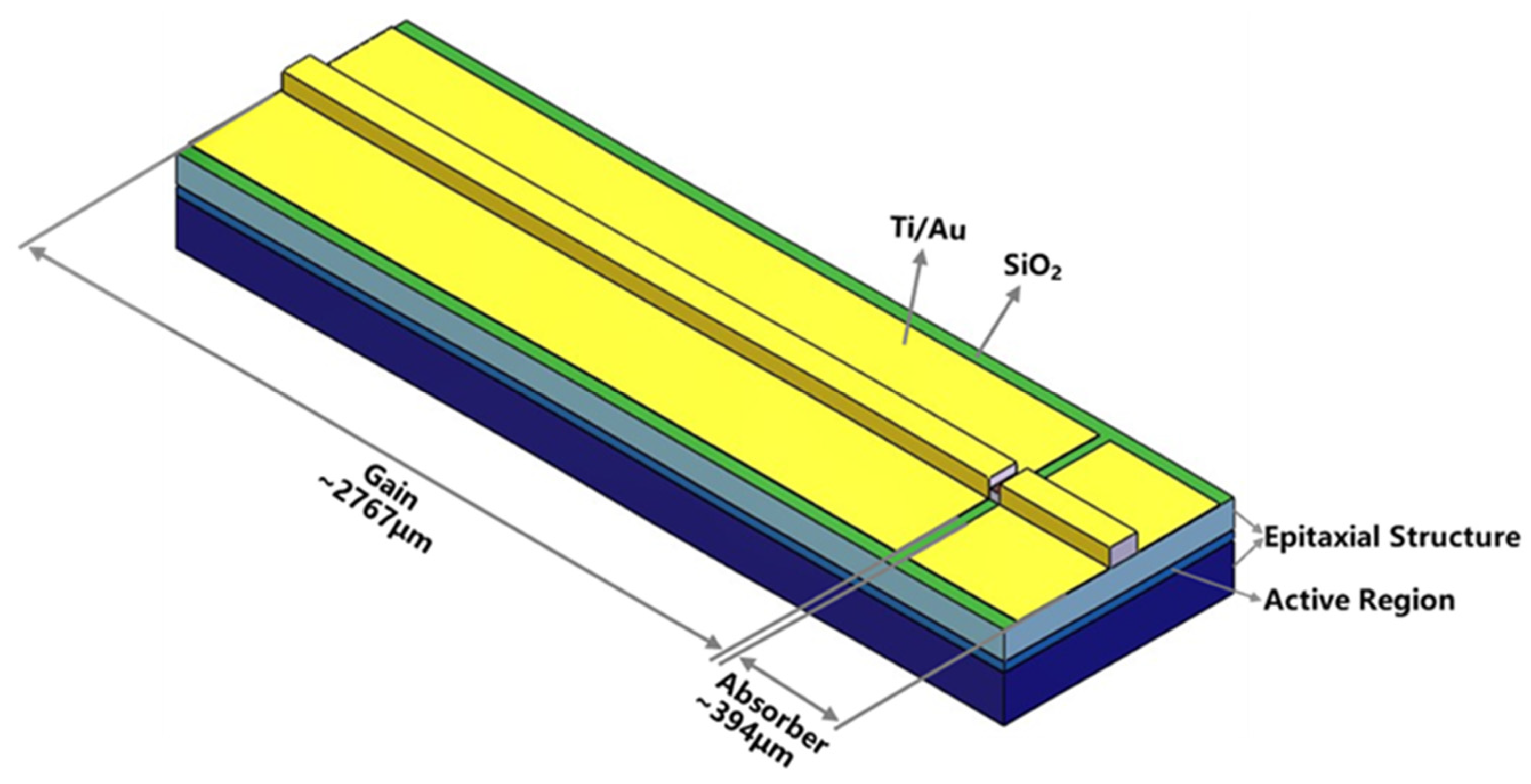
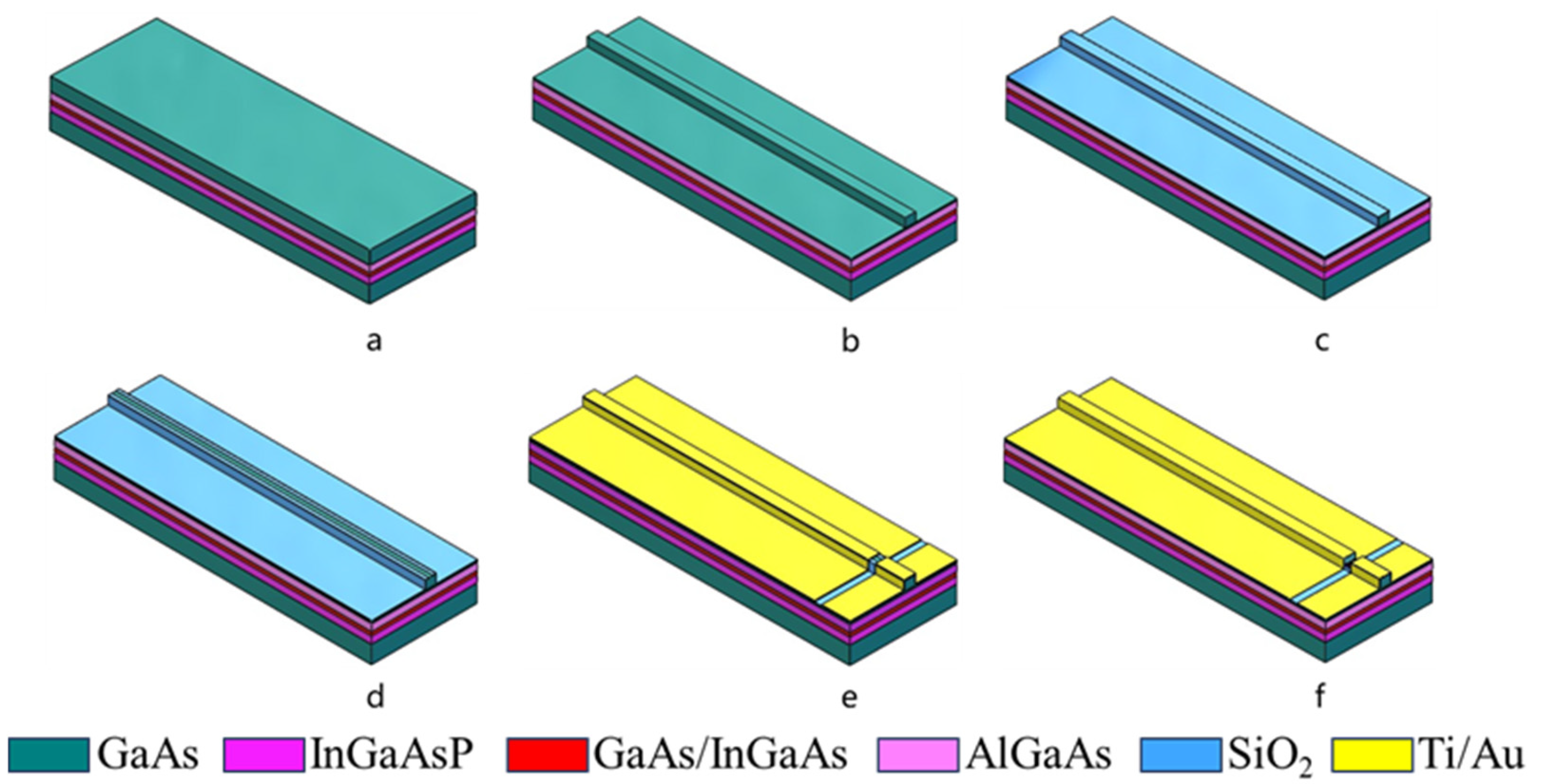








| Material | Thickness (nm) | Doping Concentration (cm−3) |
|---|---|---|
| GaAs | 250 | P, >2 × 1019 |
| Al0.55Ga0.45As | 300 | P, >8 × 1017 |
| Al0.35Ga0.65As | 300 | P, >8 × 1017 |
| Al0.3Ga0.7As | 300 | P, >8 × 1017 |
| Al0.05Ga0.95As | 200 | P, >8 × 1016 |
| GaAs | 8 | barrier |
| In0.2Ga0.8As | 7 | quantum well |
| GaAs | 8 | barrier |
| In0.2Ga0.8As | 7 | quantum well |
| GaAs | 8 | barrier |
| In0.04Ga0.96As0.9P0.1 | 200 | non-doped |
| In0.14Ga0.86As0.7P0.3 | 300 | n, 8 × 1016 |
| In0.24Ga0.76As0.5P0.5 | 100 | n, 8 × 1017 |
| In0.33Ga0.67As0.3P0.7 | 100 | n, 8 × 1017 |
| In0.42Ga0.58As0.1P0.9 | 800 | n, 8 × 1017 |
| GaAs | 200 | n, 2 × 1018 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weng, D.; Liang, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Li, X.; Sia, J.X.B.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Z.; Qu, Y.; et al. Tunable Characteristics of Optical Frequency Combs from InGaAs/GaAs Two-Section Mode-Locked Lasers. Sensors 2024, 24, 7905. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247905
Weng D, Liang Y, Qiao Z, Li X, Sia JXB, Li Z, Li L, Chen H, Zhao Z, Qu Y, et al. Tunable Characteristics of Optical Frequency Combs from InGaAs/GaAs Two-Section Mode-Locked Lasers. Sensors. 2024; 24(24):7905. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247905
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeng, Dengqun, Yanbo Liang, Zhongliang Qiao, Xiang Li, Jia Xu Brian Sia, Zaijin Li, Lin Li, Hao Chen, Zhibin Zhao, Yi Qu, and et al. 2024. "Tunable Characteristics of Optical Frequency Combs from InGaAs/GaAs Two-Section Mode-Locked Lasers" Sensors 24, no. 24: 7905. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247905
APA StyleWeng, D., Liang, Y., Qiao, Z., Li, X., Sia, J. X. B., Li, Z., Li, L., Chen, H., Zhao, Z., Qu, Y., Liu, G., Liu, C., & Wang, H. (2024). Tunable Characteristics of Optical Frequency Combs from InGaAs/GaAs Two-Section Mode-Locked Lasers. Sensors, 24(24), 7905. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24247905






