Analysis of Trace Heavy Metal in Solution Using Liquid Cathode Glow Discharge Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents and Samples
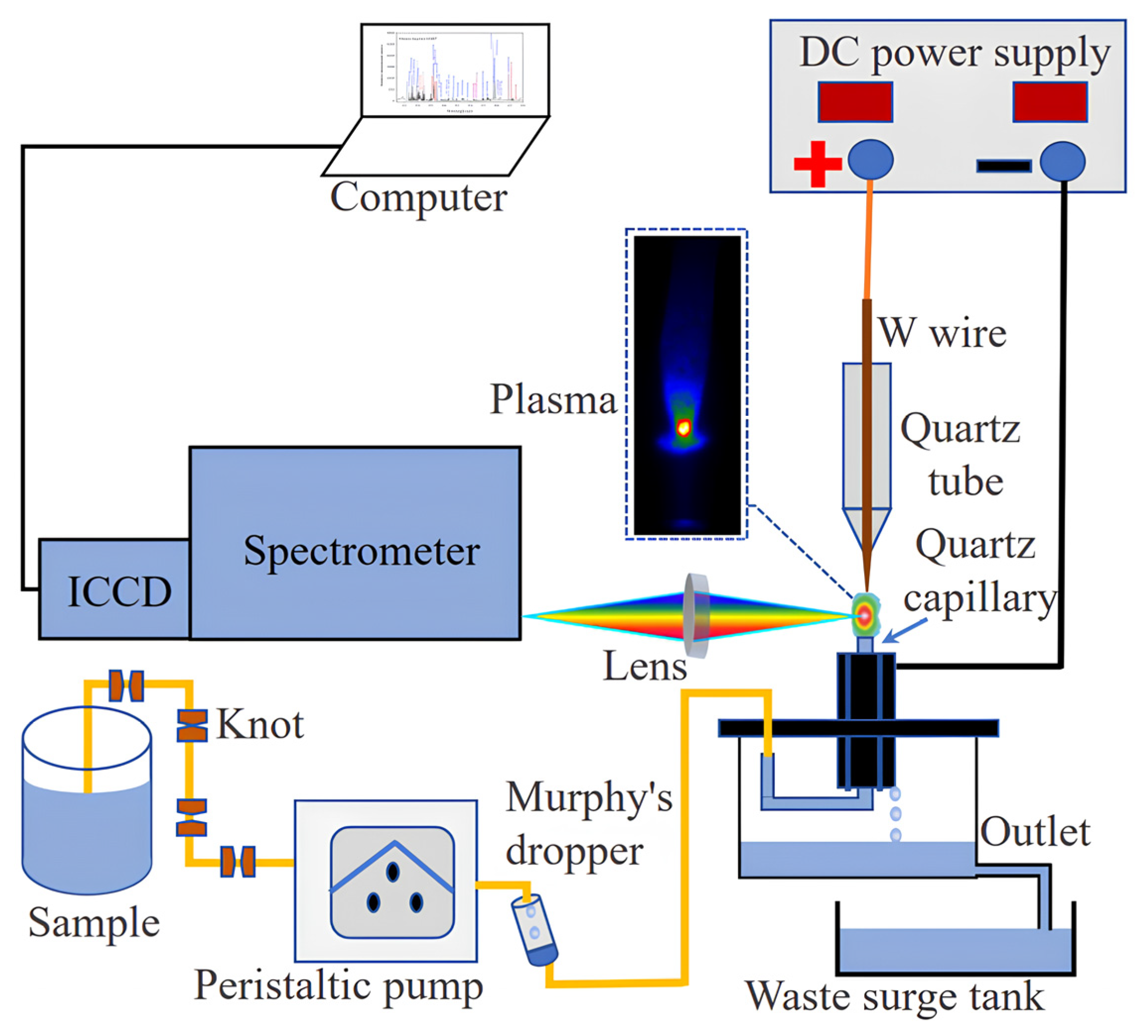
2.2. Instrumentation
3. Results and Discussion
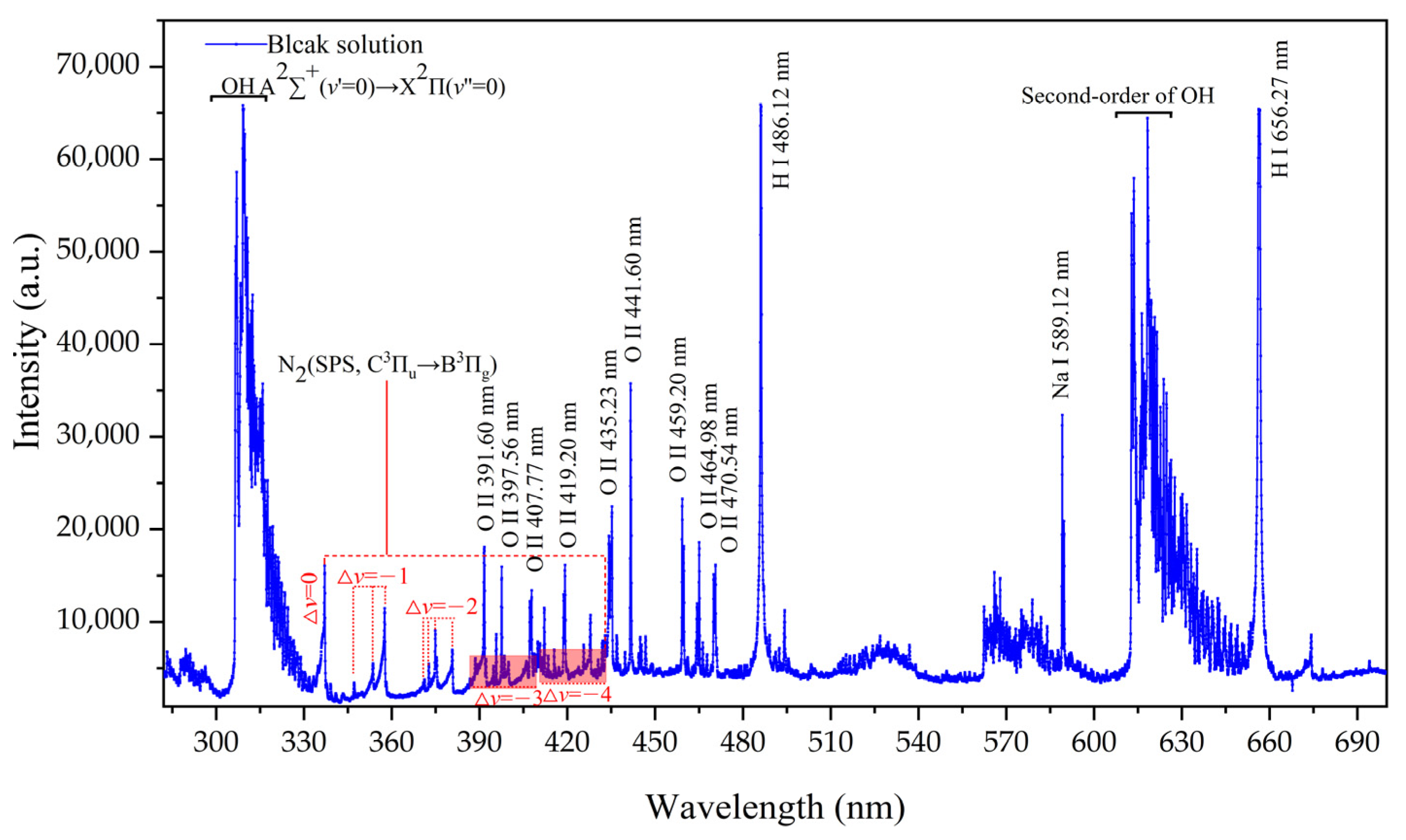
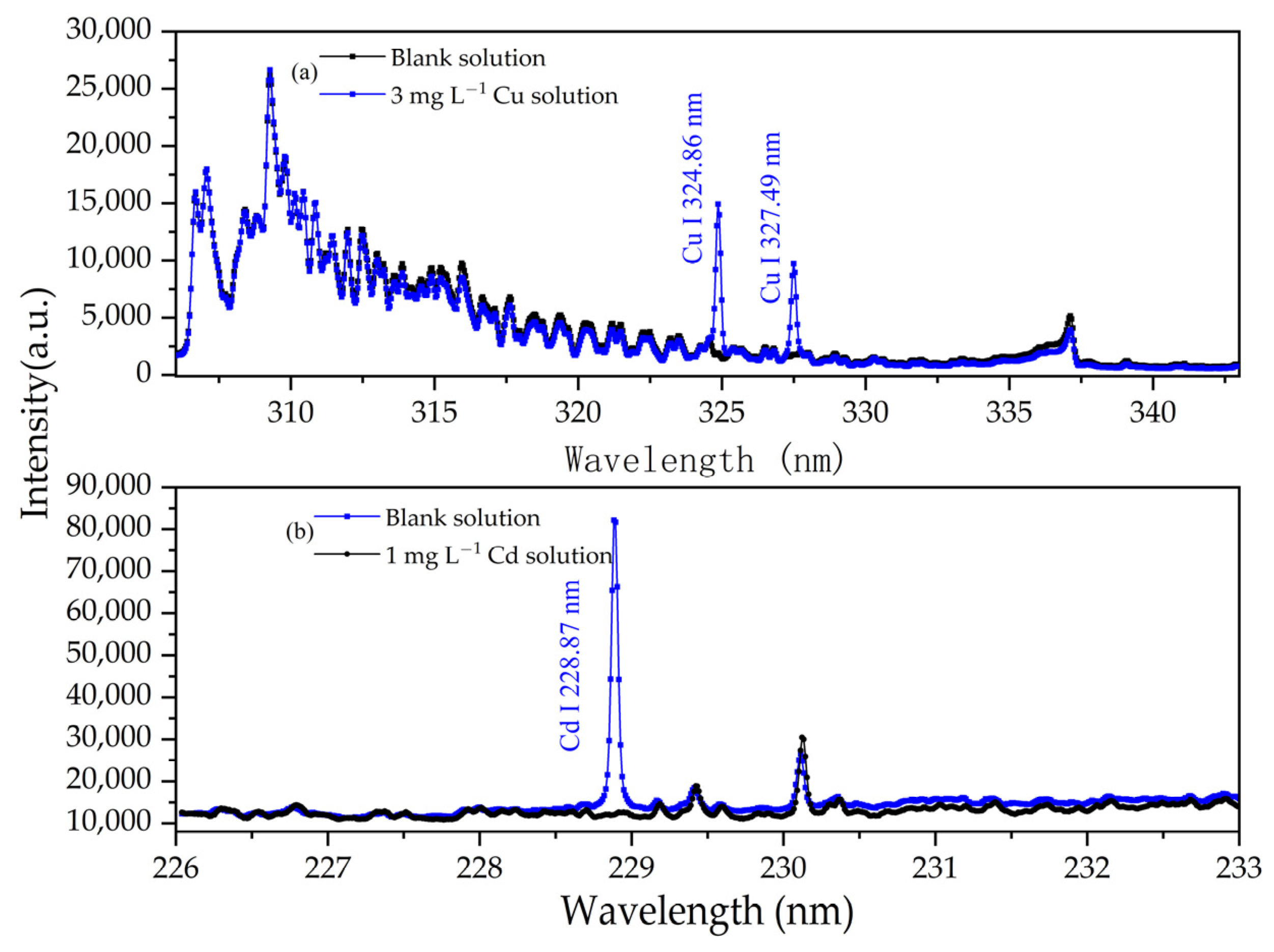
3.1. Spectral Characteristics of Reagents and Solutions of APGD-AES
3.2. Optimization of Operating Parameters
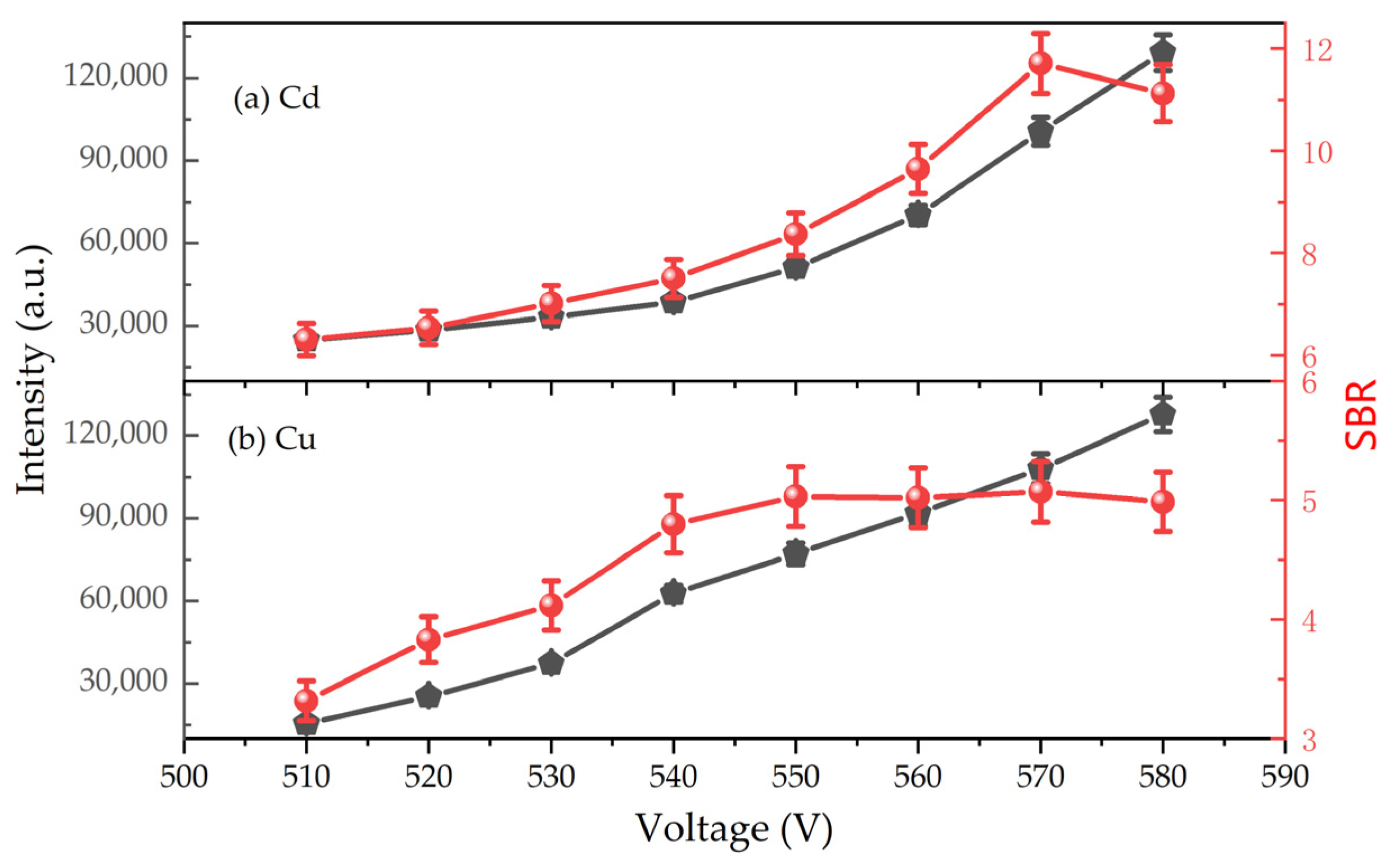
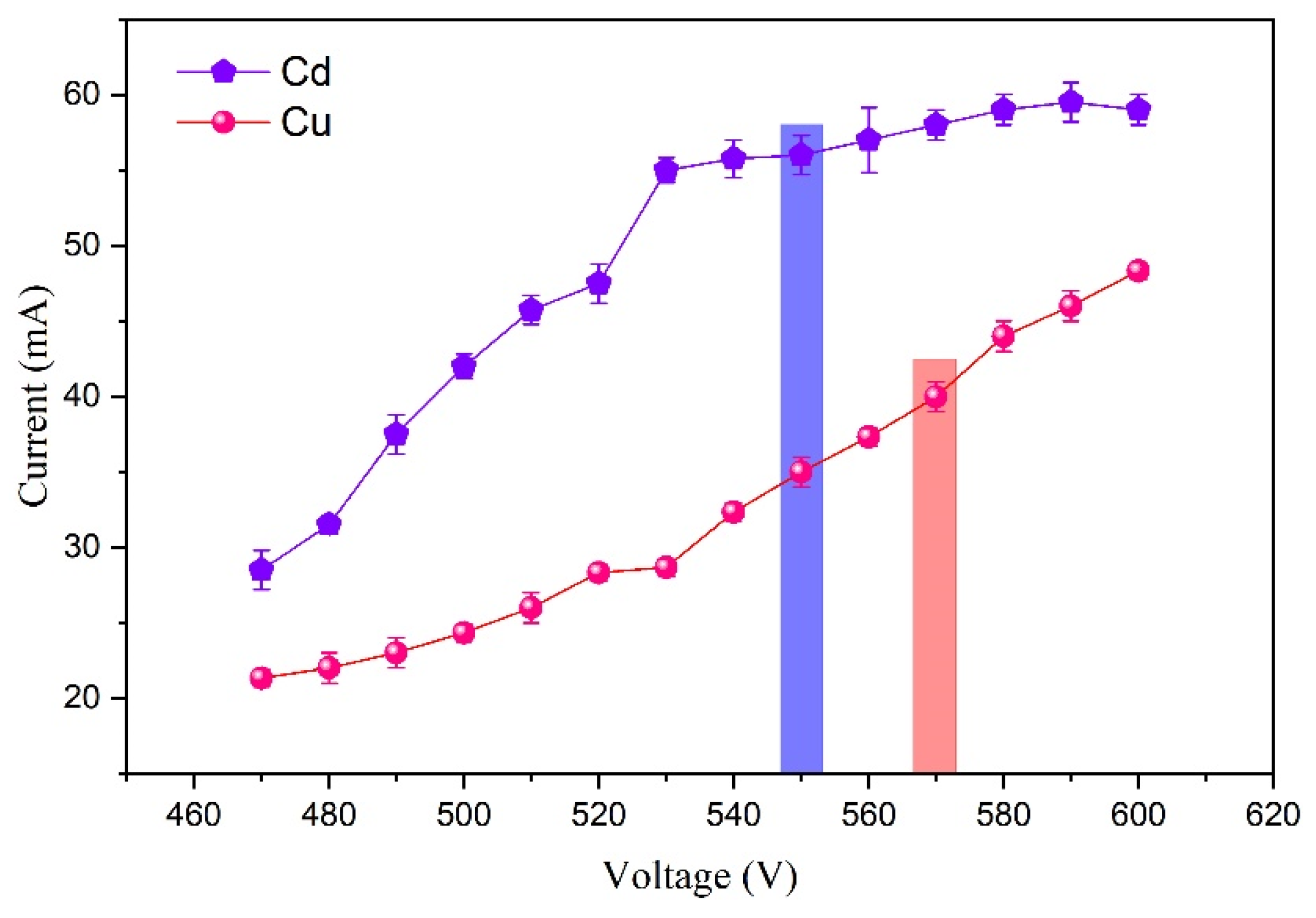
3.2.1. Effect of Discharge Voltage on Emission Signals
3.2.2. Effect of Solution Flow Rate on Emission Intensity
3.2.3. Effect of Solution pH on Emission Signal Intensity
3.3. Analytical Performance
3.4. Detection of Cu and Cd Elements in Real Water Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, K.; Mohsin, A.; Sharif, H.M.A.S.; Maryam, A.; Ali, J.; Li, X.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Ayaz, M.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Younas, M. Heavy metal pollution in the soil of a riverine basin: Distribution, source, and potential hazards. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 3095-2012; Ambient Air Quality Standard. Ecological Environment Bureau: Beijing, China, 2012. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/dqhjbh/dqhjzlbz/201203/W020120410330232398521.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2024).
- Gogoaşă, I.; Gergen, I.I.; Rada, M.; Pârvu, D.; Ciobanu, C.; Bordean, D.M.; Mǎruţoiu, C.; Moigradean, D. AAS Detection of Heavy Metal in Sheep Cheese (THE Banat Area, Romania). Bul. USAMV-CN 2006, 65, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrmošanin, J.; Pavlović, A.; Rašić Mišić, I.; Tošić, S.; Petrović, S.; Mitić, Z.; Pecev-Marinković, E.; Arsić, B. Evaluation of an Inductively Coupled Plasma–Atomic Emission Spectrometry (ICP-AES) Method for the Determination of Macro and Microelements in Trifolium L. Species. Anal. Lett. 2024, 57, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klika, K.D.; Han, J.; Busse, M.S.; Soloshonok, V.A.; Javahershenas, R.; Vanhaecke, F.; Makarem, A. Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS): An Emerging Tool in Radiopharmaceutical Science. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 30717–30727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.C.; Gong, Y.M.; Wang, J.M.; Zeng, X.B. Elemental analysis of mineral water by solution-cathode glow discharge–atomic emission spectrometry. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamroz, P.; Greda, K.; Pohl, P. Development of direct-current, atmospheric-pressure, glow discharges generated in contact with flowing electrolyte solutions for elemental analysis by optical emission spectrometry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 41, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Hu, S. Flowing and nonflowing liquid electrode discharge microplasma for metal ion detection by optical emission spectrometry. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2014, 49, 249–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserfalvi, T.; Mezei, P.; Apai, P. Emission studies on a glow discharge in atmospheric pressure air using water as a cathode. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1993, 26, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cserfalvi, T.; Mezei, P. Direct solution analysis by glow discharge: Electrolyte-cathode discharge spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1994, 9, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Schwartz, A.J.; Ray, S.J.; Hieftje, G.M. Determination of trace sodium, lithium, magnesium, and potassium impurities in colloidal silica by slurry introduction into an atmospheric-pressure solution-cathode glow discharge and atomic emission spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2013, 28, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjusha, R.; Reddy, M.A.; Shekhar, R.; Kumar, S.J. Determination of cadmium in Zircaloys by electrolyte cathode discharge atomic emission spectrometry (ELCAD-AES). Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 9850–9856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Zou, H.J.; Shi, Y. Determination of trace heavy metals in environmental and biological samples by solution cathode glow discharge-atomic emission spectrometry and addition of ionic surfactants for improved sensitivity. Talanta 2014, 119, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, R. Improvement of sensitivity of electrolyte cathode discharge atomic emission spectrometry (ELCAD-AES) for mercury using acetic acid medium. Talanta 2012, 93, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kang, Y.J.; Lu, Q.F.; Luo, H.; Lu, Z.H.; Cui, L.J.; Li, J.L. Improvement of analytical performance of liquid cathode glow discharge for the determination of bismuth using formic acid as a matrix modifier. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zu, W.; Liu, F.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, C. Determination of gallium in water samples by atomic emission spectrometry based on solution cathode glow discharge. Spectrochim. Acta B 2019, 152, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Z.L.; Jin, L.L.; Zheng, H.T.; Belshaw, N.S.; Hu, S.H. Evaluation of flow injection-solution cathode glow discharge-atomic emission spectrometry for the determination of major elements in brines. Talanta 2016, 155, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, X.M.; Lu, Q.F.; Wang, X.; Sun, D.X.; Wang, Y.Q.; Yang, W. Determination of calcium and zinc in gluconates oral solution and blood samples by liquid cathode glow discharge-atomic emission spectrometry. Talanta 2017, 175, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Lei, Z.; Peng, X.; Yang, G.; Wang, Z. Highly sensitive determination of cadmium and lead in whole blood by electrothermal vaporization-atmospheric pressure glow discharge atomic emission spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1162, 338495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Ren, M. Rapid determination of indium in water samples using a portable solution cathode glow discharge-atomic emission spectrometer. Microchem. J. 2018, 137, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, M.R.; Andrade, F.J.; Hieftje, G.M. Compact glow discharge for the elemental analysis of aqueous samples. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 7899–7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gręda, K.; Jamróz, P.; Pohl, P. The improvement of the analytical performance of direct current atmospheric pressure glow discharge generated in contact with the small-sized liquid cathode after the addition of non-ionic surfactants to electrolyte solutions. Talanta 2013, 108, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gręda, K.; Jamróz, P.; Pohl, P. Effect of the addition of non-ionic surfactants on the emission characteristic of direct current atmospheric pressure glow discharge generated in contact with a flowing liquid cathode. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2012, 28, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Hu, S. Alternating current driven atmospheric-pressure liquid discharge for the determination of elements with optical emission spectrometry. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2011, 26, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhu, Z.L.; Zheng, H.T.; He, H.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Hu, S.H. Significant sensitivity improvement of alternating current driven-liquid discharge by using formic acid medium for optical determination of elements. Talanta 2013, 106, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiderski, K.; Gręda, K.; Pohl, P.; Jamróz, P. The sensitive determination of Ag, Pb, and Tl as well as reduction of spectral interferences in a hanging drop cathode atmospheric pressure glow discharge excitation microsource equipped with a Dove prism system. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2022, 37, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.C.; Li, W.Q.; Wang, J.M.; Wang, N.S.; Zhong, C.; Luo, Y.J.; Wang, X.F.; Mao, X.F.; Lai, C.H. Analytical performance of hollow anode-solution cathode glow discharge-atomic emission spectrometry. Anal. Lett. 2020, 53, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yang, S.; Sun, D.; Lu, Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Simultaneous Determination of Multi-Metal Elements in Water Samples by Liquid Cathode Glow Discharge-Atomic Emission Spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2016, 128, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Q.; Sun, D.; Wang, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, W. Evaluation of Analytical Performance for the Simultaneous Detection of Trace Cu, Co, and Ni by Using Liquid Cathode Glow Discharge-Atomic Emission Spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2018, 145, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.L.; Winefordner, J.D. Limit of Detection: A Closer Look at the IUPAC Definition. Anal. Chem. 1983, 55, 712A–724A. [Google Scholar]
- Doroski, T.A.; King, A.M.; Fritz, M.P.; Webb, M.R. Solution–cathode glow discharge—Optical emission spectrometry of a new design and using a compact spectrograph. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2013, 28, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, R.; Karunasagar, D.; Ranijit, M.; Arunachalam, J. Determination of elemental constituents in different matrix materials and flow injection studies by the electrolyte cathode glow discharge technique with a new design. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 8157–8166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, S.W.; Lu, Q.F.; Zhang, Z.C.; Sun, D.X.; Zhang, X.M.; Wang, X.; Yang, W. Liquid cathode glow discharge as a microplasma excitation source for atomic emission spectrometry for the determination of trace heavy metals in ore samples. Anal. Lett. 2018, 51, 2128–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaltout, A. Micro plasma generation using liquid sampling-atmospheric pressure glow discharge. Microchim. Acta 2006, 155, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorska, M.; Pohl, P. The application of tetramethylammonium hydroxide for generating atmospheric pressure glow discharge in contact with alkalized flowing liquid cathode solutions—Evaluation of the analytical performance. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2021, 36, 1768–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greda, K.; Swiderski, K.; Jamróz, P.; Pohl, P. Flowing liquid anode atmospheric pressure glow discharge as an excitation source for optical emission spectrometry with the improved detectability of Ag, Cd, Hg, Pb, Tl, and Zn. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8812–8820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 18918-2002; Pollutant Discharge Standards for Water Treatment Plants. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2002. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/shjbh/swrwpfbz/200307/W020061027518964575034.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2024).
- GB 5749-2022; Ygienic Standard for Drinking Water. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2022. Available online: http://c.gb688.cn/bzgk/gb/showGb?type=online&hcno=99E9C17E3547A3C0CE2FD1FFD9F2F7BE (accessed on 4 February 2024).



| Species | Analytical Line (nm) | Power (W) | Calibration Equation | R2 | Sensitivity | LOD (μg/L) | RSD a/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 228.87 | 30.2–32.4 | I = 10,077.4 + 58.511C | 0.9846 | 58.511 | 16 | 2.9 |
| Cu | 324.86 | 22.3–23.3 | I = 4666.8 + 152.81C | 0.9979 | 152.81 | 1.31 | 4 |
| Method | LOD (μg/L) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cu | ||
| Atmospheric pressure glow discharge atomic emission spectrometry | 16 | 1.3 | This work |
| Hollow anode–liquid cathode glow discharge | 2 | 8 | [31] |
| Modified electrolyte cathode atmospheric glow discharge | 5 | 11 | [32] |
| Liquid cathode glow discharge atomic emission spectrometry | 370 | 470 | [33] |
| Liquid sampling atmospheric pressure glow discharge | 50 | 650 | [34] |
| Flowing liquid cathode atmospheric pressure glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy | 10 | - | [35] |
| Flowing liquid anode atmospheric pressure glow discharge | 6 | - | [36] |
| Sample | Element | Measured Value (µg/L) | GFAAS (µg/L) | The Maximum Value Set by the State (µg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sewage | Cd | — | 0.09 | 10 |
| Cu | 10.9 | 9.72 | 500 | |
| Tap water | Cd | — | 0.04 | 5 |
| Cu | 3.10 | 2.33 | 1000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, D.; Ma, X.; Chang, J.; Zhang, G.; Su, M.; Sikorski, M.; Detalle, V.; Bai, X. Analysis of Trace Heavy Metal in Solution Using Liquid Cathode Glow Discharge Spectroscopy. Sensors 2024, 24, 7756. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237756
Sun D, Ma X, Chang J, Zhang G, Su M, Sikorski M, Detalle V, Bai X. Analysis of Trace Heavy Metal in Solution Using Liquid Cathode Glow Discharge Spectroscopy. Sensors. 2024; 24(23):7756. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237756
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Duixiong, Xinrong Ma, Jiawei Chang, Guoding Zhang, Maogen Su, Marek Sikorski, Vincent Detalle, and Xueshi Bai. 2024. "Analysis of Trace Heavy Metal in Solution Using Liquid Cathode Glow Discharge Spectroscopy" Sensors 24, no. 23: 7756. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237756
APA StyleSun, D., Ma, X., Chang, J., Zhang, G., Su, M., Sikorski, M., Detalle, V., & Bai, X. (2024). Analysis of Trace Heavy Metal in Solution Using Liquid Cathode Glow Discharge Spectroscopy. Sensors, 24(23), 7756. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24237756






