In-Car Environment Control Using an SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface with Visual Stimuli Presented on Head-Up Display: Performance Comparison with a Button-Press Interface
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Subjects
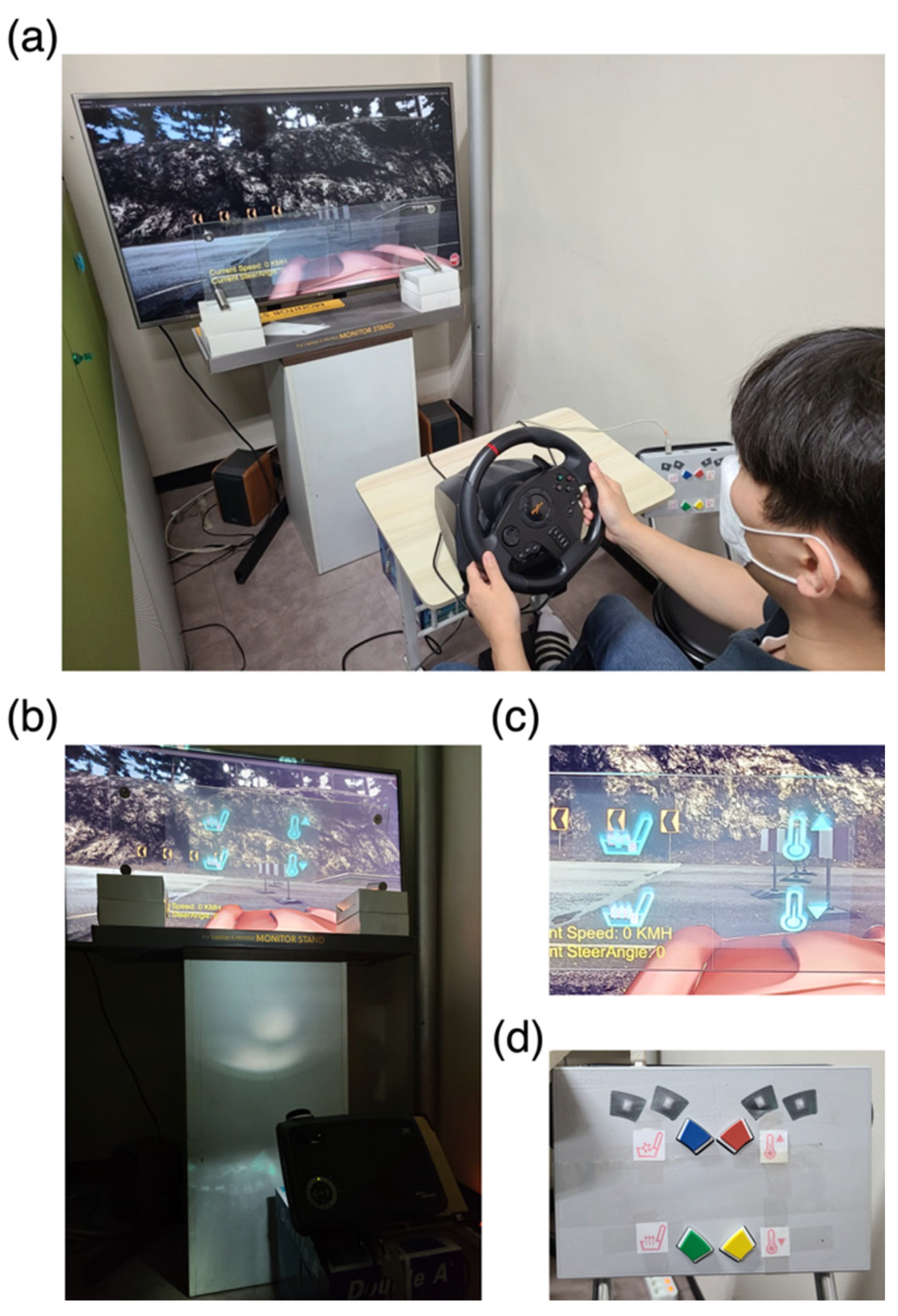
3.2. Simulated Driving Environment
3.3. Visual Stimulus Presented on HUD
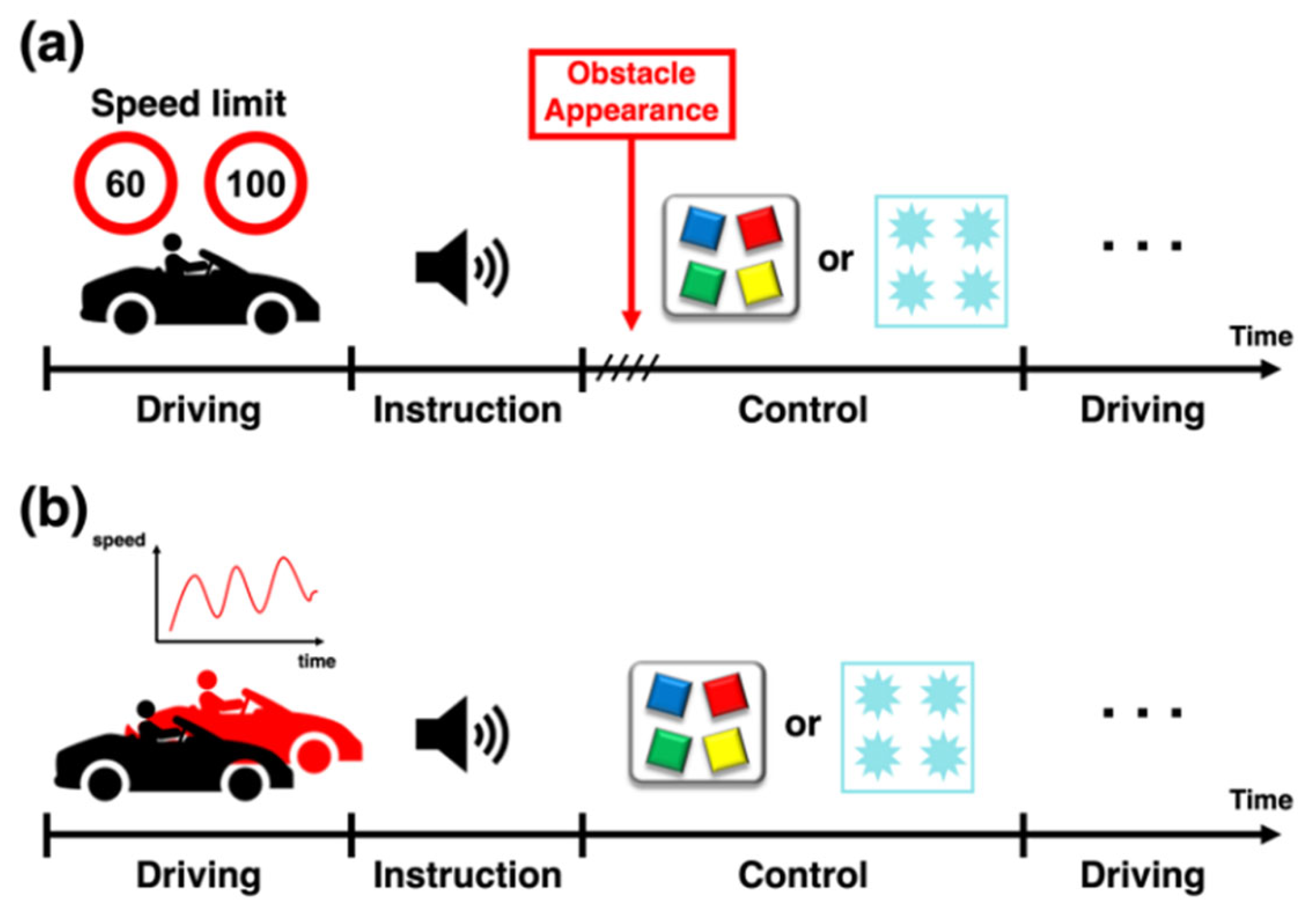
3.4. Experimental Paradigm
3.5. Data Recording and Analysis
- (1)
- Response time (obstacle avoidance test)
- (2)
- No response rate (NRR) (obstacle avoidance test)
- (3)
- Speed difference (car-following test)
- (4)
- Centerline deviation (car-following test)
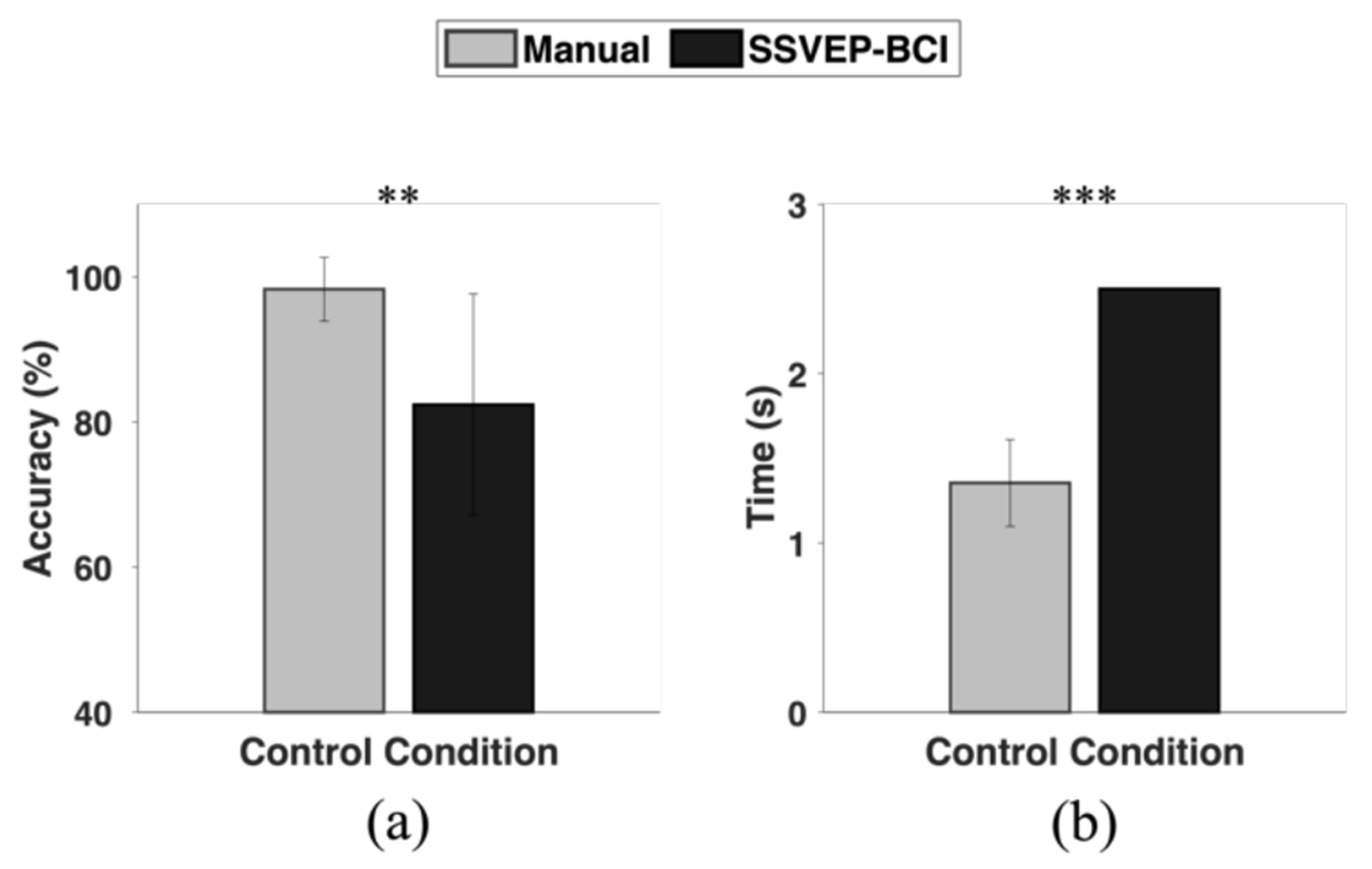
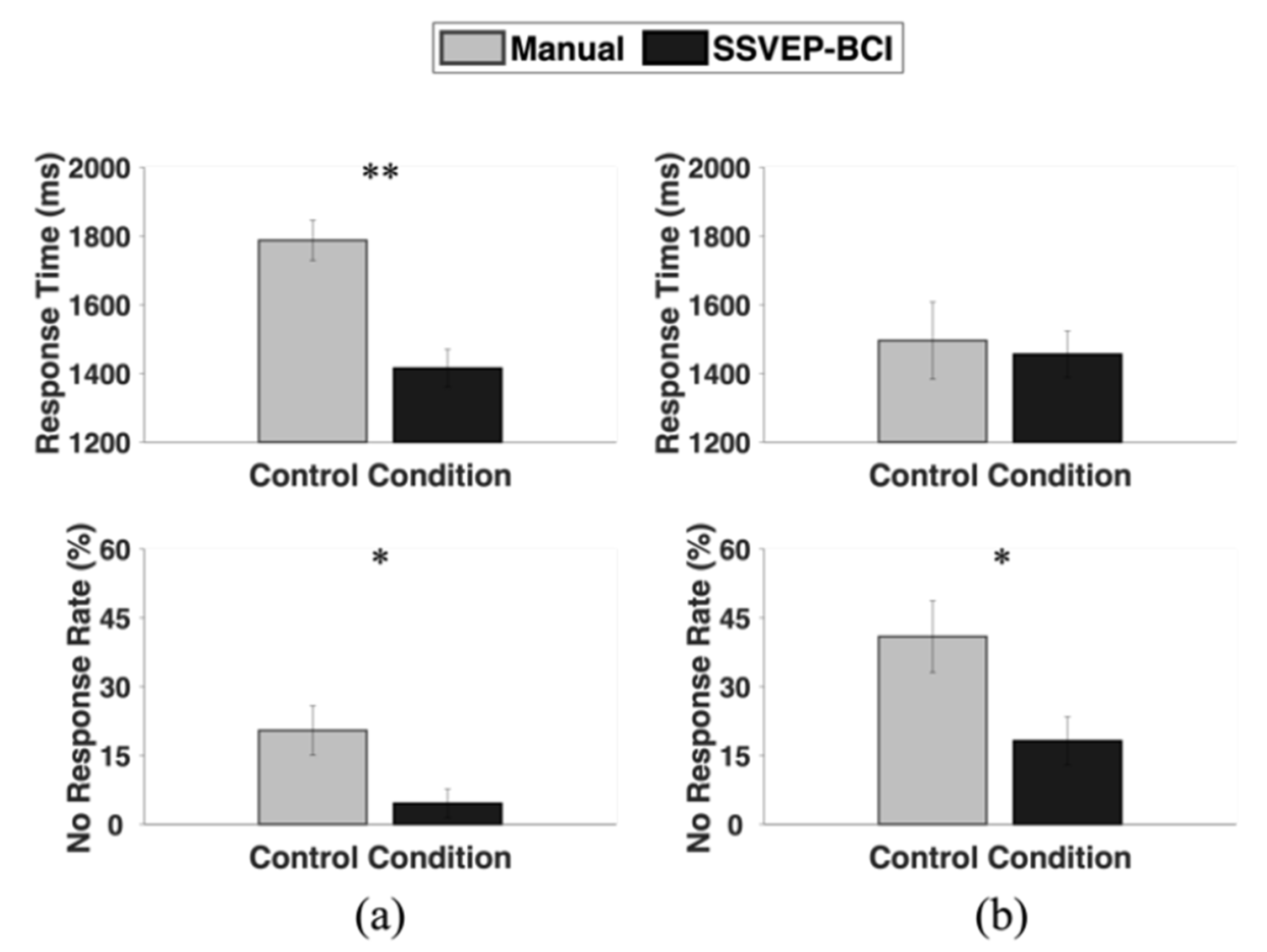
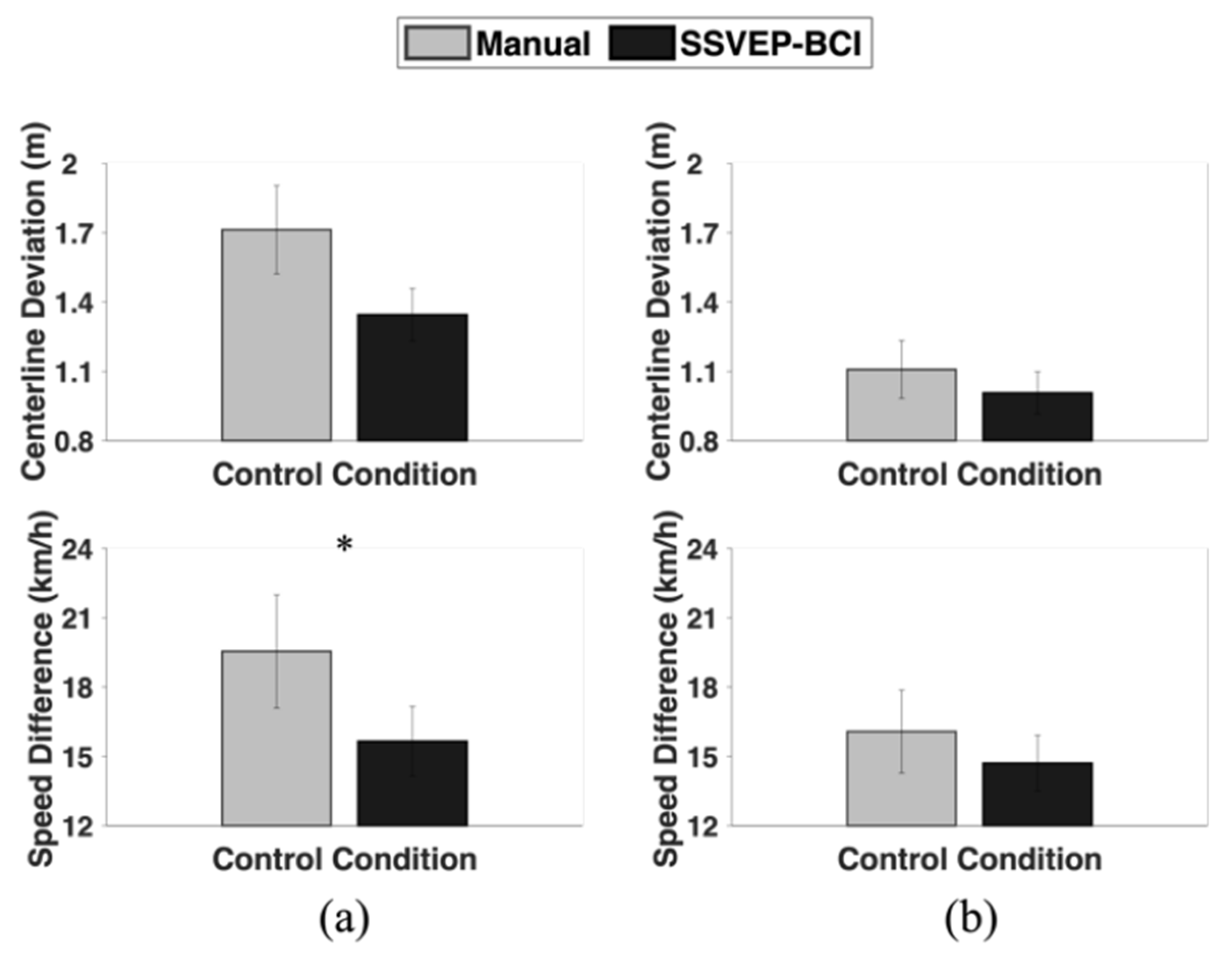
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, F.A.; Stimpson, J.P. Trends in fatalities from distracted driving in the United States, 1999 to 2008. Am. J. Public Health 2010, 100, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEvoy, S.P.; Stevenson, M.R.; Woodward, M. The prevalence of, and factors associated with, serious crashes involving a distracting activity. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2007, 39, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regev, S.; Rolison, J.; Feeney, A.; Moutari, S. Driver distraction is an under-reported cause of road accidents: An examination of discrepancy between police officers’ views and road accident reports. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Driver Distraction and Inattention, Paris, France, 20–22 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rolison, J.J.; Regev, S.; Moutari, S.; Feeney, A. What are the factors that contribute to road accidents? An assessment of law enforcement views, ordinary drivers’ opinions, and road accident records. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 115, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, J.J. Toward direct brain-computer communication. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 1973, 2, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N.; McFarland, D.J.; Pfurtscheller, G.; Vaughan, T.M. Brain–computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 767–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dornhege, G.; Millan, J.d.R.; Hinterberger, T.; McFarland, D.J.; Müller, K.-R. Toward Brain-Computer Interfacing; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sellers, E.W.; Vaughan, T.M.; Wolpaw, J.R. A brain-computer interface for long-term independent home use. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2010, 11, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.-C.; Chien, T.-Y.; Pan, J.-S.; Lin, B.-S. Novel non-contact control system for medical healthcare of disabled patients. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 5687–5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Cha, H.-S.; Im, C.-H. Development of an Online Home Appliance Control System Using Augmented Reality and an SSVEP-Based Brain–Computer Interface. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 163604–163614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Gomez, A.F.; DelPreto, J.; Gil, S.; Guenther, F.H.; Rus, D. Correcting robot mistakes in real time using EEG signals. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; IEEE: Singapore, 2017; pp. 6570–6577. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, L.D.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, I.J.; Chen, S.F.; Li, S.Y.; Chen, B.W.; Chang, J.Y.; Lin, C.T. Gaming control using a wearable and wireless EEG-based brain-computer interface device with novel dry foam-based sensors. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, M.; Yamaguchi, Y. Effects of subjective preference of colors on attention-related occipital theta oscillations. Neuroimage 2012, 59, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, S.J.; Hecker, K.G.; Krigolson, O.E.; Jamniczky, H.A. A Reinforcement-Based Learning Paradigm Increases Anatomical Learning and Retention—A Neuroeducation Study. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, M.V.; Li, X.; Shen, K.; Wilder-Smith, E.P. Can SVM be used for automatic EEG detection of drowsiness during car driving? Saf. Sci. 2009, 47, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-T.; Wu, R.-C.; Liang, S.-F.; Chao, W.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Jung, T.-P. EEG-based drowsiness estimation for safety driving using independent component analysis. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2005, 52, 2726–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-T.; Chen, Y.C.; Huang, T.Y.; Chiu, T.T.; Ko, L.W.; Liang, S.F.; Hsieh, H.Y.; Hsu, S.H.; Duann, J.R. Development of wireless brain computer interface with embedded multitask scheduling and its application on real-time driver’s drowsiness detection and warning. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 55, 1582–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Dragomir, A.; Abbasi, N.I.; Li, J.; Thakor, N.V.; Bezerianos, A. A novel real-time driving fatigue detection system based on wireless dry EEG. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2018, 12, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernea, D.; Olech, P.-S.; Ebert, A.; Kerren, A. Controlling in-vehicle systems with a commercial EEG headset: Performance and cognitive load. In Visualization of Large and Unstructured Data Sets: Applications in Geospatial Planning, Modeling and Engineering-Proceedings of IRTG 1131 Workshop 2011, Kaiserslautern, Germany, 10–11 June 2011; Schloss Dagstuhl-Leibniz-Zentrum für Informatik: Wadern, Germany, 2012; pp. 113–122. [Google Scholar]
- Bellotti, A.; Antopolskiy, S.; Marchenkova, A.; Colucciello, A.; Avanzini, P.; Vecchiato, G.; Ambeck-Madsen, J.; Ascari, L. Brain-based control of car infotainment. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), Bari, Italy, 6–9 October 2019; pp. 2166–2173. [Google Scholar]
- Regan, D. Some characteristics of average steady-state and transient responses evoked by modulated light. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1966, 20, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vialatte, F.-B.; Maurice, M.; Dauwels, J.; Cichocki, A. Steady-state visually evoked potentials: Focus on essential paradigms and future perspectives. Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 90, 418–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.; Bakardjian, H.; Cichocki, A. Fully online multicommand brain-computer interface with visual neurofeedback using SSVEP paradigm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2007, 2007, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.M.T.; Bastos, T.F.; Filho, M.S. Proposal of an SSVEP-BCI to Command a Robotic Wheelchair. J. Control Autom. Electr. Syst. 2013, 24, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Liu, P.; An, X.; Song, X.; Ming, D. An Online SSVEP-BCI System in an Optical See-Through Augmented Reality Environment. J. Neural Eng. 2020, 17, 016066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, B.; Luth, T.; Valbuena, D.; Teymourian, A.; Volosyak, I.; Graser, A. BCI demographics: How many (and what kinds of) people can use an SSVEP BCI? IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2010, 18, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Fan, X.; Jie, K.; Teng, T.; Ding, H.; Liu, Y. Using a Head-up Display-Based Steady-State Visually Evoked Potential Brain–Computer Interface to Control a Simulated Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Intel. Transport. Syst. 2014, 15, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, D.; Schmidt, A. Design Space for Driver-Based Automotive User Interfaces. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Automotive User Interfaces and Interactive Vehicular Applications, Essen, Germany, 21–22 September 2009; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, A.; Brewster, S.A.; Beruscha, F.; Krautter, W. An Evaluation of Input Controls for In-Car Interactions. In Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 6–11 May 2017; pp. 2845–2852. [Google Scholar]
- He, T.; Bi, L.; Lian, J.; Sun, H. A Brain Signals-Based Interface Between Drivers and In-Vehicle Devices. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Gothenburg, Sweden, 19–22 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.; Dey, D.; Lovett, C.; Kapoor, A. Airsim: High-fidelity visual and physical simulation for autonomous vehicles. In Field and Service Robotics: Results of the 11th International Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 12–15 September 2017; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 621–635. [Google Scholar]
- Floriano, A.; Diez, P.F.; Bastos-Filho, T. Freire. Evaluating the influence of chromatic and luminance stimuli on SSVEPs from behind-the-ears and occipital areas. Sensors 2018, 18, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, D.; Yao, D.; Xu, P. The extension of multivariate synchronization index method for SSVEP-based BCI. Neurocomput. 2017, 269, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, T.; Malinowski, P.; Müller, M.M. Modulation of oscillatory brain activity and evoked potentials in a repetition priming task in the human EEG. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annabattula, J.; Rao, S.K.; Murthy, A.S.D.; Srikanth, K.S.; Das, R.P. Advanced Submarine Integrated Weapon Control System. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2015, 8, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y. Filter bank-driven multivariate synchronization index for training-free SSVEP BCI. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2021, 29, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Jung, T.-P.; Gao, X. Filter bank canonical correlation analysis for implementing a high-speed SSVEP-based brain-computer interface. J. Neural. Eng. 2015, 12, 046008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guger, C.; Allison, B.Z.; Großwindhager, B.; Prückl, R.; Hintermüller, C.; Kapeller, C.; Bruckner, M.; Krausz, G.; Edlinger, G. How many people could use an SSVEP BCI? Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, R.; Carter, C. Comparison of Speech Input and Manual Control of In-Car Devices While on the Move. Personal Technol. 2000, 4, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghini, G.; Astolfi, L.; Vecchiato, G.; Mattia, D.; Babiloni, F. Measuring Neurophysiological Signals in Aircraft Pilots and Car Drivers for the Assessment of Mental Workload, Fatigue, and Drowsiness. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 44, 58–75. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Liang, F.; Han, L.; Zhang, Z. Vehicle Driver Drowsiness Detection Method Using Wearable EEG Based on Convolution Neural Network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 13965–13980. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mercedes-Benz VISION AVTR. Available online: https://group.mercedes-benz.com/innovation/product-innovation/design/vision-avtr-bci.html (accessed on 1 November 2023).

| Commands | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Turn on Heated Seat | Turn on Seat Ventilation | Temperature Up | Temperature Down |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Kim, M.; Nam, H.; Kwon, J.; Im, C.-H. In-Car Environment Control Using an SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface with Visual Stimuli Presented on Head-Up Display: Performance Comparison with a Button-Press Interface. Sensors 2024, 24, 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24020545
Park S, Kim M, Nam H, Kwon J, Im C-H. In-Car Environment Control Using an SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface with Visual Stimuli Presented on Head-Up Display: Performance Comparison with a Button-Press Interface. Sensors. 2024; 24(2):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24020545
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Seonghun, Minsu Kim, Hyerin Nam, Jinuk Kwon, and Chang-Hwan Im. 2024. "In-Car Environment Control Using an SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface with Visual Stimuli Presented on Head-Up Display: Performance Comparison with a Button-Press Interface" Sensors 24, no. 2: 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24020545
APA StylePark, S., Kim, M., Nam, H., Kwon, J., & Im, C.-H. (2024). In-Car Environment Control Using an SSVEP-Based Brain-Computer Interface with Visual Stimuli Presented on Head-Up Display: Performance Comparison with a Button-Press Interface. Sensors, 24(2), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24020545








