Off-Axis Integral Cavity Carbon Dioxide Gas Sensor Based on Machine-Learning-Based Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principles and Methods
2.1. Absorption Principles
2.1.1. Laser Propagation Path
2.1.2. Beer–Lambert Law
2.1.3. Principle of Integrating Cavity Output Spectrum
2.1.4. Selection of Absorption Lines
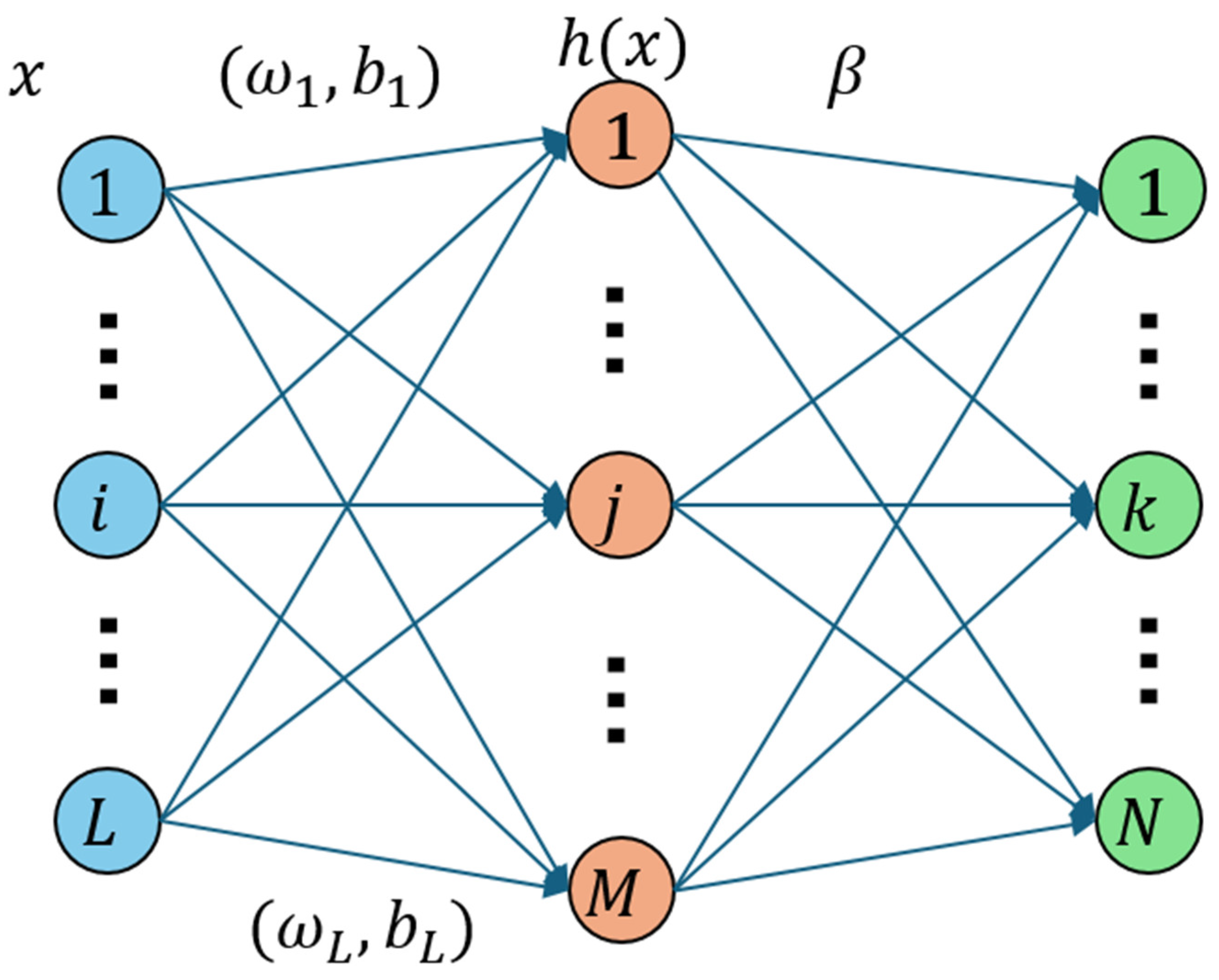
2.2. The Principle of the Extreme Learning Machine
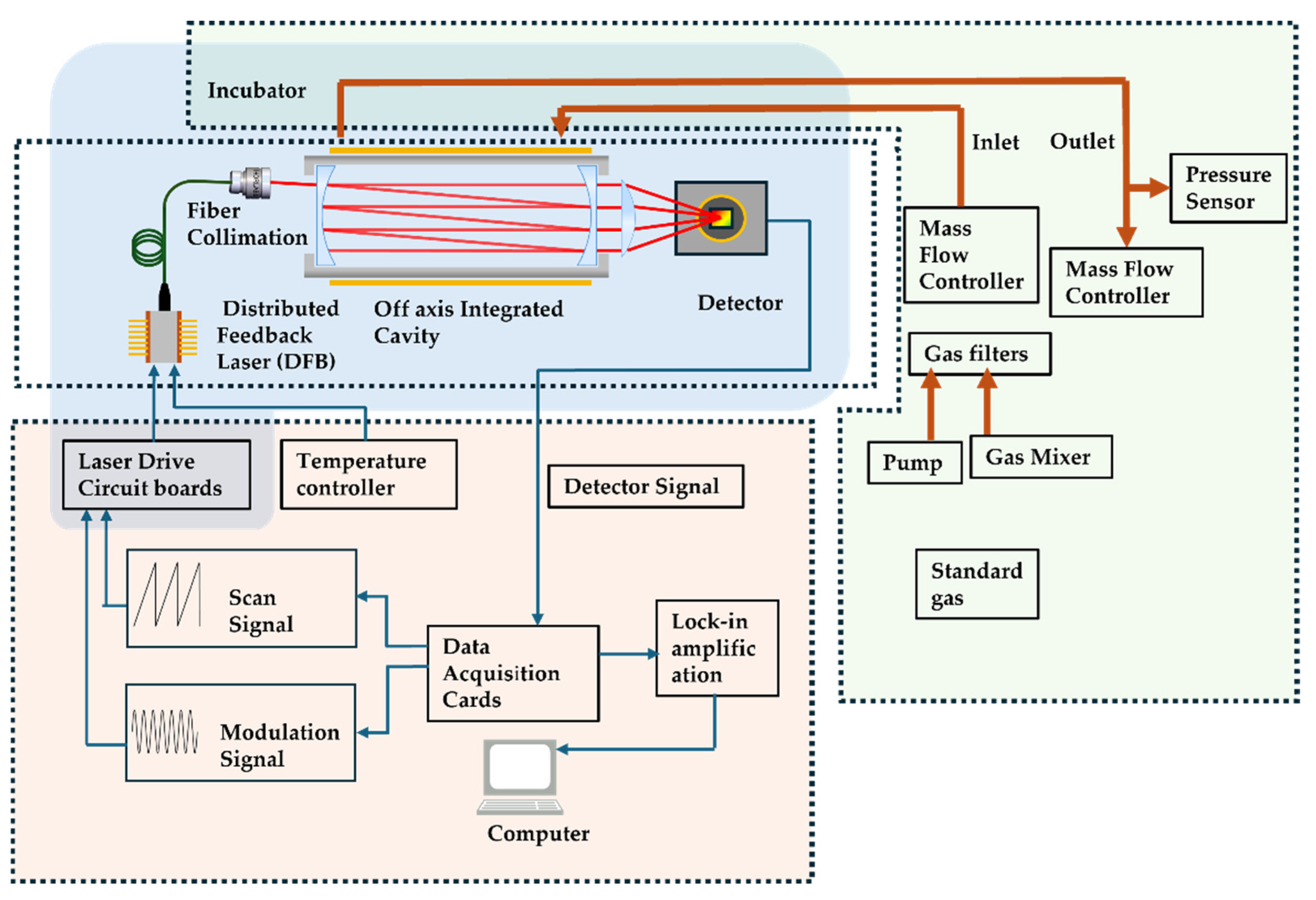
2.3. Sensor Configuration
3. Results
3.1. Gas Preparation
3.2. SNR Estimation
3.2.1. Traditional Locked-In Amplifier
3.2.2. Optimized CIC Filtering Scheme
3.2.3. Extreme Learning Machine
3.2.4. Improvement of SNR of the Detection System
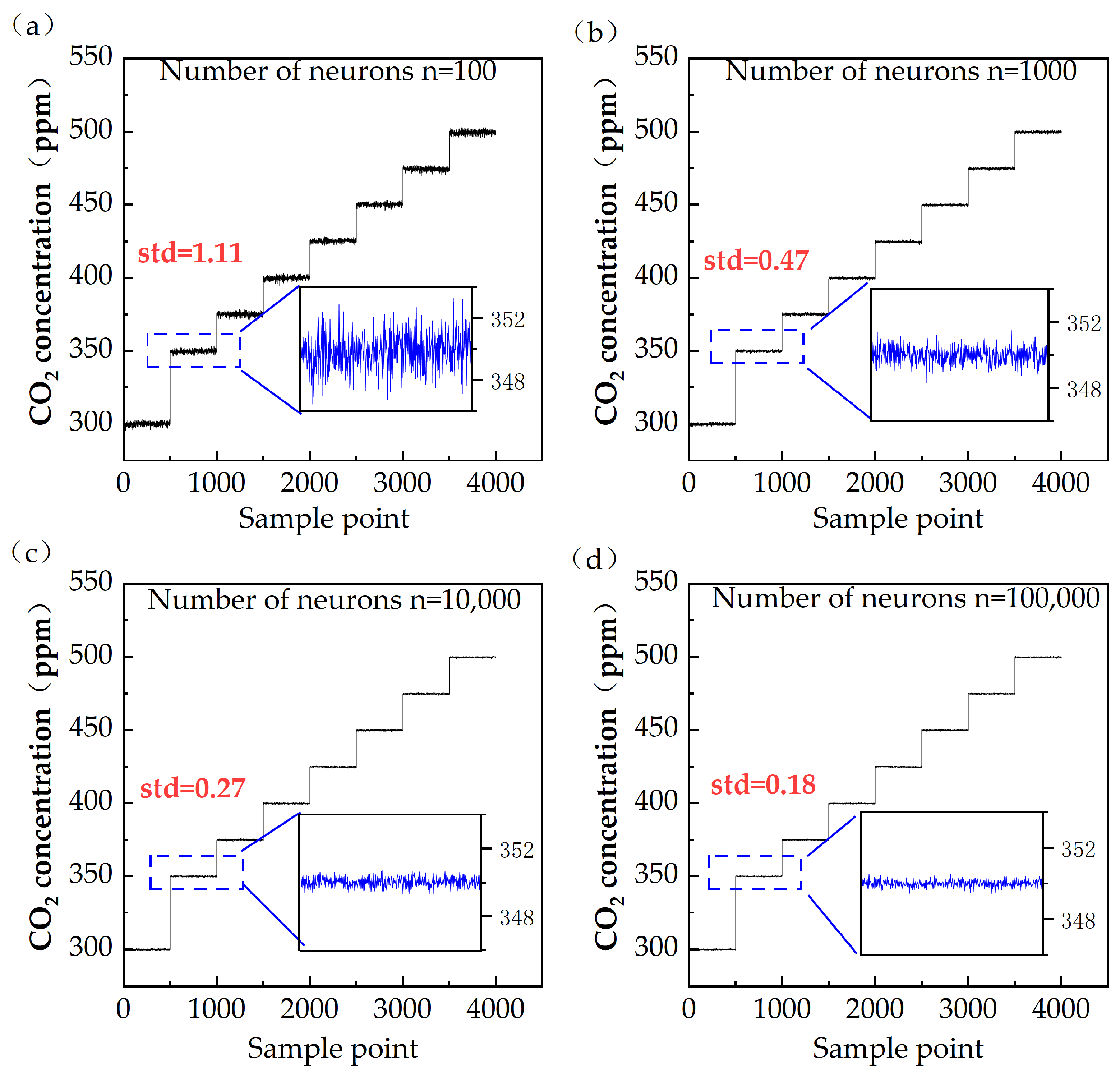
3.3. Signal Processing Performance of ELM
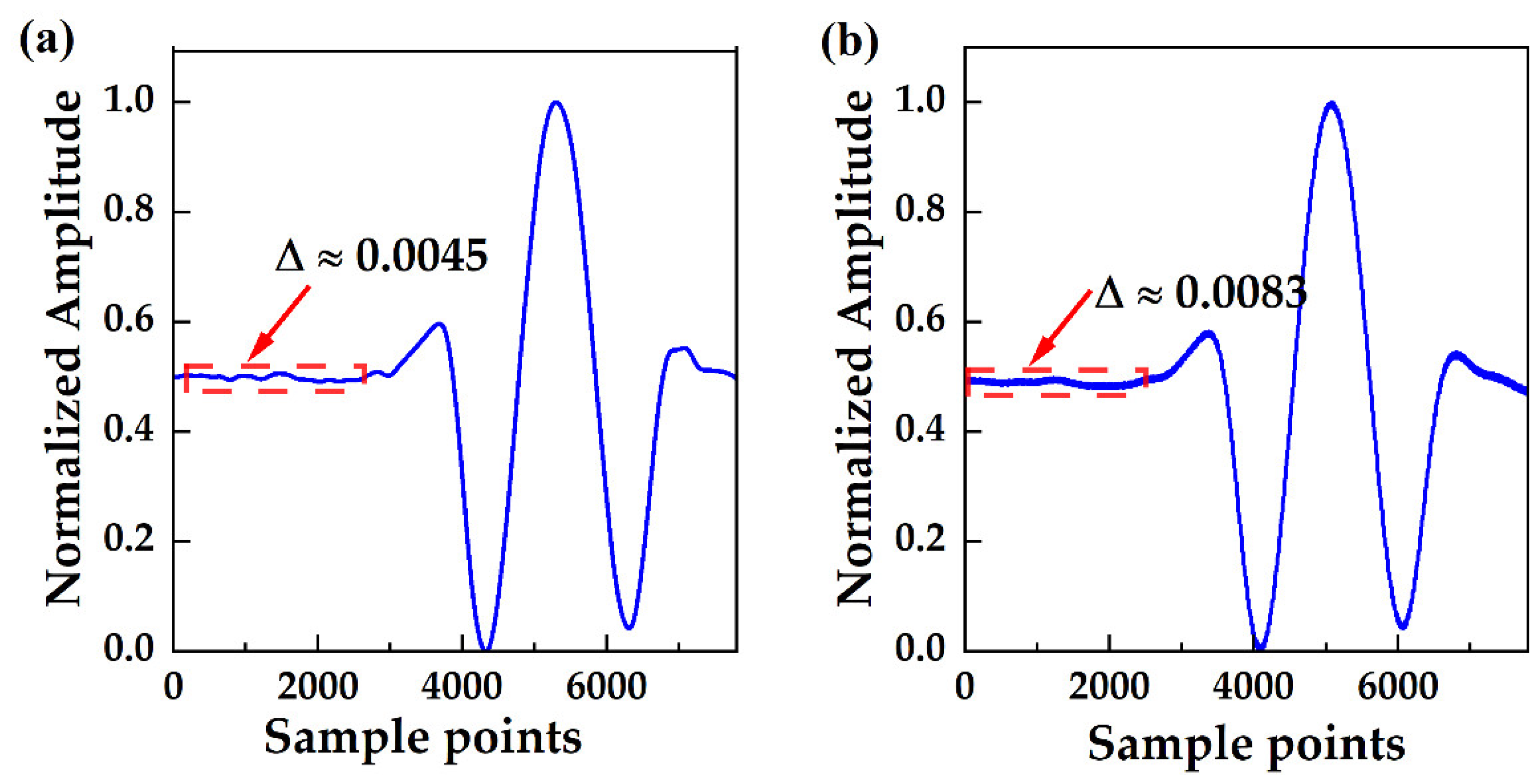
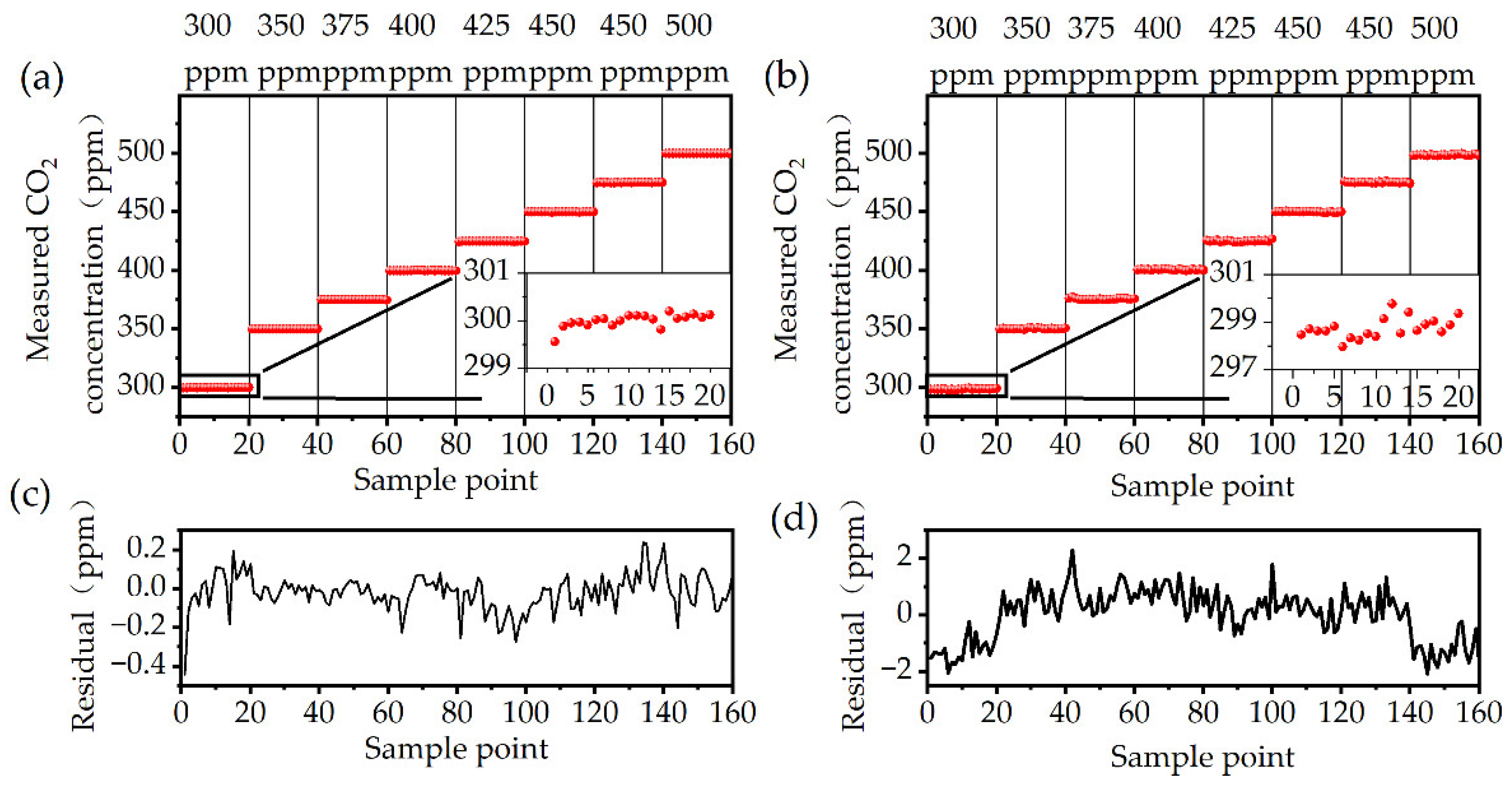
3.4. Fluctuation and Residual Analyses
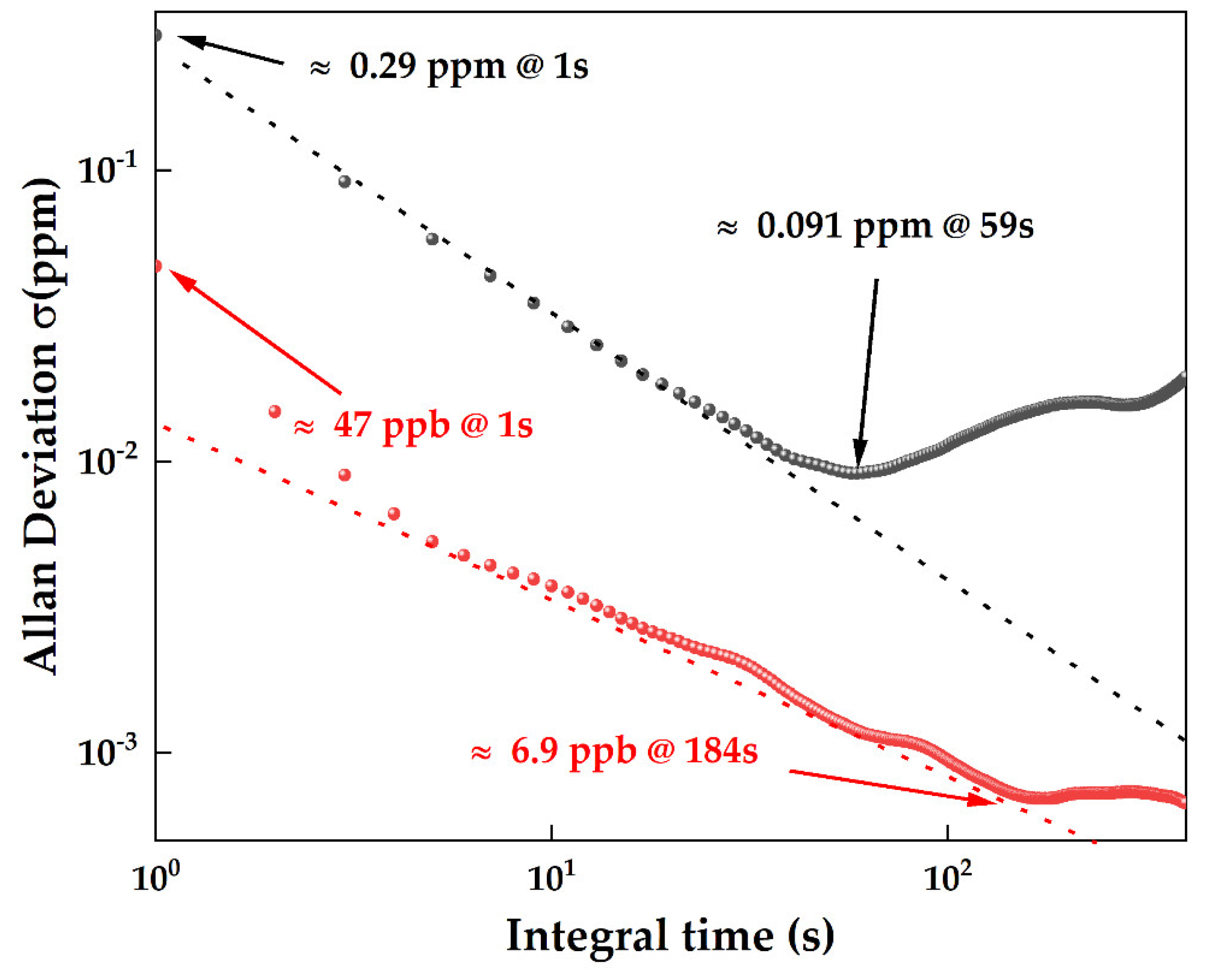
3.5. Allan Deviation Analysis and Detection Limit
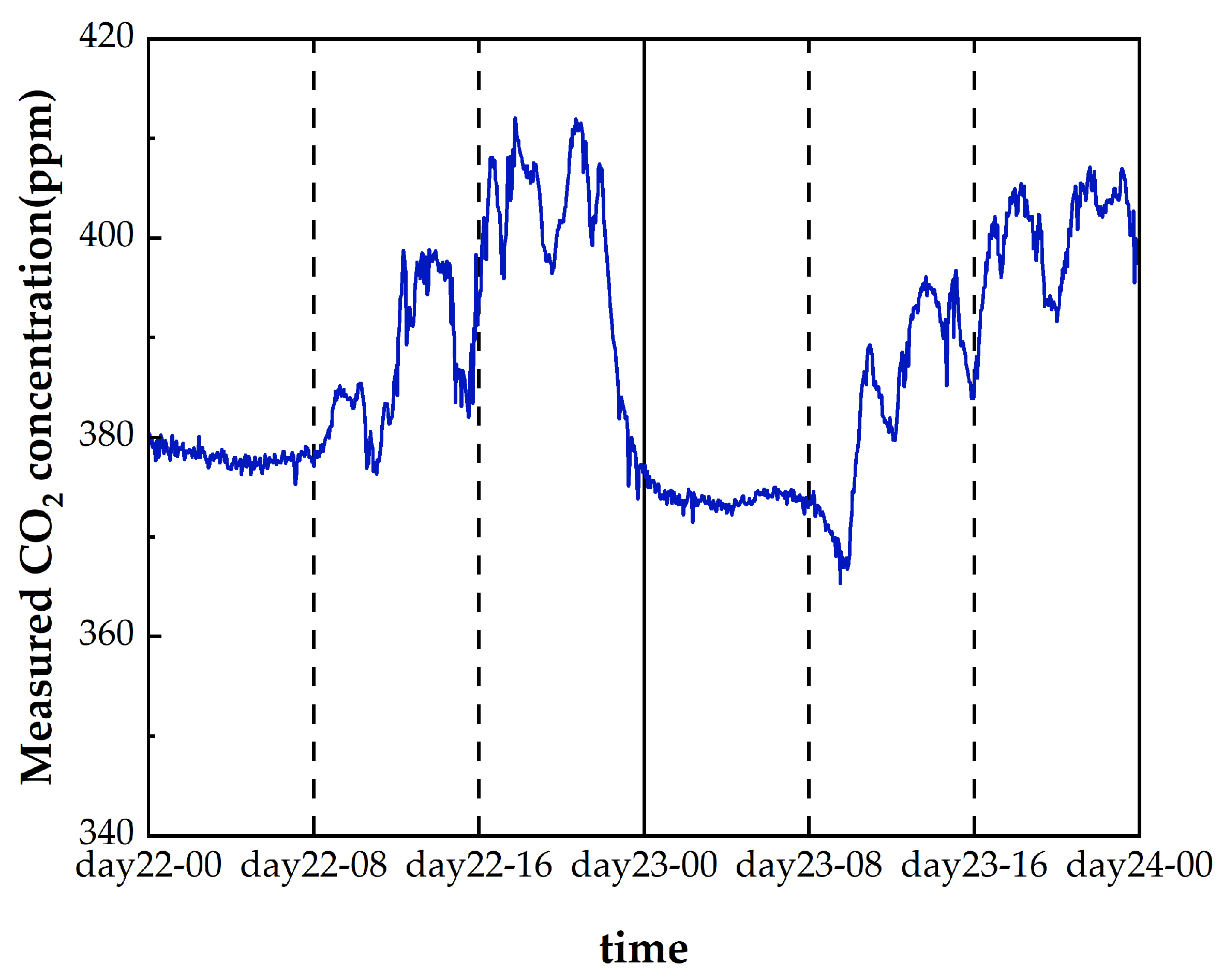
3.6. Field Test Results of Atmospheric CO2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. IPCC, 2023: Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; World Meteorological Organization (WMO). State of the Global Climate 2023 (WMO-No. 1347); Core Writing Team, Lee, H., Romero, J., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 35–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pirani, A.; Connors, S.; Péan, C.; Chen, Y.; Goldfarb, L.; Gomis, M.; Matthews, J.; Berger, S.; et al. The Physical Science Basis Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. In Climate Change 2021 The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, B.; Michel, A.P. Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy Instrument for Flow-through Measurement of Dissolved Carbon Dioxide in the Ocean. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO), Virtual, 9–14 May 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Shao, L.; Wang, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, K.; Mei, X.; Tan, T.; Gao, X. Research on real-time detection technology of dissolved gas in seawater based on off-axis integrating cavity. Chin. J. Quantum Electron. 2022, 39, 502–510. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; McCartt, A.D. Mid-Infrared Trace Detection with Parts-Per-Quadrillion Quantitation Accuracy: Expanding Frontiers of Radiocarbon Sensing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2314441121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, B.J.; Ko, K.-H.; Park, S.-K.; Lee, L.; Jeong, D.-Y. Long-Term Analysis of 14CO2 Measurement Using Mid-IR Cavity Ring-down Spectroscopy for Nuclear Power Plants. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2024, 84, 504–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumoto, M.; Kawata, Y.; Wada, S. Mid-Infrared-Scanning Cavity Ring-down CH2F2 Detection Using Electronically Tuned Cr:ZnSe Laser. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; You, S.; Li, G.; Fan, Z. Enhancing Methane Sensing with NDIR Technology: Current Trends and Future Prospects. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2023, 42, 20230062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopiuk, A.; Bielecki, Z.; Wojtas, J. Improving the Accuracy of the NDIR-Based CO2 Sensor for Breath Analysis. Metrol. Meas. Syst. 2021, 28, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventrillard, I.; Xueref-Remy, I.; Schmidt, M.; Kwok, C.Y.; Faïn, X.; Romanini, D. Comparison of Optical-Feedback Cavity-Enhanced Absorption Spectroscopy and Gas Chromatography for Ground-Based and Airborne Measurements of Atmospheric CO Concentration. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1803–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Mei, J.; Chen, J.; Tan, T.; Wang, G.; Liu, K.; Gao, X. Recent Advances and Applications of Off-Axis Integrated Cavity Output Spectroscopy. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2022, 65, 1489–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Liu, A.; Wu, X.; Zheng, C.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, K.; Pi, M.; Yan, G.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Near-Infrared Off-Axis Cavity-Enhanced Optical Frequency Comb Spectroscopy for CO2/CO Dual-Gas Detection Assisted by Machine Learning. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.B.; Lapson, L.B.; Anderson, J.M. Ultrasensitive Absorption Spectroscopy with a High-Finesse Optical Cavity and Off-Axis Alignment. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.B.; Ma, H.L.; Cao, Z.S.; Sun, M.G.; Huang, Y.B.; Zhu, W.Y.; Liu, Q. High-Sensitive Off-Axis Integrated Cavity Output Spectroscopy and Its Measurement of Ambient CO2 at 2 μm. Acta Phys. Sin. 2016, 65, 053301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tian, X.; Dong, Y.; Chen, J.; Tan, T.; Zhu, G.; Chen, W.; Gao, X. High-Sensitivity Off-Axis Integrated Cavity Output Spectroscopy Implementing Wavelength Modulation and White Noise Perturbation. Opt. Lett./Opt. Index 2019, 44, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, M.-N.; Nguyen-Ba, T.; Dewaele, D.; Cazier, F.; Zhao, W.; Nähle, L.; Chen, W. Wavelength Modulation Enhanced Off-Axis Integrated Cavity Output Spectroscopy for OH Radical Measurement at 2.8 Μm. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 362, 114654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Shao, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, K. Research on Trace Gas Measurement by ICOS with WMS. In Proceedings of the Infrared, Millimeter-Wave, and Terahertz Technologies IV, Beijing, China, 12–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chuai, Y.; Li, P.; Lin, G. Near-Infrared Off-Axis Integrated Cavity Output Spectroscopic Dual Greenhouse Gas Sensor Based on FPGA for in Situ Application. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 93901–93909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Huang, Y.; Lu, X.; Huang, J.; Liu, Q.; Qi, G.; Cao, Z. Measurement of CO2 by Wavelength Modulated Reinjection Off-Axis Integrated Cavity Output Spectroscopy at 2 Μm. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Zheng, C.; He, Q.; Yao, D.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tittel, F.K. Near-Infrared Acetylene Sensor System Using Off-Axis Integrated-Cavity Output Spectroscopy and Two Measurement Schemes. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 26205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takebayashi, Y.; Sue, K.; Furuya, T.; Hakuta, Y.; Yoda, S. Near-Infrared Spectroscopic Solubility Measurement for Thermodynamic Analysis of Melting Point Depressions of Biphenyl and Naphthalene under High-Pressure CO2. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2014, 86, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Song, Y.; Ma, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhai, S.; et al. WM-OA-ICOS Based Mid-Infrared Dual-Range Real-Time Trace Sensor for Formaldehyde Detection in Exhaled Breath. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawe, E.; Chambers, P.; Fitzpatrick, C.; Lewis, E. A Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of the Effective Gas Absorption Path Length Exhibited by an Integrating Sphere Containing CO2. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Sensors 2006 Conference, Cancun, Mexico, 23–27 October 2006. TuE71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, I.E.; Rothman, L.S.; Hargreaves, R.J.; Hashemi, R.; Karlovets, E.V.; Skinner, F.M.; Conway, E.K.; Hill, C.; Kochanov, R.V.; Tan, Y.; et al. The HITRAN2020 Molecular Spectroscopic Database. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2022, 277, 107949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.L. Research on Optimization Method of Extreme Learning Machine. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 263–266, 1478–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo-Sanz, S.; Pérez-Aracil, J.; Ascenso, G.; Del Ser, J.; Casillas-Perez, D.; Kadow, C.; Fister, D.; Barriopedro, D.; García-Herrera, R.; Giuliani, M.; et al. Analysis, Characterization, Prediction, and Attribution of Extreme Atmospheric Events with Machine Learning and Deep Learning Techniques: A Review. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2023, 55, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Lin, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. Off-Axis Integral Cavity Carbon Dioxide Gas Sensor Based on Machine-Learning-Based Optimization. Sensors 2024, 24, 5226. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24165226
Li P, Lin G, Chen J, Wang J. Off-Axis Integral Cavity Carbon Dioxide Gas Sensor Based on Machine-Learning-Based Optimization. Sensors. 2024; 24(16):5226. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24165226
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Pengbo, Guanyu Lin, Jianbo Chen, and Jianing Wang. 2024. "Off-Axis Integral Cavity Carbon Dioxide Gas Sensor Based on Machine-Learning-Based Optimization" Sensors 24, no. 16: 5226. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24165226
APA StyleLi, P., Lin, G., Chen, J., & Wang, J. (2024). Off-Axis Integral Cavity Carbon Dioxide Gas Sensor Based on Machine-Learning-Based Optimization. Sensors, 24(16), 5226. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24165226




