Moho Imaging with Fiber Borehole Strainmeters Based on Ambient Noise Autocorrelation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
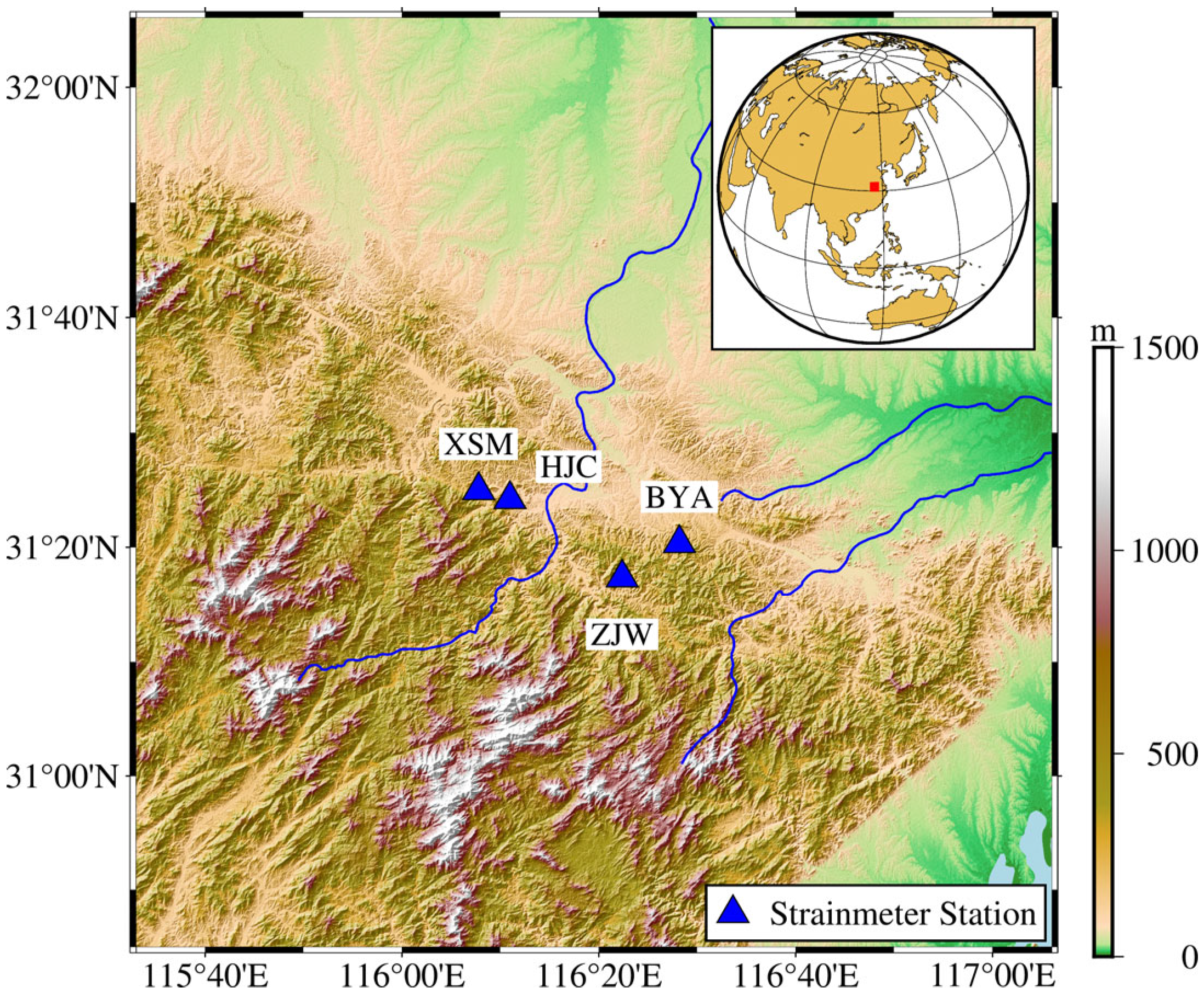
2.1. Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Data Preprocessing
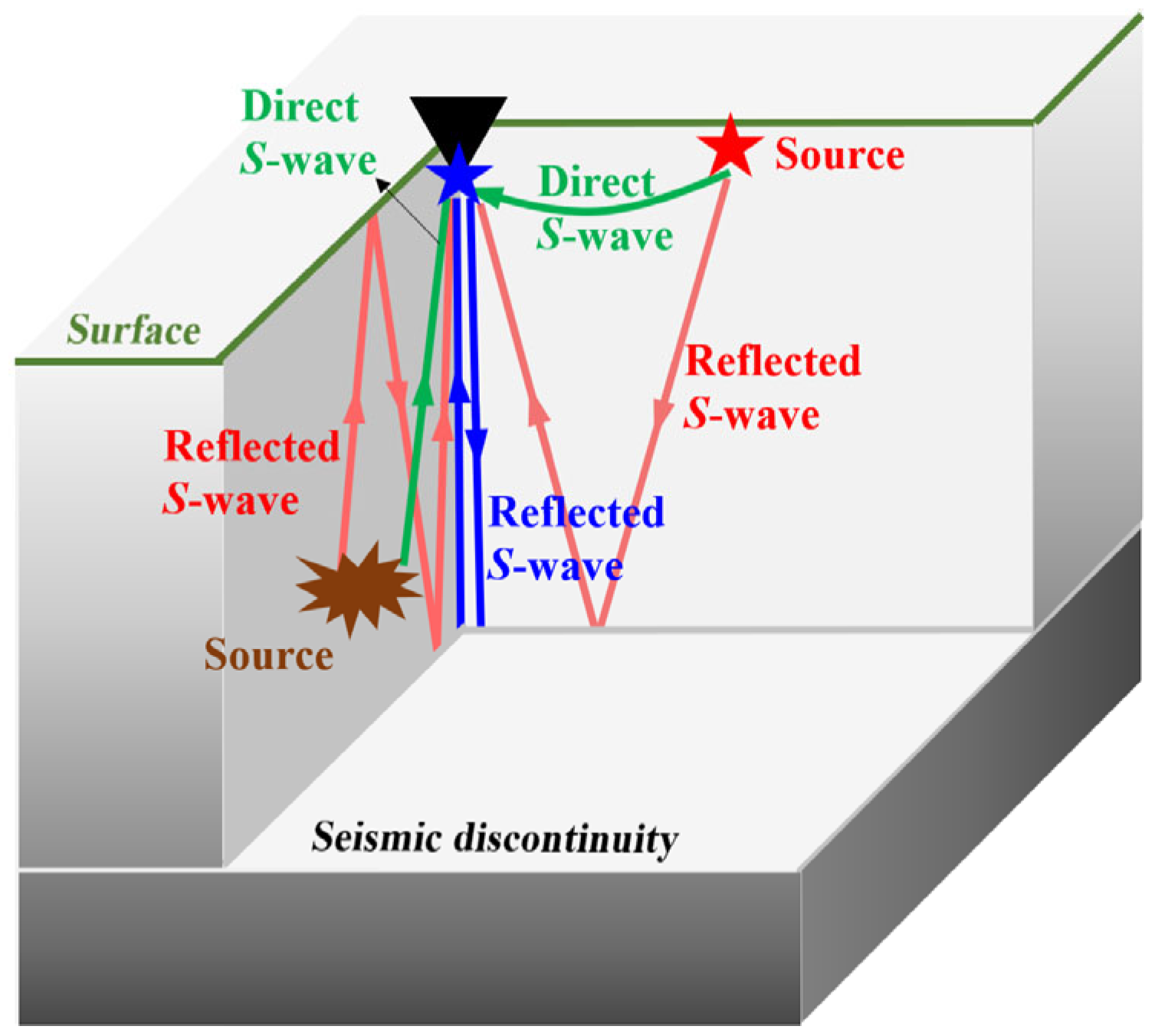
2.2.2. Phase Autocorrelation and Stacking
2.2.3. Time-Deep Conversion
3. Results
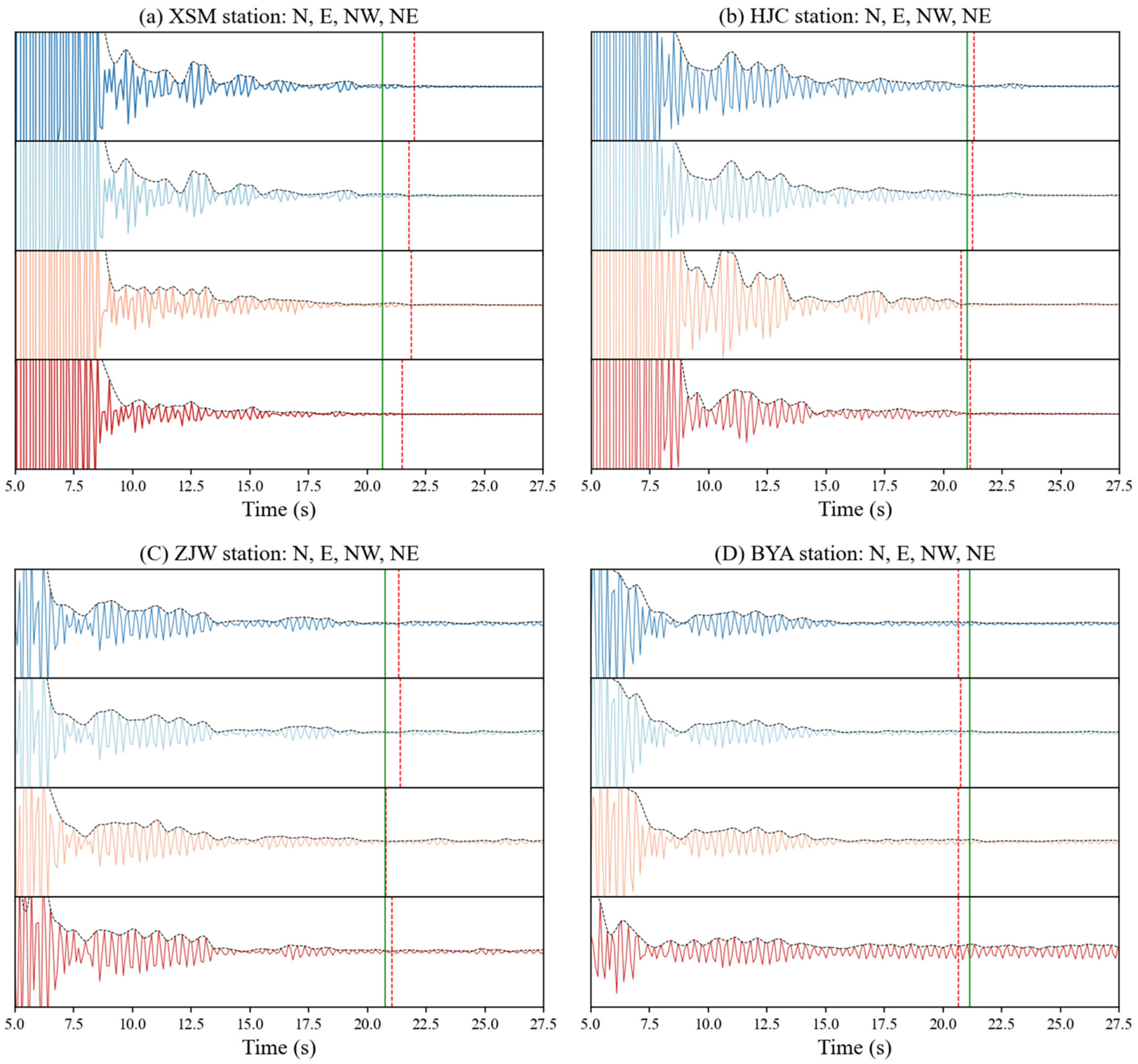
4. Discussion
| Amount of Data Required for PAC Stabilization (Days) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Station | XSM-E | XSM-N | XSM-NW | XSM-NE |
| Without quality control measures | 103.75 | 94.50 | 110.50 | 65.50 |
| Applying quality control measures | 85.00 | 75.00 | 90.75 | 60.00 |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, L.; Kanamori, H. Moho depth variation in southern California from teleseismic receiver functions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 2969–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittlinger, G.; Vergne, J.; Tapponnier, P.; Farra, V.; Poupinet, G.; Jiang, M.; Su, H.; Herquel, G. Teleseismic imaging of subducting lithosphere and Moho offsets beneath western Tibet. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2004, 221, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Artola, O.; Iglesias, A.; Schimmel, M.; Cordoba-Montiel, F. Moho reflections within seismic noise autocorrelations. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2022, 120, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.Q.; Chen, L.; Chevrot, S.; Talebian, M.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.F.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wu, Z.M.; Shokati, M.; Jiang, M.M.; et al. Structure of the Western Jaz Murian Forearc Basin, Southeast Iran, Revealed by Autocorrelation and Polarization Analysis of Teleseismic P and S Waves. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2022, 127, e2021JB023456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, F. Review on Low-noise Broadband Fiber Optic Seismic Sensor and its Applications. J. Light. Technol. 2023, 41, 4153–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, S.; Lindsey, N.; Wagner, A.M.; Daley, T.M.; Freifeld, B.; Robertson, M.; Peterson, J.; Ulrich, C.; Martin, E.R.; Ajo-Franklin, J.B. Distributed Acoustic Sensing for Seismic Monitoring of The Near Surface: A Traffic-Noise Interferometry Case Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, A.; Ajo-Franklin, J. Measurement of Surface-Wave Phase-Velocity Dispersion on Mixed Inertial Seismometer—Distributed Acoustic Sensing Seismic Noise Cross-Correlations. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2021, 111, 3432–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Atterholt, J.W.; Shen, Z.C.; Muir, J.B.; Williams, E.F.; Zhan, Z.W. Sub-Kilometer Correlation Between Near-Surface Structure and Ground Motion Measured With Distributed Acoustic Sensing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Butcher, A.; Brisbourne, A.M.; Kufner, S.K.; Kendall, J.M.; Stork, A.L. Seismic Noise Interferometry and Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS): Inverting for the Firn Layer S-Velocity Structure on Rutford Ice Stream, Antarctica. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2022, 127, 1153938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibuleac, I.M.; von Seggern, D. Crust-mantle boundary reflectors in Nevada from ambient seismic noise autocorrelations. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 189, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennett, B.L.N.; Saygin, E.; Salmon, M. Stacking autocorrelograms to map Moho depth with high spatial resolution in southeastern Australia. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 7490–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, G.; Knapmeyer-Endrun, B. Crustal thickness across the Trans-European Suture Zone from ambient noise autocorrelations. Geophys. J. Int. 2018, 212, 1237–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, G.; Knapmeyer-Endrun, B. Crustal thickness from horizontal component seismic noise auto- and cross-correlations for stations in Central and Eastern Europe. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 218, 429–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claerbout, J.F. Synthesis of a layered medium from its acoustic transmission response. Geophysics 1968, 33, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-García, C.; Lebedev, S.; Meier, T.; Xu, Y.; Le Pape, F.; Wiesenberg, L. Ambient noise autocorrelation scheme for imaging theP-wave reflectivity of the lithosphere. Geophys. J. Int. 2023, 233, 1671–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroczek, S.; Tilmann, F. Joint ambient noise autocorrelation and receiver function analysis of the Moho. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 225, 1920–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yao, H.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Shu, P.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, P.; Luo, J. High resolution upper crustal velocity and seismogenic structure of the Huoshan “seismic window” in the Dabie orogenic belt. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1110061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Zeng, R.S.; Mooney, W.D.; Hacker, B. A crustal model of the ultrahigh-pressure Dabie Shan orogenic belt, China, derived from deep seismic refraction profiling. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2000, 105, 10857–10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Yang, Z.; Tian, X.; Liu, B.; Zheng, C.; Song, X.; Gao, Z.; Qiu, Y. Crustal structure and its tectonic implications beneath the middle–lower Yangtze metallogenic belt in Anhui Province: 3D deep seismic sounding results from airgun source in inland waters. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1153938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Huang, W.; Wu, Q. Fiber optic sensors for seismic wave detection. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Information Optics and Photonics (CIOP 2022), Xi’an, China, 7–10 August 2022; pp. 599–603. [Google Scholar]
- Bensen, G.D.; Ritzwoller, M.H.; Barmin, M.P.; Levshin, A.L.; Lin, F.; Moschetti, M.P.; Shapiro, N.M.; Yang, Y. Processing seismic ambient noise data to obtain reliable broad-band surface wave dispersion measurements. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 169, 1239–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, G.T. Seismic Interferometry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel, M. Phase cross-correlations: Design, comparisons, and applications. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1999, 89, 1366–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmel, M.; Stutzmann, E.; Gallart, J. Using instantaneous phase coherence for signal extraction from ambient noise data at a local to a global scale. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 184, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmel, M.; Paulssen, H. Noise reduction and detection of weak, coherent signals through phase-weighted stacks. Geophys. J. Int. 1997, 130, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laske, G.; Masters, G.; Ma, Z.; Pasyanos, M. Update on CRUST1.0—A 1-degree global model of Earth’s crust. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2013, 15, 2658. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Q.; Li, D.; Ding, Z.; Kang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Meng, K.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Lv, Y. Crustal structure characteristics beneath the Shandong-Jiangsu-Anhui segment of the Tan-Lu fault zone and its adjacent regions using receiver functions. Chin. J. Geophys. 2022, 65, 3280–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Chen, X.; Zhan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Z. Characteristics of deep electrical structure and seismogenic structure beneath Anhui Huoshan earthquake area. Chin. J. Geophys. 2020, 63, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Xiao, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, W.; Sun, L.; Wang, X.; Wen, L. Crustal thickness and Vp/Vs variation beneath continental China revealed by receiver function analysis. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 228, 1731–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.; Rost, S.; Houseman, G. Crustal imaging across the North Anatolian Fault Zone from the autocorrelation of ambient seismic noise. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 2502–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventosa, S.; Schimmel, M.; Stutzmann, E. Extracting surface waves, hum and normal modes: Time-scale phase-weighted stack and beyond. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 211, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmel, M.; Gallart, J. Frequency-dependent phase coherence for noise suppression in seismic array data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.; Zaccarelli, L.; Shapiro, N.M.; Brenguier, F. Assessment of resolution and accuracy of the Moving Window Cross Spectral technique for monitoring crustal temporal variations using ambient seismic noise. Geophys. J. Int. 2011, 186, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, C.; Nowack, R.L. Seismic body-wave interferometry using noise autocorrelations for crustal structure. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 208, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffoni, C.; Schimmel, M.; Sabbione, N.C.; Rosa, M.L.; Connon, G. Crustal structure beneath Tierra del Fuego, Argentina, inferred from seismic P-wave receiver functions and ambient noise autocorrelations. Tectonophysics 2019, 751, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, H.H. Notes on the use of propagation of error formulas. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1966, 70C, 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- Liou, J.G.; Zhang, R.Y.; Eide, E.A.; Maruyama, S.; Wang, X.; Ernst, W.G. Metamorphism and tectonics of high-P and ultrahigh-P belts in Dabie-Sulu Regions, eastern central China. In The Tectonic Evolution of Asia; Yin, A., Harrison, T.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 300–344. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.-c.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J. Crustal structure and anisotropy beneath the Anhui province and its surroundings revealed by teleseismic receiver functions. Prog. Geophys. 2019, 34, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, P.; Smith, W. New, improved version of Generic Mapping Tools released. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1998, 79, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Station | Moho S-Wave Reflection Time (s) | Moho Depth (km) | Moho Depth in Cheng et al. (2021) [29] (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| XSM | 21.79 ± 0.19 | 38.88 ± 2.82 | 36.86 ± 3.61 |
| BYA | 20.69 ± 0.04 | 36.90 ± 2.42 | 37.47 ± 4.14 |
| HJC | 21.11 ± 0.21 | 37.66 ± 2.79 | 37.04 ± 3.70 |
| ZJW | 21.15 ± 0.24 | 37.73 ± 2.86 | 37.72 ± 4.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, G.; Huang, W.; Pan, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G. Moho Imaging with Fiber Borehole Strainmeters Based on Ambient Noise Autocorrelation. Sensors 2024, 24, 4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134252
Qi G, Huang W, Pan X, Zhang W, Zhang G. Moho Imaging with Fiber Borehole Strainmeters Based on Ambient Noise Autocorrelation. Sensors. 2024; 24(13):4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134252
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Guoheng, Wenzhu Huang, Xinpeng Pan, Wentao Zhang, and Guanxin Zhang. 2024. "Moho Imaging with Fiber Borehole Strainmeters Based on Ambient Noise Autocorrelation" Sensors 24, no. 13: 4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134252
APA StyleQi, G., Huang, W., Pan, X., Zhang, W., & Zhang, G. (2024). Moho Imaging with Fiber Borehole Strainmeters Based on Ambient Noise Autocorrelation. Sensors, 24(13), 4252. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134252







