Detecting Near-Surface Sub-Millimeter Voids in Additively Manufactured Ti-5V-5Al-5Mo-3Cr Alloy Using a Transmit-Receive Eddy Current Probe
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Motivation
1.2. Theory
1.3. Finite Element Modelling
2. Experimental Technique
2.1. Materials
2.2. Probe
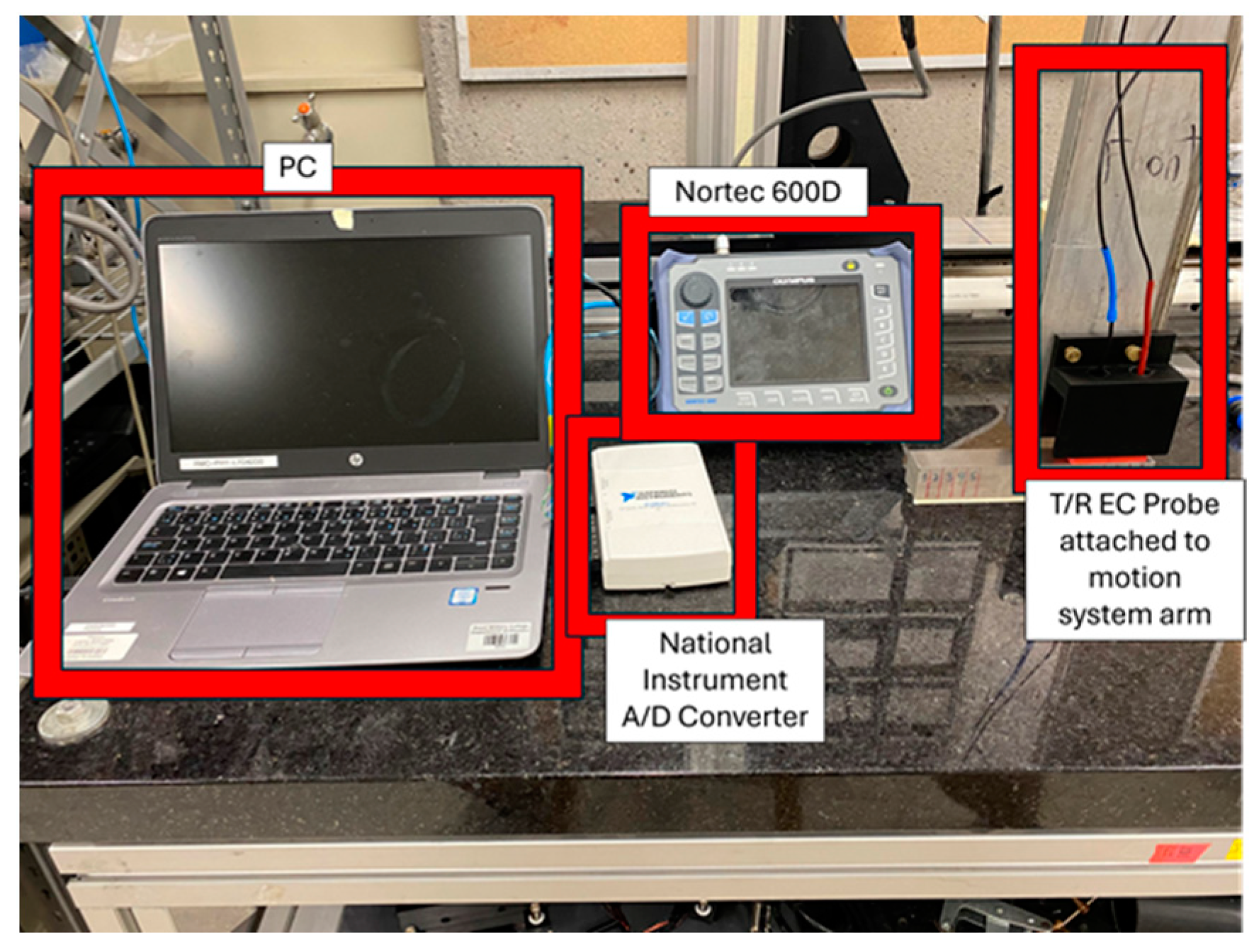
2.3. Apparatus
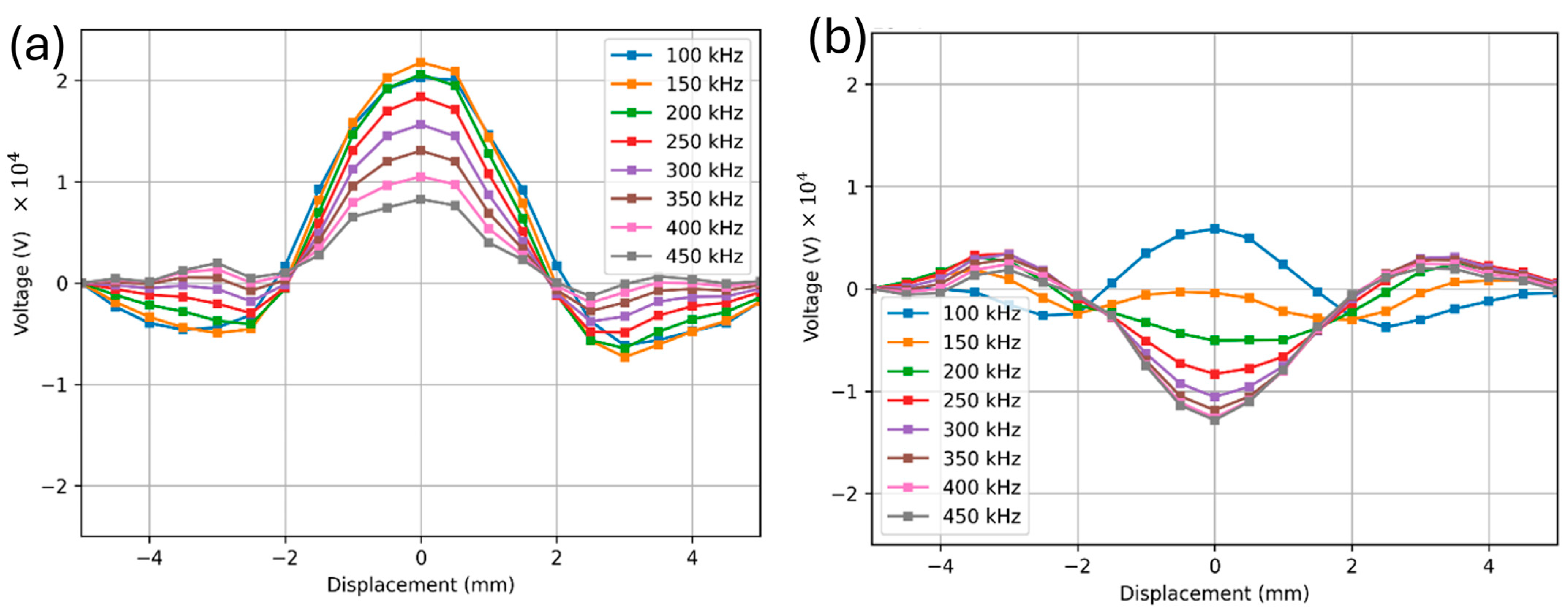
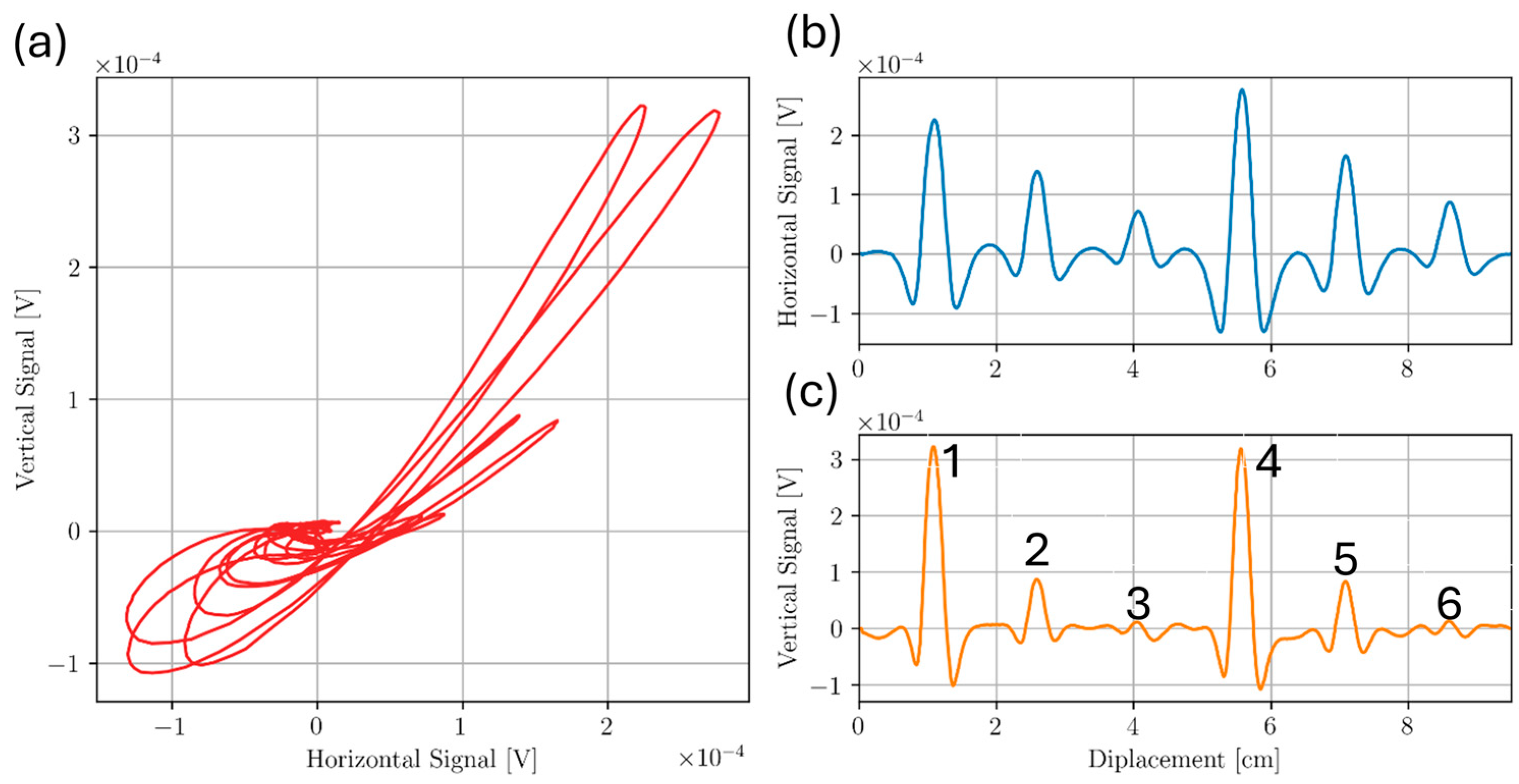
3. Results and Discussion
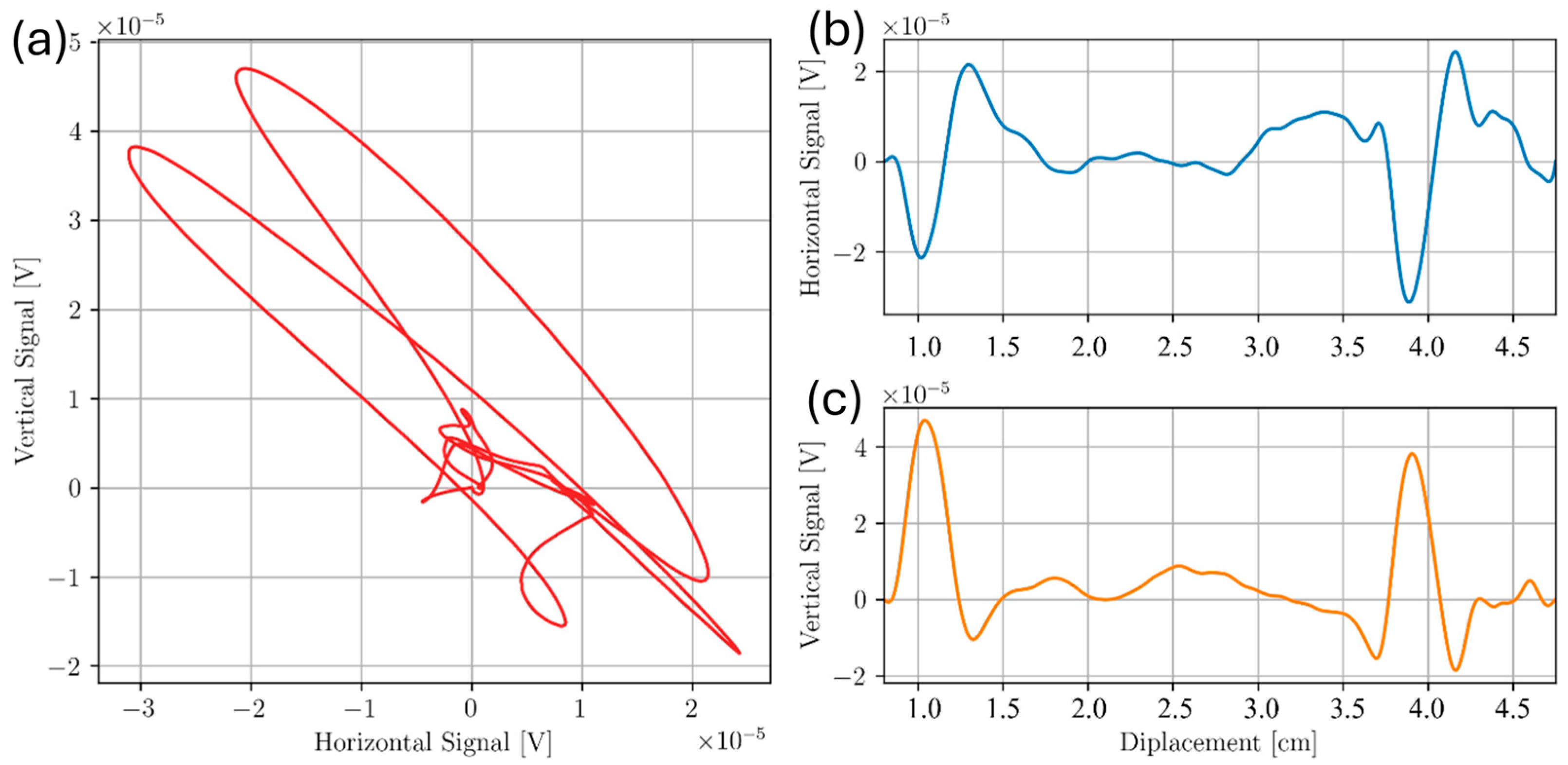
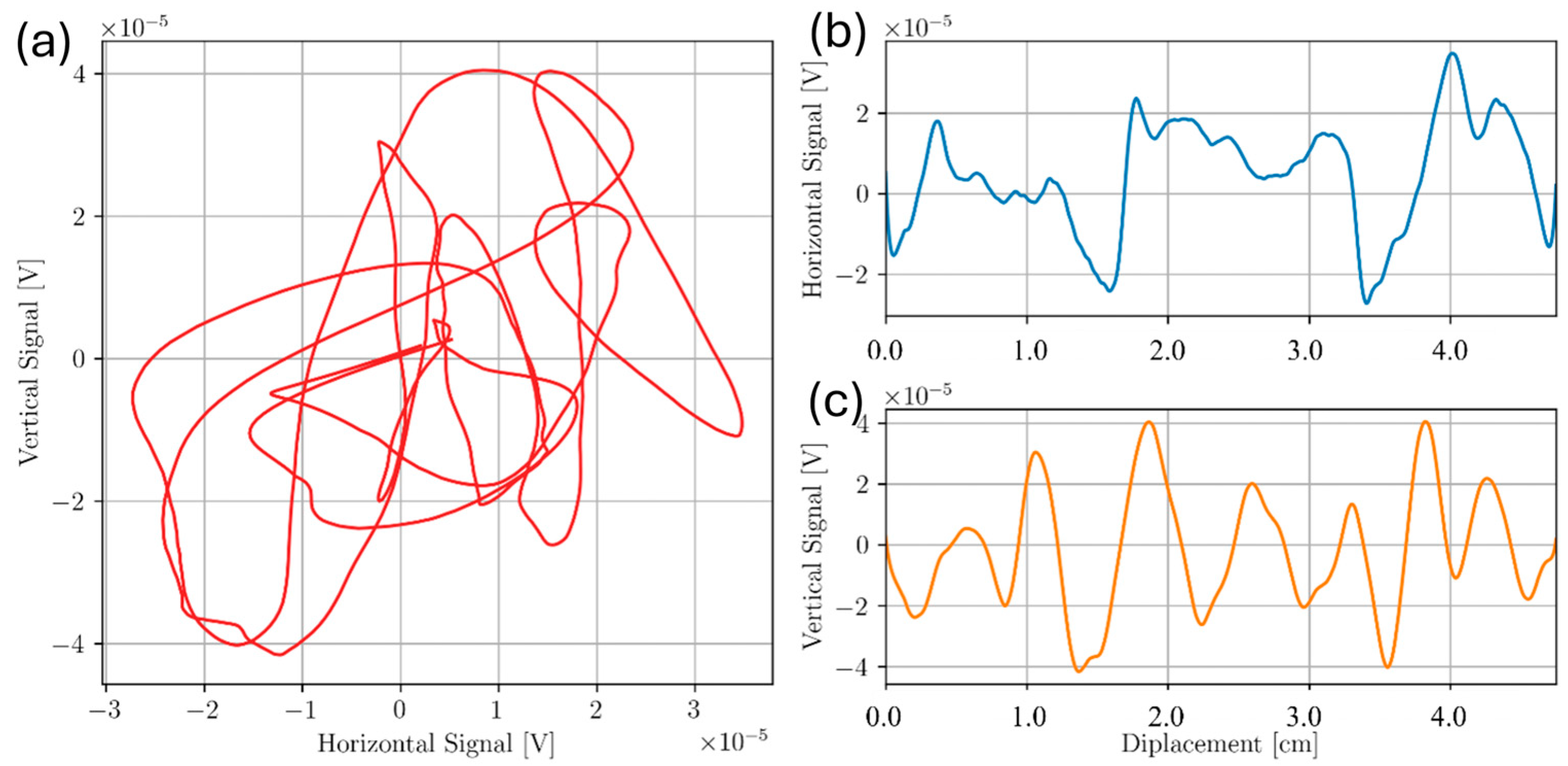
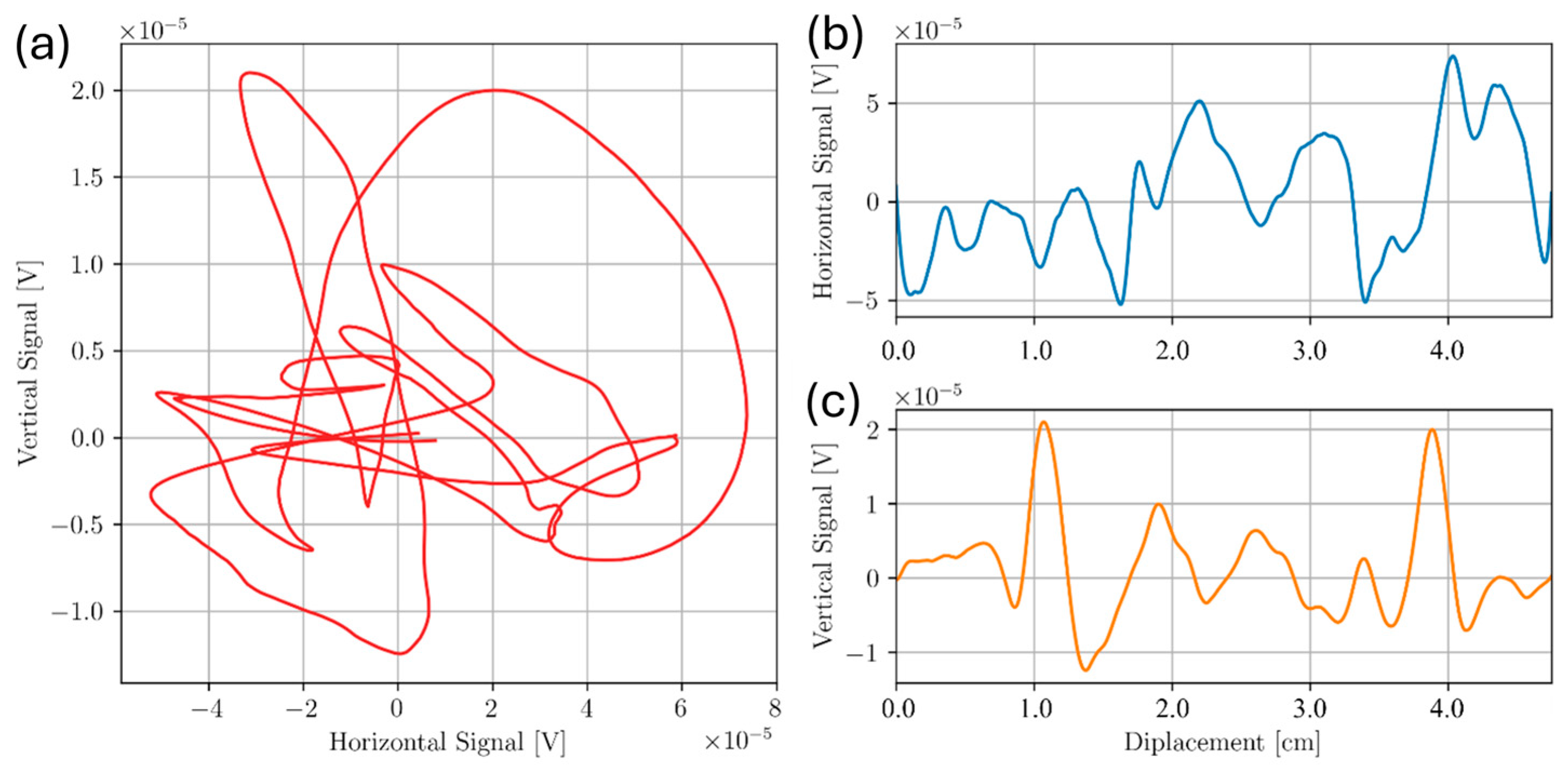
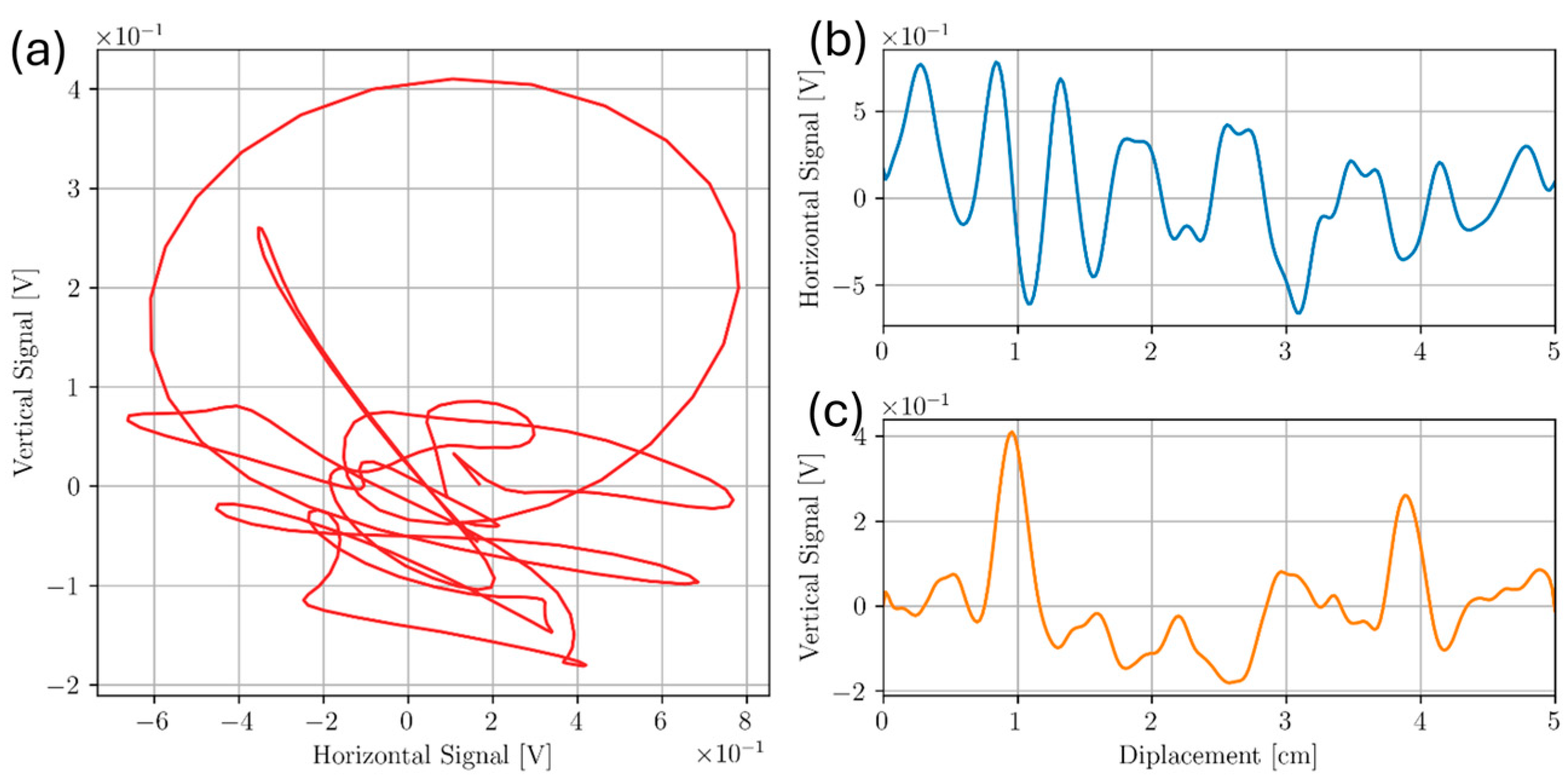
3.1. Sample D
3.2. Sample A
3.3. Sample C
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El Cheikh, H.; Courant, B.; Branchu, S.; Huang, X.; Hascot, J.Y.; Guilln, R. Direct Laser Fabrication process with coaxial powder projection of 316L steel. Geometrical characteristics and microstructure characterization of wall structures. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2012, 50, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebecca, L. Additive Manufacturing, Explained|MIT Sloan. Available online: https://mitsloan.mit.edu/ideas-made-to-matter/additive-manufacturing-explained (accessed on 17 March 2024).
- Nyamekye, P.; Leino, M.; Piili, H.; Salminen, A. Overview of Sustainability Studies of CNC Machining and LAM of Stainless Steel. Phys. Procedia 2015, 78, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, M.; Caterino, M.; Manco, P.; Fera, M.; Macchiaroli, R. The impact of Additive Manufacturing on Supply Chain design: A simulation study. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 180, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, T.J.; Hwang, T.W.; Yun, H.J.; VanTyne, C.J.; Moon, Y.H. Control of Porosity in Parts Produced by a Direct Laser Melting Process. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.M.J.; Bordonaro, G.G.; Ferro, P.; Torgersen, J.; Berto, F. Fatigue Behavior of Porous Ti-6Al-4V Made by Laser-Engineered Net Shaping. Materials 2018, 11, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Kumar, A.; Bukkapatnam, S.; Kuttolamadom, M. A Review of the Anomalies in Directed Energy Deposition (DED) Processes & Potential Solutions—Part Quality & Defects. Procedia Manuf. 2021, 53, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarfors, A.E.W.; Matsushita, T.; Siafakas, D.; Stolt, R. On the nature of the anisotropy of Maraging steel (1.2709) in additive manufacturing through powder bed laser-based fusion processing. Mater. Des. 2021, 204, 109608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benstock, D.; Cegla, F.; Stone, M. The influence of surface roughness on ultrasonic thickness measurements. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, 3028–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Turner, J.A.; Song, Y.; Ni, P.; Li, X. Enhanced ultrasonic detection of near-surface flaws using transverse-wave backscatter. Ultrasonics 2019, 98, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Tian, Q.; Hu, P.; Li, H.; Shen, S. Laser ultrasonic detection of submillimeter artificial holes in laser powder bed fusion manufactured alloys. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 169, 110030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuljan, D.; Zhou, Z. Effect of ultrasonic coupling media and surface roughness on contact transfer loss. Cogent Eng. 2022, 9, 2009092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, D.E.; Stanley, R.K. Nondestructive Evaluation: A Tool in Design, Manufacturing and Service; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecco, V.S.; Van Drunen, G.; Sharp, F.L. Atomic Energy of Canada Limited Eddy Current Manual Volume 1 Test Method; Chalk River Nuclear Laboratories: Chalk River, ON, Canada, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Babbar, V.K.; Lepine, B.; Buck, J.; Underhill, P.R.; Morelli, J.; Krause, T.W. Finite element modeling of wall-loss sizing in a steam generator tube using a pulsed eddy current probe. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1650, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, C.A.; Underhill, P.R.; Babbar, V.K.; Krause, T.W. Pulsed eddy current detection of cracks in multilayer aluminum lap joints. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, T.W.; Underhill, P.R. Selecting the correct electromagnetic inspection technology. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2019, 10, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, S. Mathematical Modeling of x-Probe Eddy Current Array Coils Used in Tube Inspection. CINDE J. 2004, 25, 6–11. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/etdeweb/biblio/20777845 (accessed on 17 March 2024).
- Obrutsky, L.; Lepine, B.; Lu, J.; Cassidy, R.; Carter, J. Eddy current technology for heat exchanger and steam generator tube inspection. In Proceedings of the Sixteenth World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, Montreal, QC, Canada, 30 August–3 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Obrutsky, L.S.; Sullivan, S.P.; Cecco, V.S. Transmit-Receive Eddy Current Probes. Chalk River. 1996. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/etdeweb/biblio/662700 (accessed on 17 March 2024).
- Geľatko, M.; Hatala, M.; Botko, F.; Vandžura, R.; Hajnyš, J. Eddy Current Testing of Artificial Defects in 316L Stainless Steel Samples Made by Additive Manufacturing Technology. Materials 2022, 15, 6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AISI Type 316L Stainless Steel, Annealed Sheet. Available online: https://www.matweb.com/search/datasheet_print.aspx?matguid=1336be6d0c594b55afb5ca8bf1f3e042 (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Spurek, M.A.; Spierings, A.B.; Lany, M.; Revaz, B.; Santi, G.; Wicht, J.; Wegener, K. In-situ monitoring of powder bed fusion of metals using eddy current testing. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 60, 103259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Tong, J.; Sheng, Z. Topology Optimization Considering Porosity Defects in Metal Additive Manufacturing. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecco, V.S.; Sullivan, S.P.; Carter, J.R.; Obrutsky, L.S. Innovations in Eddy Current Testing; Chalk River Laboratories: Chalk River, ON, Canada, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Nelligan, T.; Calderwood, C. Introduction to Eddy Current Testing | Olympus IMS. Available online: https://www.olympus-ims.com/en/ndt-tutorials/eca-tutorial/intro/ (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Griffiths, D.J. Introduction to Electrodynamics, 4th ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, J.D. Classical Electrodynamics, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Buck, J.A.; Underhill, P.R.; Mokros, S.G.; Morelli, J.E.; Babbar, V.K.; Lepine, B.; Renaud, J.; Krause, T.W. Pulsed eddy current inspection of support structures in steam generators. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 4305–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multifrequency Eddy Current Signal Analysis; Iowa State University Digital Repository: Ames, IA, USA, 1997; Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Multifrequency-eddy-current-signal-analysis-Avanindra/f3090f82dd83751be243018ed7cd4c9ff932d4f5 (accessed on 17 March 2024).
- Jung, H.J.; Song, S.J.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, D.K. A Study of Frequency Mixing Approaches for Eddy Current Testing of Steam Generator Tubes. J. Korean Soc. Nondestruct. Test. 2009, 29, 579–585. Available online: https://www.dbpia.co.kr/Journal/articleDetail?nodeId=NODE02198808 (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Mottl, Z. The quantitative relations between true and standard depth of penetration for air-cored probe coils in eddy current testing. NDT Int. 1990, 23, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mook, G.; Uchanin, V.; Hesse, O.; Deep Penetrating Eddy Currents and Probes. In 9th European Conference on NDT, Berlin, Germany: E-Journal of Nondestructive Testing, Nov. 2006. Available online: https://www.ndt.net/search/docs.php3?id=3740 (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Lu, Y.; Bowler, J.R. An analytical model of eddy current ferrite-core probes. AIP Conf. Proc. 2012, 1430, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, P.; Zhou, E.; Morton, D. The design of a ferrite-cored probe. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007 136, 221–228. [CrossRef]
- Properties of Grade 5 Titanium (Ti6Al4V or Ti 6-4)—Parts Badger. Available online: https://parts-badger.com/properties-of-grade-5-titanium/ (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Ahmed, M.; Obeidi, M.A.; Yin, S.; Lupoi, R. Influence of processing parameters on density, surface morphologies and hardness of as-built Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr alloy manufactured by selective laser melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 910, 164760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Luo, F.-L.; Sun, H.-X. Impedance Evaluation of a Probe-Coil’s Lift-off and Tilt Effect in Eddy-Current Nondestructive Inspection by 3D Finite Element Modeling. In Proceedings of the 17th World Conference on Nondestructive Testing, Shanghai, China, 25–28 October 2008; Special Issue of e-Journal of Nondestructive Testing, November 2008. pp. 25–28. Available online: https://www.ndt.net/search/docs.php3?id=6585 (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Le Bihan, Y. Lift-off and tilt effects on eddy current sensor measurements: A 3-D finite element study. EPJ Appl. Phys. 2002, 17, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





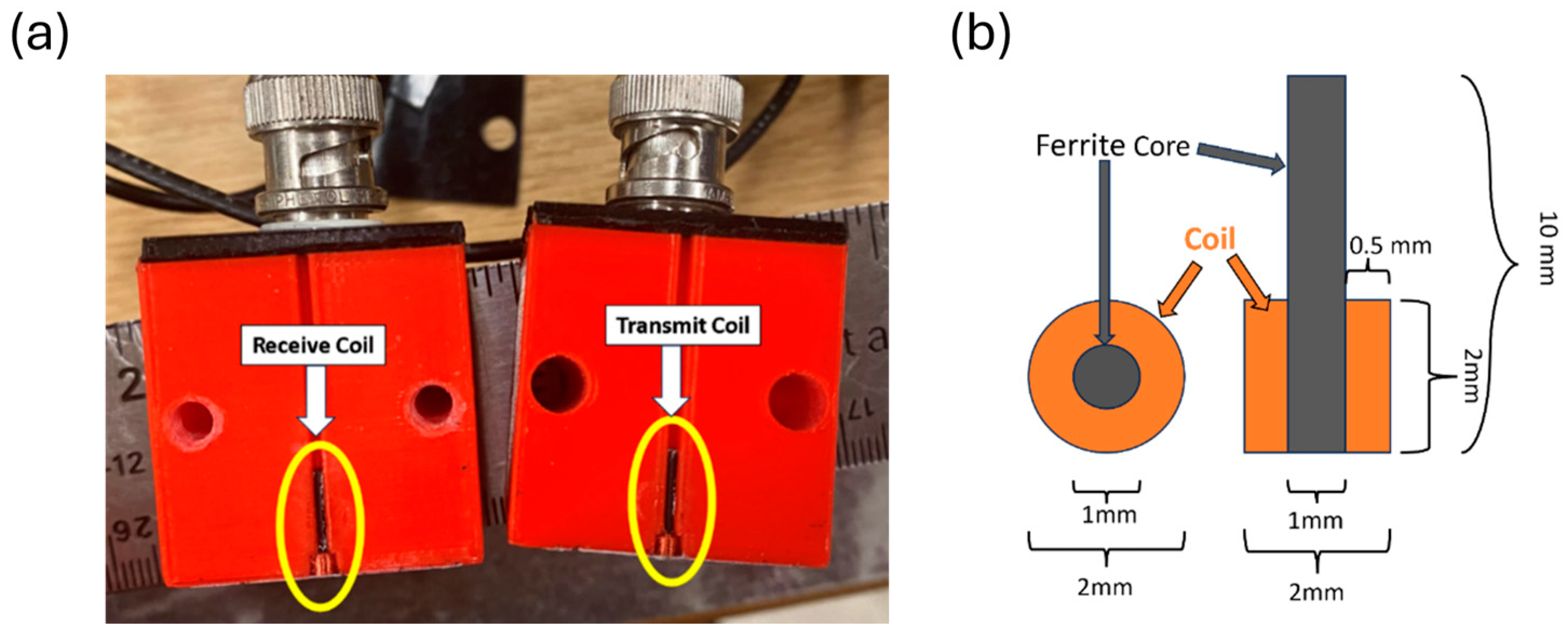


| Coil Parameters | ET Array Probe | FEM Starting | FEM Optimized | Physical Probe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coil OD (mm) | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 2 | 2 | 2.50 ± 0.03 |
| Coil ID (mm) | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 1 | 1 | 1.00 ± 0.03 |
| Coil Height (mm) | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 2 | 2 | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| Wire Gauge (AWG) | 44 | 44 | 44 | 44 |
| Number of turns | 320 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| Frequency (kHz) | 1000 | 354 | 100 | Various |
| Coil-Coil separation (mm) | 2.0 ± 0.1 | 2.5 | 4 | 4 ± 0.1 |
| Ti5553 Sample | Dimensions (Height × Width × Length) | Flaw Number and Type | Flaw Dimensions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 3 × 3 × 19 cm3 | 12 subsurface voids | 500 µm nominal diameter | ||
| B | 3 × 3 × 19 cm3 | 10 side drilled holes | Side Drill Hole Number | Diameter (mm) | Depth from inspection surface (mm) |
| 1 | 0.58 | 0.75 | |||
| 2 | 0.58 | 1.25 | |||
| 3 | 0.58 | 1.75 | |||
| 4 | 0.58 | 2.25 | |||
| 5 | 0.58 | 2.75 | |||
| 6 | 0.79 | 3.25 | |||
| 7 | 0.79 | 2.75 | |||
| 8 | 0.79 | 2.25 | |||
| 9 | 0.79 | 1.75 | |||
| 10 | 0.79 | 1.25 | |||
| C | 1 × 1 × 7 cm3 | 4 subsurface voids | 500 µm nominal diameter | ||
| D | 3 mm × 3 cm × 19 cm | 6 bottom drilled holes | Bottom Drill Hole Number | Diameter (±0.008 mm) | Depth from inspection surface (±0.02 mm) |
| 1 | 0.787 | 0.46 | |||
| 2 | 0.787 | 0.96 | |||
| 3 | 0.787 | 1.46 | |||
| 4 | 0.991 | 0.46 | |||
| 5 | 0.991 | 0.96 | |||
| 6 | 0.991 | 1.46 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halliday, B.S.; Eastmure, A.; Underhill, P.R.; Krause, T.W. Detecting Near-Surface Sub-Millimeter Voids in Additively Manufactured Ti-5V-5Al-5Mo-3Cr Alloy Using a Transmit-Receive Eddy Current Probe. Sensors 2024, 24, 4183. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134183
Halliday BS, Eastmure A, Underhill PR, Krause TW. Detecting Near-Surface Sub-Millimeter Voids in Additively Manufactured Ti-5V-5Al-5Mo-3Cr Alloy Using a Transmit-Receive Eddy Current Probe. Sensors. 2024; 24(13):4183. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134183
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalliday, Brendan Sungjin, Allyson Eastmure, Peter Ross Underhill, and Thomas Walter Krause. 2024. "Detecting Near-Surface Sub-Millimeter Voids in Additively Manufactured Ti-5V-5Al-5Mo-3Cr Alloy Using a Transmit-Receive Eddy Current Probe" Sensors 24, no. 13: 4183. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134183
APA StyleHalliday, B. S., Eastmure, A., Underhill, P. R., & Krause, T. W. (2024). Detecting Near-Surface Sub-Millimeter Voids in Additively Manufactured Ti-5V-5Al-5Mo-3Cr Alloy Using a Transmit-Receive Eddy Current Probe. Sensors, 24(13), 4183. https://doi.org/10.3390/s24134183






