Recent Advances in the Development of Portable Electrochemical Sensors for Controlled Substances
Abstract
1. Introduction
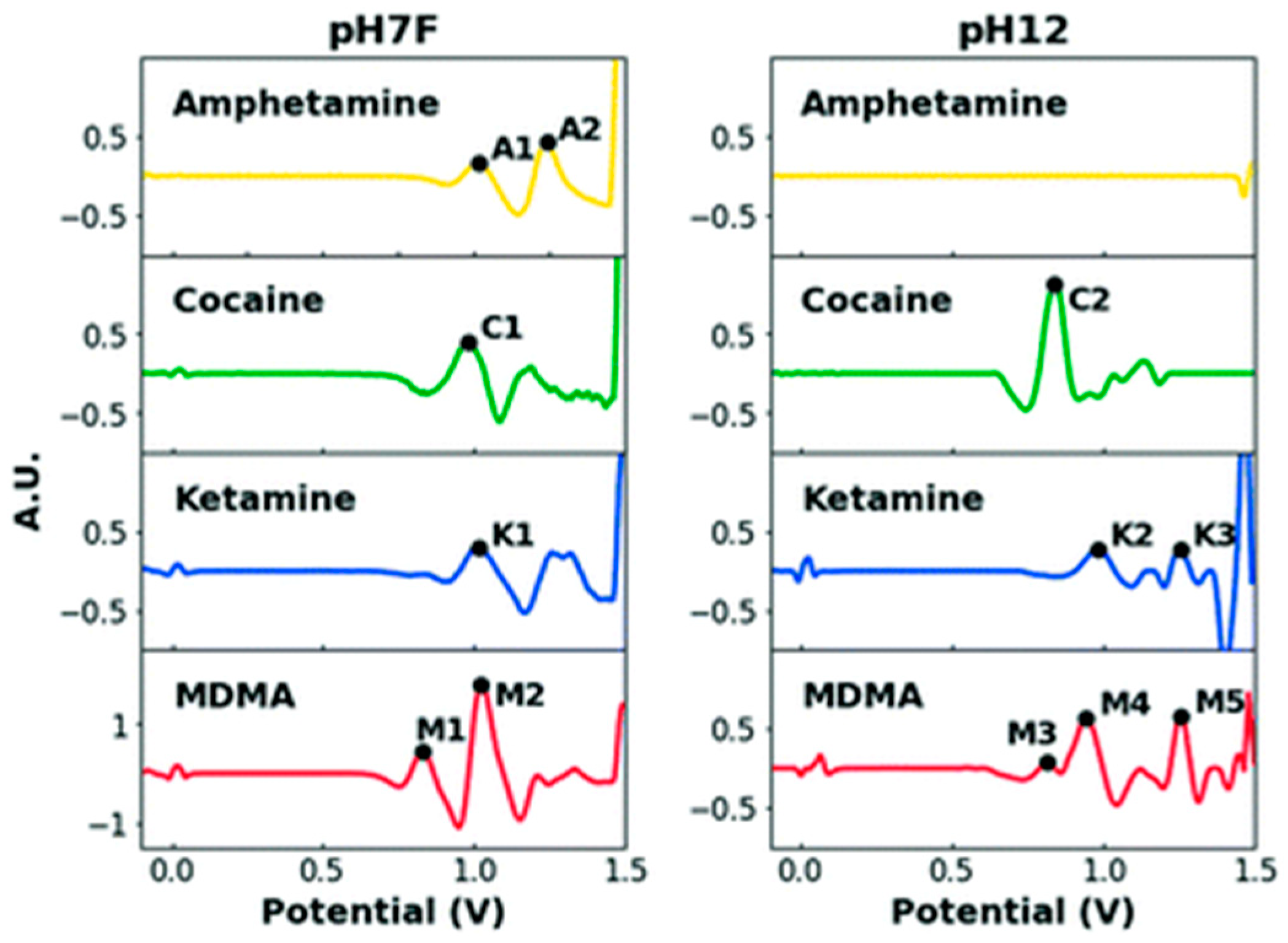
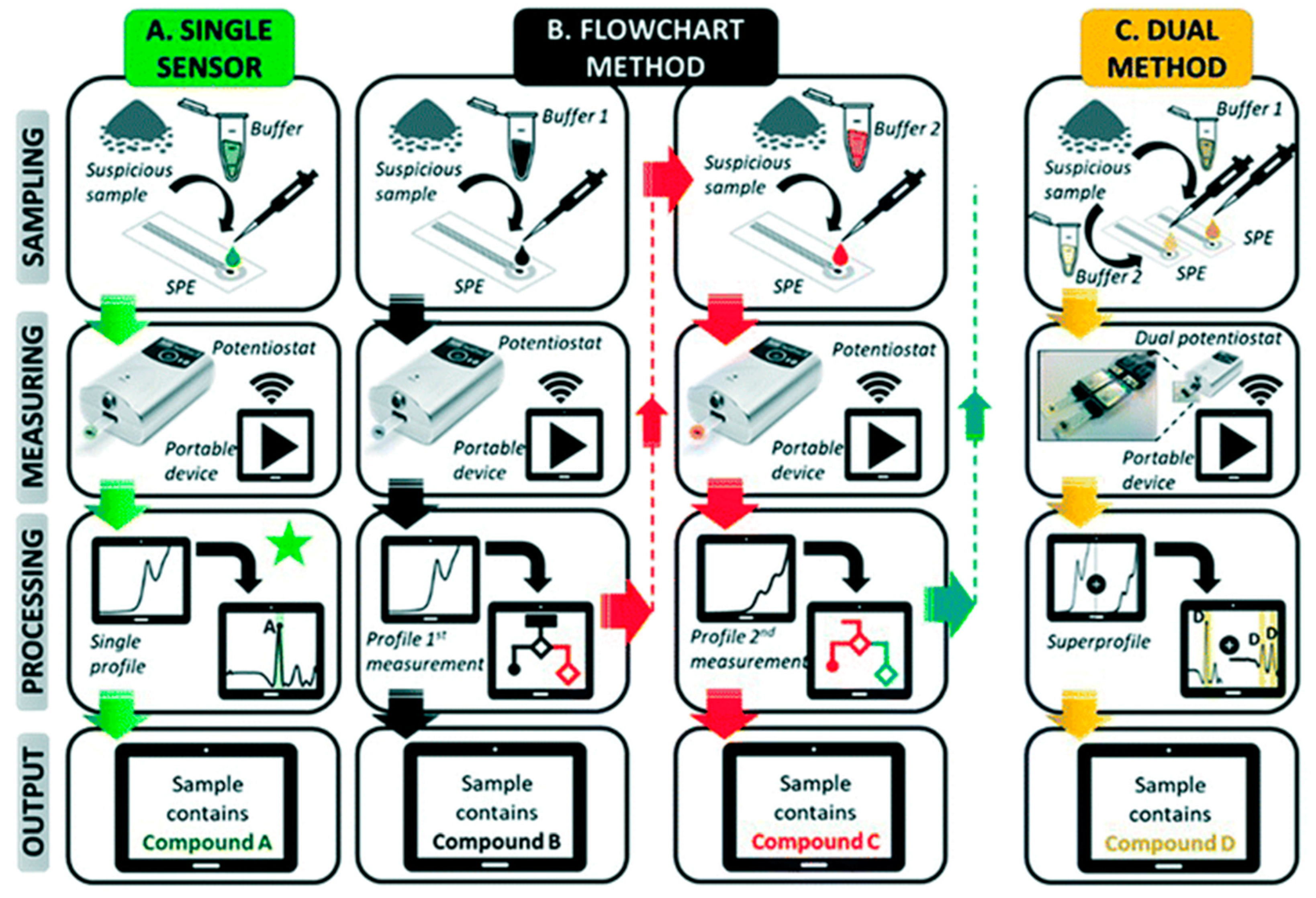
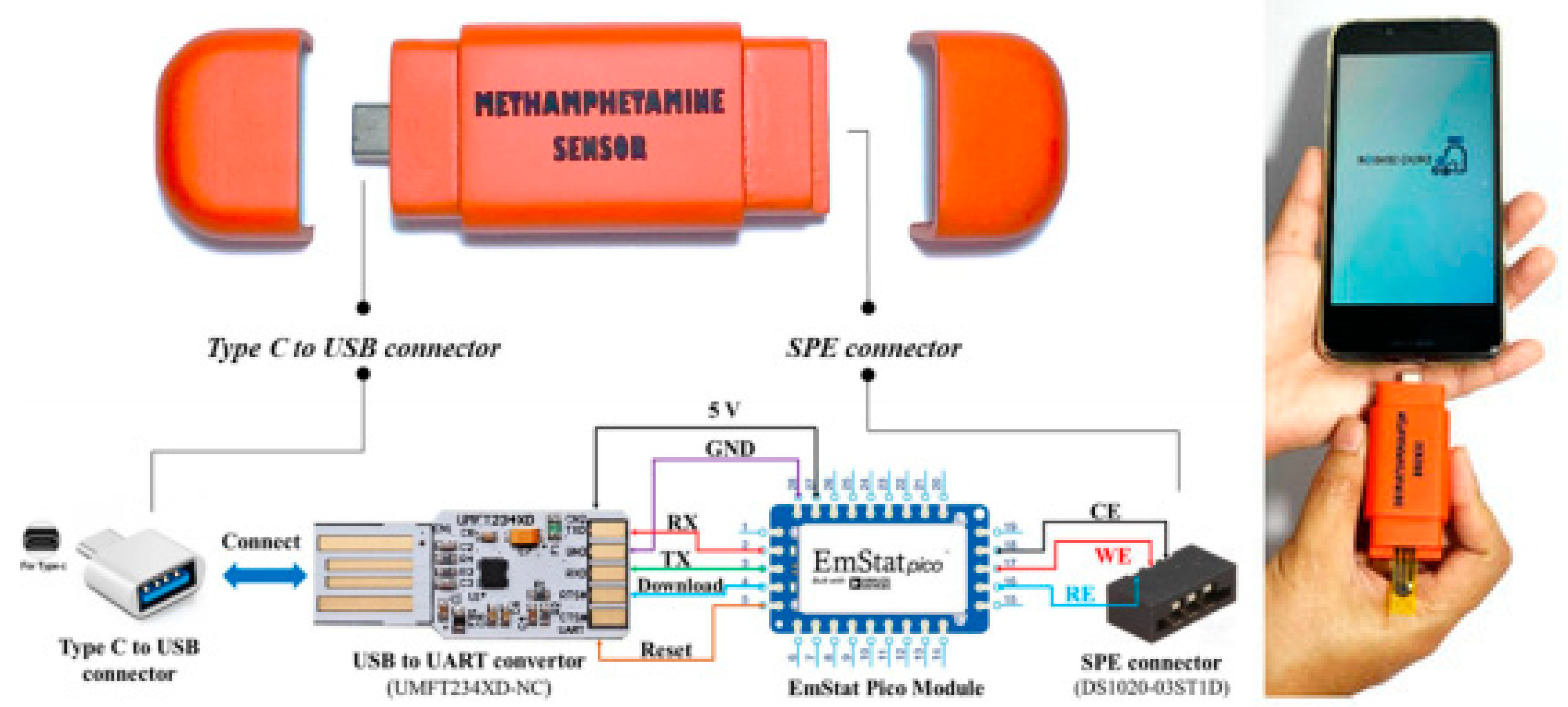
2. Sensing Using Commercially Available Carbon Screen-Printed Electrodes and Portable Potentiostats
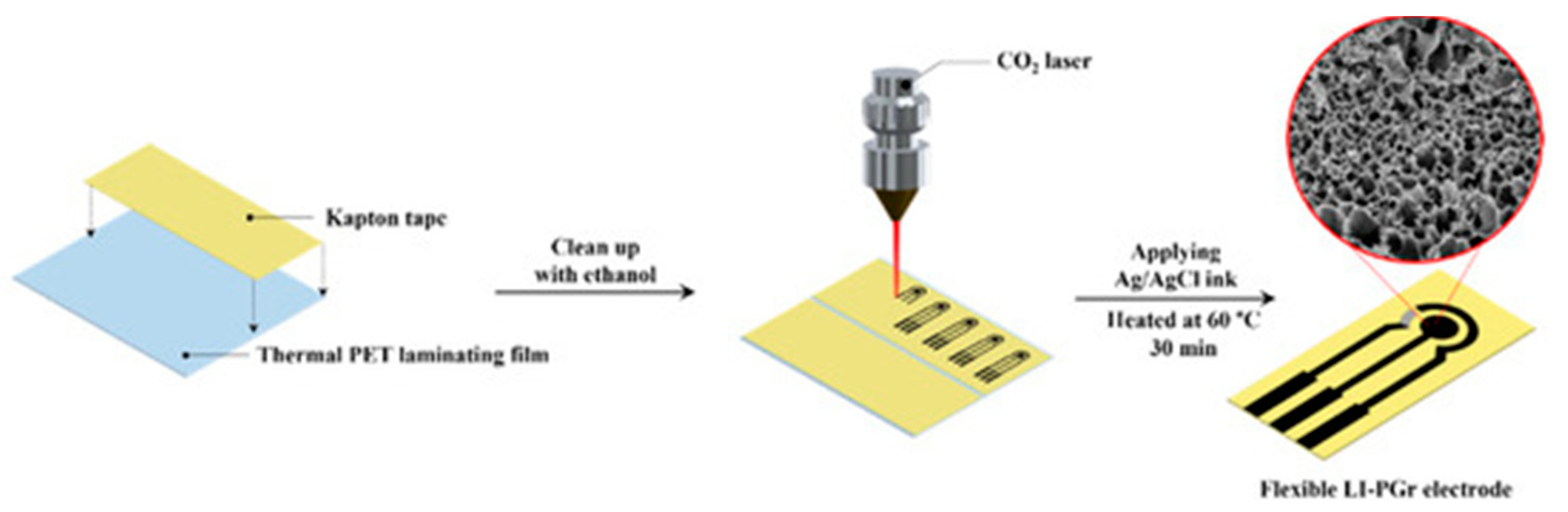
3. Sensing Using Lab-Fabricated or Modified SPE/SPE-like Electrodes and Portable Potentiostats
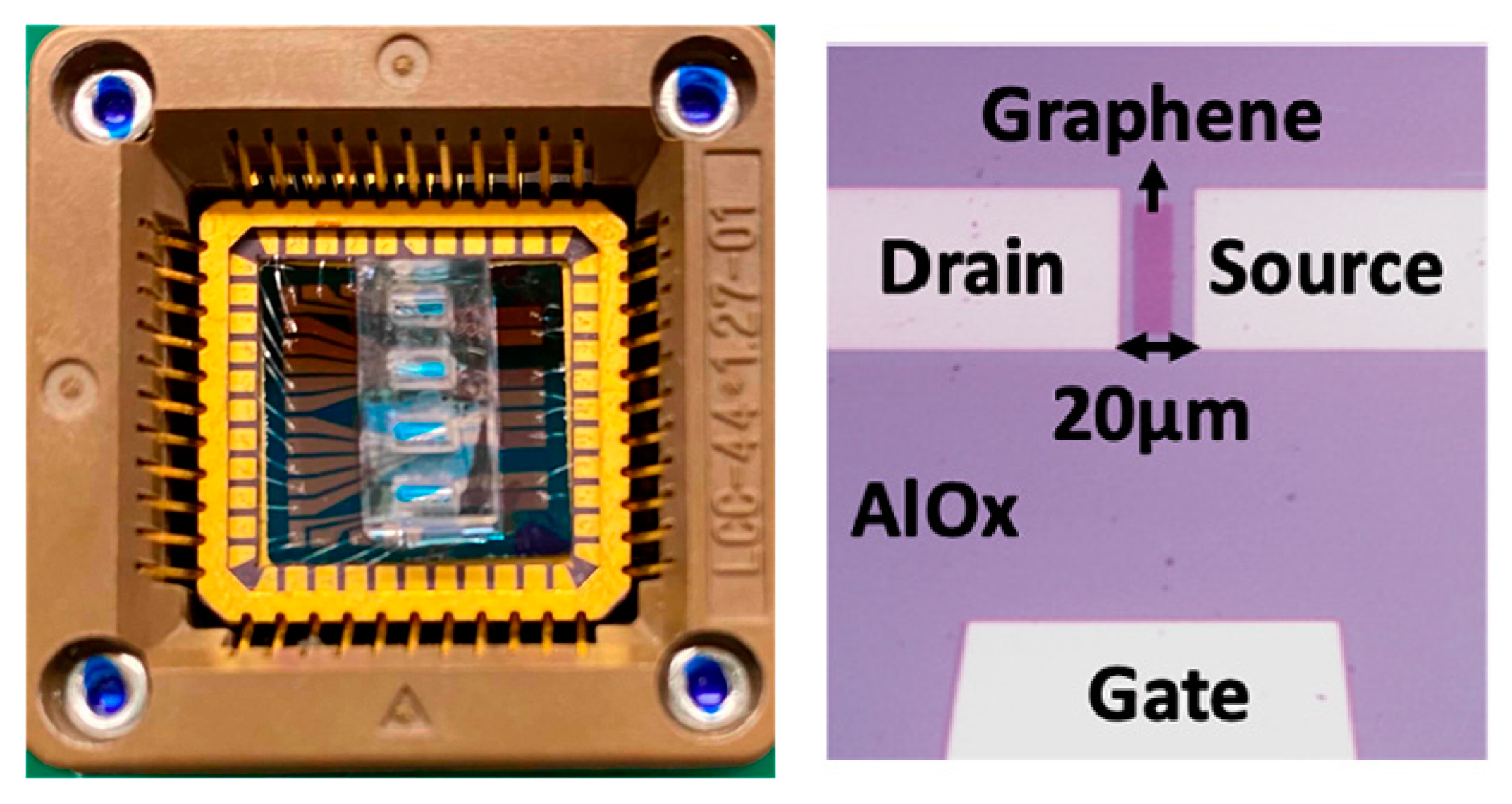
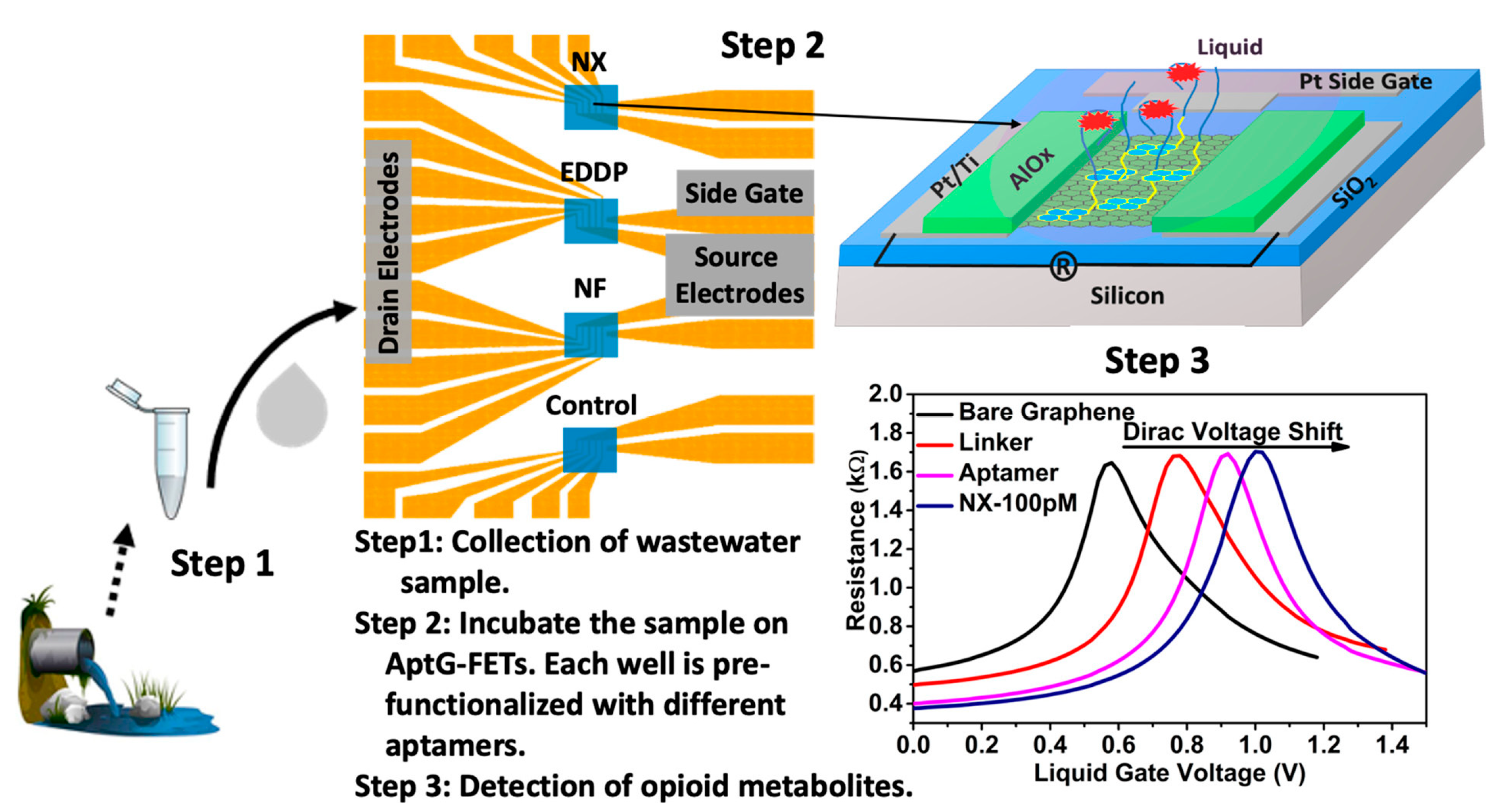
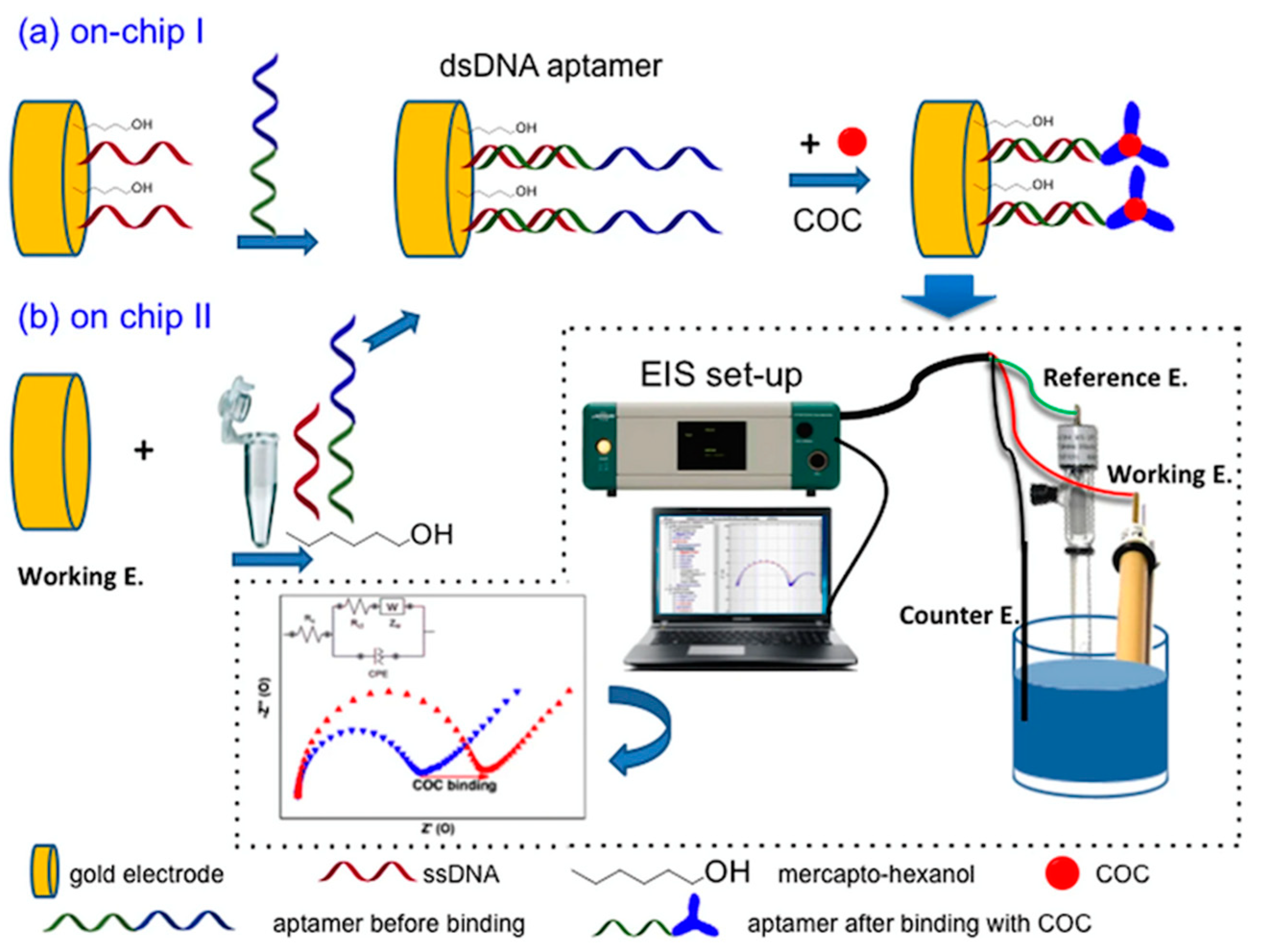
4. Affinity-Based Electrochemical Sensors
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, L.; Grillo, F.; Canfarotta, F.; Whitcombe, M.; Morgan, S.P.; Piletsky, S.; Correia, R.; He, C.; Norris, A.; Korposh, S. Carboxyl-fentanyl detection using optical fibre grating-based sensors functionalised with molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 177, 113002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truta, F.; Florea, A.; Cernat, A.; Tertis, M.; Hosu, O.; de Wael, K.; Cristea, C. Tackling the Problem of Sensing Commonly Abused Drugs Through Nanomaterials and (Bio)Recognition Approaches. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 561638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burks, R.M.; Pacquette, S.E.; Guericke, M.A.; Wilson, M.V.; Symonsbergen, D.J.; Lucas, K.A.; Holmes, A.E. DETECHIP®: A Sensor for Drugs of Abuse*. J. Forensic Sci. 2010, 55, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Wilson, M.V.; Trauernicht, M.; Holmes, A.E.; Jackson, A. Improved image analysis of DETECHIP(®) allows for increased specificity in drug discrimination. J. Forensics Res. 2012, 3, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas, M. A New Possible Alternative Colorimetric Drug Detection Test for Fentanyl. Org. Med. Chem. Int. J. 2017, 4, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Zhang, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, K.; Cao, H.; Li, X.; Yang, Z. Nanomaterial-based aptamer sensors for analysis of illicit drugs and evaluation of drugs consumption for wastewater-based epidemiology. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 130, 115975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoho, J.N.; Geier, B.; Grigsby, C.C.; Hagen, J.A.; Chávez, J.L.; Kelley-Loughnane, N. Cross-Reactive Plasmonic Aptasensors for Controlled Substance Identification. Sensors 2017, 17, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, T.; Esipenko, N.A.; Akdeniz, A.; Zhang, B.; Isaacs, L.; Anzenbacher, P., Jr. Multianalyte Sensing of Addictive Over-the-Counter (OTC) Drugs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15238–15243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penido, C.A.; Pacheco, M.T.; Zângaro, R.A.; Silveira, L., Jr. Identification of different forms of cocaine and substances used in adulteration using near-infrared Raman spectroscopy and infrared absorption spectroscopy. J. Forensic Sci. 2015, 60, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.E.; Stewart, A.; Peters, K.L.; McNaul, M.; Speers, S.J.; Fletcher, N.C.; Bell, S.E.J. Infrared and Raman screening of seized novel psychoactive substances: A large scale study of >200 samples. Analyst 2016, 141, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagar, M.; Yadav, S.; Sai, V.V.R.; Satija, J.; Bhatia, H. Emerging trends in point-of-care sensors for illicit drugs analysis. Talanta 2022, 238 Pt 2, 123048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philp, M.; Shimmon, R.; Tahtouh, M.; Fu, S. Color Spot Test As a Presumptive Tool for the Rapid Detection of Synthetic Cathinones. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 132, 57045. [Google Scholar]
- Elkins, K.M.; Weghorst, A.C.; Quinn, A.A.; Acharya, S. Colour quantitation for chemical spot tests for a controlled substances presumptive test database. Drug Test Anal. 2017, 9, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafer, K.E.; Brettell, T.A. Presumptive Color Tests of Seized Drugs. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer, M. The role of gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Instrumental techniques in forensic urine drug testing. Clin. Lab. Med. 1998, 18, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfanidis, A.; Krokos, A.; Mastrogianni, O.; Gika, H.; Raikos, N.; Theodoridis, G. Development and Validation of a Single Step GC/MS Method for the Determination of 41 Drugs and Drugs of Abuse in Postmortem Blood. Forensic Sci. 2022, 2, 473–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.B.; Lobo Castro, A.; Tarelho, S.; Domingues, P.; Franco, J.M. GC-MS—Still standing for clinical and forensic analysis: Validation of a multidrug method to detect and quantify illicit drugs. Aust. J. Forensic Sci. 2023, 55, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettell, T.A.; Lum, B.J. Analysis of Drugs of Abuse by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). In Analysis of Drugs of Abuse; Musah, R.A., Ed.; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sulej-Suchomska, A.M.; Klupczynska, A.; Dereziński, P.; Matysiak, J.; Przybyłowski, P.; Kokot, Z.J. Urban wastewater analysis as an effective tool for monitoring illegal drugs, including new psychoactive substances, in the Eastern European region. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, E.; Barroso, M.; Queiroz, J.A. LC-MS: A powerful tool in workplace drug testing. Drug Test. Anal. 2009, 1, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagihashi, G.; Tarui, T.; Miyagi, H.; Ohnishi, H.; Watanabe, T.; Yamaguchi, Y. Diagnostic accuracy for drug detection using liquid chromatography/mass spectroscopy in overdose patients. Acute Med. Surg. 2020, 7, e487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, J.; Go, A.; Moon, H.; Kim, S.; Jung, S.; Jeong, W.; Chung, H. Urine Multi-drug Screening with GC-MS or LC–MS-MS Using SALLE-hybrid PPT/SPE. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2018, 42, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merone, G.M.; Tartaglia, A.; Rossi, S.; Santavenere, F.; Bassotti, E.; D’Ovidio, C.; Bonelli, M.; Rosato, E.; de Grazia, U.; Locatelli, M.; et al. Fast Quantitative LC-MS/MS Determination of Illicit Substances in Solid and Liquid Unknown Seized Samples. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 16308–16313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, L.; Powell, J.; Pijl, E.M. An overview of forensic drug testing methods and their suitability for harm reduction point-of-care services. Harm Reduct. J. 2017, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Penido, C.A.F.; Pacheco, M.T.T.; Lednev, I.K.; Silveira, L., Jr. Raman spectroscopy in forensic analysis: Identification of cocaine and other illegal drugs of abuse. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2016, 47, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, M. Drugs of Abuse—Application of Handheld FT-IR and Raman Spectrometers. In Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy in Forensic Science; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 339–349. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Hou, X.; Zhen, C.; Wang, A.X. Sub-Part-Per-Billion Level Sensing of Fentanyl Residues from Wastewater Using Portable Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Sensing. Biosensors 2021, 11, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Cooper, J.M. Paper-based nanosensors to evaluate community-wide illicit drug use for wastewater-based epidemiology. Water Res. 2021, 189, 116559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razlansari, M.; Ulucan-Karnak, F.; Kahrizi, M.; Mirinejad, S.; Sargazi, S.; Mishra, S.; Rahdar, A.; Díez-Pascual, A.M. Nanobiosensors for detection of opioids: A review of latest advancements. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 179, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojica, E.-R.; Dai, Z. New Raman spectroscopic methods’ application in forensic science. Talanta Open 2022, 6, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, D.W.; LeBlanc, G.; Meschievitz, M.E.; Cliffel, D.E. Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 685–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, F.R.; Xavier, M.G. 6—Electrochemical Sensors. In Nanoscience and its Applications; Da Róz, A.L., Ferreira, M., de Lima Leite, F., Oliveira, O.N., Eds.; William Andrew Publishing: Norwich, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 155–178. [Google Scholar]
- Schram, J.; Parrilla, M.; Slosse, A.; Van Durme, F.; Åberg, J.; Björk, K.; Bijvoets, S.M.; Sap, S.; Heerschop, M.W.J.; De Wael, K. Paraformaldehyde-coated electrochemical sensor for improved on-site detection of amphetamine in street samples. Microchem. J. 2022, 179, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.; Dennany, L. Applications of electrochemical sensors: Forensic drug analysis. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 3, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumya, W.; Taoufik, N.; Achak, M.; Bessbousse, H.; Elhalil, A.; Barka, N. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors for the determination of diclofenac in pharmaceutical, biological and water samples. Talanta Open 2021, 3, 100026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y. Research on Detection of Sterol Doping in Sports by Electrochemical Sensors: A Review. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2022, 2022, 3394079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honeychurch, K.C. Review of Electroanalytical-Based Approaches for the Determination of Benzodiazepines. Biosensors 2019, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanghavi, B.J.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Hirsch, T.; Swami, N.S. Nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensing of neurological drugs and neurotransmitters. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroujerdi, R.; Paul, R. Graphene-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Psychoactive Drugs. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorablou, Z.; Shahdost-fard, F.; Razmi, H.; Yola, M.L.; Karimi-Maleh, H. Recent advances in developing optical and electrochemical sensors for analysis of methamphetamine: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Imanzadeh, H.; Sefid-Sefidehkhan, Y. An Overview on Electrochemical Sensors based on Nanomaterials for Determination of Drugs of Abuse. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 162–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rycke, E.; Stove, C.; Dubruel, P.; De Saeger, S.; Beloglazova, N. Recent developments in electrochemical detection of illicit drugs in diverse matrices. Biosens Bioelectron 2020, 169, 112579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltorak, L.; Sudhölter, E.; Puit, M. Electrochemical cocaine (bio)sensing. From solid electrodes to soft junctions. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 114, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, R.S.; Brown, K.; Dennany, L. Electrochemical Methodologies for the Detection of Traditional and Emerging Illicit Drugs. ECS Meet. Abstr. 2022, MA2022-02, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Miranda Ferrari, A.; Rowley-Neale, S.J.; Banks, C.E. Screen-printed electrodes: Transitioning the laboratory in-to-the field. Talanta Open 2021, 3, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, M.; Slosse, A.; Van Echelpoel, R.; Montiel, N.F.; Van Durme, F.; De Wael, K. Portable Electrochemical Detection of Illicit Drugs in Smuggled Samples: Towards More Secure Borders. Chem. Proc. 2021, 5, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Van Echelpoel, R.; Schram, J.; Parrilla, M.; Daems, D.; Slosse, A.; Van Durme, F.; De Wael, K. Electrochemical methods for on-site multidrug detection at festivals. Sens. Diagn. 2022, 1, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, M.; Felipe Montiel, N.; Durme, F.; De Wael, K. Derivatization of amphetamine to allow its electrochemical detection in illicit drug seizures. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 337, 129819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, M.; Joosten, F.; De Wael, K. Enhanced electrochemical detection of illicit drugs in oral fluid by the use of surfactant-mediated solution. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, A.-M.; Parrilla, M.; Sleegers, N.; Slosse, A.; Van Durme, F.; van Nuijs, A.; Oprean, R.; Cristea, C.; De Wael, K. Investigating the electrochemical profile of methamphetamine to enable fast on-site detection in forensic analysis. Talanta 2023, 255, 124208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barfidokht, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Seenivasan, R.; Liu, S.; Hubble, L.J.; Wang, J.; Hall, D.A. Wearable electrochemical glove-based sensor for rapid and on-site detection of fentanyl. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisahas, K.; Soleh, A.; Somsiri, S.; Senglan, P.; Promsuwan, K.; Saichanapan, J.; Kanatharana, P.; Thavarungkul, P.; Lee, K.; Chang, K.H.; et al. Electrochemical Sensor for Methamphetamine Detection Using Laser-Induced Porous Graphene Electrode. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Song, Z.; Cai, H.; Fang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Wearable and flexible electrochemical sensors for sweat analysis: A review. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghian, E.; Marzi Khosrowshahi, E.; Sohouli, E.; Ahmadi, F.; Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M.; Safarifard, V. A new electrochemical sensor for the detection of fentanyl lethal drug by a screen-printed carbon electrode modified with the open-ended channels of Zn(ii)-MOF. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 9271–9277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; Ye, R.; Samuel, E.L.G.; Yacaman, M.J.; Yakobson, B.I.; Tour, J.M. Laser-induced porous graphene films from commercial polymers. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, T.B.; Endo, N.; Duvallet, C.; Ghaeli, N.; Hess, K.; Alm, E.J.; Matus, M.; Chai, P.R. “Waste Not, Want Not”—Leveraging Sewer Systems and Wastewater-Based Epidemiology for Drug Use Trends and Pharmaceutical Monitoring. J. Med. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, R.Z.; do Nascimento, C.A.; Linden, R. Evaluation of Illicit Drug Consumption by Wastewater Analysis Using Polar Organic Chemical Integrative Sampler as a Monitoring Tool. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 596875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huizer, M.; ter Laak, T.L.; de Voogt, P.; van Wezel, A.P. Wastewater-based epidemiology for illicit drugs: A critical review on global data. Water Res. 2021, 207, 117789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannwarth, A.; Morelato, M.; Benaglia, L.; Been, F.; Esseiva, P.; Delemont, O.; Roux, C. The use of wastewater analysis in forensic intelligence: Drug consumption comparison between Sydney and different European cities. Forensic Sci. Res. 2019, 4, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, S.; Thomas, K.V.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Vandam, L.; Griffiths, P. Testing wastewater to detect illicit drugs: State of the art, potential and research needs. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Rana, M.; Geiwitz, M.; Khan, N.I.; Catalano, M.; Ortiz-Marquez, J.C.; Kitadai, H.; Weber, A.; Dweik, B.; Ling, X.; et al. Rapid, Multianalyte Detection of Opioid Metabolites in Wastewater. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 3704–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, S.; Zhu, B.; Rong, G.; Sawan, M. Towards wearable and implantable continuous drug monitoring: A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Castrignanò, E.; Estrela, P.; Frost, C.G.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Community Sewage Sensors towards Evaluation of Drug Use Trends: Detection of Cocaine in Wastewater with DNA-Directed Immobilization Aptamer Sensors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, H.; Bacon, A.; Joseph, K.M.; Gwandaru, W.R.W.; Bhide, A.; Sankhala, D.; Dhamu, V.N.; Prasad, S. A Rapid Response Electrochemical Biosensor for Detecting Thc In Saliva. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaryashree; Takeda, Y.; Kanai, M.; Hatano, A.; Yoshimi, Y.; Kida, M. A “Single-Use” Ceramic-Based Electrochemical Sensor Chip Using Molecularly Imprinted Carbon Paste Electrode. Sensors 2020, 20, 5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, Z. Recent Advances in the Development of Portable Electrochemical Sensors for Controlled Substances. Sensors 2023, 23, 3140. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063140
Dai Z. Recent Advances in the Development of Portable Electrochemical Sensors for Controlled Substances. Sensors. 2023; 23(6):3140. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063140
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Zhaohua. 2023. "Recent Advances in the Development of Portable Electrochemical Sensors for Controlled Substances" Sensors 23, no. 6: 3140. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063140
APA StyleDai, Z. (2023). Recent Advances in the Development of Portable Electrochemical Sensors for Controlled Substances. Sensors, 23(6), 3140. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063140





