Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearing Based on a Priority Elimination Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Methods
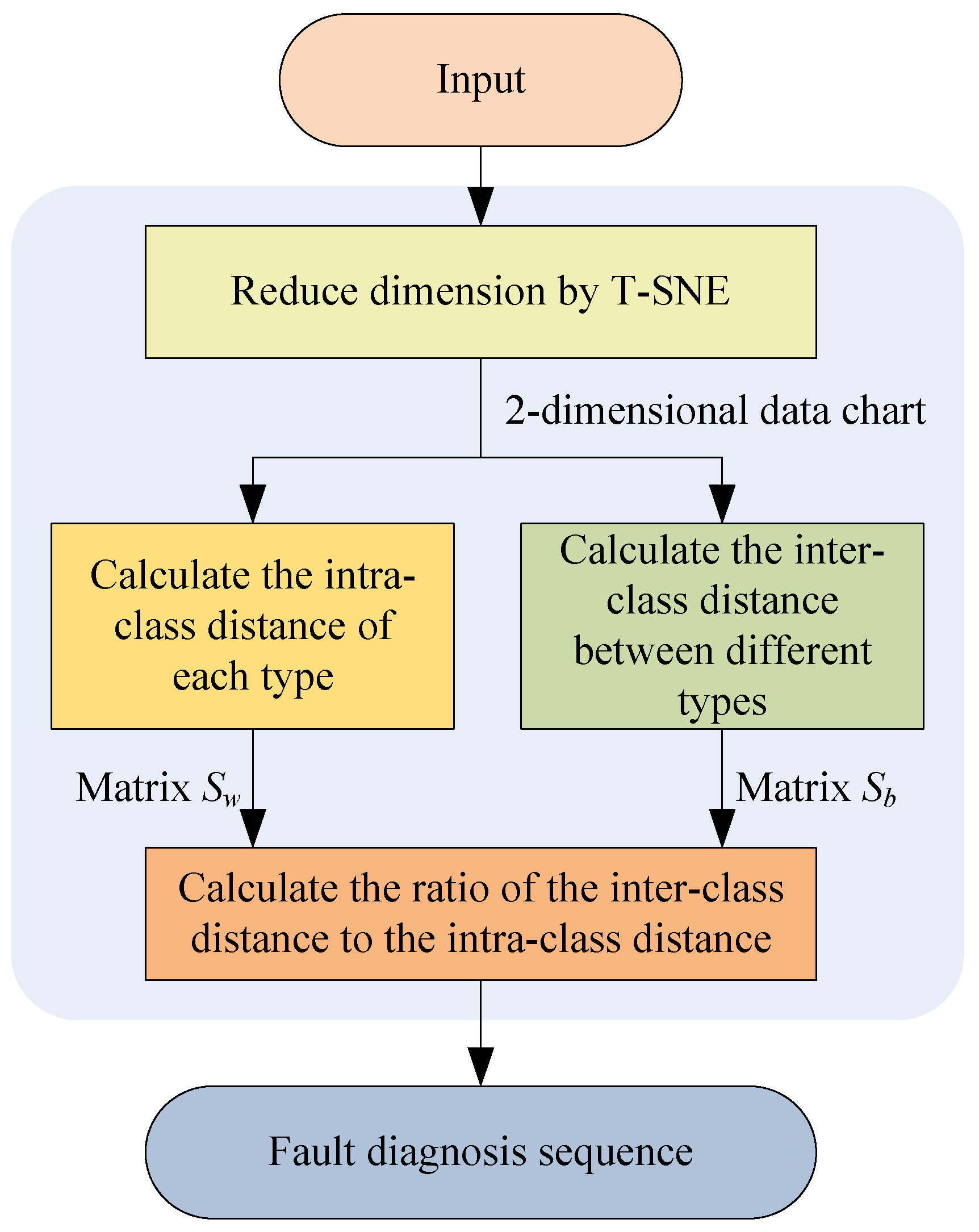
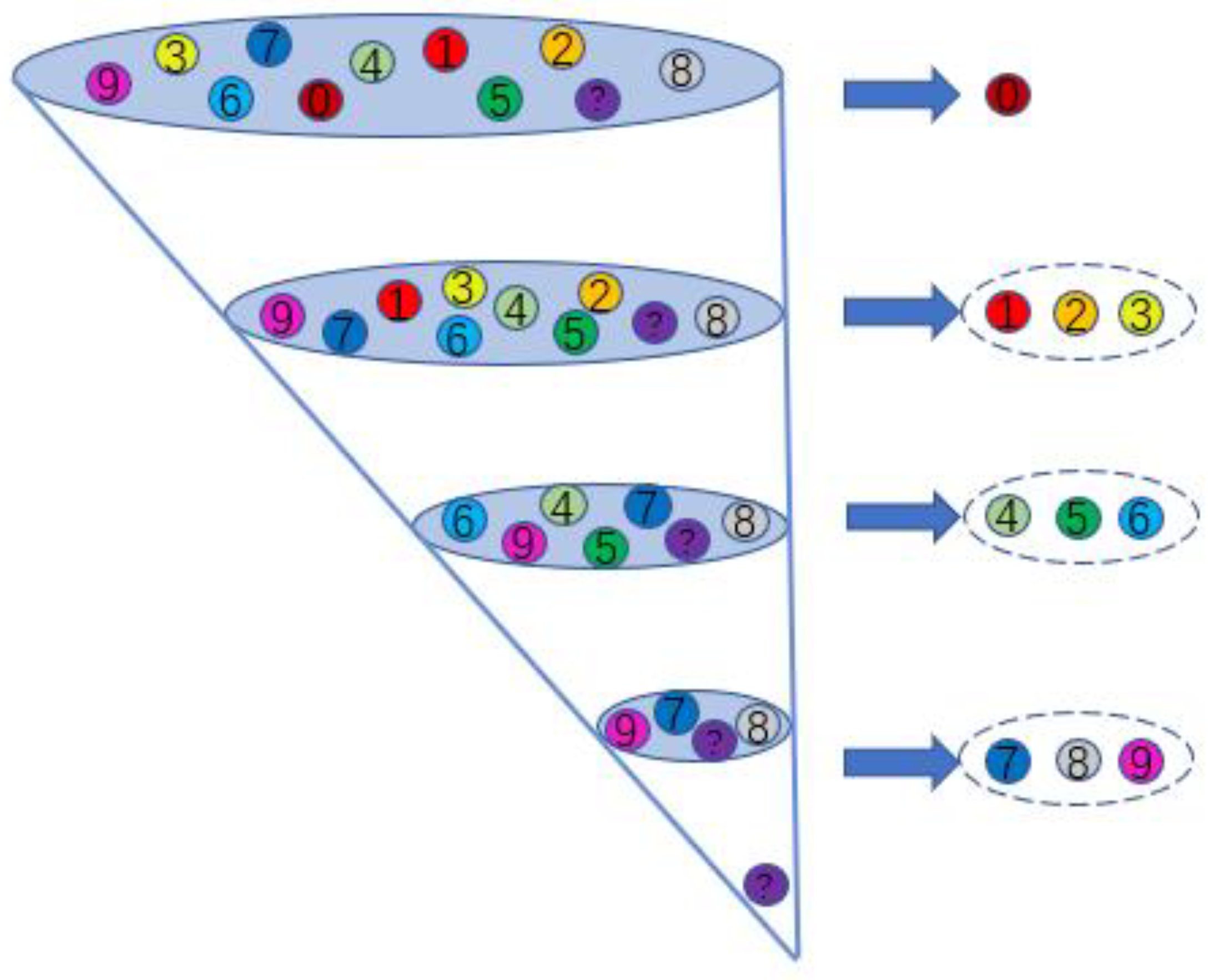
2.1. Priority Elimination Method
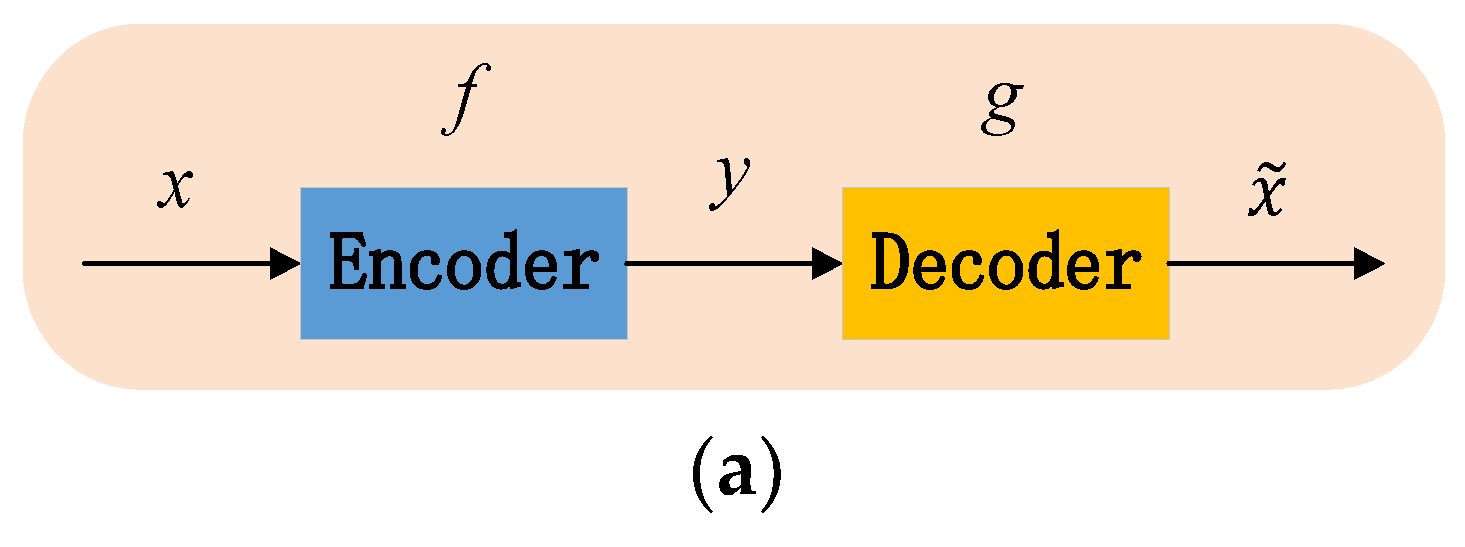
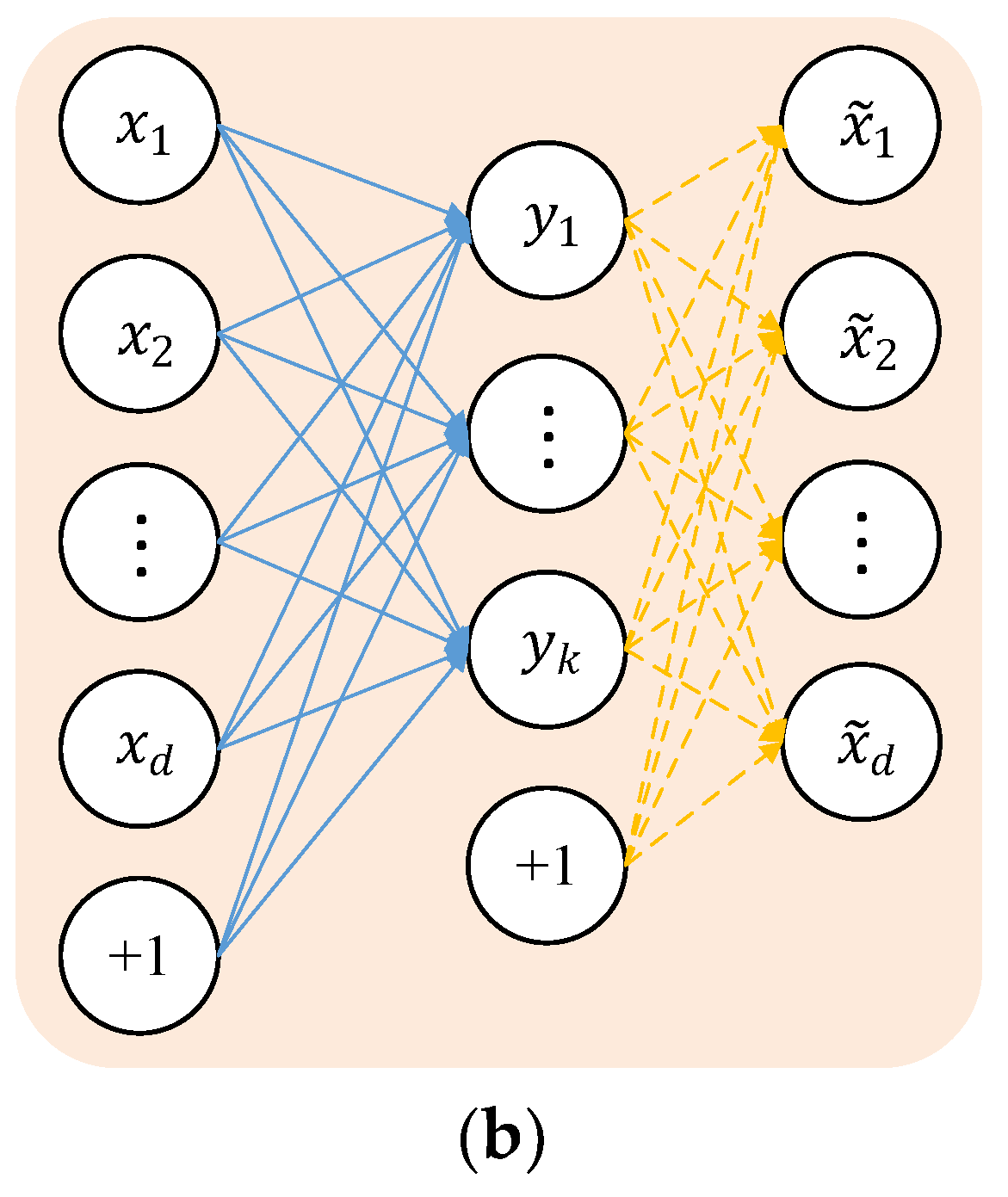
2.2. SSAE Network
2.3. XGBoost Algorithm
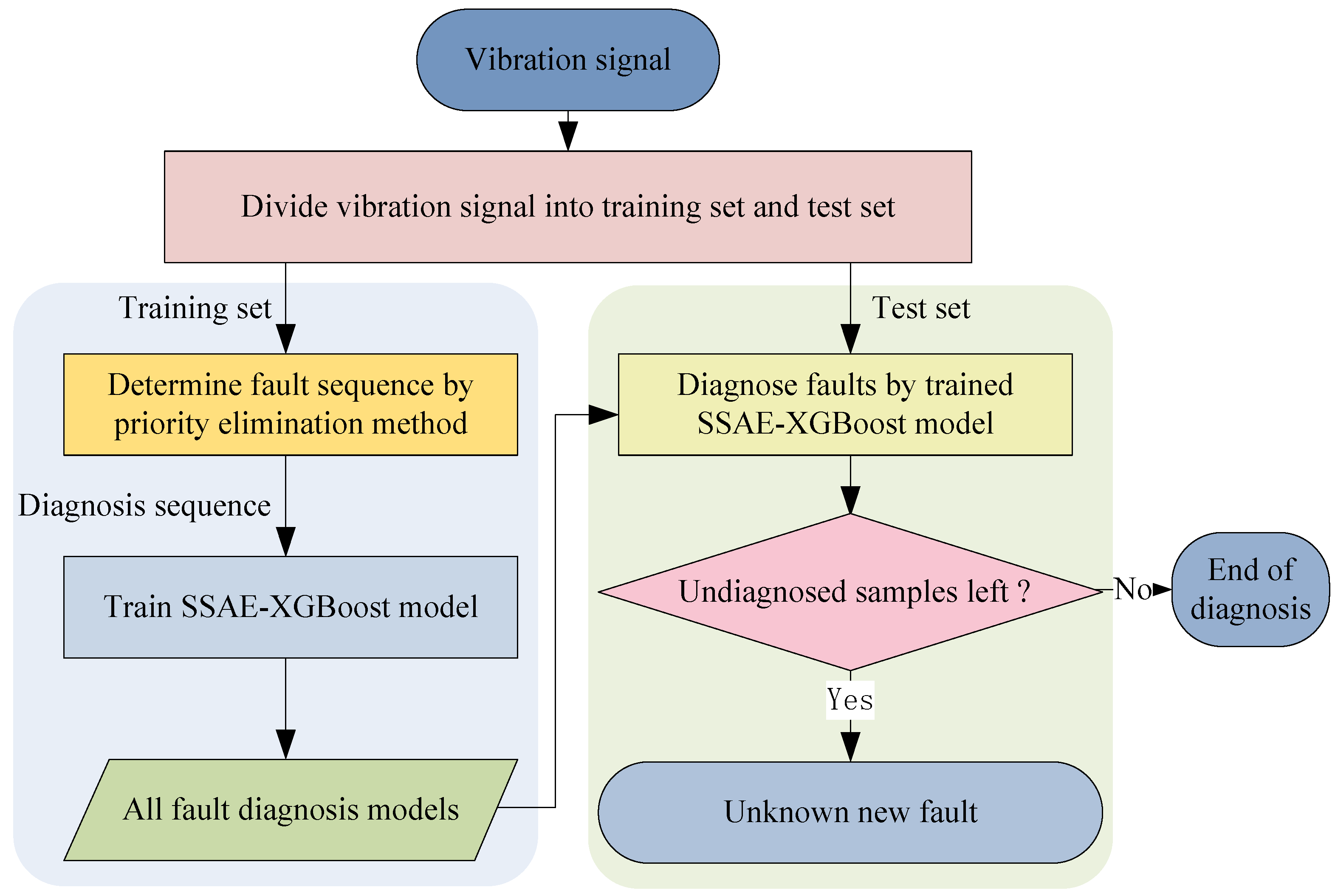
3. Fault Diagnosis Process
4. Experimental Validation
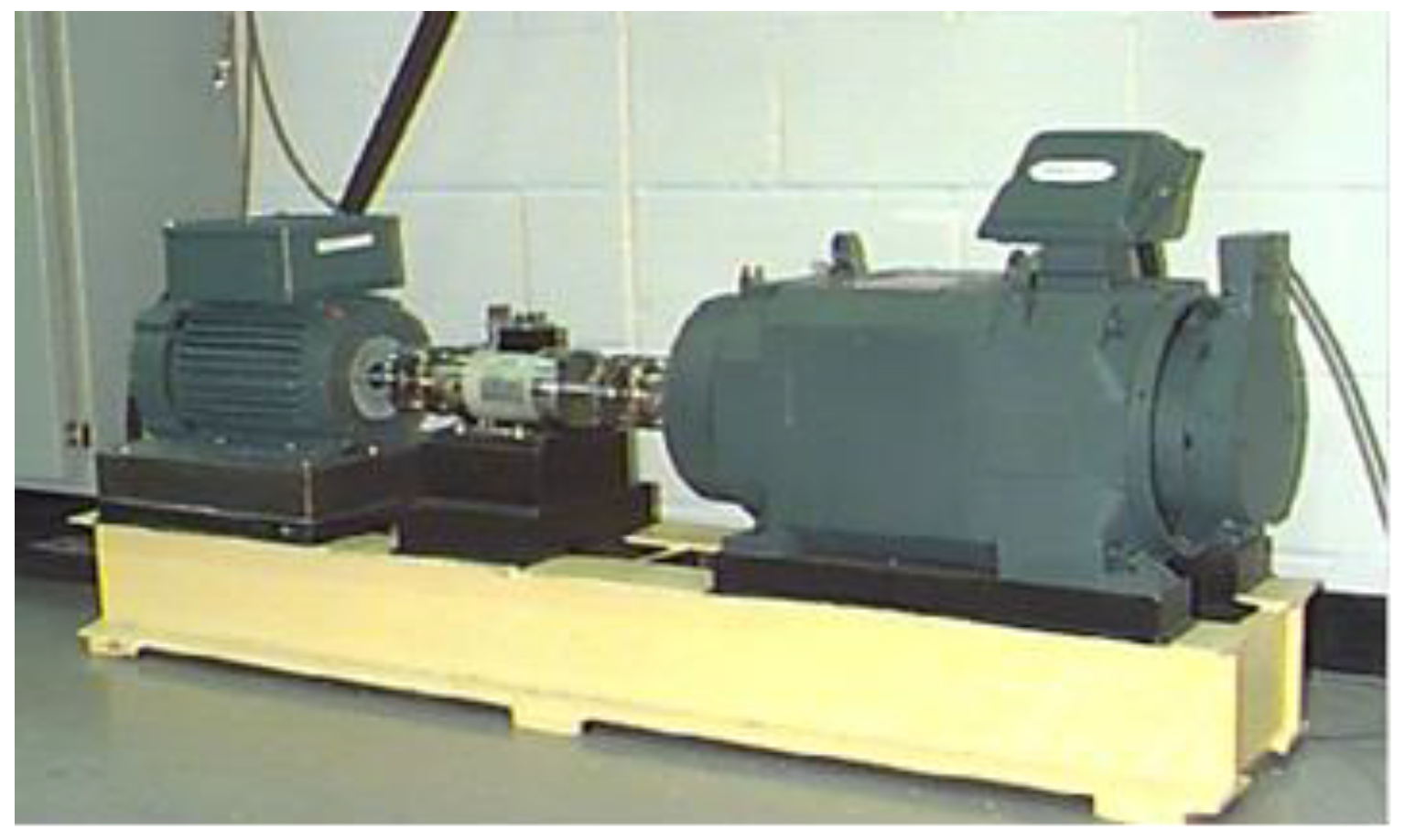
4.1. Experimental Data
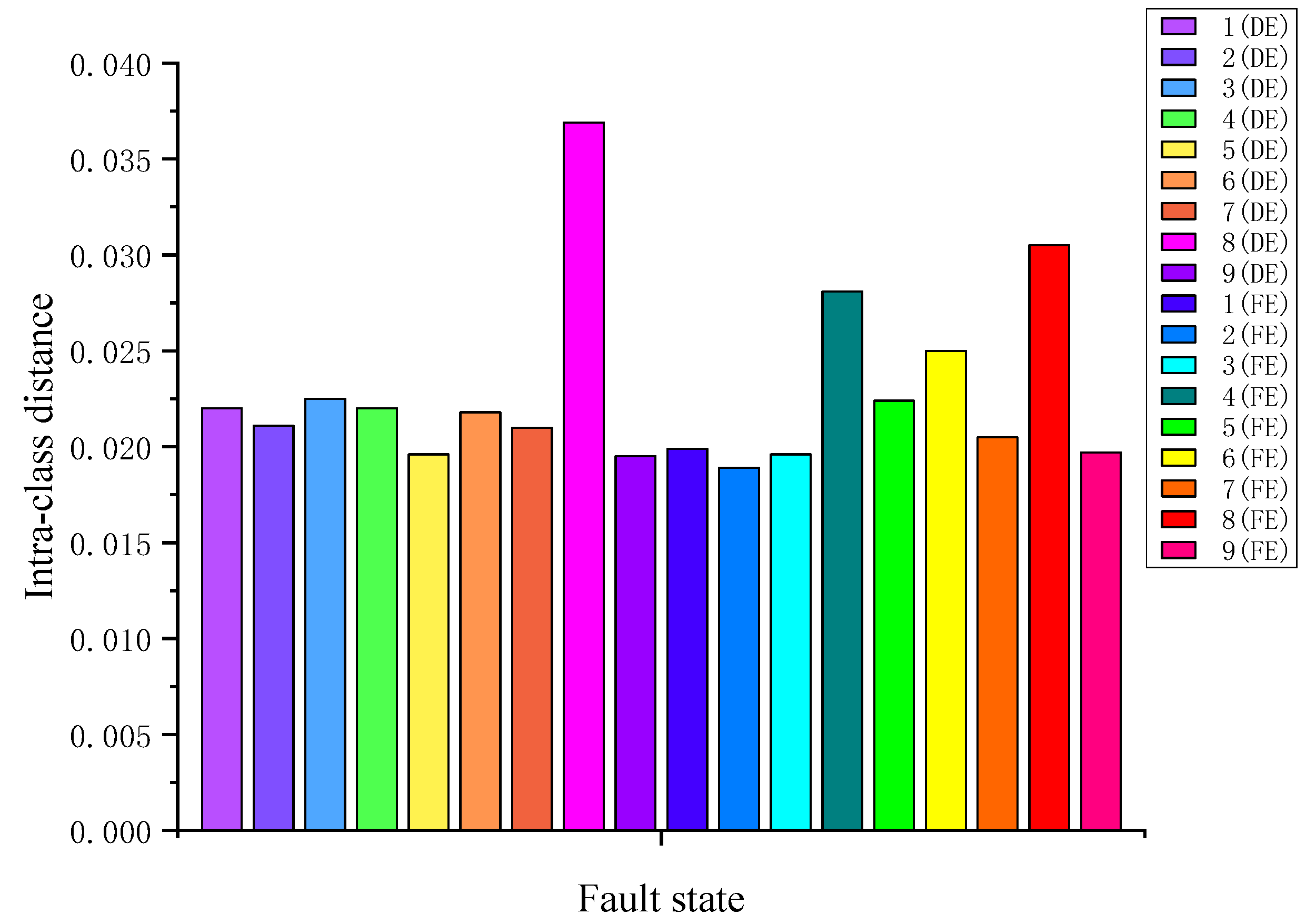
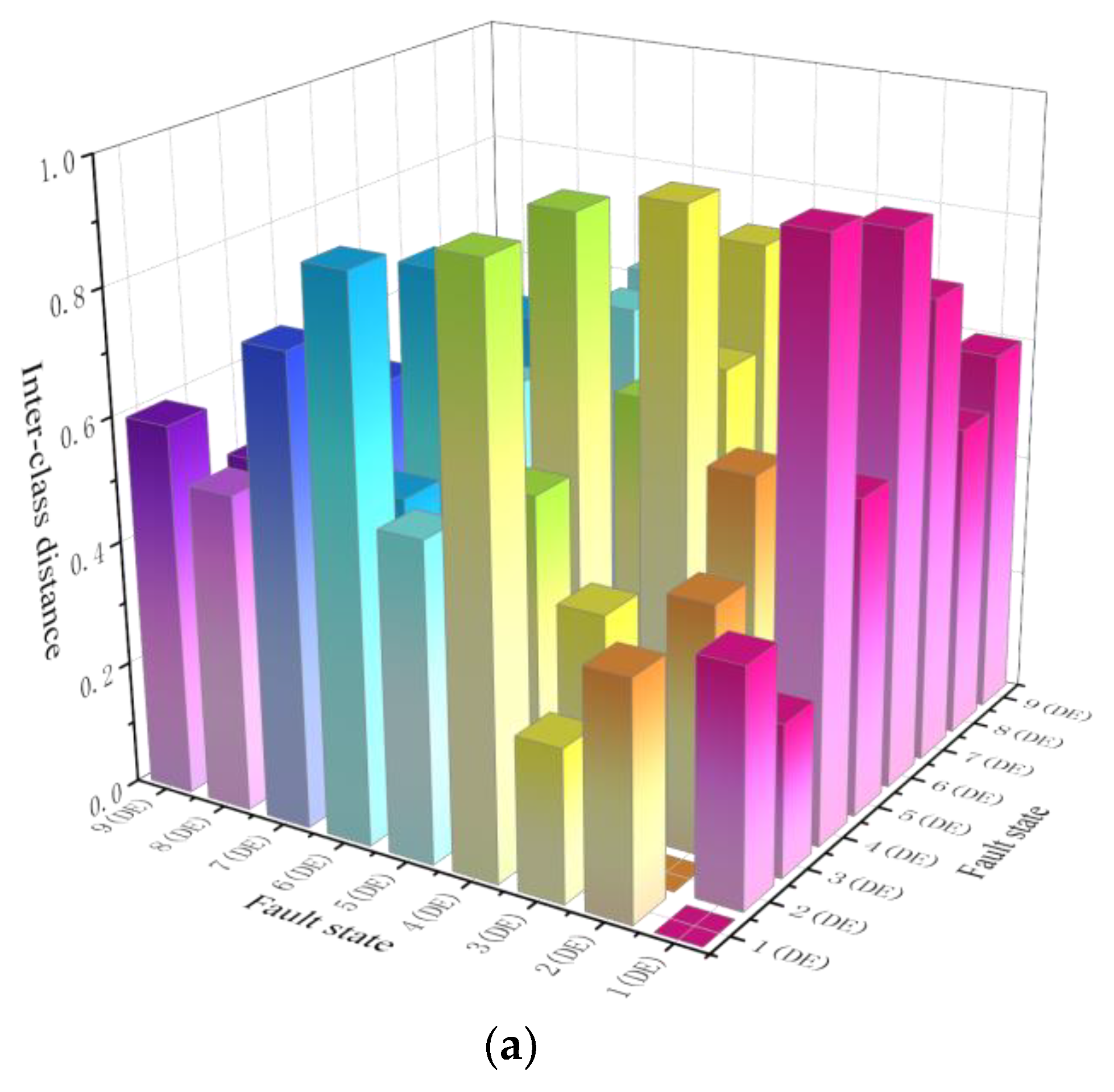
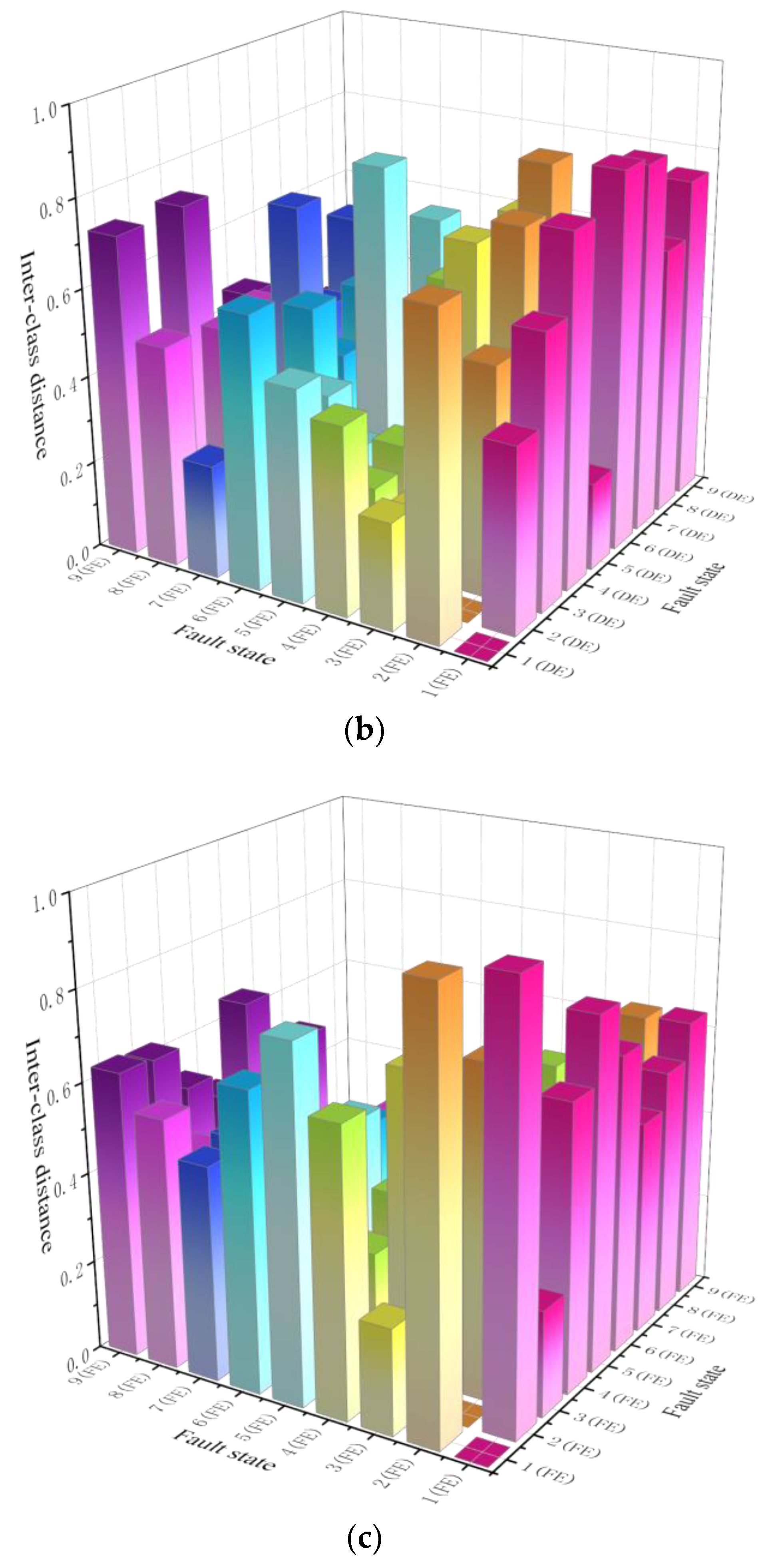
4.2. Priority Diagnosis Sequence
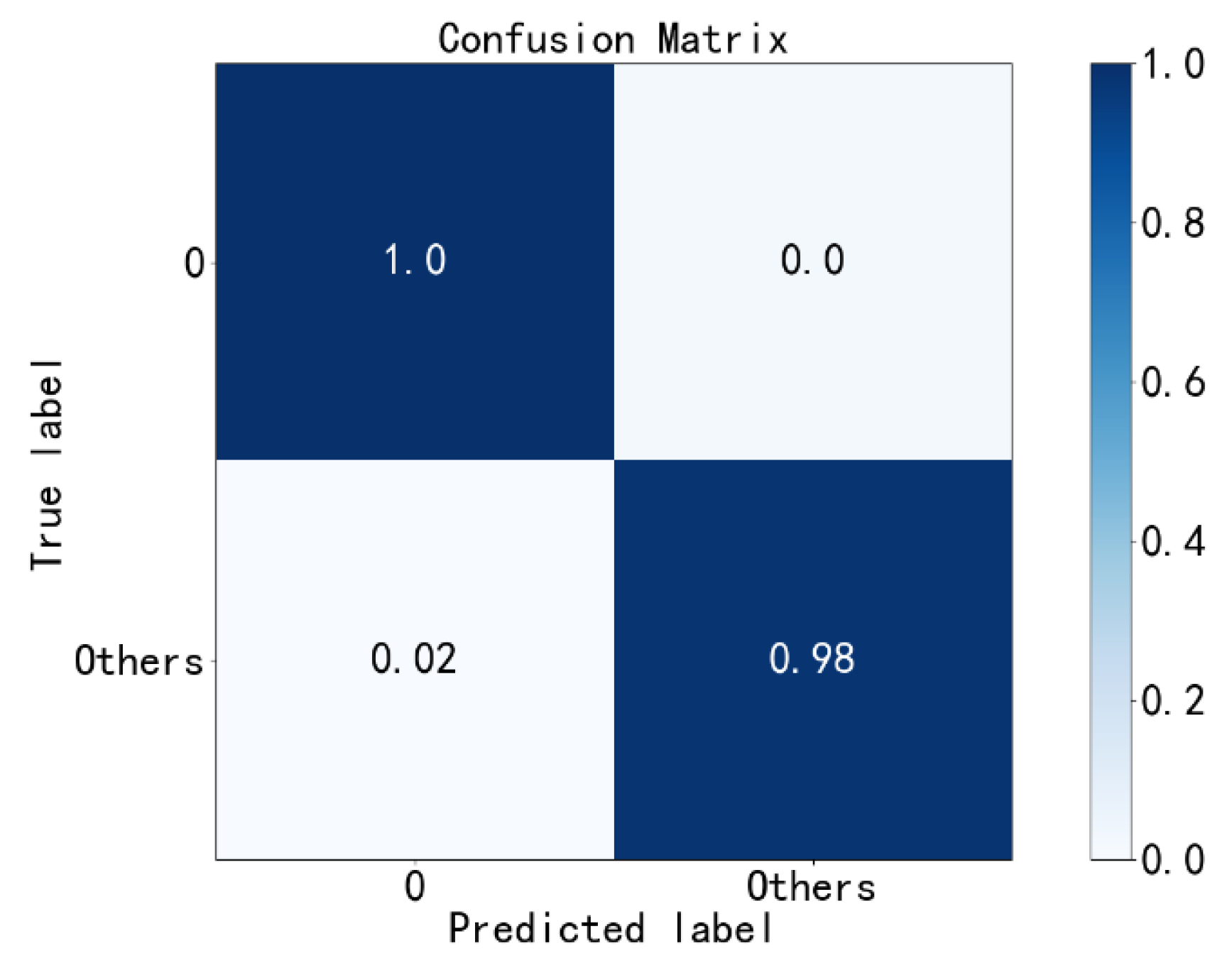
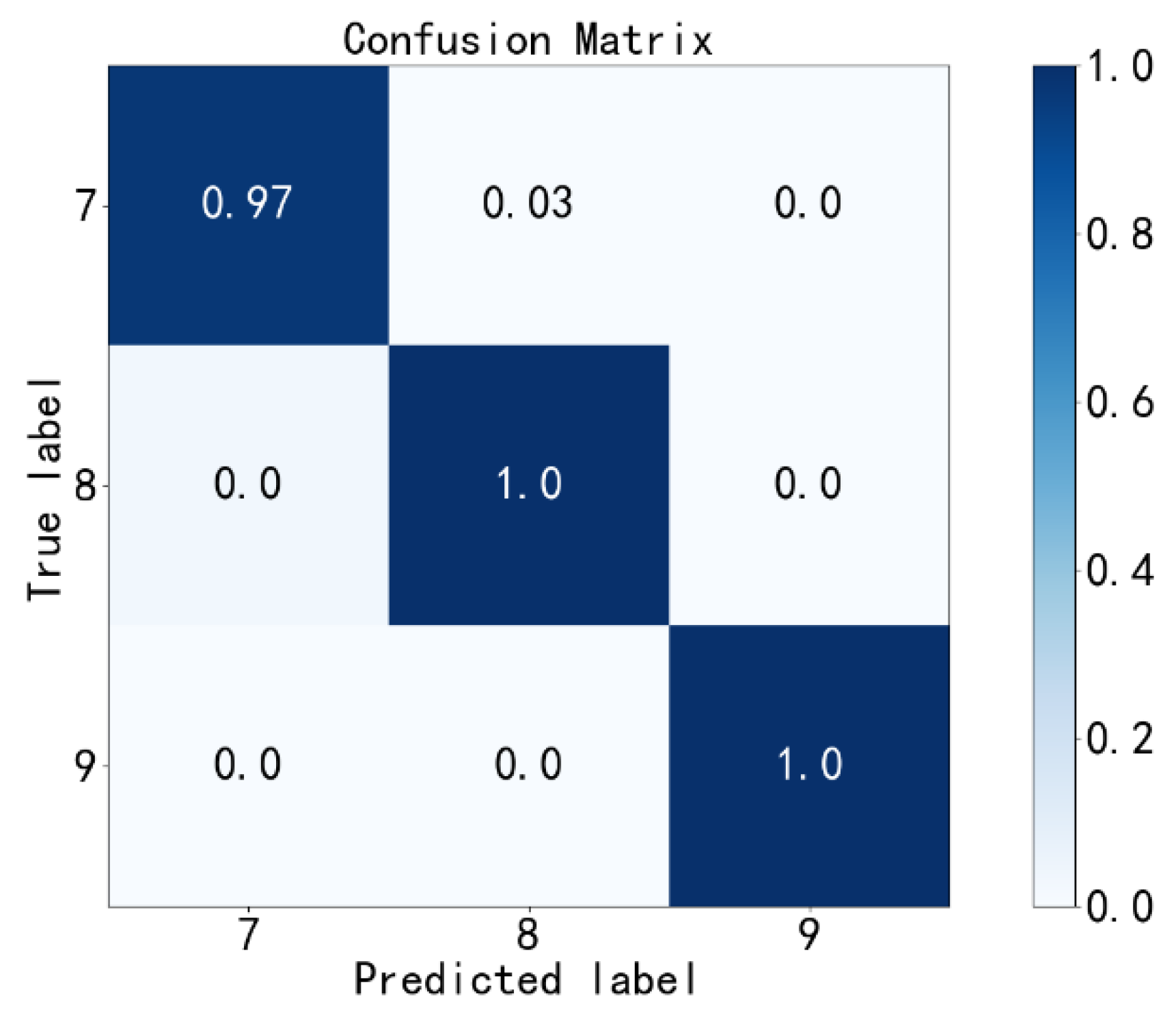
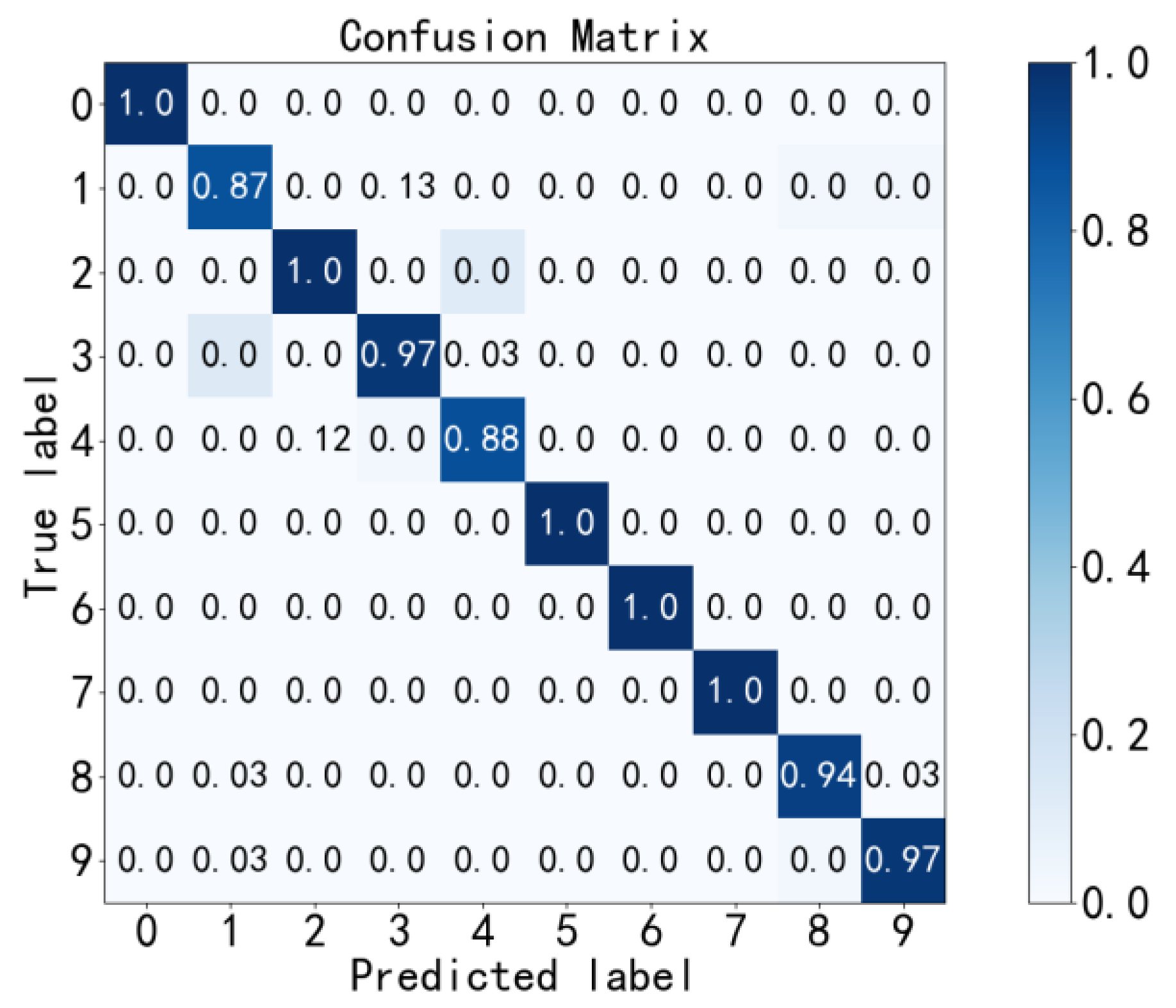
4.3. Diagnosis Results
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- In terms of the improvement of the fault diagnosis accuracy, PE improves the fault diagnosis accuracy of all methods. The SSAE-XGBoost model combined with the PE method increases the fault diagnosis accuracy from 96.3% to 99.27%, which is also significantly higher than some classical algorithms with or without PE.
- (2)
- In the aspect of the identification of unknown faults, the fault data that do not appear in the training set are put into the test set. SSAE-XGBoost with PE can improve the accuracy of fault diagnosis from 86.96% to 92.34%, which is superior to other classical fault diagnosis methods with or without PE.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, H.; Li, C.; Li, H. An Improved Eemd with Multiwavelet Packet for Rotating Machinery Multi-Fault Diagnosis. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2013, 36, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez, P.; Alonso, J.B.; Ferrer, M.A.; Travieso, C.M. Review of Automatic Fault Diagnosis Systems Using Audio and Vibration Signals. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2014, 44, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.; Jang, J.; Won, S.; Jha, M.S.; Lee, Y.O. Supervised Health Stage Prediction Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Bearing Wear. Sensors 2020, 20, 5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Islam, M.R.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.M.; Pecht, M. A Hybrid Feature Selection Scheme for Reducing Diagnostic Performance Deterioration Caused by Outliers in Data-Driven Diagnostics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3299–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Si, X.S.; Qin, A.S.; Lv, Y.R.; Zhang, Q.H. Machinery Fault Diagnosis Scheme Using Redefined Dimensionless Indicators and Mrmr Feature Selection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 40313–40326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Kumar, A.; Parkash, C.; Vashishtha, G.; Tang, H.; Glocawz, A.; Dong, A.; Xiang, J. Development of Entropy Measure for Selecting Highly Sensitive Wpt Band to Identify Defective Components of an Axial Piston Pump. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 203, 109225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Dong, F.; Ding, E.; Wu, S.; Fan, C. Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis Using Modified Lfda and Emd with Sensitive Feature Selection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 3715–3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Huang, Y. Time-Frequency Representation Based on an Adaptive Short-Time Fourier Transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 5118–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Kumar, A.; Parkash, C.; Vashishtha, G.; Tang, H.S.; Xiang, J.W. A Novel Entropy-Based Sparsity Measure for Prognosis of Bearing Defects and Development of a Sparsogram to Select Sensitive Filtering Band of an Axial Piston Pump. Measurement 2022, 203, 111997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep Learning in Neural Networks: An Overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Kang, H.J. Rolling Element Bearing Fault Diagnosis Using Convolutional Neural Network and Vibration Image. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2019, 53, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jung, J.H.; Ko, J.U.; Kong, H.B.; Lee, J.; Youn, B.D. Direct Connection-Based Convolutional Neural Network (DC-CNN) for Fault Diagnosis of Rotor Systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 172043–172056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Li, C. Rolling-Element Bearing Fault Diagnosis Using Improved Lenet-5 Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G.E.; Osindero, S.; Teh, Y.W. A Fast Learning Algorithm for Deep Belief Nets. Neural Comput. 2006, 18, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Du, G.; Shen, C.; Chen, N.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Z. An End-to-End Model Based on Improved Adaptive Deep Belief Network and Its Application to Bearing Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 63584–63596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.Z.; Xu, L.T.; Zhang, Y.M.; Pei, Z.M. Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis Based on Intelligent Optimized Self-Adaptive Deep Belief Network. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 31, 055009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Wu, S. Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearing Using Deep Wavelet Auto-Encoder with Extreme Learning Machine. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2018, 140, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Jia, M.; Liu, Z. Semisupervised Deep Sparse Auto-Encoder with Local and Nonlocal Information for Intelligent Fault Diagnosis of Rotating Machinery. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wen, G.; Dong, S.; Zhou, H.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Memory Residual Regression Autoencoder for Bearing Fault Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yuan, H.; Liu, H.; Lu, C. Fault Diagnosis for Rolling Bearing Based on Sift-Kpca and Svm. Eng. Comput. 2017, 34, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Chen, L.; Hu, X. Rolling Element Bearing Fault Diagnosis by Combining Adaptive Local Iterative Filtering, Modified Fuzzy Entropy and Support Vector Machine. Entropy 2018, 20, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Song, H.; Xiao, S. A Study on Fault Diagnosis Method of Rolling Bearing Based on Wavelet Packet and Improved BP Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Frontiers of Materials Synthesis and Processing (FMSP 2017), Changsha, China, 28–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yao, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, Y. Multiscale Local Features Learning Based on Bp Neural Network for Rolling Bearing Intelligent Fault Diagnosis. Measurement 2020, 153, 107419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, S.R.; Bakhit, P.R.; Ishak, S. An Extreme Gradient Boosting Method for Identifying the Factors Contributing to Crash/near-Crash Events: A Naturalistic Driving Study. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 46, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, S. A Novel Bearing Fault Classification Method Based on Xgboost: The Fusion of Deep Learning-Based Features and Empirical Features. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anowar, F.; Sadaoui, S.; Selim, B. Conceptual and Empirical Comparison of Dimensionality Reduction Algorithms (PCA, KPCA, LDA, MDS, SVD, LLE, ISOMAP, LE, ICA, t-SNE). Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 40, 100378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengio, Y.; Lamblin, P.; Popovici, D.; Larochelle, H. Greedy Layer-Wise Training of Deep Networks. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS 2006, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 December 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Maddikunta PK, R.; Kaluri, R.; Singh, S.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Alazab, M.; Tariq, U. A Novel PCA-Firefly Based Xgboost Classification Model for Intrusion Detection in Networks Using Gpu. Electronics 2020, 9, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, X.; Ren, Z. An Intelligent Fault Diagnosis Method of Rolling Bearing with Wide Convolution Kernel Network. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Automation, Control and Robotics Engineering, CACRE 2020, Dalian, China, 19–20 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
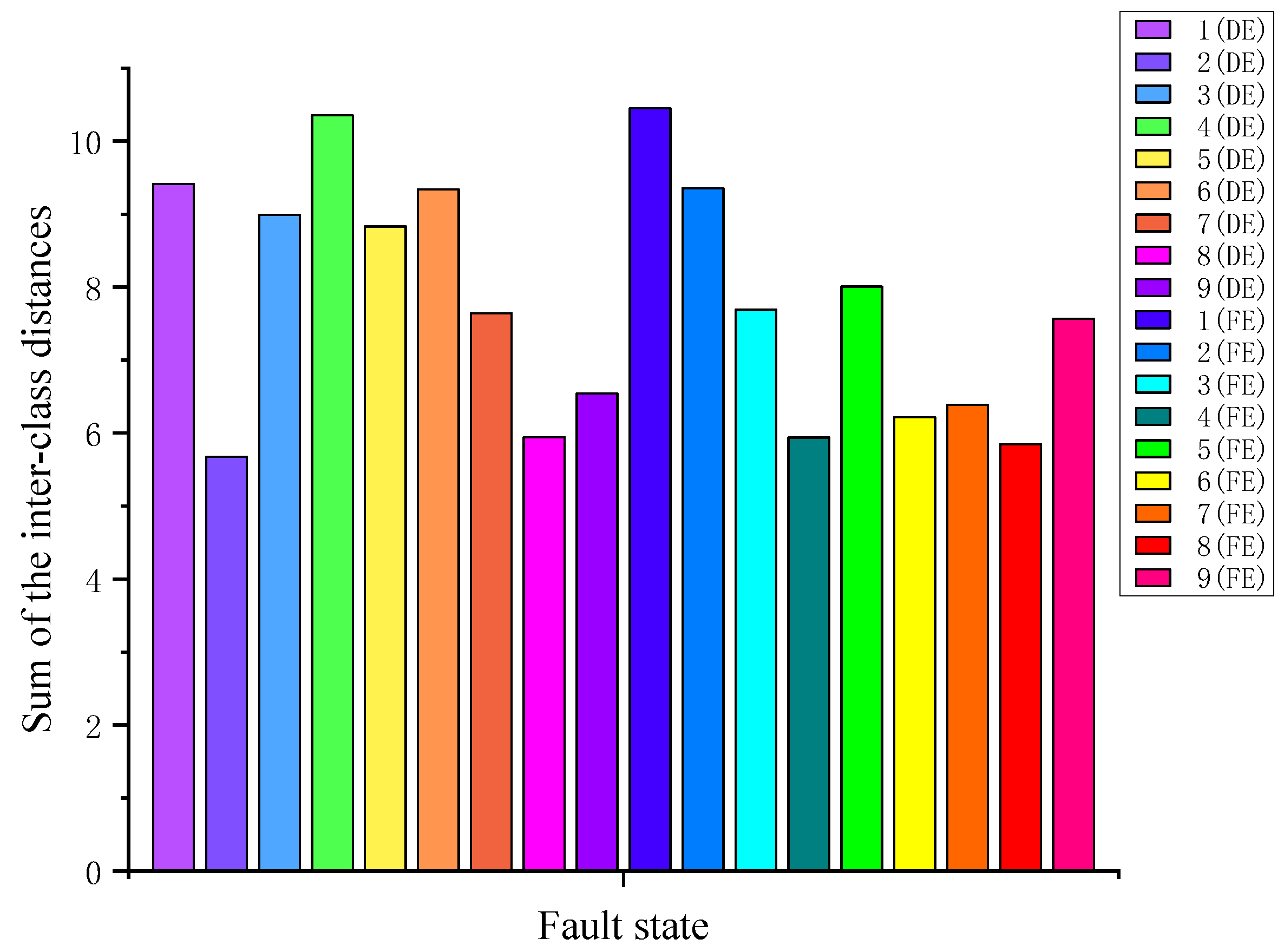
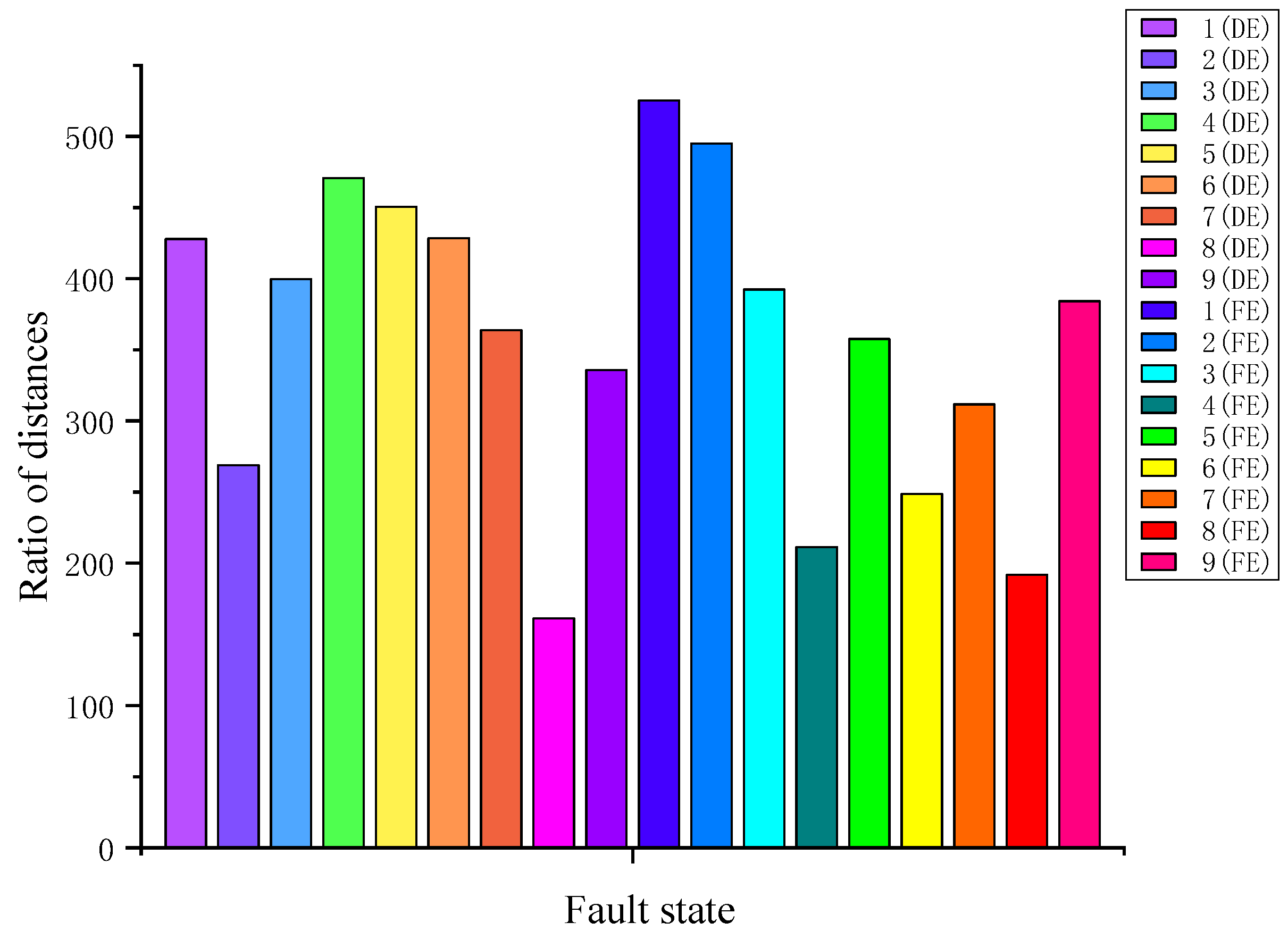


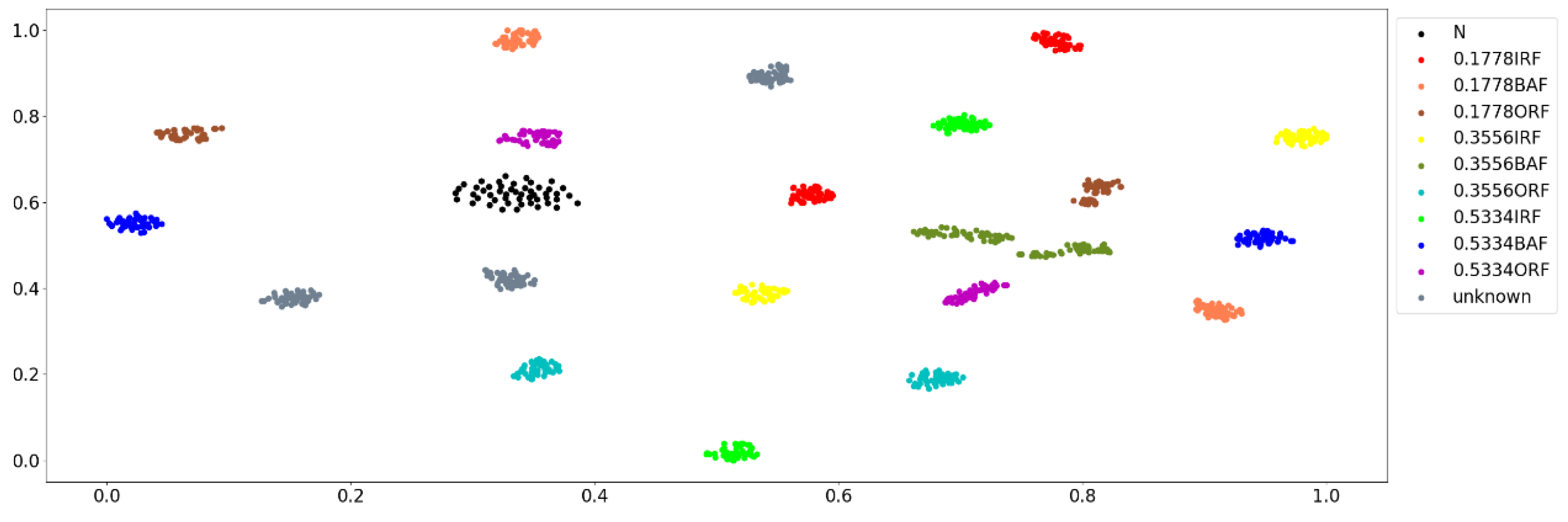
| Fault Type | Fault Diameter/mm | Collecting Position | Sample Number | Label |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRF | 0.1778 | DE | 102,400 | 1 |
| FE | 102,400 | 1 | ||
| 0.3556 | DE | 102,400 | 2 | |
| FE | 102,400 | 2 | ||
| 0.5334 | DE | 102,400 | 3 | |
| FE | 102,400 | 3 | ||
| ORF | 0.1778 | DE | 102,400 | 4 |
| FE | 102,400 | 4 | ||
| 0.3556 | DE | 102,400 | 5 | |
| FE | 102,400 | 5 | ||
| 0.5334 | DE | 102,400 | 6 | |
| FE | 102,400 | 6 | ||
| BAF | 0.1778 | DE | 102,400 | 7 |
| FE | 102,400 | 7 | ||
| 0.3556 | DE | 102,400 | 8 | |
| FE | 102,400 | 8 | ||
| 0.5334 | DE | 102,400 | 9 | |
| FE | 102,400 | 9 | ||
| Normal state | 0 | DE | 204,800 | 0 |
| Fault Type | IRF | BAF | ORF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average ratio of Sb to Sw | 418.17 | 291.37 | 361.22 |
| SSAE | Number of hidden layers | 3 |
| Network structure | 1024-512-256-128-10 | |
| Optimizer | Adam | |
| Iterations | 60 | |
| XGBoost | Max depth | 5 |
| Min child weight | 1 | |
| N estimators | 80 | |
| Min child weight | 0.12 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) | Methods | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSAE-XGBoost | 96.30 | PE-SSAE-XGBoost | 99.27 |
| CNN | 96.82 | PE-CNN | 97.53 |
| SVM | 94.78 | PE-SVM | 95.26 |
| DBN | 93.19 | PE-DBN | 95.67 |
| Methods | Accuracy (%) | Methods | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSAE-XGBoost | 86.96 | PE-SSAE-XGBoost | 92.34 |
| CNN | 84.19 | PE-CNN | 90.27 |
| SVM | 82.42 | PE-SVM | 89.51 |
| DBN | 81.03 | PE-DBN | 89.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, C.; Zhou, J.; Han, B.; Li, W.; Zhao, H. Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearing Based on a Priority Elimination Method. Sensors 2023, 23, 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042320
Xiang C, Zhou J, Han B, Li W, Zhao H. Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearing Based on a Priority Elimination Method. Sensors. 2023; 23(4):2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042320
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Chuan, Jiahui Zhou, Bing Han, Weichen Li, and Hongge Zhao. 2023. "Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearing Based on a Priority Elimination Method" Sensors 23, no. 4: 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042320
APA StyleXiang, C., Zhou, J., Han, B., Li, W., & Zhao, H. (2023). Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearing Based on a Priority Elimination Method. Sensors, 23(4), 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042320








