Improving Speech Recognition Performance in Noisy Environments by Enhancing Lip Reading Accuracy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Lip Reading
2.2. Audiovisual Speech Recognition
3. Architecture and Methods
3.1. Automatic Speech Recognition
3.1.1. Audio Frontend
3.1.2. Audio Backend
3.2. Visual Speech Recognition
3.2.1. Visual Frontend
3.2.2. Visual Backend
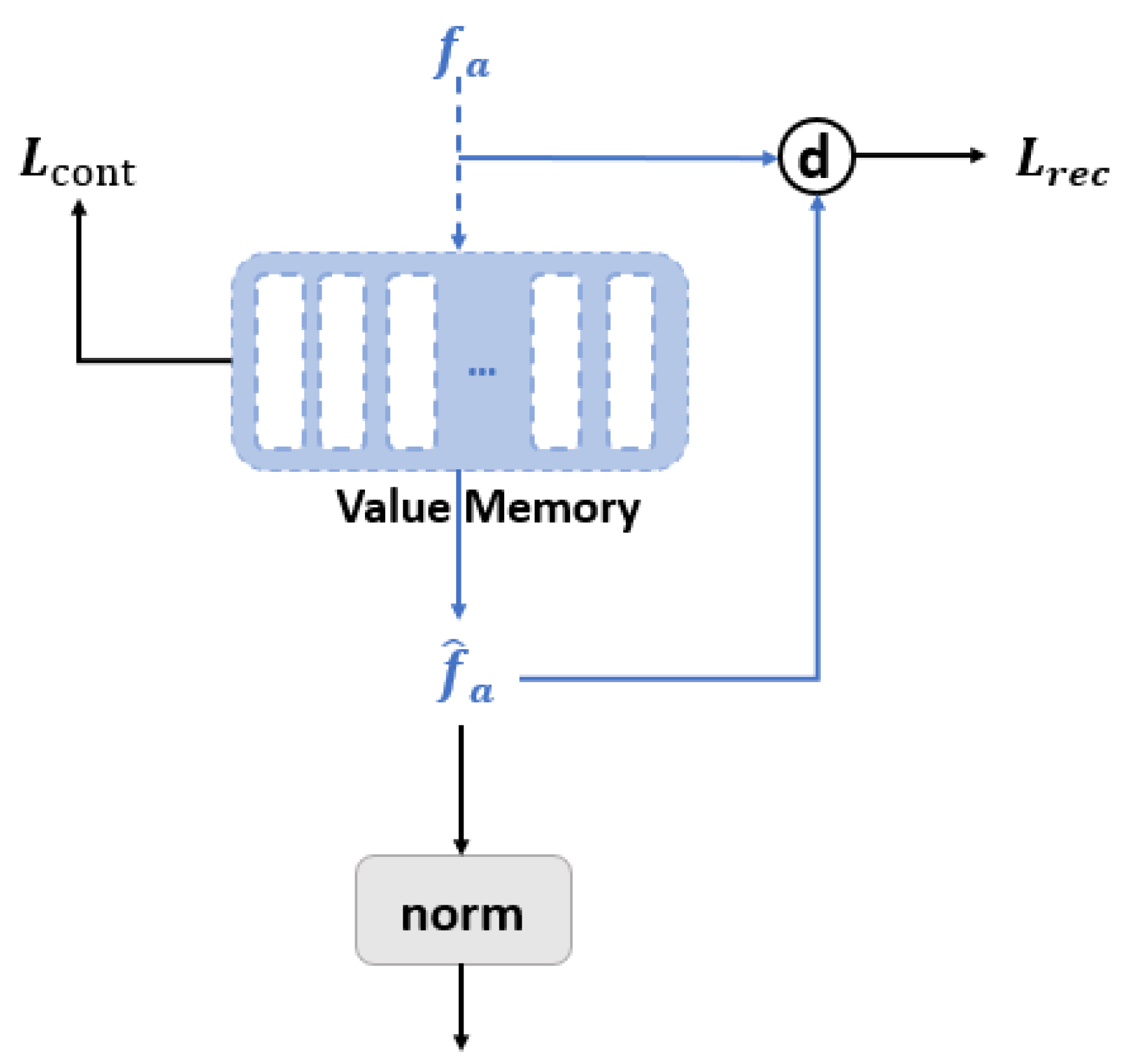
3.3. Joint Cross-Modal Fusion Module
3.4. Decoders
3.5. Loss Function
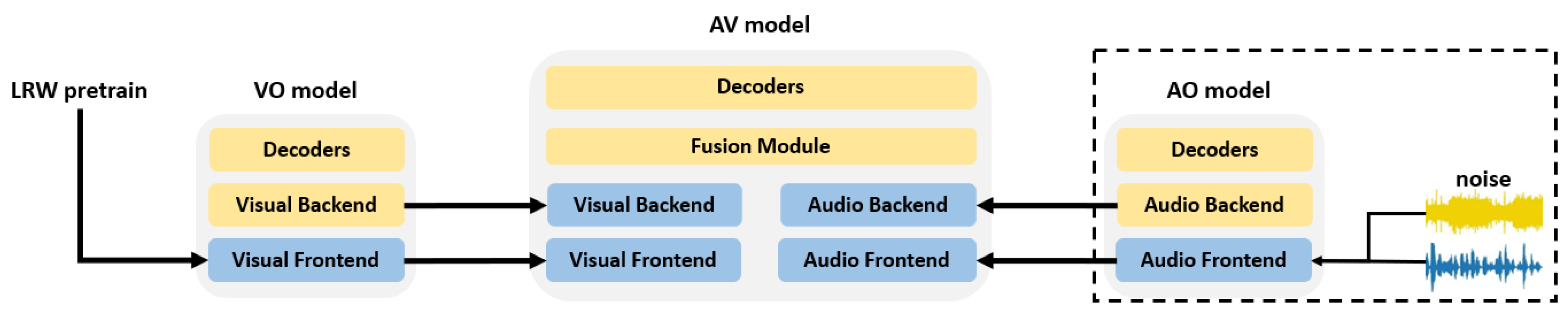
3.6. Training Pipeline
3.7. Decoding
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset and Evaluation Metric
4.2. Experimental Settings
4.3. Experimental Results
4.3.1. Comparison Experiments
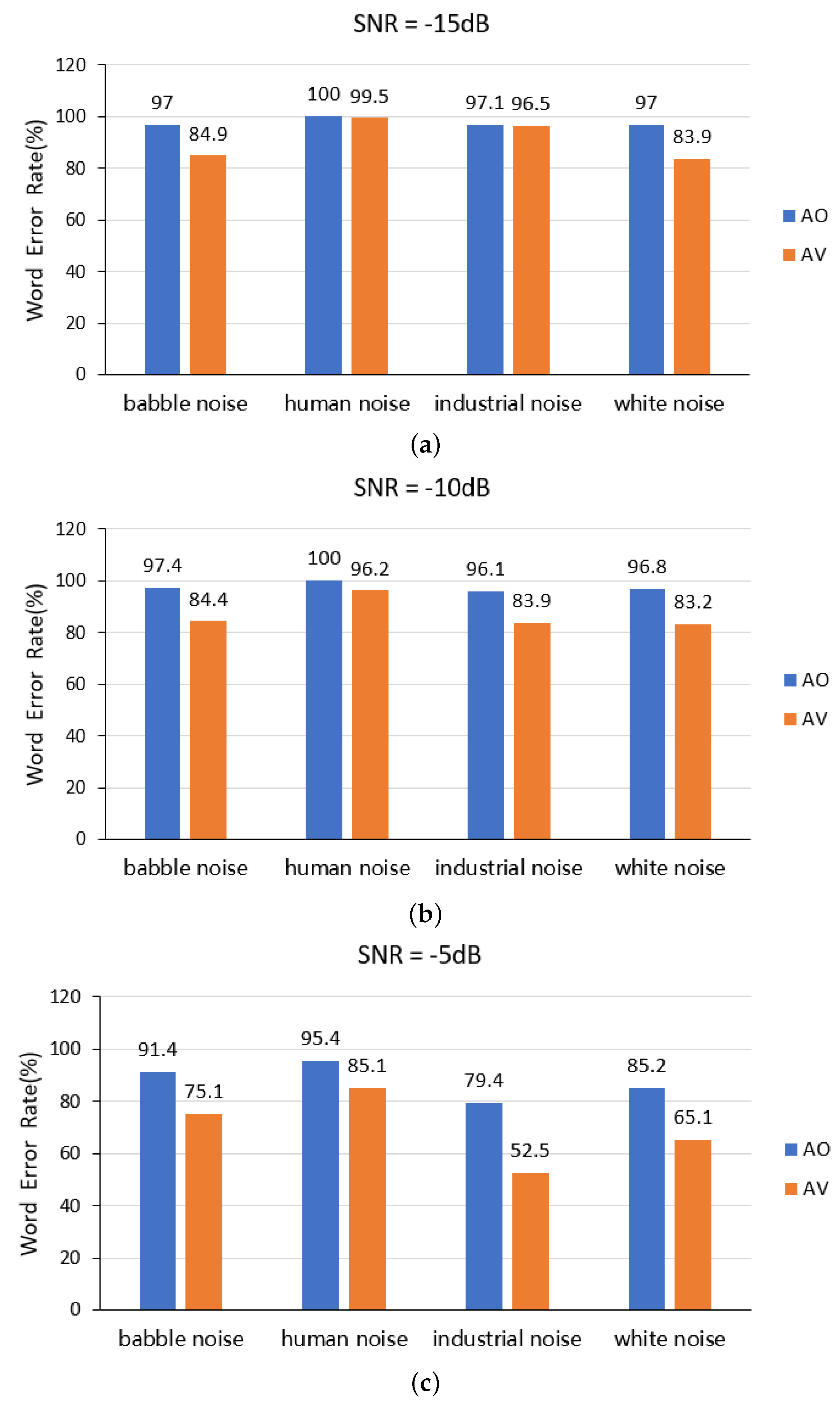
4.3.2. Noise Environment Comparison Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, R.; Chu, W.; Chang, P.; Xiao, J. CASS-NAT: CTC alignment-based single step non-autoregressive transformer for speech recognition. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 5889–5893. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.L. Transformer-based end-to-end speech recognition with local dense synthesizer attention. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 5899–5903. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R.; Grauman, K. Visualvoice: Audio-visual speech separation with cross-modal consistency. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 15490–15500. [Google Scholar]
- Subakan, C.; Ravanelli, M.; Cornell, S.; Bronzi, M.; Zhong, J. Attention is all you need in speech separation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.; Sun, B.; Li, S. Multimodal Sparse Transformer Network for Audio-Visual Speech Recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afouras, T.; Chung, J.S.; Senior, A.; Vinyals, O.; Zisserman, A. Deep audio-visual speech recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 44, 8717–8727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Petridis, S.; Pantic, M. End-to-end audio-visual speech recognition with conformers. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 7613–7617. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Hsu, W.N.; Lakhotia, K.; Mohamed, A. Learning audio-visual speech representation by masked multimodal cluster prediction. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.02184. [Google Scholar]
- Praveen, R.G.; de Melo, W.C.; Ullah, N.; Aslam, H.; Zeeshan, O.; Denorme, T.; Pedersoli, M.; Koerich, A.L.; Bacon, S.; Cardinal, P.; et al. A Joint Cross-Attention Model for Audio-Visual Fusion in Dimensional Emotion Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 2486–2495. [Google Scholar]
- Assael, Y.M.; Shillingford, B.; Whiteson, S.; De Freitas, N. Lipnet: End-to-end sentence-level lipreading. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.01599. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.S.; Senior, A.; Vinyals, O.; Zisserman, A. Lip reading sentences in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6447–6456. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, B.; Ma, P.; Petridis, S.; Pantic, M. Lipreading using temporal convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 6319–6323. [Google Scholar]
- Koumparoulis, A.; Potamianos, G. Accurate and Resource-Efficient Lipreading with Efficientnetv2 and Transformers. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 8467–8471. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, P.; Wang, Y.; Petridis, S.; Shen, J.; Pantic, M. Training strategies for improved lip-reading. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 23–27 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 8472–8476. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, P.; Petridis, S.; Pantic, M. Visual speech recognition for multiple languages in the wild. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2022, 4, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Yeo, J.H.; Ro, Y.M. Distinguishing Homophenes using Multi-head Visual-audio Memory for Lip Reading. In Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 22. [Google Scholar]
- Sterpu, G.; Saam, C.; Harte, N. How to teach DNNs to pay attention to the visual modality in speech recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2020, 28, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterpu, G.; Saam, C.; Harte, N. Attention-based audio-visual fusion for robust automatic speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, Boulder, CO, USA, 16–20 October 2018; pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Braga, O.; Makino, T.; Siohan, O.; Liao, H. End-to-end multi-person audio/visual automatic speech recognition. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 6994–6998. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, S.X.; Wu, J.; Ghorbani, S.; Wu, B.; Kang, S.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Meng, H.; Yu, D. Audio-visual recognition of overlapped speech for the lrs2 dataset. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 6984–6988. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Chen, P.; Gong, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, Z. Leveraging Uni-Modal Self-Supervised Learning for Multimodal Audio-Visual Speech Recognition. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.07996. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, S.; Baevski, A.; Collobert, R.; Auli, M. wav2vec: Unsupervised pre-training for speech recognition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.05862. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, J.; Rivière, M.; Zheng, W.; Kharitonov, E.; Xu, Q.; Mazaré, P.E.; Karadayi, J.; Liptchinsky, V.; Collobert, R.; Fuegen, C.; et al. Libri-light: A benchmark for asr with limited or no supervision. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 7669–7673. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Hong, J.; Park, S.J.; Ro, Y.M. Multi-modality associative bridging through memory: Speech sound recollected from face video. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 296–306. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Kim, H.G.; Choi, D.H.; Kim, H.I.; Ro, Y.M. Video prediction recalling long-term motion context via memory alignment learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 3054–3063. [Google Scholar]
- Petridis, S.; Stafylakis, T.; Ma, P.; Tzimiropoulos, G.; Pantic, M. Audio-visual speech recognition with a hybrid ctc/attention architecture. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Spoken Language Technology Workshop (SLT), Athens, Greece, 18–21 December 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 513–520. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A.; Fernández, S.; Gomez, F.; Schmidhuber, J. Connectionist temporal classification: Labelling unsegmented sequence data with recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–29 June 2006; pp. 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, S.; Hori, T.; Kim, S.; Hershey, J.R.; Hayashi, T. Hybrid CTC/attention architecture for end-to-end speech recognition. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2017, 11, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.S.; Zisserman, A. Lip Reading in the Wild. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 8024–8035. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- King, D.E. Dlib-ml: A machine learning toolkit. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2009, 10, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar]
- Baevski, A.; Zhou, Y.; Mohamed, A.; Auli, M. wav2vec 2.0: A framework for self-supervised learning of speech representations. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 12449–12460. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, X.; Hou, P.; Tang, H.; Song, M. Hearing lips: Improving lip reading by distilling speech recognizers. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 6917–6924. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, F.; Wang, S. Spatio-temporal fusion based convolutional sequence learning for lip reading. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 713–722. [Google Scholar]


| Stage | Modules | Audio Waveform |
|---|---|---|
| Audio Frontend | wav2vec 2.0 | |
| Audio Backend | 1D convolution | |
| Transformer Encoder |
| Stage | Modules | Image Sequence () |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Frontend | 3D convolution | |
| MoCo v2 | ||
| Visual Backend | 1D convolution | |
| Multi-head K-V Memory |
| Stage | Modules | Fusion Features |
|---|---|---|
| Fusion Module | Joint Cross-Modal Fusion | |
| Linear | ||
| Transformer Encoder |
| Methods | WER (%) |
|---|---|
| Visual-only (VO) (↓) | |
| LIBS [35] | 65.3 |
| TM-CTC * [6] | 54.7 |
| Conv-seq2seq [36] | 51.7 |
| TM-seq2seq * [6] | 50.0 |
| LF-MMI TDNN * [20] | 48.9 |
| MVM [16] | 44.5 |
| LU-SSL Transformer [21] | 43.2 |
| E2E Conformer * [7] | 42.4 |
| Ours | 40.1 |
| Audio-only (AO) (↓) | |
| TM-CTC * [6] | 10.1 |
| TM-seq2seq * [6] | 9.7 |
| CTC/attention * [27] | 8.2 |
| LF-MMI TDNN * [20] | 6.7 |
| E2E Conformer * [7] | 4.3 |
| LU-SSL Transformer [21] | 2.7 |
| Ours | 2.7 |
| Audio-Visual(AV)(↓) | |
| TM-seq2seq * [6] | 8.5 |
| TM-CTC * [6] | 8.2 |
| LF-MMI TDNN * [20] | 5.9 |
| E2E Conformer * [7] | 4.2 |
| LU-SSL Transformer [21] | 2.8 |
| Ours | 2.8 |
| Modality | Model | 15 dB | −10 dB | −5 dB | 0 dB | 5 dB | Clean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AO | Afouras et al. [6] | - | - | - | 58.5% | - | 10.5% |
| Ours | 97% | 97.4% | 91.4% | 32.5% | 7.2% | 2.7% | |
| AV | Afouras et al. [6] | - | - | - | 33.5% | - | 9.4% |
| Xichen Pan et al. [21] | 88.9% | 88.2% | 77.1% | 24.5% | 6.3% | 2.8% | |
| Ours | 84.9% | 84.4% | 75.1% | 22.4% | 5.9% | 2.8% |
| Modality | Model | −5 dB | 0 dB | 5 dB | 10 dB | 15 dB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AO | Ours | 95.4% | 69.3% | 26.2% | 7.8% | 3.9% |
| AV | Xichen Pan et al. [21] | 87.4% | 58.9% | 20.9% | 6.6% | 3.6% |
| Ours | 85.1% | 57.2% | 20.7% | 6.0% | 3.5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, R. Improving Speech Recognition Performance in Noisy Environments by Enhancing Lip Reading Accuracy. Sensors 2023, 23, 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042053
Li D, Gao Y, Zhu C, Wang Q, Wang R. Improving Speech Recognition Performance in Noisy Environments by Enhancing Lip Reading Accuracy. Sensors. 2023; 23(4):2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042053
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dengshi, Yu Gao, Chenyi Zhu, Qianrui Wang, and Ruoxi Wang. 2023. "Improving Speech Recognition Performance in Noisy Environments by Enhancing Lip Reading Accuracy" Sensors 23, no. 4: 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042053
APA StyleLi, D., Gao, Y., Zhu, C., Wang, Q., & Wang, R. (2023). Improving Speech Recognition Performance in Noisy Environments by Enhancing Lip Reading Accuracy. Sensors, 23(4), 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23042053







