Malaria Detection Using Advanced Deep Learning Architecture
(This article belongs to the Section Intelligent Sensors)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
3. Life Cycle
4. Clinical Features of Malaria and General Pathogenesis
5. Diagnosis
6. Treatment and Prevention
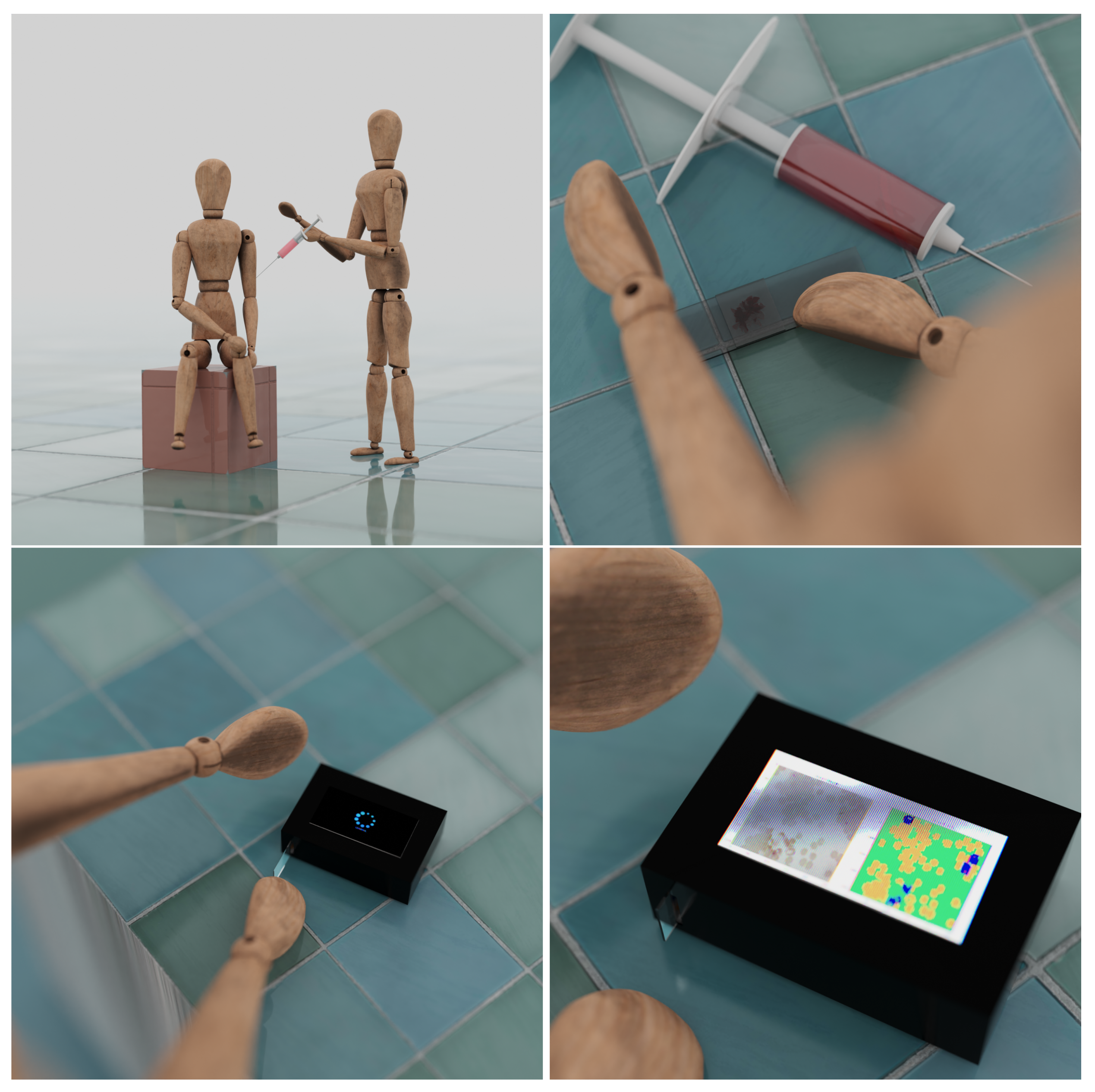
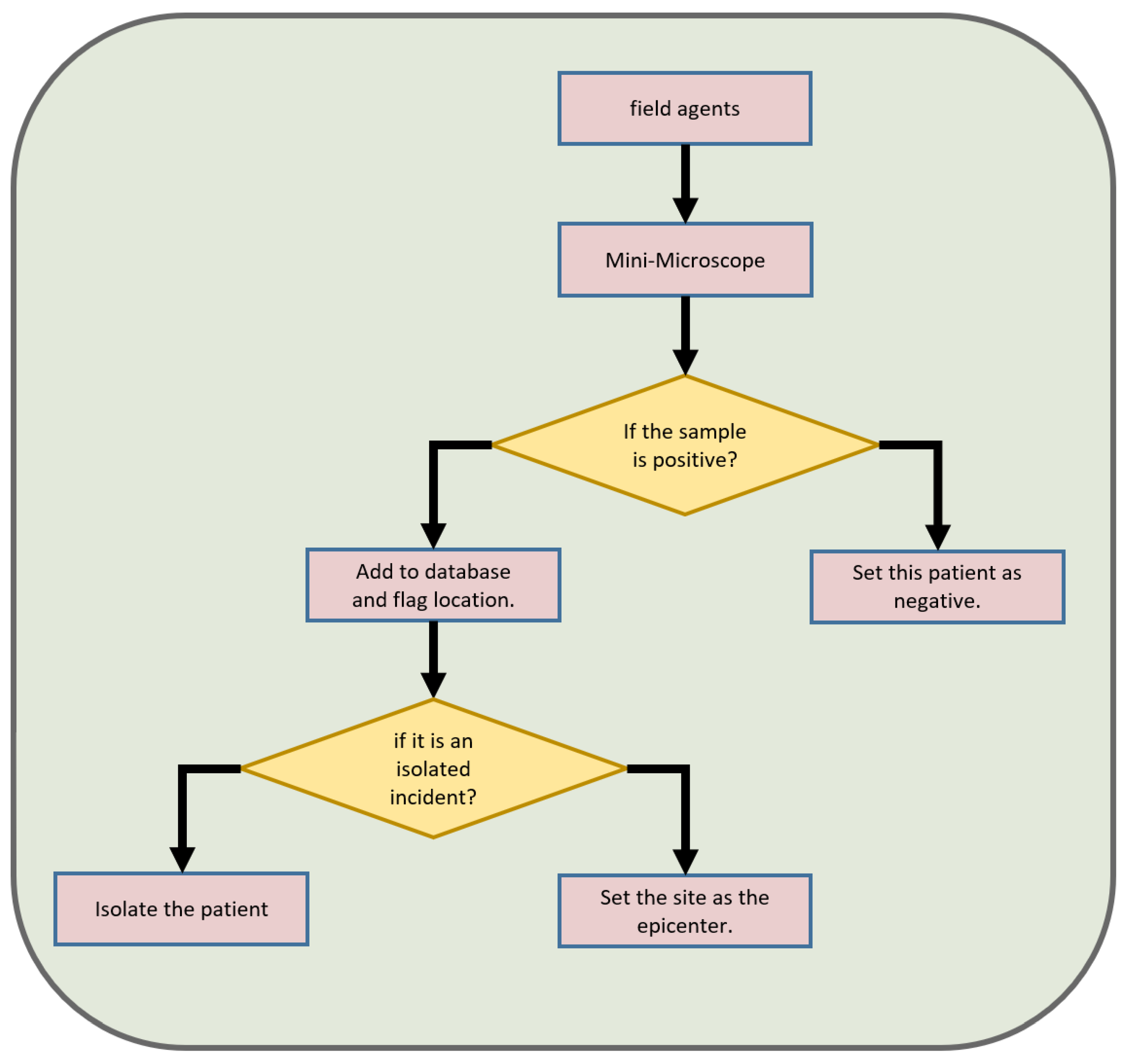
7. Proposed Solution
| Algorithm 1 NAdam training algorithm. |
|
NAdam Algorithm
8. The Dataset
8.1. Labels
- Healthy cells;
- Infected cells.
8.2. Preprocessing
8.3. Normalization
8.4. Augmentation
- Horizontal flip;
- Vertical flip;
- Random noise addition;
- Random rotation;
- Random zoom;
- Random hue shift.
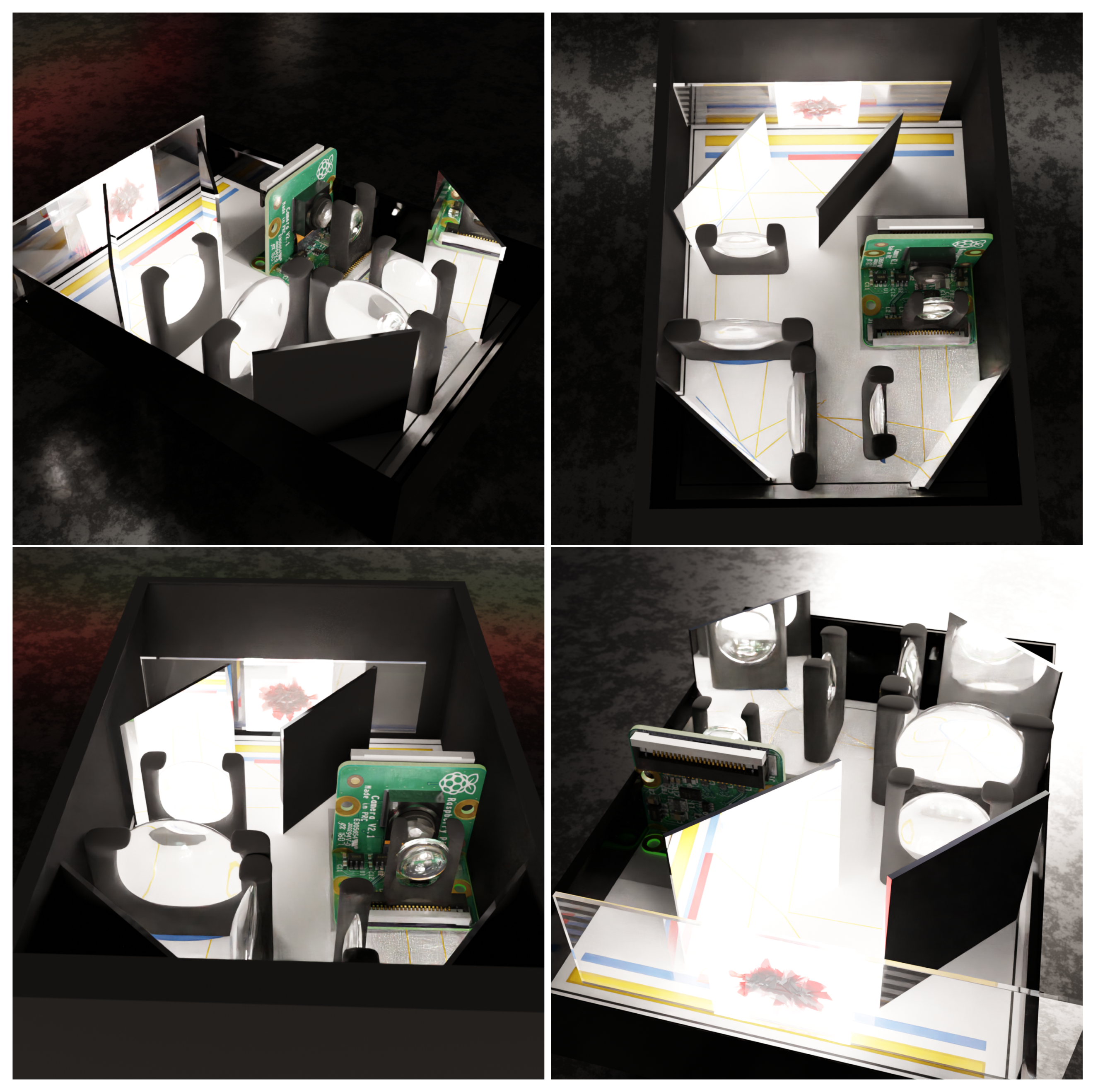
9. Our System
10. Hardware
- CPU: Ryzen Threadripper 2950X 16c/32t;
- RAM: 128GB;
- GPU: NVidia RTX 3090 24GB.
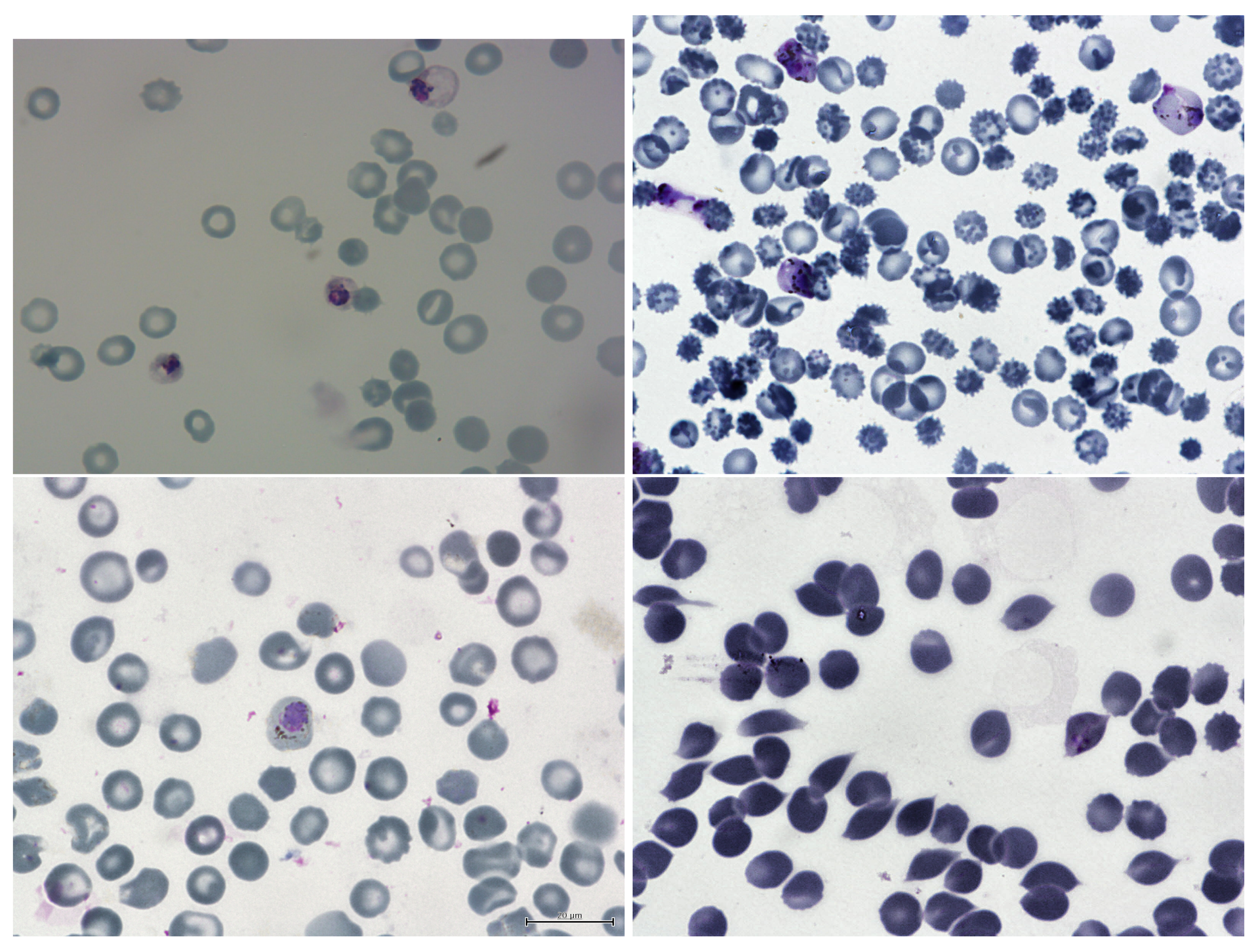
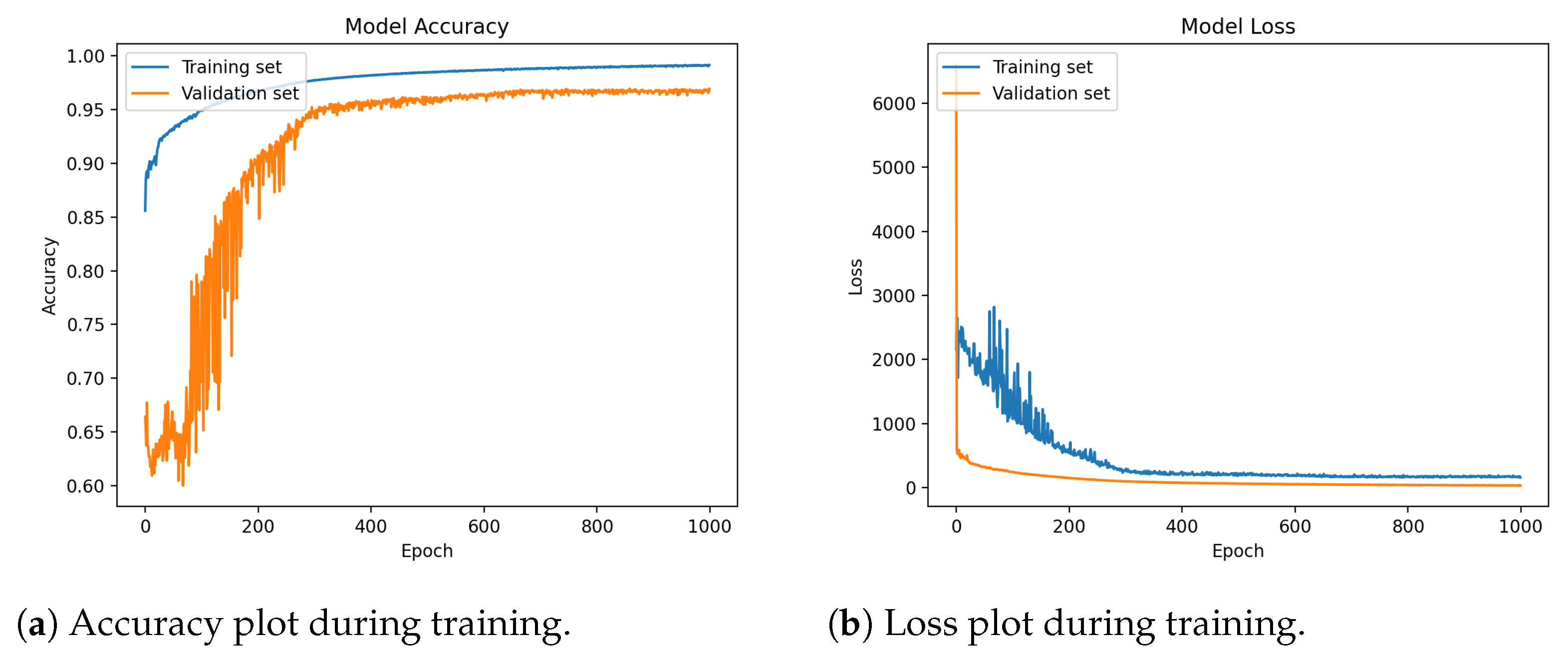
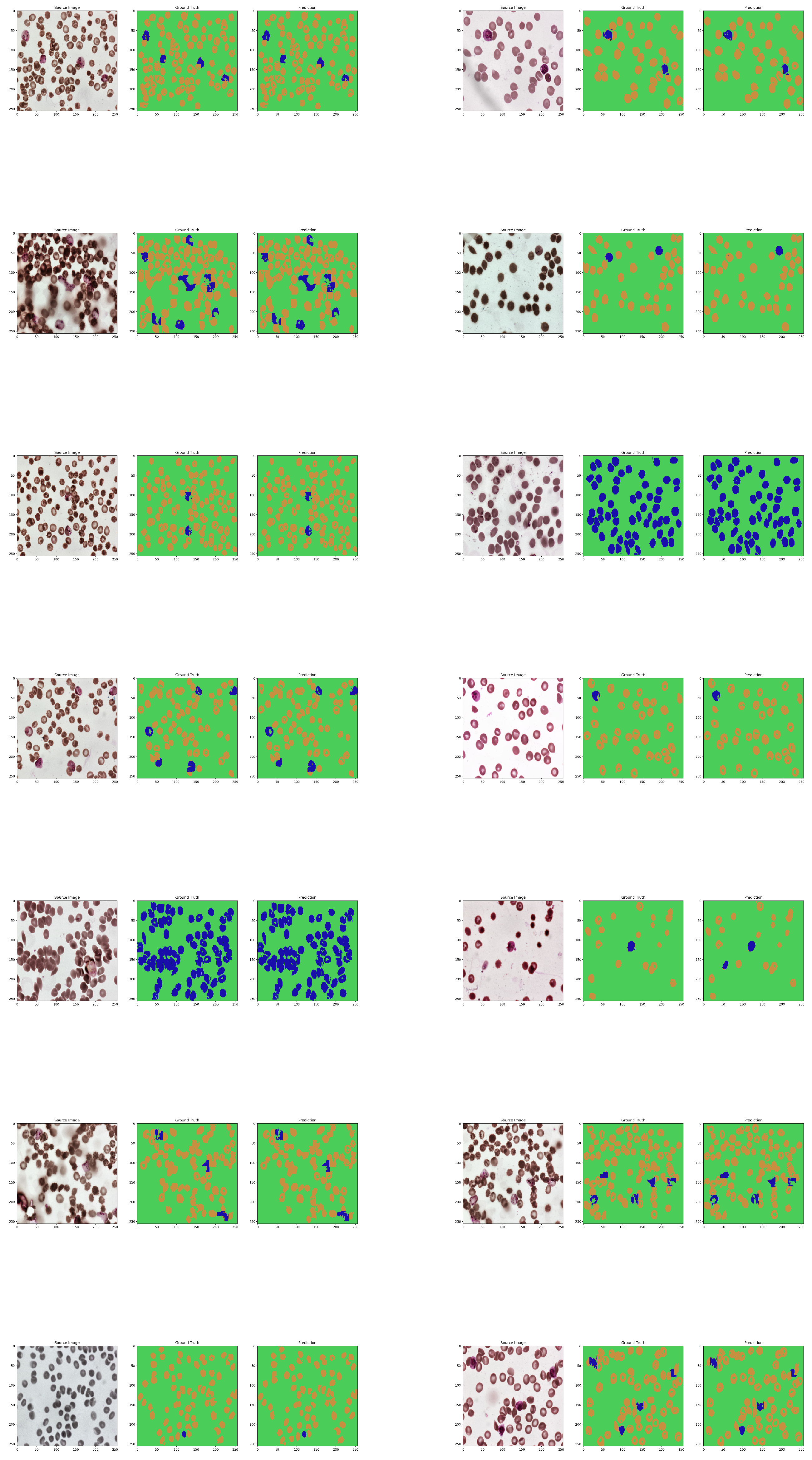
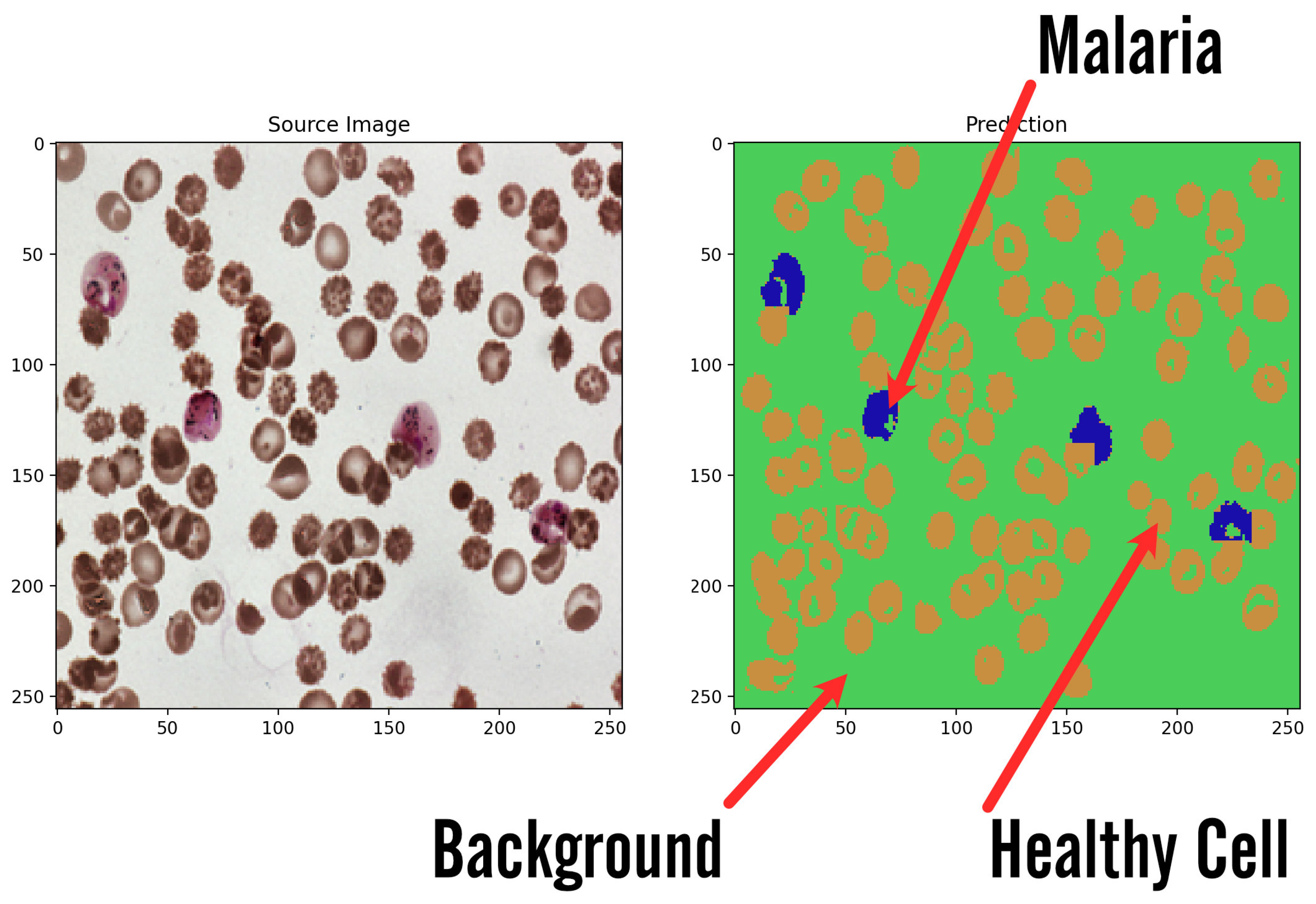
11. Results
Visualization
| Algorithm 2 Cells counting algorithm. |
|
12. Conclusions
13. Future Possibilities
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mourier, T.; de Alvarenga, D.A.M.; Kaushik, A.; de Pina-Costa, A.; Douvropoulou, O.; Guan, Q.; Guzmán-Vega, F.J.; Forrester, S.; de Abreu, F.V.S.; Júnior, C.B.; et al. The genome of the zoonotic malaria parasite Plasmodium simium reveals adaptations to host switching. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykersma, A. The new zoonotic malaria: Plasmodium cynomolgi. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2021, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menkin-Smith, L.; Winders, W.T. Plasmodium Vivax Malaria; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, N.M.; Lampah, D.A.; Kenangalem, E.; Simpson, J.A.; Poespoprodjo, J.R.; Sugiarto, P.; Anstey, N.M.; Price, R.N. Major burden of severe anemia from non-falciparum malaria species in Southern Papua: A hospital-based surveillance study. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, S.; Douglas, N.M.; Lampah, D.A.; Simpson, J.A.; Kenangalem, E.; Sugiarto, P.; Anstey, N.M.; Poespoprodjo, J.R.; Price, R.N. Plasmodium malariae infection associated with a high burden of anemia: A hospital-based surveillance study. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Guidelines for Malaria; Technical report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Raouf, S.; Mpimbaza, A.; Kigozi, R.; Sserwanga, A.; Rubahika, D.; Katamba, H.; Lindsay, S.W.; Kapella, B.K.; Belay, K.A.; Kamya, M.R.; et al. Resurgence of malaria following discontinuation of indoor residual spraying of insecticide in an area of Uganda with previously high-transmission intensity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, B.; Zongo, I.; Dicko, A.; Chandramohan, D.; Snow, R.W.; Ockenhouse, C. Resurgent and delayed malaria. Malar. J. 2022, 21, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelsattar, A.; Hassan, A.N. Assessment of malaria resurgence vulnerability in Fayoum, Egypt Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Egypt. J. Remote. Sens. Space Sci. 2021, 24, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, M.M.; Moser, K.A.; Kabuya, J.B.B.; Cunningham, C.; Juliano, J.J. Antimalarial drug resistance and implications for the WHO global technical strategy. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2021, 8, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI; Akkaya, I.; Andrychowicz, M.; Chociej, M.; Litwin, M.; McGrew, B.; Petron, A.; Paino, A.; Plappert, M.; Powell, G.; et al. Solving Rubik’s Cube with a Robot Hand. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.07113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.L.; Jensen, B.F.; Mahlmann, T.; Togelius, J.; Yannakakis, G.N. Ai for general strategy game playing. In Handbook of Digital Games; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 274–304. [Google Scholar]
- Woźniak, M.; Wieczorek, M.; Siłka, J. Deep Neural Network with Transfer Learning in Remote Object Detection from Drone. In Proceedings of the 5th International ACM Mobicom Workshop on Drone Assisted Wireless Communications for 5G and Beyond, Sydney, Australia, 17 October 2022; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Park, K.S.; Ha, Y.G. Image preprocessing for efficient training of YOLO deep learning networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (BigComp), Shanghai, China, 15–17 January 2018; pp. 635–637. [Google Scholar]
- Woźniak, M.; Siłka, J.; Wieczorek, M. Deep learning based crowd counting model for drone assisted systems. In Proceedings of the 4th ACM MobiCom Workshop on Drone Assisted Wireless Communications for 5G and Beyond, Virtual Event, 29 October 2021; pp. 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Creswell, A.; White, T.; Dumoulin, V.; Arulkumaran, K.; Sengupta, B.; Bharath, A.A. Generative adversarial networks: An overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2018, 35, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, K.; Wu, S.; Gu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, C.; Qiao, Y.; Change Loy, C. Esrgan: Enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yasenko, L.; Klyatchenko, Y.; Tarasenko-Klyatchenko, O. Image noise reduction by denoising autoencoder. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 11th International Conference on Dependable Systems, Services and Technologies (DESSERT), Kyiv, Ukraine, 14–18 May 2020; pp. 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Rouphael, R.; Noizet, M.; Prévost, S.; Deleau, H.; Steffenel, L.A.; Lucas, L. Neural Denoising for Spectral Monte Carlo Rendering; The Eurographics Association: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. Bisenet: Bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 325–341. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Dana, K.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Tyagi, A.; Agrawal, A. Context encoding for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7151–7160. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2021; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240040496 (accessed on 22 November 2022).
- Howes, R.E.; Battle, K.E.; Mendis, K.N.; Smith, D.L.; Cibulskis, R.E.; Baird, J.K.; Hay, S.I. Global epidemiology of Plasmodium vivax. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatem, A.J.; Jia, P.; Ordanovich, D.; Falkner, M.; Huang, Z.; Howes, R.; Hay, S.I.; Gething, P.W.; Smith, D.L. The geography of imported malaria to non-endemic countries: A meta-analysis of nationally reported statistics. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mischlinger, J.; Rönnberg, C.; Álvarez-Martínez, M.J.; Bühler, S.; Paul, M.; Schlagenhauf, P.; Petersen, E.; Ramharter, M. Imported malaria in countries where malaria is not endemic: A comparison of semi-immune and nonimmune travelers. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00104-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, K.; Hentzschel, F.; Valkiūnas, G.; Marti, M. Plasmodium asexual growth and sexual development in the haematopoietic niche of the host. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moxon, C.A.; Gibbins, M.P.; McGuinness, D.; Milner Jr, D.A.; Marti, M. New insights into malaria pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2020, 15, 315–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varo, R.; Chaccour, C.; Bassat, Q. Update on malaria. Med. Clin. 2020, 155, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanghi, G.; Vaughan, A.M. Plasmodium vivax pre-erythrocytic stages and the latent hypnozoite. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 85, 102447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brejt, J.A.; Golightly, L.M. Severe malaria: Update on pathophysiology and treatment. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 32, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, N.J. Anaemia and malaria. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, D.A. Malaria pathogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a025569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauserman, M.; Conroy, A.L.; North, K.; Patterson, J.; Bose, C.; Meshnick, S. An overview of malaria in pregnancy. Semin. Perinatol. 2019, 43, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Malaria Microscopy Quality Assurance Manual-Version 2; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Mathison, B.A.; Pritt, B.S. Update on malaria diagnostics and test utilization. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2009–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahittikorn, A.; Masangkay, F.R.; Kotepui, K.U.; Milanez, G.D.J.; Kotepui, M. Quantification of the misidentification of Plasmodium knowlesi as Plasmodium malariae by microscopy: An analysis of 1569 P. knowlesi cases. Malar. J. 2021, 20, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Treatment of Malaria: Guidelines for Clinicians (United States); Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/diagnosis_treatment/clinicians1.html (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2016. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/dpdx/malaria/ (accessed on 3 December 2022).
- Januszek, R.; Siłka, W.; Sabatowski, K.; Malinowski, K.P.; Heba, G.; Surowiec, S.; Chyrchel, M.; Rzeszutko, Ł.; Bryniarski, L.; Surdacki, A.; et al. Procedure-Related Differences and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Treated with Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Assisted by Optical Coherence Tomography between New and Earlier Generation Software (Ultreon™ 1.0 Software vs. AptiVue™ Software). J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2022, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartuś, S.; Siłka, W.; Kasprzycki, K.; Sabatowski, K.; Malinowski, K.P.; Rzeszutko, Ł.; Chyrchel, M.; Bryniarski, L.; Surdacki, A.; Bartuś, K.; et al. Experience with Optical Coherence Tomography Enhanced by a Novel Software (Ultreon™ 1.0 Software)—The First One Hundred Cases. Medicina 2022, 58, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo Higuita, N.I.; White, B.P.; Franco-Paredes, C.; McGhee, M.A. An update on prevention of malaria in travelers. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, 20499361211040690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitri, L.E.; Widaningrum, T.; Endharti, A.T.; Prabowo, M.H.; Winaris, N.; Nugraha, R.Y.B. Malaria diagnostic update: From conventional to advanced method. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, D.; Lefèvre, T.; Moiroux, N.; Pennetier, C.; Chandre, F.; Cohuet, A. Behavioural adaptations of mosquito vectors to insecticide control. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 34, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.; Siłka, J.; Woźniak, M.; Garg, S.; Hassan, M.M. Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network Model for Human Face Detection in Risk Situations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 4820–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagur, P.K.; McCoy, J.P., Jr. Collection, storage, and preparation of human blood cells. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2015, 73, 5.1.1–5.1.16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abayomi-Alli, O.O.; Damaševičius, R.; Wieczorek, M.; Woźniak, M. Data augmentation using principal component resampling for image recognition by deep learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing, Zakopane, Poland, 12–14 October 2020; pp. 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, D.; Kawale, K.; Shah, M.; Randive, S.; Mapari, R. Malaria parasite detection using deep learning:(Beneficial to humankind). In Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), Madurai, India, 13–15 May 2020; pp. 984–988. [Google Scholar]
- Razin, W.R.W.M.; Gunawan, T.S.; Kartiwi, M.; Yusoff, N.M. Malaria Parasite Detection and Classification using CNN and YOLOv5 Architectures. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 8th International Conference on Smart Instrumentation, Measurement and Applications (ICSIMA), Melaka, Malaysia, 26–28 September 2022; pp. 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- Alqudah, A.; Alqudah, A.M.; Qazan, S. Lightweight Deep Learning for Malaria Parasite Detection Using Cell-Image of Blood Smear Images. Rev. D’Intell. Artif. 2020, 34, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, L. An effective convolutional neural network for classifying red blood cells in malaria diseases. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2020, 12, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turuk, M.; Sreemathy, R.; Kadiyala, S.; Kotecha, S.; Kulkarni, V. CNN Based Deep Learning Approach for Automatic Malaria Parasite Detection. IAENG Int. J. Comput. Sci. 2022, 49, 745–753. [Google Scholar]
- Shekar, G.; Revathy, S.; Goud, E.K. Malaria detection using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 4th international conference on trends in electronics and informatics (ICOEI)(48184), Tirunelveli, India, 15–17 June 2020; pp. 746–750. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, A.; Zunair, H.; Rahman, M.S.; Yuki, J.Q.; Biswas, S.; Alam, M.A.; Alam, N.B.; Mahdy, M. Improving malaria parasite detection from red blood cell using deep convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.10418. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, D.R.; Yong, W.X.; Yapeter, J.; Subburaj, K.; Chandramohanadas, R. A deep learning approach to the screening of malaria infection: Automated and rapid cell counting, object detection and instance segmentation using Mask R-CNN. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 88, 101845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sağlam, S.; Tat, F.; Bayar, S. Fpga implementation of cnn algorithm for detecting malaria diseased blood cells. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Symposium on Advanced Electrical and Communication Technologies (ISAECT), Rome, Italy, 27–29 November 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]




| Article | Type | Year | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ours | Seg-Sem CNN | 2022 | 99.68% |
| Divyansh et al. [48] | CNN | 2020 | 95.7% |
| Razin et al. [49] | YOLOv5 CNN | 2022 | 96.21% |
| Alqudah et al. [50] | Lightweight CNN | 2020 | 98.85% |
| Quan et al. [51] | ADCN | 2020 | 97.47% |
| Turuk et al. [52] | Integrated CNN | 2022 | 93.89% |
| Shekar et al. [53] | Fine-Tuned CNN | 2020 | 95.99% |
| Rahman et al. [54] | TL-VGG16 | 2019 | 97.77% |
| Loh et al. [55] | Mask R-CNN | 2021 | 94.57% |
| Sağlam et al. [56] | FPGA CNN | 2019 | 94.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siłka, W.; Wieczorek, M.; Siłka, J.; Woźniak, M. Malaria Detection Using Advanced Deep Learning Architecture. Sensors 2023, 23, 1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031501
Siłka W, Wieczorek M, Siłka J, Woźniak M. Malaria Detection Using Advanced Deep Learning Architecture. Sensors. 2023; 23(3):1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031501
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiłka, Wojciech, Michał Wieczorek, Jakub Siłka, and Marcin Woźniak. 2023. "Malaria Detection Using Advanced Deep Learning Architecture" Sensors 23, no. 3: 1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031501
APA StyleSiłka, W., Wieczorek, M., Siłka, J., & Woźniak, M. (2023). Malaria Detection Using Advanced Deep Learning Architecture. Sensors, 23(3), 1501. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23031501





