A Review on the Effects of Thermal Inversions and Electromagnetic Fields on Cell Cultures and Wireless Communications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Voosen, P. In a paradox, cleaner air is now adding to global warming. Science 2022, 377, 353–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaas, J.; Jia, H.; Smith, C.; Albright, A.L.; Aas, W.; Bellouin, N.; Boucher, O.; Doutriaux-Boucher, M.; Forster, P.M.; Grosvenor, D.; et al. Robust evidence for reversal of the trend in aerosol effective climate forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 12221–12239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: An analysis of data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Ren, L.; Yue, X.; Liao, H. Fast climate responses to emission reductions in aerosol and ozone precursors in China during 2013–2017. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 7131–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Pan, X.; Guo, X.; Li, G. Health impact of China’s air pollution prevention and control action plan: An analysis of national air quality monitoring and mortality data. Lancet Planet Health 2016, 2, e313–e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arneth, A.; Unger, N.; Kulmala, M.; Andreae, M.O. Clean the air, heat the planet? Science 2009, 326, 672–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jbaily, A.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Lee, T.H.; Kamareddine, L.; Verguet, S.; Dominici, F. Air pollution exposure disparities across US population and income groups. Nature 2022, 601, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Air Pollution: How It Affects Our Health. 2022. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/air/health-impacts-of-air-pollution/health-impacts-of-air-pollution (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- World Health Organization. Household Air Pollution and Health. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/household-air-pollution-and-health (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Trinh, T.T.; Trinh, T.T.; Le, T.T.; Nguyen, H.; Tu, B.M. Temperature inversion and air pollution relationship, and its effects on human health in Hanoi City, Vietnam. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Jones, C.D.; Cox, P.M. Strong present-day aerosol cooling implies a hot future. Nature 2005, 435, 1187–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, A. On the atmospheric transmission of sun radiation and on dust in the air. Geog. Ann. 1929, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Schwartz, S.E.; Hales, M.; Cess, R.D.; Coakley, J.A.; Hansen, J.E.; Hofmann, D.J. Climate Forcing by Anthropogenic Aerosols. Science 1992, 255, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keywood, M.; Paton-Walsh, C.; Lawrence, M.; George, C.; Formenti, P.; Schofield, R.; Cleugh, H.; Borgford-Parnell, N.; Capon, A. Atmospheric goals for sustainable development. Science 2023, 379, 246–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Saini, A.; Li, W.; Hung, H.; Hao, C.; Li, K.; Lee, P.; Wentzell, J.J.B.; et al. Uncovering global-scale risks from commercial chemicals in air. Nature 2021, 600, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, N.; Gao, H.O. Using cellular communication networks to detect air pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9442–9451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messer, H.; Zinevich, A.; Alpert, P. Environmental monitoring by wireless communication networks. Science 2006, 312, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas-Sánchez, A.Á.; Lopez-Martin, M.E.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, J.A.; Ares-Pena, F.J. Technique for Determination of Particulate Matter Pollution in the Atmosphere Using Waveguide Slot Linear Array Antennas: A Feasibility Study. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2016, 13, 1502–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Sánchez, A.Á.; Lopez-Martin, M.E.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, J.A.; Ares-Pena, F.J. Design of Polyimide-Coated Yagi-Uda Antennas for Monitoring the Relative Humidity Level. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 961–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayón-Buján, B.; Salas-Sánchez, A.Á.; Rodríguez-González, J.A.; López-Martín, M.E.; Ares-Pena, F.J. Using Antenna Arrays with Only One Active Element for Beam Reconfiguration and Sensitive Study in Dielectric Media. Sensors 2021, 21, 6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Sánchez, A.A.; Rauch, J.; López-Martín, M.E.; Rodríguez-González, A.; Franceschetti, G.; Ares-Pena, F.J. Feasibility Study on Measuring the Particulate Matter Level in the Atmosphere by Means of Yagi-Uda-Like Antennas. Sensors 2020, 20, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueiro-Benavides, R.A.; Vidal, J.M.L.; Sánchez, A.Á.S.; Rodríguez-González, J.A.; Ares-Pena, F.J.; López-Martín, M.E. Radiofrequency at 2.45 GHz increases toxicity, pro-inflammatory and pre-apoptotic activity caused by black carbon in the RAW 264.7 macrophage cell line. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 142681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Communications Commission. “America’s 5G Future”. Available online: www.fcc.gov/5G (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Witze, A. 5G data networks threaten forecasts. Nature 2019, 569, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witze, A. Global 5G wireless deal threatens weather forecasts. Nature 2019, 575, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voosen, P. New deal won’t prevent 5G communication networks from interfering with weather forecasts. Science 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkin, G. Forecasters fear 5G wireless technology will muck up weather predictions. Science 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, S.; Gelatt, C.D., Jr.; Vecchi, M.P. Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 1983, 220, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Mikecz, A.; Scharf, A. Pollution—Bring the field into the lab. Nature 2022, 602, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueiro-Benavides, R.A.; Vidal, J.M.L.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, J.A.; Ares-Pena, F.J.; López-Martín, E. The HL-60 human promyelocytic cell line constitutes an effective in vitro model for evaluating toxicity, oxidative stress and necrosis/apoptosis after exposure to black carbon particles and 2.45 GHz radiofrequency. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simko, M.; Hartwig, C.; Lantow, M.; Lupke, M.; Mattsson, M.O.; Rollwitz, J. HSP70 expression and free radical release after exposure to non-thermal radio-frequency electromagnetic fields and ultrafine particles inhuman Mono Mac 6 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 161, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCleese, D.; Schofield, J.T.; Taylor, F.W.; Abdou, W.A.; Aharonson, O.; Banfield, D.; Calcutt, S.B.; Heavens, N.G.; Irwin, P.G.J.; Kass, D.M.; et al. Intense polar temperature inversion in the middle atmosphere on Mars. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhusudhan, N.; Harrington, J.; Stevenson, K.B.; Nymeyer, S.; Campo, C.J.; Wheatley, P.J.; Deming, D.; Blecic, J.; Hardy, R.A.; Lust, N.B.; et al. A high C/O ratio and weak thermal inversion in the atmosphere of exoplanet WASP-12b. Nature 2011, 469, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, K.B.; Mandell, A.M.; Tamburo, P.; Gandhi, S.; Pinhas, A.; Madhusudhan, N.; Deming, D. Evidence for a Dayside Thermal Inversion and High Metallicity for the Hot Jupiter WASP-18b. Astrophys. J. 2017, 850, L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Wu, S. Long-term Changes in Extreme Air Pollution Meteorology and the Implications for Air Quality. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Effects Institute. State of Global Air 2020; Special Report; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nawrot, T.S.; Perez, L.; Künzli, N.; Munters, E.; Nemery, B. Public health importance of triggers of myocardial infarction: A comparative risk assessment. Lancet 2011, 377, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.; Veronesi, B.; Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Gehr, P.; Chen, L.C.; Geiser, M.; Reed, W.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Schürch, S.; Schulz, H. Translocation and potential neurological effects of fine and ultrafine particles a critical update. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2006, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Mora-Tiscareño, A.; Ontiveros, E.; Gómez-Garza, G.; Barragán-Mejía, G.; Broadway, J.; Chapman, S.; Valencia-Salazar, G.; Jewells, V.; Maronpot, R.R.; et al. Air pollution, cognitive deficits and brain abnormalities: A pilot study with children and dogs. Brain Cogn. 2008, 68, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Outdoor Air Pollution—IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 109. Available online: http://publications.iarc.fr/Book-And-Report-Series/Iarc-Monographs-On-The-Identification-Of-Carcinogenic-Hazards-To-Humans/Outdoor-Air-Pollution-2015 (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Lo Sciuto, G. Air pollution effects on the intensity of received signal in 3G/4G mobile terminal. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2019, 10, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeis, S.; Schäfer, K.; Münkel, C. Surface-based remote sensing of the mixing-layer height—A review. Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeis, S.; Schäfer, K.; Münkel, C. Observation of the structure of the urban boundary layer with different ceilometers and validation by RASS data. Meteorol. Z. 2009, 18, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haij, M.; Wauben, W.; Klein Baltink, H. Determination of mixing layer height from ceilometer backscatter profiles. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6362, 63320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath-Spangler, E.L.; Denning, A.S. Global seasonal variations of midday planetary boundary layer depth from CALIPSO space-borne LIDAR. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2013, 118, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, P.; Messer, H.; David, N. Mobile networks aid weather monitoring. Nature 2016, 537, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, N.; Sendik, O.; Messer, H.; Alpert, P. Cellular network infrastructure: The future of fog monitoring? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, N.; Gao, O. Using cell-phone tower signals for detecting the precursors of fog. J. Geosphys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 1325–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, J.S.; Adelakun, A.O.; Edward, O.V. Comparative study on radio refractivity gradient in the troposphere using chaotic quantifiers. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibeh, G.F.; Agbo, G.A. Estimation of Tropospheric Refractivity with Artificial Neural Network at Minna, Nigeria. Glob. J. Sci. Front. Res. 2012, 12, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Yardim, C.; Gerstoft, P.; Hodgkiss, W.S. Estimation of radio refractivity from Radar clutter using Bayesian Monte Carlo analysis. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2006, 54, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepecik, C.; Navruz, I. A novel hybrid model for inversion problem of atmospheric refractivity estimation. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2018, 84, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, T.T.; Masters, M.F.; Miers, R.E. Determining dielectric constants using a parallel plate capacitor. Am. J. Phys. 2005, 73, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Jarvis, J. Transmission/Reflection and short circuit line permittivity measurements. NIST 1992. Available online: https://nvlpubs.nist.gov/nistpubs/Legacy/TN/nbstechnicalnote1341.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Gradinarsky, L.; Brage, H.; Lagerholm, B.; Björn, I.N.; Folestad, S. In situ monitoring and control of moisture content in pharmaceutical powder processes using an open-ended coaxial probe. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 1847–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguchi, T.; Udagawa, M.; Nanba, N.; Maki, M.; Ishimine, Y. Measurements of Dielectric Constant of Volcanic Ash Erupted from Five Volcanoes in Japan. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 45, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, R.P.; Baican, R.; Schubert, E. Soot particle properties in the microwave range. In Proceedings of the 1993 23rd European Microwave Conference, Madrid, Spain, 6–10 September 1993; pp. 959–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA-454/R-00-039; U.S. EPA. Current Knowledge of Particulate Matter (pm) Continuous Emission Monitoring. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/ttn/emc/cem/pmcemsknowfinalrep.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- EPA/600/R-08/139F; Integrated Science Assessment (ISA) for Particulate Matter (Final Report, Dec 2009). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/isa/integrated-science-assessment-isa-particulate-matter (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Simões-Amaral, S.; Andrade de Carvalho, J., Jr.; Martins Costa, M.A.; Pinheiro, C. An overview of particulate matter measurement instruments. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1327–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA/600/R-19/188; Integrated Science Assessment (ISA) for Particulate Matter (Final Report, 2019). U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. Available online: http://ofmpub.epa.gov/eims/eimscomm.getfile?p_download_id=539935 (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Moosmüller, H.; Arnott, W.P.; Rogers, C.F.; Bowen, J.L.; Gillies, J.A.; Pierson, W.R.; Collins, J.F.; Durbin, T.D.; Norbeck, J.M. Time Resolved Characterization of Diesel Particulate Emissions. 1. Instruments for Particle Mass Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehadi, A.; Moosmüller, H.; Campbell, D.E.; Ham, W.; Schweizer, D.; Tarnay, L.; Hunter, J. Laboratory and field evaluation of real-time and near real-time PM2.5 smoke monitors. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2020, 70, 158–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moosmüller, H.; Arnott, W.P.; Rogers, C.F. Methods for real time, in situ measurement of aerosol light absorption. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1997, 47, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmüller, H.; Chakrabarty, K.; Arnott, W.P. Aerosol light absorption and its measurement: A review. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2009, 110, 844–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, H. Atmospheric light absorption—A review. Atmos. Environ. 1993, 27, 293–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T.; et al. AERONET—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Tanré, D.; Smirnov, A.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Abuhassan, N.; Newcomb, W.W.; Schafer, J.S.; Chatenet, B.; Lavenu, F.; et al. An emerging ground-based aerosol climatology: Aerosol optical depth from AERONET. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 12067–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loría-Salazar, S.M.; Holmes, H.A.; Arnott, W.P.; Barnard, J.C.; Moosmüller, H. Evaluation of MODIS columnar aerosol retrievals using AERONET in semi-arid Nevada and California, U.S.A., during the summer of 2012. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Nakajima, T. Remote sensing of tropospheric aerosols from space: Past, present, and future. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 1999, 80, 2229–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.I.; Tanré, D.; Boucher, O. A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoff, R.M.; Christopher, S.A. Remote sensing of particulate pollution from space: Have we reached the promised land? J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 645–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkelaar, A.V.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Kahn, R.; Levy, R.; Verduzco, C.; Villeneuve, P.J. Global Estimates of Ambient Fine Particulate Matter Concentrations from Satellite-Based Aerosol Optical Depth: Development and Application. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Christopher, S.A.; Wang, J.; Gehrig, R.; Lee, Y.; Kumar, N. Satellite remote sensing of particulate matter and air quality assessment over global cities. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5880–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoleni, C.; Kuhns, H.D.; Moosmüller, H. Monitoring automotive particulate matter emissions with lidar: A review. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 1077–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grusha, G.V. Antennas for the remote measurement systems of the gaseous pollution concentration. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Antenna Theory and Techniques, Sevastopol, Ukraine, 9–12 September 2003; Volume 2, pp. 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonouchi, M. Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozar, D.M. Microwave Engineering, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sihvola, A.H. How Strict are theoretical bounds for dielectric properties of mixtures? IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sci. 2002, 40, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, T.C. Effective Medium Theory: Principles and Applications, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kärkkäinen, K.K.; Sihvola, A.H.; Nikoskinen, K.I. Effective Permittivity of Mixtures: Numerical Validation by the FDTD Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärkkäinen, K.K.; Sihvola, A.H.; Nikoskinen, K.I. Analysis of a Three-Dimensional Dielectric Mixture with Finite Difference Method. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Park, Y.H.; Shin, J.Y.; Lee, D.W. Size Determination of Diesel Soot Particles Using Flow and Sedimentation Fiel-Flow Fractionation. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 3265–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesel Exhaust Particle Size. Rev. 2002.11. Available online: www.dieselnet.com (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- EM Software and Systems. 2017, FEKO v2017.1. Available online: https://altairhyperworks.com/product/FEKO (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- CST Studio Suite. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/products/electronics/ansys-hfss (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Schmid & Partner Engineering AG, Reference Manual for the SEMCAD Simulation Plat-Form for Electromagnetic Compatibility, Antenna Design and Dosimetry. 2009. Available online: www.semcad.com (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Rodríguez, J.A.; Ares, F.; Moreno, E.; Franceschetti, G. Design of shunt slot arrays without weak excitations. Electron. Lett. 1999, 35, 1396–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khac, T.V.; Carson, C.T. Impedance properties of longitudinal slot antenna in the broad face of rectangular waveguide. IEEE Trans. 1973, 21, 708–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.S. Antenna Theory and Design; IEEE Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, R. An improved design procedure for small arrays of shunt slots. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1983, 31, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.S.; Stern, G.J. Resonant Length of Longitudinal Slots and Validity of Circuit Representation: Theory and Experiment. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1985, 33, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengarajan, S.; Steinbeck, M. Longitudinal Slots in Dielectric-Filled Rectangular Waveguides. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 1993, 6, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.; O’Loughlin, W. The design of slot arrays including internal mutual coupling. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1986, 34, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orefice, M.; Elliott, R.S. Design of waveguide-fed series slot arrays. IEE Proc. 1982, 129, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengarajan, S.R. Compound radiating slots in a broad wall of a rectangular waveguide. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1999, 37, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulick, J.J.; Elliott, R.S. The design of linear and planar arrays of waveguide-fed longitudinal slots. Electromagnetics 1990, 10, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Ortego, I.; Sierra-Pérez, M.; Zhang, M.; Hirokawa, J.; Ando, M. Mutual Coupling in Longitudinal Arrays of Compound Slots. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 2013, 46, 59–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Kumar, R.; Mishra, N.; Patil, H.Y. A superstrate and FSS-loaded high gain circularly polarized twist waveguide array. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2023, 65, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Mishra, N.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, K.; Patil, H.Y. A superstrate and FSS embedded dual band waveguide aperture array with improved far-field characteristics. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2023, 65, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.S.; Stern, S.J. The design of microstrip dipole arrays including mutual coupling, part I: Theory. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1981, 2, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Alexopoulos, N.G.; Lepeltier, P.M.; Stern, G.J. Design of transversely fed EMC microstrip dipole arrays including mutual coupling. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1990, 38, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Chandra, A.; Mishra, N.; Chaudhary, R. A Frequency Tunable Dielectric Resonator Antenna with Reduction of Cross Polarisation for Wi-MAX and Sub 6 GHz 5G Applications. Def. Sci. J. 2023, 73, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pall, M.L. Wi-Fi is an important threat to human health. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, A.A. Electromagnetic fields instantaneously modulate nitric oxide signaling in challenged biological systems. BBRC 2012, 426, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.R.; Thatte, H.S.; Silvia, M.T.; Golan, D.E. Transmembrane calcium influx induced by ac electric fields. Faseb. J. 1999, 13, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.L.; Teli, T.; Harrison, B.S. Electromagnetic field devices and their effects on nociception and peripheral inflammatory pain mechanisms. Ltern. Ther. Health Med. 2016, 22, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.M.; Donaldson, K.; Stone, V. Role of calcium in the induction of TNFα expression by macrophages on exposure to ultrafine particles. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2002, 46, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, N.; Hayashi, S.; Gosselink, J.; Ishii, H.; Ishimatsu, Y.; Mukae, H.; Hogg, J.C.; van Eeden, S.F. Calcium dependent and independent cytokine synthesis by air pollution particle-exposed human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 225, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Martín, M.E.; Sueiro-Benavides, R.A.; Leiro-Vidal, J.M.; Rodríguez-González, J.A.; Ares-Pena, F.J. Can Electromagnetic Fields Modulate Inflammation and Cell Death by Acting on the Immune System? IEEE Access 2023, 1, 92167–92187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
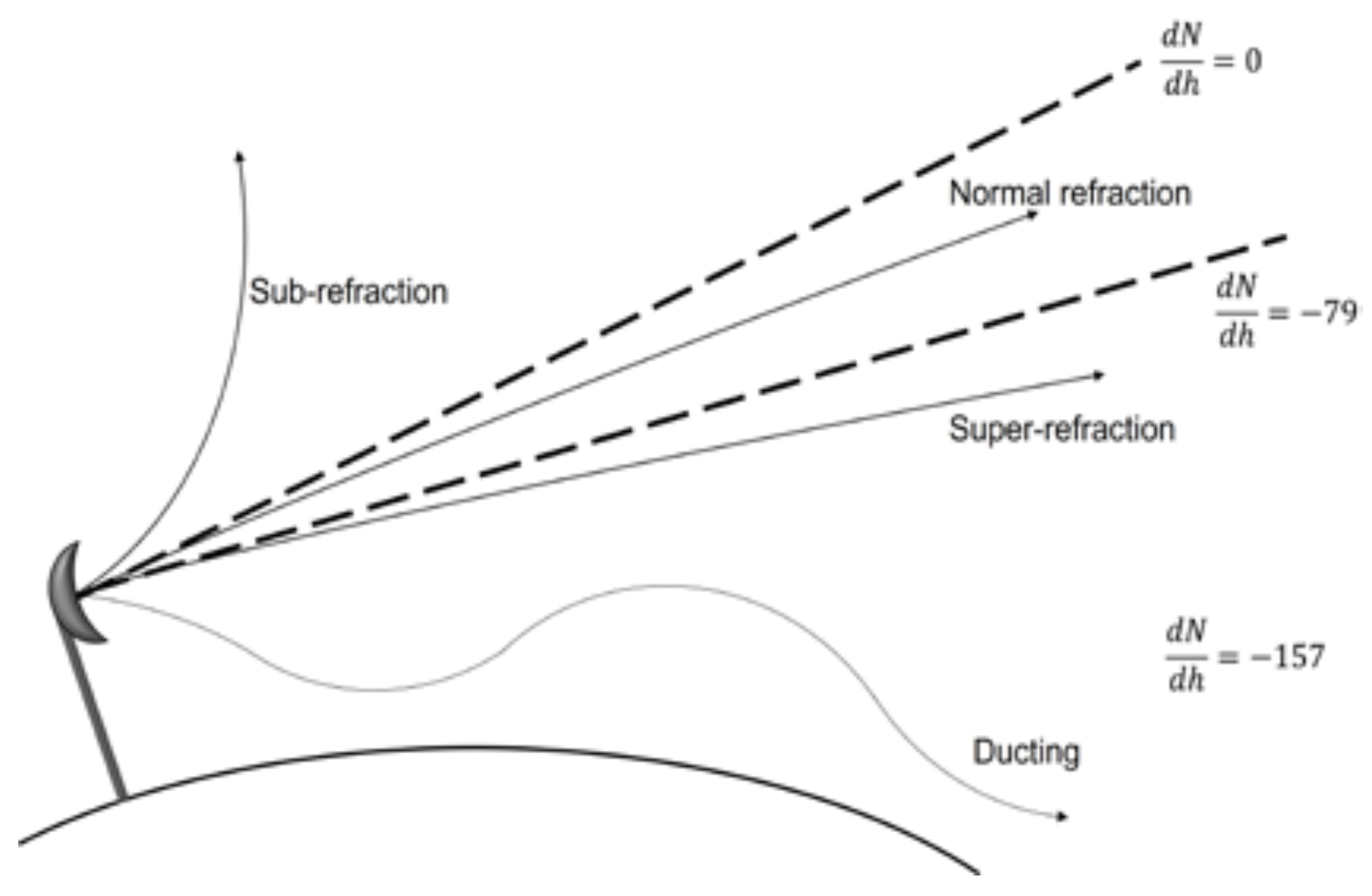

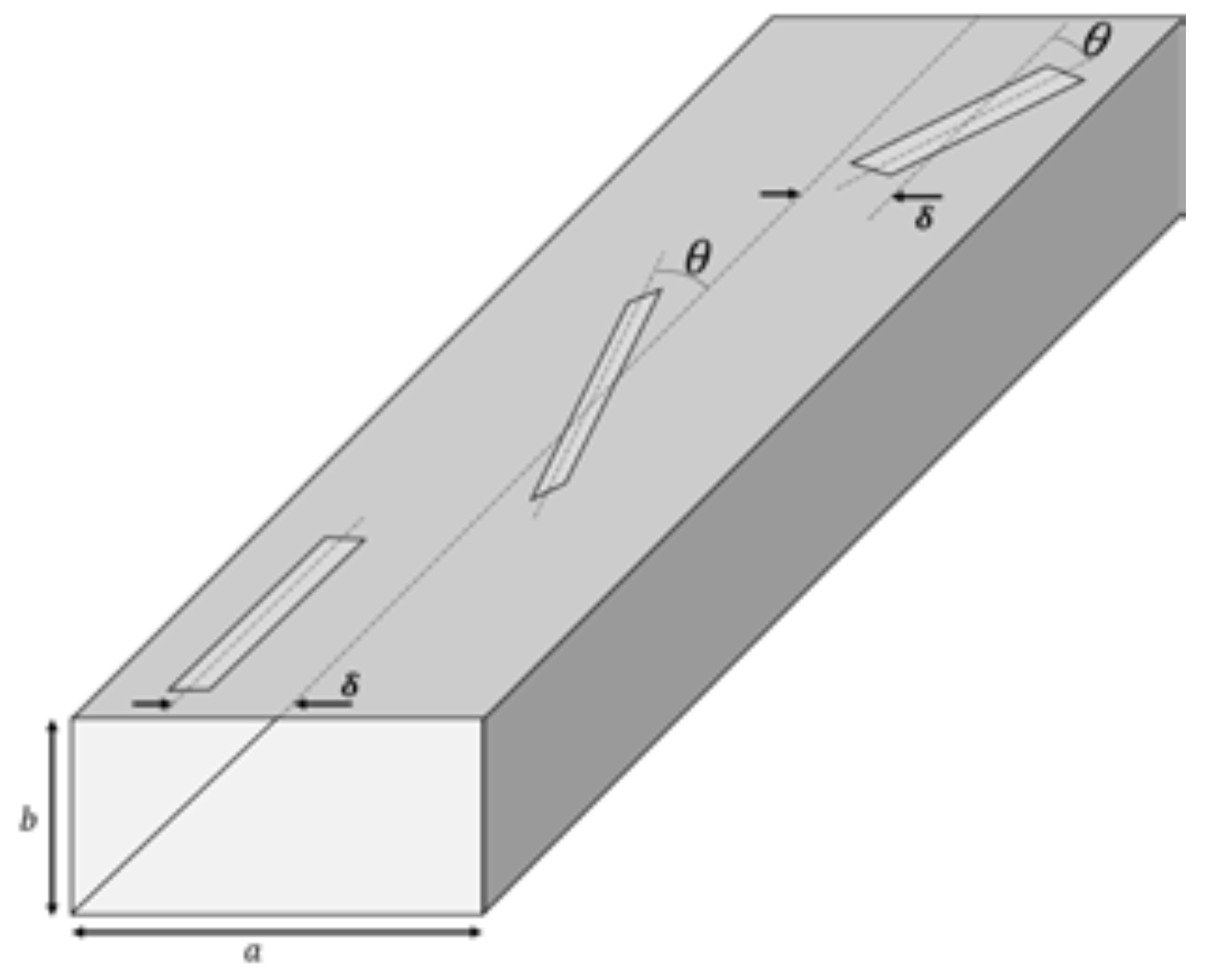


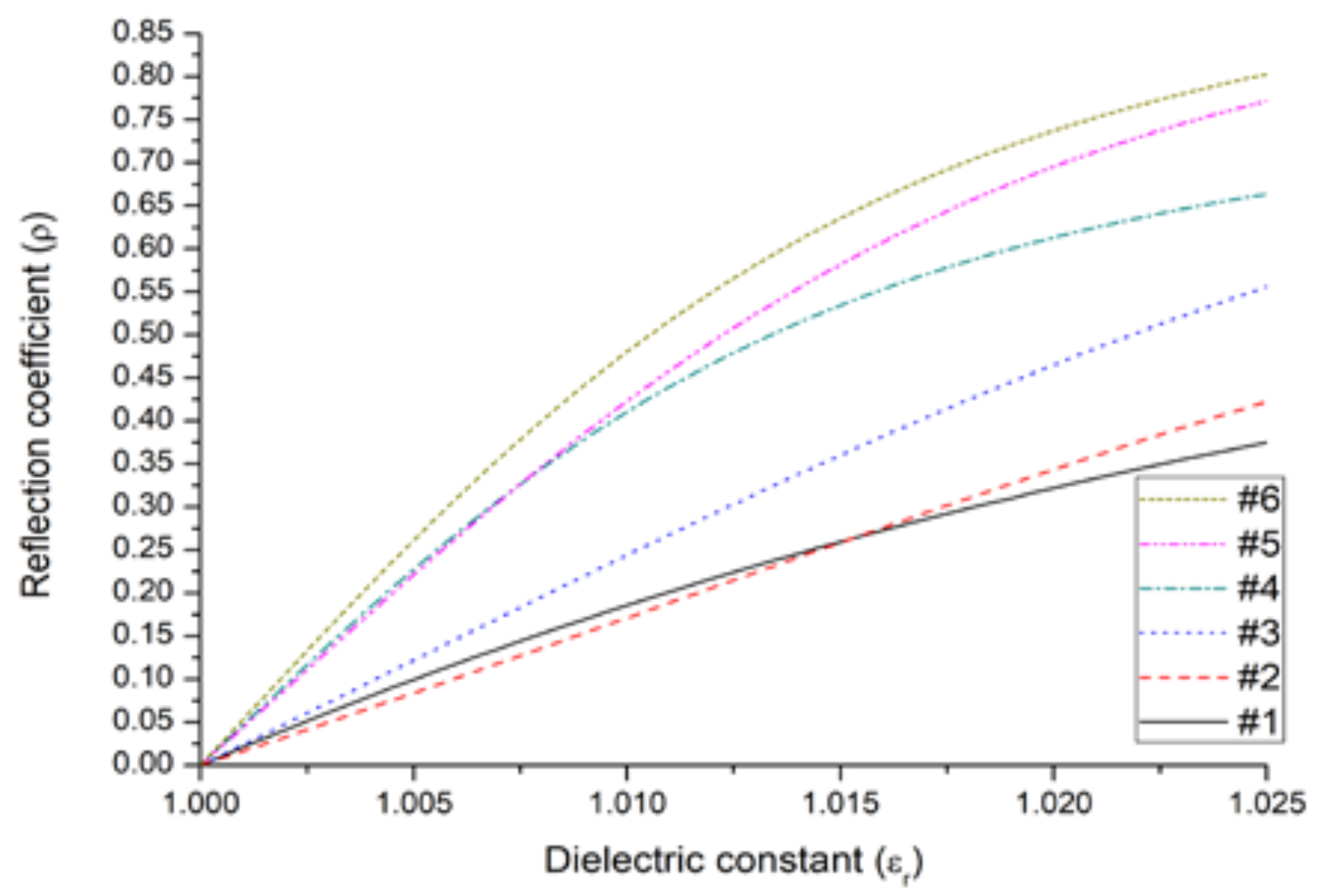



| Antenna | Element i | Length | Spacing |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 1 | 0.4732 | 0.3414 |
| 2 | 0.3525 | 0.1108 | |
| 3 | 0.2157 | 0.1435 | |
| 4 | 0.4768 | - | |
| #2 | 1 | 1.2267 | 0.3109 |
| 2 | 1.1679 | 0.2663 | |
| 3 | 1.2770 | 0.2722 | |
| 4 | 1.2867 | - | |
| #3 | 1 | 2.2643 | 0.2340 |
| 2 | 2.1643 | 0.2465 | |
| 3 | 2.3371 | 0.2328 | |
| 4 | 2.2473 | - | |
| #4 | 1 | 3.1841 | 0.2895 |
| 2 | 3.1646 | 0.3277 | |
| 3 | 3.3171 | 0.2652 | |
| 4 | 3.2444 | - | |
| #5 | 1 | 4.2677 | 0.2303 |
| 2 | 4.1525 | 0.2103 | |
| 3 | 4.3593 | 0.2568 | |
| 4 | 4.1907 | - | |
| #6 | 1 | 5.3820 | 0.2633 |
| 2 | 5.1481 | 0.1688 | |
| 3 | 5.2826 | 0.1858 | |
| 4 | 5.3174 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Álvarez, C.; López-Martín, M.E.; Rodríguez-González, J.A.; Ares-Pena, F.J. A Review on the Effects of Thermal Inversions and Electromagnetic Fields on Cell Cultures and Wireless Communications. Sensors 2023, 23, 9567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239567
López-Álvarez C, López-Martín ME, Rodríguez-González JA, Ares-Pena FJ. A Review on the Effects of Thermal Inversions and Electromagnetic Fields on Cell Cultures and Wireless Communications. Sensors. 2023; 23(23):9567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239567
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Álvarez, Cibrán, María Elena López-Martín, Juan Antonio Rodríguez-González, and Francisco José Ares-Pena. 2023. "A Review on the Effects of Thermal Inversions and Electromagnetic Fields on Cell Cultures and Wireless Communications" Sensors 23, no. 23: 9567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239567
APA StyleLópez-Álvarez, C., López-Martín, M. E., Rodríguez-González, J. A., & Ares-Pena, F. J. (2023). A Review on the Effects of Thermal Inversions and Electromagnetic Fields on Cell Cultures and Wireless Communications. Sensors, 23(23), 9567. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239567





