Low-Cost ZnO Spray-Coated Optical Fiber Sensor for Detecting VOC Biomarkers of Diabetes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
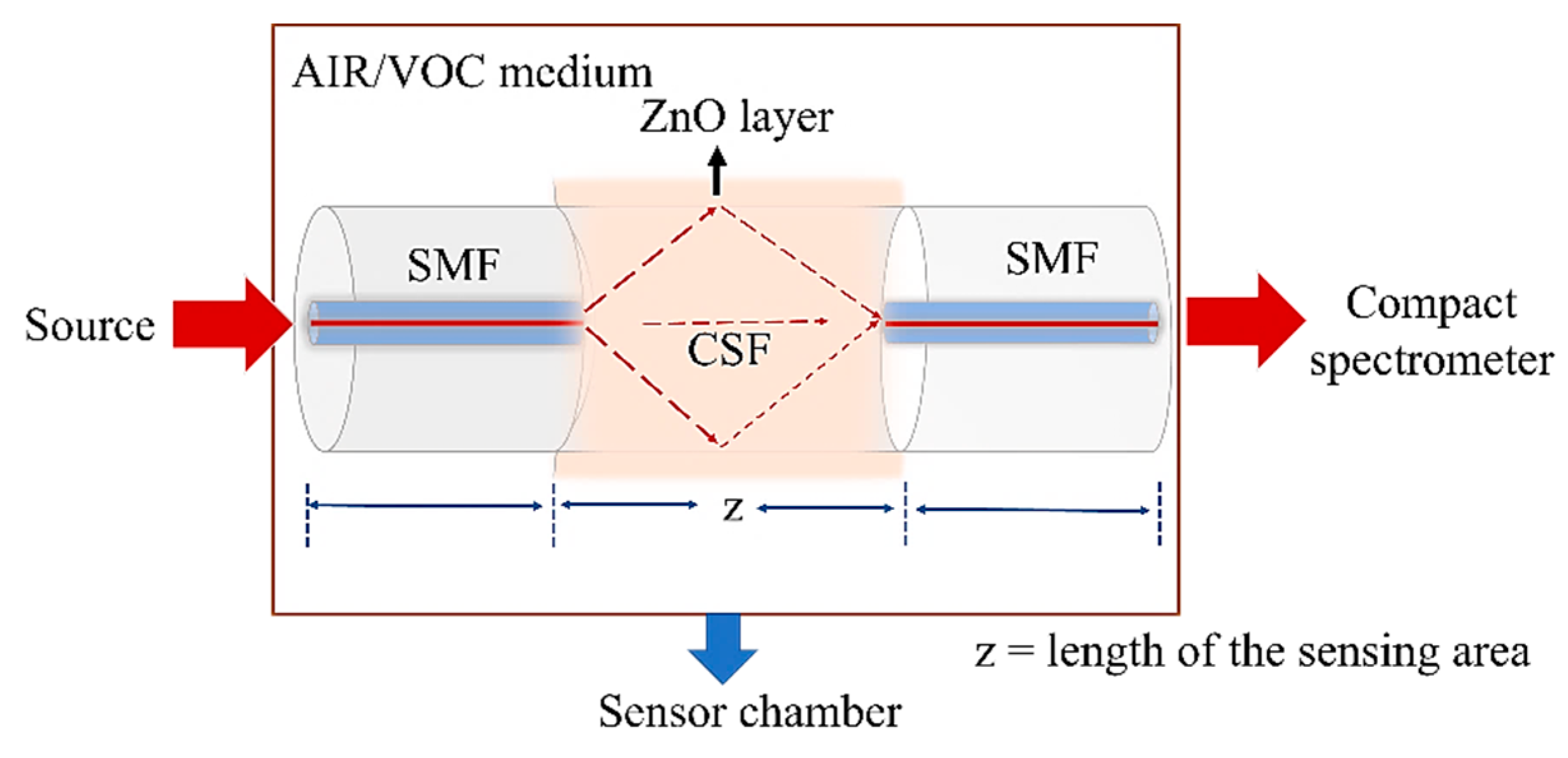
2.2. Sensor Design
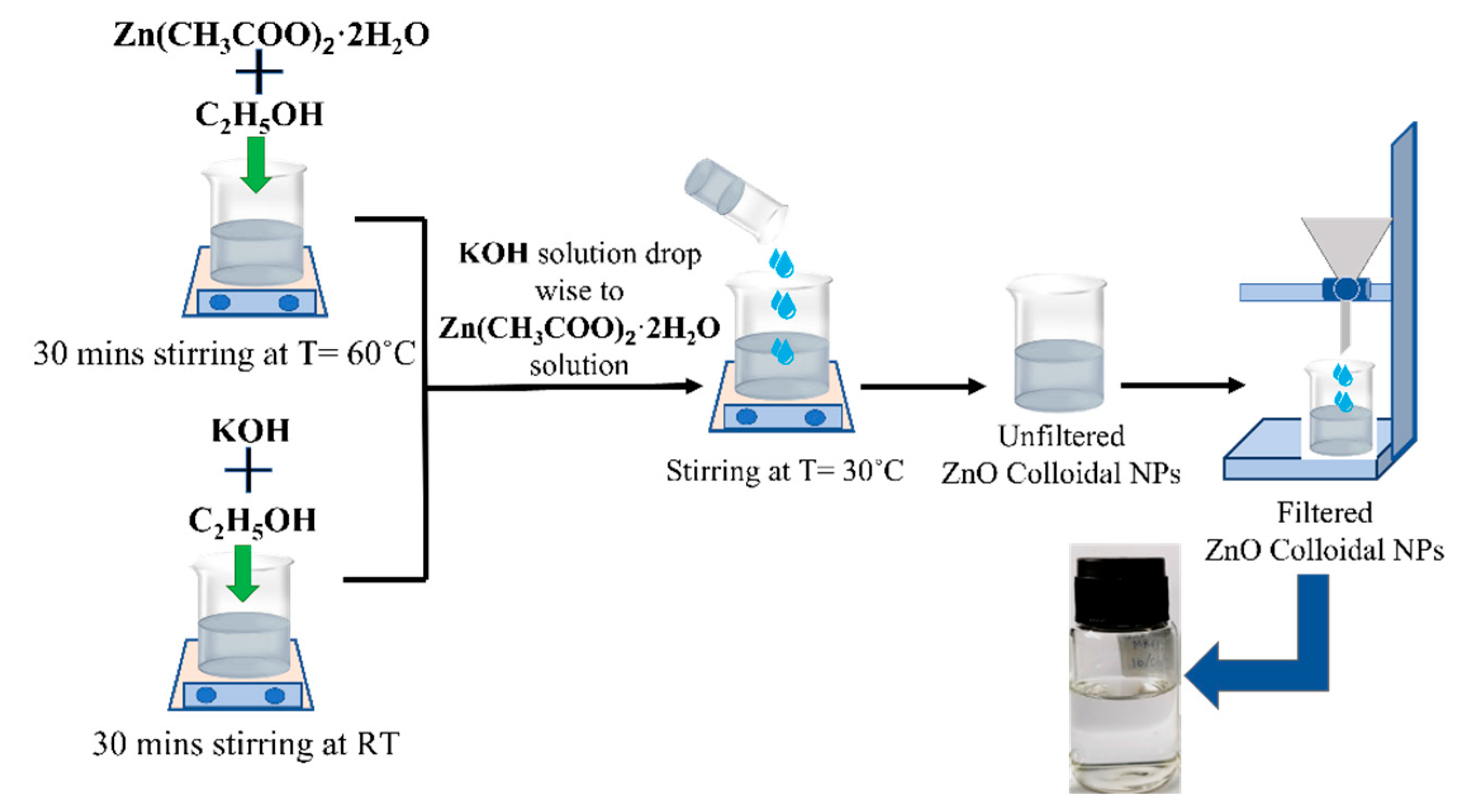
2.3. Synthesis of Colloidal ZnO Solutions
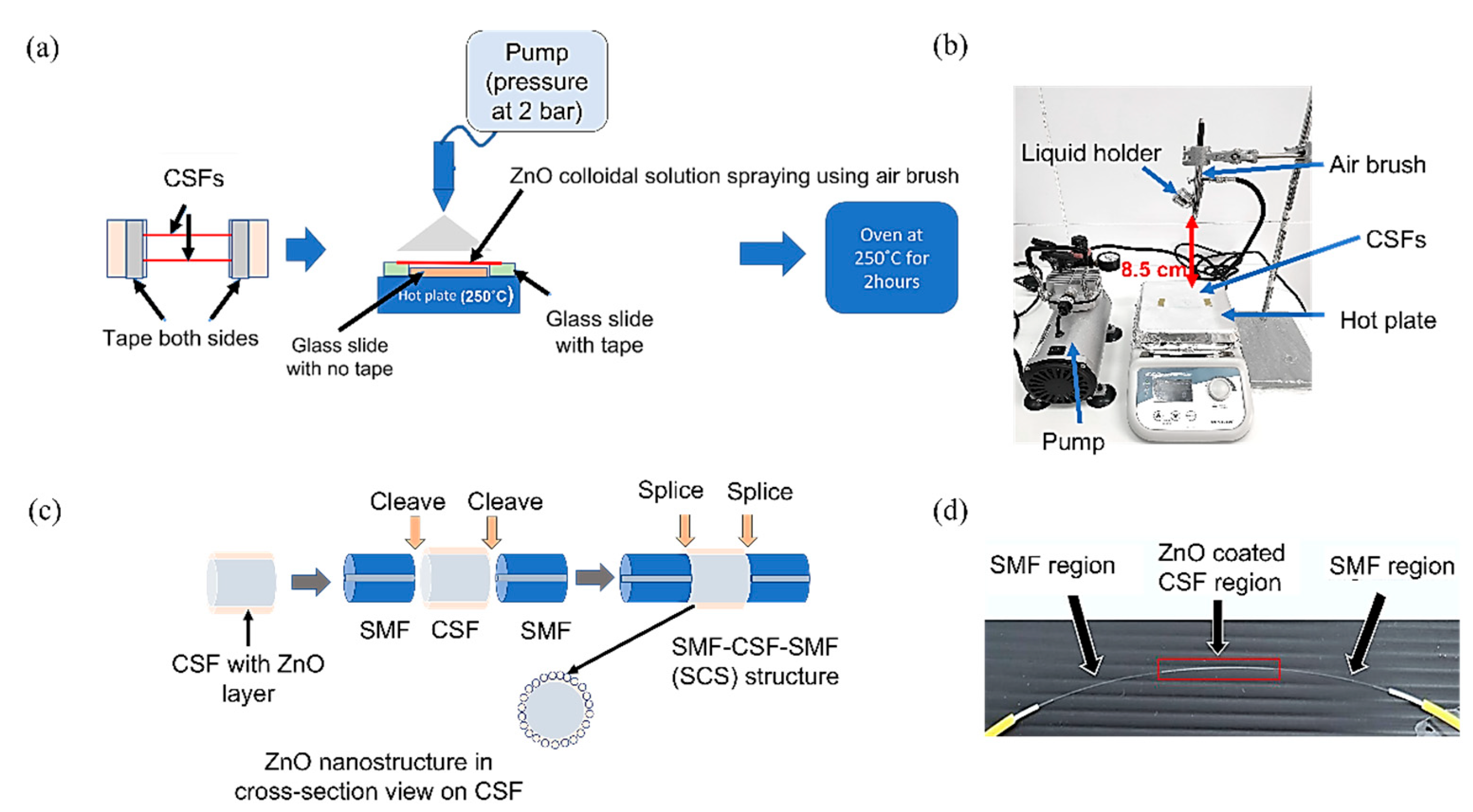
2.4. Sensor Fabrication
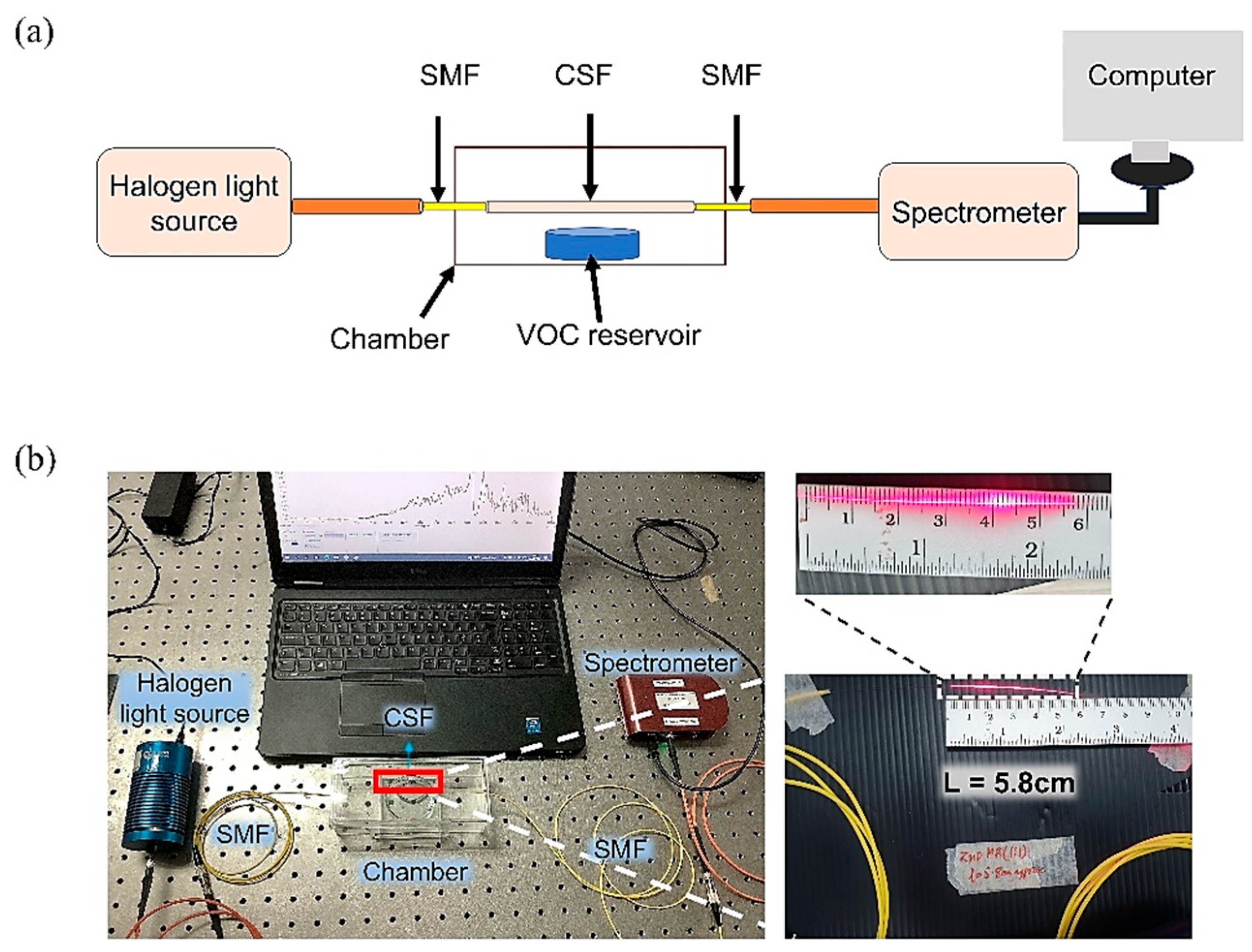
2.5. Optical Setup
2.6. VOC Vapor Preparation
3. Results and Discussions
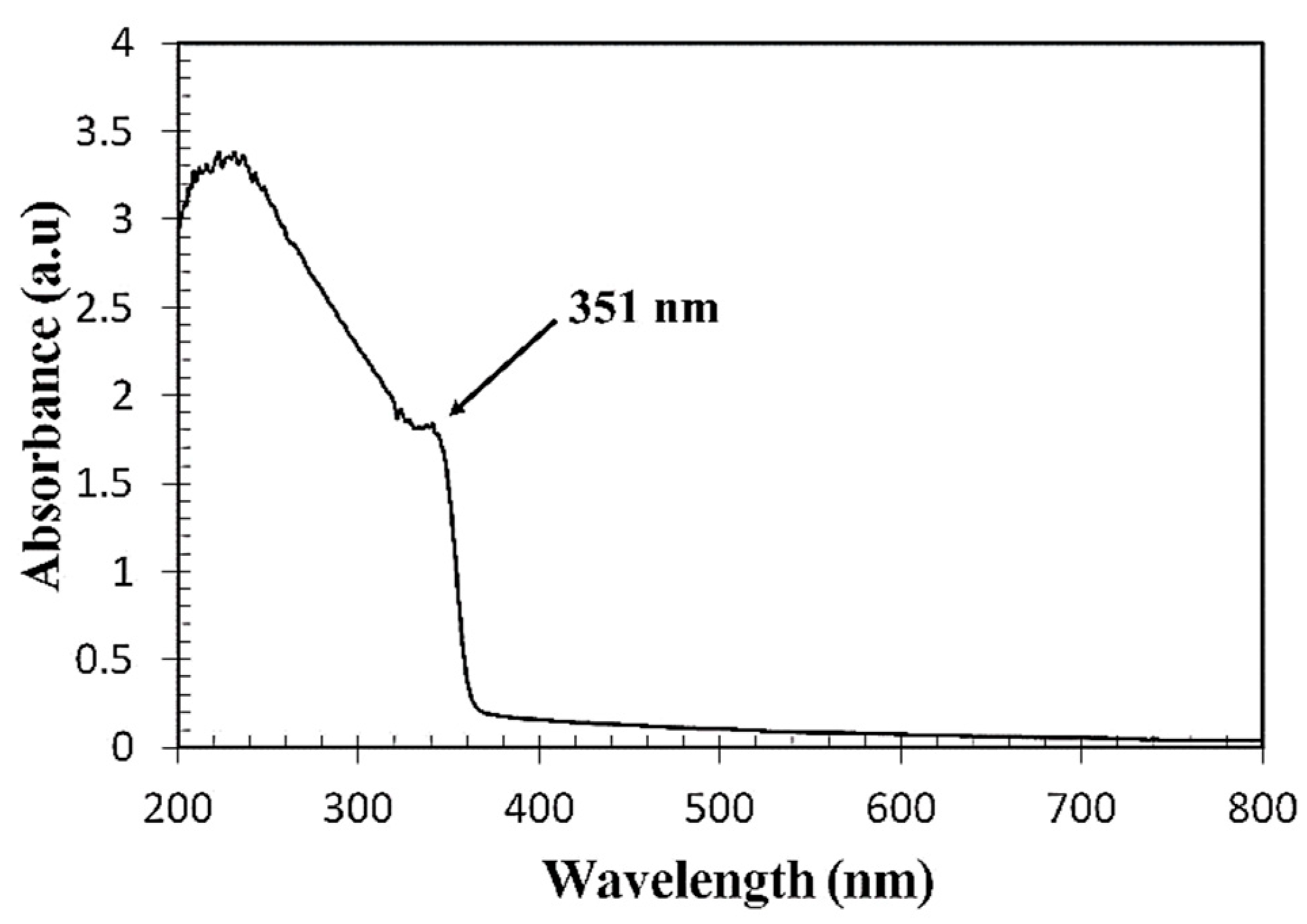
3.1. Optical Properties of the Prepared ZnO Colloidal Solution
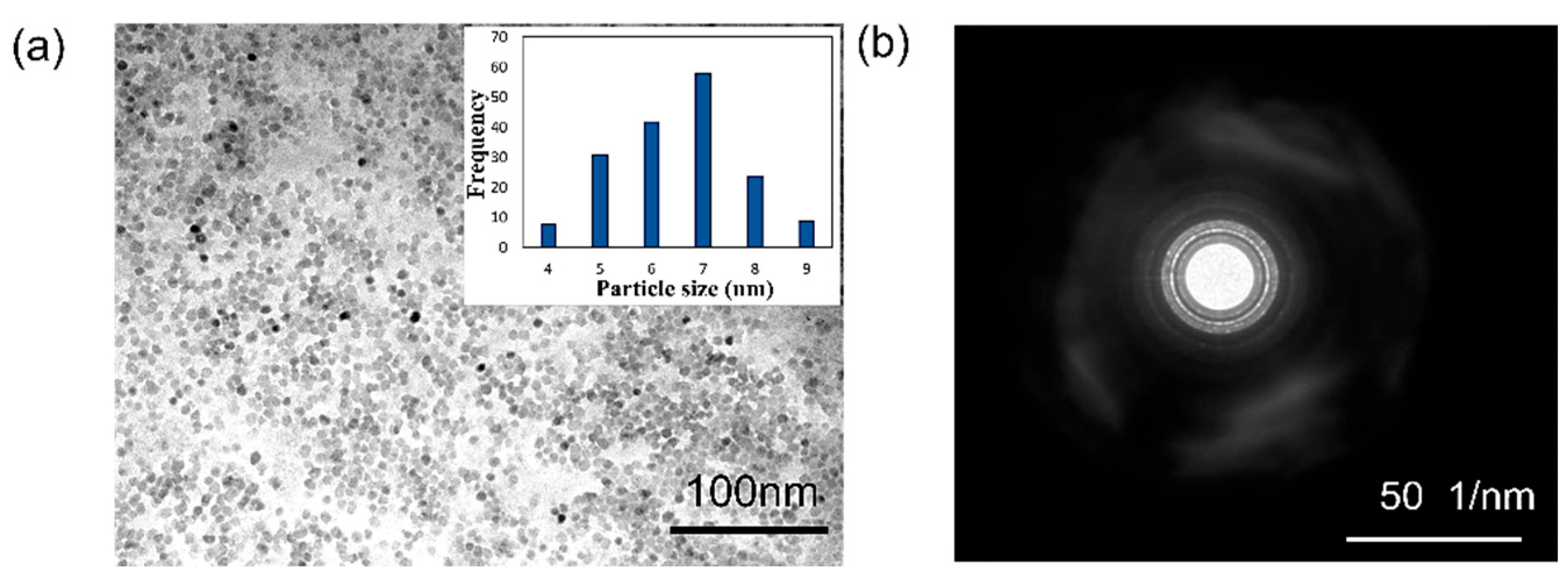
3.2. Particle Size Distribution and Surface Charges of the ZnO Colloidal Nanoparticles
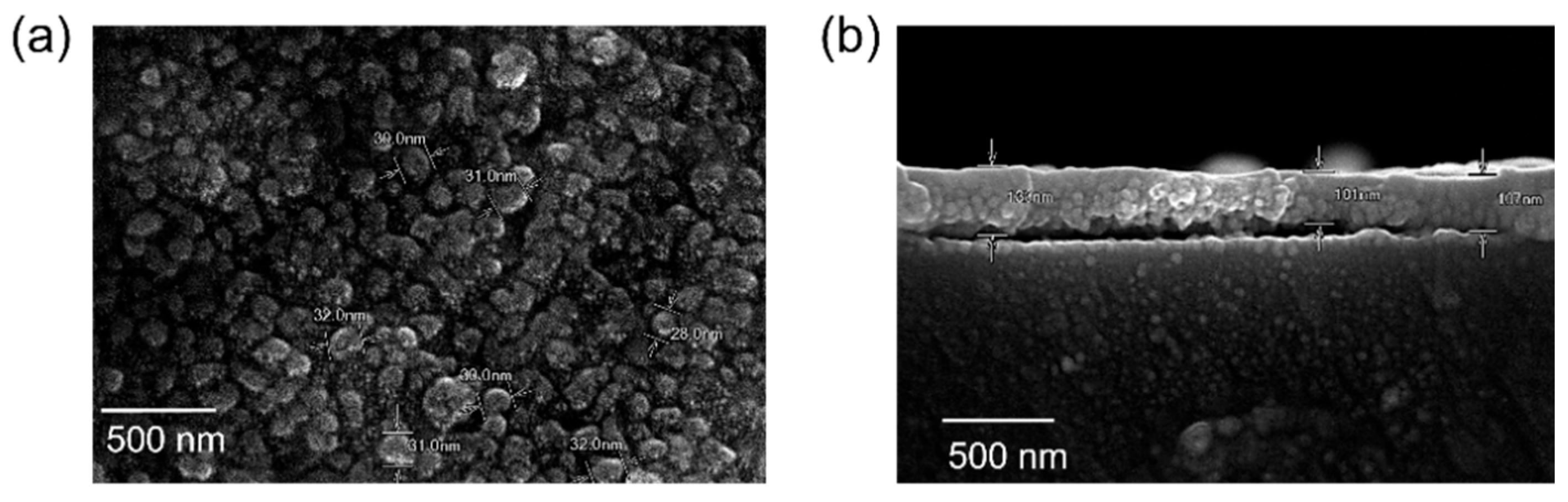
3.3. Surface Morphology of the ZnO Layer Coated on the Fiber Sensor
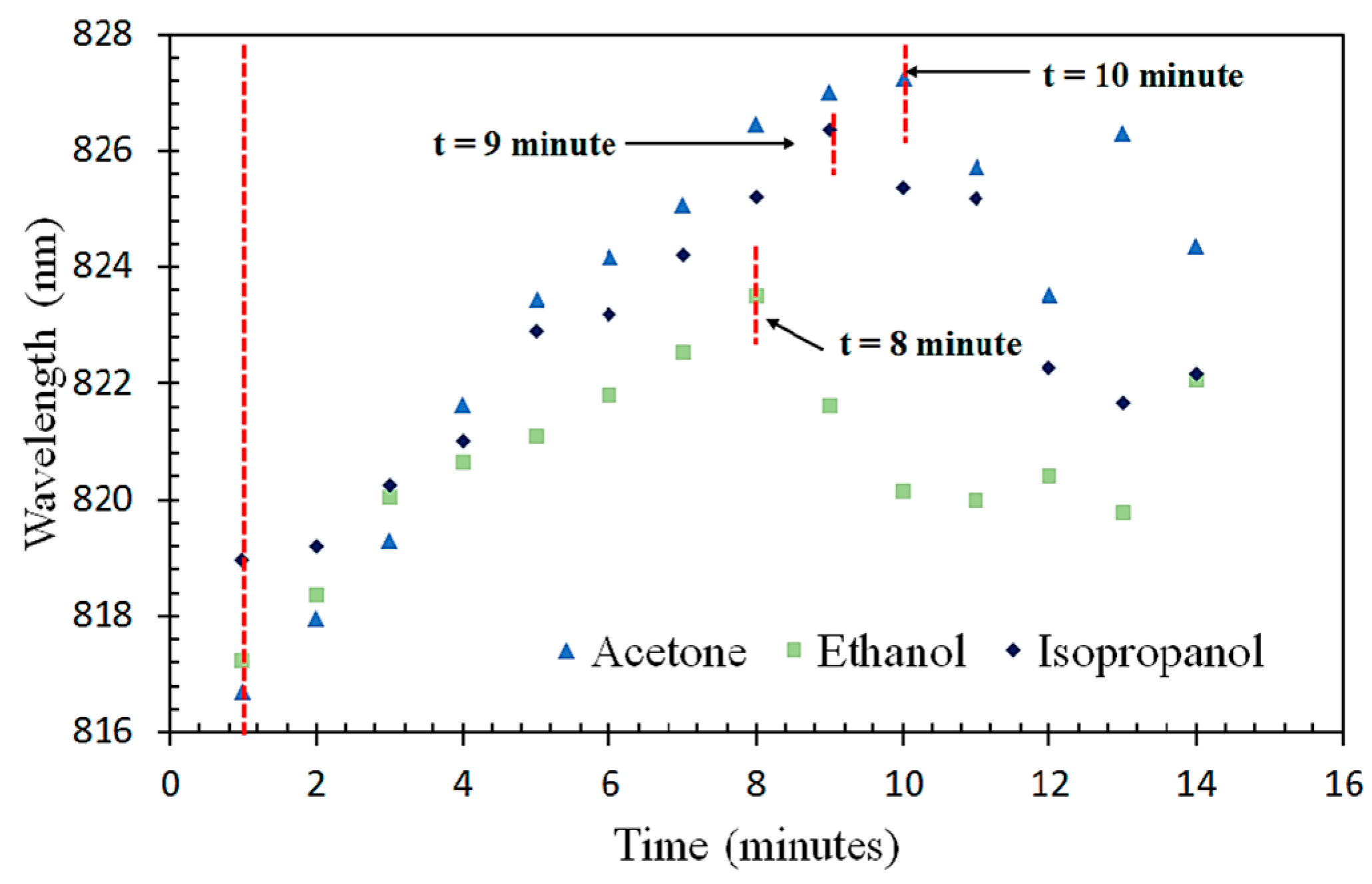
3.4. Saturation Time of VOC Absorption on the Fiber Sensor
3.5. Sensing Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shirasu, M.; Touhara, K. The scent of disease: Volatile organic compounds of the human body related to disease and disorder. J. Biochem. 2011, 150, 257–266. [Google Scholar]
- Minh, T.D.C.; Blake, D.R.; Galassetti, P.R. The clinical potential of exhaled breath analysis for diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2012, 97, 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Amann, A.; de Lacy Costello, B.; Miekisch, W.; Schubert, J.; Buszewski, B.; Pleil, J.; Ratcliffe, N.; Risby, T. The human volatilome: Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in exhaled breath, skin emanations, urine, feces and saliva. J. Breath Res. 2014, 8, 034001. [Google Scholar]
- Saasa, V.; Malwela, T.; Beukes, M.; Mokgotho, M.; Liu, C.-P.; Mwakikunga, B. Sensing technologies for detection of acetone in human breath for diabetes diagnosis and monitoring. Diagnostics 2018, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righettoni, M.; Tricoli, A.; Gass, S.; Schmid, A.; Amann, A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Breath acetone monitoring by portable Si: WO3 gas sensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 738, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metem, P.; Patchoo, W.; Mohammed, W.S.; Viphavakit, C. Numerical investigation of Au-silane functionalised optical fibre sensor for volatile organic compounds biomarker (VOCs) detection. In Proceedings of the Optical Fibers and Sensors for Medical Diagnostics, Treatment and Environmental Applications XXI, Online, 6–11 March 2021; pp. 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, K.; Fardindoost, S.; Ravishankara, A.; Tasnim, N.; Hoorfar, M. Exhaled breath analysis for diabetes diagnosis and monitoring: Relevance, challenges and possibilities. Biosensors 2021, 11, 476. [Google Scholar]
- Leopold, J.H.; van Hooijdonk, R.; Sterk, P.J.; Abu-Hanna, A.; Schultz, M.J.; Bos, L.D. Glucose prediction by analysis of exhaled metabolites—A systematic review. BMC Anesthesiol. 2014, 14, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, T.; Wang, X.-Y.; Zhao, Z.-H.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Yao, H.-C.; Wang, J.-S.; Li, Z.-J. Highly sensitive and selective acetone sensor based on C-doped WO3 for potential diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 199, 210–219. [Google Scholar]
- Righettoni, M.; Schmid, A.; Amann, A.; Pratsinis, S.E. Correlations between blood glucose and breath components from portable gas sensors and PTR-TOF-MS. J. Breath Res. 2013, 7, 037110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salehi, S.; Nikan, E.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Mortazavi, Y. Highly sensitive carbon nanotubes–SnO2 nanocomposite sensor for acetone detection in diabetes mellitus breath. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 205, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, S.; Banerjee, D.; Ray, I.; Sen, A. Detection of biomarker in breath: A step towards noninvasive diabetes monitoring. Curr. Sci. 2008, 94, 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, C.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X. Determination of acetone in human breath by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and solid-phase microextraction with on-fiber derivatization. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 810, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, M.-Y.; Lin, Y.-T.; Tung, T.-W.; Chang, L.-Y.; Zan, H.-W.; Meng, H.-F.; Lu, C.-J.; Tao, Y.-T. Room-temperature-operated organic-based acetone gas sensor for breath analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 260, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Königstein, K.; Abegg, S.; Schorn, A.N.; Weber, I.C.; Derron, N.; Krebs, A.; Gerber, P.A.; Schmidt-Trucksäss, A.; Güntner, A.T. Breath acetone change during aerobic exercise is moderated by cardiorespiratory fitness. J. Breath Res. 2020, 15, 016006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahangiri-Manesh, A.; Mousazadeh, M.; Nikkhah, M. Fabrication of chemiresistive nanosensor using molecularly imprinted polymers for acetone detection in gaseous state. Iran. Polym. J. 2022, 31, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.-C.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, S.-H.; Chen, W.; Hu, B. Solid Phase Microextraction for Human Breath Analysis of Environmental and Occupational Exposures: A Review. Adv. Sample Prep. 2022, 3, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Sahay, P. Breath analysis using laser spectroscopic techniques: Breath biomarkers, spectral fingerprints, and detection limits. Sensors 2009, 9, 8230–8262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Mbi, A.; Shepherd, M. A study on breath acetone in diabetic patients using a cavity ringdown breath analyzer: Exploring correlations of breath acetone with blood glucose and glycohemoglobin A1C. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 10, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilmohan, S.T.; Milligan, D.B.; McEwan, M.J.; Freeman, C.G.; Wilson, P.F. Quantitative analysis of trace gases of breath during exercise using the new SIFT–MS technique. Redox Rep. 2000, 5, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, E.; Tinnevelt, G.H.; Brodrick, E.; Williams, M.; Davies, A.N.; van Manen, H.-J.; Buydens, L.M. Increasing conclusiveness of clinical breath analysis by improved baseline correction of multi capillary column–ion mobility spectrometry (MCC-IMS) data. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 127, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, N.; Jamalabadi, H.; Tavoli, F. Breath acetone sensors as non-invasive health monitoring systems: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 20, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluza, D.; Węgrzyn, K.; Kaczmarczyk, B.; Gniadek, M.; Maksymiuk, K.; Michalska, A. An electrochemical approach to quantification of volatile organic solvents dispersed in solution–towards bipolar electrode sensors. Electroanalysis 2022, 34, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L.; Lu, G. Non-invasive blood glucose monitoring for diabetics by means of breath signal analysis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 173, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Bai, Y.; Li, L.; Sun, F.; Hao, M.; Li, T.; Lu, Q.; Li, L. Bioinspired Flexible Volatile Organic Compounds Sensor Based on Dynamic Surface Wrinkling with Dual-Signal Response. Small 2019, 15, 1900216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swargiary, K.; Metem, P.; Kulatumyotin, C.; Thaneerat, S.; Ajchareeyasoontorn, N.; Jitpratak, P.; Bora, T.; Mohammed, W.S.; Dutta, J.; Viphavakit, C. ZnO Nanorods Coated Single-Mode–Multimode–Single-Mode Optical Fiber Sensor for VOC Biomarker Detection. Sensors 2022, 22, 6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swargiary, K.; Jarutatsanangkoon, P.; Suwanich, P.; Jolivot, R.; Mohammed, W.S. Single-step 3D-printed integrated optical system and its implementation for a sensing application using digital light processing technology. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swargiary, K.; Jolivot, R.; Mohammed, W.S. Demonstration of a Polymer-Based Single Step Waveguide by 3D Printing Digital Light Processing Technology for Isopropanol Alcohol-Concentration Sensor. Photonic Sens. 2022, 12, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.; Viphavakit, C. A review on all-optical fiber-based VOC sensors: Heading towards the development of promising technology. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 338, 113455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Semenova, Y.; Wang, P.; Farrell, G. High sensitivity SMS fiber structure based refractometer—Analysis and experiment. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 7937–7944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Farrell, G.; Yan, W. Investigation on single-mode–multimode–single-mode fiber structure. J. Light. Technol. 2008, 26, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Cui, X.; Lai, T.; Ren, J.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, M.; Wang, B.; Xiao, X.; Wang, Y. Gas sensors based on TiO2 nanostructured materials for the detection of hazardous gases: A review. Nano Mater. Sci. 2021, 3, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, A.; Meher, S.; Alex, Z. Metal oxide thin films coated evanescent wave based fiber optic VOC sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 338, 113459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.K.; Swargiary, K.; Kongsawang, N.; Jitpratak, P.; Ajchareeyasoontorn, N.; Udomkittivorakul, J.; Viphavakit, C. Recent Advances in Sensing Materials Targeting Clinical Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Biomarkers: A Review. Biosensors 2023, 13, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hardan, N.; Abdullah, M.; Aziz, A.A.; Ahmad, H.; Low, L. ZnO thin films for VOC sensing applications. Vacuum 2010, 85, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ly, A.; Lahem, D.; Zhang, C.; Debliquy, M. A novel low-concentration isopropanol gas sensor based on Fe-doped ZnO nanoneedles and its gas sensing mechanism. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 3230–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Arif, N.A.A.; Shaari, S.; Ehsan, A.A. Intensity Loss of ZnO Coated on Fiber Optic. J. Nanomater. 2023, 2023, 9645272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, W.S.; Smith, P.W.; Gu, X. All-fiber multimode interference bandpass filter. Opt. Lett. 2006, 31, 2547–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, W.S.; Gu, X.; Meier, J.; Smith, P.W. Maximizing on-axis coupling efficiency between single mode fiber and multimode specialty fibers using multi-mode interference. In Proceedings of the Quantum Electronics and Laser Science Conference, Long Beach, CA, USA, 21–26 May 2006; p. JThC92. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, W.S.; Mehta, A.; Johnson, E.G. Wavelength tunable fiber lens based on multimode interference. J. Light. Technol. 2004, 22, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.-K.; Shan, C.-X.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, Q.; Shen, D.-Z. Large-scale synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and their application as phosphors in light-emitting devices. Opt. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 2682–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illakkiya, J.T.; Hemalatha, S.; Oommen, R.; Rajalakshmi, P.U. Characterization of ZnO Nanoparticles synthesized by wet chemical method. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2014, 6, 2159–2161. [Google Scholar]
- Baruah, S.; Dutta, J. Effect of seeded substrates on hydrothermally grown ZnO nanorods. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2009, 50, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.; Limprapassorn, P.; Kongruttanachok, N.; Viphavakit, C. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Optical Sensor for Isopropanol Vapor. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2022, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimman, S.; Balakrishnan, L.; Meher, S.; Sivacoumar, R.; Alex, Z. ZnO nanoparticles based fiber optic gas sensor. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Uttar Pradesh, India, 21–25 December 2015; p. 050052. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Huang, J.; Xiao, H.; Yang, M. ZnO-coated SMS structure interrogated by a fiber ring laser for chemical sensing. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2014, 25, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renganathan, B.; Ganesan, A. Fiber optic gas sensor with nanocrystalline ZnO. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2014, 20, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinavel, S.; Vadivel, S.; Balaji, G. Development of ethanol and acetone gas sensing performance of MgCo2O4 nanosensors by clad modified fiber optical method. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2019, 48, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

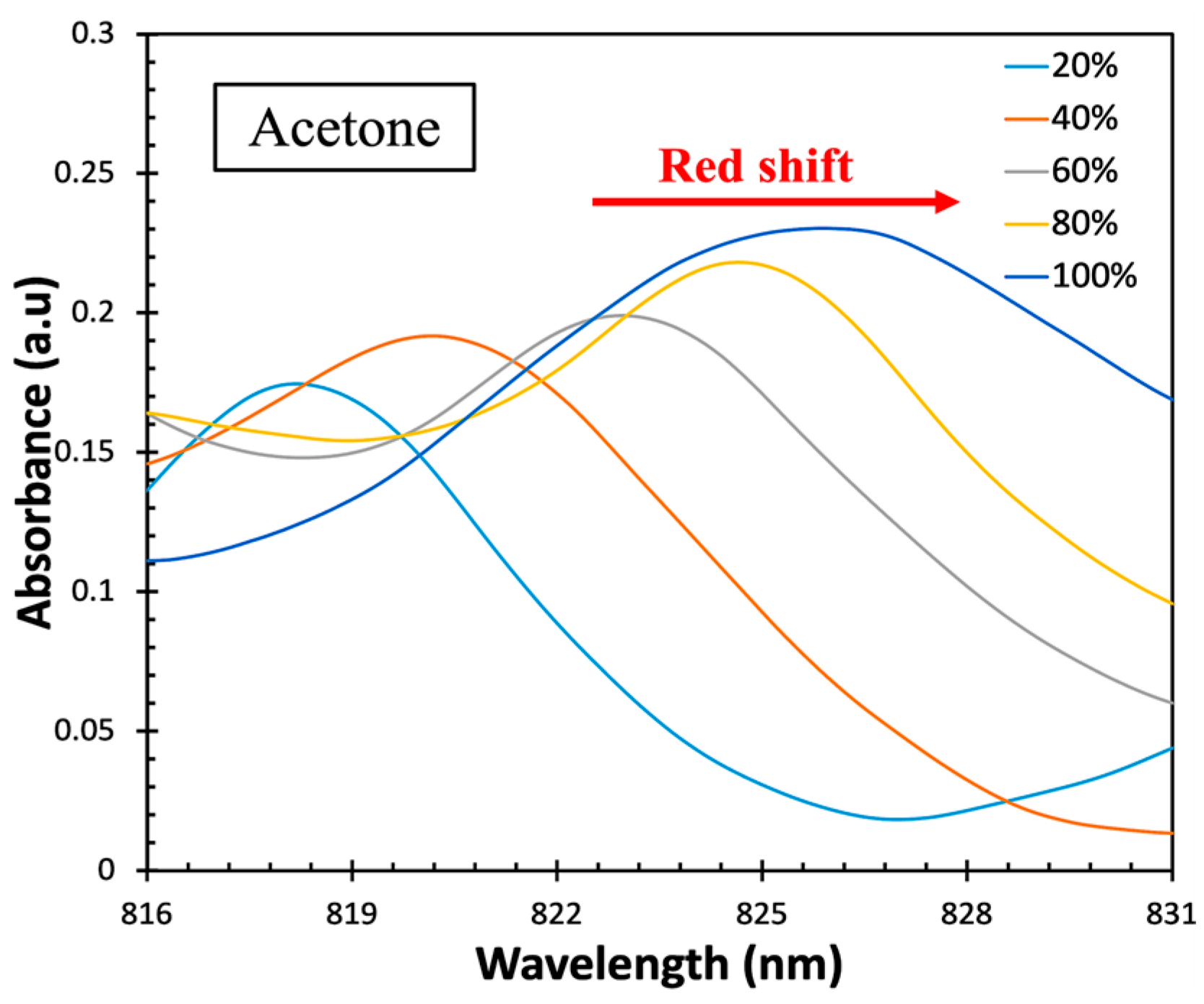
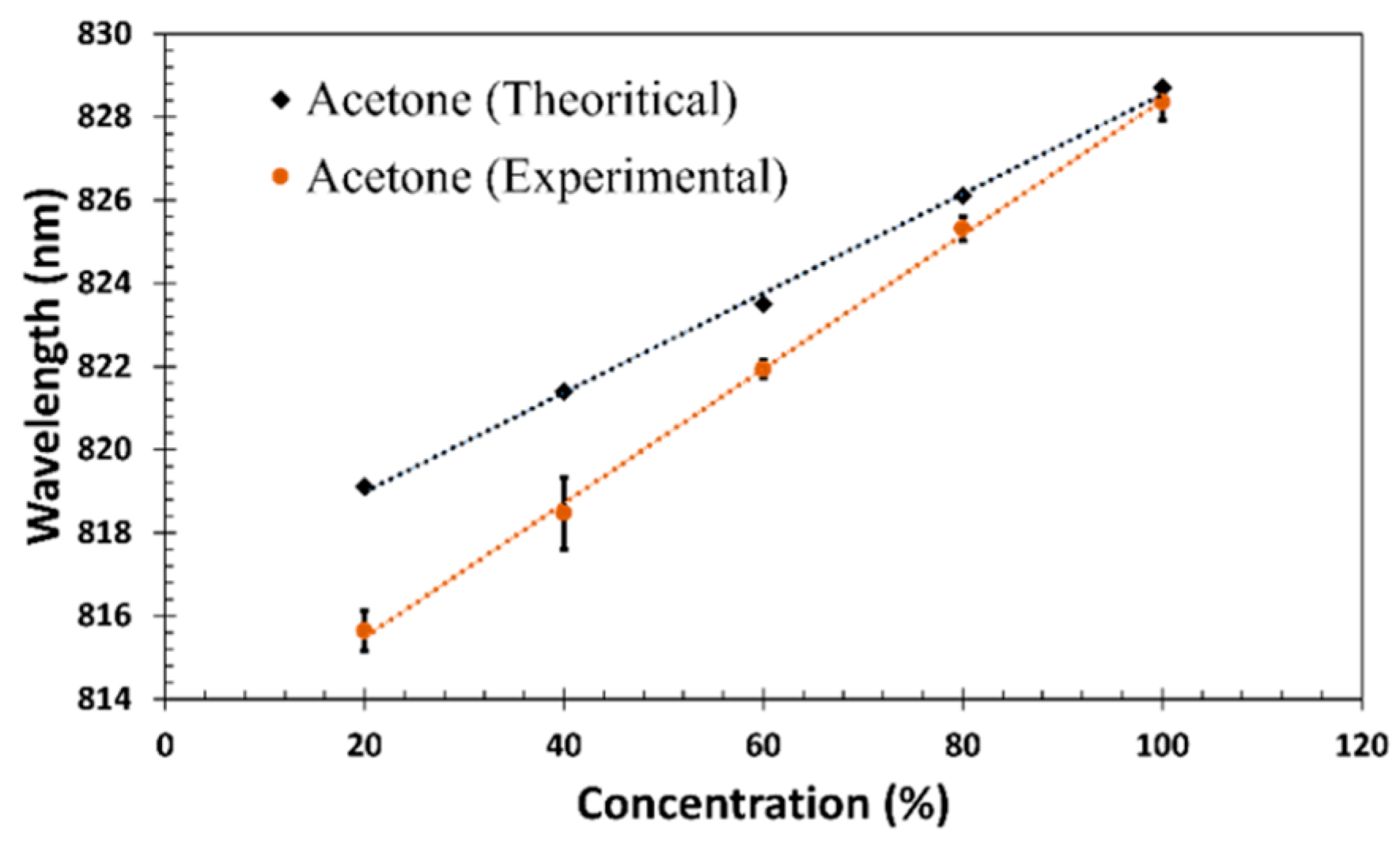
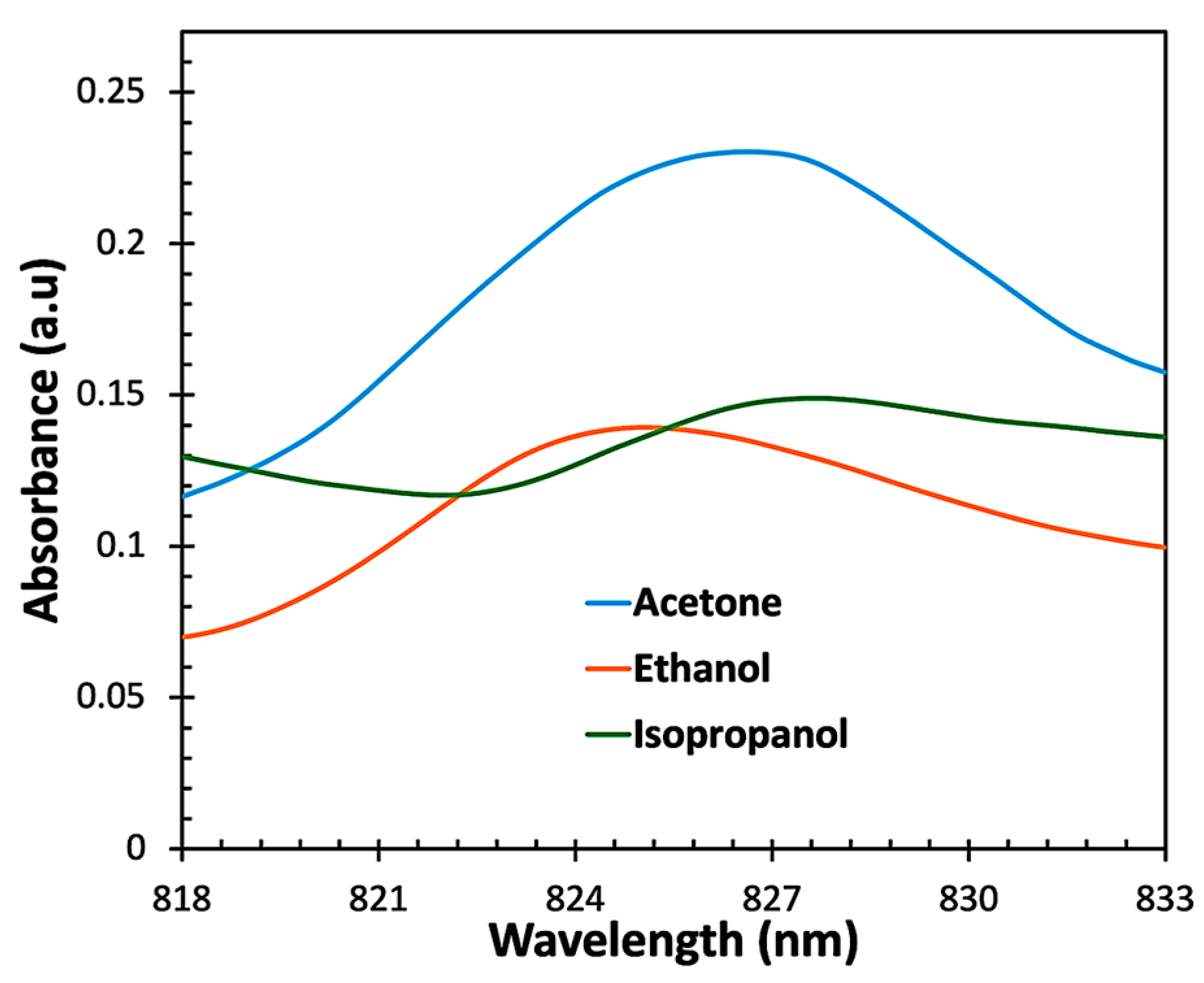
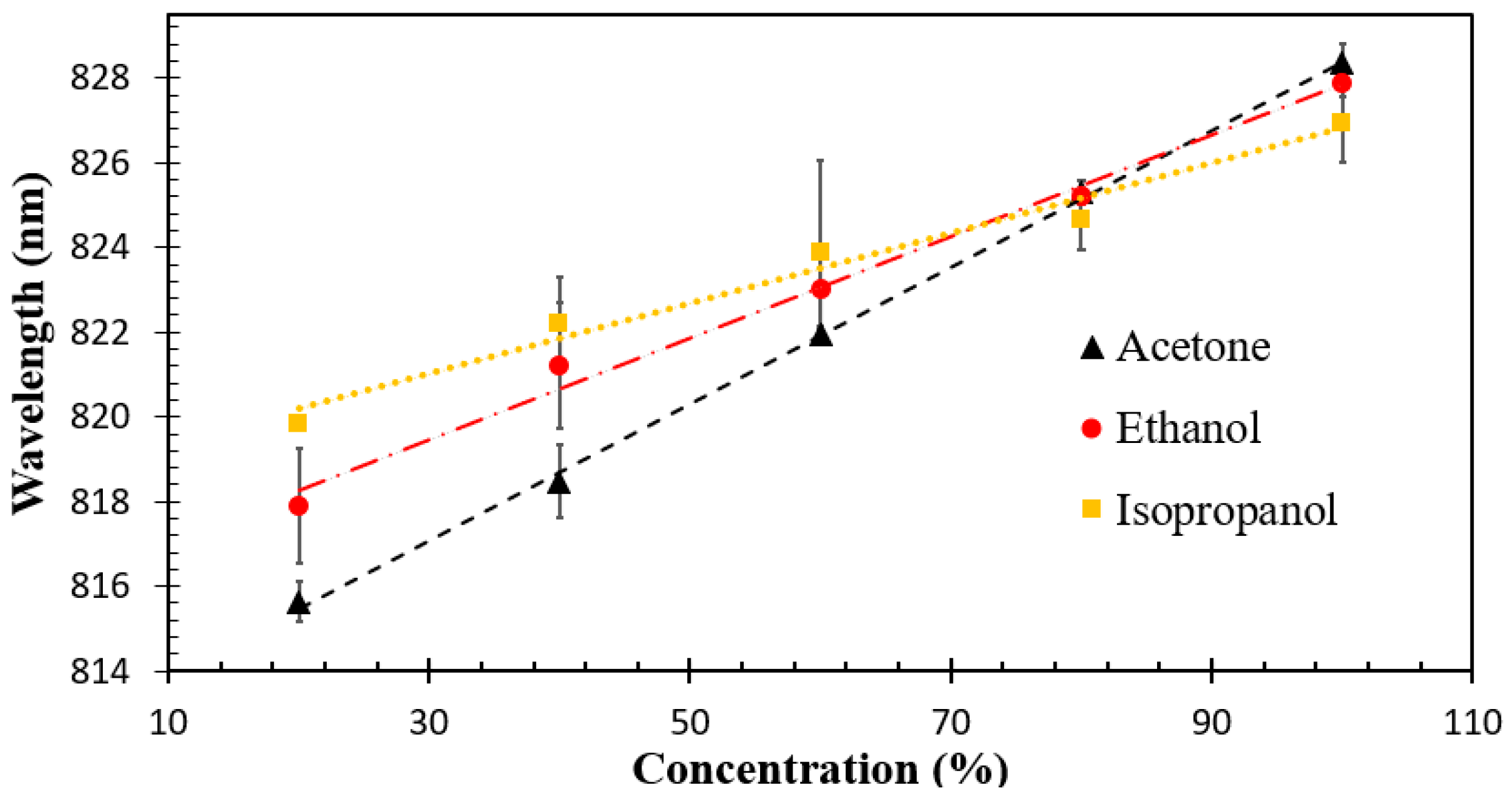
| Material and Method | Structure | Test Gases | Concentration | Sensitivity/Response | Response Time | Working Temperature | Ref. |
| ZnO nanorods (Hydrothermal) | SMS fiber structure | Isopropanol | 20–100% | 0.053 nm/% IPA vapor | 9 min | RT | [26] |
| ZnO nanoparticles (Aqueous chemical route) | Clad-modified optical fiber | Acetone | 50–250 ppm | 14 | NA | RT | [45] |
| ZnO film (Atomic layer deposition) | SMS fiber structure | Ethanol | 50–100% | 50% ethanol:0.065 fitted curve 62% ethanol:0.056 fitted curve | 5 min | RT | [46] |
| Nanocrystalline ZnO | Clad-modified optical fiber | Acetone | 0–500 ppm | −0.27 counts/100 ppm | 48 min | RT | [47] |
| Magnesium cobalt oxide (MgCo2O4) (Hydrothermal) | Clad-modified optical fiber | Acetone | 500 ppm | 42 × 10−3 k/Pa | 25 s | RT | [48] |
| ZnO nanoparticles (Aqueous chemical route) | SMS fiber structure | Acetone, ethanol, and isopropanol | 20–100% | 0.16 nm/% acetone vapor 0.08 nm/% IPA vapor 0.07 nm/% ethanol vapor | Acetone: 10 min Isopropanol: 9 min Ethanol: 8 min | RT | Present work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Swargiary, K.; Jitpratak, P.; Pathak, A.K.; Viphavakit, C. Low-Cost ZnO Spray-Coated Optical Fiber Sensor for Detecting VOC Biomarkers of Diabetes. Sensors 2023, 23, 7916. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187916
Swargiary K, Jitpratak P, Pathak AK, Viphavakit C. Low-Cost ZnO Spray-Coated Optical Fiber Sensor for Detecting VOC Biomarkers of Diabetes. Sensors. 2023; 23(18):7916. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187916
Chicago/Turabian StyleSwargiary, Kankan, Pannathorn Jitpratak, Akhilesh Kumar Pathak, and Charusluk Viphavakit. 2023. "Low-Cost ZnO Spray-Coated Optical Fiber Sensor for Detecting VOC Biomarkers of Diabetes" Sensors 23, no. 18: 7916. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187916
APA StyleSwargiary, K., Jitpratak, P., Pathak, A. K., & Viphavakit, C. (2023). Low-Cost ZnO Spray-Coated Optical Fiber Sensor for Detecting VOC Biomarkers of Diabetes. Sensors, 23(18), 7916. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23187916









