Objective Methods of Muscle Tone Diagnosis and Their Application—A Critical Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Muscle Tone
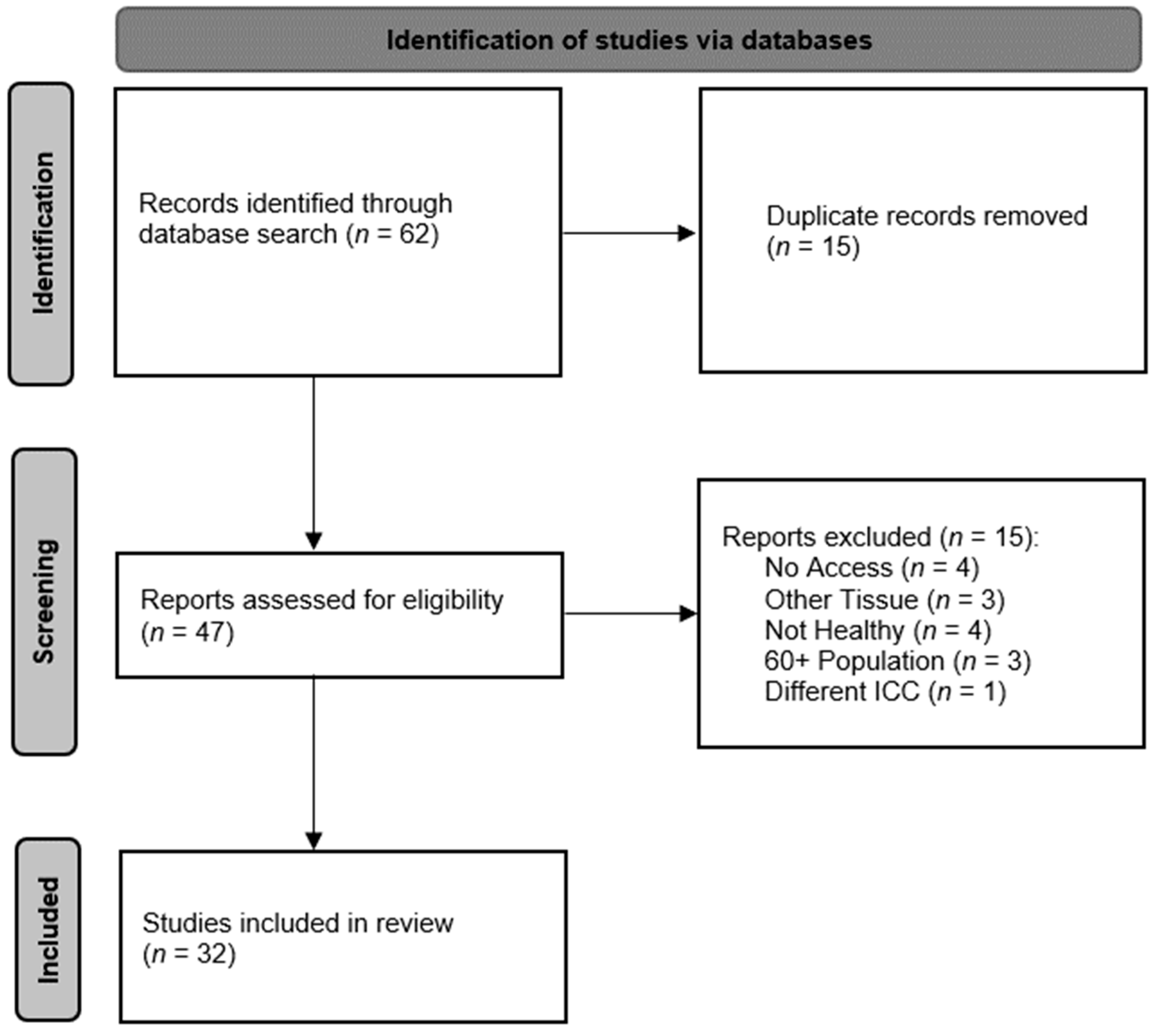
3. Methods
4. Objective Methods of Muscle Tone Diagnosis
| MyotonPRO | CMT | SWE (SSI) | MRE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of studies included | 15 | 2 | 16 | 2 |
| Number of ICC indexes included | 240 | 10 | 123 | 14 |
| Diagnosed muscles: | ||||
| Abductor Digiti Minimi | X | |||
| Along spine (not specified) | X | |||
| Biceps Brachii | X | X | ||
| Biceps Femoris | X | X | ||
| Deltoideus Anterior | X | |||
| Diaphragma | X | |||
| Erector Spinae | X | X | ||
| Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis | X | |||
| Flexor Carpi Ulnaris | X | |||
| Gastrocnemius Medialis | X | X | ||
| Gastrocnemius Lateralis | X | X | ||
| Gluteus Maximus | X | |||
| Infraspinatus | X | X | X | |
| Longissimus Thoracis | X | |||
| Masseter | X | X | ||
| Multifidus | X | X | ||
| Rectus Femoris | X | X | X | |
| Soleus | X | |||
| Splenius Capitis | X | |||
| Supraspinatus | X | |||
| Tibialis Anterior | X | |||
| Trapezius | X | |||
| Vastus Medialis | X | X | ||
| Vastus Lateralis | X | X | X | |
| ICCAvg (95% CI) | 0.86 (0.84–0.88) | 0.90 (0.87–0.93) | 0.83 (0.80–0.85) | 0.90 (0.85–0.95) |
| ICCmin–ICCmax | 0.06–1.00 | 0.75–0.99 | 0.08–1.00 | 0.16–1.00 |
| 95% CIAvg | 0.74–0.93 | 0.82–0.97 | 0.67–0.92 | 0.65–0.98 |
| Intergroup variability (%) | 15 | 29 | 17 | 22 |
| Intragroup variability (%) | 85 | 71 | 83 | 78 |
| Studies included | [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,55,61,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,88,89] | |||
| ICC | Intraclass Correlation Coefficient | |||
| ICCAvg | Average ICC of all included studies | |||
| CI | Confidence Interval | |||
| 95% CIAvg | Average 95% confidence interval for ICC of all included studies | |||
| CMT | Computerized Muscle Tonometer | |||
| SWE | Shear–Wave Elastography | |||
| SSI | Supersonic Shear Imaging | |||
| MRE | Magnetic Resonance Elastography | |||
5. Application of Objective Methods in Muscle Tone Diagnosis
5.1. Physiotherapy
5.2. Ergonomics
5.3. Sport
5.4. Basic Research
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Véle, F. Vyšetření Hybných Funkcí z Pohledu Neurofyziologie; Triton: Praha, Czech Republic, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Haladová, E.; Nechvátalová, L. Vyšetřovací Metody Hybného Systému; Národní Centrum Ošetřovatelství a Nelékařských Zdravotnických Oborů: Brno, Czech Republic, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kolar, P. Clinical Rehabilitation; Alena Kobesová: Praha, Czech Republic, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Véle, F. Kineziologie, 2nd ed.; Triton: Praha, Czech Republic, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly, J. Travell, Simons & Simons’ Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: The Trigger Point Manual; Wolters Kluwer Health: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, M. A Textbook of Physiology, 6th ed.; Macmillan and Co.: London, UK, 1892; Volume Part III. [Google Scholar]
- Clemmesen, S. Some studies on muscle tone. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1951, 44, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, J.J.; Kreimeyer, D.; Aalderks, M.; Gallagher, T. A comparison of dorsal and volar resting hand splints in the reduction of hypertonus. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1982, 36, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Masi, A.T.; Hannon, J.C. Human resting muscle tone (HRMT): Narrative introduction and modern concepts. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2008, 12, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenn, W.O.; Garvey, P.H. The measurement of the elasticity and viscosity of skeletal muscle in normal and pathological cases; a study of socalled “muscle tonus”. J. Clin. Investig. 1934, 13, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, G.D.; Mense, S. Understanding and measurement of muscle tone as related to clinical muscle pain. Pain 1998, 75, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleip, R. Fascial plasticity—A new neurobiological explanation Part 2. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2003, 7, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, D.G.; Travell, J.G.; Simons, L.S. Travell & Simons’ Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction: Upper Half of Body; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1999; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Latash, M.L.; Zatsiorsky, V. Biomechanics and Motor Control: Defining Central Concepts; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, R. Disorders of Skeletal Muscle. In The Musculoskeletal System, 2nd ed.; Sambrook, P., Taylor, T., Ellis, A., Eds.; Systems of the Body; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 109–122. [Google Scholar]
- Darby, S.A.; Frysztak, R.J. Neuroanatomy of the Spinal Cord. In Clinical Anatomy of the Spine, Spinal Cord, and ANS, 3rd ed.; Cramer, G.D., Darby, S.A., Eds.; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 341–412. [Google Scholar]
- Katner, T.L.; Kasarskis, E.J. Muscle Tone. In Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences; Daroff, R.B., Aminoff, M.J., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 194–196. [Google Scholar]
- Shortland, A.P. Muscle tone is not a well-defined term. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, J.; Kulshreshtha, D.; Almotiri, M.; Jog, M. Muscle Tone Physiology and Abnormalities. Toxins 2021, 13, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, N.A.; Latash, M.L.; Turvey, M.T. Dexterity and Its Development; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rychlíková, E. Manuální Medicína: Průvodce Diagnostikou a Léčbou Vertebrogenních Poruch, 2nd ed.; Maxdorf: Praha, Czech Republic, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, J.B. Response to stretch of hypertonic muscle groups in hemiplegia. Br. Med. J. 1959, 1, 1504–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Smith, M.B. Interrater reliability of a modified Ashworth scale of muscle spasticity. Phys. Ther. 1987, 67, 206–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehler, E.J.N. Spasticita-klinické škály. Neurol. Praxi 2015, 16, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Tognella, F.; Mainar, A.; Vanhoutte, C.; Goubel, F. A mechanical device for studying mechanical properties of human muscles in vivo. J. Biomech. 1997, 30, 1077–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, E. Innervation and “tonus” of striated muscle in man. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 1943, 97, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, E.D.; Bronk, D.W. The discharge of impulses in motor nerve fibres: Part II. The frequency of discharge in reflex and voluntary contractions. J. Physiol. 1929, 67, i3–i151. [Google Scholar]
- Mullix, J.; Warner, M.; Stokes, M. Testing muscle tone and mechanical properties of rectus femoris and biceps femoris using a novel hand held MyotonPRO device: Relative ratios and reliability. Work. Pap. Health Sci. 2012, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Peipsi, A.; Kerpe, R.; Jäger, H.; Soeder, S.; Gordon, C.; Schleip, R. Myoton pro: A novel tool for the assessment of mechanical properties of fascial tissues. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2012, 16, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, L.; Samuel, D.; Stokes, M. Quadriceps muscle tone, elasticity and stiffness in older males: Reliability and symmetry using the MyotonPRO. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2012, 55, e31–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.N.; Li, Y.P.; Liu, C.L.; Zhang, Z.J. Assessing the elastic properties of skeletal muscle and tendon using shearwave ultrasound elastography and MyotonPRO. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, J.P.; Koppenhaver, S.L.; Michener, L.A.; Proulx, L.; Bisagni, F.; Cleland, J.A. Characterization of tissue stiffness of the infraspinatus, erector spinae, and gastrocnemius muscle using ultrasound shear wave elastography and superficial mechanical deformation. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2018, 38, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohr, C.; Braumann, K.M.; Reer, R.; Schroeder, J.; Schmidt, T. Reliability of tensiomyography and myotonometry in detecting mechanical and contractile characteristics of the lumbar erector spinae in healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 118, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albin, S.R.; Koppenhaver, S.L.; Bailey, B.; Blommel, H.; Fenter, B.; Lowrimore, C.; Smith, A.C.; McPoil, T.G. The effect of manual therapy on gastrocnemius muscle stiffness in healthy individuals. Foot 2019, 38, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, J.; Chen, G.; Lu, Y.; Ren, W.; Xu, W.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Reliability of a portable device for quantifying tone and stiffness of quadriceps femoris and patellar tendon at different knee flexion angles. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, S.; Salkin, Y. An investigation of the sex-related differences in the stiffness of the Achilles tendon and gastrocnemius muscle: Inter-observer reliability and inter-day repeatability and the effect of ankle joint motion. Foot 2019, 41, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.P.; Feng, Y.N.; Liu, C.L.; Zhang, Z.J. Paraffin therapy induces a decrease in the passive stiffness of gastrocnemius muscle belly and Achilles tendon: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2020, 99, e19519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.F.; Chang, T.T.; Zhang, Z.J. The Reliability of MyotonPRO in Assessing Masseter Muscle Stiffness and the Effect of Muscle Contraction. Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e926578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo-Sánchez, A.; Abián, P.; Sánchez-Infante, J.; Esteban-Gacía, P.; Jiménez, F.; Abián-Vicén, J. Objective Assessment of Regional Stiffness in Vastus Lateralis with Different Measurement Methods: A Reliability Study. Sensors 2021, 21, 3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel-Santos, F.; Rodrigues Manica, S.; Masi, A.T.; Lagoas-Gomes, J.; Santos, M.B.; Ramiro, S.; Sepriano, A.; Nair, K.; Gomes-Alves, P.; Costa, J.; et al. Lumbar myofascial physical properties in healthy adults: Myotonometry vs. shear wave elastography measurements. Acta Reumatol. Port. 2021, 46, 110–119. [Google Scholar]
- Çevik Saldıran, T.; Kara, İ.; Kutlutürk Yıkılmaz, S. Quantification of the forearm muscles mechanical properties using Myotonometer: Intra- and Inter-Examiner reliability and its relation with hand grip strength. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2022, 67, 102718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Liu, C.L.; Zhang, Z.J. Feasibility of Using a Portable MyotonPRO Device to Quantify the Elastic Properties of Skeletal Muscle. Med. Sci. Monit. 2022, 28, e934121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muckelt, P.E.; Warner, M.B.; Cheliotis-James, T.; Muckelt, R.; Hastermann, M.; Schoenrock, B.; Martin, D.; MacGregor, R.; Blottner, D.; Stokes, M. Protocol and reference values for minimal detectable change of MyotonPRO and ultrasound imaging measurements of muscle and subcutaneous tissue. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGowen, J.M.; Hoppes, C.W.; Forsse, J.S.; Albin, S.R.; Abt, J.; Koppenhaver, S.L. Myotonometry is Capable of Reliably Obtaining Trunk and Thigh Muscle Stiffness Measures in Military Cadets during Standing and Squatting Postures. Mil. Med. 2023, usad179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.A. Pressure threshold meter: Its use for quantification of tender spots. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1986, 67, 836–838. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.A. Tissue compliance meter for objective, quantitative documentation of soft tissue consistency and pathology. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1987, 68, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawchuk, G.; Herzog, W. The reliability and accuracy of a standard method of tissue compliance assessment. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 1995, 18, 298–301. [Google Scholar]
- Horikawa, M.; Ebihara, S.; Sakai, F.; Akiyama, M. Non-invasive measurement method for hardness in muscular tissues. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1993, 31, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Mak, A.F. Effective elastic properties for lower limb soft tissues from manual indentation experiment. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 1999, 7, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, M.; Nosaka, K.; Yoneda, T.; Minamitani, K. Changes in hardness of the human elbow flexor muscles after eccentric exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 82, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, C.T.; Stephens, J.U.; Stroppel, S.L. Assessing the spastic condition of individuals with upper motoneuron involvement: Validity of the myotonometer. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2001, 82, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arokoski, J.P.; Surakka, J.; Ojala, T.; Kolari, P.; Jurvelin, J.S. Feasibility of the use of a novel soft tissue stiffness meter. Physiol. Meas. 2005, 26, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šifta, P.; Otáhal, S.; Süssová, J.; Jaeger, M. Measurement of viscoelastic properties of soft tissue in spastic syndrome. In Proceedings of the 4th Congress for Neurorehabilitation, Hong Kong, China, 12–16 February 2006; Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair. p. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Ylinen, J.; Teittinen, I.; Kainulainen, V.; Kautiainen, H.; Vehmaskoski, K.; Hakkinen, A. Repeatability of a computerized muscle tonometer and the effect of tissue thickness on the estimation of muscle tone. Physiol. Meas. 2006, 27, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kysela, M.; Kolář, M. Myotonometer—Device for measurements of viscoelastic characteristics of soft tissues. In Proceedings of the 2016 ELEKTRO, Strbske Pleso, Slovakia, 16–18 May 2016; pp. 556–560. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, C.T.; Deshner, W.P.; Romo, J.W.; Suoja, E.S.; Fehrer, S.C.; Mikhailenok, E.L. Myotonometer intra- and interrater reliabilities. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2003, 84, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerins, C.M.; Moore, S.D.; Butterfield, T.A.; McKeon, P.O.; Uhl, T.L. Reliability of the myotonometer for assessment of posterior shoulder tightness. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2013, 8, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pamukoff, D.N.; Bell, S.E.; Ryan, E.D.; Blackburn, J.T. The Myotonometer: Not a Valid Measurement Tool for Active Hamstring Musculotendinous Stiffness. J. Sport Rehabil. 2016, 25, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.L.; Ji, W.; Howell, J.N.; Conatser, R.R., Jr. In Vivo Measurement of Human Tissue Compliance. SAE Trans. 2007, 116, 824–834. [Google Scholar]
- Alamaki, A.; Hakkinen, A.; Malkia, E.; Ylinen, J. Muscle tone in different joint positions and at submaximal isometric torque levels. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordevic, S.; Stancin, S.; Meglic, A.; Milutinovic, V.; Tomazic, S. MC sensor--a novel method for measurement of muscle tension. Sensors 2011, 11, 9411–9425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukashiro, S.; Noda, M.; Shibayama, A. In Vivo determination of muscle viscoelasticity in the human leg. Acta Physiol. Scand. 2001, 172, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, S.F.; Shinagawa, M.; Sato, T. Sonoelastic determination of human skeletal muscle elasticity. J. Biomech. 1995, 28, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, K.; Kneezel, T.; Castaneda, B.; Parker, K.J. Quantitative sonoelastography for the in vivo assessment of skeletal muscle viscoelasticity. Phys. Med. Biol. 2008, 53, 4063–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikdar, S.; Shah, J.P.; Gilliams, E.; Gebreab, T.; Gerber, L.H. Assessment of myofascial trigger points (MTrPs): A new application of ultrasound imaging and vibration sonoelastography. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2008, 2008, 5585–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, K.J.; Doyley, M.M.; Rubens, D.J. Imaging the elastic properties of tissue: The 20 year perspective. Phys. Med. Biol. 2011, 56, R1–R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bercoff, J.; Tanter, M.; Fink, M. Supersonic shear imaging: A new technique for soft tissue elasticity mapping. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2004, 51, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, H.T.; Ng, G.Y.; Leung, V.Y.; Fu, S.N. Quantitative estimation of muscle shear elastic modulus of the upper trapezius with supersonic shear imaging during arm positioning. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, K.; Martins, N.; Pereira, W.; Oliveira, L. Triceps surae elasticity modulus measured by shear wave elastography is not correlated to the plantar flexion torque. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2017, 7, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taş, S.; Onur, M.R.; Yılmaz, S.; Soylu, A.R.; Korkusuz, F. Shear Wave Elastography Is a Reliable and Repeatable Method for Measuring the Elastic Modulus of the Rectus Femoris Muscle and Patellar Tendon. J. Ultrasound Med. 2017, 36, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfuraih, A.M.; O’Connor, P.; Hensor, E.; Tan, A.L.; Emery, P.; Wakefield, R.J. The effect of unit, depth, and probe load on the reliability of muscle shear wave elastography: Variables affecting reliability of SWE. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2018, 46, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, C.; Tang, C.; Zhang, Z. Modulation in Elastic Properties of Upper Trapezius with Varying Neck Angle. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2019, 2019, 6048562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, C.; Tang, C.; Zhang, Z. Regional Elastic Properties of the Achilles Tendon Is Heterogeneously Influenced by Individual Muscle of the Gastrocnemius. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2019, 2019, 8452717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatres, A.; Aarab, Y.; Nougaret, S.; Garnier, F.; Larcher, R.; Amalric, M.; Klouche, K.; Etienne, P.; Subra, G.; Jaber, S.; et al. Real-time shear wave ultrasound elastography: A new tool for the evaluation of diaphragm and limb muscle stiffness in critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Z.; Ren, L.J.; Cheng, C.L.; Zheng, Y.P. Mapping of Back Muscle Stiffness along Spine during Standing and Lying in Young Adults: A Pilot Study on Spinal Stiffness Quantification with Ultrasound Imaging. Sensors 2020, 20, 7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Yu, H.K.; Sheng, S.Y.; Liang, S.M.; Lu, H.; Gu, L.X.; Fu, P.; Pan, M. Measurement consistency of dynamic stretching muscle stiffness evaluated using shear wave elastography: Comparison among different stretched levels and ROI sizes. Med. Ultrason. 2021, 23, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olchowy, C.; Olchowy, A.; Hadzik, J.; Dąbrowski, P.; Mierzwa, D. Dentists can provide reliable shear wave elastography measurements of the stiffness of masseter muscles: A possible scenario for a faster diagnostic process. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. Off. Organ Wroc. Med. Univ. 2021, 30, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Karam, M.; Mukhina, E.; Daras, N.; Rivals, I.; Pillet, H.; Skalli, W.; Connesson, N.; Payan, Y.; Rohan, P.Y. Reliability of B-mode ultrasound and shear wave elastography in evaluating sacral bone and soft tissue characteristics in young adults with clinical feasibility in elderly. J. Tissue Viability 2022, 31, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Yue, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Long, C.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ma, X. SWEmean of Quadriceps, a Potential Index of Complication Evaluation to Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2022, 17, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roots, J.; Trajano, G.S.; Drovandi, C.; Fontanarosa, D. Variability of Biceps Muscle Stiffness Measured Using Shear Wave Elastography at Different Anatomical Locations with Different Ultrasound Machines. Ultrasound. Med. Biol. 2023, 49, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresner, M.A.; Rose, G.H.; Rossman, P.J.; Muthupillai, R.; Manduca, A.; Ehman, R.L. Magnetic resonance elastography of skeletal muscle. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2001, 13, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazoglou, S.; Braun, J.; Hamhaber, U.; Sack, I. Two-dimensional waveform analysis in MR elastography of skeletal muscles. Phys. Med. Biol. 2005, 50, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazoglou, S.; Rump, J.; Braun, J.; Sack, I. Shear wave group velocity inversion in MR elastography of human skeletal muscle. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 56, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatt, D.; Papazoglou, S.; Braun, J.; Sack, I. Viscoelasticity-based MR elastography of skeletal muscle. Phys. Med. Biol. 2010, 55, 6445–6459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, G.; Kruse, S.A.; Lomas, D.J. General review of magnetic resonance elastography. World J. Radiol. 2016, 8, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrank, F.; Warmuth, C.; Gorner, S.; Meyer, T.; Tzschatzsch, H.; Guo, J.; Uca, Y.O.; Elgeti, T.; Braun, J.; Sack, I. Real-time MR elastography for viscoelasticity quantification in skeletal muscle during dynamic exercises. Magn. Reson. Med. 2020, 84, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Hong, S.J.; Yoon, J.S.; Oh, C.H.; Cha, J.G.; Kim, H.K.; Bolster, B., Jr. Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) for measurement of muscle stiffness of the shoulder: Feasibility with a 3 T MRI system. Acta Radiol. 2016, 57, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, D.; Numano, T.; Ueki, T.; Habe, T.; Maeno, T.; Takamoto, K.; Igarashi, K.; Maharjan, S.; Mizuhara, K.; Nishijo, H. Magnetic resonance elastography of the supraspinatus muscle: A preliminary study on test-retest repeatability and wave quality with different frequencies and image filtering. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 71, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maršáková, K.; Nováková, T. Objektivizace výskytu svalového hypertonu metodou termografie u dětí a dospívajících s bolestmi hlavy cervikogenního původu. In Proceedings of the Sborník Příspěvků. Pohybové Aktivity Jako Prostředek Ovlivňování Člověka, Vědecká Konference FTVS UK, Praha, Czech Republic, 24 January 2003; pp. 179–182. [Google Scholar]
- Botar-Jid, C.; Damian, L.; Dudea, S.M.; Vasilescu, D.; Rednic, S.; Badea, R. The contribution of ultrasonography and sonoelastography in assessment of myositis. Med. Ultrason. 2010, 12, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Domire, Z.J.; McCullough, M.B.; Chen, Q.; An, K.N. Wave attenuation as a measure of muscle quality as measured by magnetic resonance elastography: Initial results. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelissen, J.L.; Sinkus, R.; Nicolay, K.; Nederveen, A.J.; Oomens, C.W.J.; Strijkers, G.J. Magnetic resonance elastography of skeletal muscle deep tissue injury. NMR Biomed. 2019, 32, e4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, H.J.; Gay, R.E.; Thompson, J.M.; Manduca, A.; An, K.N.; Ehman, R.E.; Basford, J.R. Quantification of Myofascial Taut Bands. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 97, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Sánchez, C.; Ortiz-Lucas, M.; Bravo-Esteban, E.; Mayoral-del Moral, O.; Herrero-Gállego, P.; Gómez-Soriano, J. Myotonometry as a measure to detect myofascial trigger points: An inter-rater reliability study. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 115004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusiak, J.; Kisiel-Sajewicz, K.; Jaskolska, A.; Jaskolski, A. Higher muscle passive stiffness in Parkinson’s disease patients than in controls measured by myotonometry. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusiak, J.; Jaskolska, A.; Budrewicz, S.; Koszewicz, M.; Jaskolski, A. Increased muscle belly and tendon stiffness in patients with Parkinson’s disease, as measured by myotonometry. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 2119–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.J.; He, W.; Cheng, L.G.; Li, S.; Pan, Y.S.; Gao, J. Ultrasound shear wave elastography in assessment of muscle stiffness in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A primary observation. Clin. Imaging 2016, 40, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Du, L.J.; He, W.; Li, S.; Cheng, L.G. Ultrasound Strain Elastography in Assessment of Muscle Stiffness in Acute Levodopa Challenge Test: A Feasibility Study. Ultrasound. Med. Biol. 2016, 42, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; He, W.; Du, L.J.; Li, S.; Cheng, L.G.; Shih, G.; Rubin, J. Ultrasound strain elastography in assessment of resting biceps brachii muscle stiffness in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A primary observation. Clin. Imaging 2016, 40, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilescu, D.; Vasilescu, D.; Dudea, S.; Botar-Jid, C.; Sfrangeu, S.; Cosma, D. Sonoelastography contribution in cerebral palsy spasticity treatment assessment, preliminary report: A systematic review of the literature apropos of seven patients. Med. Ultrason. 2010, 12, 306–310. [Google Scholar]
- Numano, T.; Habe, T.; Ito, D.; Onishi, T.; Takamoto, K.; Mizuhara, K.; Nishijo, H.; Igarashi, K.; Ueki, T. A new technique for motion encoding gradient-less MR elastography of the psoas major muscle: A gradient-echo type multi-echo sequence. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 63, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcaraz-Clariana, S.; Garcia-Luque, L.; Garrido-Castro, J.L.; Fernandez-de-Las-Penas, C.; Carmona-Perez, C.; Rodrigues-de-Souza, D.P.; Alburquerque-Sendin, F. Paravertebral Muscle Mechanical Properties and Spinal Range of Motion in Patients with Acute Neck or Low Back Pain: A Case-Control Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Shin, W.-S. Characteristics of shoulder pain, muscle tone and isokinetic muscle function according to the scapular position of elite boxers. Phys. Ther. Rehabil. Sci. 2020, 9, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llurda-Almuzara, L.; Perez-Bellmunt, A.; Lopez-de-Celis, C.; Aiguade, R.; Seijas, R.; Casasayas-Cos, O.; Labata-Lezaun, N.; Alvarez, P. Normative data and correlation between dynamic knee valgus and neuromuscular response among healthy active males: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennant, L.M.; Nelson-Wong, E.; Kuest, J.; Lawrence, G.; Levesque, K.; Owens, D.; Prisby, J.; Spivey, S.; Albin, S.R.; Jagger, K.; et al. A Comparison of Clinical Spinal Mobility Measures to Experimentally Derived Lumbar Spine Passive Stiffness. J. Appl. Biomech. 2020, 36, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Kudas, S.; Ozcan, A.S.; Ipek, A.; Karaoglanoglu, M.; Arslan, H.; Bozkurt, M. Real-time sonoelastography of the Achilles tendon: Pattern description in healthy subjects and patients with surgically repaired complete ruptures. Skeletal. Radiol. 2012, 41, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra-Ano, P.; Ingles, M.; Espi-Lopez, G.V.; Sempere-Rubio, N.; Aguilar-Rodriguez, M. Biomechanical and viscoelastic properties of the ankle muscles in men with previous history of ankle sprain. J. Biomech. 2021, 115, 110191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Yu, Y.F.; Ding, W.L.; Yu, J.Y.; Song, L.; Feng, Y.N.; Zhang, Z.J. Quantification of the Masseter Muscle Hardness of Stroke Patients Using the MyotonPRO Apparatus: Intra- and Inter-Rater Reliability and Its Correlation with Masticatory Performance. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e928109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.A.; Sinkus, R.; Gandevia, S.C.; Herbert, R.D.; Bilston, L.E. Measuring changes in muscle stiffness after eccentric exercise using elastography. NMR Biomed. 2012, 25, 852–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, P.; Macgregor, L.J.; Barnhill, E.; Johnson, C.L.; Perrins, M.; Hunter, A.; Brown, C.; van Beek, E.J.R.; Roberts, N. MR elastography measurement of the effect of passive warmup prior to eccentric exercise on thigh muscle mechanical properties. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariji, Y.; Katsumata, A.; Hiraiwa, Y.; Izumi, M.; Iida, Y.; Goto, M.; Sakuma, S.; Ogi, N.; Kurita, K.; Ariji, E. Use of sonographic elastography of the masseter muscles for optimizing massage pressure: A preliminary study. J. Oral Rehabil. 2009, 36, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.R.; Park, G.Y.; Kwon, J.G. The change of intrinsic stiffness in gastrocnemius after intensive rehabilitation with botulinum toxin a injection in spastic diplegic cerebral palsy. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 36, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kablan, N.; Alaca, N.; Tatar, Y. Comparison of the Immediate Effect of Petrissage Massage and Manual Lymph Drainage Following Exercise on Biomechanical and Viscoelastic Properties of the Rectus Femoris Muscle in Women. J. Sport Rehabil. 2021, 30, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Bellmunt, A.; Simon, M.; Lopez-de-Celis, C.; Ortiz-Miguel, S.; Gonzalez-Rueda, V.; Fernandez-de-Las-Penas, C. Effects on Neuromuscular Function after Ischemic Compression in Latent Trigger Points in the Gastrocnemius Muscles: A Randomized Within-Participant Clinical Trial. J. Manipulative Physiol. Ther. 2022, 45, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Kim, T.-H. Effect of neuro dynamic technique and instrument assisted soft tissue mobilization on lower extremity muscle tone, stiffness, static balance in stroke patients. J. Korean Phys. Ther. 2020, 32, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milerská, I.; Lhotská, L. Investigation of Muscle Imbalance. In Proceedings of the 8th European Medical and Biological Engineering Conference: Proceedings of the EMBEC 2020, Portorož, Slovenia, 29 November–3 December 2020; pp. 733–739. [Google Scholar]
- Barassi, G.; Giannuzzo, G.; De Santis, R.; Dragonetti, A. Adaptive neuromodulation in the treatment of spasticity. J. Adv. Health Care 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albin, S.R.; Koppenhaver, S.L.; MacDonald, C.W.; Capoccia, S.; Ngo, D.; Phippen, S.; Pineda, R.; Wendlandt, A.; Hoffman, L.R. The effect of dry needling on gastrocnemius muscle stiffness and strength in participants with latent trigger points. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2020, 55, 102479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megna, M.; Marvulli, R.; Fari, G.; Gallo, G.; Dicuonzo, F.; Fiore, P.; Ianieri, G. Pain and Muscles Properties Modifications after Botulinum Toxin Type A (BTX-A) and Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave (rESWT) Combined Treatment. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 19, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.H. Effects of Thoracic Mobilization and Extension Exercise on Thoracic Alignment and Shoulder Function in Patients with Subacromial Impingement Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Healthcare 2020, 8, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Park, S.; Kim, J. Effect of Walking with Combat Boots on the Muscle Tone and Stiffness of Lower Extremity. J. Int. Acad. Phys. Ther. Res. 2020, 11, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Seo, D.W.; Cha, J.Y. Mouthguard-effect of high-intensity weight training on masticatory muscle tone and stiffness in taekwondo athletes. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2020, 16, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Bernal, M.I.; Heredia-Rizo, A.M.; Gonzalez-Garcia, P.; Cortes-Vega, M.D.; Casuso-Holgado, M.J. Validity and reliability of myotonometry for assessing muscle viscoelastic properties in patients with stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oha, K.; Viljasoo, V.; Merisalu, E. Prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders, assessment of parameters of muscle tone and health status among office workers. J. Agron. Res. 2010, 8, 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Roja, Z.; Kalkis, V.; Vain, A.; Kalkis, H.; Eglite, M. Assessment of skeletal muscle fatigue of road maintenance workers based on heart rate monitoring and myotonometry. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2006, 1, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Peipsi, A.; Stokes, M.; Knicker, A.; Abeln, V. Feasibility of monitoring muscle health in microgravity environments using Myoton technology. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2015, 53, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, V.; Duffield, R.; Watsford, M. The effects of compression garments on performance of prolonged manual-labour exercise and recovery. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geregei, A.; Shitova, E.; Malakhova, I.; Shuporin, E.; Bondaruk, E.; Efimov, A.; Takh, V.K. Up-to-date techniques for examining safety and physiological efficiency of industrial exoskeletons. Health Risk Anal. 2020, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, A.; Rabal-Pelay, J.; Berzosa, C.; Gutierrez, H.; Cimarras-Otal, C.; Lacarcel-Tejero, B.; Bataller-Cervero, A.V. Effect of a Long Exercise Program in the Reduction of Musculoskeletal Discomfort in Office Workers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klich, S.; Ficek, K.; Krymski, I.; Klimek, A.; Kawczynski, A.; Madeleine, P.; Fernandez-de-Las-Penas, C. Quadriceps and Patellar Tendon Thickness and Stiffness in Elite Track Cyclists: An Ultrasonographic and Myotonometric Evaluation. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 607208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klich, S.; Krymski, I.; Kawczyński, A. Viscoelastic properties of lower extremity muscles after elite track cycling sprint events: A case report. Cent. Eur. J. Sport Sci. Med. 2020, 29, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.C.; Lee, C.L.; Chang, N.J. Acute Effects of Dynamic Stretching Followed by Vibration Foam Rolling on Sports Performance of Badminton Athletes. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2020, 19, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saldiran, T.C.; Atici, E.; Rezaei, D.A.; Ozturk, O.; Uslu, B.; Ozcan, B.A.; Okudan, B. The Acute Effects of Different Intensity Whole-Body Vibration Exposure on Muscle Tone and Strength of the Lower Legs, and Hamstring Flexibility: A Pilot Study. J. Sport Rehabil. 2020, 30, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, O.; Delioglu, K.; Firat, T. The effects of hamstring training methods on muscle viscoelastic properties in healthy young individuals. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2021, 31, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-T.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-J.J. Stiffness of the gastrocnemius–Achilles tendon complex between amateur basketball players and the non-athletic general population. Front Physiol. 2020, 11, 606706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Sanchez, A.; Abian, P.; Sousa, F.; Jimenez, F.; Abian-Vicen, J. Influence of Badminton Practice on Age-Related Changes in Patellar and Achilles Tendons. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2021, 29, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-H.; Lee, D.-H.; Kim, S.-E.; Seo, D.-K. Correlation between contraction ratio, endurance, and muscle tone of cervical muscles. Phys. Ther. Rehabil. Sci. 2020, 9, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomar, J.; Baiget, E.; Corbi, F. Influence of Strength, Power, and Muscular Stiffness on Stroke Velocity in Junior Tennis Players. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, K.; Namiki, C.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Saito, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Ishii, M.; Okumura, T.; Tohara, H. Association between myotonometric measurement of masseter muscle stiffness and maximum bite force in healthy elders. J. Oral Rehabil. 2020, 47, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berzosa, C.; Gutierrez, H.; Bascuas, P.J.; Arbones, I.; Bataller-Cervero, A.V. Muscle Tone and Body Weight Predict Uphill Race Time in Amateur Trail Runners. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basti, A.; Yalcin, M.; Herms, D.; Hesse, J.; Aboumanify, O.; Li, Y.; Aretz, Z.; Garmshausen, J.; El-Athman, R.; Hastermann, M.; et al. Diurnal variations in the expression of core-clock genes correlate with resting muscle properties and predict fluctuations in exercise performance across the day. BMJ Open Sport Exerc. Med. 2021, 7, e000876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.S.; Lee, M.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Chen, W.C.; Huang, W.C. Beneficial effects of a negative ion patch on eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage, inflammation, and exercise performance in badminton athletes. Chin. J. Physiol. 2020, 63, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arda, K.; Ciledag, N.; Aktas, E.; Aribas, B.K.; Kose, K. Quantitative assessment of normal soft-tissue elasticity using shear-wave ultrasound elastography. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domire, Z.J.; McCullough, M.B.; Chen, Q.; An, K.N. Feasibility of using magnetic resonance elastography to study the effect of aging on shear modulus of skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Biomech. 2009, 25, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debernard, L.; Robert, L.; Charleux, F.; Bensamoun, S.F. Analysis of thigh muscle stiffness from childhood to adulthood using magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) technique. Clin. Biomech. 2011, 26, 836–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.; Barnhill, E.; Gray, C.; Brown, C.; van Beek, E.J.R.; Roberts, N.; Greig, C.A. Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) shows significant reduction of thigh muscle stiffness in healthy older adults. Geroscience 2020, 42, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taş, S.; Aktaş, D. Menstrual Cycle does not Affect the Mechanical Properties of Muscle and Tendon. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2020, 10, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khowailed, I.A.; Lee, H. Neuromuscular Control of Ankle-stabilizing Muscles-specific Effects of Sex and Menstrual Cycle. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensamoun, S.F.; Ringleb, S.I.; Chen, Q.; Ehman, R.L.; An, K.N.; Brennan, M. Thigh muscle stiffness assessed with magnetic resonance elastography in hyperthyroid patients before and after medical treatment. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 26, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullough, M.B.; Domire, Z.J.; Reed, A.M.; Amin, S.; Ytterberg, S.R.; Chen, Q.; An, K.N. Evaluation of muscles affected by myositis using magnetic resonance elastography. Muscle Nerve 2011, 43, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basford, J.R.; Jenkyn, T.R.; An, K.N.; Ehman, R.L.; Heers, G.; Kaufman, K.R. Evaluation of healthy and diseased muscle with magnetic resonance elastography. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakonaki, E.E.; Allen, G.M. Magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound and real-time ultrasound elastography of the thigh muscles in congenital muscle dystrophy. Skeletal. Radiol. 2010, 39, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; An, S.Y.; Park, W.; Hwang, J.H. Detection of early changes in the muscle properties of the pectoralis major in breast cancer patients treated with radiotherapy using a handheld myotonometer. Support Care Cancer 2021, 29, 2581–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewit, K. Manipulative Therapy: Musculoskeletal Medicine; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kopecká, B.; Ravnik, D.; Jelen, K.; Bittner, V. Objective Methods of Muscle Tone Diagnosis and Their Application—A Critical Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167189
Kopecká B, Ravnik D, Jelen K, Bittner V. Objective Methods of Muscle Tone Diagnosis and Their Application—A Critical Review. Sensors. 2023; 23(16):7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167189
Chicago/Turabian StyleKopecká, Barbora, David Ravnik, Karel Jelen, and Václav Bittner. 2023. "Objective Methods of Muscle Tone Diagnosis and Their Application—A Critical Review" Sensors 23, no. 16: 7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167189
APA StyleKopecká, B., Ravnik, D., Jelen, K., & Bittner, V. (2023). Objective Methods of Muscle Tone Diagnosis and Their Application—A Critical Review. Sensors, 23(16), 7189. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167189





