Reconfiguration Error Correction Model for an FBG Shape Sensor Based on the Sparrow Search Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
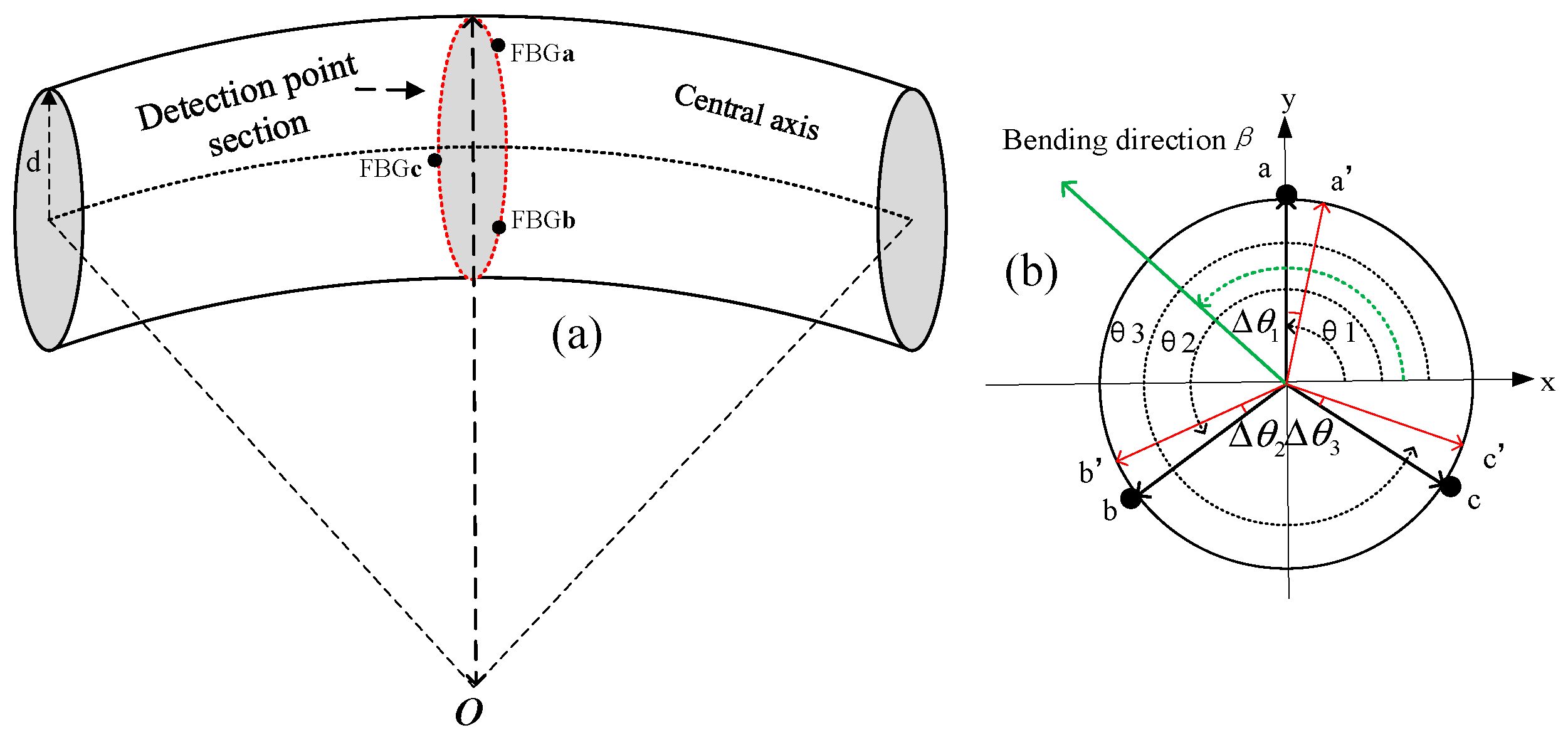
2. FBG Shape Sensing Error Model
2.1. Curvature Error and Bending Direction Error Correction Model
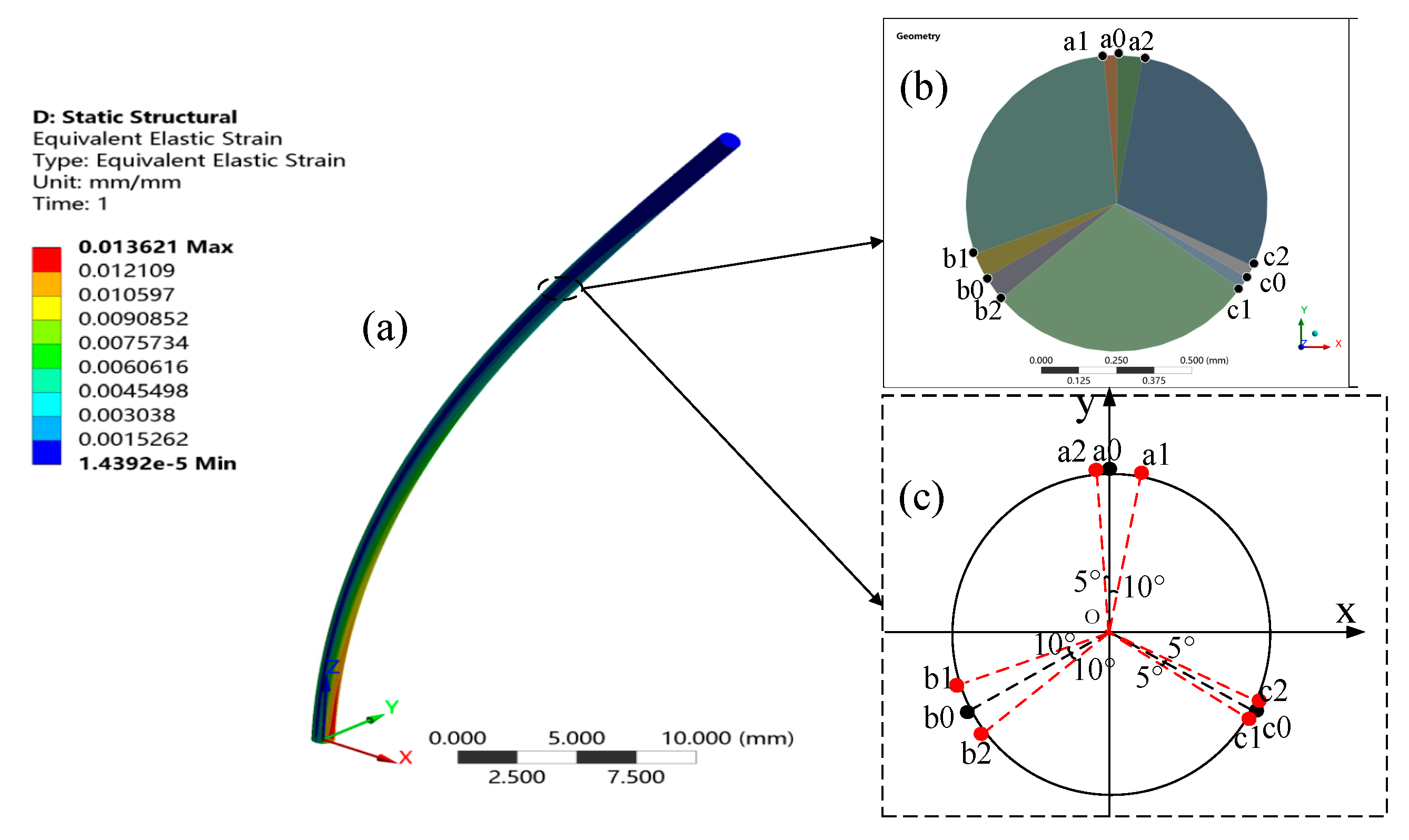
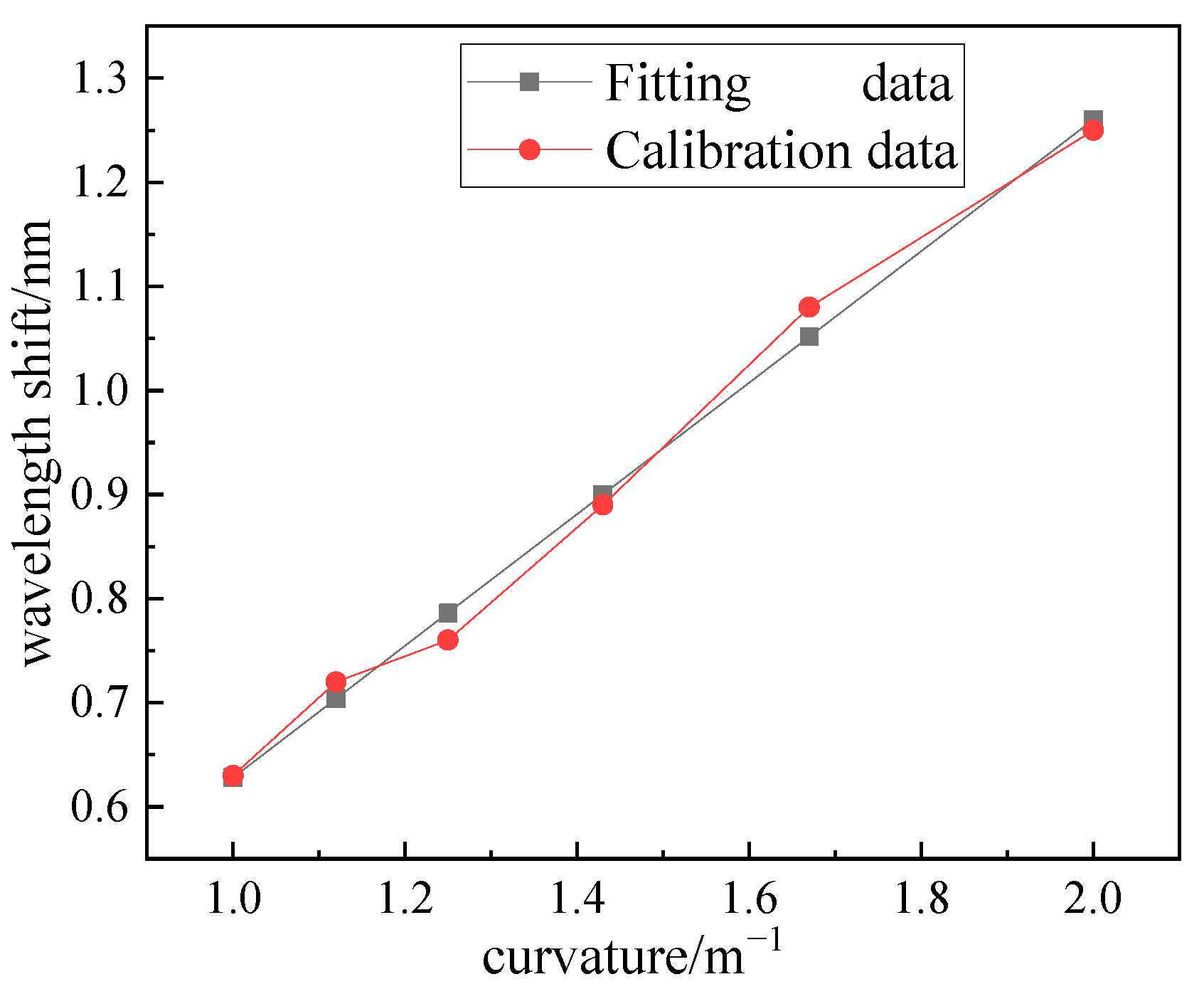
2.2. Error Correction Model Verification and Analysis
3. Experiment
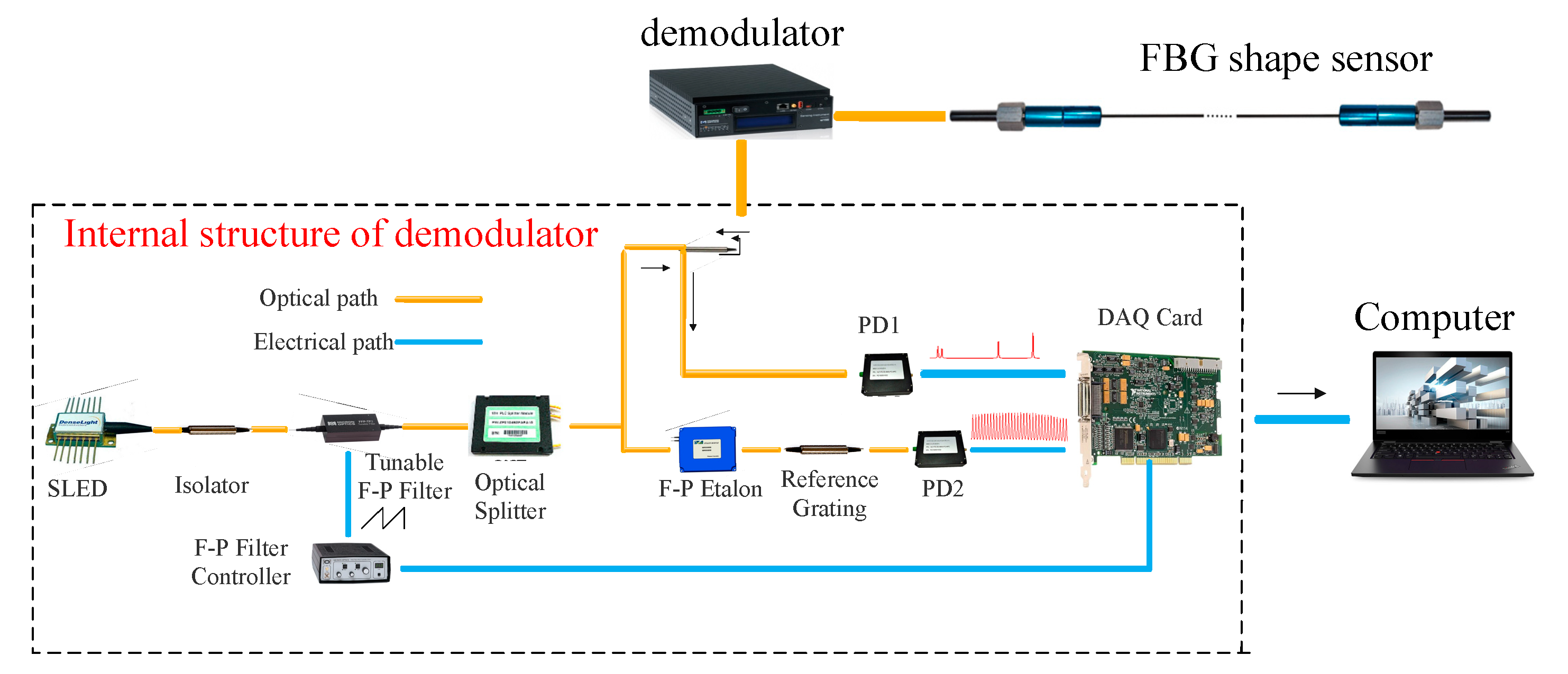
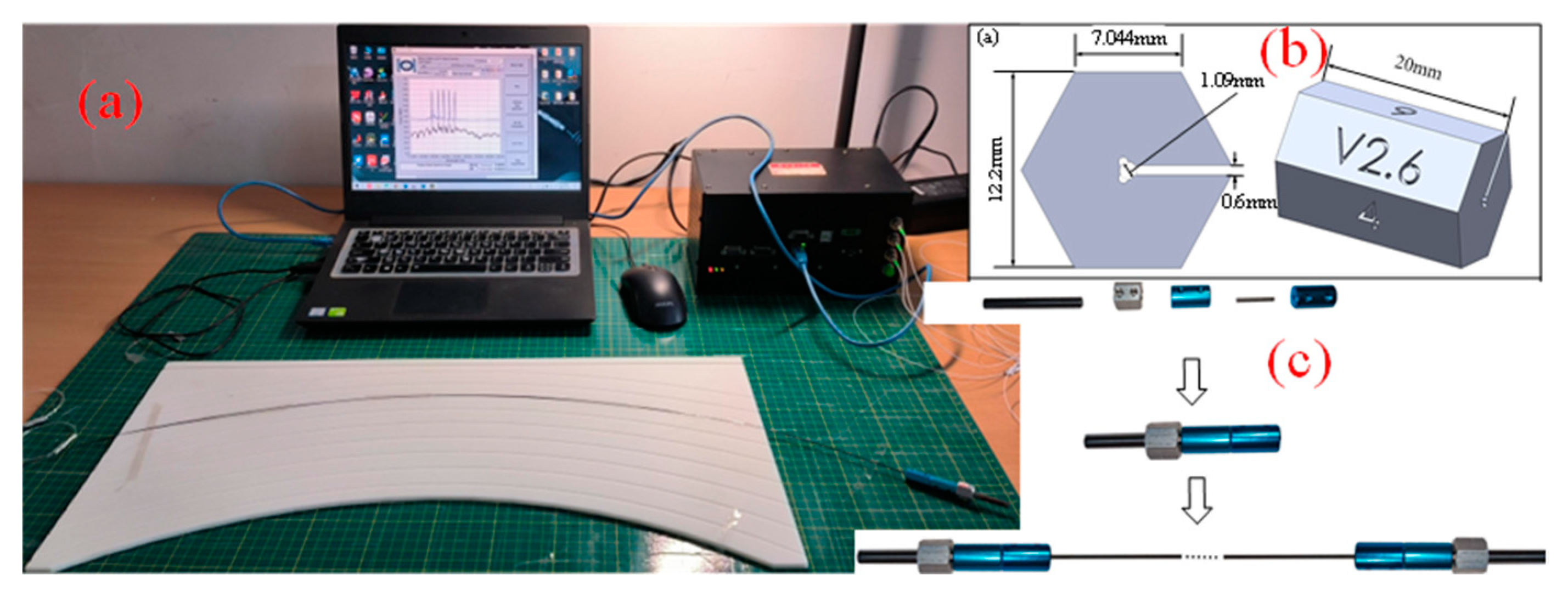
3.1. Experimental System and Sensor Calibration
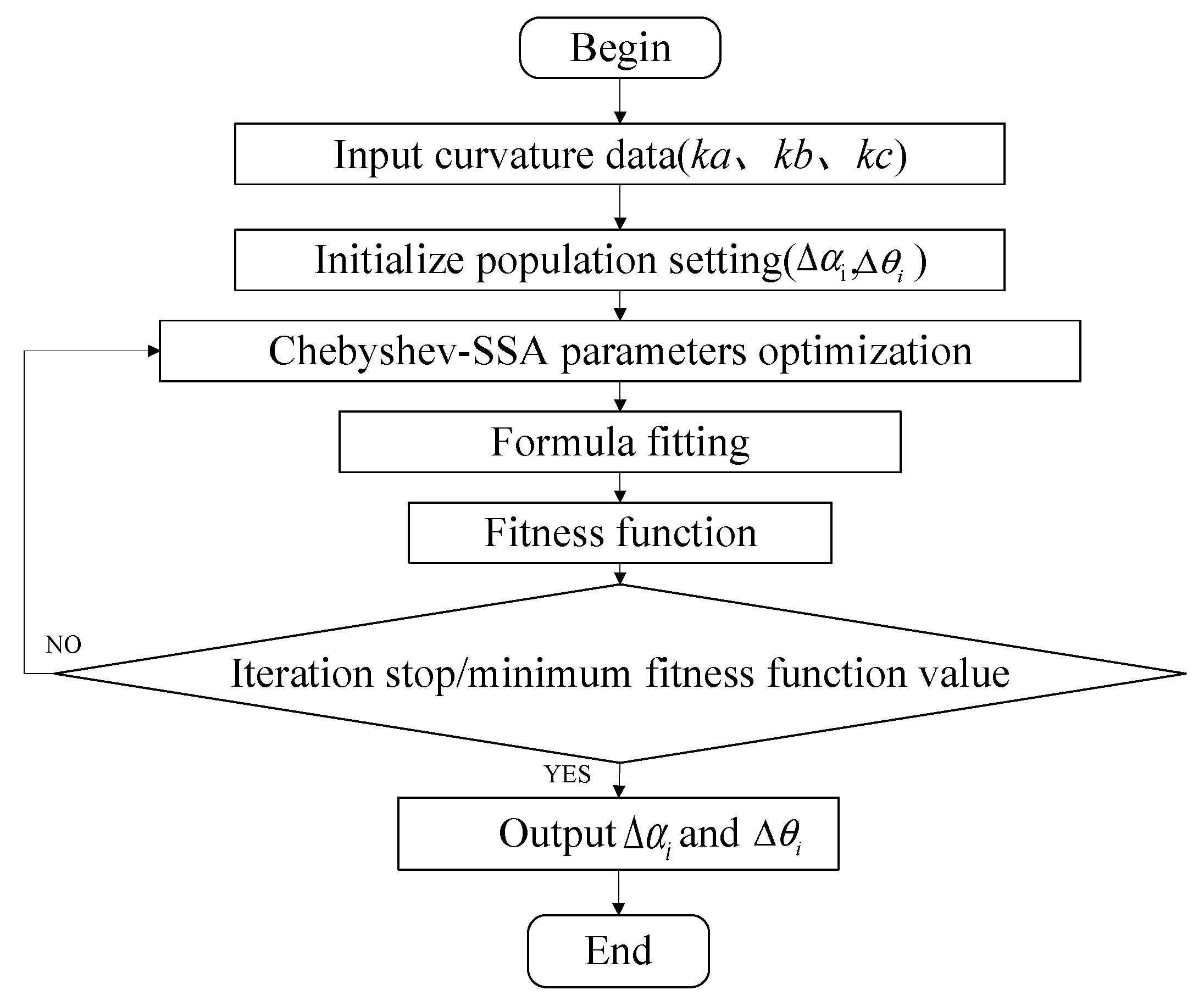
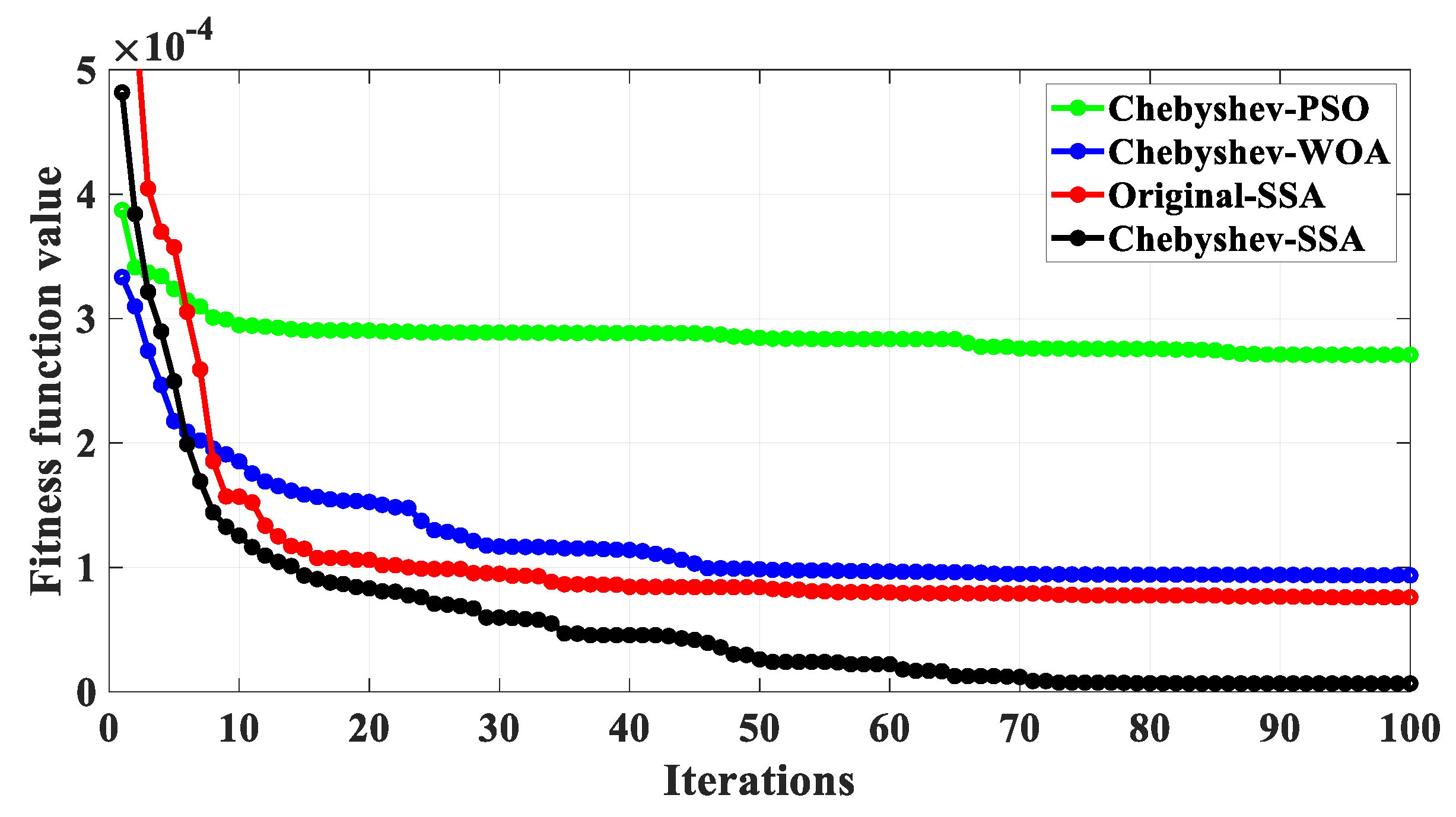
3.2. Optimization Model
- Enter the measured curvatures ka, kb, and kc for FBG a, FBG b, and FBG c in the fixed curvature state, respectively.
- Initialize the inputs and set the placement angles θ1, θ2, and θ3 of the FBG sensor. In this paper, θ1 = 90°, θ2 = 210°, and θ3 = 330°.
- Set the FBG calibration direction deviation Δθi and placement angle deviation Δαi, and Δθi and Δαi are randomly assigned and coded within a certain range.
- Δθi and Δαi are substituted into Equation (10) to obtain the theoretical curvatures k1, k2, and k3, and are optimized using Chebyshev-SSA.
- The optimal parameters of Δθi and Δαi are output when the value of the fitness function ∆k is minimized or at the end of the iteration. Otherwise, steps (3) to (5) are repeated.
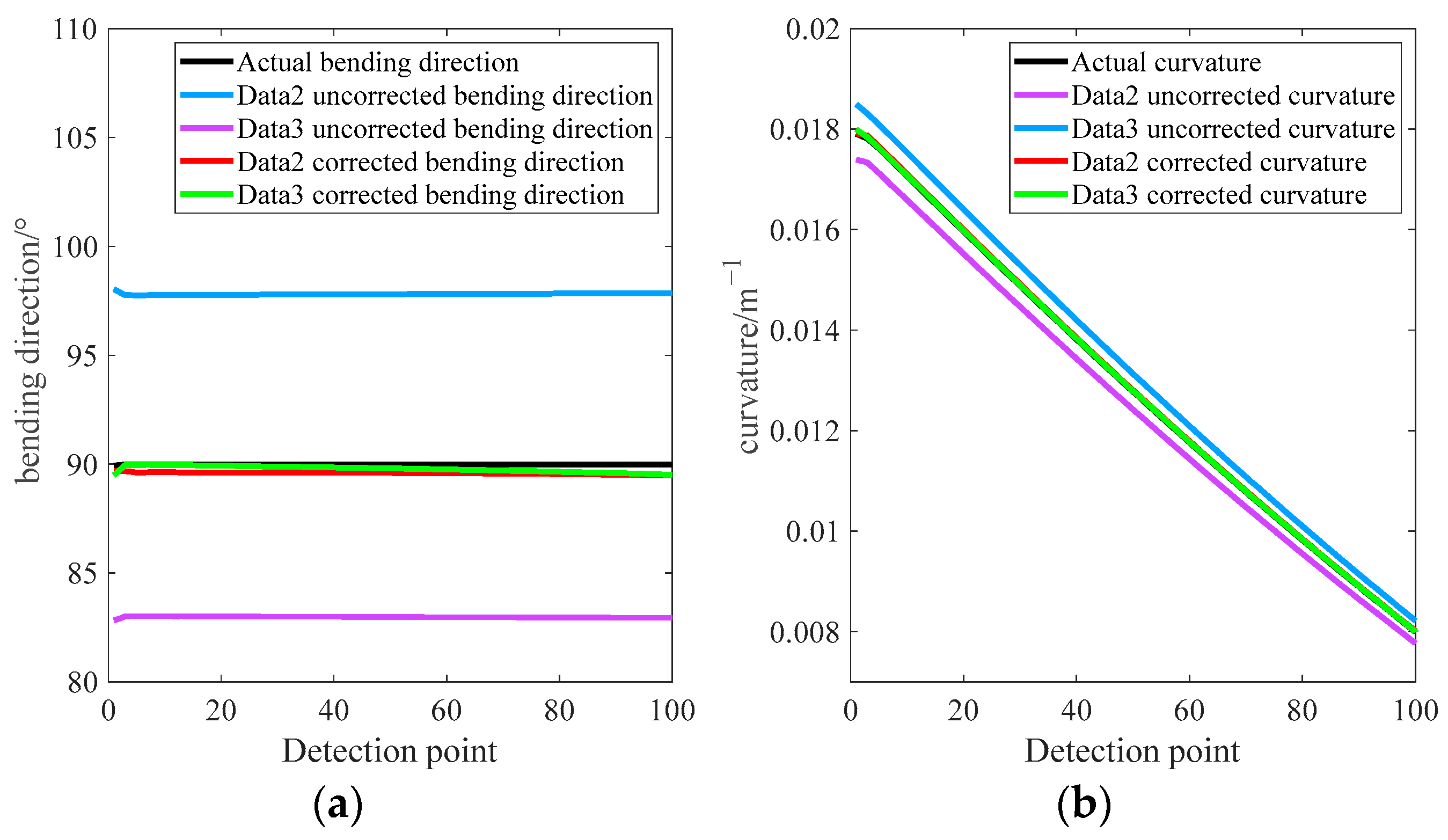
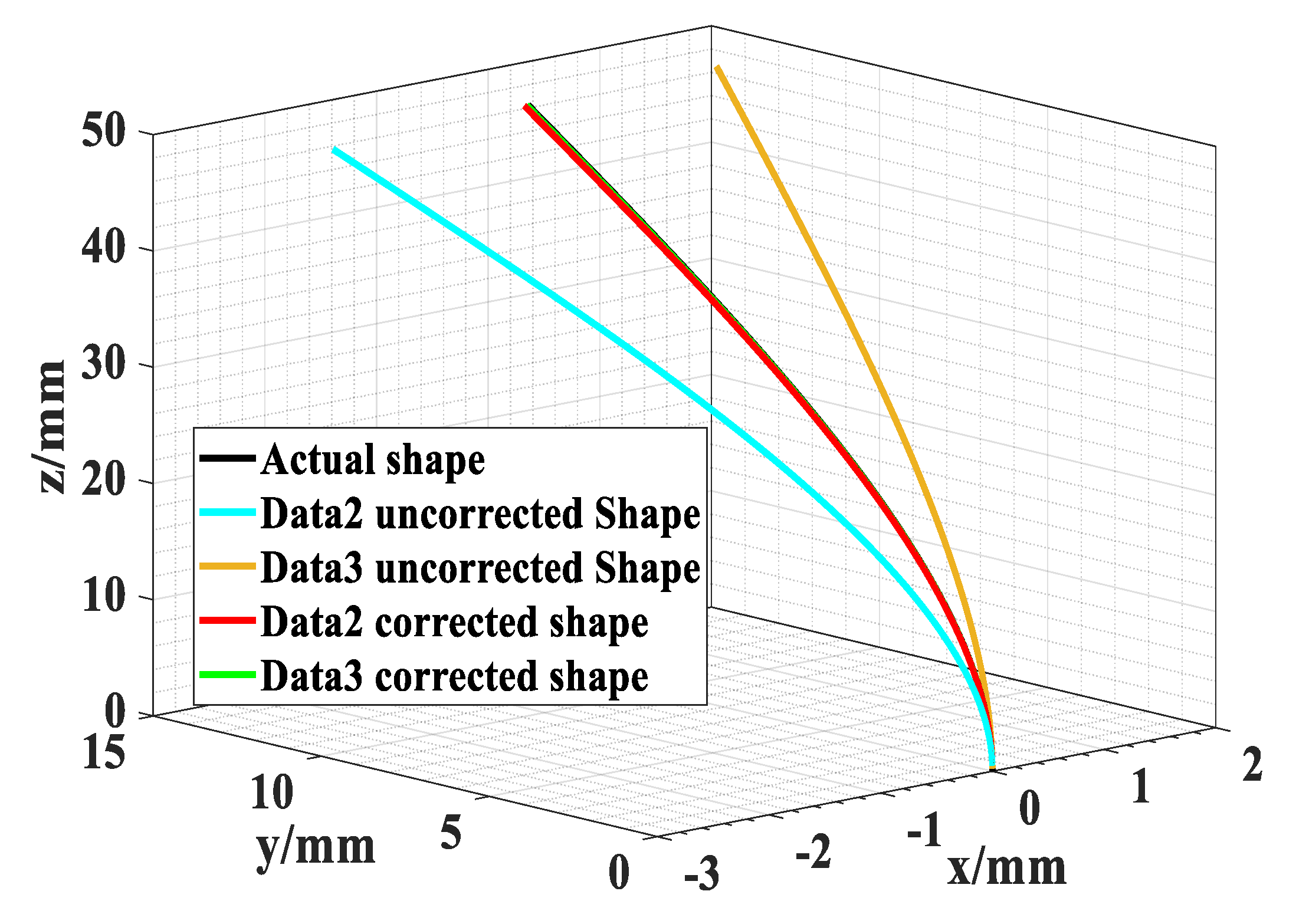
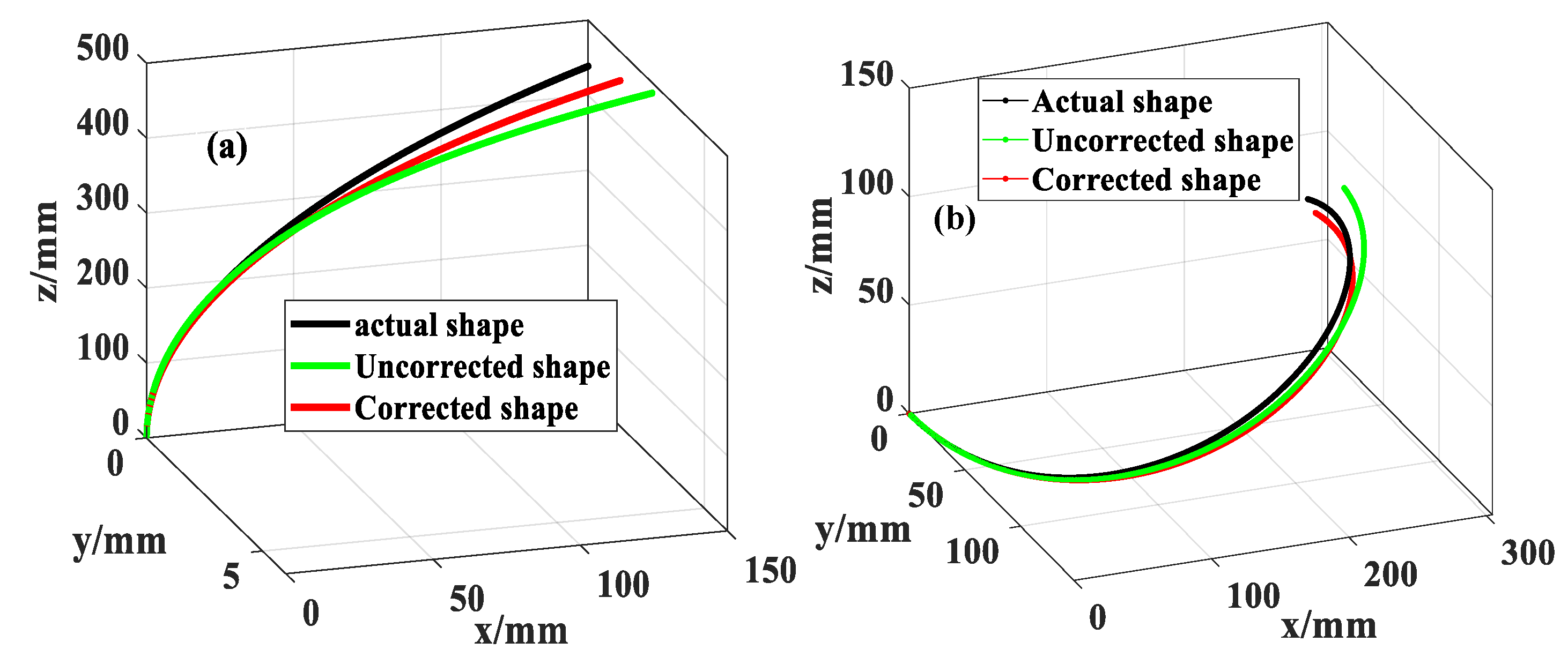
3.3. Shape Reconfiguration
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Ahmad, O.; Ourak, M.; Van Roosbroeck, J.; Vlekken, J.; Vander Poorten, E. Improved FBG-Based Shape Sensing Methods for Vascular Catheterization Treatment. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4687–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lu, B.; Li, B.; Guo, H.; Liu, Y.H. Robust Three-Dimensional Shape Sensing for Flexible Endoscopic Surgery Using Multi-Core FBG Sensors. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 4835–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.F.; Li, C.L.; Dong, H.J.; Liu, X.; Sun, T.; Grattan, K.T.; Zhao, J. Fiber Bragg Grating-based sensor system for sensing the shape of flexible needles. Measurement 2023, 206, 112251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, I.; Adam, J.M.; Calderón, P.A.; Sales, S. Fiber Optic Shape Sensors: A comprehensive review. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2021, 139, 106508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.L.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, T. Distributed Real-Time Monitoring of Residual Stress During Packaging Process of Optical Fiber Shape Sensor. Acta Opt. Sin. 2022, 42, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Floris, I.; Madrigal, J.; Sales, S.; Adam, J.M.; Calderón, P.A. Experimental study of the influence of FBG length on optical shape sensor performance. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 126, 105878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Zhu, Z.W.; Zheng, B. Experimental study on an FBG strain sensor. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2018, 40, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harasim, D. Temperature-insensitive bending measurement method using optical fiber sensors–ScienceDirect. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 332, 113207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.K.; Kuang, K.B.; Qin, H.Y. Novel Fiber Bragg Grating Tilt Sensor with High Sensitivity. Acta Opt. Sin. 2022, 42, 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Idrisov, R.; Floris, I.; Rothhardt, M. Characterization and calibration of shape sensors based on multicore optical fibre. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2021, 61, 102319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.P.; Chen, Z.Q.; Zhuang, W. Error analysis and calibration for FBG shape reconfiguration based on non-orthogonal curvatures. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 38, 386–393. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, T.; Xie, Y.; Duan, C. Self-calibration method of optical fiber shape sensor placement angle deviation based on GA. Measurement 2022, 202, 111844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Guo, J.; Chatrasingh, M.; Kim, S.; Iordachita, I. Shape determination during needle insertion with curvature measurements. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.H.; Dong, M.L.; He, Y.L.; Sun, G.; Zhou, K. Three-dimensional shape multi-core fiber reconfiguration method of flexible mechanism by introducing curvature and angle correction. Infrared Laser Eng. 2021, 50, 120–126. [Google Scholar]
- Jäckle, S.; Strehlow, J.; Heldmann, S. Shape Sensing with Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors: A Realistic Model of Curvature Interpolation for Shape Reconfiguration; Springer Science and Business Media GmbH: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 258–263. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.P.; Rogge, M.D. Shape sensing using multi-core fiber optic cable and parametric curve solutions. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 2967–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Soto, M.A.; Tang, M. Distributed shape sensing using Brillouin scattering in multi-core fibers. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 25211–25223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parent, F.; Loranger, S.; Mandal, K.K.; Iezzi, V.L.; Lapointe, J.; Boisvert, J.S.; Baiad, M.D.; Kadoury, S.; Kashyap, R. Enhancement of accuracy in shape sensing of surgical needles using optical frequency domain reflectometry in optical fibers Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 2210–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackle, S.; Eixmann, T.; Schulz-Hildebrandt, H.; Hüttmann, G.; Pätz, T. Fiber optical shape sensing of flexible instruments for endovascular navigation. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesthuis, R.J.; Kemp, M.; van den Dobbelsteen, J.J.; Misra, S. Three-Dimensional Needle Shape Reconfiguration Using an Array of Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 19, 1115–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.C.; Dupont, P.E. FBG-based Shape Sensing Tubes for Continuum Robots. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 3531–3537. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, X.; Chen, X.; Fan, H.; Shi, F.; Cheng, X.; Qian, J. Separation method of bending and torsion in shape sensing based on FBG sensors array. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 9367–9383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.K.; Shen, B. A novel swarm intelligence optimization approach: Sparrow search algorithm. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2020, 8, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Mu, X.D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z. Chaos sparrow search optimization algorithm. J. Beijing Univ. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2021, 47, 1712–1720. [Google Scholar]
- Mitic, M.; Vukovic, N.; Petrovic, M.; Miljković, Z. Chaotic fruit fly optimization algorithm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2015, 89, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.R.; Liu, H.Y.; Sun, X.Y. 2D Chebyshev-Sine map for image encryption. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. Ed. 2019, 46, 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Hua, P.D.; Ding, Z.Y.; Liu, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Pan, M.; Guo, H.; Zhang, T.; Liu, L.; et al. Reconfiguration error model of distributed shape sensing based on the reentered frame in OFDR. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 43255–43270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floris, I.; Calderón, P.A.; Sales, S.; Adam, J.M. Effects of core position uncertainty on optical shape sensor accuracy. Measurement 2019, 139, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, I.; Sales, S.; Calderón, P.A.; Adam, J.M. Measurement uncertainty of multicore optical fiber sensors used to sense curvature and bending direction. Measurement 2019, 132, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Data Group | Data2 | Data3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bending direction/° | 80 | 90 | 200 | 210 | 330 | 80 | 90 | 200 | 210 | 330 | |
| Rmax/% | Uncorrected | 2.2 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 1.9 | 0.8 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 2.0 |
| Corrected | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.06 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.5 | |
| Detection Point | Placement Angle Deviation/° | Calibration Direction Deviation/° | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBGa | FBGb | FBGc | FBGa | FBGb | FBGc | |
| Point1 | 0 | −3.9 | 7.5 | 3.9 | 12.5 | 2.2 |
| Point2 | 7.5 | −4.5 | 4.3 | 1.6 | −8.0 | 1.8 |
| Point3 | 2 | 5.3 | −6.1 | −9.2 | 8.4 | −7.4 |
| Point4 | −4.1 | 10.5 | 5.8 | 11.2 | −4.3 | 8.1 |
| Point5 | 2.3 | 14.8 | 9.4 | 9.1 | 9.2 | −3.5 |
| Radius of Curvature r/mm | Tail Point Reconfiguration Error | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncorrected Error | Corrected Error | |||
| Absolute Error/mm | Relative Error/% | Absolute Error/mm | Relative Error/% | |
| 600 | 11.80 | 2.54 | 4.63 | 0.99 |
| 700 | 11.66 | 2.51 | 5.23 | 1.13 |
| 800 | 11.72 | 2.52 | 4.38 | 0.94 |
| 900 | 10.67 | 2.29 | 4.21 | 0.91 |
| 1000 | 12.50 | 2.69 | 5.65 | 1.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, Q.; Liu, F. Reconfiguration Error Correction Model for an FBG Shape Sensor Based on the Sparrow Search Algorithm. Sensors 2023, 23, 7052. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167052
Shang Q, Liu F. Reconfiguration Error Correction Model for an FBG Shape Sensor Based on the Sparrow Search Algorithm. Sensors. 2023; 23(16):7052. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167052
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Qiufeng, and Feng Liu. 2023. "Reconfiguration Error Correction Model for an FBG Shape Sensor Based on the Sparrow Search Algorithm" Sensors 23, no. 16: 7052. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167052
APA StyleShang, Q., & Liu, F. (2023). Reconfiguration Error Correction Model for an FBG Shape Sensor Based on the Sparrow Search Algorithm. Sensors, 23(16), 7052. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167052






