Recent Progress in Self-Powered Sensors Based on Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerators
Abstract
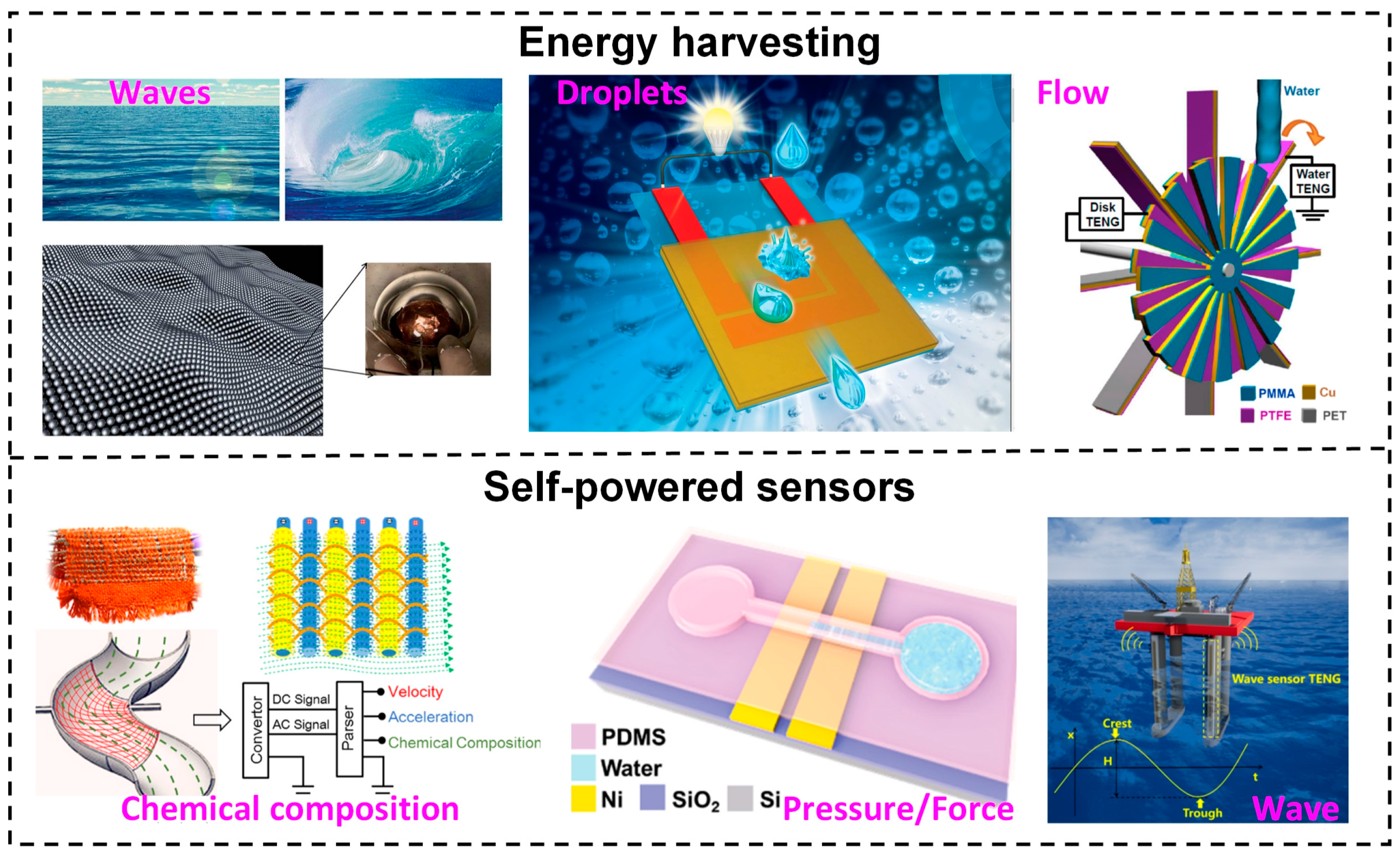
1. Introduction
2. Liquid–Solid Contact Triboelectric Nanogenerator
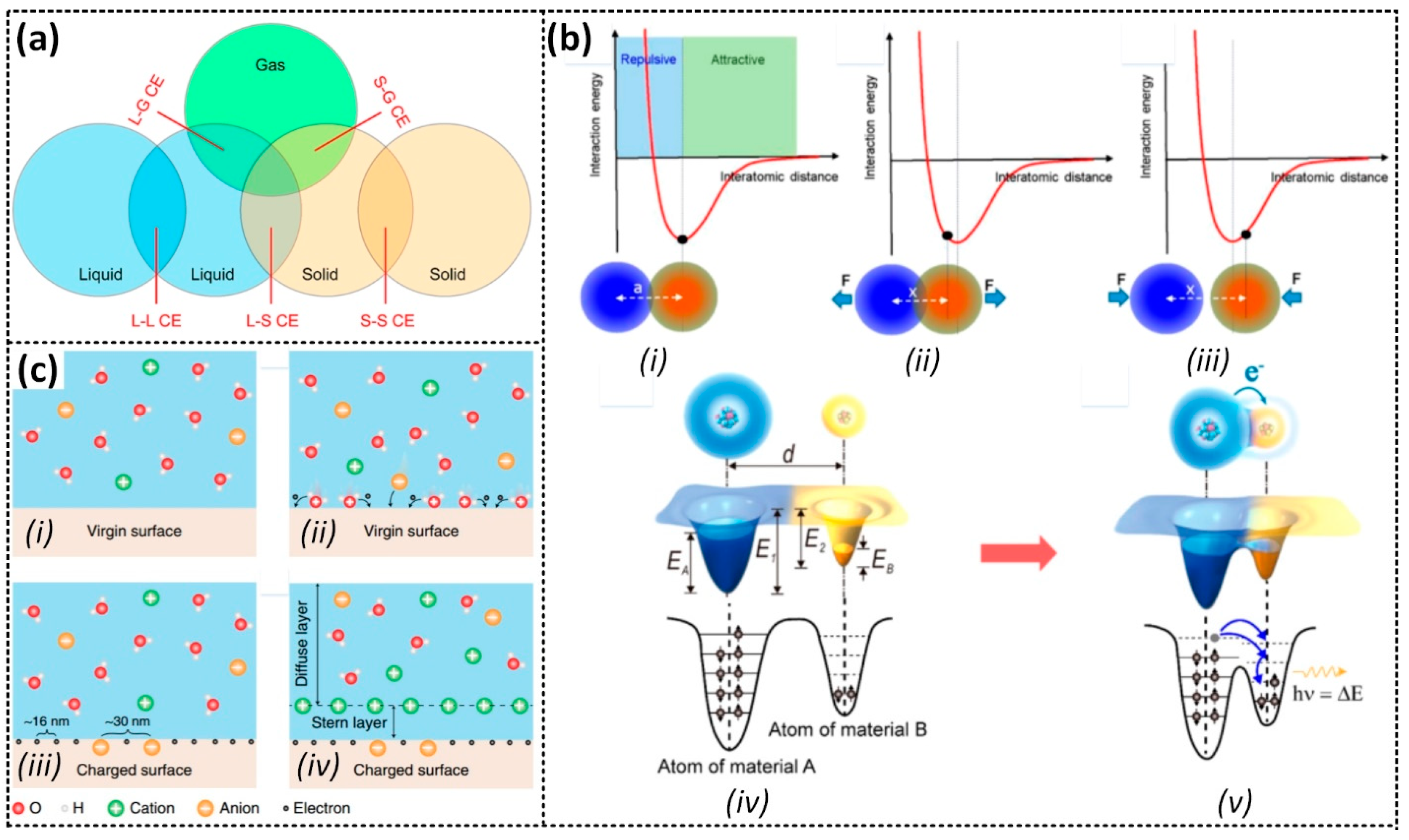
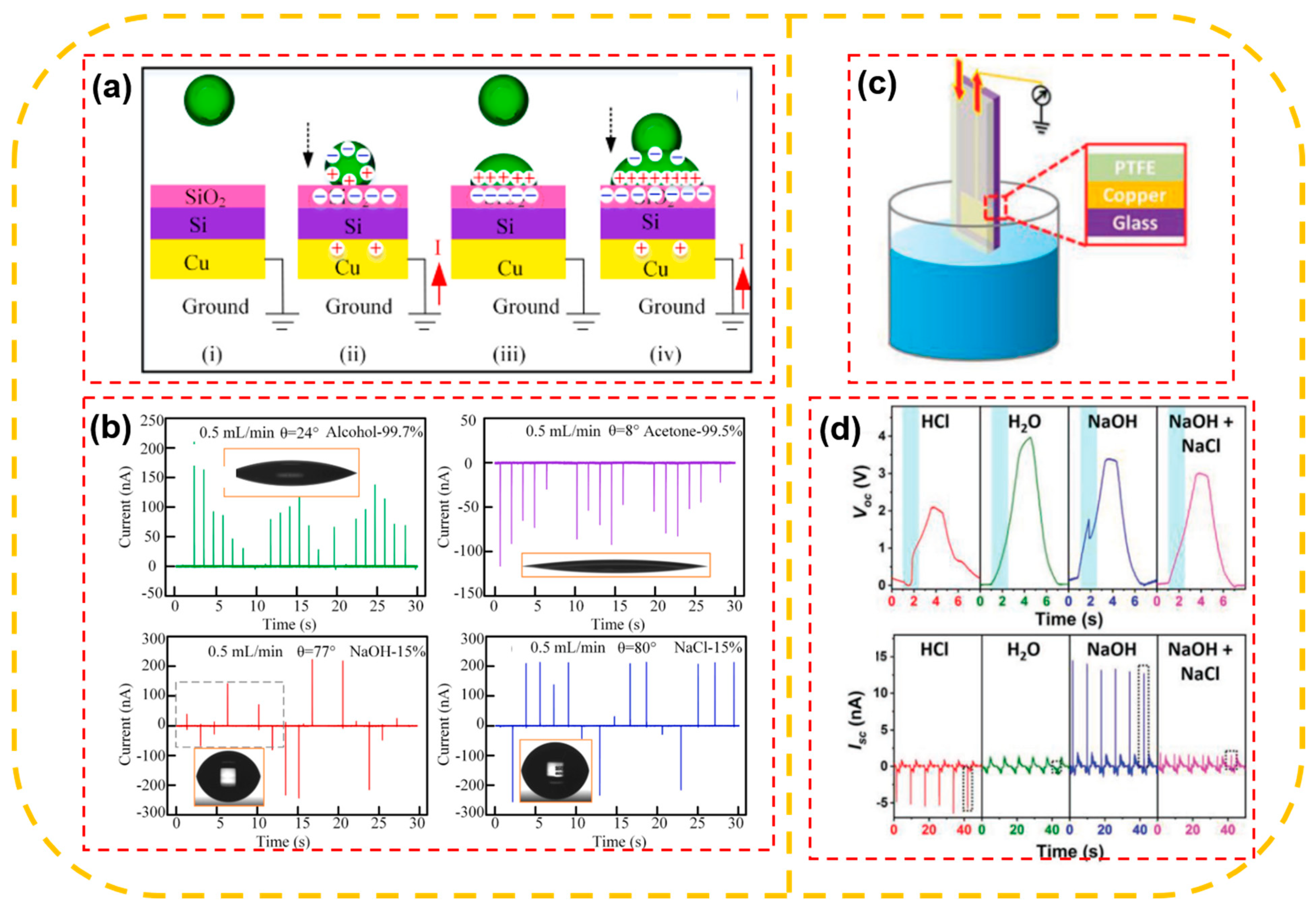
2.1. Mechanism of Liquid–Solid Contact Electrification
2.2. Basic Mode of Operation of Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator
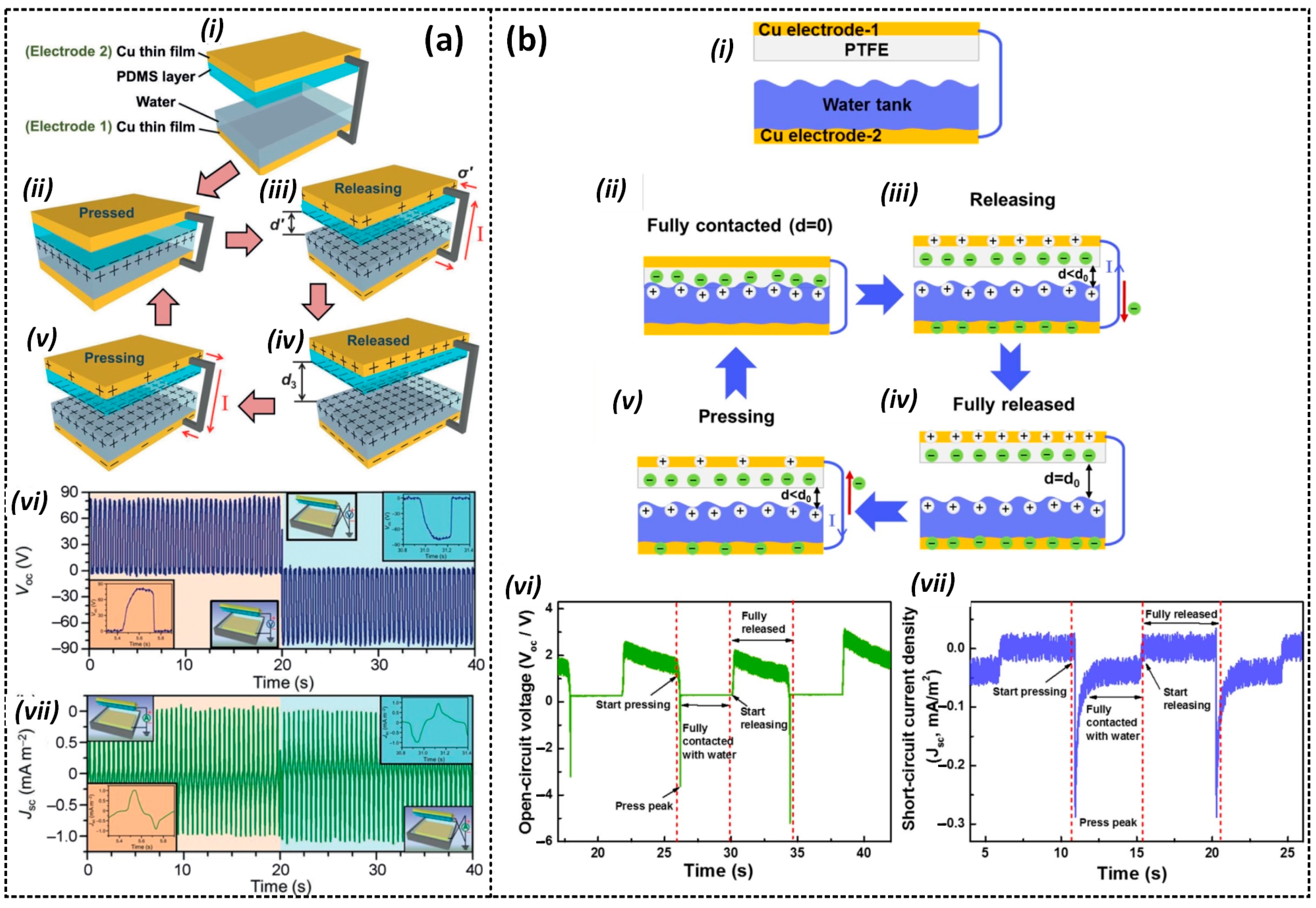
2.2.1. Contact-Separation Mode
2.2.2. Lateral Sliding Mode
2.2.3. Free-Standing Mode
2.2.4. Single-Electrode Mode
2.3. Interacting Modes of Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator
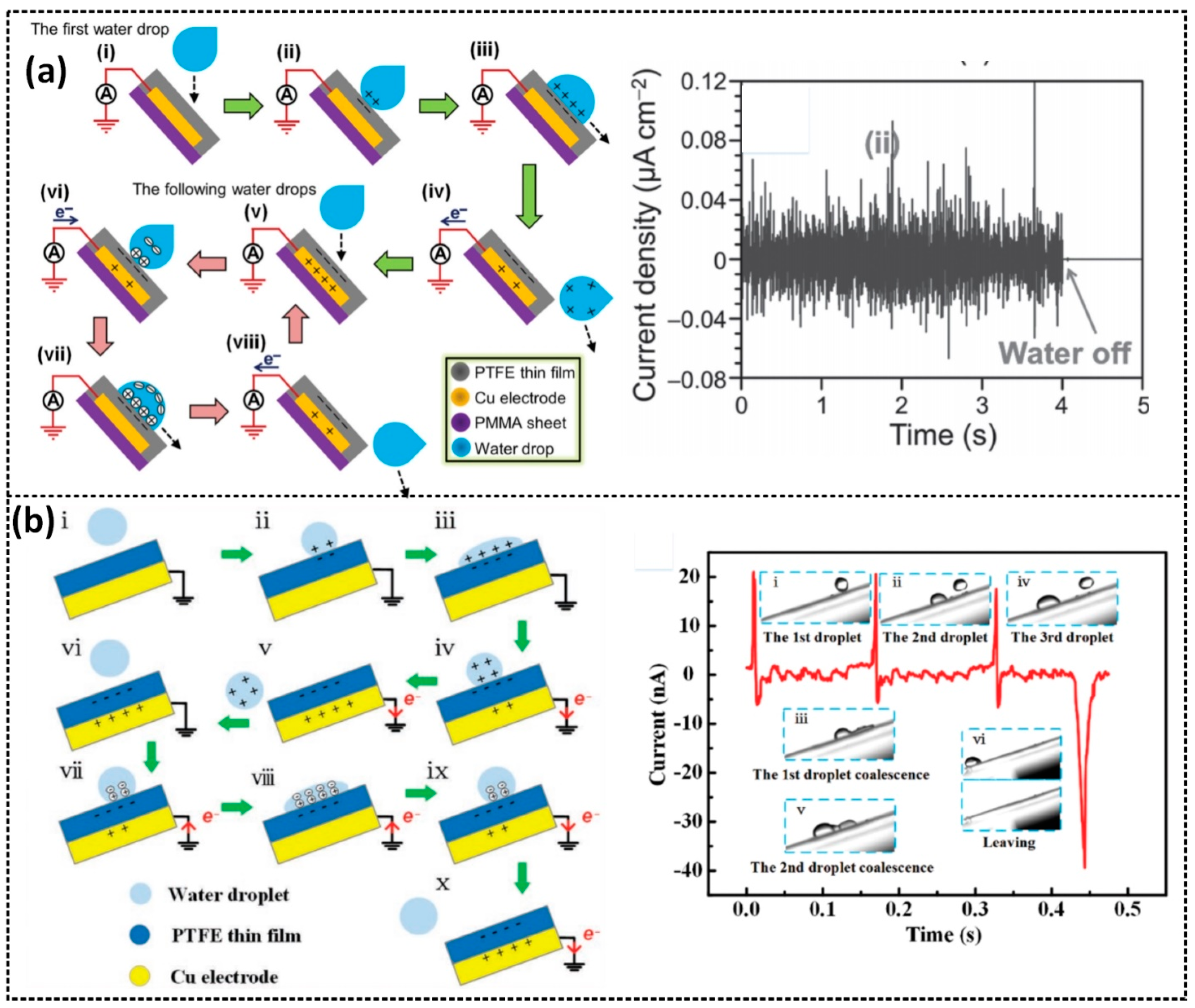
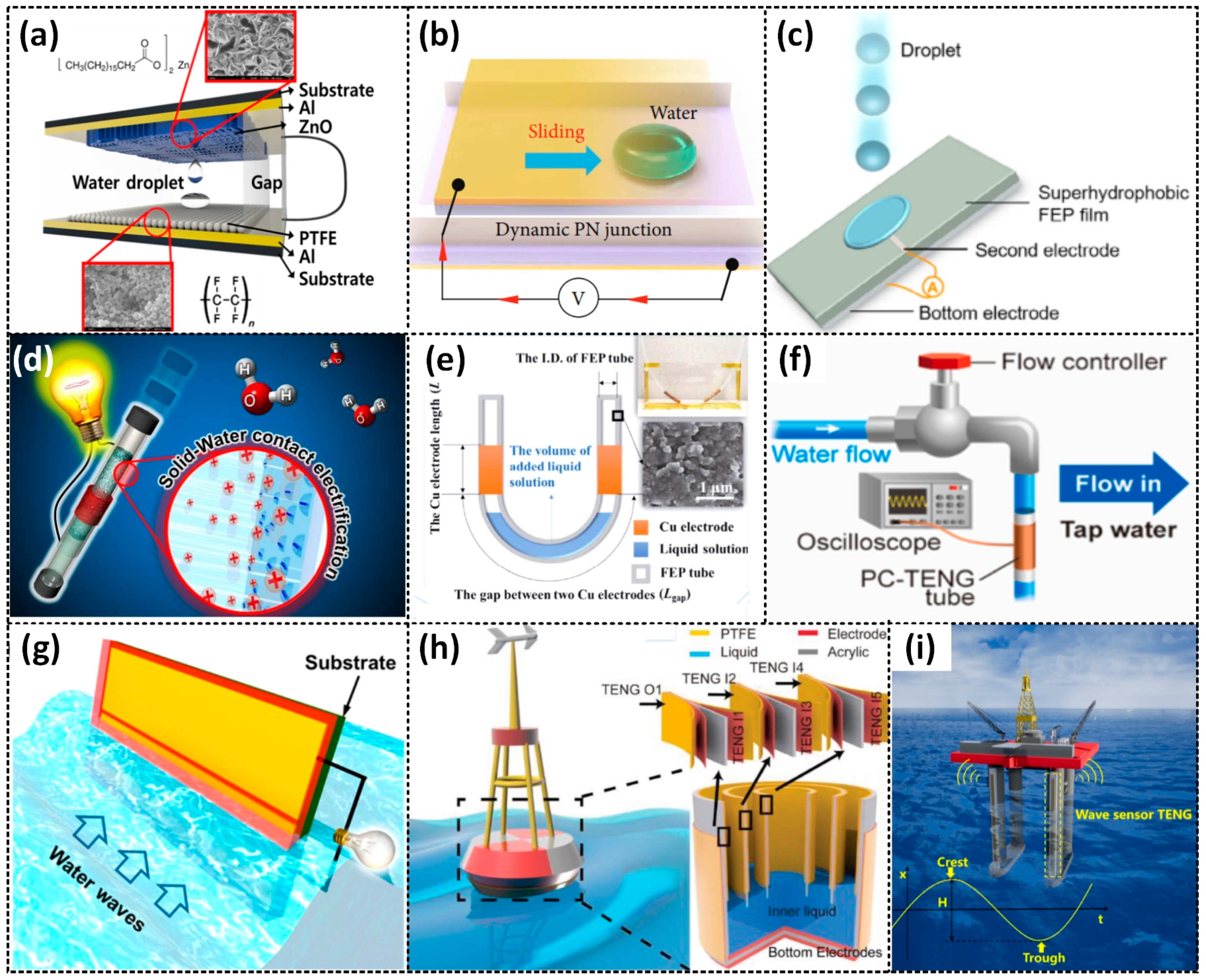
2.3.1. Droplet-Based L–S TENG
2.3.2. Flow-Based L–S TENG
2.3.3. Wave-Based L–S TENG
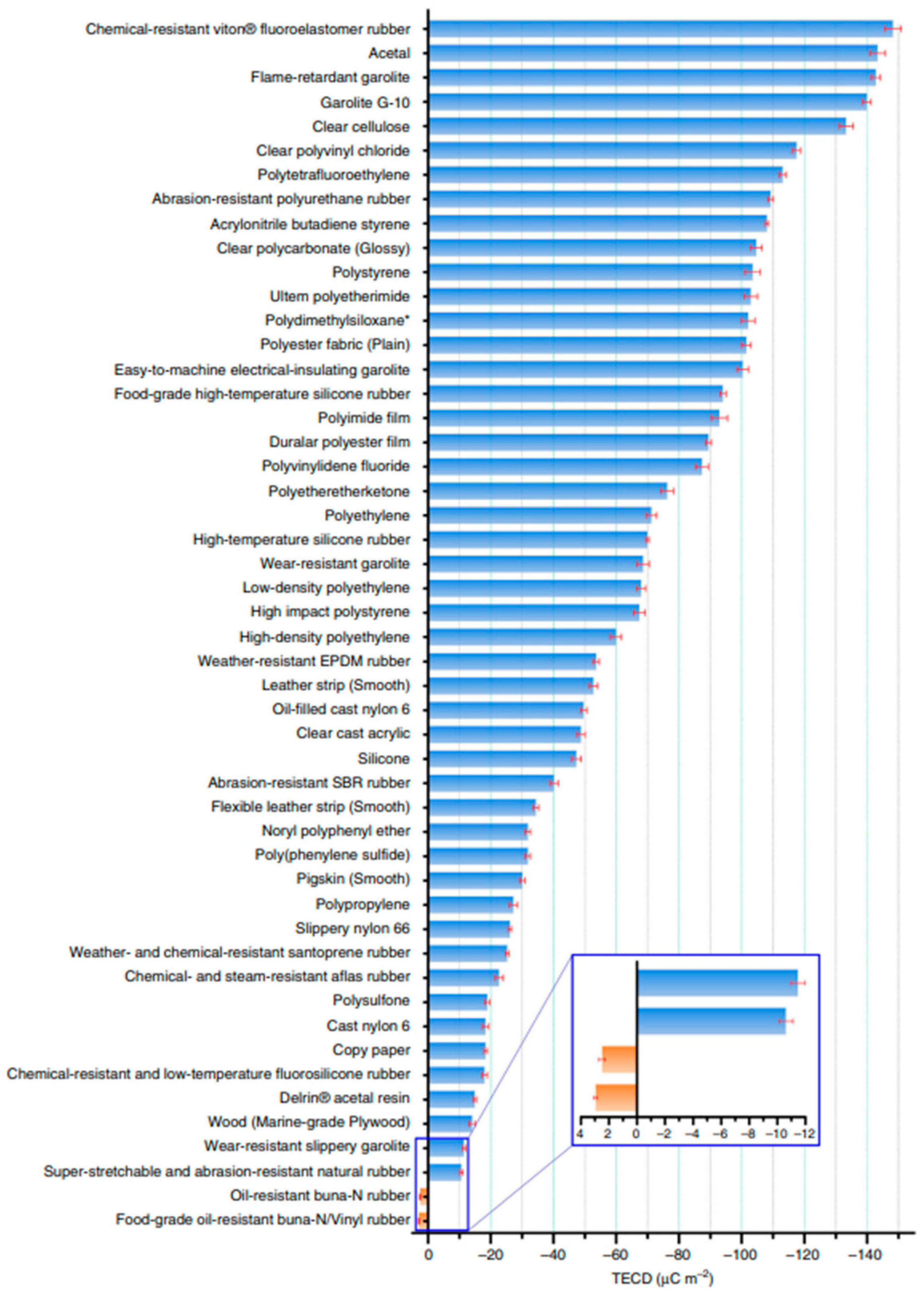
3. Affecting Parameter on L–S TENG Performance
4. L–S TENGs as Self-Powered Active Pressure/Touch Sensors
4.1. L–S TENGs as Self-Powered Physical Sensors
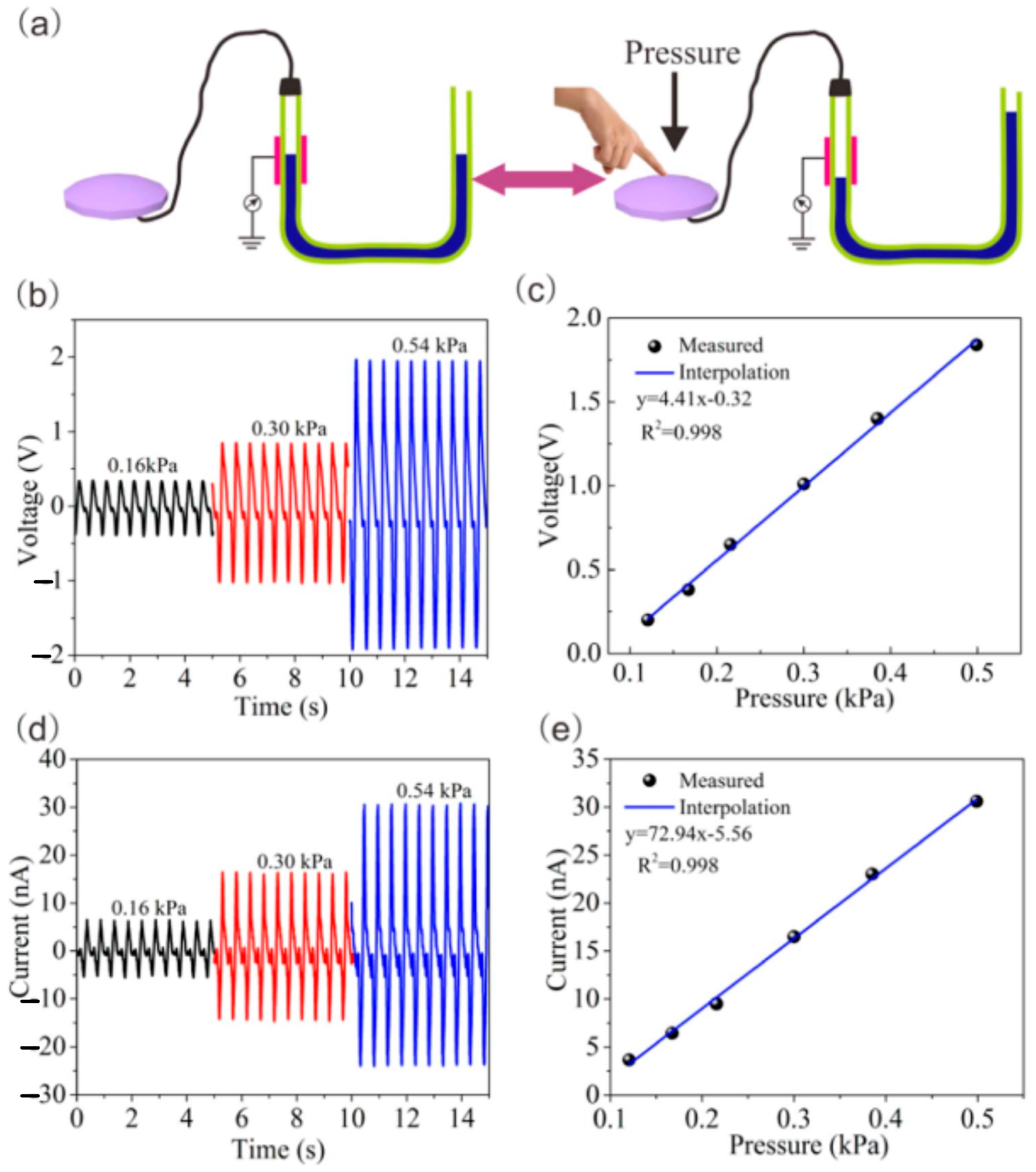
4.2. L–S TENGs as Self-Powered Pressure/Force Sensors
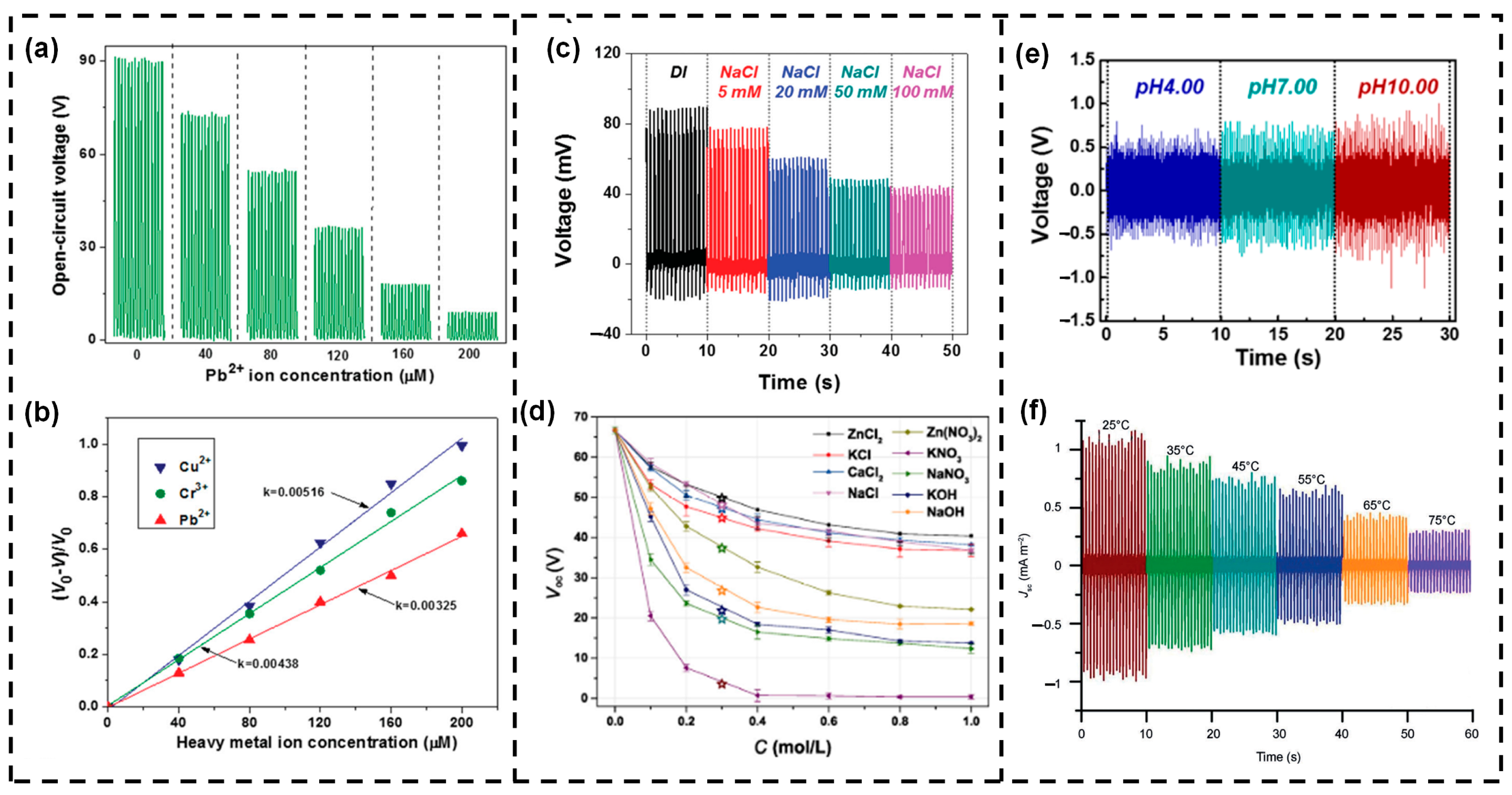
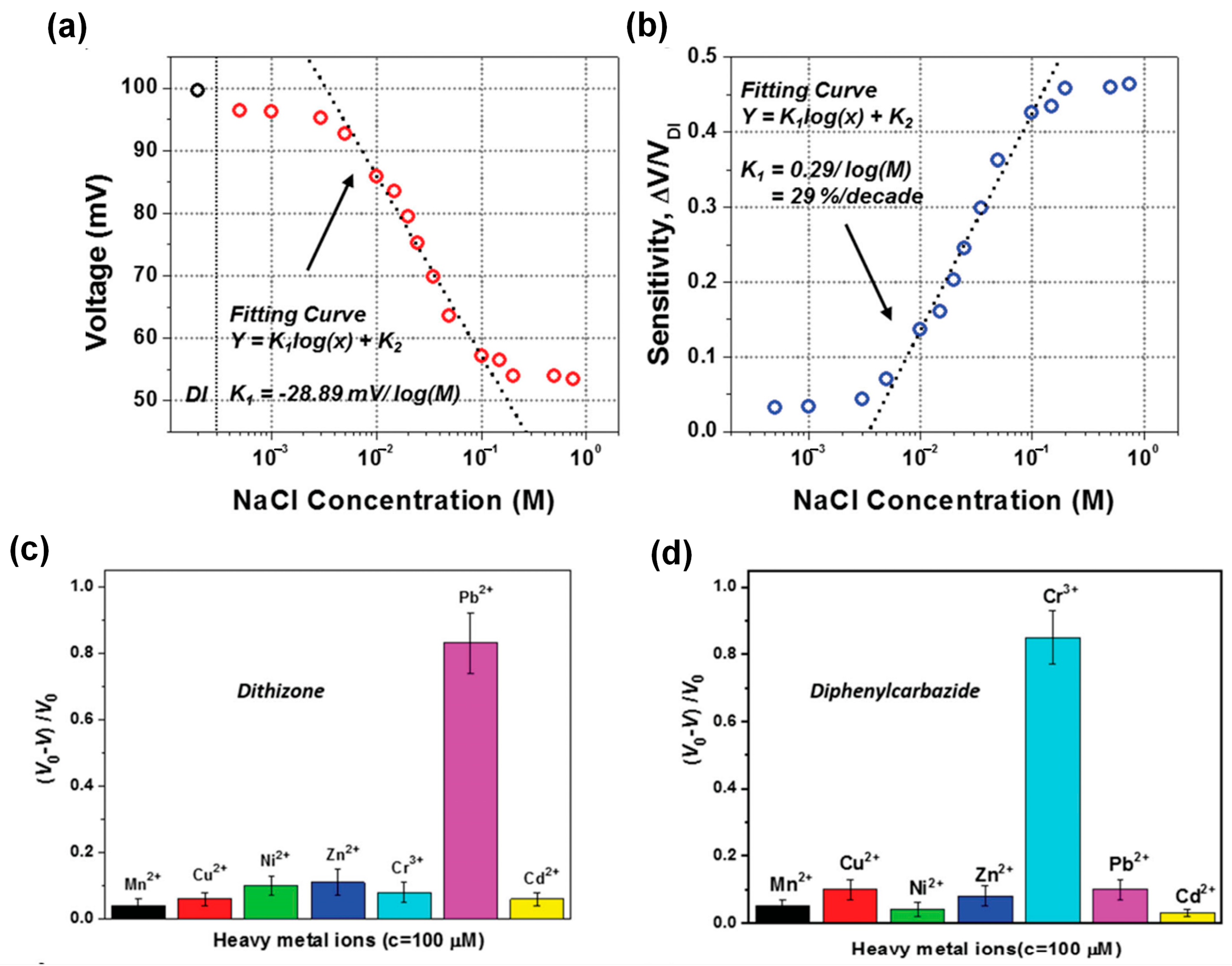
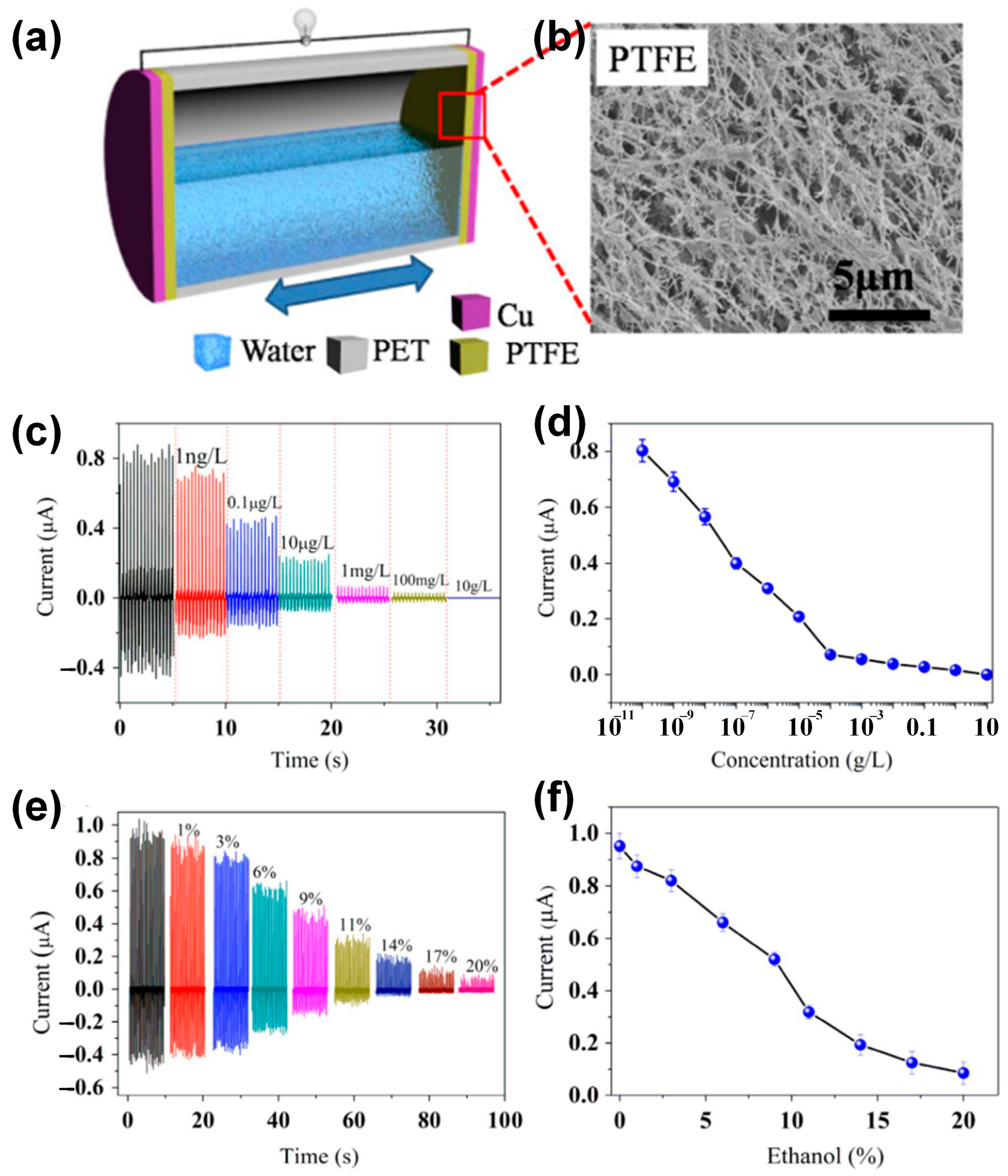
5. L–S TENGs as Self-Powered Chemical/Environment Sensors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, G.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W. Design and optimization of bio-inspired wave-like channel for a PEM fuel cell applying genetic algorithm. Energy 2020, 192, 116670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muetze, A.; Vining, J.G. Ocean Wave Energy Conversion—A Survey. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2006 IEEE Industry Applications Conference Forty-First IAS Annual Meeting 2006, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–12 October 2006; pp. 1410–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Sabzehgar, R.; Moallem, M. A review of ocean wave energy conversion systems. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Electrical Power & Energy Con-ference (EPEC) 2009, Montreal, QC, Canada, 22–23 October 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Tran, V.H.; Wang, J.; Fuh, Y.-K.; Lin, L. Direct-Write Piezoelectric Polymeric Nanogenerator with High Energy Conversion Efficiency. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Tang, W.; Han, C.; Fan, F.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Comparison, Equivalent Transformation, and Conjunction Operations of Electromagnetic Induction Generator and Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Mechanical Energy. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3580–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Song, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.L. Direct-Current Nanogenerator Driven by Ultrasonic Waves. Science 2007, 316, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Jun, L.L.; Simiao, C.; Zi, N.Y. Triboelectric Nanogenerators; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Xu, M.; Dong, M.; Guo, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.L. Water-solid triboelectric nanogenerators: An alternative means for har-vesting hydropower. Renew Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 115, 109366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Jiang, T.; Xu, L. Toward the blue energy dream by triboelectric nanogenerator networks. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Lin, Z.-H.; Jing, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.L. Integrated Multilayered Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Biomechanical Energy from Human Motions. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3713–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Chen, J.; Lin, L. Progress in triboelectric nanogenerators as a new energy technology and self-powered sensors. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2250–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chung, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S. Cylindrical water triboelectric nanogenerator via controlling geometrical shape of anodized aluminum for enhanced electrostatic induction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 25014–25018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Lin, Z.H.; Jing, Q.; Bai, P.; Pan, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Toward large-scale energy harvesting by a nanoparticle-enhanced triboe-lectric nanogenerator. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.H.; Cheng, G.; Lee, S.; Pradel, K.C.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting water drop energy by a sequential contact-electrification and elec-trostatic-induction process. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4690–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as flexible power sources. npj Flex. Electron. 2017, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheedarala, R.K.; Duy, L.C.; Ahn, K.K. Double characteristic BNO-SPI-TENGs for robust contact electrification by vertical contact separation mode through ion and electron charge transfer. Nano Energy 2018, 44, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; He, T.; Lee, C. More than energy harvesting–Combining triboelectric nanogenerator and flexible electronics technology for enabling novel micro-/nano-systems. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 851–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Gao, R.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.-J.; Wang, Z.L. Liquid-FEP-based U-tube triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting water-wave energy. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4062–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F. Solid-liquid triboelectrification in smart U-tube for multifunctional sensors. Nano Energy 2017, 40, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, M.-L.; Jeon, S.-B.; Han, J.-W.; Choi, Y.-K. Ferrofluid-based triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid generator for sensitive and sus-tainable vibration energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2017, 31, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J.; Tian, J.J.; Kuang, S.Y.; Ouyang, H.; Yan, L.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, Z.; Zhu, G. Biocide-Free Antifouling on Insulating Surface by Wave-Driven Triboelectrification-Induced Potential Oscillation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 3, 1600187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.-L.; Ahn, K.-K. Triboelectric Enhancement of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane Using Magnetic Nanoparticle for Water-Based Energy Harvesting. Polymers 2022, 14, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.-D.; Vo, C.-P.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Vu, D.-L.; Ahn, K.K. Liquid-solid contact electrification based on discontinuous-conduction tribo-electric nanogenerator induced by radially symmetrical structure. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Jiang, T.; Fan, F.R.; Yu, A.F.; Zhang, C.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.L. Liquid-Metal Electrode for High-Performance Triboelectric Nano-generator at an Instantaneous Energy Conversion Efficiency of 70.6%. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3718–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J.; Zhu, G.; Fan, Y.J.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Charging at the Nanostructured Solid/Liquid Interface for Area-Scalable Wave Energy Conversion and Its Use in Corrosion Protection. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7671–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheedarala, R.K.; Shahriar, M.; Ahn, J.H.; Hwang, J.Y.; Ahn, K.K. Harvesting liquid stream energy from unsteady peristaltic flow induced pulsatile Flow-TENG (PF-TENG) using slipping polymeric surface inside elastomeric tubing. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 104017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as new energy technology and self-powered sensors–principles, problems and per-spectives. Faraday Discuss. 2014, 176, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.-H.; Park, J.; Kim, W.K.; Yang, Y.; Lee, E.; Han, C.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.S. An effective energy harvesting method from a natural water motion active transducer. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3279–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Lin, Z.-H.; Du, Z.-L.; Wang, Z.L. Simultaneously Harvesting Electrostatic and Mechanical Energies from Flowing Water by a Hybridized Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1932–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Y.; Xiang, S.; Tao, C.; Yang, S.; Fan, X. Self-Powered All-in-One Fluid Sensor Textile with Enhanced Triboelectric Effect on All-Immersed Dendritic Liquid–Solid Interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30819–30826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.-B.; Seol, M.-L.; Kim, D.; Park, S.-J.; Choi, Y.-K. Self-Powered Ion Concentration Sensor with Triboelectricity from Liquid-Solid Contact Electrification. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1600006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.L.; Ding, W.; Kien, P.T.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.L. A highly-sensitive wave sensor based on liquid-solid interfacing triboelectric nanogenerator for smart marine equipment. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Choi, D.; Kwon, J.-Y.; Choi, D. A self-powered triboelectric microfluidic system for liquid sensing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 14069–14076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.; Wang, X.; Niu, S.; Li, S.; Yin, Y.; Dai, K.; Zhang, G.; Lin, L.; Wen, Z.; Guo, H.; et al. A highly shape-adaptive, stretchable design based on conductive liquid for energy harvesting and self-powered biomechanical monitoring. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Self-powered ammonia nanosensor based on the integration of the gas sensor and triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2018, 49, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Hasan, D.; He, T.; Shi, Q.; Lee, C. Self-Powered Dual-Mode Amenity Sensor Based on the Water–Air Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10337–10346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators: Fundamental physics and potential applications. Friction 2020, 8, 481–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Wang, A.C. On the origin of contact-electrification. Mater. Today 2019, 30, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Contact Electrification at the Liquid–Solid Interface. Chem. Rev. 2021, 122, 5209–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Xu, L.; Wang, A.C.; Wang, Z.L. Quantifying electron-transfer in liquid-solid contact electrification and the formation of electric double-layer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Ren, Z.; Xu, L.; Lin, S.; Zhan, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Probing Contact-Electrification-Induced Electron and Ion Transfers at a Liq-uid-Solid Interface. Adv Mater. 2020, 32, e1905696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.-H.; Cheng, G.; Lin, L.; Lee, S.; Wang, Z.L. Water-Solid Surface Contact Electrification and its Use for Harvesting Liquid-Wave Energy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12545–12549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Kim, D.Y.; Yun, J.; Kim, B.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, D.; Lee, S. Direct-current triboelectric nanogenerator via water electrification and phase control. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.Y.; Khan, U.; Kim, S.-W. Water droplet-driven triboelectric nanogenerator with superhydrophobic surfaces. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chan, S.; Wang, L.; Daoud, W.A. Water tank triboelectric nanogenerator for efficient harvesting of water wave energy over a broad frequency range. Nano Energy 2018, 44, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Hwang, W. Theoretical study of micro/nano roughness effect on water-solid triboelectrification with experimental approach. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahian, S.A.; Cheedarala, R.K.; Ahn, K.K. A study of sustainable green current generated by the fluid-based triboelectric nano-generator (FluTENG) with a comparison of contact and sliding mode. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, D.; Rahman, Z.U.; Zhou, F. Liquid–solid contact triboelectrification and its use in self-powered na-nosensor for detecting organics in water. Nano Energy 2016, 30, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Hao, X.; Li, M.; He, B.; Sun, W.; Zhang, K.; Liao, L.; Pan, Y.; Huang, J.; Qin, A. A Multifunction Freestanding Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Low-Frequency Mechanical Sloshing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 54716–54724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Su, Y.; Bai, P.; Chen, J.; Jing, Q.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Water Wave Energy by Asymmetric Screening of Electrostatic Charges on a Nanostructured Hydrophobic Thin-Film Surface. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6031–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.J.; Kuang, S.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhu, G. Highly Adaptive Solid–Liquid Interfacing Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Diverse Water Wave Energy. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4280–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Kim, D.W.; Yoo, D.; Cha, K.J.; La, M.; Kim, D.S. Spontaneous occurrence of liquid-solid contact electrification in nature: Toward a robust triboelectric nanogenerator inspired by the natural lotus leaf. Nano Energy 2017, 36, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; La, M.; Cho, S.; Yun, Y.; Choi, J.H.; Ra, Y.; Park, S.J.; Choi, D. Monocharged electret based liquid-solid interacting triboelectric nanogenerator for its boosted electrical output performance. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kil Yun, B.; Soo Kim, H.; Joon Ko, Y.; Murillo, G.; Hoon Jung, J. Interdigital electrode based triboelectric nanogenerator for effective energy harvesting from water. Nano Energy 2017, 36, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Chung, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Moon, J.H.; Lee, S.; Cho, M.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S. Design and optimization of rotating triboelectric nanogenerator by water electrification and inertia. Nano Energy 2016, 27, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Xu, L.; Zhan, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.L. Dripping channel based liquid triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and sensing. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 10510–10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, D.; Liu, Z. Triboelectric nanogenerator based on a moving bubble in liquid for mechanical energy harvesting and water level monitoring. Nano Energy 2022, 95, 106998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shi, Q.; Ho, J.S.; Lee, C. Study of thin film blue energy harvester based on triboelectric nanogenerator and seashore IoT applications. Nano Energy 2019, 66, 104167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.; Park, S.-C.; Lee, S.; Sim, J.-Y.; Song, I.; Choi, D.; Lim, H.; Kim, D.S. Biomimetic anti-reflective triboelectric nanogenerator for concurrent harvesting of solar and raindrop energies. Nano Energy 2018, 57, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ma, T. Triboelectricity-based self-charging droplet capacitor for harvesting low-level ambient energy. Nano Energy 2020, 74, 104795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Lee, S.; Park, S.M.; Cho, H.; Hwang, W.; Kim, D.S. Energy harvesting model of moving water inside a tubular system and its application of a stick-type compact triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 2481–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhou, X.; Feng, S.; Xu, C.; Zheng, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, K.; et al. Polarized Water Driven Dynamic PN Junction-Based Direct-Current Generator. Research 2021, 2021, 7505638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Zheng, M.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator as a Probe for Measuring the Charge Transfer between Liquid and Solid Surfaces. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 14830–14837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Pan, C.; Wang, Z.L. Networks of High Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Liq-uid-Solid Interface Contact Electrification for Harvesting Low-Frequency Blue Energy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1800705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Z. Robust Working Mechanism of Water Droplet-Driven Triboelectric Nanogenerator: Triboelectric Output versus Dynamic Motion of Water Droplet. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1901547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.T.; Vo, C.P.; Nguyen, T.H.; Ahn, K.K. A Direct-Current Triboelectric Nanogenerator Energy Harvesting System Based on Water Electrification for Self-Powered Electronics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, W.; Jin, Y.; Gao, S.; Yang, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z. Harvesting energy from high-frequency impinging water droplets by a droplet-based electricity generator. Ecomat 2021, 3, e12116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helseth, L. Electrical energy harvesting from water droplets passing a hydrophobic polymer with a metal film on its back side. J. Electrost. 2016, 81, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-Y.; Kim, H.K.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Shin, D.-M. Water-Through Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Ti-Mesh for Harvesting Liquid Flow. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2018, 72, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Chung, J.; Shin, G.; Sim, J.-Y.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, S.; Hwang, W. Toward sustainable output generation of liquid–solid contact triboelectric nanogenerators: The role of hierarchical structures. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Cao, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.L.; Yin, F. A droplet-based electricity generator for large-scale raindrop energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2022, 100, 107443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munirathinam, K.; Kim, D.-S.; Shanmugasundaram, A.; Park, J.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Lee, D.-W. Flowing water-based tubular triboelectric nanogenerators for sustainable green energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2022, 102, 107675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.S.; Lin, S.; Lee, J.H.; Ryu, H.; Kim, T.Y.; Zhong, H.; Chen, H.; Kim, S.-W. Triboelectrification-Induced Large Electric Power Generation from a Single Moving Droplet on Graphene/Polytetrafluoroethylene. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7297–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Feng, S.; Lu, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhang, P.; Yu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, K.; et al. Direct Current Electricity Generation from Dynamic Polarized Water–Semiconductor Interface. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 14180–14187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xu, C.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, H.; Liu, H.; Xu, G.; Wang, G.; Zhou, G.; Zeng, Q.; et al. A high voltage direct current droplet-based electricity generator inspired by thunderbolts. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helseth, L. A water droplet-powered sensor based on charge transfer to a flow-through front surface electrode. Nano Energy 2020, 73, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ning, X.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Yin, J.; Guo, W. Performance and power management of droplets-based electricity generators. Nano Energy 2022, 92, 106705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijewardhana, K.R.; Shen, T.-Z.; Jayaweera, E.; Shahzad, A.; Song, J.-K. Hybrid nanogenerator and enhancement of water–solid contact electrification using triboelectric charge supplier. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Song, Y.; Deng, X.; Leung, M.; Yang, Z.; Xu, R.X.; et al. A droplet-based electricity generator with high instantaneous power density. Nature 2020, 578, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Zheng, Y.; Li, T.; Feng, M.; Cui, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, D. Liquid-solid triboelectric nanogenerators array and its applications for wave energy harvesting and self-powered cathodic protection. Energy 2021, 217, 119388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F. Water-solid triboelectrification with self-repairable surfaces for water-flow energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2019, 61, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Duan, J.; Zhao, Y.; He, B.; Tang, Q. Generators to harvest ocean wave energy through electrokinetic principle. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Xie, Y.; Luo, N.; Feng, Y.; Wang, N.; Feng, M.; et al. Gas-liquid two-phase flow-based triboelectric nanogenerator with ultrahigh output power. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eadd0464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, D.L.; Le, C.D.; Ahn, K.K. Functionalized graphene oxide/polyvinylidene fluoride composite membrane acting as a triboelectric layer for hydropower energy harvesting. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 9549–9559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.L.; Ahn, K.K. High-Performance Liquid-Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Polyvinylidene Fluoride and Magnetic Nanoparticle Composites Film. In Proceedings of the 2021 24th International Conference on Mechatronics Technology (ICMT), Singapore, 18–22 December 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.L.; Le, C.D.; Vo, C.P.; Ahn, K.K. Surface polarity tuning through epitaxial growth on polyvinylidene fluoride membranes for enhanced performance of liquid-solid triboelectric nanogenerator. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 223, 109135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helseth, L.E.; Guo, X.D. Contact Electrification and Energy Harvesting Using Periodically Contacted and Squeezed Water Droplets. Langmuir 2015, 31, 3269–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.-H.; Cheng, G.; Wu, W.; Pradel, K.C.; Wang, Z.L. Dual-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Water Energy and as a Self-Powered Ethanol Nanosensor. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6440–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardeen, J. Electrical Conductivity of Metals. J. Appl. Phys. 1940, 11, 88–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Park, J.; Kwon, S.-H.; Kim, Y.S. Fluidic Active Transducer for Electricity Generation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Chen, H.; Su, Z.; Chen, X.; Miao, L.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, H. Highly Compressible Integrated Supercapacitor-Piezoresistance-Sensor System with CNT-PDMS Sponge for Health Monitoring. Small 2017, 13, 1702091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Lee, J.; Hyeon, T.; Lee, M.; Kim, D.-H. Fabric-Based Integrated Energy Devices for Wearable Activity Monitors. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6329–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Shao, H.; Jiang, L.; Qu, L. Self-powered wearable graphene fiber for information expression. Nano Energy 2017, 32, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Tong, K.; Pei, Q. A Water-Based Silver-Nanowire Screen-Print Ink for the Fabrication of Stretchable Conductors and Wearable Thin-Film Transistors. Adv Mater. 2016, 28, 5986–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Pei, Z.; Xue, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhi, C. Nanostructured Polypyrrole as a flexible electrode material of superca-pacitor. Nano Energy 2016, 22, 422–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Dai, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, A.C.; Xu, C.; et al. Quantifying the triboelectric series. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Niu, S.; Lin, L.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Y.S.; Wang, Z.L. Maximum Surface Charge Density for Triboelectric Nanogenerators Achieved by Ionized-Air Injection: Methodology and Theoretical Understanding. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6720–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.-G.; Jiang, S.-Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, N.-Y.; Ding, J.-N.; Zhang, W. Effect of argon plasma treatment on the output performance of triboelectric nanogenerator. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 412, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Deng, W.; Jin, L.; Chun, F.; Pan, H.; Gu, B.; Zhang, H.; Lv, Z.; Yang, W.; et al. Self-Powered Acceleration Sensor Based on Liquid Metal Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Vibration Monitoring. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7440–7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, N.; Wen, Z.; Cheng, P.; Zheng, H.; Shao, H.; Xia, Y.; Chen, C.; Lan, H.; Xie, X.; et al. Liquid-Metal-Based Super-Stretchable and Structure-Designable Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Wearable Electronics. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helseth, L.E.; Guo, X.D. Hydrophobic polymer covered by a grating electrode for converting the mechanical energy of water droplets into electrical energy. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 045007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Studying the droplet sliding velocity and charge transfer at a liquid–solid in-terface. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 5696–5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Jiang, T.; Liu, G.; Xiao, T.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Xi, F.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Networks Integrated with Power Management Module for Water Wave Energy Harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.; Xie, X.; Wen, Z.; Zheng, H.; Lan, H.; Shao, H.; Sun, X.; Zhong, J.; Lee, S.-T. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Driven Self-Powered Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting Based on Hematite Photoanodes. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 8625–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Guo, H.; Fan, X.; Wen, Z.; Yeh, M.-H.; Yu, C.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectrification-Enabled Self-Powered Detection and Removal of Heavy Metal Ions in Wastewater. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2983–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Ren, Z.; Shao, J.; Deng, C.; Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Microfluidic Transport System Based on Triboelectric Nano-generator and Electrowetting Technique. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, C.P.; Shahriar, M.; Le, C.D.; Ahn, K.K. Mechanically Active Transducing Element Based on Solid–Liquid Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Self-Powered Sensing. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 6, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, G.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Mei, J.; Appleton, A.L.; Kim, D.H.; Wang, H.; Bao, Z. Flexible polymer transistors with high pressure sensitivity for application in electronic skin and health monitoring. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Hwang, D.; Yu, Z.; Takei, K.; Park, J.; Chen, T.; Ma, B.; Javey, A. User-interactive electronic skin for instantaneous pressure visu-alization. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Someya, T.; Sekitani, T.; Iba, S.; Kato, Y.; Kawaguchi, H.; Sakurai, T. A large-area, flexible pressure sensor matrix with organic field-effect transistors for artificial skin applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9966–9970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Lee, C. Self-powered liquid triboelectric microfluidic sensor for pressure sensing and finger motion monitoring applications. Nano Energy 2016, 30, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Lee, C. Using Water as A Self-Generated Triboelectric Sensor for Pressure and Flow Rate Measurement. In Proceedings of the Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 April 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wan, D.; Fang, R.; Yuan, Z.; Zhuo, K.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H. Water-based triboelectric nanogenerator for wireless energy trans-mission and self-powered communication via a solid-liquid-solid interaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 605, 154765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Luo, H.; Gao, D.; Zhou, X.; Cui, P.; Thangavel, G.; Parida, K.; Lee, P.S. Self-restoring, waterproof, tunable microstructural shape memory triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered water temperature sensor. Nano Energy 2019, 61, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, M.; Ma, Z.; Ouyang, H.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Niu, H.; Pan, X.; Xu, M.; Li, Z.; et al. Self-Powered Distributed Water Level Sensors Based on Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Ship Draft Detecting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, D.; Yu, X.; Cheng, T.; Bao, G.; Wang, Z.L. Flow and level sensing by waveform coupled liquid-solid con-tact-electrification. Mater. Today Phys. 2021, 18, 100372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadegh, B.; Polygerinos, P.; Keplinger, C.; Wennstedt, S.; Shepherd, R.F.; Gupta, U.; Shim, J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Pneumatic Networks for Soft Robotics that Actuate Rapidly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriar, M.; Vo, C.P.; Ahn, K.K. Self-powered flexible PDMS channel assisted discrete liquid column motion based triboe-lectric nanogenerator (DLC-TENG) as mechanical transducer. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2019, 6, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yeh, M.H.; Lin, Z.H.; Guo, H.; Yang, P.K.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Yu, R.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Triboelectric Nanosensor for Microfluidics and Cavi-ty-Confined Solution Chemistry. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11056–11063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, C.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wong, C.P.; Bando, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator as self-powered active sensors for detecting liquid/gaseous water/ethanol. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, P.; Sun, K.; Wang, C.; Diao, D. Intelligently detecting and identifying liquids leakage combining triboelectric nanogenerator based self-powered sensor with machine learning. Nano Energy 2019, 56, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Tsao, Y.-H.; Chiu, C.-M.; Yoo, D.; Lin, Z.-H.; Kim, D.S. A smart pipet tip: Triboelectricity and thermoelectricity assisted in situ evaluation of electrolyte concentration. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, S.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Array as a Probe for In Situ Dynamic Mapping of Interface Charge Transfer at a Liquid–Solid Contacting. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 1646–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, F.; Wang, A.C.; Xu, L.; Lin, S.; Shao, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Electron Transfer as a Liquid Droplet Contacting a Polymer Surface. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 17565–17573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Zhang, L.; Guo, H.; Chen, C.; Wu, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.L. Signal Output of Triboelectric Nanogenerator at Oil–Water–Solid Multiphase Interfaces and its Application for Dual-Signal Chemical Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1902793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, Q.T.; Vu, D.L.; Le, C.D.; Ahn, K.K. Recent Progress in Self-Powered Sensors Based on Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Sensors 2023, 23, 5888. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135888
Nguyen QT, Vu DL, Le CD, Ahn KK. Recent Progress in Self-Powered Sensors Based on Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Sensors. 2023; 23(13):5888. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135888
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Quang Tan, Duy Linh Vu, Chau Duy Le, and Kyoung Kwan Ahn. 2023. "Recent Progress in Self-Powered Sensors Based on Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerators" Sensors 23, no. 13: 5888. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135888
APA StyleNguyen, Q. T., Vu, D. L., Le, C. D., & Ahn, K. K. (2023). Recent Progress in Self-Powered Sensors Based on Liquid–Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Sensors, 23(13), 5888. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23135888







