Forward and Backward Walking: Multifactorial Characterization of Gait Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Procedures
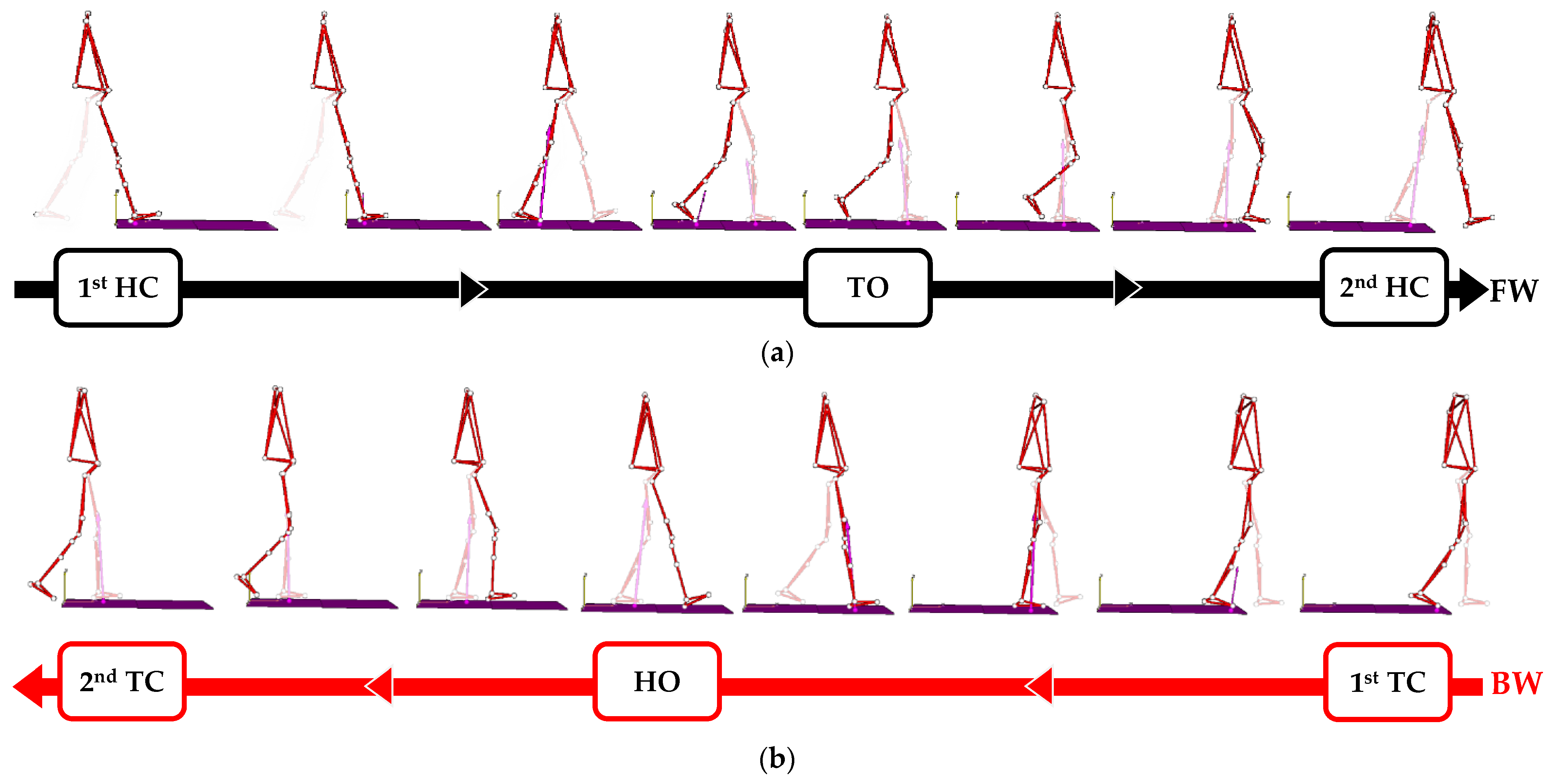
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Spatial–Temporal Parameters
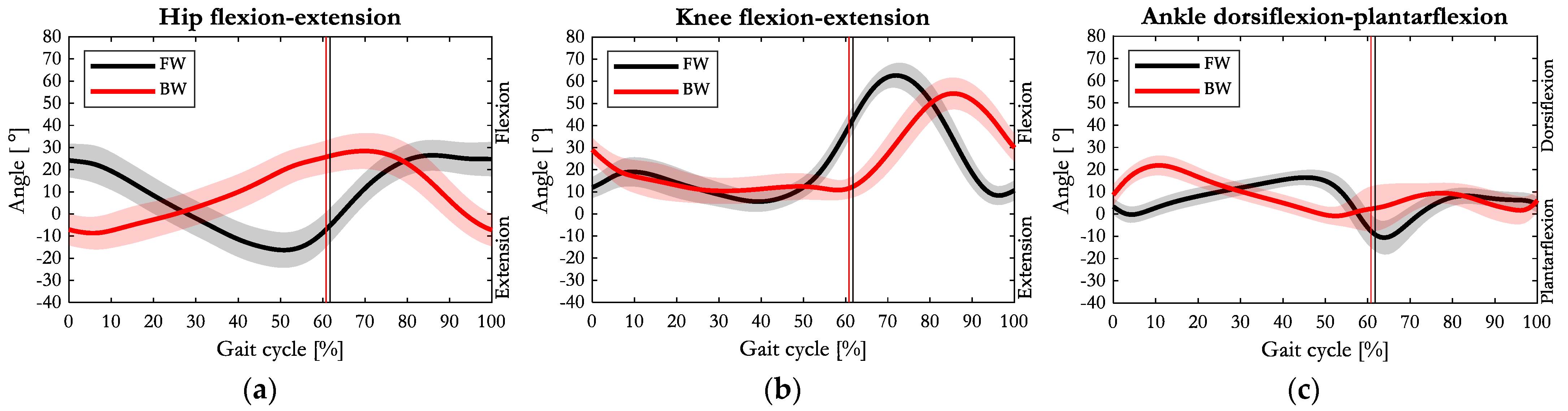
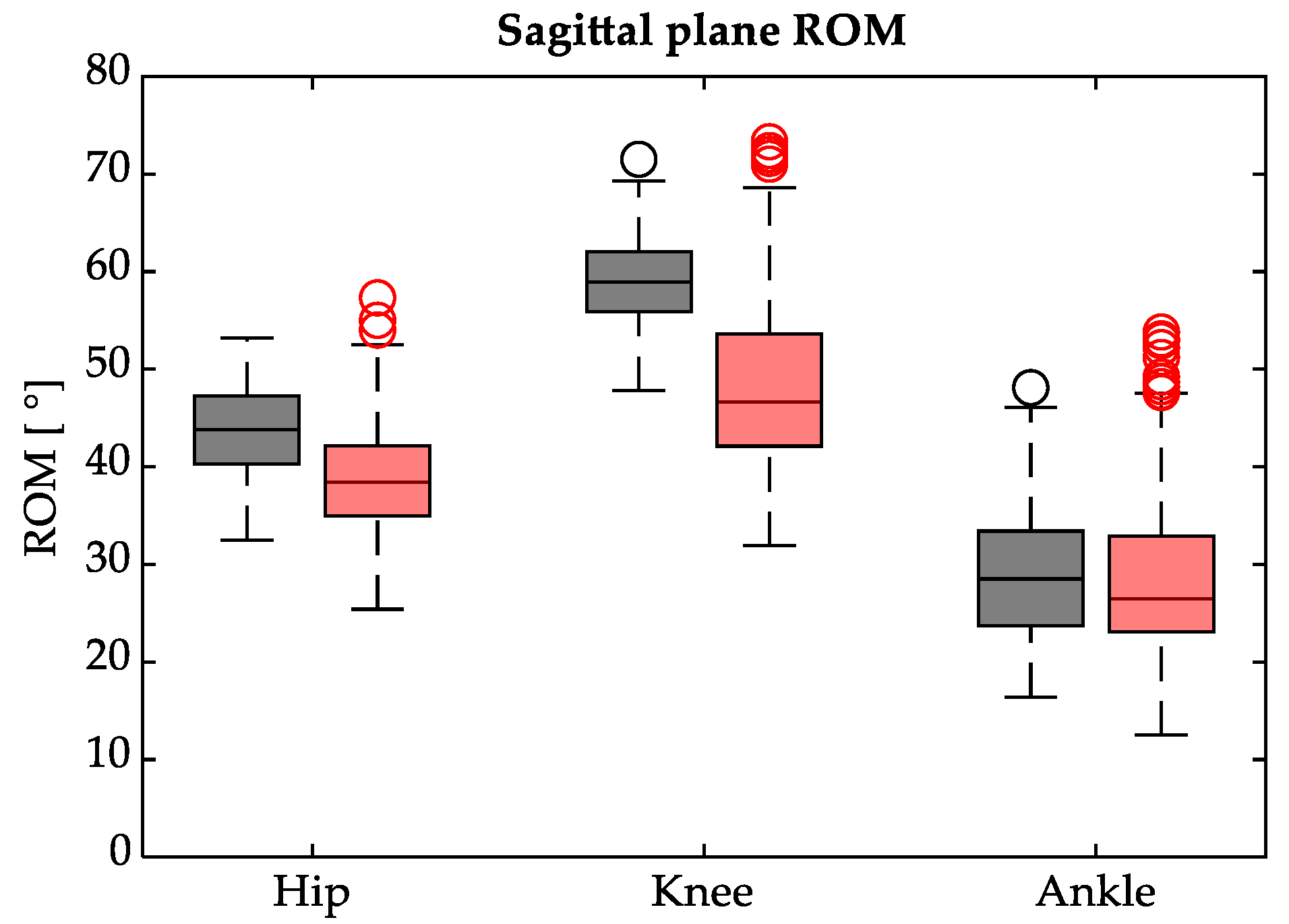
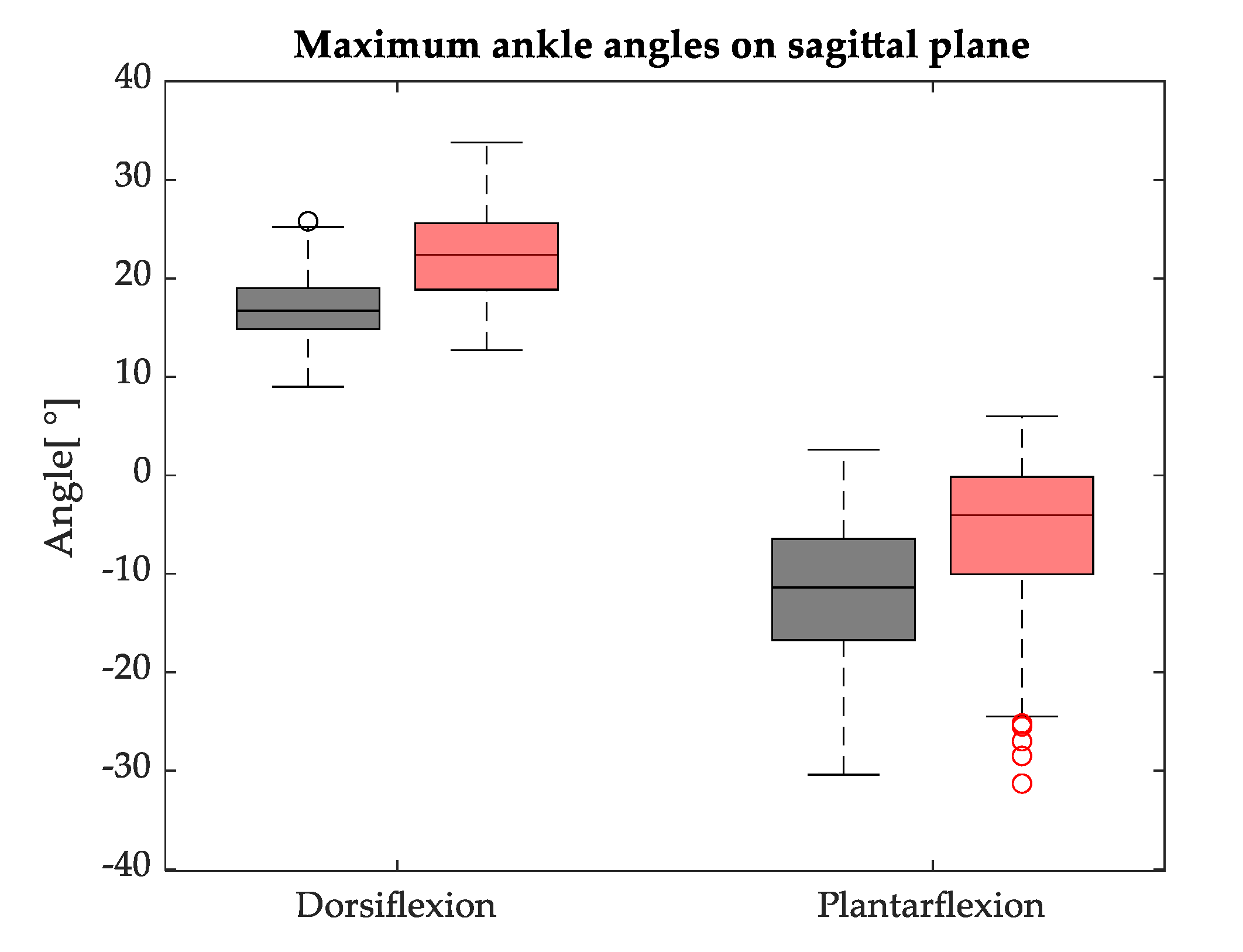
3.2. Kinematics
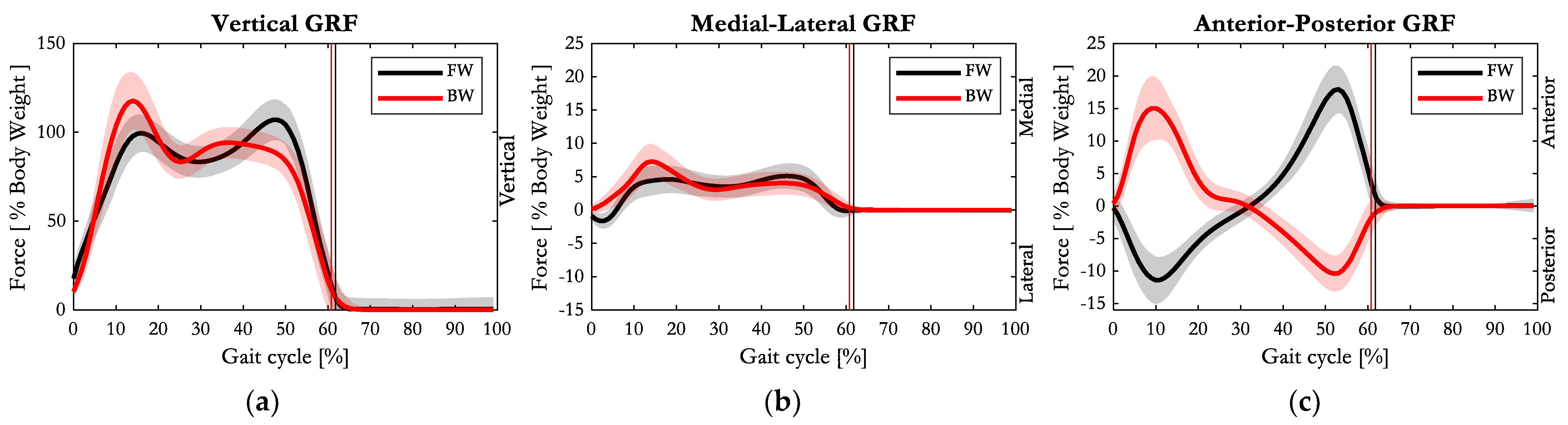
3.3. Kinetics
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial–Temporal Parameters
4.2. Kinematics
4.3. Kinetics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDonald, K.A.; Cusumano, J.P.; Hieronymi, A.; Rubenson, J. Humans Trade off Whole-Body Energy Cost to Avoid Overburdening Muscles While Walking. Proc. R. Soc. B 2022, 289, 20221189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capodaglio, P.; Gobbi, M.; Donno, L.; Fumagalli, A.; Buratto, C.; Galli, M.; Cimolin, V. Effect of Obesity on Knee and Ankle Biomechanics during Walking. Sensors 2021, 21, 7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muro-de-la-Herran, A.; Garcia-Zapirain, B.; Mendez-Zorrilla, A. Gait Analysis Methods: An Overview of Wearable and Non-Wearable Systems, Highlighting Clinical Applications. Sensors 2014, 14, 3362–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridao-Fernández, C.; Pinero-Pinto, E.; Chamorro-Moriana, G. Observational Gait Assessment Scales in Patients with Walking Disorders: Systematic Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2085039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pilar Duque Orozco, M.; Abousamra, O.; Church, C.; Lennon, N.; Henley, J.; Rogers, K.J.; Sees, J.P.; Connor, J.; Miller, F. Reliability and Validity of Edinburgh Visual Gait Score as an Evaluation Tool for Children with Cerebral Palsy. Gait Posture 2016, 49, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.; Bartlett, D. Gross Motor Function Classification System: Impact and Utility. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2003, 46, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinetti, M.E. Performance-Oriented Assessment of Mobility Problems in Elderly Patients. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1986, 34, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, E.V.; Hukuda, M.E.; Escorcio, R.; Voos, M.C.; Caromano, F.A. Development and Reliability of the Functional Evaluation Scale for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, Gait Domain: A Pilot Study: The Functional Evaluation Scale for DMD. Physiother. Res. Int. 2015, 20, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, C.; Poewe, W.; Rascol, O.; Sampaio, C.; Stebbins, G.T. The Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS): Status and Recommendations. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 738–750. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, M.; Jankovic, J.; Suteerawattananon, M.; Wankadia, S.; Caroline, K.S.; Vuong, K.D.; Protas, E. Clinical Gait and Balance Scale (GABS): Validation and Utilization. J. Neurol. Sci. 2004, 217, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donno, L.; Sansone, V.; Galluzzo, A.; Frigo, C.A. Walking in the Absence of Anterior Cruciate Ligament: The Role of the Quadriceps and Hamstrings. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtaruzzaman; Shafie, A.A.; Khan, R. Gait analysis: Systems, technologies, and importance. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2016, 16, 1630003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milane, T.; Hansen, C.; Chardon, M.; Bianchini, E.; Vuillerme, N. Comparing Backward Walking Performance in Parkinson’s Disease with and without Freezing of Gait—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, D.-I. Association of Regular Walking and Body Mass Index on Metabolic Syndrome among an Elderly Korean Population. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 106, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, G.A.; Kelley, K.S.; Tran, Z.V. Walking and Resting Blood Pressure in Adults: A Meta-Analysis. Prev. Med. 2001, 33, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deslandes, A.; Moraes, H.; Ferreira, C.; Veiga, H.; Silveira, H.; Mouta, R.; Pompeu, F.A.M.S.; Coutinho, E.S.F.; Laks, J. Exercise and Mental Health: Many Reasons to Move. Neuropsychobiology 2009, 59, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, J.; Aspinall, P. The Restorative Benefits of Walking in Urban and Rural Settings in Adults with Good and Poor Mental Health. Health Place 2011, 17, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Kim, J.; Son, J.; Kim, Y. Kinematic and Kinetic Analysis during Forward and Backward Walking. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Pang, J.; Lu, J.; Kang, M.; Chen, B.; Jones, R.K.; Zhan, H.; Liu, A. The Immediate Effect of Backward Walking on External Knee Adduction Moment in Healthy Individuals. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 4232990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, J.; An, R. Effectiveness of Backward Walking Training on Balance Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gait Posture 2019, 68, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, G.S.; Taylor, Z. Complexity, Symmetry and Variability of Forward and Backward Walking at Different Speeds and Transfer Effects on Forward Walking: Implications for Neural Control. J. Biomech. 2019, 97, 109377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, W.; An, R. Effectiveness of Backward Walking Training on Spatial–temporal Gait Characteristics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2018, 60, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMark, L.A.; Fox, E.J.; Manes, M.R.; Conroy, C.; Rose, D.K. The 3-Meter Backward Walk Test (3MBWT): Reliability and Validity in Individuals with Subacute and Chronic Stroke. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2022, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, D.A.; Pluck, N.; Yang, J.F. Backward Walking: A Simple Reversal of Forward Walking? J. Mot. Behav. 1989, 21, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Deursen, R.W.M.; Flynn, T.W.; McCrory, J.L.; Morag, E. Does a Single Control Mechanism Exist for Both Forward and Backward Walking? Gait Posture 1998, 7, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimunová, M.; Bozděch, M.; Skotáková, A.; Grün, V.; Válková, H. Comparison of Forward and Backward Gait in Males with and without Intellectual Disabilities. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2021, 65, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.B.; Õunpuu, S.; Tyburski, D.; Gage, J.R. A Gait Analysis Data Collection and Reduction Technique. Hum. Mov. Sci. 1991, 10, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, T.; Weisberger, A.; Ray, J.; Hasan, S.; Shiavi, R.; Spengler, D. Relationship between Vertical Ground Reaction Force and Speed during Walking, Slow Jogging, and Running. Clin. Biomech. 1996, 11, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Participants | Age [years] | Body Height [m] | Body Mass [kg] | BMI [kg/m2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 Females | 26.03 ± 1.96 | 1.66 ± 0.04 | 56.51 ± 9.06 | 20.49 ± 3.27 |
| 12 Males | 26.23 ± 2.19 | 1.80 ± 0.05 | 73.25 ± 5.96 | 22.54 ± 1.14 |
| Sample | 26.13 ± 2.03 | 1.73 ± 0.08 | 64.88 ± 11.37 | 21.52 ± 2.61 |
| FW | BW | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 1st Q | 3rd Q | Median | 1st Q | 3rd Q | ||
| Average speed | [m/s] | 1.1 | 1 | 1.2 | 0.8 * | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| Normalised Average speed | [% height/s] | 62.45 | 58.89 | 67.81 | 49.14 * | 44.4 | 52.7 |
| Stance phase | [% gait cycle] | 61.75 | 60.69 | 62.92 | 60.77 * | 59.52 | 62.76 |
| Swing phase | [% gait cycle] | 38.25 | 37.08 | 39.3 | 39.22 * | 37.23 | 40.48 |
| Double support phase | [% gait cycle] | 11.76 | 10.62 | 12.82 | 10.86 * | 9.58 | 12.68 |
| Stride length | [m] | 1.25 | 1.19 | 1.31 | 1.12 * | 1.06 | 1.19 |
| Normalised Stride length | [% height] | 72.43 | 68.94 | 75.43 | 65.35 * | 61.16 | 68.96 |
| Step length | [m] | 0.62 | 0.59 | 0.66 | 0.56 * | 0.52 | 0.6 |
| Step width | [m] | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.14 * | 0.11 | 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Donno, L.; Monoli, C.; Frigo, C.A.; Galli, M. Forward and Backward Walking: Multifactorial Characterization of Gait Parameters. Sensors 2023, 23, 4671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104671
Donno L, Monoli C, Frigo CA, Galli M. Forward and Backward Walking: Multifactorial Characterization of Gait Parameters. Sensors. 2023; 23(10):4671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104671
Chicago/Turabian StyleDonno, Lucia, Cecilia Monoli, Carlo Albino Frigo, and Manuela Galli. 2023. "Forward and Backward Walking: Multifactorial Characterization of Gait Parameters" Sensors 23, no. 10: 4671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104671
APA StyleDonno, L., Monoli, C., Frigo, C. A., & Galli, M. (2023). Forward and Backward Walking: Multifactorial Characterization of Gait Parameters. Sensors, 23(10), 4671. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104671









