Balance Assessment Using a Smartwatch Inertial Measurement Unit with Principal Component Analysis for Anatomical Calibration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Recruitment
2.2. Balance Experiment
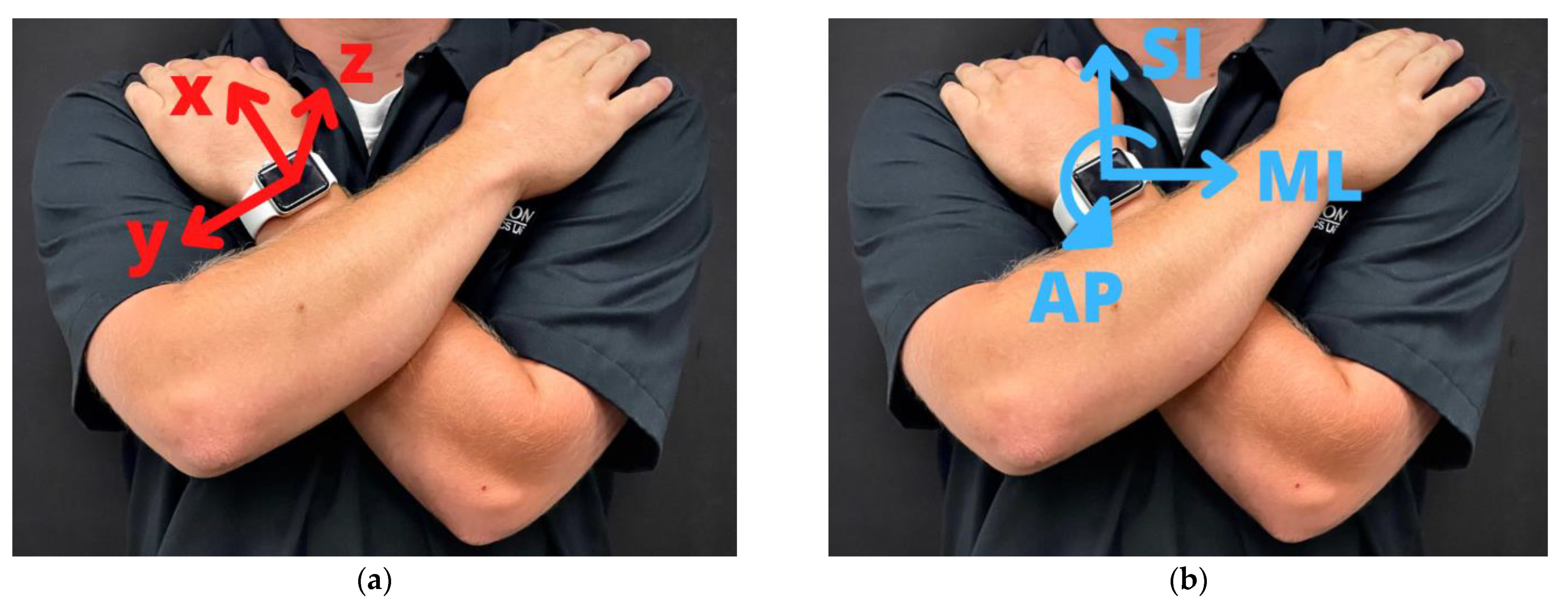
2.3. Hardware Devices and Data Acquisition Software
2.4. Calibration Algorithm
2.4.1. Gravity Target Vector
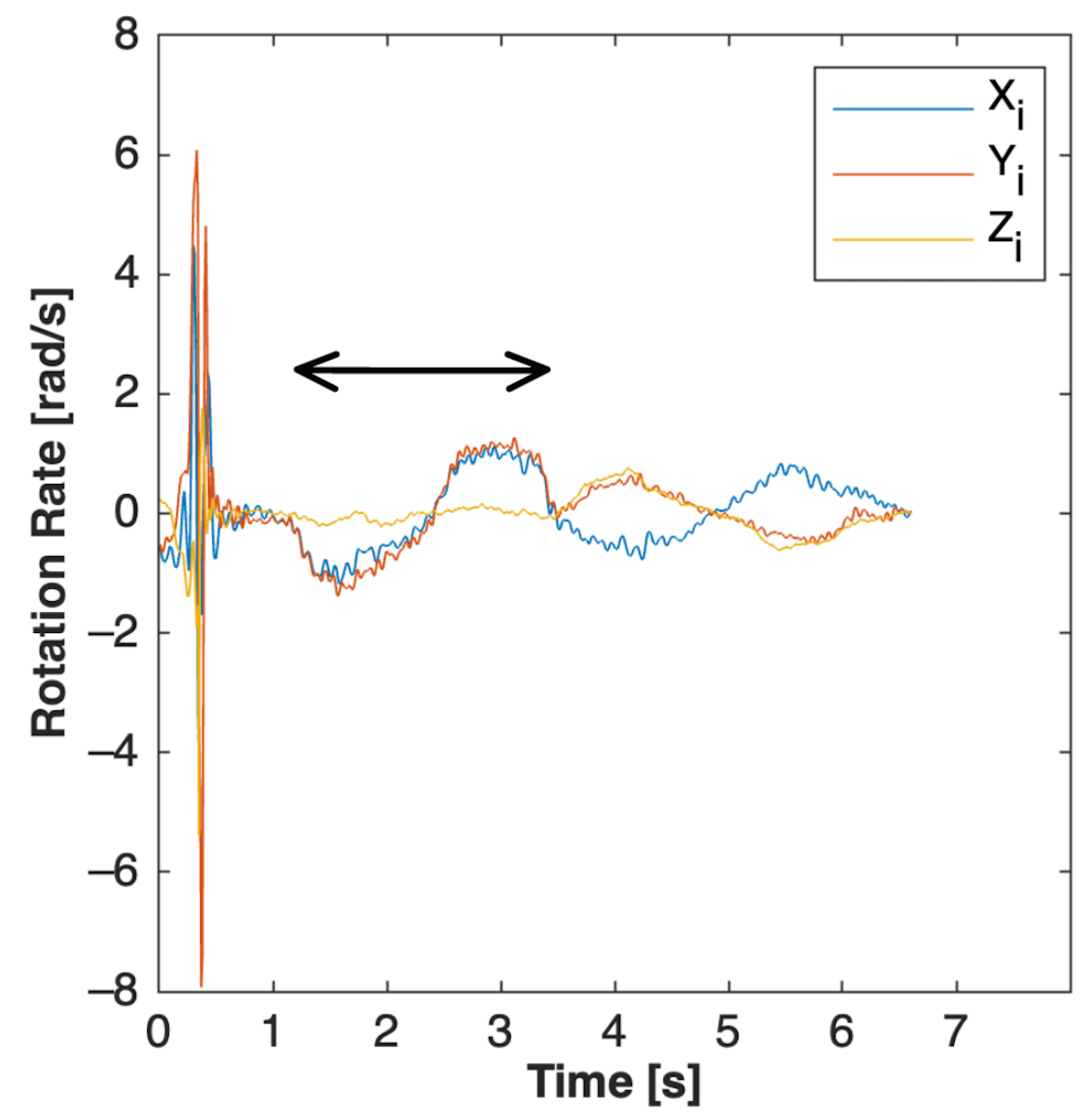
2.4.2. PCA Methods for the Forward Flexion Maneuver
2.4.3. PCA Methods for the Lateral Bending Maneuver
2.4.4. PCA Methods for the Chest Tap Maneuver
2.4.5. Cross-Product Utilization
2.5. Statistical Methods
2.5.1. Smartwatch versus SPIMU Correlation Design
2.5.2. Smartwatch versus Force Plate Correlation Design
2.5.3. Smartwatch Repeated-Measures Analysis of Variance across Pose Types
3. Results
3.1. Smartwatch versus SPIMU Correlation Results
3.1.1. AP Correlation Results
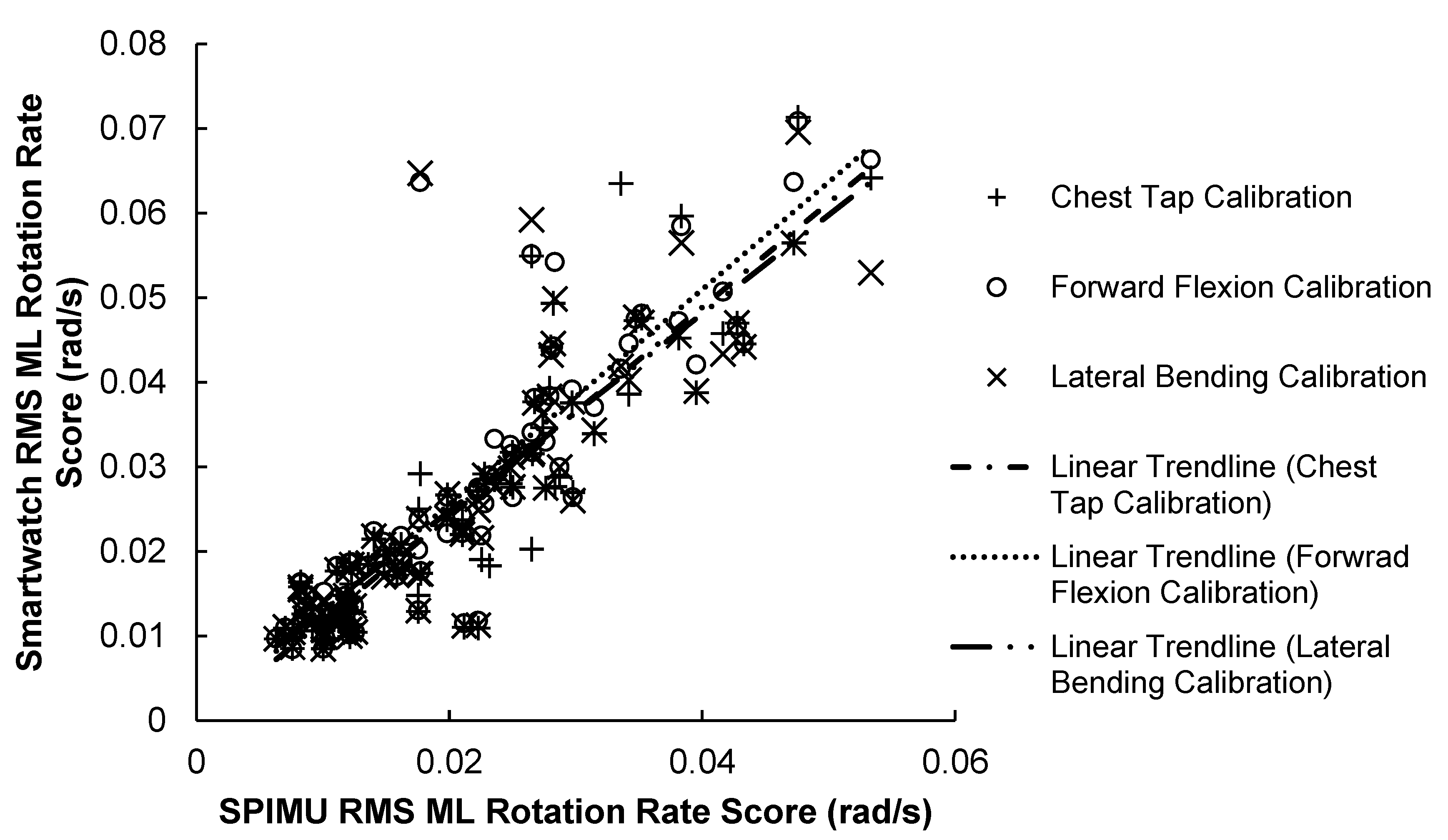
3.1.2. ML Correlation Results
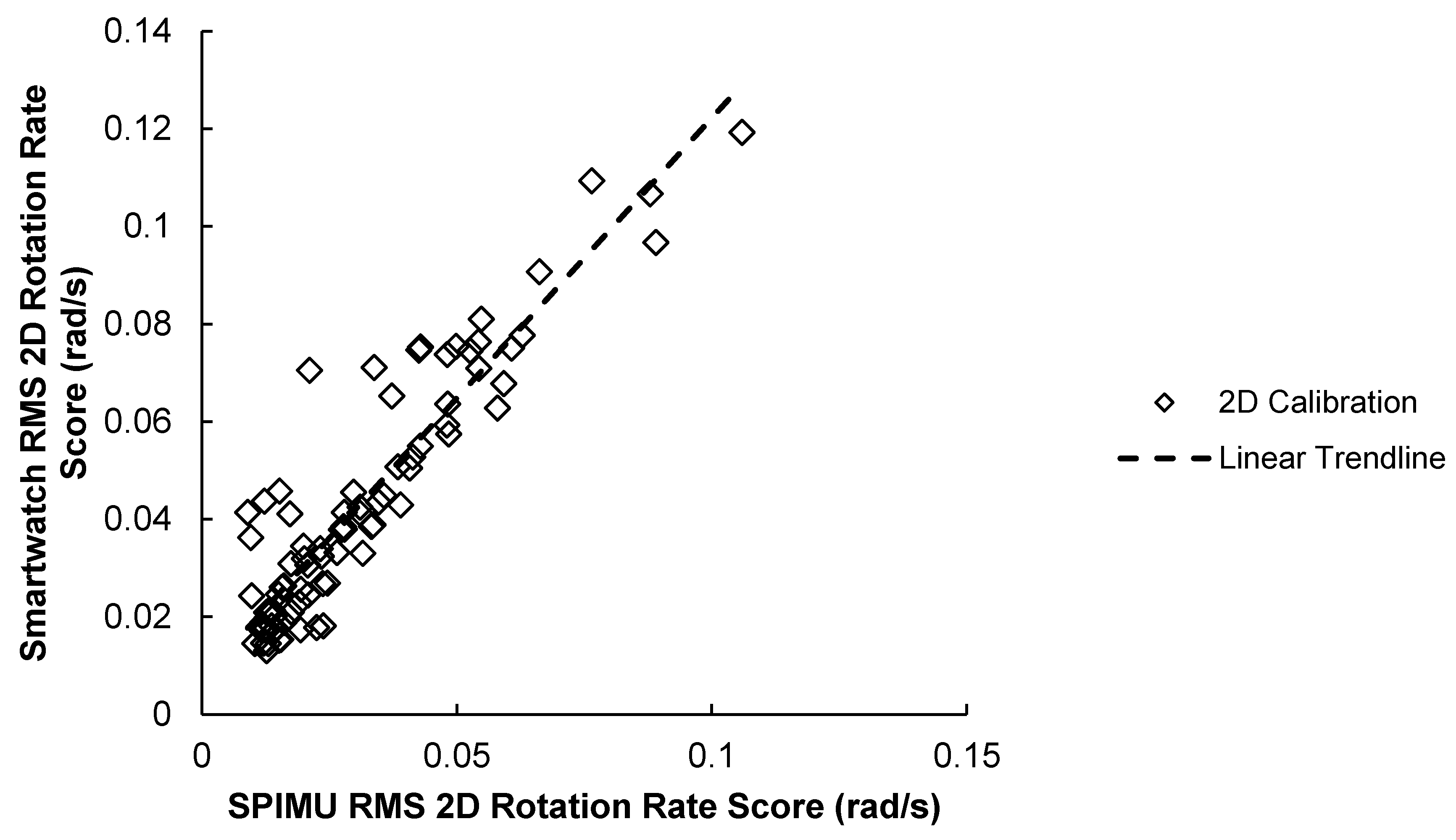
3.1.3. 2D Correlation Results
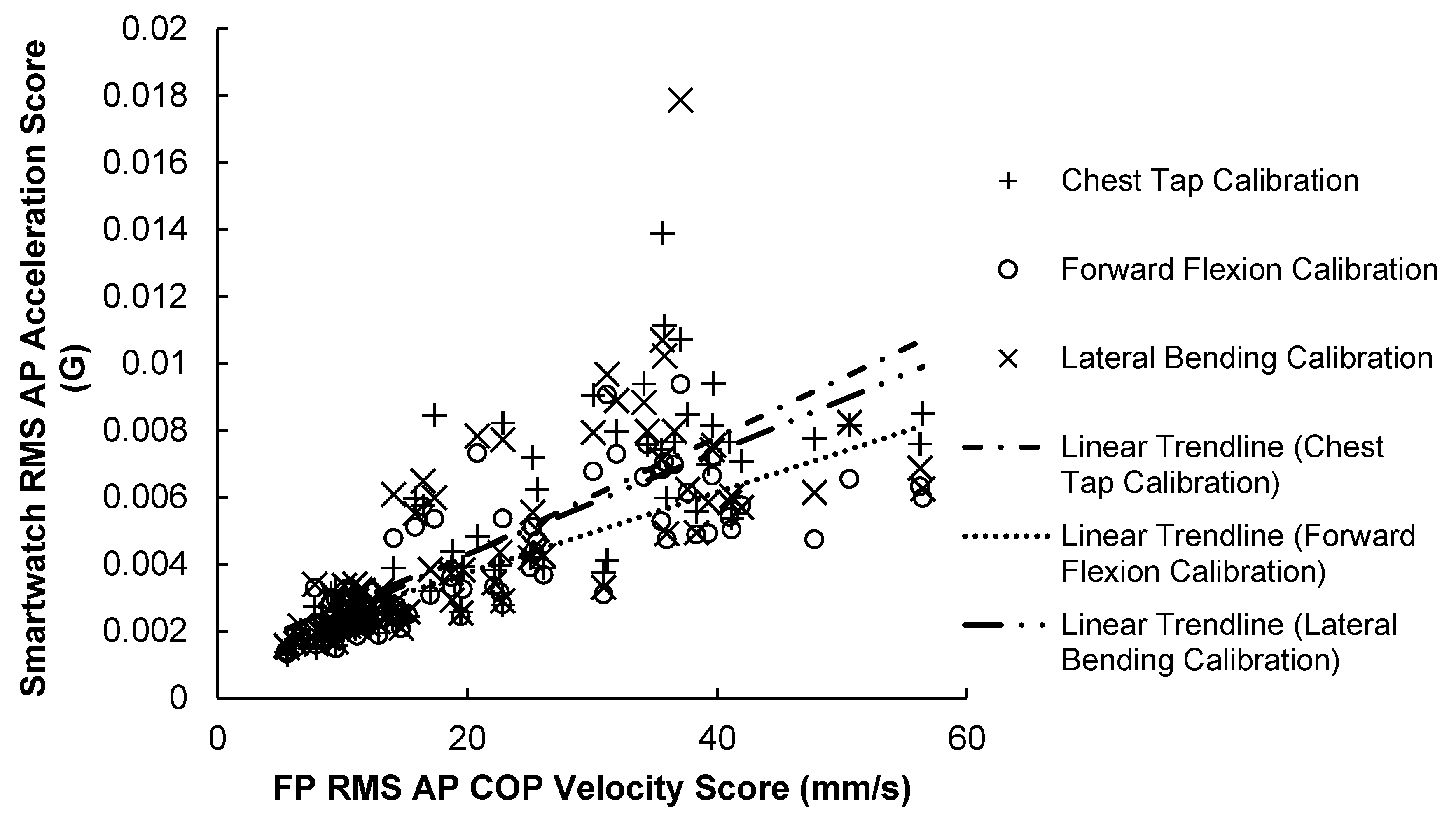
3.2. Smartwatch versus Force Plate Correlation Results
3.2.1. AP Correlation Results
3.2.2. ML Correlation Results
3.2.3. 2D Correlation Results
3.3. Smartwatch Repeated-Measures Analysis of Variance Results
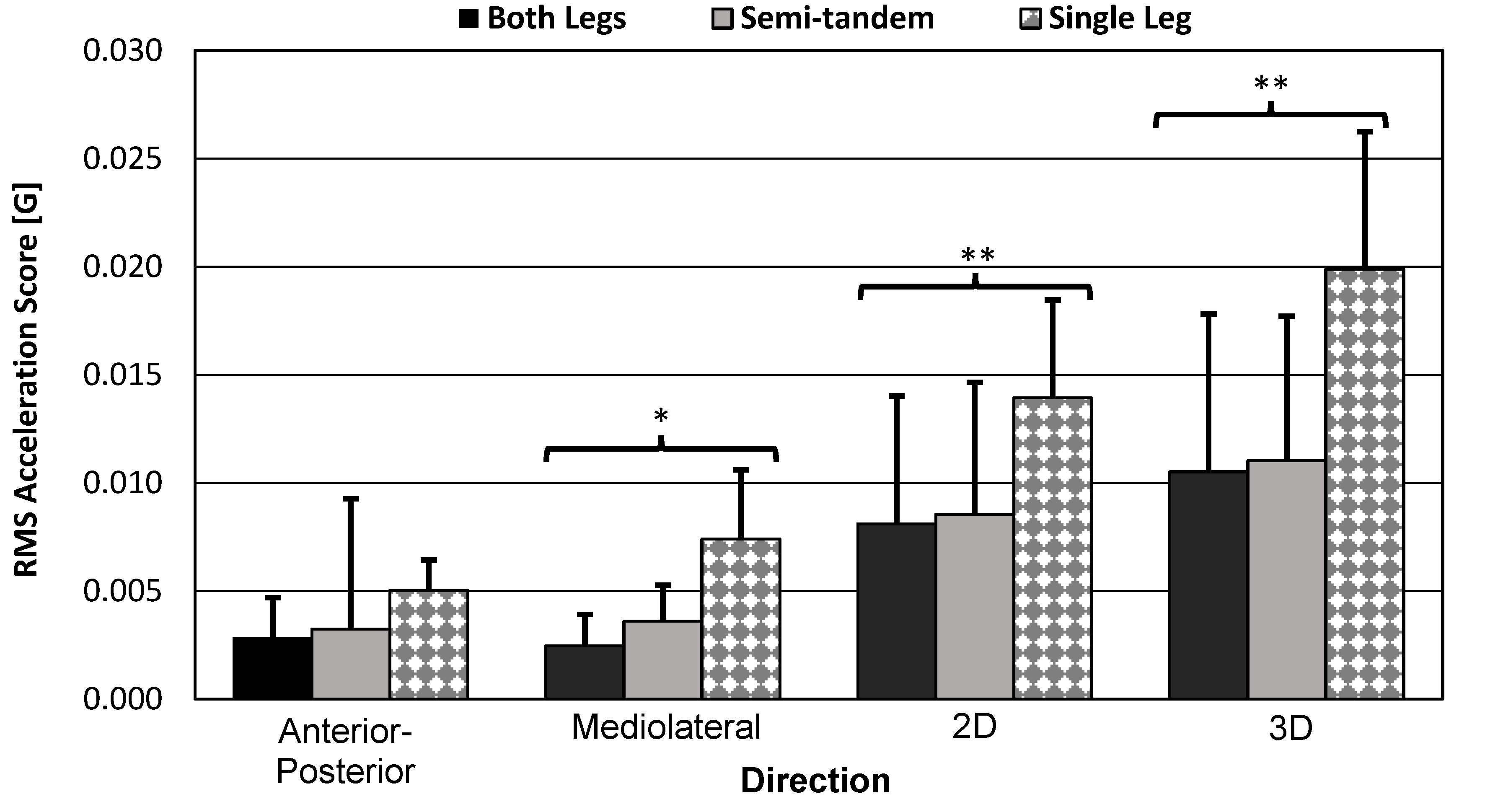
3.3.1. RMANOVA Acceleration-Based Score Results
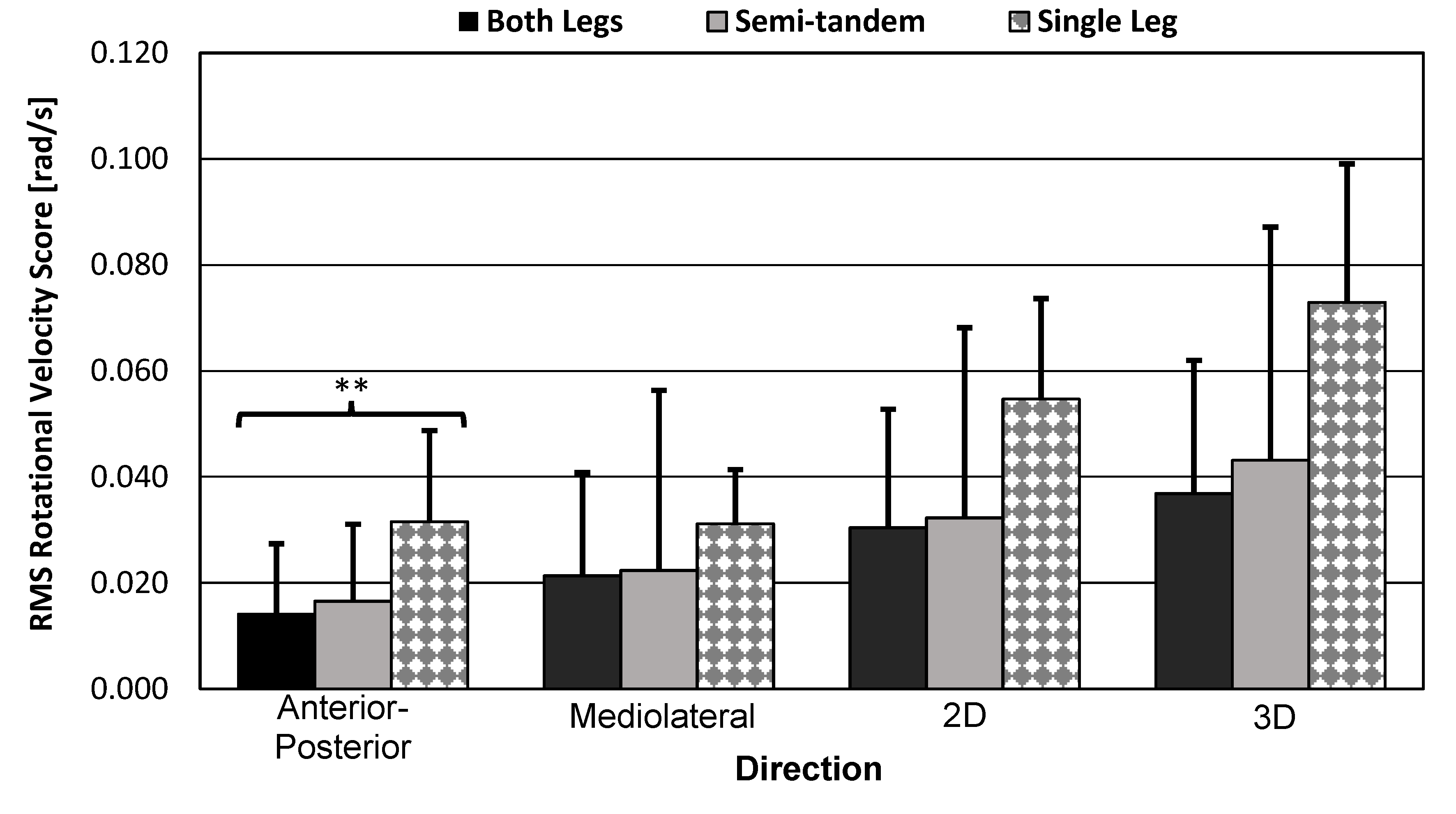
3.3.2. RMANOVA Rotational Velocity-Based Score Results
3.3.3. Bar Graph and Standard Error Bars of the Smartwatch Scores
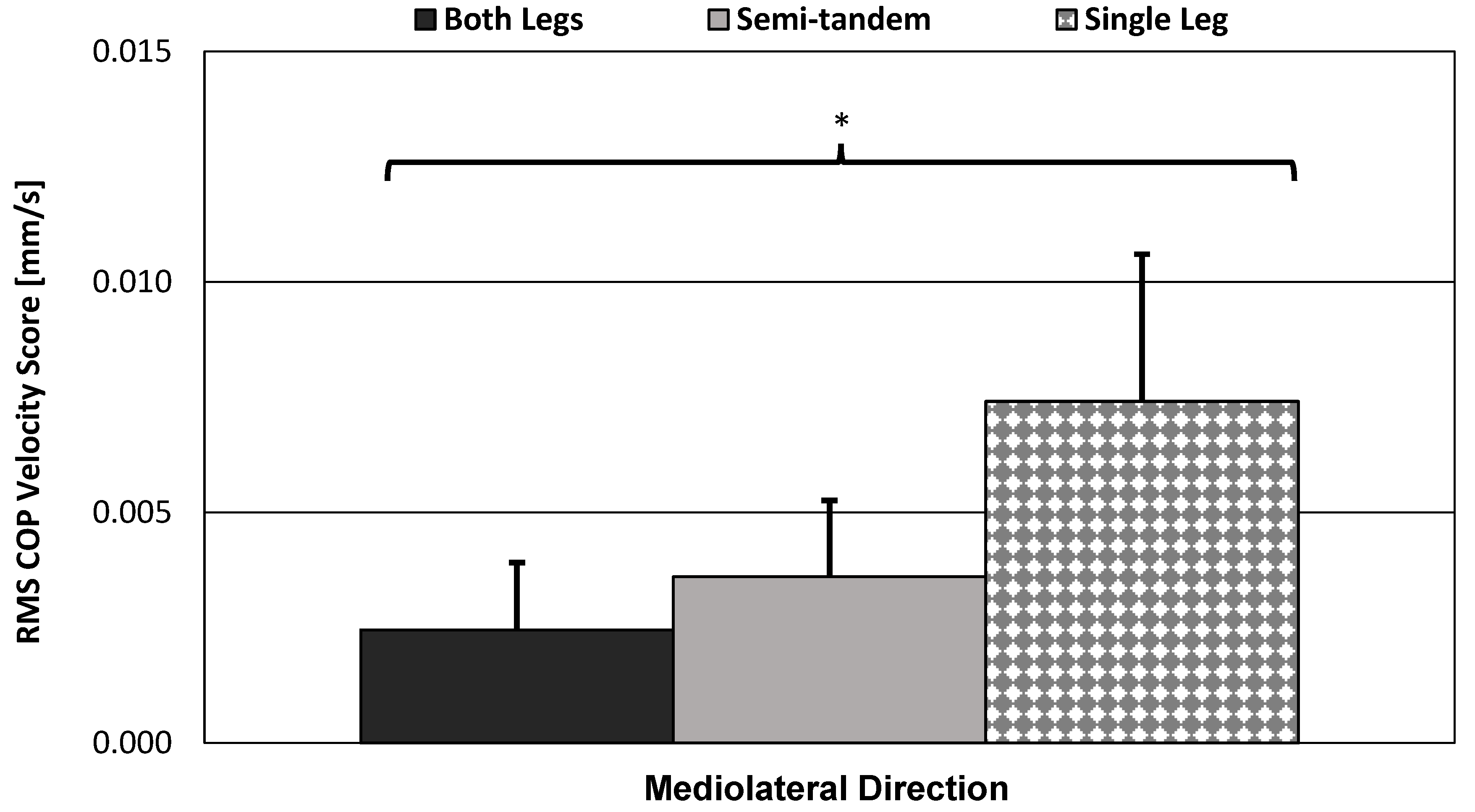
3.3.4. Bar Graph and Standard Error Bars of the Force-Plate Scores
3.4. Qualitative Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Key Findings
- Acceleration scores in the ML, 2D, and 3D directions.
- Rotational scores in the AP direction.
4.2. Limitations of RMANOVA Statistical Results
4.3. Optional Improvement to Calibration Algorithm
4.4. Future Development of IMU-Based Posturography
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greene, B.R.; McManus, K.; Ader, L.G.M.; Caulfield, B. Unsupervised Assessment of Balance and Falls Risk Using a Smartphone and Machine Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alashram, A.R.; Annino, G.; Raju, M.; Padua, E. Effects of physical therapy interventions on balance ability in people with traumatic brain injury: A systematic review. Neurorehabilitation 2020, 46, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulding, A.; Jones, I.; Taylor, R.; Piggot, J.; Taylor, D. Dynamic and static tests of balance and postural sway in boys: Effects of previous wrist bone fractures and high adiposity. Gait Posture 2003, 17, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, S.P.; D’Hondt, E.; Fink, P.W.; Lenoir, M.; Hills, A.P. The effects of pediatric obesity on dynamic joint malalignment during gait. Clin. Biomech. 2014, 29, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, L.; Korner-Bitensky, N. Usefulness of the Berg Balance Scale in Stroke Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, C.A.; Cassidy, J.D.; Klassen, T.P.; Rosychuk, R.J.; Rowe, B.H. Development of a Clinical Static and Dynamic Standing Balance Measurement Tool Appropriate for Use in Adolescents. Phys. Ther. 2005, 85, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, K.; Wooddauphinee, S.; Williams, J.I.; Maki, B.; Gayton, D. Measuring Balance in the Elderly: Validation of an Instrument. Can. J. Public Health 1992. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1468055/ (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Hsieh, K.L.; Roach, K.L.; Wajda, D.A.; Sosnoff, J.J. Smartphone technology can measure postural stability and discriminate fall risk in older adults. Gait Posture 2018, 67, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghislieri, M.; Gastaldi, L.; Pastorelli, S.; Tadano, S.; Agostini, V. Wearable Inertial Sensors to Assess Standing Balance: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, C.; Ludlow, C.; Rieger, B. Measuring postural stability with an inertial sensor: Validity and sensitivity. Med. Devices Èvid. Res. 2015, 8, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heebner, N.R.; Akins, J.S.; Lephart, S.M.; Sell, T.C. Reliability and validity of an accelerometry based measure of static and dynamic postural stability in healthy and active individuals. Gait Posture 2015, 41, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siepmann, C.; Kowalczuk, P. Understanding continued smartwatch usage: The role of emotional as well as health and fitness factors. Electron. Mark. 2021, 31, 795–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, R.V.; Perkins, N.C. Determining anatomical frames via inertial motion capture: A survey of methods. J. Biomech. 2020, 106, 109832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laidig, D.; Weygers, I.; Seel, T. Self-Calibrating Magnetometer-Free Inertial Motion Tracking of 2-DoF Joints. Sensors 2022, 22, 9850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, K.E.; Chen, Y.-P.; Howard, A. Method for the Determination of Relative Joint Axes for Wearable Inertial Sensor Applications. 2021, pp. 9512–9517. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9636686 (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- McGrath, T.; Fineman, R.; Stirling, L. An Auto-Calibrating Knee Flexion-Extension Axis Estimator Using Principal Component Analysis with Inertial Sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’donovan, K.J.; Kamnik, R.; O’keeffe, D.T.; Lyons, G.M. An inertial and magnetic sensor based technique for joint angle measurement. J. Biomech. 2007, 40, 2604–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, P.; Xiao, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Review of the Upright Balance Assessment Based on the Force Plate. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, G.-M.; Kwon, Y.-R.; Kim, D.-Y.; Ko, J.; Kim, J.-W. The influence of height on test-retest reliability of postural balance measures in healthy young adults. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, A.; Frykberg, G. Correlations between force plate measures for assessment of balance. Clin. Biomech. 2000, 15, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, D.; Park, D.; Yoo, B.; Choi, J.-O.; Hong, J.; Choi, T.Y.; Park, E.S.; Rha, D.-W. Evaluation of sitting and standing postural balance in cerebral palsy by center-of-pressure measurement using force plates: Comparison with clinical measurements. Gait Posture 2022, 92, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melecky, R.; Socha, V.; Kutilek, P.; Hanakova, L.; Takac, P.; Schlenker, J.; Svoboda, Z. Quantification of Trunk Postural Stability Using Convex Polyhedron of the Time-Series Accelerometer Data. J. Health Eng. 2016, 2016, 1621562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, C.; Zhao, L.; Ryan, J.; Komaba, Y.; Inomata, A.; Caulfield, B. Quantification of postural control deficits in patients with recent concussion: An inertial-sensor based approach. Clin. Biomech. 2017, 42, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, M.; Horak, F.B.; Zampieri, C.; Carlson-Kuhta, P.; Nutt, J.G.; Chiari, L. Trunk accelerometry reveals postural instability in untreated Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.; Cohen, P.; West, S.G.; Aiken, L.S. Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dewan, B.M.; James, C.R.; Kumar, N.A.; Sawyer, S.F. Kinematic Validation of Postural Sway Measured by Biodex Biosway (Force Plate) and SWAY Balance (Accelerometer) Technology. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8185710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.; Cho, M.; Ki, C.-S. Correct Use of Repeated Measures Analysis of Variance. Ann. Lab. Med. 2009, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Calibration Method (Type of Motion) | Known Axes (Method of Discovery) | Axis Found by Cross Product | Equation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward flexion (rotational velocity) | SI axis (gravity vector) ML axis (PCA vector) | AP axis | |
| Lateral bending (rotational velocity) | SI axis (gravity vector) AP axis (PCA vector) | ML axis | |
| Chest tap (acceleration) | SI axis (gravity vector) AP axis (PCA vector) | ML axis |
| Smartwatch Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest-Tap Calibration | Forward Flexion Calibration | Lateral Bending Calibration | ||
| SPIMU score | Pearson correlation | 0.884 | 0.970 | 0.953 |
| p-value (two-tailed) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Number of Data Points | 84 | 84 | 84 | |
| Smartwatch Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest-Tap Calibration | Forward Flexion Calibration | Lateral Bending Calibration | ||
| SPIMU score | Pearson correlation | 0.901 | 0.887 | 0.861 |
| p-value (two-tailed) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Number of Data Points | 84 | 84 | 84 | |
| Smartwatch 2D Score | ||
|---|---|---|
| (2D Calibration Method) | ||
| SPIMU score | Pearson correlation | 0.919 |
| p-value (two-tailed) | <0.001 | |
| Number of Data Points | 84 |
| Smartwatch Score | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest-Tap Calibration | Forward Flexion Calibration | Lateral Bending Calibration | SPIMU | ||
| Force-plate score | Pearson correlation | 0.819 | 0.794 | 0.721 | 0.281 |
| p-value (two-tailed) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.010 | |
| Number of Data Points | 84 | 84 | 84 | 84 | |
| Smartwatch Score | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest-Tap Calibration | Forward Flexion Calibration | Lateral Bending Calibration | SPIMU | ||
| Force-plate score | Pearson correlation | 0.729 | 0.758 | 0.799 | 0.711 |
| p-value (two-tailed) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Number of Data Points | 84 | 84 | 84 | 84 | |
| Smartwatch 2D Score | SPIMU | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (2D Calibration Method) | |||
| Force-plate score | Pearson correlation | 0.468 | 0.593 |
| p-value (two-tailed) | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Number of Data Points | 84 | 84 |
| Device | Direction | Pose-Type within-Subject Effects on RMS Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error DOF | Factor DOF | F | p-Value | ||
| Smartwatch (forward flexion) | AP | 18.44 | 1.09 | 1.73 | 0.205 |
| ML | 21.51 | 1.27 | 40.70 * | <0.001 | |
| 2D | 34 | 2.00 | 8.08 ** | 0.002 | |
| 3D | 34 | 2.00 | 16.06 ** | <0.001 | |
| SPIMU | AP | 34 | 2.00 | 3.31 | 0.048 |
| ML | 19.10 | 1.12 | 20.43 * | <0.001 | |
| 2D | 34 | 2.00 | 15.49 ** | <0.001 | |
| 3D | 34 | 2.00 | 17.16 ** | <0.001 | |
| Force plate (COP Vel.) | AP | 18.15 | 1.07 | 61.27 * | <0.001 |
| ML | 18.62 | 1.10 | 83.23 * | <0.001 | |
| 2D | 17.52 | 1.03 | 52.17 * | <0.001 | |
| Device | Calibration Method | Direction | Pose-Type Within-Subject Effects | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Error DOF | Factor DOF | F | p-Value | ||
| Smartwatch (forward flexion) | AP | 34 | 2.00 | 9.59 ** | <0.001 |
| ML | 25.51 | 1.5 | 0.41 | 0.609 | |
| 2D | 34 | 2.00 | 3.40 | 0.028 | |
| 3D | 34 | 2.00 | 6.55 | 0.004 | |
| SPIMU | AP | 20.59 | 1.21 | 24.74 * | <0.001 |
| ML | 34 | 2.00 | 12.23 ** | <0.001 | |
| 2D | 23.64 | 1.39 | 23.33 * | <0.001 | |
| 3D | 23.53 | 1.38 | 37.47 * | <0.001 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Presley, B.M.; Sklar, J.C.; Hazelwood, S.J.; Berg-Johansen, B.; Klisch, S.M. Balance Assessment Using a Smartwatch Inertial Measurement Unit with Principal Component Analysis for Anatomical Calibration. Sensors 2023, 23, 4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104585
Presley BM, Sklar JC, Hazelwood SJ, Berg-Johansen B, Klisch SM. Balance Assessment Using a Smartwatch Inertial Measurement Unit with Principal Component Analysis for Anatomical Calibration. Sensors. 2023; 23(10):4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104585
Chicago/Turabian StylePresley, Benjamin M., Jeffrey C. Sklar, Scott J. Hazelwood, Britta Berg-Johansen, and Stephen M. Klisch. 2023. "Balance Assessment Using a Smartwatch Inertial Measurement Unit with Principal Component Analysis for Anatomical Calibration" Sensors 23, no. 10: 4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104585
APA StylePresley, B. M., Sklar, J. C., Hazelwood, S. J., Berg-Johansen, B., & Klisch, S. M. (2023). Balance Assessment Using a Smartwatch Inertial Measurement Unit with Principal Component Analysis for Anatomical Calibration. Sensors, 23(10), 4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23104585







