A Smartphone-Based Disposable Hemoglobin Sensor Based on Colorimetric Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principle
2.1. Device Principle
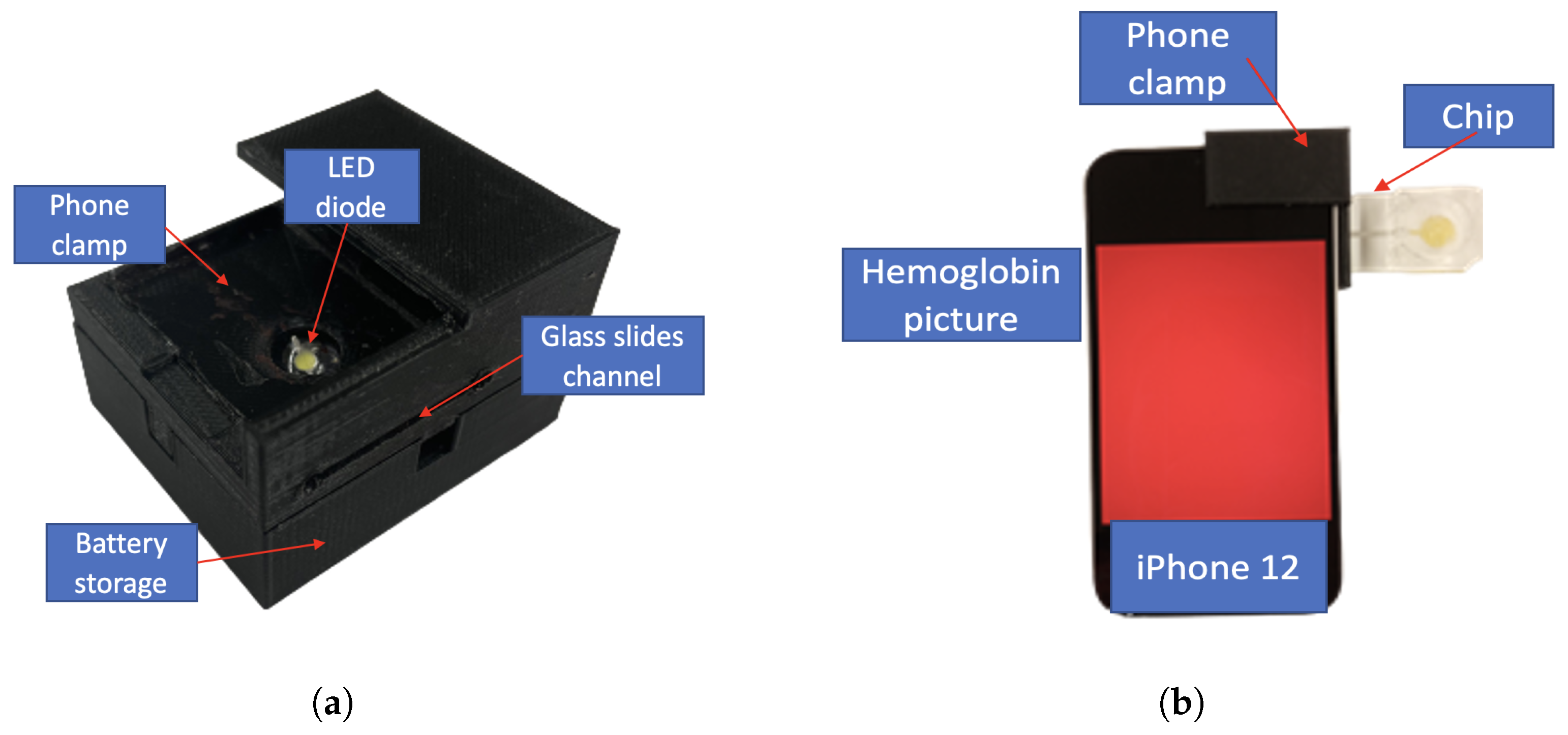
2.2. Optical Instrument
2.3. Colorimetric Measurement
3. Materials and Methods
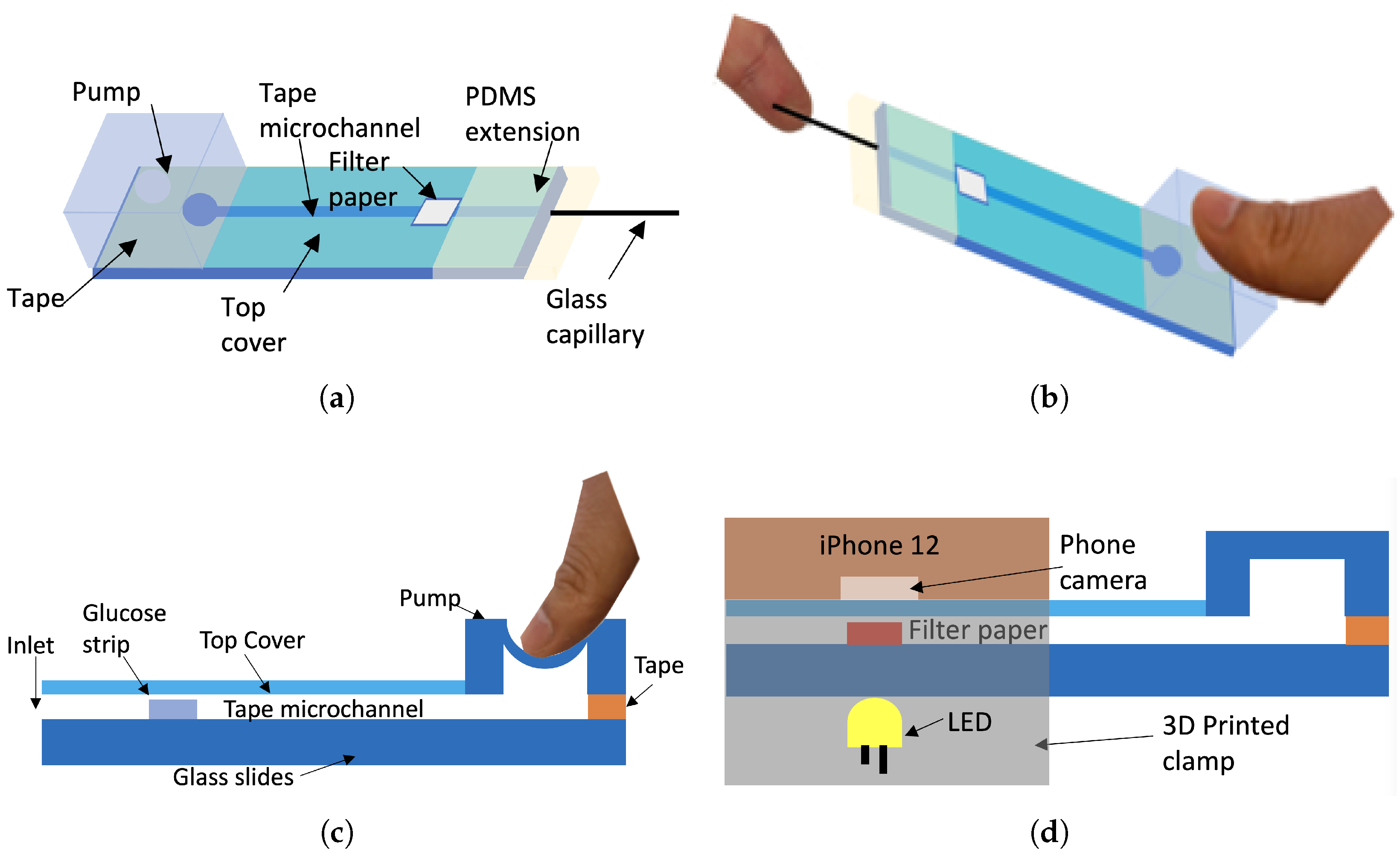
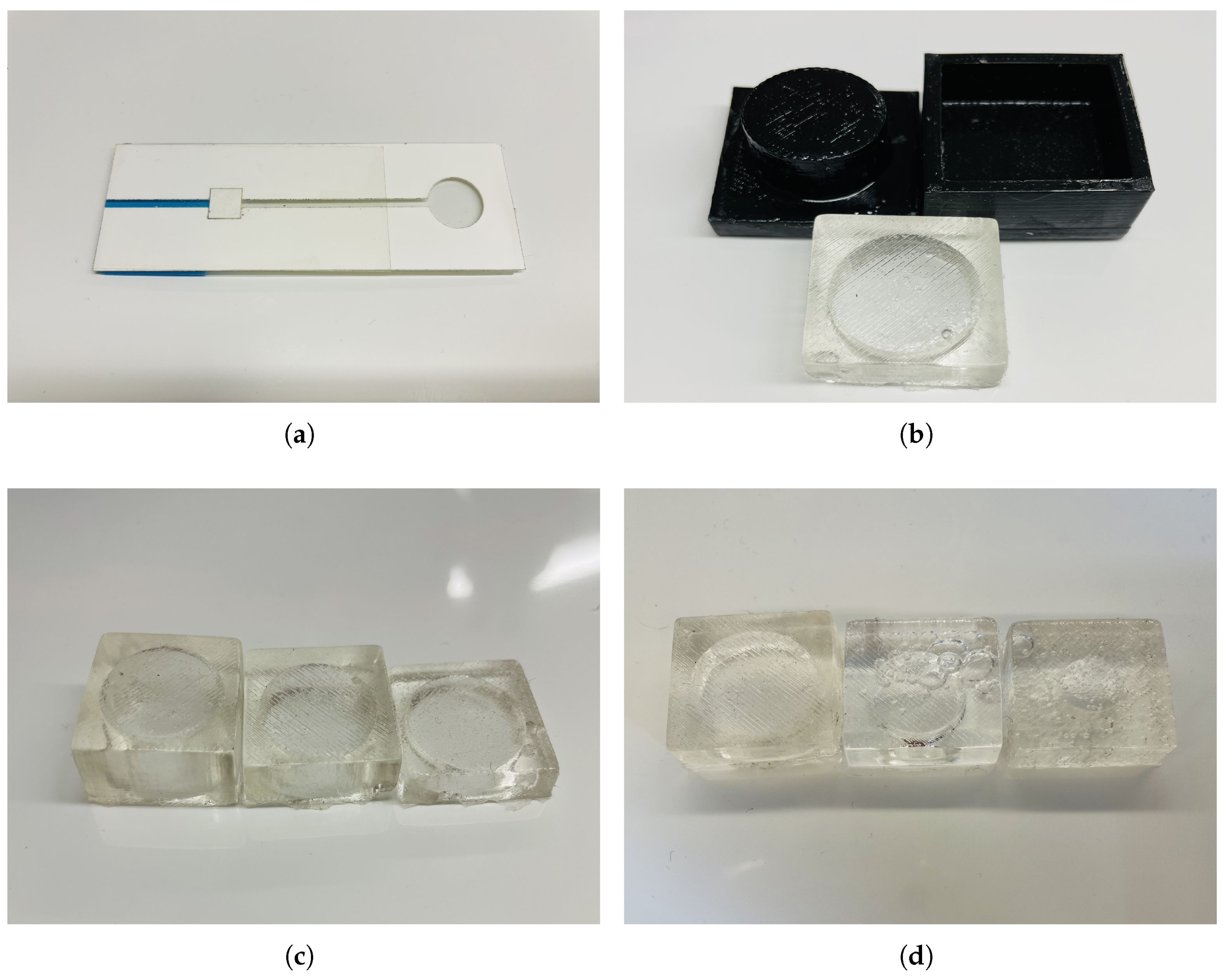
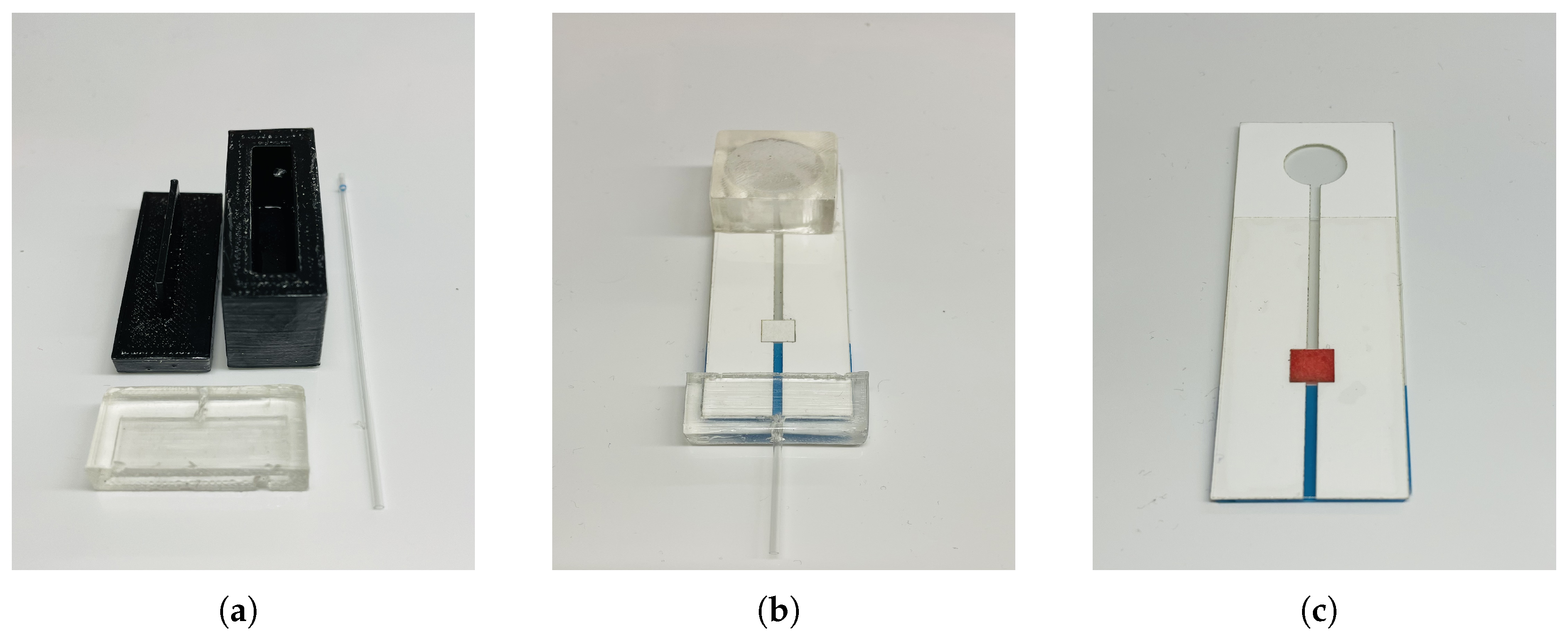
3.1. Microfluidics Channel
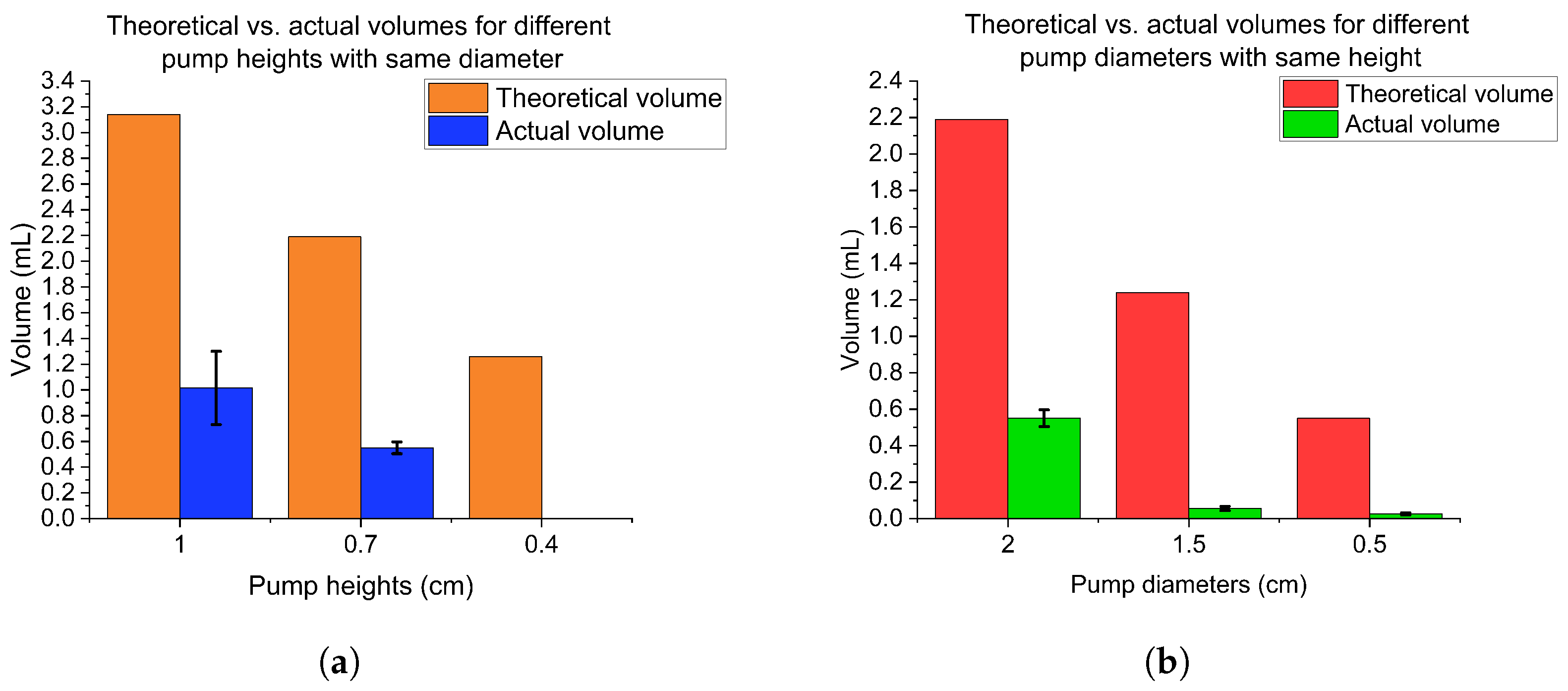
3.2. Micropump
3.3. Assembly and Operation
3.4. Phone Clamp
3.5. Materials
4. Results
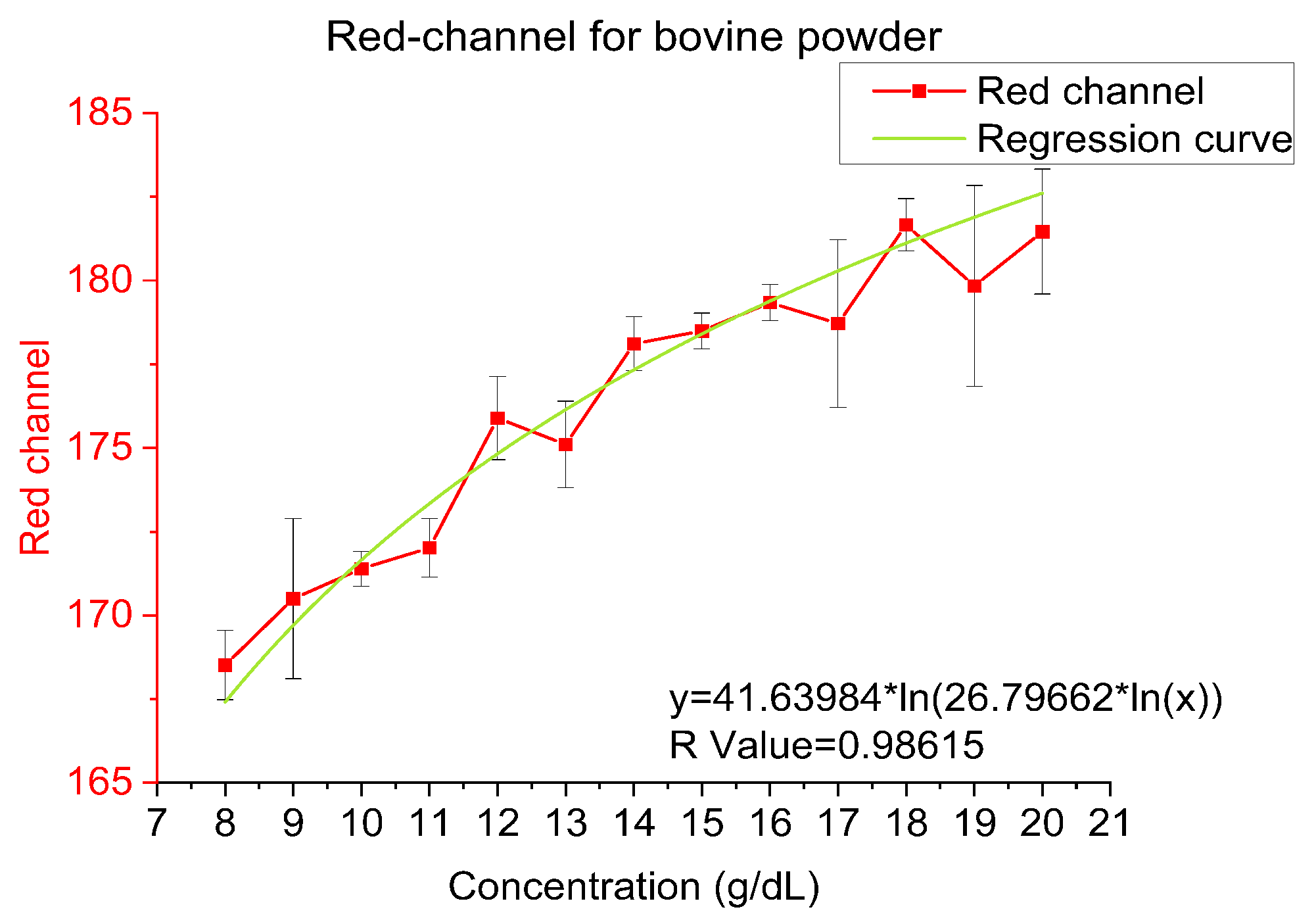
4.1. Bovine Hemoglobin Powder
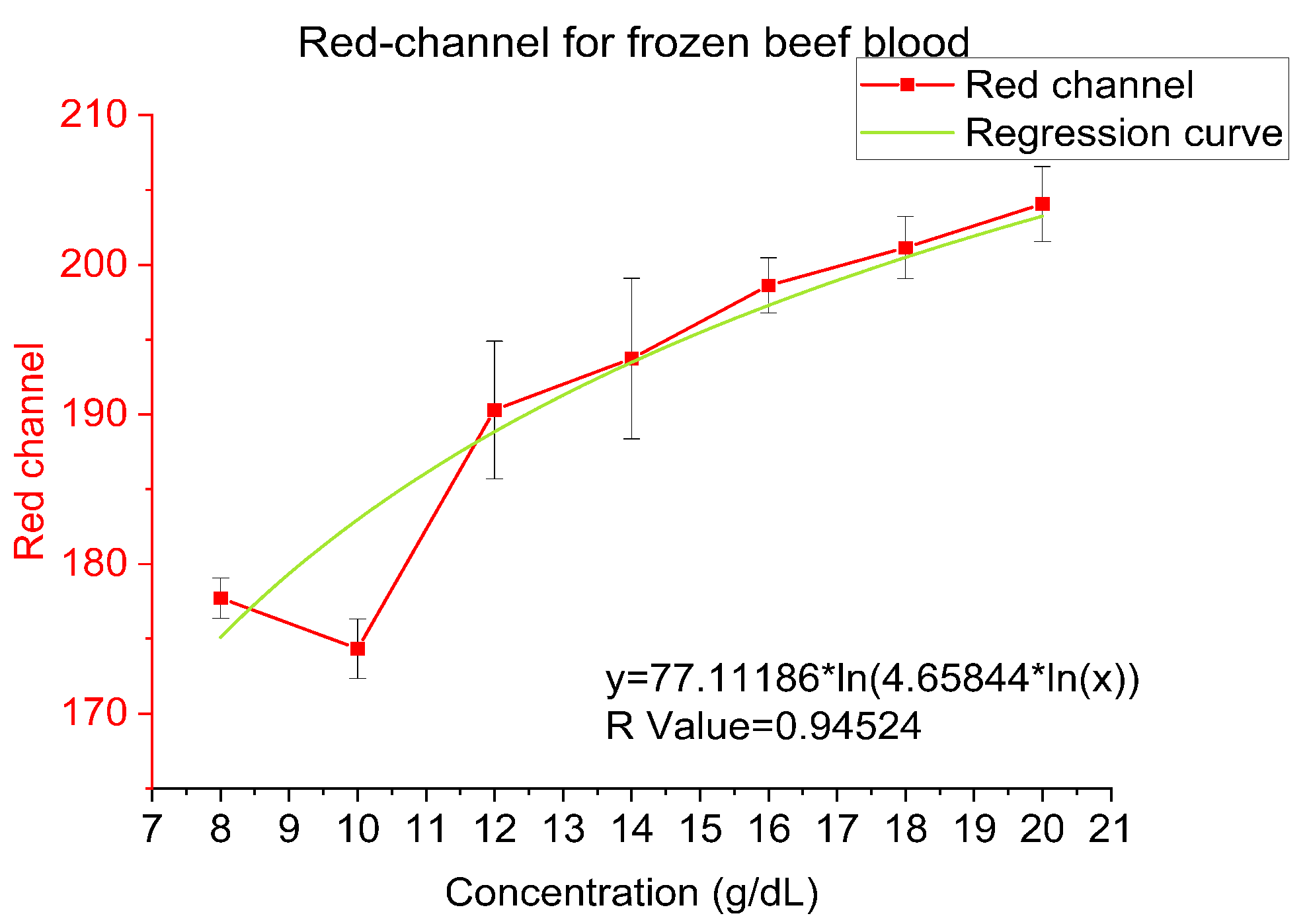
4.2. Frozen Beef Blood
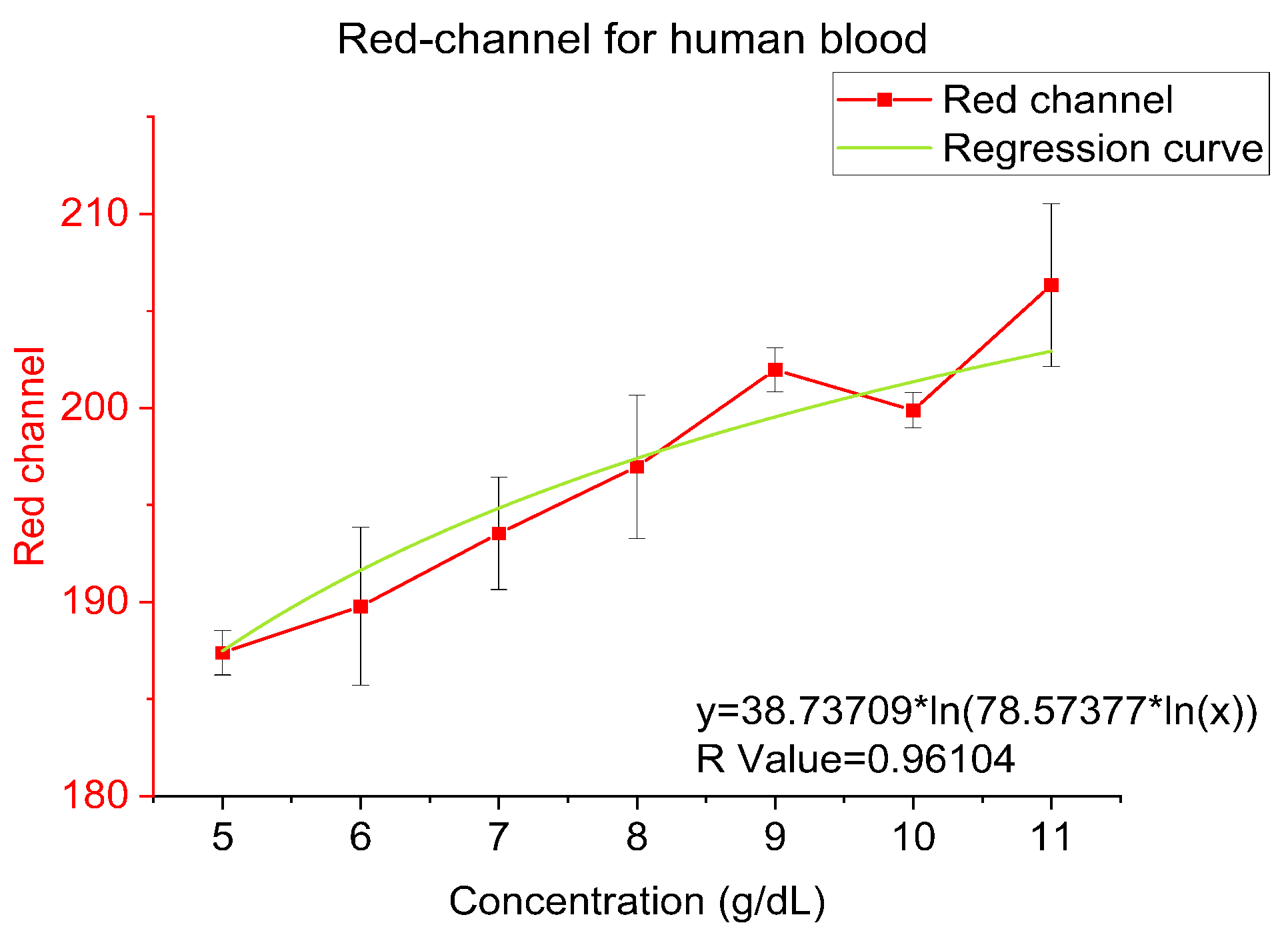
4.3. Human Blood
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nathan, D.G.; Gunn, R.B. Thalassemia: The consequences of unbalanced hemoglobin synthesis. Am. J. Med. 1966, 41, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemoglobin. Mount Sinai Health System. Available online: https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/tests/hemoglobin (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Doshi, R.; Panditrao, A. Non-invasive optical sensor for hemoglobin determination. Measurement 2013, 3, 559–562. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, M.H. Management of sickle cell diseas. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, R.D., Jr.; Mei, Z.; Mapango, C.; Jefferds, M.E.D. Methods and analyzers for hemoglobin measurement in clinical laboratories and field settings. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1450, 147–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemoglobin Testing & White Blood Cell Count (WBC). HemoCue. Available online: https://www.hemocue.com/en/solutions/hematology (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Drummond, T.G.; Hill, M.G.; Barton, J.K. Electrochemical and sensors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamholz, A.E.; Weigl, B.H.; Finlayson, B.A.; Yager, P. Quantitative analysis of molecular interaction in a microfluidic channel: The t-sensor. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 5340–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Park, J.-K. Magnetic force-based multiplexed immunoassay using superparamagnetic nanoparticles in microfluidic channel. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 657–664. [Google Scholar]
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, P.S.; Tachikawa, K.; Manz, A. Micro total analysis systems. Latest advancements and trends. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3887–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, D.R.; Iossifidis, D.; Auroux, P.-A.; Manz, A. Micro total analysis systems. 1. introduction, theory, and technology. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 2623–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Martins-Green, M.; Liu, Y. Microfabrication of cylindrical microfluidic channel networks for microvascular researc. Biomed. Microdevices 2012, 14, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piyasena, M.E.; Graves, S.W. The intersection of flow cytometry with microfluidics and microfabrication. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1044–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weibel, D.B.; DiLuzio, W.R.; Whitesides, G.M. Microfabrication meets microbiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.W.Y.; Lei, K.F.; Shi, G.; Li, W.J.; Huang, Q. Microfluidic channel fabrication by pdms-interface bonding. Smart Mater. Struct. 2005, 15, S112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ali, J.; Sorger, P.K.; Jensen, K.F. Cells on chips. Nature 2006, 442, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quake, S.R.; Scherer, A. From micro-to nanofabrication with soft materials. Science 2000, 290, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, A.R.; Lee, D.; Do, T.; Holtze, C.; Weitz, D.A. Glass coating for pdms microfluidic channels by sol–gel methods. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 516–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, D.C.; McDonald, J.C.; Schueller, O.J.; Whitesides, G.M. Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly (dimethylsiloxane). Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 4974–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, C.; Taylor, H.; Avram, M.; Miao, J.; Franssila, S. A practical guide for the fabrication of microfluidic devices using glass and silicon. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 016505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yager, P.; Edwards, T.; Fu, E.; Helton, K.; Nelson, K.; Tam, M.R.; Weigl, B.H. Microfluidic diagnostic technologies for global public health. Nature 2006, 442, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, Y.-G.; Wang, F.-B.; He, F.-Y.; Xia, X.-H. A simple, disposable microfluidic device for rapid protein concentration and purification via direct-printing. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1496–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Do, J.; Premasiri, W.R.; Ziegler, L.D.; Klapperich, C.M. Rapid point-of-care concentration of bacteria in a disposable microfluidic device using meniscus dragging effect. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 3265–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Kim, J.; Jeon, C.-W.; Han, K.-H. A disposable microfluidic device with a reusable magnetophoretic functional substrate for isolation of circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 4113–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eletxigerra, U.; Martinez-Perdiguero, J.; Merino, S. Disposable microfluidic immuno-biochip for rapid electrochemical detection of tumor necrosis factor alpha biomarker. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, G.S.; Chiu, D.T. Disposable microfluidic devices: Fabrication, function, and application. BioTechniques 2005, 38, 429–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Si, J.; Li, Z. Fabrication techniques for microfluidic paper-based analytical devices and their applications for biological testing: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 774–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.K.; Sakib, N.; Love, R.R.; Ahamed, S.I. Rgb pixel analysis of fingertip video image captured from sickle cell patient with low and high level of hemoglobin. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 8th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 19–21 October 2017; pp. 499–505. [Google Scholar]
- Jakovels, D.; Rubins, U.; Spigulis, J. Rgb imaging system for mapping and monitoring of hemoglobin distribution in skin. In Imaging Spectrometry XVI; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2011; Volume 8158, pp. 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Nishidate, I.; Maeda, T.; Niizeki, K.; Aizu, Y. Estimation of melanin and hemoglobin using spectral reflectance images reconstructed from a digital rgb image by the wiener estimation method. Sensors 2013, 13, 7902–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tania, M.H.; Lwin, K.T.; Shabut, A.M.; Najlah, M.; Chin, J.; Hossain, M.A. Intelligent image-based colourimetric tests using machine learning framework for lateral flow assays. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 139, 112843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakasabapathy, M.K.; Sadasivam, M.; Singh, A.; Preston, C.; Thirumalaraju, P.; Venkataraman, M.; Bormann, C.L.; Draz, M.S.; Petrozza, J.C.; Shafiee, H. An automated smartphone-based diagnostic assay for point-of-care semen analysis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaai7863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebian, S.; Javanmard, M. Compact and automated particle counting platform using smartphone-microscopy. Talanta 2021, 228, 122244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Q.; Jing, H.; Li, Y.; Yisibashaer, W.; Chen, J.; Li, B.N.; Zhang, Y. Smartphone based visual and quantitative assays on upconversional paper sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Z.; Williams, A.; Liau, P.; Stephens, T.G.; Drury, C.; Chiles, E.N.; Su, X.; Javanmard, M.; Bhattacharya, D. Development of a portable toolkit to diagnose coral thermal stress. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accu-Answer Isaw 4 in 1 Multifunctional Blood Glucose Meter/Cholesterol/Glucose/Hemoglobin/Uric Acid/Lancets-(silvergrey), äù accu answer official store malaysia, en. Available online: https://accuanswer.com/products/accu-answer-registered-isaw-registered-4-in-1-multifunctional-blood-glucose-meter-cholesterol-glucose-hemoglobin-uric-acid-lancets-silver-grey- (accessed on 15 August 2021).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Z.; Tayyab, M.; Lin, Z.; Raji, H.; Javanmard, M. A Smartphone-Based Disposable Hemoglobin Sensor Based on Colorimetric Analysis. Sensors 2023, 23, 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010394
Meng Z, Tayyab M, Lin Z, Raji H, Javanmard M. A Smartphone-Based Disposable Hemoglobin Sensor Based on Colorimetric Analysis. Sensors. 2023; 23(1):394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010394
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Zhuolun, Muhammad Tayyab, Zhongtian Lin, Hassan Raji, and Mehdi Javanmard. 2023. "A Smartphone-Based Disposable Hemoglobin Sensor Based on Colorimetric Analysis" Sensors 23, no. 1: 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010394
APA StyleMeng, Z., Tayyab, M., Lin, Z., Raji, H., & Javanmard, M. (2023). A Smartphone-Based Disposable Hemoglobin Sensor Based on Colorimetric Analysis. Sensors, 23(1), 394. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010394





