Multi-Layered QCA Content-Addressable Memory Cell Using Low-Power Electronic Interaction for AI-Based Data Learning and Retrieval in Quantum Computing Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
- An XOR/XNOR gate with a multi-layer structure based on the electron interactions is proposed;
- Based on the proposed XNOR gate, a CAM cell is designed and expanded to a 1 × 2 CAM to check the modularity and expandability;
- A memory cell targeting the optimization of area and time complexity is proposed and verified through circuit simulation;
- The accuracy of the designed cell is mathematically verified using physical proof;
- An additional circuit targeting the optimization of power consumption is proposed;
- An associative memory structure that can be efficiently used for data learning and retrieval based on artificial intelligence, such as neural networks, machine learning, and deep learning is designed.
2. Related Works
2.1. Background of QCA
2.2. Conventional QCA XOR Gates
2.3. Conventional QCA CAM Cells
3. Proposed CAM Cell
4. Physical Proof and Performance Analysis
4.1. Physical Proof of the Proposed XNOR Gate
4.2. Simulation and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verleysen, M.; Sirletti, B.; Vandemeulebroecke, A.M.; Jespers, P.G.A. Neural Networks for High-Storage Content-Addressable Memory: VLSI Circuit and Learning Algorithm. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1989, 24, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Gong, M.; He, H. Deep associative neural network for associative memory based on unsupervised representation learning. Neural Netw. 2019, 113, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Chandra, S.; Fiete, I.R. Content Addressable Memory Without Catastrophic Forgetting by Heteroassociation with a Fixed Scaffold. In Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning, Baltimore, MA, USA, 17–23 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, R. Don’t Forget About Associative Memories. The Gradient, 7 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Haron, N.Z.; Hamdioui, S. Why is CMOS scaling coming to an END? In Proceedings of the 3rd International Design and Test Workshop, Monastir, Tunisia, 20–22 December 2008; pp. 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Lent, C.S.; Tougaw, P.D.; Porod, W.; Bernstein, G.H. Quantum cellular automata. Nanotechnology 1993, 4, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.; Farazkish, R.; Navi, K. New quantum dot cellular automata cell arrangements. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2013, 10, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angizi, S.; Alkaldy, E.; Bagherzadeh, N.; Navi, K. Novel robust single layer wire crossing approach for exclusive OR sum of products logic design with quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Low Power Electron. 2014, 10, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigh, M.R.; Mustafa, M.; Ahmad, F. Performance evaluation of efficient XOR structures in quantum-dot cellular automata (QCA). Circuits Syst. 2013, 4, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajitha, D.; Ramanaiah, K.V.; Sumalatha, V. An efficient design of XOR gate and its applications using QCA. I-Manag. J. Electron. Eng. 2015, 5, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; Beigh, M.R. Design and implementation of quantum cellular automata based novel parity generator and checker circuits with minimum complexity and cell count. Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2013, 51, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Khosroshahy, M.B.; Moaiyeri, M.H.; Angizi, S.; Bagherzadeh, N.; Navi, K. Quantum-dot cellular automata circuits with reduced external fixed inputs. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2017, 50, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorhosseini, M.; Hejazi, A.R. A fault-tolerant and efficient XOR structure for modular design of complex QCA circuits. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2017, 27, 1850115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabi, A.M.; Roohi, A.; Khademolhosseini, H.; Sheikhfaal, S.; Angizi, S.; Navi, K.; DeMara, R.F. Towards ultra-efficient QCA reversible circuits. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2017, 49, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safoev, N.; Jeon, J.C. A novel controllable inverter and adder/subtractor in quantum-dot cellular automata using cell interaction based XOR gate. Microelectron. Eng. 2020, 222, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabi, A.M.; Sayedsalehi, S.; Angizi, S.; Navi, K. Efficient QCA exclusive-or and multiplexer circuits based on a nano electronic compatible designing approach. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 463967. [Google Scholar]
- Almatrood, A.; George, A.K.; Singh, H. Low-Power Multiplexer Structures Targeting Efficient QCA Nanotechnology Circuit Designs. Electronics 2021, 10, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.C. Designing nanotechnology QCA–multiplexer using majority function-based NAND for quantum computing. J. Supercomput. 2021, 77, 1562–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedi, S.; Navimpipour, N.J. An efficient structure for designing a nano-scale fault-tolerant 2:1 multiplexer based on quantum-dot cellular automata. Optik 2022, 251, 168409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianpour, M.; Sabbaghi-Nadooshan, R.; Navi, K. A novel design of 8-bit adder/subtractor by quantum-dot cellular automata. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 2014, 80, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidinejad, A.; Selamat, A. Design of first adder/subtractor using quantum-dot cellular automata. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 403, 3392–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safoev, N.; Jeon, J.C. Design of high-performance QCA incrementer/decrementer circuit based on adder/subtractor methodology. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2020, 72, 102927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erniyazov, S.; Jeon, J.C. Carry save adder and carry look ahead adder using inverter chain based coplanar QCA full adder for low energy dissipation. Microelectron. Eng. 2019, 211, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudasama, A.; Sasamal, T.N.; Yadav, J. An efficient design of Vedic multiplier using ripple carry adder in Quantum-dot Cellular Automata. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2018, 65, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safoev, N.; Jeon, J.C. Design and Evaluation of Cell Interaction Based Vedic Multiplier Using Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata. Electronics 2020, 9, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Gorgin, S.; Mohammadi, M. Design of non-restoring divider in quantum-dot cellular automata technology. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2017, 11, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatrood, A.F.; Singh, H. QCA circuit design of n-bit non-restoring binary array divider. J. Eng. 2018, 2018, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I.; Jeon, J.C. Non-Restoring Array Divider Using Optimized CAS Cells Based on Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata with Minimized Latency and Power Dissipation for Quantum Computing. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshan, M.G.; Gholami, M. Novel D Latches and D Flip-Flops with Set and Reset Ability in QCA Nanotechnology Using Minimum Cells and Area. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2018, 57, 3223–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasamal, T.N.; Singh, A.K.; Ghanekar, U. Design of QCA-Based D Flip Flop and Memory Cell Using Rotated Majority Gate, Smart Innovations in Communication and Computational Sciences. Adcances Intell. Syst. Comput. 2019, 670, 233–247. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, J.C. Low Complexity QCA Universal Shift Register Design Using Multiplexer and D Flip-Flop Based on Electronic Correlations. J. Supercomput. 2019, 76, 6438–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilnathan, S.; Kumaravel, S. Power-efficient implementation of pseudo-random number generator using quantum dot cellular automata-based D flip flop. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2020, 85, 106658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaviya, M.; Bavithra, S.; Soorya, M.; Sowndarya, S.; Senthilnathan, S. Design of Linear Feedback Shift Register in Quantum Dot Cellular Automata. Int. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2019, 6, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Roshan, M.G.; Gholami, M. 4-Bit serial shift register with reset ability and 4-bit LFSR in QCA technology using minimum number of cells and delay. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2019, 78, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Khamesinia, M.S. An Efficient Design of Parallel and Serial Shift Registers Based on Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2021, 60, 2400–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I.; Jeon, J.C. Quantum LFSR Structure for Random Number Generation Using QCA Multilayered Shift Register for Cryptographic Purposes. Sensors 2022, 22, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhu, A.; Gupta, S. A Majority Gate Based RAM Cell design with Least Feature Size in QCA. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. 2019, 32, 1150–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, M.; Xiaohu, Z.; Lai, K.K.; Afro, S. A Cost-Aware Efficient RAM Structure Based on Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata Nanotechnology. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2019, 58, 3961–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah-Al-Shafi, M.; Bahar, A.N. A New Structure for Random Access Memory Using Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata. Sens. Lett. 2019, 17, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, A.H.; Alkaldy, E.; Zainal, M.S.; Navi, K.; Nor, D. Optimal design of RAM cell using novel 2:1 multiplexer in QCA technology. Circuit World 2019, 46, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah-Al-Shafi, M.; Ziaur, R. Analysis and modeling of sequential circuits in QCA nano computing: RAM and SISO register study. Solid State Electron. Lett. 2019, 1, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Xie, G.; Cheng, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. An Ultra-Low Cost Multilayer RAM in Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2020, 67, 3397–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadpour, S.S.; Mohammad, M.; Heikalabad, S.R. Efficient designs of quantum-dot cellular automata multiplexer and RAM with physical proof along with power analysis. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 1672–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardinha, L.H.B.; Silva, D.S.; Vieira, M.A.M.; Vieira, L.F.M.; Neto, O.P.V. TCAM/CAM-QCA:(Ternary) Content Addressable Memory using Quantum-dot Cellular Automata. Microelectron. J. 2015, 46, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikalabad, S.R.; Navin, A.H.; Hosseinzadeh, M. Content addressable memory cell in quantum-dot cellular automata. Microelectron. Eng. 2016, 163, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosroshahy, M.B.; Moaiyeri, M.H.; Navi, K. Design and evaluation of a 5-input majority gate-based content-addressable memory cell in quantum-dot cellular automata, In Proceedings of the 19th International Symposium on Computer Architecture and Digital Systems, Kish Island, Iran, 21–22 December 2017.
- Sadoghifar, A.; Heikalabad, S.R. A Content-Addressable Memory structure using quantum cells in nanotechnology with energy dissipation analysis. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2018, 537, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navi, K.; Sayedsalehi, S.; Farazkish, R.; Azghadi, M.R. Five-Input Majority Gate, a New Device for Quantum-Dot Cellular Automata. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2010, 7, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walus, K.; Dysart, T.J.; Jullien, G.A.; Budiman, R.A. QCADesigner: A rapid design and simulation tool for quantum-dot cellular automata. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2004, 3, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.D. Area-time complexity for VLSI. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Pittsburgh, AR, USA, 30 April 1997. [Google Scholar]
- QCADesigner-E. Available online: https://github.com/FSillT/QCADesigner-E (accessed on 9 November 2022).






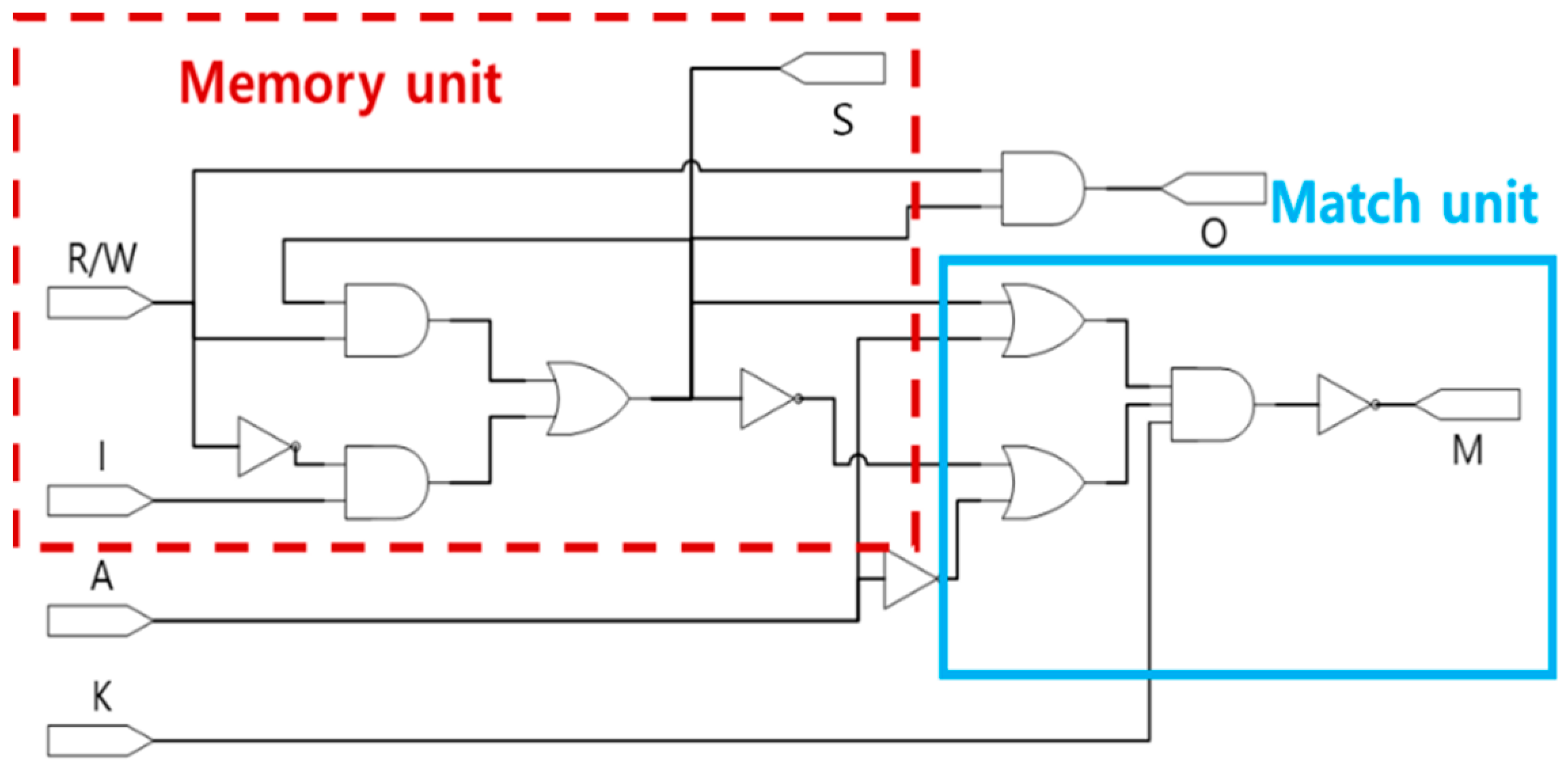










| R/W | I | S(t − 1) | S(t) | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | X | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | X | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | X | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | X | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| K | A | S | M |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | X | X | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Parameters | Bistable Approximation | Coherence Vector |
|---|---|---|
| Cell size | 18 nm | 18 nm |
| Dot diameter | 5 nm | 5 nm |
| Cell separation | 2 nm | 2 nm |
| Layer separation | 11.5 nm | 11.5 nm |
| Clock high | 9.8 × 10−22 J | 9.8 × 10−22 J |
| Clock low | 3.8 × 10−23 J | 3.8 × 10−23 J |
| Clock shift | 0 | 0 |
| Clock amplitude factor | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Relative permittivity | 12.9 | 12.9 |
| Number of samples | 12800 | - |
| Maximum iteration per sample | 100 | |
| Convergence tolerance | 1.0 × 10−3 | - |
| Temperature | - | 1 K |
| Relaxation time | - | 1.0 × 10−15 s |
| Time step | - | 1.0 × 10−16 s |
| Radius of effect | 65 nm | 80 nm |
| Circuit | Cell Count | Area (nm2) | Latency (Clock Cycle) | Cost | Crossover |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [11] | 62 | 70,278 | 1 | 70,278 | Coplanar |
| [12] | 28 | 21,004 | 0.75 | 11,815 | Coplanar |
| [13] | 38 | 38,804 | 1 | 38,804 | Coplanar |
| [14] | 14 | 11,564 | 0.25 | 723 | Coplanar |
| [15] | 17 | 19,044 | 0.5 | 4761 | Coplanar |
| Proposed | 8 | 3364 | 0.25 | 210 | Multilayer |
| Circuit. | Area (nm2) | Latency (Clock Cycle) | Cost | Crossover |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [44] | 368,764 | 5.75 | 1.22 × 107 | Multilayer |
| [45] | 110,644 | 2 | 4.43 × 105 | Coplanar |
| [46] | 110,644 | 2 | 4.43 × 105 | Coplanar |
| [47] | 40,764 | 1.5 | 9.17 × 104 | Coplanar |
| Proposed | 34,444 | 1.5 | 7.75 × 104 | Multilayer |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, J.-C.; Almatrood, A.; Kim, H.-I. Multi-Layered QCA Content-Addressable Memory Cell Using Low-Power Electronic Interaction for AI-Based Data Learning and Retrieval in Quantum Computing Environment. Sensors 2023, 23, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010019
Jeon J-C, Almatrood A, Kim H-I. Multi-Layered QCA Content-Addressable Memory Cell Using Low-Power Electronic Interaction for AI-Based Data Learning and Retrieval in Quantum Computing Environment. Sensors. 2023; 23(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Jun-Cheol, Amjad Almatrood, and Hyun-Il Kim. 2023. "Multi-Layered QCA Content-Addressable Memory Cell Using Low-Power Electronic Interaction for AI-Based Data Learning and Retrieval in Quantum Computing Environment" Sensors 23, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010019
APA StyleJeon, J.-C., Almatrood, A., & Kim, H.-I. (2023). Multi-Layered QCA Content-Addressable Memory Cell Using Low-Power Electronic Interaction for AI-Based Data Learning and Retrieval in Quantum Computing Environment. Sensors, 23(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23010019






