Adaptive Model for Magnetic Particle Mapping Using Magnetoelectric Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Imaging MNPs
Sensing MNPs with Magnetoelectric Sensors
2.2. Modeling the MPM Imaging System
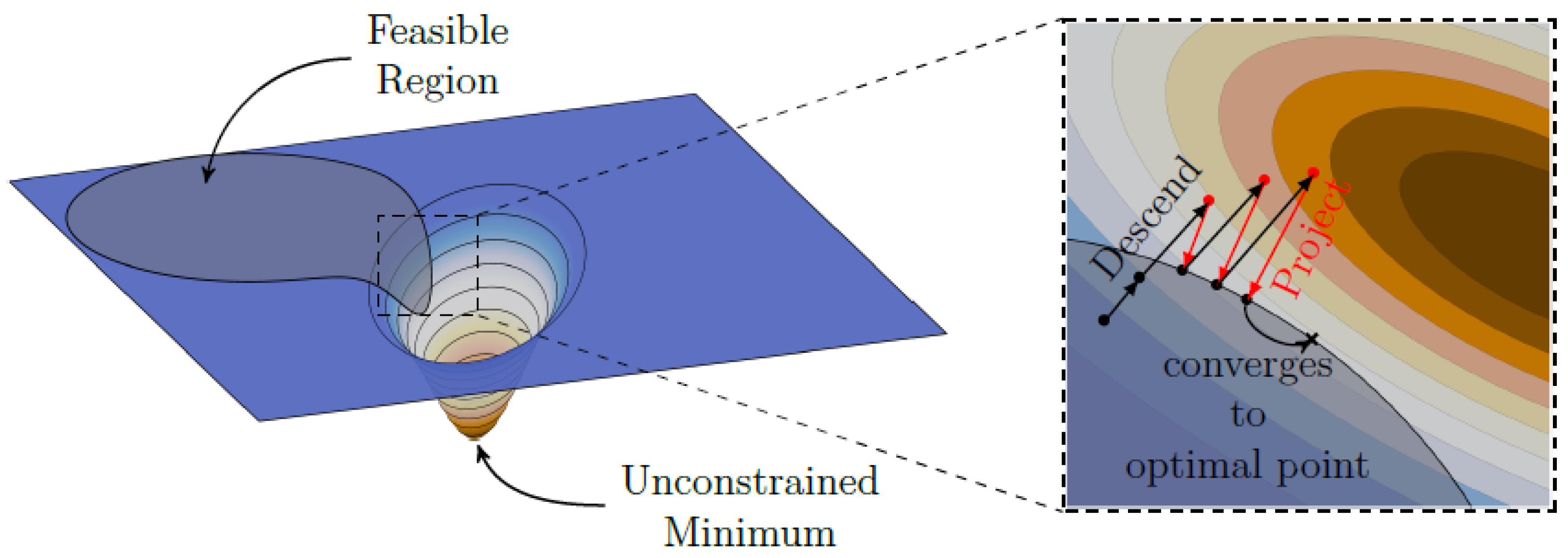
2.3. Inverse Problem
2.4. Algorithm
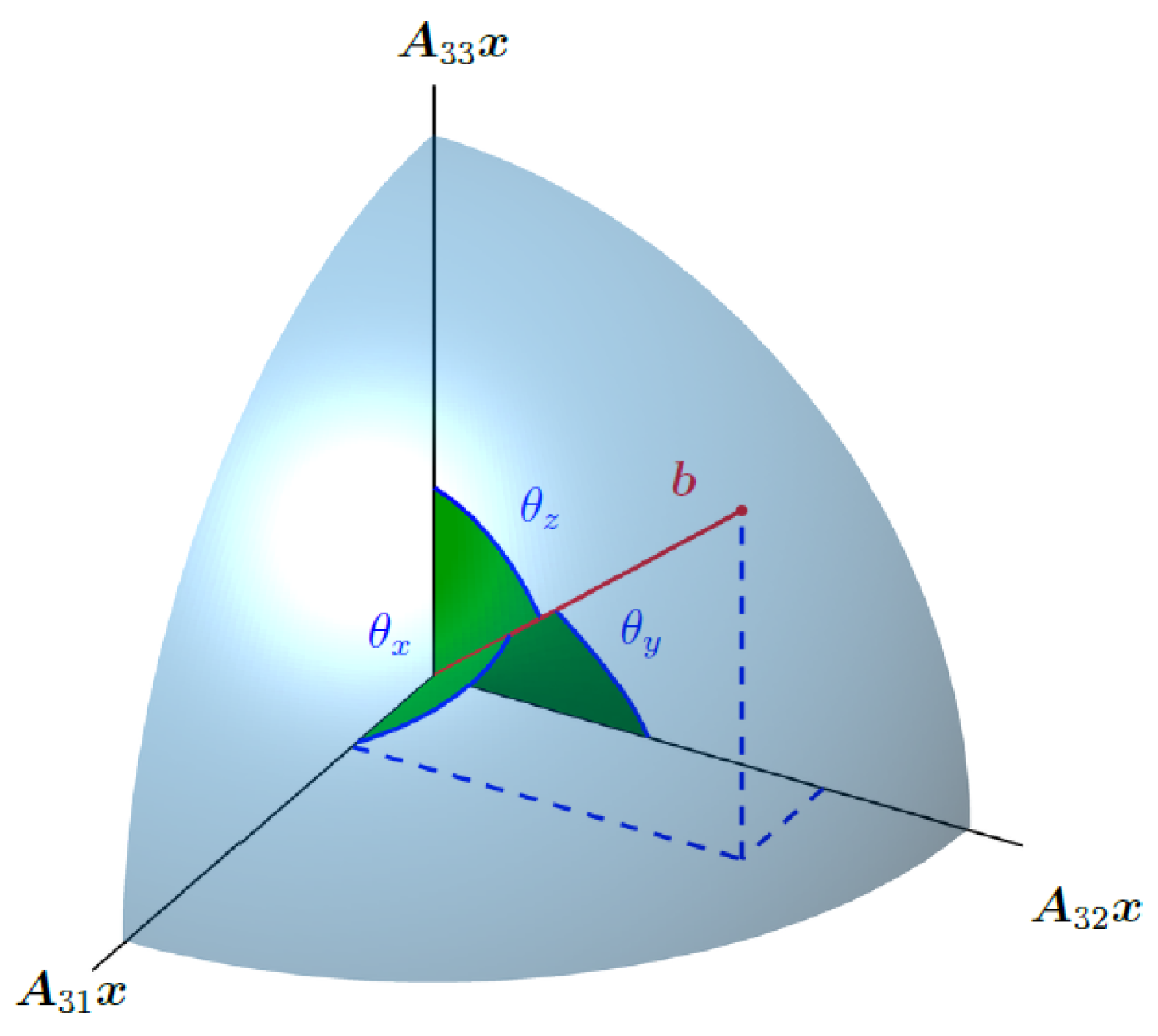
2.4.1. Estimating Sensor Sensitive Axis
| Algorithm 1 Model Estimation For Sensitive Axis |
|
2.4.2. Estimating Sensor Sensitive Axis and Magnetic Moment Direction
| Algorithm 2 Model Estimation |
|
2.4.3. Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
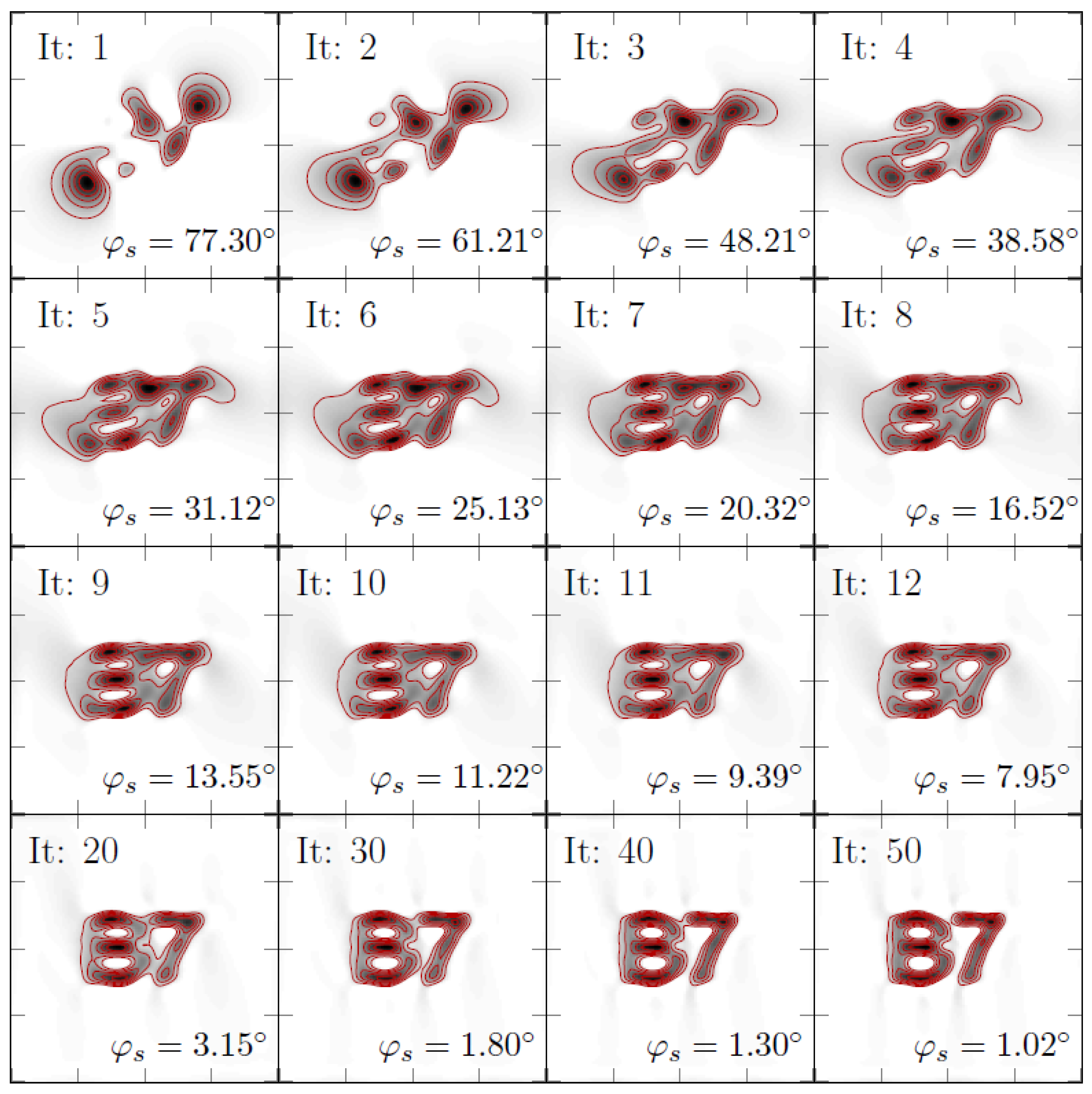
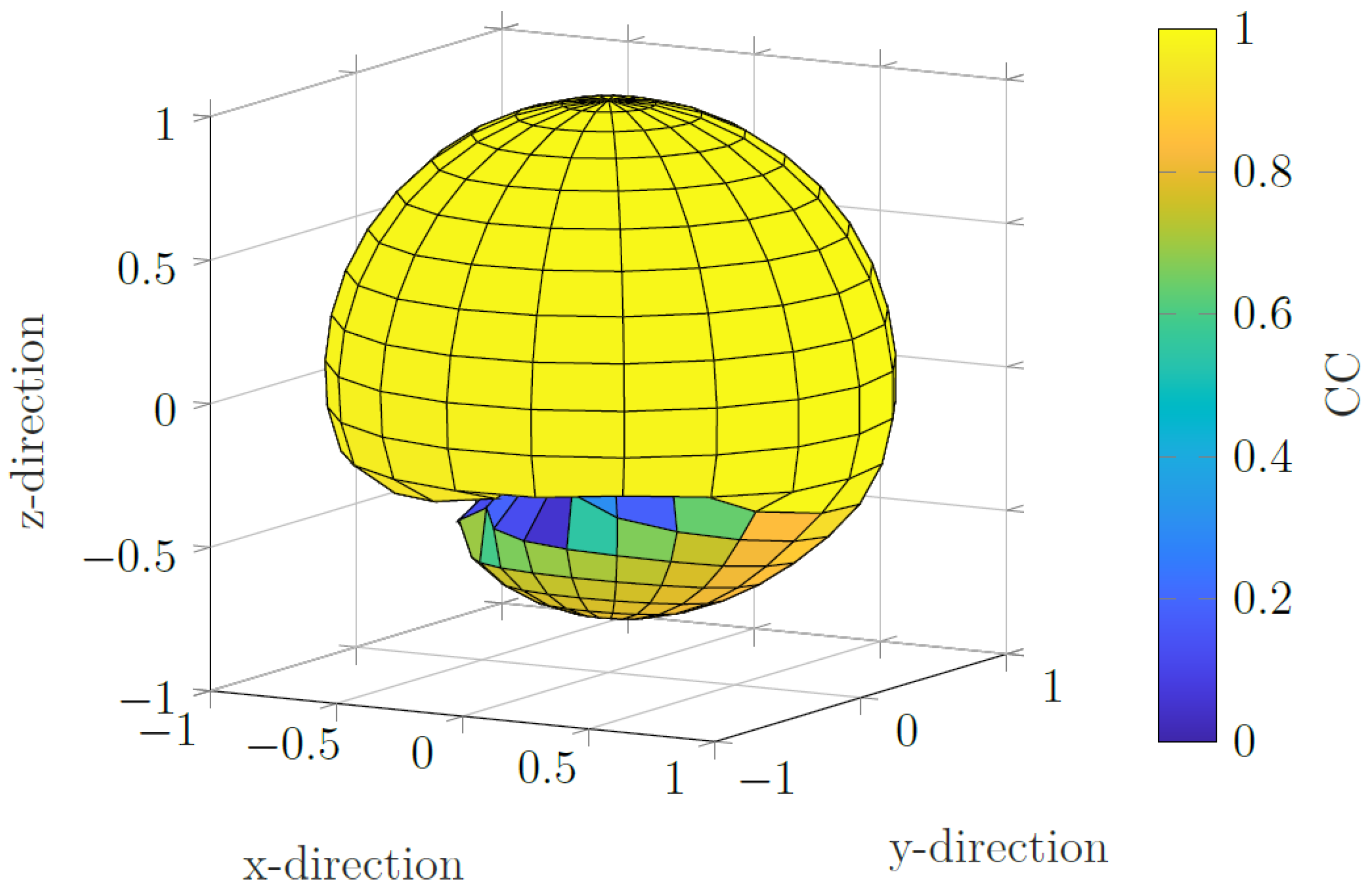
3.1. Simulation
3.1.1. Case I
3.1.2. Case II
3.2. Experiment
Reconstruction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPM | Magnetic Particle Mapping; |
| MNP | Magnetic Nanoparticle; |
| PSF | Point-Spread-Function. |
Appendix A. On Notion of Resolution in Inverse Problems
- The columns can be understood as the spatial spread of a delta-like input, i.e., the Point-Spread Function.
- The rows can be understood as the convolution of the MNP distribution with the Point-Spread Function. It is the (scaled) averaging function of the system.
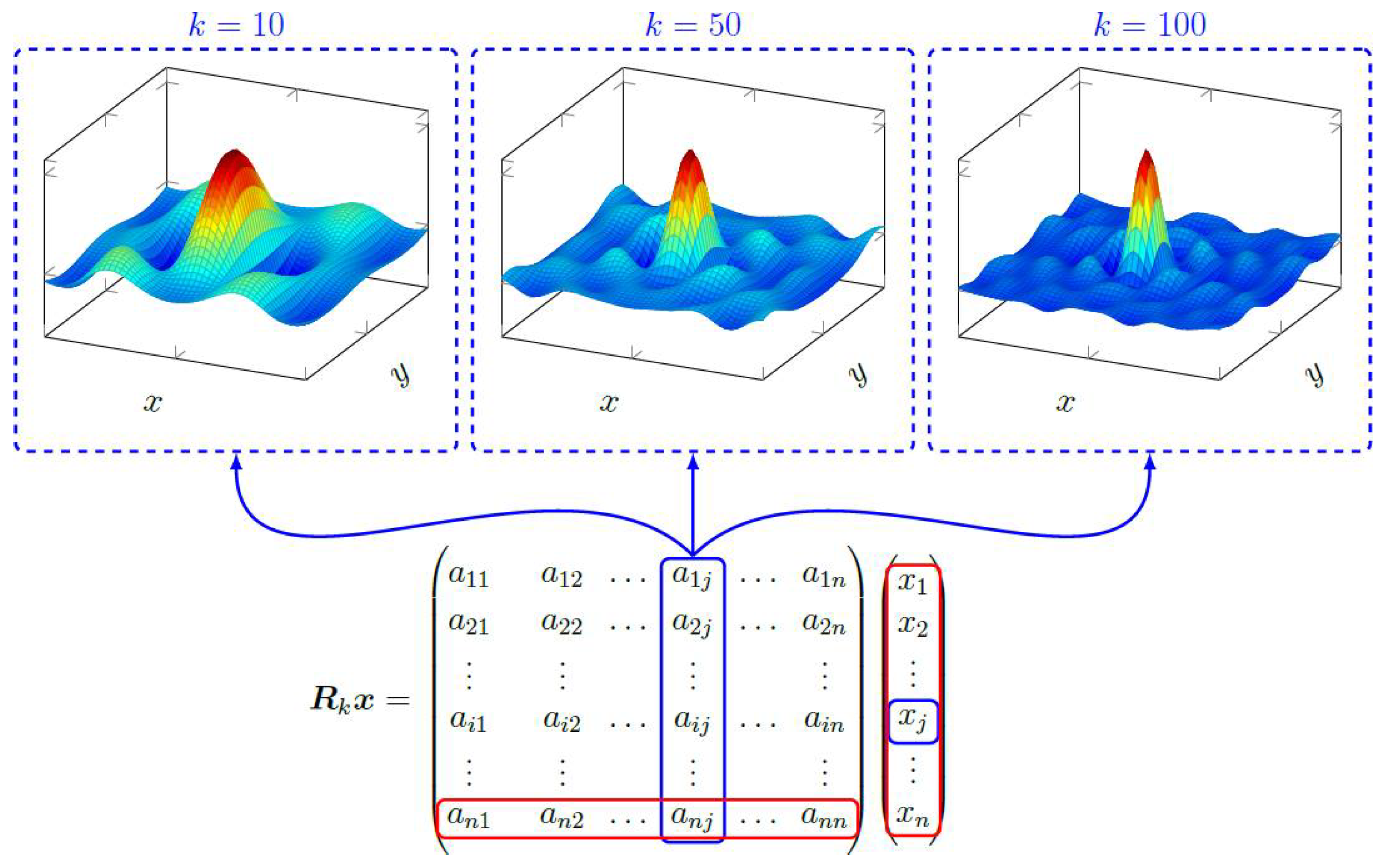
Appendix B. Estimation of Magnetic Content
References
- Hansen, P.C. Deblurring Images: Matrices, Spectra and Filtering. J. Electron. Imaging 2007, 17, 019901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hansen, P.C. Discrete Inverse Problems: Insight and Algorithms; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Galatsanos, N.P.; Stark, H. Projection-based blind deconvolution. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1994, 11, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundur, D.; Hatzinakos, D. Blind image deconvolution revisited. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1996, 13, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Weiss, Y.; Durand, F.; Freeman, W.T. Understanding and evaluating blind deconvolution algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2009, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1964–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, R.M.; Zabel, S.; Galka, A.; Lukat, N.; Wagner, J.M.; Kirchhof, C.; Quandt, E.; McCord, J.; Selhuber-Unkel, C.; Siniatchkin, M.; et al. Magnetic particle mapping using magnetoelectric sensors as an imaging modality. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durdaut, P. Ausleseverfahren und Rauschmodellierung für Magnetoelektrische und Magnetoelastische Sensorsysteme. Ph.D. Thesis, Christian-Abrechts-Universität zu Kiel, Kiel, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weizenecker, J.; Gleich, B.; Rahmer, J.; Dahnke, H.; Borgert, J. Three-dimensional real-time in vivo magnetic particle imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2009, 54, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, T.; Buzug, T.M. Magnetic Particle Imaging: An Introduction to Imaging Principles and Scanner Instrumentation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 1–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeser, M.; Knopp, T.; Szwargulski, P.; Friedrich, T.; Von Gladiss, A.; Kaul, M.; Krishnan, K.M.; Ittrich, H.; Adam, G.; Buzug, T.M. Towards Picogram Detection of Superparamagnetic Iron-Oxide Particles Using a Gradiometric Receive Coil. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Schilling, M.; Ludwig, F. Spatial and temperature resolutions of magnetic nanoparticle temperature imaging with a scanning magnetic particle spectrometer. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Schilling, M.; Ludwig, F. Magnetic nanoparticle temperature imaging with a scanning magnetic particle spectrometer. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2018, 29, 115903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Schilling, M.; Ludwig, F. Excitation frequency dependence of temperature resolution in magnetic nanoparticle temperature imaging with a scanning magnetic particle spectrometer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 471, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Schilling, M.; Ludwig, F. Magnetic nanoparticle-based biomolecule imaging with a scanning magnetic particle spectrometer. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 225101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebl, M.; Steinhoff, U.; Wiekhorst, F.; Haueisen, J.; Trahms, L. Quantitative imaging of magnetic nanoparticles by magnetorelaxometry with multiple excitation coils. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, 6607–6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rühmer, D.P. Zweidimensionale Scanning-Magnetrelaxometrie mit Fluxgate-Sensoren. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Braunschweig, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaufenthaler, A.; Schier, P.; Middelmann, T.; Liebl, M.; Wiekhorst, F.; Baumgarten, D. Quantitative 2D magnetorelaxometry imaging of magnetic nanoparticles using optically pumped magnetometers. Sensors 2020, 20, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schier, P.; Liebl, M.; Steinhoff, U.; Handler, M.; Wiekhorst, F.; Baumgarten, D. Optimizing Excitation Coil Currents for Advanced Magnetorelaxometry Imaging. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 2020, 62, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Feldman, M.D.; Kim, J.; Condit, C.; Emelianov, S.; Milner, T.E. Detection of magnetic nanoparticles in tissue using magneto-motive ultrasound. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4183–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; He, B. Magnetoacoustic imaging of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles embedded in biological tissues with microsecond magnetic stimulation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrmohammadi, M.; Qu, M.; Ma, L.L.; Romanovicz, D.K.; Johnston, K.P.; Sokolov, K.V.; Emelianov, S.Y. Pulsed magneto-motive ultrasound imaging to detect intracellular accumulation of magnetic nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 415105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepúlveda, N.G.; Thomas, I.M.; Wikswo, J.P. Magnetic Susceptibility Tomography for Three-Dimensional Imaging of Diamagnetic and Paramagnetic Objectcts. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1994, 30, 5062–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficko, B.W.; Nadar, P.M.; Hoopes, P.J.; Diamond, S.G. Development of a magnetic nanoparticle susceptibility magnitude imaging array. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, 1047–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficko, B.W.; Nadar, P.M.; Diamond, S.G. Spectroscopic AC susceptibility imaging (sASI) of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 375, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ficko, B.W.; Giacometti, P.; Diamond, S.G. Extended arrays for nonlinear susceptibility magnitude imaging. Biomed. Tech. 2015, 60, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Durme, R.; Coene, A.; Crevecoeur, G.; Dupre, L. Model-based optimal design of a magnetic nanoparticle tomographic imaging setup. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; pp. 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorulmaz, O.; Demirel, O.B.; Çukur, T.; Saritas, E.U.; Çetin, A.E. A Blind Deconvolution Technique Based on Projection Onto Convex Sets for Magnetic Particle Imaging. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.07506. [Google Scholar]
- Huong Giang, D.T.; Dang, D.X.; Toan, N.X.; Tuan, N.V.; Phung, A.T.; Duc, N.H. Distance magnetic nanoparticle detection using a magnetoelectric sensor for clinical interventions. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Qian, X.; Lu, M.C.; Mei, L.; Rupprecht, S.; Yang, Q.X.; Zhang, Q.M. A Room Temperature Ultrasensitive Magnetoelectric Susceptometer for Quantitative Tissue Iron Detection. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukat, N.; Friedrich, R.M.; Spetzler, B.; Kirchhof, C.; Arndt, C.; Thormählen, L.; Faupel, F.; Selhuber-Unkel, C. Mapping of magnetic nanoparticles and cells using thin film magnetoelectric sensors based on the delta-E effect. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 309, 112023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, G.M. A Primer on Integral Equations of the First Kind; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, G.; Potthast, R. Inverse Modeling: An Introduction to the Theory and Methods of Inverse Problems and Data Assimilation; Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolduc, E.; Knee, G.C.; Gauger, E.M.; Leach, J. Projected gradient descent algorithms for quantum state tomography. Npj Quantum Inf. 2017, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, E.; Kirchhof, C.; Hrkac, V.; Kienle, L.; Jahns, R.; Knöchel, R.; Quandt, E.; Meyners, D. Biasing of magnetoelectric composites. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Peralta Menendez, R.G.; Gonzalez Andino, S.L.; Lütkenhöner, B. Figures of merit to compare distributed linear inverse solutions. Brain Topogr. 1996, 9, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M. A simple method for determining the spatial resolution of a general inverse problem. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.S.; Donoho, D.L.; Saunders, M.A. Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM Rev. 2001, 43, 129–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, M.; Boccacci, P. Introduction to Inverse Problems in Imaging; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangerth, W. A Notion of Resolution in Inverse Problems. Computational Science Stack Exchange. Available online: https://scicomp.stackexchange.com/q/36537 (accessed on 18 December 2020).






| s Known | s Unknown | |
|---|---|---|
| known | Case 0 | Case I |
| unknown | Case I | Case II |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Friedrich, R.-M.; Faupel, F. Adaptive Model for Magnetic Particle Mapping Using Magnetoelectric Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030894
Friedrich R-M, Faupel F. Adaptive Model for Magnetic Particle Mapping Using Magnetoelectric Sensors. Sensors. 2022; 22(3):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030894
Chicago/Turabian StyleFriedrich, Ron-Marco, and Franz Faupel. 2022. "Adaptive Model for Magnetic Particle Mapping Using Magnetoelectric Sensors" Sensors 22, no. 3: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030894
APA StyleFriedrich, R.-M., & Faupel, F. (2022). Adaptive Model for Magnetic Particle Mapping Using Magnetoelectric Sensors. Sensors, 22(3), 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22030894







