An Experimental Study on Combustion and Cycle-by-Cycle Variations of an N-Butanol Engine with Hydrogen Direct Injection under Lean Burn Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
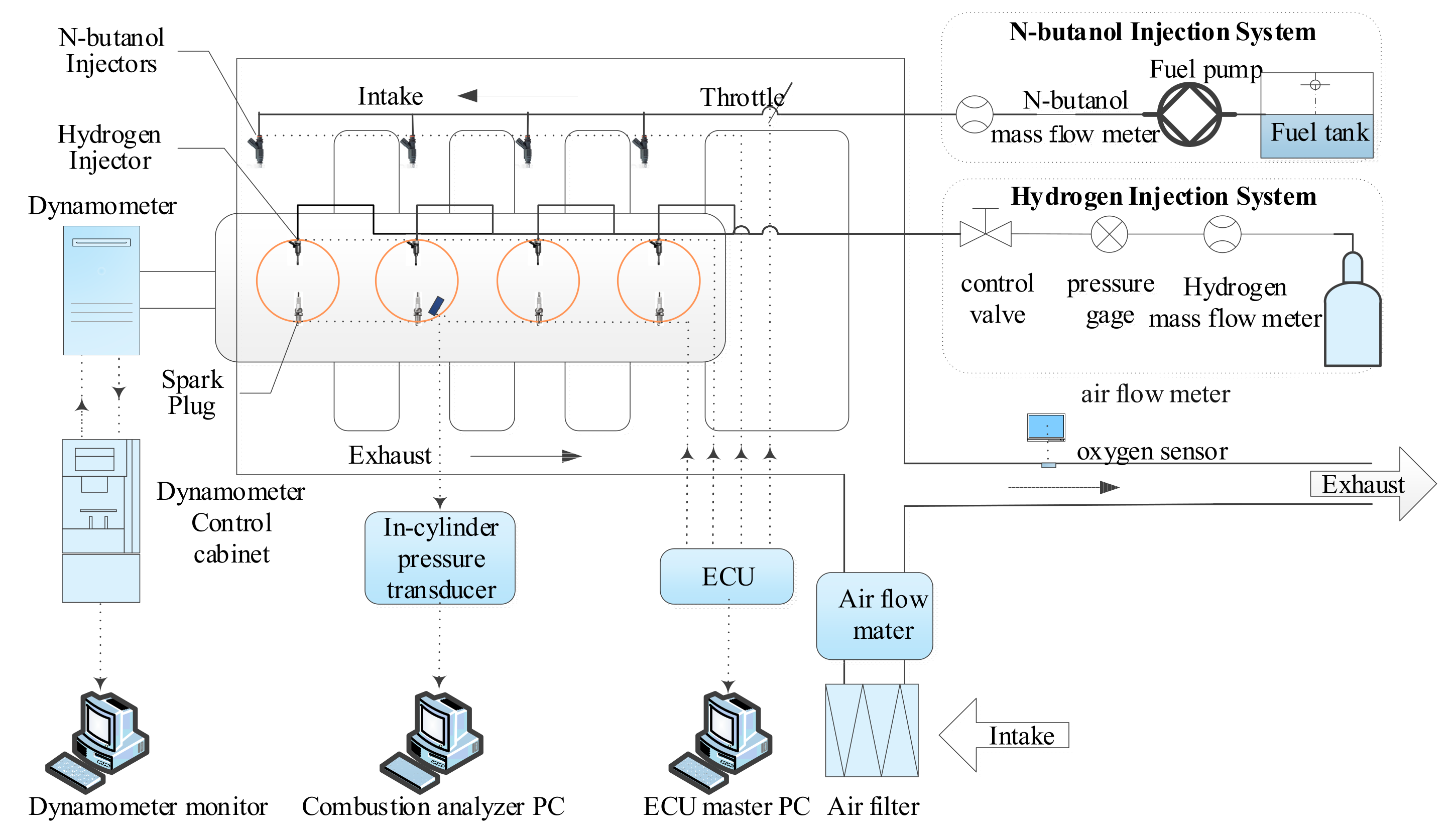
2. Experimental Apparatus and Procedures
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Definition of Correlated Parameters
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. MBT Spark Timings
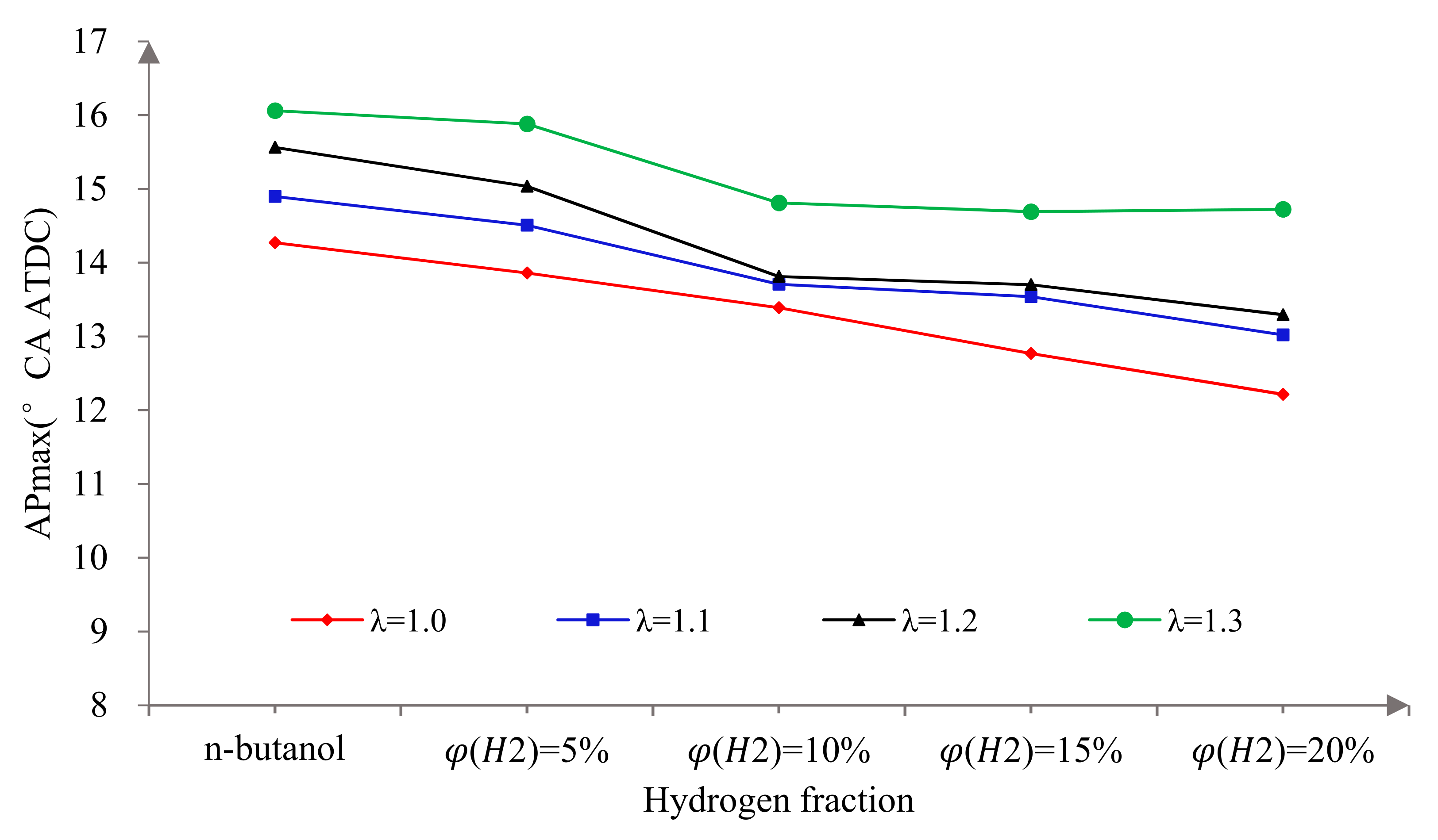
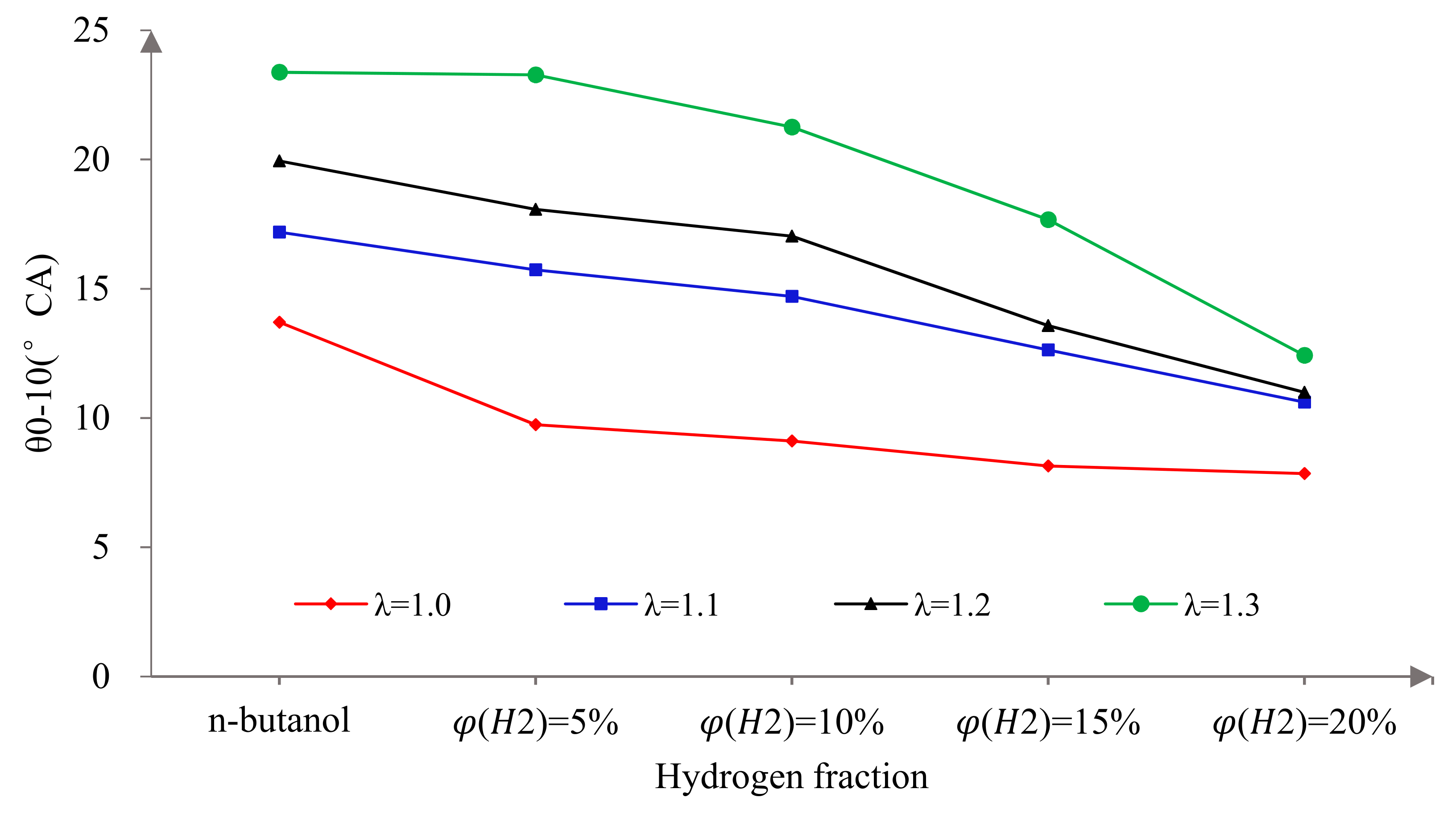
3.2. Combustion Characteristics
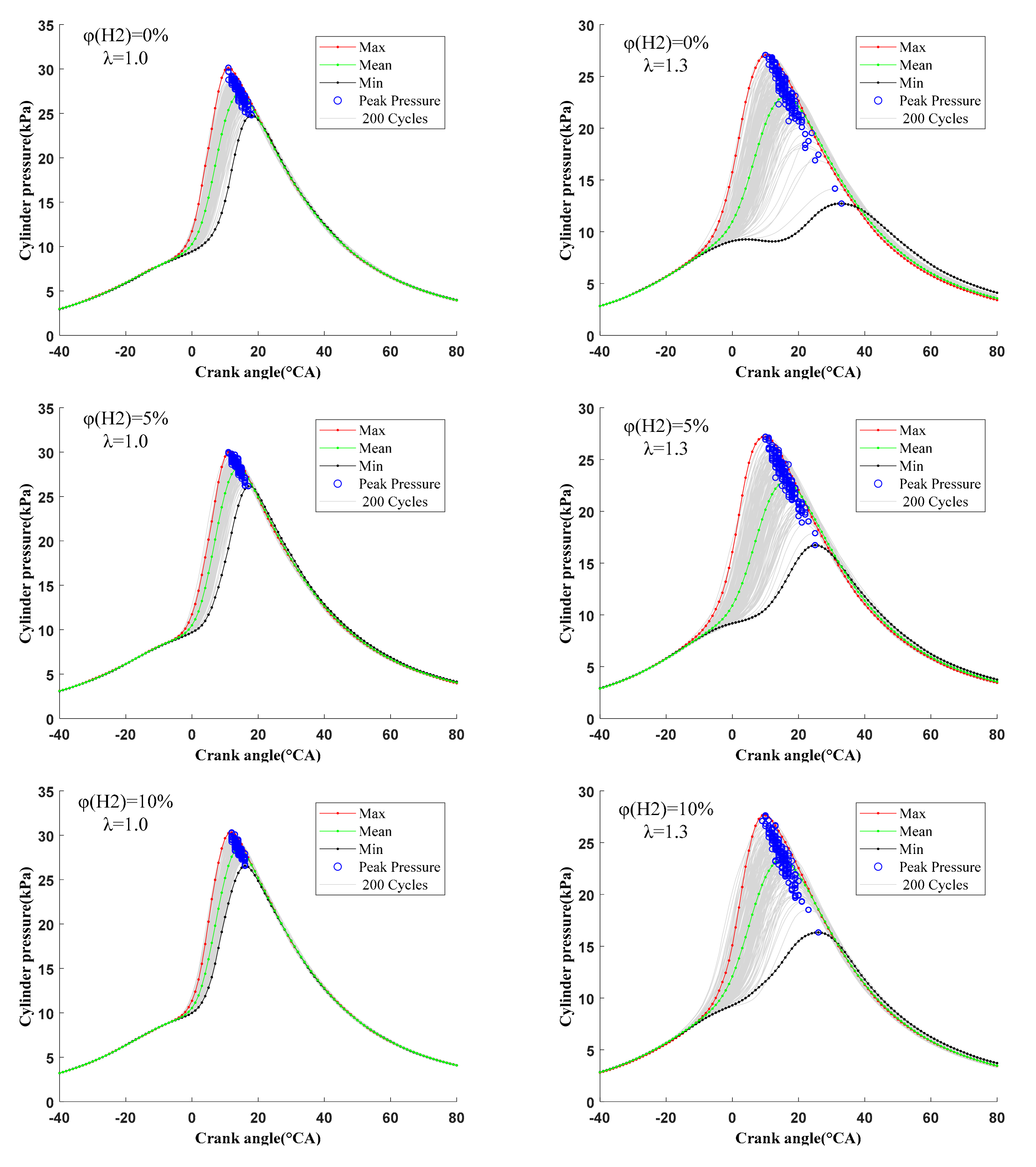
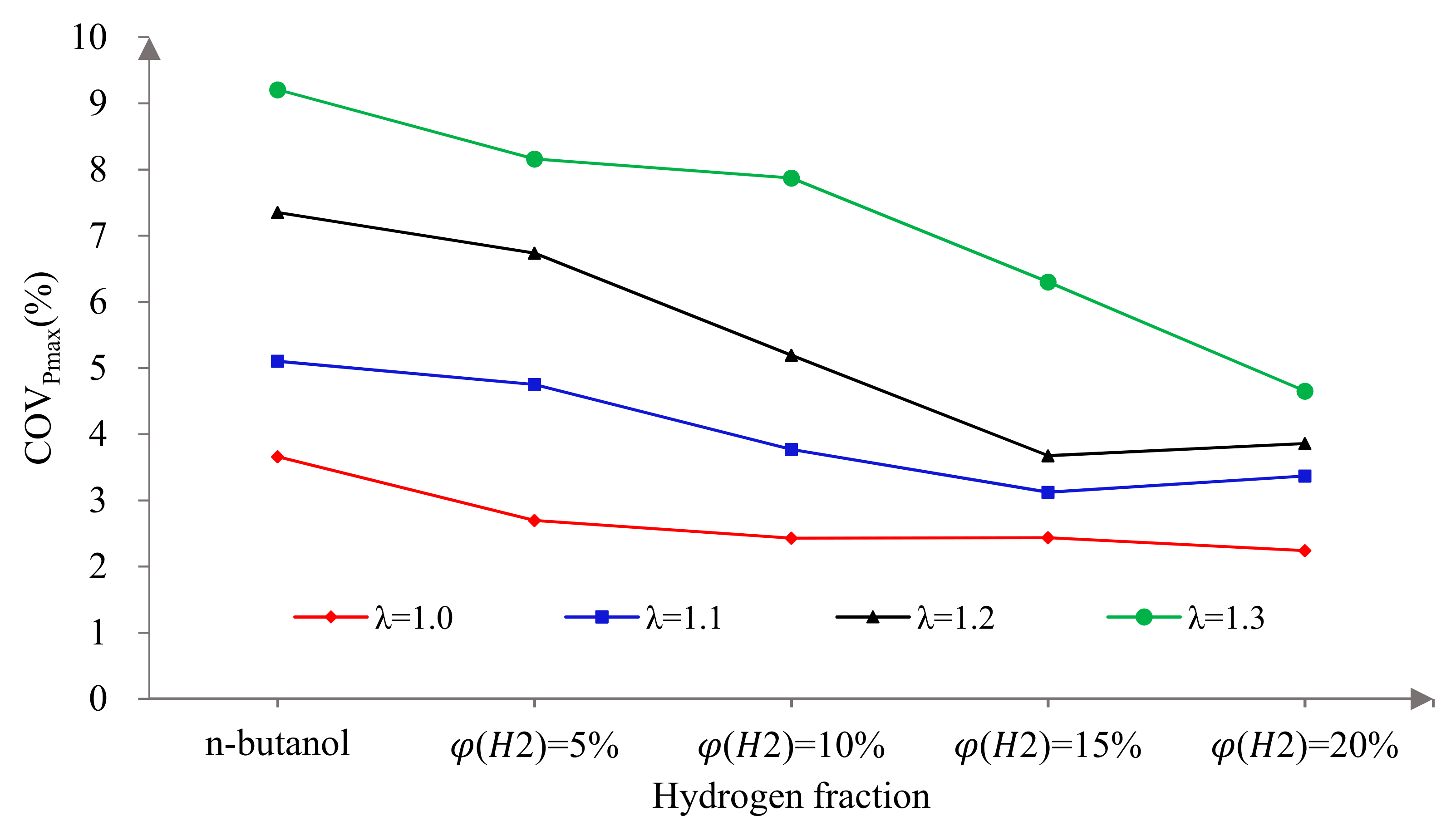
3.3. Cycle-by-Cycle Variation
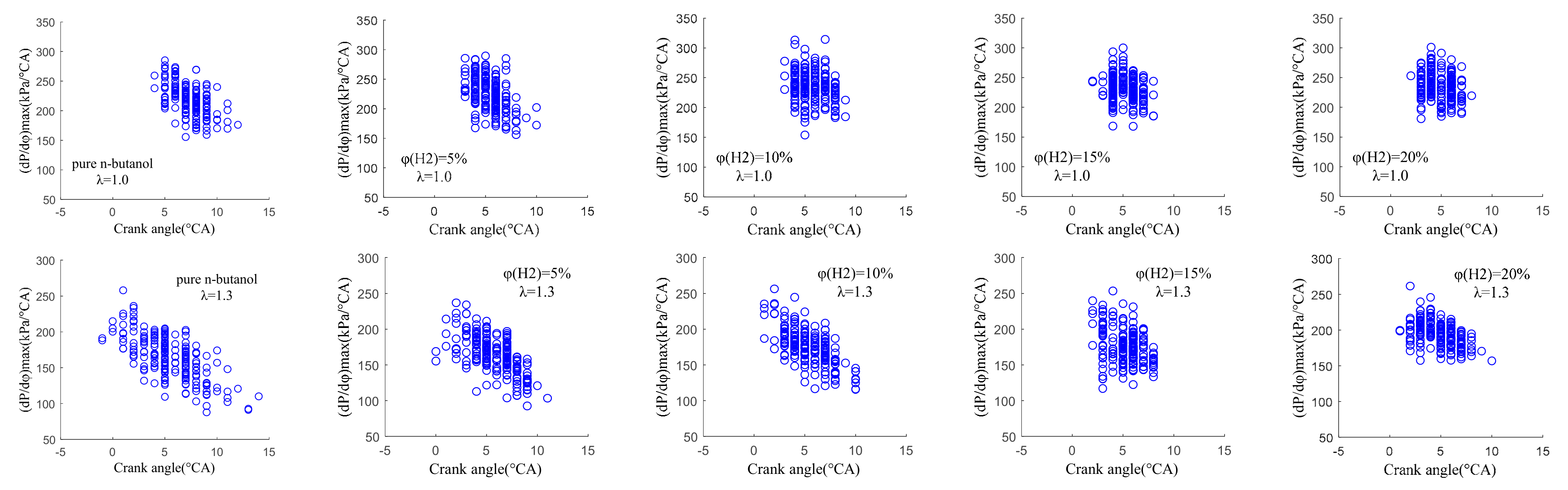
3.3.1. Cycle-by-Cycle Variation of Derived Pressure
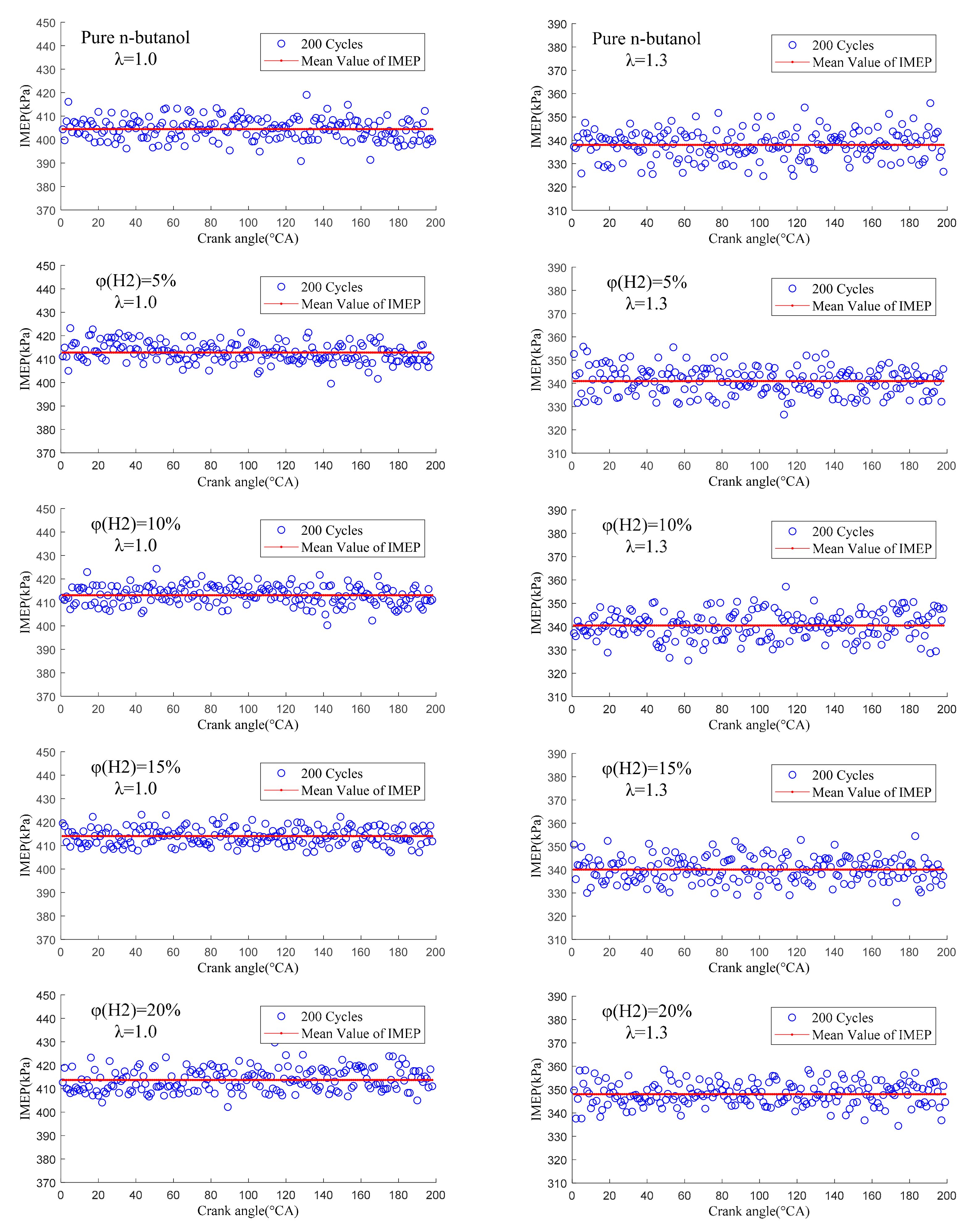
3.3.2. Cycle-by-Cycle Variation of Indicated Mean Effective
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
| SI | Spark ignition |
| MAP | Intake manifold absolute pressure |
| λ | Excess air ratio |
| φ(𝐻2) | Hydrogen fraction |
| MBT | Minimum ignition advance for best torque |
| TDC | Top dead center |
| ATDC | After top dead center |
| BTDC | Before top dead center |
| IMEP | Indicated mean effective pressure |
| Pmax | Peak in-cylinder pressure |
| APmax | Position of Pmax |
| (dP/dφ)max | Maximum rate of pressure rise |
| θ0–10 | Flame development duration |
| θ10–90 | Rapid combustion duration |
| COV | Coefficient of variance |
References
- Wierzbicki, S.; Duda, K.; Mikulski, M. Renewable Fuels for Internal Combustion Engines. Energies 2021, 14, 7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, G.B.; de Melo, T.C.C.; da Silva, K.M. GDI flex fuel engine: Influence of different fuels on the performance. Int. J. Engine Res. 2021, 22, 3407–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W. Naphtha as a Fuel for Internal Combustion Engines. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2021, 22, 1119–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Qi, W.; Wang, X.; Su, X. Potentials of EGR and lean mixture for improving fuel consumption and reducing the emissions of high-proportion butanol-gasoline engines at light load. Fuel 2020, 266, 116959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, S.; Ibrahim, M.M. Comparison of the hydrogen powered homogeneous charge compression ignition mode with multiple injection schedules and the dual fuel mode using a twin-cylinder engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Yao, M.; Liu, H.; Lee, C.-f.F.; Ji, J. Progress in the production and application of n-butanol as a biofuel. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 4080–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, H.L.; Srna, A.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Kook, S.; Taylor, R.A.; Yeoh, G.H.; Medwell, P.R.; Chan, Q.N. A Review of Hydrogen Direct Injection for Internal Combustion Engines: Towards Carbon-Free Combustion. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veza, I.; Said, M.F.M.; Latiff, Z.A. Improved Performance, Combustion and Emissions of SI Engine Fuelled with Butanol: A Review. Int. J. Automot. Mech. Eng. 2020, 17, 7648–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, S.; Pereira, R.; Wahl, S.A.; Rocha, I. Metabolic engineering strategies for butanol production in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 2571–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. Metabolic engineering for the production of butanol, a potential advanced biofuel, from renewable resources. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 2283–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.H.T.; Wu, X.; Lu, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.-T. Engineering Clostridium cellulovorans for highly selective n-butanol production from cellulose in consolidated bioprocessing. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021, 118, 2703–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, T.; Su, G.; He, J. Enhanced direct fermentation from food waste to butanol and hydrogen by an amylolytic Clostridium. Renew. Energy 2020, 153, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanti, I.; Krishna, M.M.; Chandra, M.R. Butanol blend reduces pollutants in spark ignition engine. Int. J. Mech. Prod. Eng. Res. Dev. 2020, 10, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Nour, M. Flash boiling combustion of isomeric butanol and gasoline surrogate blends using constant volume spray chamber and GDI optical engine. Fuel 2021, 286, 119328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelbach, C.A.; Tomlin, A.S. Influence of Iso-Butanol Blending with a Reference Gasoline and Its Surrogate on Spark-Ignition Engine Performance. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 19665–19688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Liu, D.; Li, X. Knock analysis of bio-butanol in TISI engine based on chemical reaction kinetics. Energy 2022, 239, 122190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanapal, B.; Pillai, T.M.; Chellappa, B.; Sathyamurthy, R. Effect of Iso-Butanol Blends in Spark Ignition Engine as an Alternative. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. E 2021, 102, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.A.; Yahyah, H.; Farooq, A.A.; Buyondo, K.A.; Olupot, P.W.; Nura, S.S.; Sanni, T.; Hannington, T.; Ukundimana, Z.; Hassan, A.S.; et al. Characteristics of ultrafine particle emission from light-vehicle engine at city transport-speed using after-treatment device fueled with n-butanol-hydrogen blend. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2021, 3, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Guo, Z.; He, L.; Dong, W.; Sun, P.; Shi, W.; Du, Y.; He, F. Effect of gasoline/n-butanol blends on gaseous and particle emissions from an SI direct injection engine. Fuel 2018, 229, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Ding, Y.; Du, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zuo, X. Experimental comparative study on combustion and particle emission of n-butanol and gasoline adopting different injection approaches in a spark engine equipped with dual-injection system. Fuel 2018, 211, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristian, S.; Constantin, P.; Niculae, N.; Alexandru, C.; Cristian, N.; Rareş, G. The study of the spark ignition engine operation at fuelling with n-butanol-gasoline blends. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 180, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Y, L.; W, H.; Z, W.; A1, Y.Q.C.; Z, L.; L, X. Experimental study on the application of n-butanol and n-butanol/kerosene blends as fuel for spark ignition aviation piston engine. Fuel 2021, 304, 121362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ji, C.; Shi, C.; Ge, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, J. Development of cyclic variation prediction model of the gasoline and n-butanol rotary engines with hydrogen enrichment. Fuel 2021, 299, 120891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, N.S.; Yu, X.; Leblanc, S.; Zheng, M.; Ting, D.; Li, T. Combustion Characterization of Neat n-Butanol in an SI Engine; SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Yu, X.; He, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Study on combustion and emission characteristics of a n-butanol engine with hydrogen direct injection under lean burn conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 7550–7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Ji, C.; Wang, S.; Cong, X.; Shi, L. Enhancing idle performance of an n-butanol rotary engine by hydrogen enrichment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 6434–6442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Ji, C.; Wang, S.; Cong, X.; Shi, L.; Yang, J. Investigation on combustion and emissions characteristics of a hydrogen-blended n-butanol rotary engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 26142–26151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Ji, C.; Wang, S.; Cong, X.; Shi, L. Research on performance of a hydrogen/n-butanol rotary engine at idling and varied excess air ratios. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 162, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Ji, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Yang, J. Optimizing the idle performance of an n-butanol fueled Wankel rotary engine by hydrogen addition. Fuel 2020, 288, 119614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ji, C.; Wang, S. Investigation on the lean combustion performance of a hydrogen-enriched n-butanol engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 136, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Yu, X.; Shi, W.; Huang, S.; Li, G.; Guo, Z.; He, F. Numerical research on effect of hydrogen blending fractions on idling performance of an n-butanol ignition engine with hydrogen direct injection. Fuel 2019, 258, 116082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, D.; Qi, W. Comparative study on air dilution and hydrogen-enriched air dilution employed in a SI engine fueled with iso-butanol-gasoline. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 10895–10905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raviteja, S.; Kumar, G.N. Effect of hydrogen addition on the performance and emission parameters of an SI engine fueled with butanol blends at stoichiometric conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 9563–9569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Liu, D. Effects of hydrogen additions on premixed rich flames of four butanol isomers. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 3833–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Ji, C.; Wang, S.; Shi, L.; Cong, X. Effect of ignition timing on performance of a hydrogen-enriched n-butanol rotary engine at lean condition. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 161, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Yu, X.; Shi, W. Effect of exhaust gas recirculation and hydrogen direct injection on combustion and emission characteristics of a n-butanol SI engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 17961–17974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Yin, P. Effect of hydrogen peroxide additive on the combustion and emission characteristics of an n-butanol homogeneous charge compression ignition engine. Energy 2019, 169, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, L.; Li, R.; Zuo, X.; Sun, Y. Effect of addition of hydrogen and exhaust gas recirculation on characteristics of hydrogen gasoline engine. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 8288–8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Yu, X.; Sang, T.; Chen, Z.; Cui, S.; Xu, M.; Yu, L. Experimental study on combustion and emissions of an SI engine with gasoline port injection and acetone-butanol-ethanol (ABE) direct injection. Fuel 2021, 284, 119037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, S.K.; Rout, A.K.; Sahoo, N. Effect of Compression Ratio on Thermal Efficiency and Cycle-by-Cycle Variation of a Biogas-Fueled SI Engine(Conference Paper); Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 29, pp. 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzer, C.; Pasternak, M.; Seidel, L.; Ravet, F.; Mauss, F. Computationally efficient prediction of cycle-to-cycle variations in spark-ignition engines. Int. J. Engine Res. 2020, 21, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wu, H.; Du, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, L.; Niu, R. Research on cycle-by-cycle variations of an SI engine with hydrogen direct injection under lean burn conditions. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 109, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Methanol | Ethanol | Butanol | Gasoline | Hydrogen | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CH3OH | C2H5OH | C4H9OH | C5–C12 | H2 |
| Cetane number | 3 | 8 | 25 | 5–25 | - |
| Research octane number | 111 | 108 | 96 | 80–99 | - |
| Density, gL−1 | 792 c | 789 c | 808 c | 720–780 c | 0.089 a,b |
| Viscosity (Pa·s) at 20 °C | 0.61 | 1.2 | 3.64 | 0.28–0.59 | - |
| Lower caloric value, MJkg−1 | 19.9 | 26.8 | 33.1 | 42.7 | 119.7 |
| Latent heat of evaporation, MJkg−1 (25 °C) | 1.11 | 0.9 | 0.58 | 0.38–0.50 | - |
| Saturated vapor pressure, kPa (38 °C) | 31.69 | 13.8 | 2.27 | 31.01 | - |
| Stoichiometric air–fuel ratio | 6.49 | 9.02 | 11.21 | 14.7 | 34.5 |
| Flammability limits (Vol%) | 6.0–36.5 | 4.3–19.0 | 1.4–11.2 | 0.6–8.0 | 4.0–76.0 |
| Oxygen content (Mass%) | 50 | 34.8 | 21.6 | - | - |
| Laminar flame speed, cms−1 (25 °C) | 68 | 63– | 48–53 | 37–43 | 185 |
| Autoignition temperature, °C | 470 | 434 | 385 | ~300 | 585 |
| Minimum ignition energy, mJ | 0.215 | 0.63– | - | 0.24 | 0.02 |
| Engine Parameter | Parameter Values |
|---|---|
| Engine Type | four cylinders; dual injection; spark-ignited |
| Compression ratio | 9.6:1 |
| Bore × Stroke, mm | 82.5 × 92.8 |
| Displaced volume, L | 1.984 |
| Maximum power, kW | 132 (5000–6000 rpm) |
| Maximum torque, N·m | 320 (1600–4000 rpm) |
| Parameter | Manufacturer | Range | Precision | Production Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Luoyang Nanfeng Electromechanic Equipment Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | 0~6000 rpm | ≤±1 r/min | CW160 |
| Torque | Luoyang Nanfeng Electromechanic Equipment Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | 0~600 N·m | ≤±0.28 N·m | CW160 |
| Excess air ratio | ETAS Engineering TOOLS | 0.700~32.767 | ≤±1.5% | LAMBDA LA4 |
| N-butanol mass flow meter | ONO SOKKI (Onokazu detector) | 0.2~82 kg/h | ±0.01 g/s | Ono Sokki DF-2420 |
| Hydrogen mass flow meter | Beijing SINCERITY | 0.2~1 kg/h | ±0.2% | DMF-1-1AB |
| Crank angle | Kistler Instrument China Ltd. | 0~720° | ≤±0.5° | Kistler-2614B4 |
| Cylinder pressure | DEWETRON GmbH. | 0~20 MPa | ≤±0.5% | AVL-GU13Z-24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, W.; Yu, X.; Shi, W.; Chen, Z.; Liu, H.; Yu, H.; Xing, X.; Xu, T. An Experimental Study on Combustion and Cycle-by-Cycle Variations of an N-Butanol Engine with Hydrogen Direct Injection under Lean Burn Conditions. Sensors 2022, 22, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031229
Shang W, Yu X, Shi W, Chen Z, Liu H, Yu H, Xing X, Xu T. An Experimental Study on Combustion and Cycle-by-Cycle Variations of an N-Butanol Engine with Hydrogen Direct Injection under Lean Burn Conditions. Sensors. 2022; 22(3):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031229
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Weiwei, Xiumin Yu, Weibo Shi, Zhao Chen, Huiying Liu, He Yu, Xiaoxue Xing, and Tingfa Xu. 2022. "An Experimental Study on Combustion and Cycle-by-Cycle Variations of an N-Butanol Engine with Hydrogen Direct Injection under Lean Burn Conditions" Sensors 22, no. 3: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031229
APA StyleShang, W., Yu, X., Shi, W., Chen, Z., Liu, H., Yu, H., Xing, X., & Xu, T. (2022). An Experimental Study on Combustion and Cycle-by-Cycle Variations of an N-Butanol Engine with Hydrogen Direct Injection under Lean Burn Conditions. Sensors, 22(3), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22031229





