Tuning the Surface Functionality of Fe3O4 for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Heavy Metal Ions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation
2.2. Chemicals and Materials
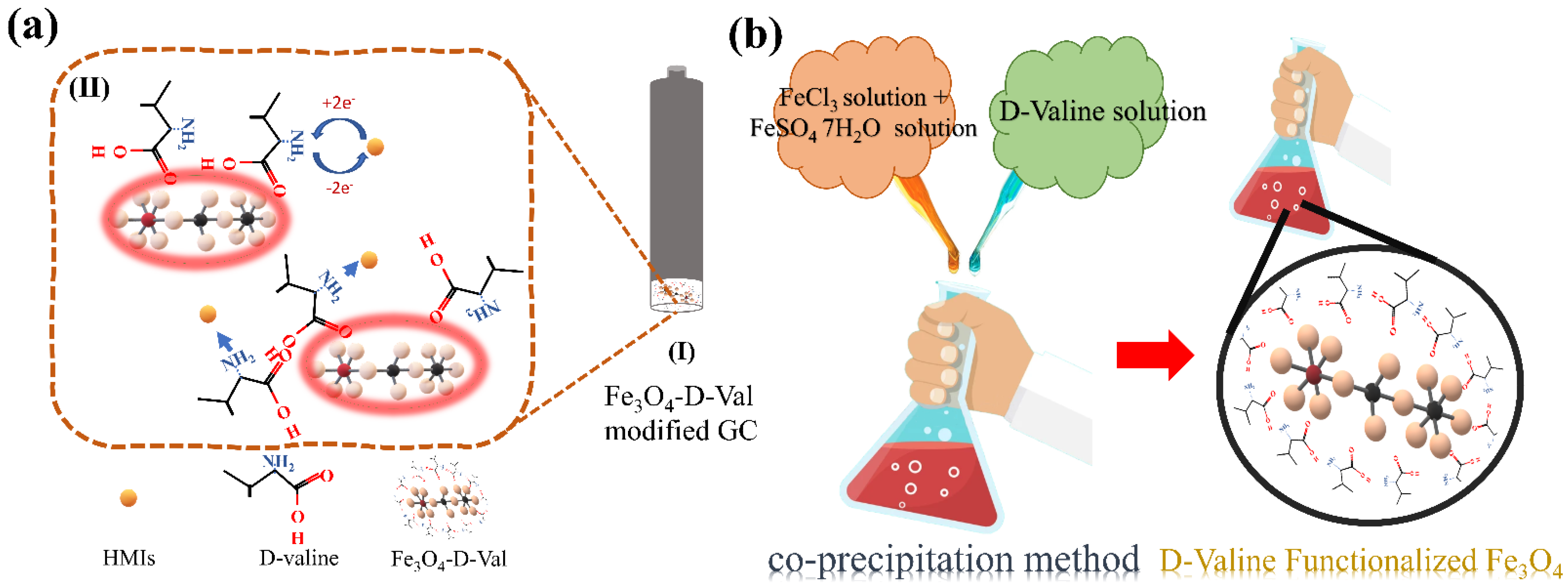
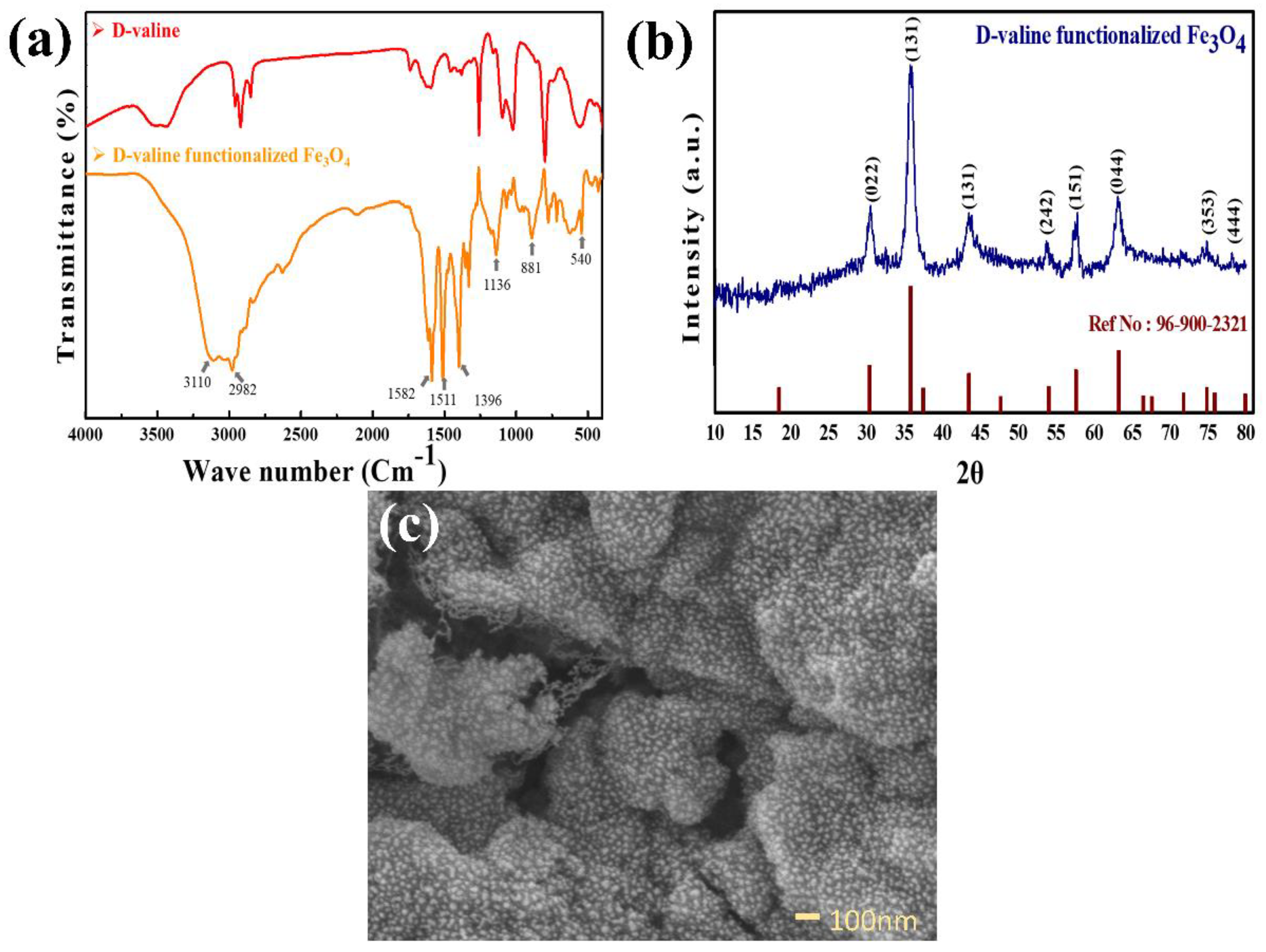
2.3. Synthesis of Functionalized Fe3O4
2.4. Electrode Modification
3. Results and Discussion
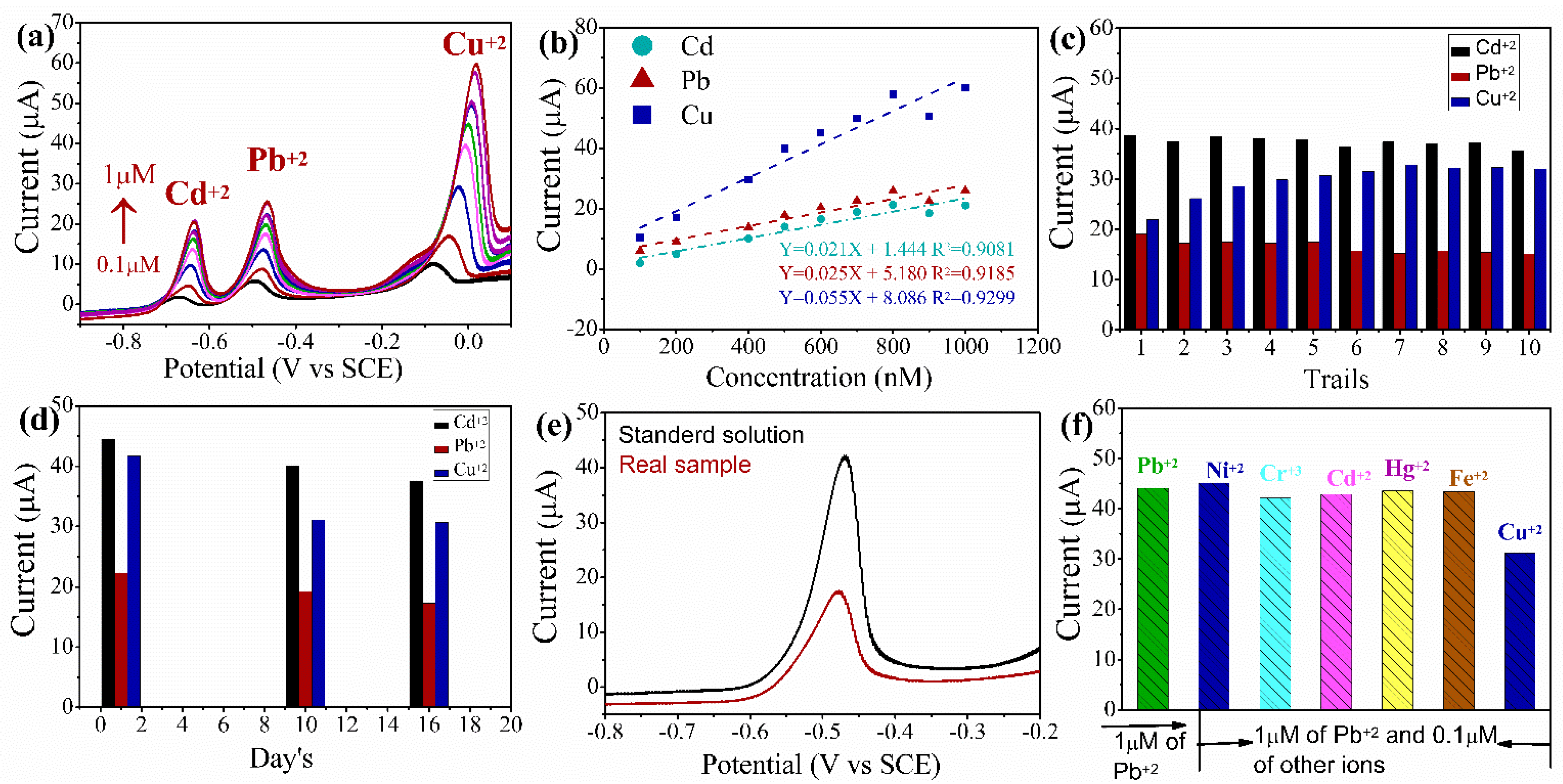
3.1. Electrochemical Detection of HMIs
3.2. Influence of Deposition Potential
3.3. Influence of pH of the Electrolyte
3.4. Influence of Deposition Time
3.5. Individual Detection of HMIs (Pb+2, Cd+2, and Cu+2) by SWASV
3.6. Simultaneous Detection of the HMIs by SWASV
3.7. Reproducibility, Stability and Interference Study’s
3.8. Real-Time Applications Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsu, P.C.; Guo, Y.L. Antioxidant Nutrients and Lead Toxicity. Toxicology 2002, 180, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, T.; Kobayashi, E.; Suwazono, Y.; Uetani, M.; Oishi, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Nogawa, K. Estimation of Cumulative Cadmium Intake Causing Itai-Itai Disease. Toxicol. Lett. 2005, 159, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.A.; Tsuji, J.S.; Garry, M.R.; McArdle, M.E.; Goodfellow, W.L.; Adams, W.J.; Menzie, C.A. Critical Review of Exposure and Effects: Implications for Setting Regulatory Health Criteria for Ingested Copper. Environ. Manag. 2020, 65, 131–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malik, L.A.; Bashir, A.; Qureashi, A.; Pandith, A.H. Detection and Removal of Heavy Metal Ions: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1495–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, A.; Packman, H.; Leung, Y.L.; Coles, B.J.; Kreissig, K.; Little, S.H.; Van De Flierdt, T.; Rehkämper, M. Evaluation of Optimized Procedures for High-Precision Lead Isotope Analyses of Seawater by Multiple Collector Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 11232–11241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na Kim, H.; Xiu Ren, W.; Seung Kim, J.; Yoon, J. Fluorescent and Colorimetric Sensors for Detection of Lead, Cadmium, and Mercury Ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3210–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altunay, N.; Elik, A.; Bingöl, D. Simple and Green Heat-Induced Deep Eutectic Solvent Microextraction for Determination of Lead and Cadmium in Vegetable Samples by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry: A Multivariate Study. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 198, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forzani, E.S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Tao, N. Detection of Heavy Metal Ions in Drinking Water Using a High-Resolution Differential Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawan, S.; Maalouf, R.; Errachid, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Metal and Metal Oxide Nanoparticles in the Voltammetric Detection of Heavy Metals: A Review. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 116014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.; Ktari, N.; Gningue-Sall, D.; Madani, A.; Aaron, S.E.; Aaron, J.-J.; Mekhalif, Z.; Delhalle, J.; Chehimi, M.M. Polipirrol: Polímero Conductor Reactivo y Funcional Para La Detección Electroquímica Selectiva de Metales Pesados En Agua. Emergent Mater. 2020, 3, 815–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Mai, Y.; Luan, A.; Jin, H.; Jian, J.; Jin, Q. Batch Microfabrication of Highly Integrated Silicon-Based Electrochemical Sensor and Performance Evaluation via Nitrite Water Contaminant Determination. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 335, 135660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochab, A.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, S.; Saxena, R. Recent Advances in Carbon Based Nanomaterials as Electrochemical Sensor for Toxic Metal Ions in Environmental Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 45, 3741–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.K.; Singh, P.; Singh, J.; Sachan, S.; Srivastava, S.; Singh, S.K. Nanocarbon-Based Electrochemical Detection of Heavy Metals. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 2472–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragay, G.; Pons, J.; Merkoçi, A. Recent Trends in Macro-, Micro-, and Nanomaterial-Based Tools and Strategies for Heavy-Metal Detection. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 3433–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Li, P.H.; Chen, S.H.; Xiao, X.Y.; Tang, X.H.; Lin, C.H.; Huang, X.J.; Liu, W.Q. Nanometal Oxides with Special Surface Physicochemical Properties to Promote Electrochemical Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. Small 2020, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Y.; Meng, Q.Q.; Luo, T.; Jia, Y.; Sun, B.; Li, Q.X.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, X.J. Facet-Dependent Electrochemical Properties of Co 3 O 4 Nanocrystals toward Heavy Metal Ions. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Gao, C.; Meng, F.L.; Li, H.H.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, X.J. SnO2/Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for the Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Cadmium(II), Lead(II), Copper(II), and Mercury(II): An Interesting Favorable Mutual Interference. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. Highly Sensitive and Selective Electrochemical Sensor Based on Porous Graphitic Carbon Nitride/CoMn2O4 Nanocomposite toward Heavy Metal Ions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 346, 130539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, C.Y.; Xie, X.Y.; Wei, Y.Y.; Shen, W.; Wang, J.P.; Yang, M. Highly Sensitive and Selective Electrochemical Detection of Pb(II) in Serum via an α-Fe2O3/NiO Heterostructure: Evidence from Theoretical Calculations and Adsorption Investigation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 344, 130295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Chen, L.; Jiang, R.; Ye, J.; Li, H.; Shi, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, G.; Hou, J.; Guo, X. ZnFe2O4Nanoparticles for Electrochemical Determination of Trace Hg(II), Pb(II), Cu(II), and Glucose. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 4026–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besenhard, M.O.; LaGrow, A.P.; Hodzic, A.; Kriechbaum, M.; Panariello, L.; Bais, G.; Loizou, K.; Damilos, S.; Margarida Cruz, M.; Thanh, N.T.K.; et al. Co-Precipitation Synthesis of Stable Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with NaOH: New Insights and Continuous Production via Flow Chemistry. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos Guivar, J.A.; Sadrollahi, E.; Menzel, D.; Ramos Fernandes, E.G.; López, E.O.; Torres, M.M.; Arsuaga, J.M.; Arencibia, A.; Litterst, F.J. Magnetic, Structural and Surface Properties of Functionalized Maghemite Nanoparticles for Copper and Lead Adsorption. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 28763–28779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohapatra, S.; Pramanik, P. Synthesis and Stability of Functionalized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using Organophosphorus Coupling Agents. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 339, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, T.; Hilt, J.Z. Functionalization of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Small Molecules and the Impact on Reactive Oxygen Species Generation for Potential Cancer Therapy. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 576, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylova, M.; Kim, D.K.; Berry, C.C.; Zagorodni, A.; Toprak, M.; Curtis, A.S.G.; Muhammed, M. BSA Immobilization on Amine-Functionalized Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 2344–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Jiang, C. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Surface Functionalization Strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jijana, A.N.; Mphuthi, N.; Shumbula, P.; Vilakazi, S.; Sikhwivhilu, L. The Ultra-Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of As(III) in Ground Water Using Disposable L-Cysteine/Lipoic Acid Functionalised Gold Nanoparticle Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes. Electrocatalysis 2021, 12, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arantes, T.M.; Sardinha, A.; Baldan, M.R.; Cristovan, F.H.; Ferreira, N.G. Lead Detection Using Micro/Nanocrystalline Boron-Doped Diamond by Square-Wave Anodic Stripping Voltammetry. Talanta 2014, 128, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhu, X.; Duan, X.; Lu, L.; Yu, Y. Graphene-Derived Nanomaterials as Recognition Elements for Electrochemical Determination of Heavy Metal Ions: A Review. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralikrishna, S.; Sureshkumar, K.; Varley, T.S.; Nagaraju, D.H.; Ramakrishnappa, T. Analytical Methods In Situ Reduction and Functionalization of Graphene Oxide with L -Cysteine for Simultaneous Electrochemical Determination of Cadmium (II). Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 8698–8705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.F.; Zhao, L.J.; Jiang, T.J.; Li, S.S.; Yang, M.; Huang, X.J. Sensitive and Selective Electrochemical Detection of Heavy Metal Ions Using Amino-Functionalized Carbon Microspheres. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 760, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, S.L.; Ee, S.J.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Leong, K.C.; Chen, P. Graphene Quantum Dots Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 172, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, A.; Riaz, S.; Ashraf, R.; Naseem, S. Magnetic and Magnetization Properties of Iron Oxide Thin Films by Microwave Assisted Sol–Gel Route. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2015, 74, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haavik, C.; Stølen, S.; Fjellvåg, H.; Hanfland, M.; Häusermann, D. Equation of State of Magnetite and Its High-Pressure Modification: Thermodynamics of the Fe-O System at High Pressure. Am. Mineral. 2000, 85, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.S.U.; Qureshi, M.T.; Sultana, K.; Rehman, W.; Khan, M.Y.; Asif, M.H.; Farooq, M.; Sultana, N. Single Step Growth of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Use as Glucose Biosensor. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 4451–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralikrishna, S.; Nagaraju, D.H.; Balakrishna, R.G.; Surareungchai, W.; Ramakrishnappa, T.; Shivanandareddy, A.B. Hydrogels of Polyaniline with Graphene Oxide for Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Determination of Lead Ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 990, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvina, V.; Krishna, S.M.; Nagaraju, D.H.; Melo, J.S.; Balakrishna, R.G. Polypyrrole-Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Hydrogels: A Promising Electrode Material for the Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Heavy Metal Ions. Mater. Lett. 2018, 232, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, A.; Soltani-Felehgari, F.; Madrakian, T.; Ghaedi, H.; Rezaeivala, M. Fabrication and Application of a New Modified Electrochemical Sensor Using Nano-Silica and a Newly Synthesized Schiff Base for Simultaneous Determination of Cd2+, Cu2+ and Hg2+ Ions in Water and Some Foodstuff Samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 771, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Deng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Lv, J.; Li, T.; Xu, J.; Chen, S.W.; Wang, J. Graphene Aerogel-Metal-Organic Framework-Based Electrochemical Method for Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Heavy-Metal Ions. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, A.; Shah, A.; Nisar, J.; Ashiq, M.N.; Akhter, M.S.; Shah, A.H. Selective and Simultaneous Detection of Zn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, Cu2+, Hg2+ and Sr2+ Using Surfactant Modified Electrochemical Sensors. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 323, 134592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Shi, H.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, X.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Acid-Etched Fe/Fe2O3 nanoparticles Encapsulated into Carbon Cloth as a Novel Voltammetric Sensor for the Simultaneous Detection of Cd2+ and Pb2. Analyst 2021, 146, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamuna, A.; Hong, C.Y.; Chen, S.M.; Chen, T.W.; Alabdullkarem, E.A.; Soylak, M.; Mana AL-Anazy, M.; Ajmal Ali, M.; Liu, X. Highly Selective Simultaneous Electrochemical Detection of Trace Level of Heavy Metals in Water Samples Based on the Single-Crystalline Co3O4 Nanocubes Modified Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 887, 115159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Wang, X.; Cui, X.; Wang, F.; Ji, H.; Du, X.; Lu, X. GaOOH-Modified Metal-Organic Frameworks UiO-66-NH2: Selective and Sensitive Sensing Four Heavy-Metal Ions in Real Wastewater by Electrochemical Method. Talanta 2021, 234, 122679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Wei, F.; Dong, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Han, X. UiO-66 Based Electrochemical Sensor for Simultaneous Detection of Cd(II) and Pb(II). Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 131, 108785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, H.; Wu, Y.; Fan, Y. A Fe-OSA/Nafion Composite Film-Decorated Glassy Carbon Electrode as a Sensor for Detection of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cu(II). Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 5618–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Yu, X.; Wei, S.; Boukherroub, R.; Zhang, Y. Double-Side Effect of B/C Ratio on BDD Electrode Detection for Heavy Metal Ion in Water. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 145430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, P.; Kan, K.; Lv, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, B.; Bai, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K. Efficient Ultra-Trace Electrochemical Detection of Cd2+, Pb2+ and Hg2+ Based on Hierarchical Porous S-Doped C3N4 Tube Bundles/Graphene Nanosheets Composite. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 130317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerakumar, P.; Veeramani, V.; Chen, S.M.; Madhu, R.; Liu, S. Bin Palladium Nanoparticle Incorporated Porous Activated Carbon: Electrochemical Detection of Toxic Metal Ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.X.; Yu, X.Y.; Gao, C.; Liu, J.H.; Compton, R.G.; Huang, X.J. Enhancing Selectivity in Stripping Voltammetry by Different Adsorption Behaviors: The Use of Nanostructured Mg-Al-Layered Double Hydroxides to Detect Cd(Ii). Analyst 2013, 138, 1812–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, E.; Pizarro, J.; Godoy, F.; Segura, R.; Gómez, A.; Agurto, N.; Sepúlveda, P. An Electrochemical Sensor for the Determination of Cu(II) Using a Modified Electrode with Ferrocenyl Crown Ether Compound by Square Wave Anodic Stripping Voltammetry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 251, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.X.; Yu, X.Y.; Gao, C.; Jiang, Y.J.; Han, D.D.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, X.J. Non-Conductive Nanomaterial Enhanced Electrochemical Response in Stripping Voltammetry: The Use of Nanostructured Magnesium Silicate Hollow Spheres for Heavy Metal Ions Detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 790, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Modification Material | Measurement Technique | LOD | Sensitivity | Ref | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb+2 | Cd+2 | Cu+2 | ||||
| Pg-C3N4/CoMn2O4 | SWASV | 0.014 μM | 0.021 μM | Pb+2:22.39 (μA/μM cm2) | [18] | |
| CI-DPTU/GCE | SWASV | 11.0 nM | 6.45 nM | 7.85 nM | [40] | |
| ae-Fe/Fe2O3@cc | DPASV | 0.5 ppb | 0.42 ppb | Pb+2: 408.0 Cd+2: 338.7 (μA/μM cm2) | [41] | |
| Co3O4-NC/SPCE | DPV | 0.00722 μM | 0.00173 μM | Pb+2: 16.73 Cu+2: 11.46 (μA/μM cm2) | [42] | |
| UiO-66- NH2/GaOOH | DPV | 0.028 μM | 0.016 μM | 0.019 μM | [43] | |
| UiO-66/Bi/GCE | SWASV | 0.94 µg/L | 2.01 µg/L | [44] | ||
| Fe-OSA | DPV | 0.0360 μM | 0.0192 μM | [45] | ||
| SBDDE | SWASV | 5–120 μg/L | Pb+2: 0.42 (μA/μM cm2) | [46] | ||
| S-doped C3N4 tube bundles/graphene nanosheets composite | SWASV | 0.78 nM | 2.30 nM | [47] | ||
| Pd1.5/PAC-900 | DPV | 50 nM | 41 nM | 66 nM | Pb+2: 109.1 Cd+2: 72.9 Cu+2: 21.8 (μA/μM cm2) | [48] |
| Mg–Al-LDH/Nafion | SWASV | 0.20 nM | Cd+2: 13.86 mA mM−1 | [49] | ||
| CB-15-crown-5-GEC, GC/FcIB15C5 | DPV, SWASV | 2.3, 0.11 g/L | [50] | |||
| D-valine functionalized Fe3O4 | SWASV | 4.59 nM | 11.29 nM | 20.07 nM | Pb+2: 1.275 Cd+2: 0.518 Cu+2: 0.291 (μA/nM cm2) | This work |
| Metal Ions | LOD a (nM) | Sensitivity (μA/nM cm2) | LOD b (nM) | Sensitivity (μA/nM cm2) | WHO Standard Values (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb+2 | 4.59 | 1.275 | 18.89 | 0.3101 | 0.01 |
| Cd+2 | 11.29 | 0.518 | 18.38 | 0.3186 | 0.003 |
| Cu+2 | 20.07 | 0.291 | 7.481 | 0.7832 | 2.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
K. S., M.K.; Nagaraju, D.H.; Yhobu, Z.; H. N., N.K.; Budagumpi, S.; Kumar Bose, S.; P., S.; Palakollu, V.N. Tuning the Surface Functionality of Fe3O4 for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. Sensors 2022, 22, 8895. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228895
K. S. MK, Nagaraju DH, Yhobu Z, H. N. NK, Budagumpi S, Kumar Bose S, P. S, Palakollu VN. Tuning the Surface Functionality of Fe3O4 for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. Sensors. 2022; 22(22):8895. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228895
Chicago/Turabian StyleK. S., Manjunatha Kumara, D. H. Nagaraju, Zhoveta Yhobu, Nayan Kumar H. N., Srinivasa Budagumpi, Shubhankar Kumar Bose, Shivakumar P., and Venkata Narayana Palakollu. 2022. "Tuning the Surface Functionality of Fe3O4 for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Heavy Metal Ions" Sensors 22, no. 22: 8895. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228895
APA StyleK. S., M. K., Nagaraju, D. H., Yhobu, Z., H. N., N. K., Budagumpi, S., Kumar Bose, S., P., S., & Palakollu, V. N. (2022). Tuning the Surface Functionality of Fe3O4 for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. Sensors, 22(22), 8895. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228895







