A Design and Application of Municipal Service Platform Based on Cloud-Edge Collaboration for Smart Cities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- We develop an reference model based on cloud-edge collaboration specially for municipal service platform. We point out the main content and challenges of cloud-edge collaboration, including resource collaboration, application collaboration, service collaboration, and security collaboration.
- (2)
- We design and implement a smart e-government self-service system based on the above reference model. The experimental results show that the cloud-edge collaboration mode can provide a better user experience.
- (3)
- We propose a transaction model to study the optimal allocation strategy for the optimal allocation of computing resources and communication resources in the cloud-edge collaboration. The findings show that the evolutionary and the Nash equilibrium are the optimal solutions, respectively.
2. Cloud-Edge Collaboration
2.1. Resource Collaboration
2.2. Application Collaboration
2.3. Service Collaboration
2.4. Security Collaboration
3. Dynamic Resource Allocation Model
3.1. MSPs Model
3.2. MSDs Model
3.3. Formulation of the Evolutionary Game
4. Design and Implementation of E-Government Self-Service System
4.1. User Requirement Analysis
- (1)
- The system can comprehensively handle the business of urban management departments and break the data isolated islands among these departments.
- (2)
- Urban residents can easily access the system and realize municipal business “one-stop” service through self-service. These municipal businesses include identity authentication and identification, business query, Business declaration and payment.
- (3)
- The municipal business services provided should be flexible, easy to expand and uninstall according to business needs, as well as meet relevant security requirements.
4.2. System Architecture Design
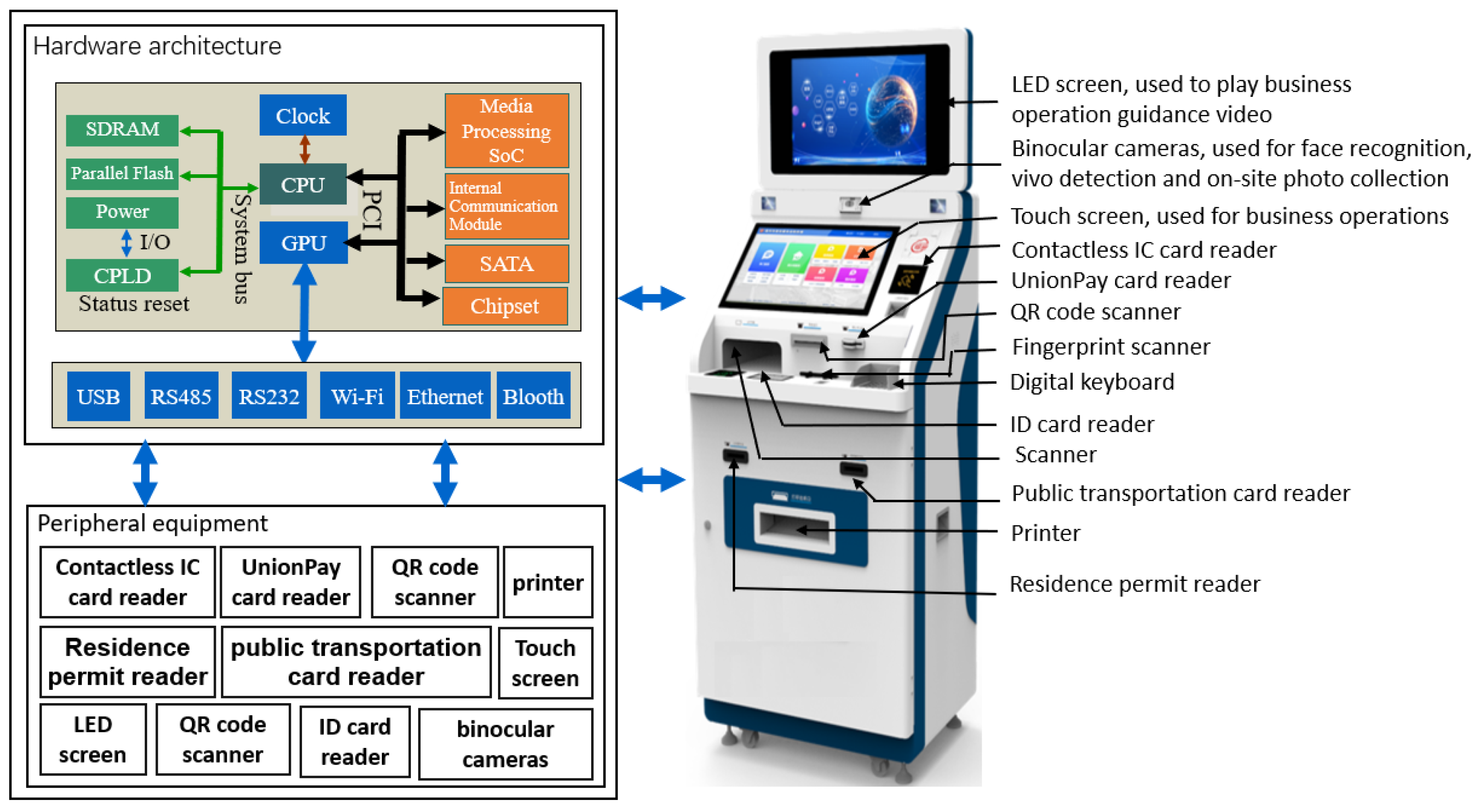
4.3. Edge Self-Service Terminal Design
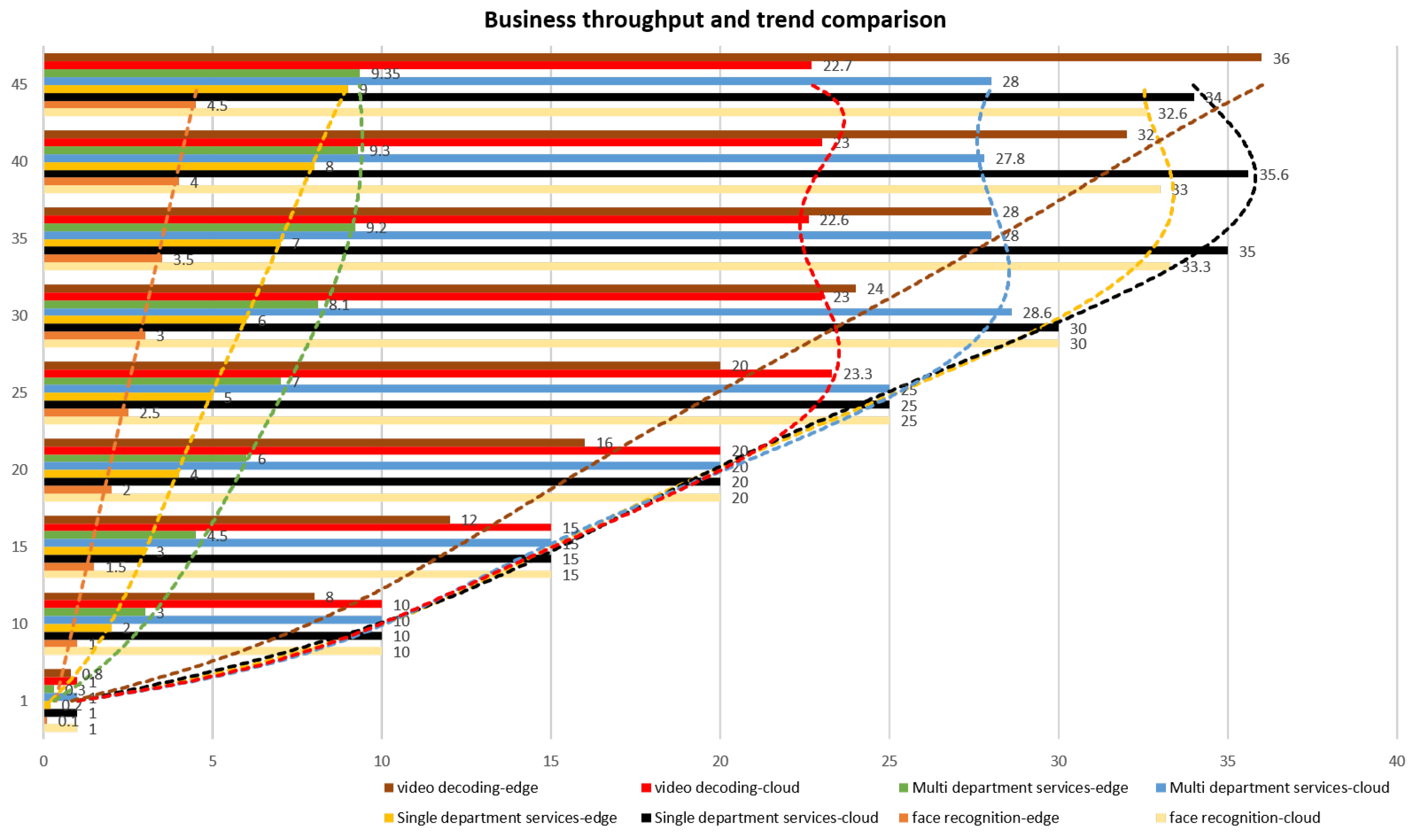
4.4. Result Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights. 2019. Available online: https://www.un.org/development/desa/pd/news/world-population-prospects-2019-0 (accessed on 18 July 2022).
- Law, K.H.; Lynch, J.P. Smart City: Technologies and Challenges. IT Prof. 2019, 21, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Y. Smart cities for emergency management. Nature 2020, 578, 515–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Lee, T.Y.; Zhang, W. Smart Cities in China: A Brief Overview. IT Prof. 2021, 23, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S.; Buyya, R. A Taxonomy and Future Directions for Sustainable Cloud Computing: 360 Degree View. ACM Comput. Surv. 2019, 51, 104–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhuraibi, Y.; Paraiso, F.; Djarallah, N.; Merle, P. Elasticity in cloud computing: State of the art and research challenges. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2017, 11, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parast, F.K.; Sindhav, C.; Nikam, S.; Yekta, H.I.; Kent, K.B.; Hakak, S. Cloud computing security: A survey of service-based models. Comput. Secur. 2022, 114, 102580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakak, S.; Khan, W.Z.; Gilkar, G.A.; Imran, M.; Guizani, N. Securing Smart Cities through Blockchain Technology: Architecture, Requirements, and Challenges. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, L.U.; Yaqoob, I.; Tran, N.H.; Kazmi, S.A.; Dang, T.N.; Hong, C.S. Edge-computing-enabled smart cities: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 10200–10232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Q.; Hu, S.; Li, C.; Li, G.; Shi, W. Resource scheduling in edge computing: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 2131–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, B.; Li, Z. Energy-efficient dynamic computation offloading and cooperative task scheduling in mobile cloud computing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2018, 18, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Dang, J.; Li, Z.; Gong, H.; Zhang, F.; Oh, S. Modeling analysis and cost-performance ratio optimization of virtual machine scheduling in cloud computing. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2020, 31, 1518–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sharma, S.C.; Goel, A.; Singh, S.P. A comprehensive survey for scheduling techniques in cloud computing. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2019, 143, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, H. Design of secure authenticated key management protocol for cloud computing environments. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2019, 18, 1276–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ding, C.; Zhang, N.; Liu, X.; Zhou, A.; Cao, J.; Shen, X. A cloud-guided feature extraction approach for image retrieval in mobile edge computing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2019, 20, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jošilo, S.; Dán, G. Computation offloading scheduling for periodic tasks in mobile edge computing. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2020, 28, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Xu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, W.; Wei, X.; Lu, J. EdgeLSTM: Towards Deep and Sequential Edge Computing for IoT Applications. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2021, 29, 1895–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.L.C.G.H.Z. Multi-UAV Network Assisted Intelligent Edge Computing:Challenges and Opportunities. China Commun. 2022, 19, 258–278. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, C.; Zhou, A.; Liu, Y.; Chang, R.N.; Hsu, C.H.; Wang, S. A Cloud-Edge Collaboration Framework for Cognitive Service. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2020, 10, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, X.; Hu, J. A Fast Hierarchical Physical Topology Update Scheme for Edge-Cloud Collaborative IoT Systems. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2021, 29, 2254–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lan, X.; Ren, J.; Cai, L. Efficient computing resource sharing for mobile edge-cloud computing networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2020, 28, 1227–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Feng, T.; Xu, F.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, C. Collaborative clustering parallel reinforcement learning for edge-cloud digital twins manufacturing system. China Commun. 2022, 19, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, S.; Yao, Y.; Wang, F.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Chu, Y.; Ji, L.; Jia, K.; Shen, T.; et al. Edge-Cloud Polarization and Collaboration: A Comprehensive Survey for AI. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-p.; Liu, B.; Lin, W.-w.; Cheng, H.-w. Survey of Cloud-edge Collaboration. Comput. Sci. 2021, 48, 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Ota, K.; Kumrai, T.; Dong, M.; Kishigami, J.; Guo, M. Smart Infrastructure Design for Smart Cities. IT Prof. 2017, 19, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Chen, Y.; Lu, M. Smart city information processing under internet of things and cloud computing. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 3676–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.; Kang, Q.; Sun, D. Object tracking for a smart city using IoT and edge computing. Sensors 2019, 19, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.N.; Li, Q.L.; Yin, J.F. Design of Integrated Service Platform for Smart City Based on Cloud Computing. Intell. Build. Smart City 2021, 11, 135–136. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Park, S.; Shahkarami, S.; Sankaran, R.; Ferrier, N.; Beckman, P. Goal-driven scheduling model in edge computing for smart city applications. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2022, 167, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Feng, T.; Liu, X.; Xu, F.; Zhao, C. Edge-cloud collaborative intelligent production scheduling based on digital twin. J. China Univ. Posts Telecommun. 2022, 29, 108–120. [Google Scholar]
- Arthurs, P.; Gillam, L.; Krause, P.; Wang, N.; Halder, K.; Mouzakitis, A. A taxonomy and survey of edge cloud computing for intelligent transportation systems and connected vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 6206–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Q.; Xiong, H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, C.M. Blockchain-Enabled Privacy-Preserving Authentication Mechanism for Transportation CPS With Cloud-Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2022, 33, 6206–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngu, A.H.; Metsis, V.; Coyne, S.; Srinivas, P.; Salad, T.; Mahmud, U.; Chee, K.H. Personalized Watch-Based Fall Detection Using a Collaborative Edge-Cloud Framework. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2022, 24, 2250048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, C.; Wu, D. Construction of a smart management system for physical health based on IoT and cloud computing with big data. Comput. Commun. 2021, 179, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinky, H.; Khalfi, B.; Hamdaoui, B.; Rayes, A. Adaptive edge-centric cloud content placement for responsive smart cities. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, T.; Chen, X.; He, S.; Guo, D.; Wu, J. Reverse auction-based computation offloading and resource allocation in mobile cloud-edge computing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2022, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q. Dynamic resource allocation strategy in mobile edge cloud computing environment. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2021, 2021, 8381998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Deng, S.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, R.; Dustdar, S.; Zomaya, A.Y. Mobility-Aware Offloading and Resource Allocation for Distributed Services Collaboration. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2022, 33, 2428–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jin, Y.; Qian, Z.; Xiao, M.; Ge, J.; Lu, S. LOCUS: User-Perceived Delay-Aware Service Placement and User Allocation in MEC Environment. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2021, 33, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Yeo, C.K. Market-based dynamic resource allocation in Mobile Edge Computing systems with multi-server and multi-user. Comput. Commun. 2021, 165, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Computing Consortium of Industrial Internet. White Paper on Edge Computing and Cloud Computing Collaboration 2020. Available online: http://www.ecconsortium.org/Uploads/file/20201210/1607532948372540.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2022).
- Forti, S.; Ferrari, G.L.; Brogi, A. Secure cloud-edge deployments, with trust. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 102, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisco Systems, Inc. Cisco Annual Internet Report (2018–2023) [R/OL]. 9 March 2020. Available online: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/executive-perspectives/annual-internet-report/white-paper-c11-741490.html (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Zhou, P.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y. Design and Optimization of Solar-Powered Shared Electric Autonomous Vehicle System for Smart Cities. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrino, S.; Peruzzi, G.; Pozzebon, A. LoPATraN: Low Power Asset Tracking by Means of Narrow Band IoT (NB-IoT) Technology. Sensors 2021, 21, 3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, S.; Platis, A.; Vidal, R.; Gomez, C. Energy Consumption Model of SCHC Packet Fragmentation over Sigfox LPWAN. Sensors 2022, 22, 2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.P.; Jung, W.S.; Yoo, D.S.; Oh, H. Design and Implementation of a Multi-Hop Real-Time LoRa Protocol for Dynamic LoRa Networks. Sensors 2022, 22, 3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabduljabbar, R. An IoT smart clothing system for the visually impaired using NFC technology. Int. J. Sens. Netw. 2022, 38, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Węglarski, M.; Jankowski-Mihułowicz, P.; Pitera, G.; Jurków, D.; Dorczyński, M. LTCC flow sensor with RFID interface. Sensors 2020, 20, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darroudi, S.M.; Caldera-Sànchez, R.; Gomez, C. Bluetooth mesh energy consumption: A model. Sensors 2019, 19, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Ye, Y. Monitoring of clinical signs of intravenous infusion patients with ZigBee wireless technology. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2022, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonadio, A.; Chiti, F.; Fantacci, R. Performance Analysis of an Edge Computing SaaS System for Mobile Users. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ometov, A.; Molua, O.L.; Komarov, M.; Nurmi, J. A survey of security in cloud, edge, and fog computing. Sensors 2022, 22, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSA. Top Threats to Cloud Computing: Deep Dive—A Case Study Analysis for ‘The Treacherous 12: Top Threats to Cloud Computing’ and a Relative Security Industry Breach Analysis. 6 August 2018. Available online: https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/download/top-threats-to-cloud-computing-deep-dive/ (accessed on 2 August 2022).
- Raza, M.T.; Lu, S.; Gerla, M. vepc-sec: Securing lte network functions virtualization on public cloud. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 14, 3287–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Wang, Q.; Huang, M.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Shen, C.; Ren, K. Building In-the-Cloud Network Functions: Security and Privacy Challenges. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 1888–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, Q.; Susilo, W. A secure cloud data sharing protocol for enterprise supporting hierarchical keyword search. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2022, 19, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Xie, X.; Huang, L. Achieving secure and dynamic range queries over encrypted cloud data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 34, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumalaisamy, M.; Basheer, S.; Selvarajan, S.; Althubiti, S.A.; Alenezi, F.; Srivastava, G.; Lin, J.C.W. Interaction of Secure Cloud Network and Crowd Computing for Smart City Data Obfuscation. Sensors 2022, 22, 7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaraweera, G.D.; Chang, J.M. Security and privacy implications on database systems in Big Data era: A survey. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2019, 33, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Xiao, N.; Chen, T.; Wang, J. Fog-to-multicloud cooperative eHealth data management with application-aware secure deduplication. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2022, 19, 3136–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K. Security threats in cloud computing environments. Int. J. Secur. Its Appl. 2012, 6, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Xie, S.; Cai, J.; Wang, C.; Hong, Y.; Kui, X. Novel private data access control scheme suitable for mobile edge computing. China Commun. 2021, 18, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, B.; Zhong, H.; Min, G.; Xu, Y.; Liu, L. A Practical and Efficient Bidirectional Access Control Scheme for Cloud-Edge Data Sharing. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2021, 33, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, X. A secure anonymous identity-based scheme in new authentication architecture for mobile edge computing. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 15, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, B.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, M. An Efficient Identity Authentication Scheme With Provable Security and Anonymity for Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Syst. J. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Jia, Y.; Liu, C.; Cheng, X.; Yu, J.; Lv, W. Edge computing security: State of the art and challenges. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 1608–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, C. A Parallel Secure Flow Control Framework for Private Data Sharing in Mobile Edge Cloud. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2022, 33, 4638–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ma, J.; Miao, Y.; Liu, X.; Choo, K.K.R.; Yang, R.; Wang, X. Lightweight privacy-preserving medical diagnosis in edge computing. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2020, 15, 1606–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, G.; Dai, H.; Liu, G. PFLF: Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning Framework for Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2022, 17, 1905–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, O.E. Transaction cost economics: How it works; where it is headed. Economist 1998, 146, 23–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Operational Data Committee. Technical Specification of Intelligent Edge Computing Gateway [ODCC-2021-04002]. 2021. Available online: http://www.odcc.org.cn/download/p-1437612304326152193.html (accessed on 2 January 2022).




| Features | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| computing paradigm | Provides distributed nearby computing and storage services at the edge of the network, focuses on the analysis of real-time and short-term data, and supports the real-time intelligent processing and execution of local business better. | Provides centralized on-demand remote computing and storage self-services in the network center, focuses on the analysis of non-real-time and long-term big data, and provides better support for business decision-making. |
| devices | Embedded smart devices or credit-card-size computers with weak computing power, generally have waterproof and dustproof design. Not only data consumers but also data producers. | High performance server located in the data center with powerful and dynamically adjustable computing power. |
| advantages | Low latency, low energy consumption, high business security, and high personal privacy. | Self-service, resource pooling and sharing, elastic scaling, and service measurable. |
| typical scenarios | In the field of intelligent manufacturing, factories use IoT gateway, industrial robots, and sensors for data localization processing, such as data acquisition, filtering, cleaning and real-time control. Moreover, the IoT gateway provides the ability of heterogeneous protocol fusion and realizes the unified access of industrial networks. In the field of smart cities, managers realize the collection, analysis and real-time control of various data through various sensors, drones, cameras, and embedded computers. In the field of live games, edge computing provides Content Delivery Network (CDN) with rich storage resources and audio and video rendering capabilities closer to users, especially in Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) scenes. | Comprehensive big data applications. For example, the Hangzhou’s City Brain is a smart city cloud platform, which aims to improve the urban management by using of big data, cloud computing, AI, and other technologies. High-performance computing applications. For example, aerodynamic design and analysis, weather forecast and meteorological research, virtual simulation of digital twin cities, etc. Huge business volume fluctuation; applications with sudden increase of system load due to the unpredictable access volume of the client. Once the system load is too large, there may be problems such as system downtime, inaccessible services, and poor customer experience. Such cloud platforms include Amazon, Microsoft Azure, IBM Cloud, etc. |
| Service Type | Latency/ms | Bandwidth/Mbps |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud computing | >=15 | =<20 |
| Edge computing | =<5 | >=100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Lee, T.-Y.; Lee, W.-T.; Xu, L. A Design and Application of Municipal Service Platform Based on Cloud-Edge Collaboration for Smart Cities. Sensors 2022, 22, 8784. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228784
Yang J, Lee T-Y, Lee W-T, Xu L. A Design and Application of Municipal Service Platform Based on Cloud-Edge Collaboration for Smart Cities. Sensors. 2022; 22(22):8784. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228784
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jingmin, Trong-Yen Lee, Wen-Ta Lee, and Li Xu. 2022. "A Design and Application of Municipal Service Platform Based on Cloud-Edge Collaboration for Smart Cities" Sensors 22, no. 22: 8784. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228784
APA StyleYang, J., Lee, T.-Y., Lee, W.-T., & Xu, L. (2022). A Design and Application of Municipal Service Platform Based on Cloud-Edge Collaboration for Smart Cities. Sensors, 22(22), 8784. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22228784






