A Novel Point Set Registration-Based Hand–Eye Calibration Method for Robot-Assisted Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Our method is a simultaneous closed-form solution, which guarantees an optimal solution;
- Unlike other simultaneous solutions, our solution is obtained by solving three nonlinear least-square fitting problems, leading to three overdetermined equation systems. Thus, it is not sensitive to the nonlinearities present in measurements in the form of noise and errors;
- In comparison with the nonlinear iterative approaches, our method requires only simple matrix operations. Thus, it is computationally efficient;
- Our method achieves better results than the state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods.
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
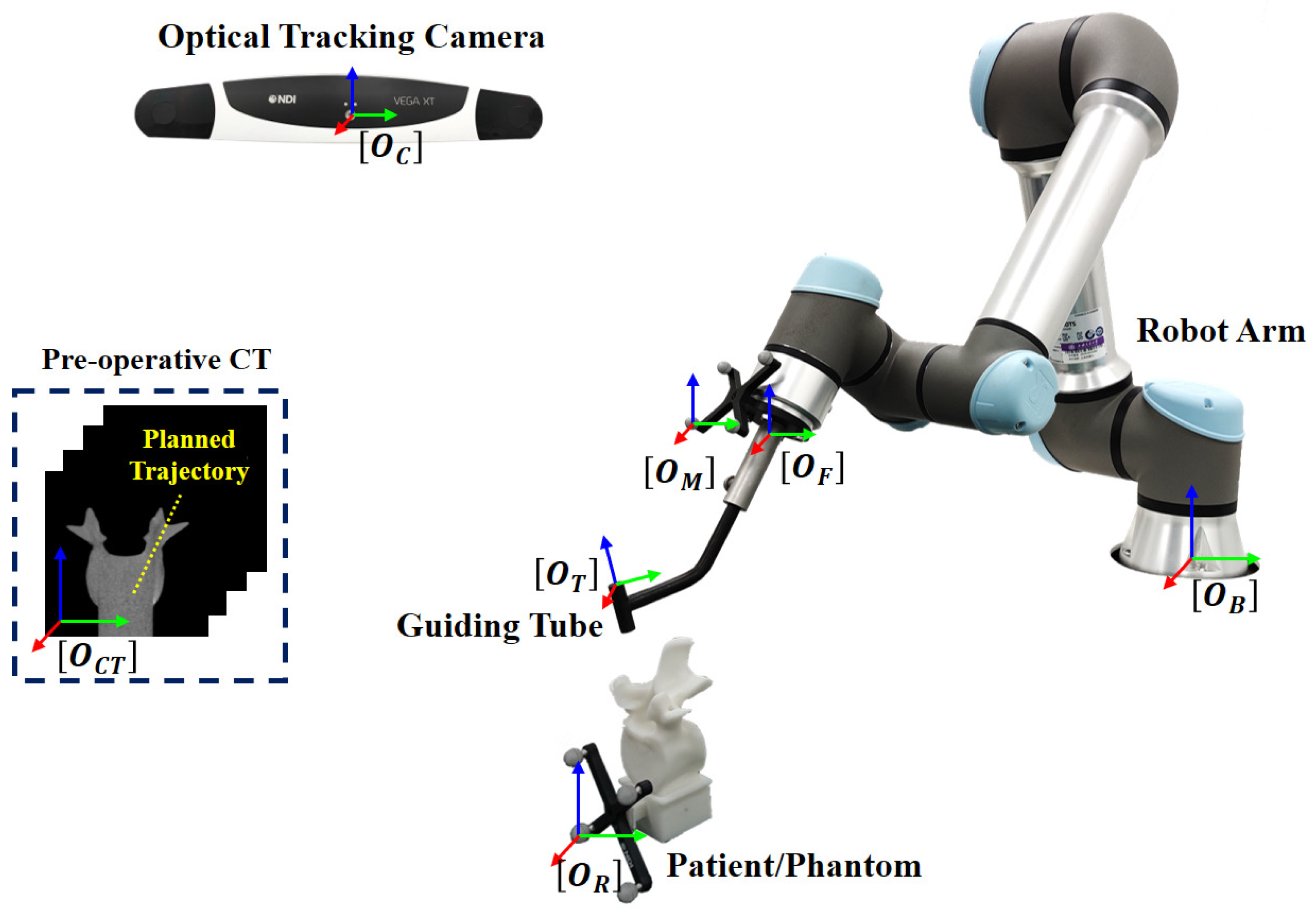
3.1. System Overview
3.2. Registration-Based Hand–Eye Calibration
3.2.1. Tool-Tip Calibration
3.2.2. Solving Hand–Eye Calibration via Paired-Point Matching
3.3. Guiding Tube Calibration
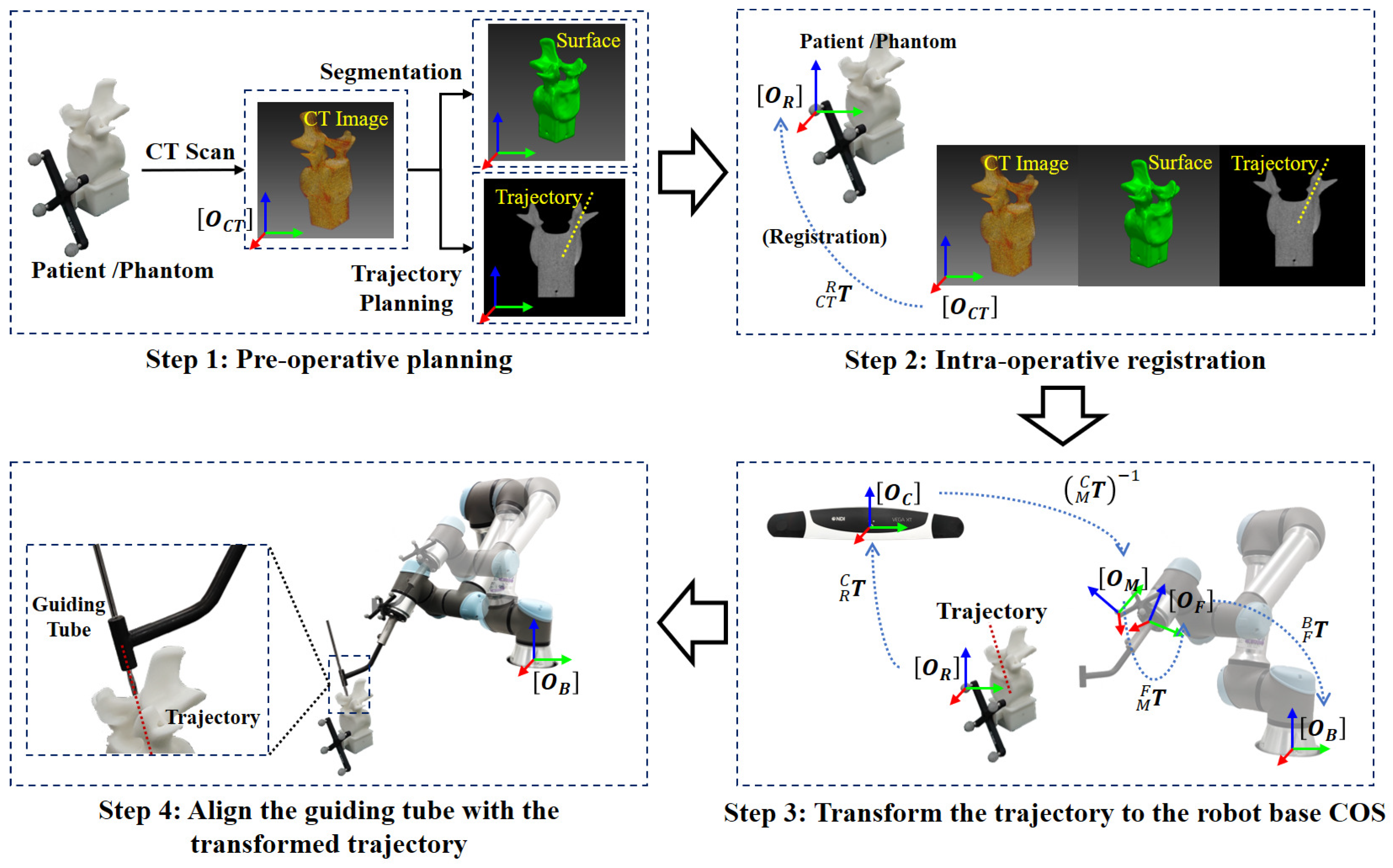
3.4. Robot-Assisted Pedicle Screw Insertion
3.4.1. Pre-Operative Planning
3.4.2. Intra-Operative Registration
3.4.3. Transforming the Planned Trajectory to the Robot Base COS and Aligning the Guiding Tube with the Transformed Trajectory
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Metrics
4.2. Investigation of the Influence of the Range of Robot Movement to the Hand–Eye Calibration
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Hand–Eye Calibration Methods
4.4. Overall System Accuracy Study
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| COS | Coordinate System |
| SVD | Singular Value Decomposition |
| RHC | Registration-based Hand–eye Calibration |
| 3D | Three-dimension |
References
- Tian, N.F.; Xu, H.Z. Image-guided pedicle screw insertion accuracy: A meta-analysis. Int. Orthop. 2009, 33, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Du, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Xue, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hao, D. Comparison of accuracy of pedicle screw insertion among 4 guided technologies in spine surgery. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2017, 23, 5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.Q.; Priola, S.M.; Ramjist, J.M.; Guha, D.; Dobashi, Y.; Lee, K.; Lu, M.; Androutsos, D.; Yang, V. Machine vision augmented reality for pedicle screw insertion during spine surgery. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 72, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomiichuk, V.; Fleischhammer, J.; Molliqaj, G.; Warda, J.; Alaid, A.; von Eckardstein, K.; Schaller, K.; Tessitore, E.; Rohde, V.; Schatlo, B. Robotic versus fluoroscopy-guided pedicle screw insertion for metastatic spinal disease: A matched-cohort comparison. Neurosurg. Focus 2017, 42, E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molliqaj, G.; Schatlo, B.; Alaid, A.; Solomiichuk, V.; Rohde, V.; Schaller, K.; Tessitore, E. Accuracy of robot-guided versus freehand fluoroscopy-assisted pedicle screw insertion in thoracolumbar spinal surgery. Neurosurg. Focus 2017, 42, E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Jung, W.I.; Chang, B.S.; Lee, C.K.; Kang, K.T.; Yeom, J.S. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial of robot-assisted vs freehand pedicle screw fixation in spine surgery. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2017, 13, e1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, K.A.; Murphy, J.S.; Devito, D.P. Accuracy of robot-assisted pedicle screw insertion in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Is triggered electromyographic pedicle screw stimulation necessary? J. Spine Surg. 2018, 4, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ren, H. Finding the kinematic base frame of a robot by hand-eye calibration using 3D position data. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2016, 14, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yu, X.; Li, C.; Li, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, L. Space calibration of the cranial and maxillofacial robotic system in surgery. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2016, 21, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shiu, Y.C.; Ahmad, S. Calibration of wrist-mounted robotic sensors by solving homogeneous transform equations of the form AX= XB. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, R.Y.; Lenz, R.K. A new technique for fully autonomous and efficient 3 d robotics hand/eye calibration. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1989, 5, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C. Extrinsic calibration of a vision sensor mounted on a robot. Ieee Trans. Robot. Autom. 1992, 8, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.C.; Kamel, M. Finding the position and orientation of a sensor on a robot manipulator using quaternions. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1991, 10, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniilidis, K. Hand-eye calibration using dual quaternions. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1999, 18, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreff, N.; Horaud, R.; Espiau, B. On-line hand-eye calibration. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling (Cat. No. PR00062), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 8 October 1999; pp. 430–436. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.C.; Chou, J.C. Eight-space quaternion approach for robotic hand-eye calibration. In Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics. Intelligent Systems for the 21st Century, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 22–25 October 1995; Volume 4, pp. 3316–3321. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y. Hand-eye calibration based on screw motions. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06), Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2006; Volume 3, pp. 1022–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, H.; Shiu, Y.C. A noise-tolerant algorithm for robotic hand-eye calibration with or without sensor orientation measurement. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. 1993, 23, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.Q.; Arbter, K.; Hirzinger, G. Active self-calibration of robotic eyes and hand-eye relationships with model identification. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 1998, 14, 158–166. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Huang, X.; Jiang, L. A flexible solution to AX= XB for robot hand-eye calibration. In Proceedings of the 10th WSEAS International Conference on Robotics, Control and Manufacturing Technology, Hangzhou, China, 11–13 April 2010; pp. 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, G.Z. A computationally efficient method for hand–eye calibration. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 1775–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, Q.; Wang, T.; Chirikjian, G.S. Simultaneous hand-eye and robot-world calibration by solving the AX = YB problem without correspondence. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2015, 1, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, H.; Chirikjian, G.S. New probabilistic approaches to the AX= XB hand-eye calibration without correspondence. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 4365–4371. [Google Scholar]
- Aiguo, L.; Lin, W.; Defeng, W. Simultaneous robot-world and hand-eye calibration using dual-quaternions and Kronecker product. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2010, 5, 1530–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Suominen, O.; Gotchev, A.; Morales, E.R. Methods for simultaneous robot-world-hand–eye calibration: A comparative study. Sensors 2019, 19, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsh, R.L.; DeSouza, G.N.; Kak, A.C. An iterative approach to the hand-eye and base-world calibration problem. In Proceedings of the 2001 ICRA, IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 01CH37164), Seoul, Korea, 21–26 May 2001; Volume 3, pp. 2171–2176. [Google Scholar]
- Strobl, K.H.; Hirzinger, G. Optimal hand-eye calibration. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Beijing, China, 9–15 October 2006; pp. 4647–4653. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, M.; Eastman, R.D.; Hong, T. An overview of robot-sensor calibration methods for evaluation of perception systems. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Performance Metrics for Intelligent Systems, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 19–21 August 2012; pp. 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, I.; Jayarathne, U.; Rankin, A.; Peters, T.M.; Chen, E. Hand-eye calibration for surgical cameras: A procrustean perspective-n-point solution. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özgüner, O.; Shkurti, T.; Huang, S.; Hao, R.; Jackson, R.C.; Newman, W.S.; Çavuşoğlu, M.C. Camera-robot calibration for the da vinci robotic surgery system. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 17, 2154–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberti, A.; Piccinelli, N.; Meli, D.; Muradore, R.; Fiorini, P. Improving rigid 3-d calibration for robotic surgery. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2020, 2, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Pan, B.; Guo, Y.; Fu, Y.; Niu, G. Vision-based hand–eye calibration for robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2020, 15, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Fruit detection and positioning technology for a Camellia oleifera C. Abel orchard based on improved YOLOv4-tiny model and binocular stereo vision. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 211, 118573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valassakis, E.; Dreczkowski, K.; Johns, E. Learning Eye-in-Hand Camera Calibration from a Single Image. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, London, UK, 8–11 November 2021; pp. 1336–1346. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, J.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Yang, F. Feature points extraction of defocused images using deep learning for camera calibration. Measurement 2022, 188, 110563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kuc, T.Y.; Lee, K.H. Hand-eye calibration using images restored by deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics-Asia (ICCE-Asia), Seoul, Korea, 1–3 November 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Low, K.L. Linear least-squares optimization for point-to-plane icp surface registration. Chapel Hill Univ. North Carol. 2004, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Khamene, A.; Sauer, F. A novel phantom-less spatial and temporal ultrasound calibration method. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Palm Springs, CA, USA, 26–29 October 2005; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, P. Linear Algebra; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, M. Solving the robot-world/hand-eye calibration problem using the Kronecker product. J. Mech. Robot. 2013, 5, 031007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Categories | Solutions | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Separable solutions [10,11,12,13,14] | Solve the rotation part first; then, solve the translational part. | Error propagation problem. |
| Simultaneous solutions [15,16,17] | Solve the rotational and translational parts at the same time. | Sensitive to the nonlinearities present in measurements in the form of noise and errors. |
| Iterative solutions [8,18,19,20,21] | Solve a nonlinear optimization problem by minimizing the error by iteration. | Computationally expensive; may not always converge on the optimal solution. |
| Probabilistic methods [22,23] | Solve the calibration problem without the assumption of exact correspondence between the data streams. | Computationally expensive. |
| d [mm] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L [mm] | Mean | Max. | Mean | Max. |
| 30 | 1.17 | 1.40 | 0.87 | 1.25 |
| 60 | 0.86 | 1.09 | 0.83 | 0.93 |
| 90 | 0.82 | 0.95 | 0.72 | 0.91 |
| 120 | 0.86 | 1.06 | 0.75 | 0.90 |
| 150 | 0.71 | 1.11 | 0.70 | 0.85 |
| 200 | 0.70 | 0.88 | 0.68 | 0.96 |
| d [mm] | Computation Time [ms] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L [mm] | Mean | Max. | Mean | Max. | |
| Tsai [11] | 0.74 | 0.92 | 0.75 | 0.88 | 1.18 |
| Andreff [15] | 0.73 | 0.87 | 0.70 | 0.92 | 2.23 |
| Chou [13] | 0.73 | 0.84 | 0.69 | 0.89 | 0.82 |
| Shah [40] | 0.74 | 0.92 | 0.72 | 0.97 | 0.63 |
| Wu [8] | 0.72 | 0.88 | 0.68 | 0.90 | 26.84 |
| Ours | 0.70 | 0.88 | 0.68 | 0.96 | 2.21 |
| Plastic Phantom | 3D-Printed Vertebrae | Pig Vertebrae | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| d [mm] | Mean | 0.70 | 0.66 | 0.71 |
| Max. | 0.85 | 0.79 | 0.82 | |
| [mm] | Mean | 0.93 | 0.90 | 1.01 |
| Max. | 1.15 | 1.13 | 1.52 | |
| Mean | 0.72 | 0.79 | 0.82 | |
| Max. | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.96 | |
| Mean | 1.04 | 0.96 | 1.11 | |
| Max. | 1.45 | 1.24 | 1.38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, G. A Novel Point Set Registration-Based Hand–Eye Calibration Method for Robot-Assisted Surgery. Sensors 2022, 22, 8446. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22218446
Sun W, Liu J, Zhao Y, Zheng G. A Novel Point Set Registration-Based Hand–Eye Calibration Method for Robot-Assisted Surgery. Sensors. 2022; 22(21):8446. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22218446
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Wenyuan, Jihao Liu, Yuyun Zhao, and Guoyan Zheng. 2022. "A Novel Point Set Registration-Based Hand–Eye Calibration Method for Robot-Assisted Surgery" Sensors 22, no. 21: 8446. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22218446
APA StyleSun, W., Liu, J., Zhao, Y., & Zheng, G. (2022). A Novel Point Set Registration-Based Hand–Eye Calibration Method for Robot-Assisted Surgery. Sensors, 22(21), 8446. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22218446







