Monitoring Subsidence Area with the Use of Satellite Radar Images and Deep Transfer Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
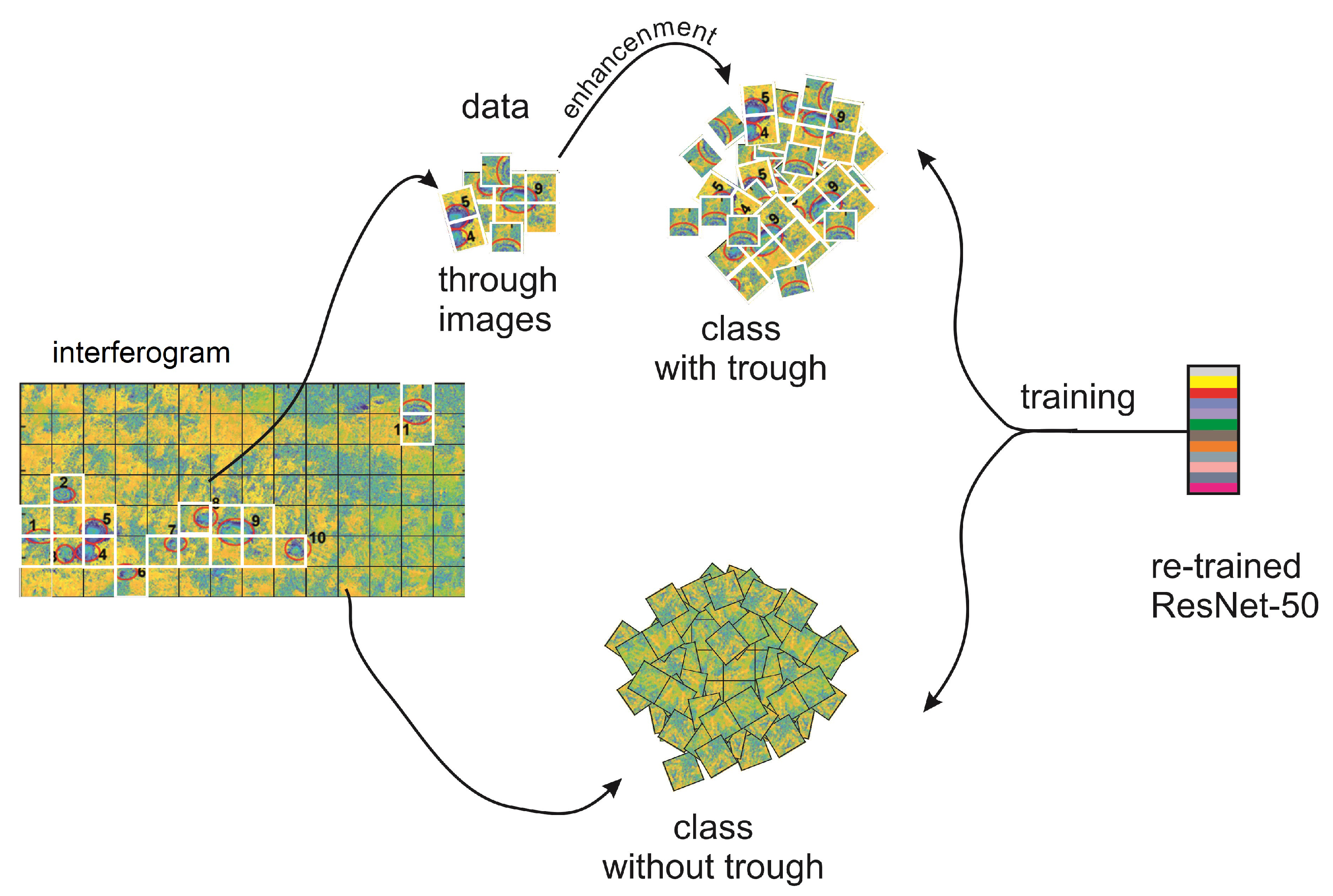
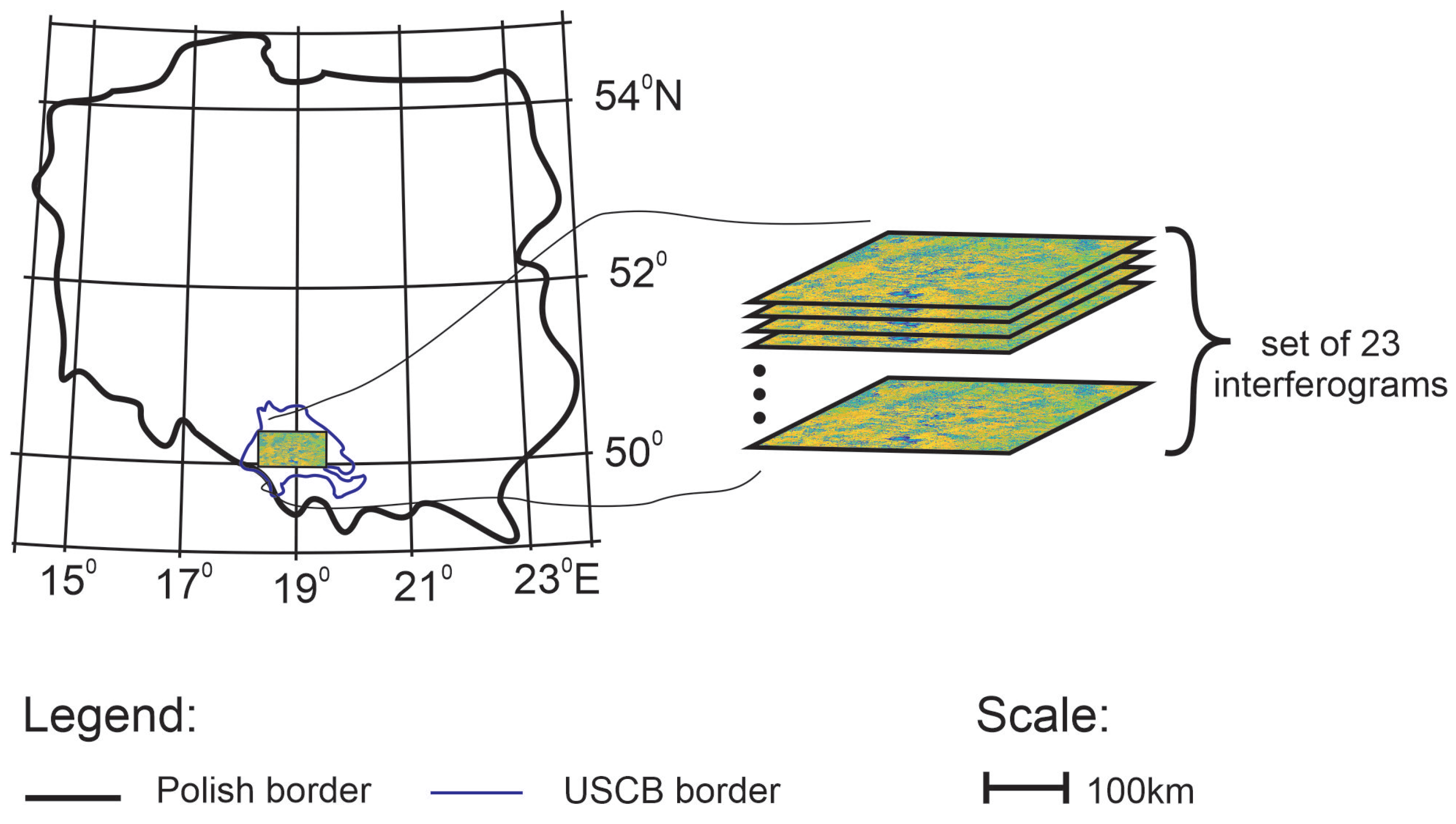
2. Materials and Methods
- All images were of the same size, selected based on the nature of the subsidence occurring in the analyzed area;
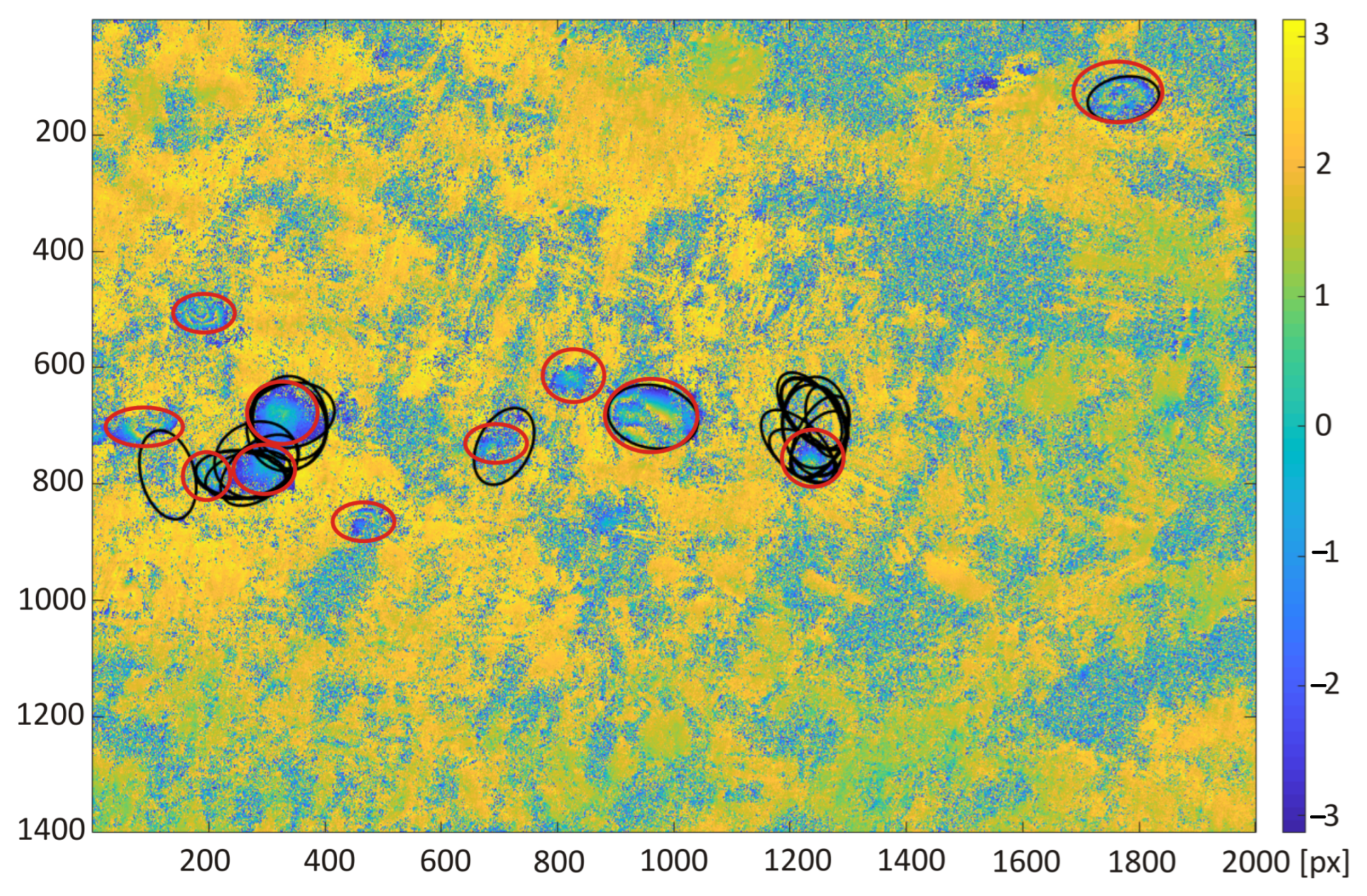
- Each image showed only one subsidence trough;
- Of the analyzed set 23 interferograms, a negative set was created that contains fragments of the interferogram with no visible subsidence troughs;
- Specified proportions were kept between the troughs containing the set and the interferogram fragments without a visible subsidence area;
- In the cross-validation stage, the ratio of the learning set to the test set was 70/30.
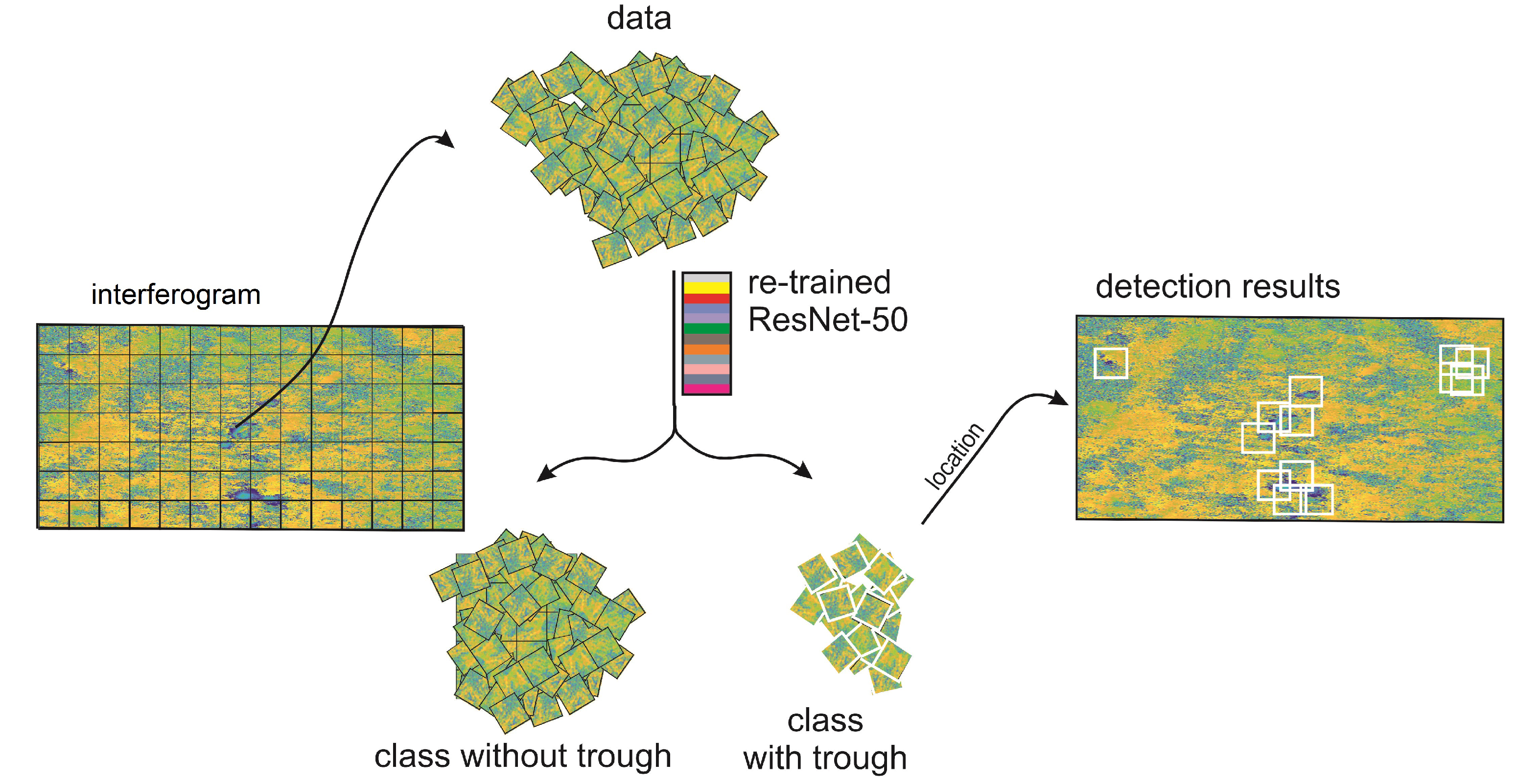
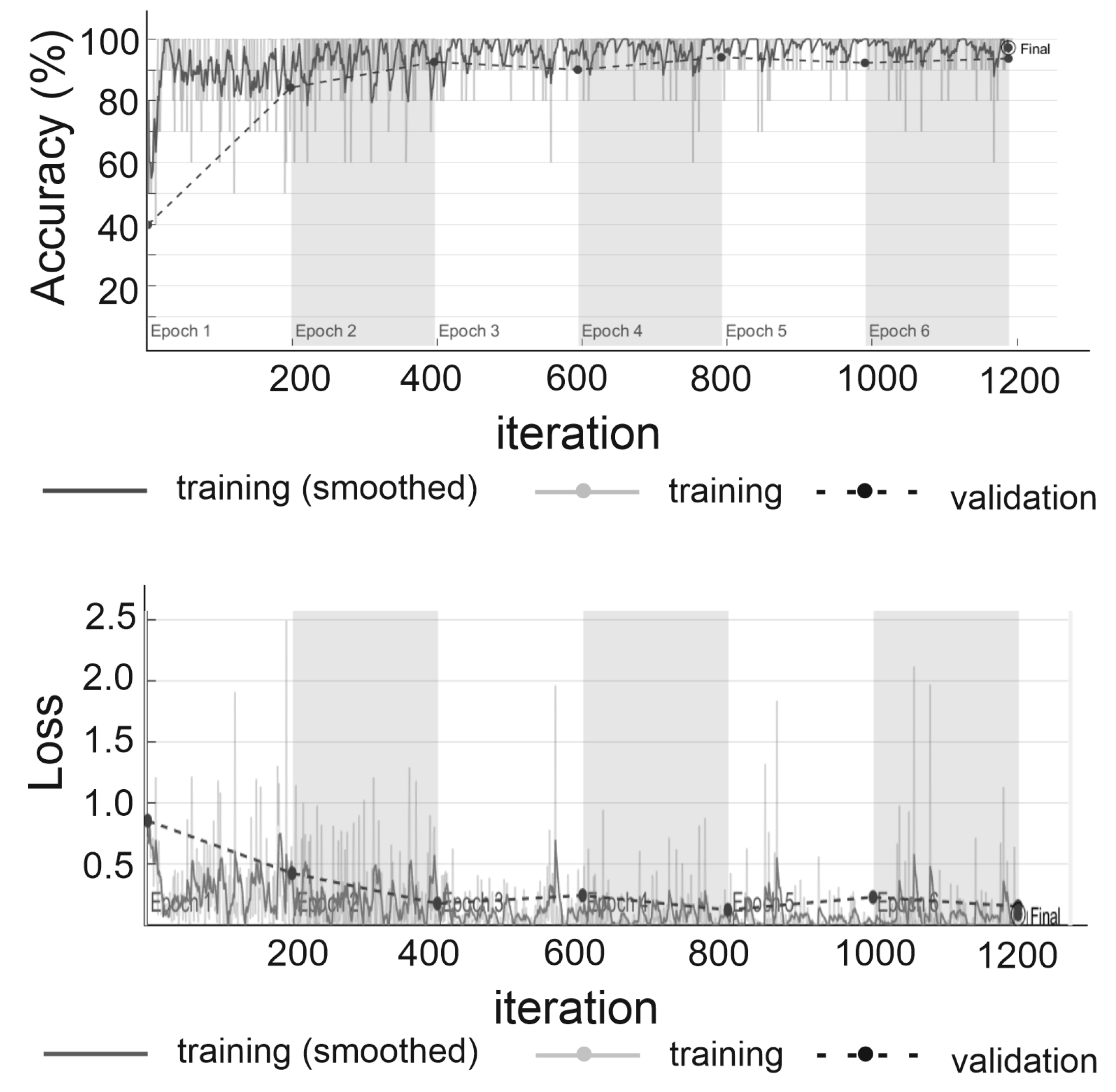
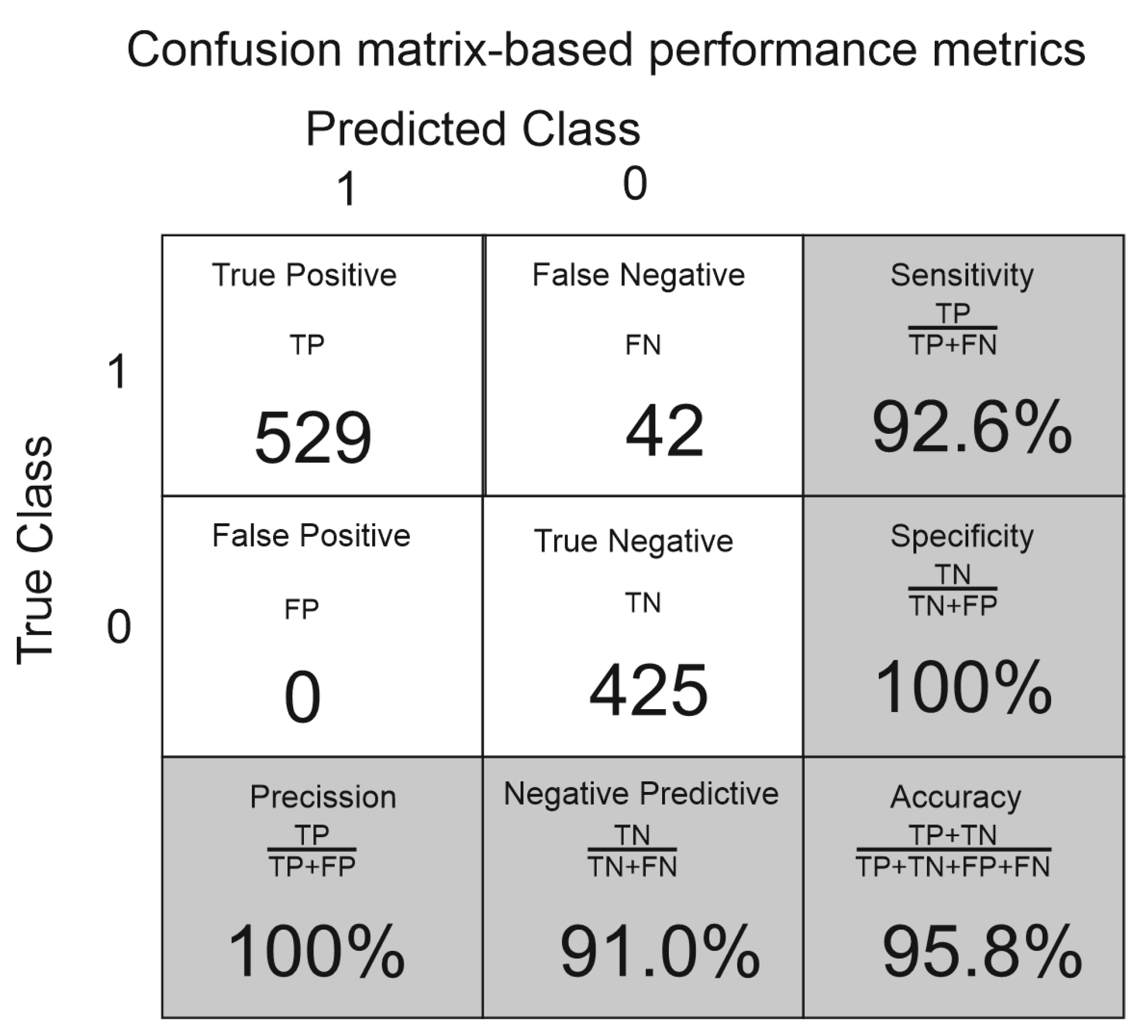
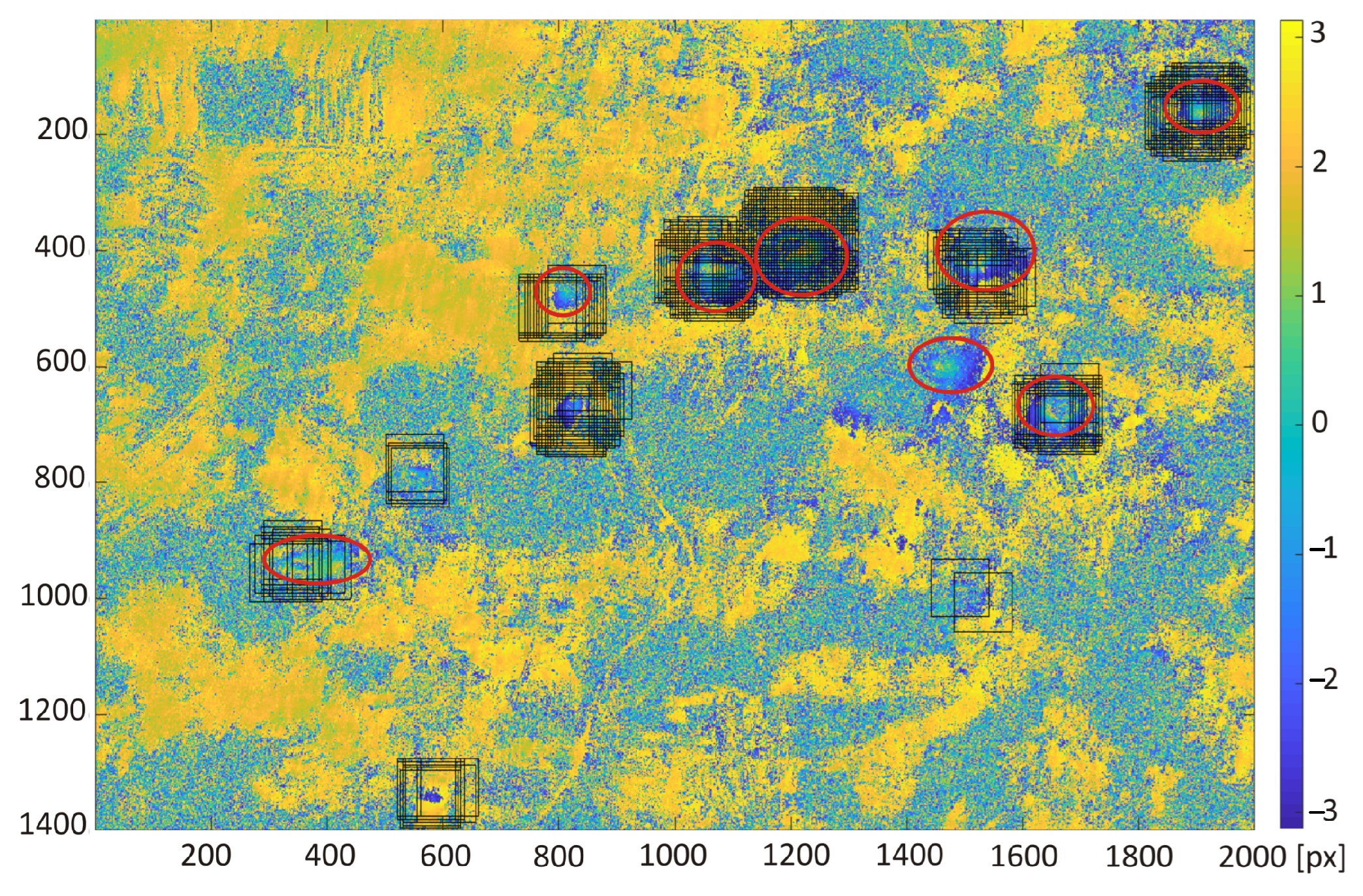
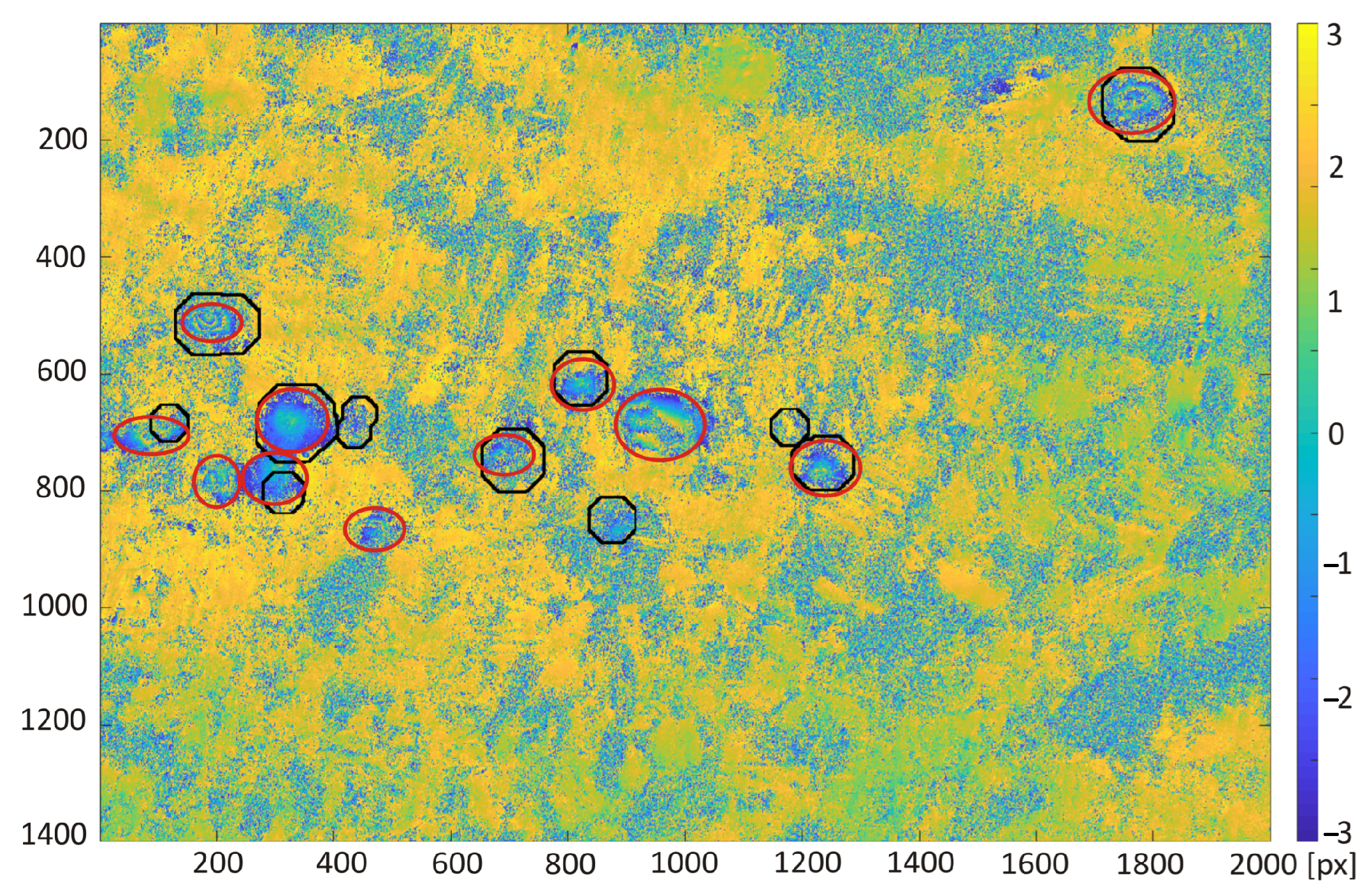
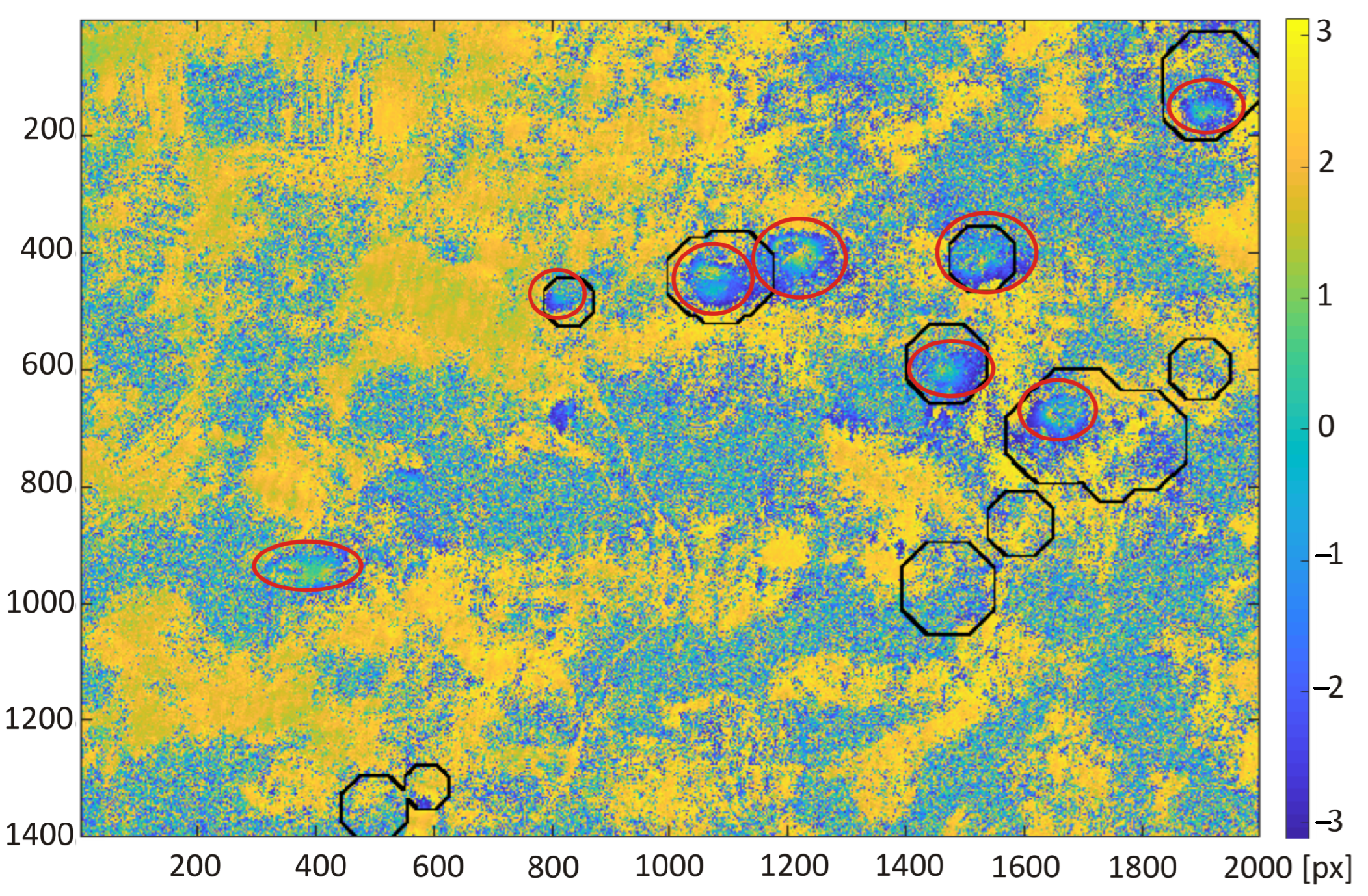
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| CT | Circlet transform |
| DInSAR | Differential interferometry synthetic aperture radar |
| GNSS | Global navigation satellite systems |
| HT | Hough transform |
| ResNet | Residual Network |
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture radar |
| USCB | Upper Silesian Coal Basin |
References
- Sedighi, M.; Arabi, S.; Nankali, H.; Amighpey, M.; Tavakoli, F.; Soltanpour, A.; Motagh, M. Subsidence Detection Using InSAR and Geodetic Measurements in the North-West of Iran. In Proceedings of the 2009 Fringe Workshop, Frascati, Italy, 30 November–4 December 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Porzycka, S.; Strzelczyk, J. Preliminary results of ground deformations monitoring within mining area of Prosper-Haniel coal mine. In Proceedings of the 12th International Multidisciplinary scientific Geoconference SGEM 2012, Albena, Bulgaria, 17–23 June 2012; Volume 2, pp. 895–899. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Dzurisin, D. InSAR Imaging of Aleutian Volcanoes: Monitoring a Volcanic Arc From Space; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nádudvari, A. Using radar interferometry and SBAS technique to detect surface subsidence relating to coal mining in Upper Silesia from 1993–2000 and 2003–2010. Environ. Socio-Econ. Stud. 2016, 4, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Xu, J.; Jung, J.; Yun, S.H.; Zeng, E.; Brooks, E.; Dolk, M.; Narasimhalu, L. Machine Learning on Satellite Radar Images to Estimate Damages After Natural Disasters. In Proceedings of the SIGSPATIAL/GIS 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 3–6 November 2020; pp. 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umowa Społeczna. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/aktywa-panstwowe/umowa-spoleczna (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Jung, H.; Kim, S.; Jung, H.; Min, K.; Won, J. Satellite observation of coal mining subsidence by persistent scatterer analysis. Eng. Geol. 2017, 92, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Chang, H.; Rizos, C. Mine subsidence monitoring using multi-source satellite SAR images. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2007, 73, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, A.; Grzybek, R. An evaluation of processing InSAR Sentinel-1A/B data for correlation of mining subsidence with mining induced tremors in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin Poland. In Proceedings of the E3S Web Conferences, Gdańsk, Poland, 22–25 June 2018; Volume 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluszek-Filipiak, K.; Borkowski, A. Integration of DInSAR and SBAS Techniques to Determine Mining-Related Deformations Using Sentinel-1 Data: The Case Study of Rydułtowy Mine in Poland. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnec, C.; Delacourt, C. Three years of mining subsidence monitored by SAR interferometry, near Gardanne, France. J. Appl. Geophys. 2000, 43, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, G.; Tomas, R.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.; Delgado, J.; Mallorqui, J.; Duque, S.; Mulas, J. Advanced DInSAR analysis on mining areas: La Union case study (Murcia, SE Spain). Eng. Geol. 2007, 90, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmuller, U.; Strozzi, T.; Werner, C. Monitoring of mining-induced surface deformation in the Ruhrgebiet (Germany) with SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 24–28 July 2000; Volume 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curlander, J.; McDonough, R. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Systems and Signal Processing; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Massonnet, D.; Rossi, M.; Carmona, C. The displacement field of the Landers earthquake mapped by radar interferometry. Nature 1991, 364, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus. Available online: www.copernicus.eu (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Fu, H.; Zhu, J.; Zuo, T. A framework for correcting ionospheric artifacts and atmospheric effects to generate high accuracy InSAR DEM. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Yu, C.; Li, Z.; He, X. Statistical assessment metrics for InSAR atmospheric correction: Applications to generic atmospheric correction online service for InSAR (GACOS) in Eastern China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 96, 102289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Z.; Penna, N.; Crippa, P. Generic atmospheric correction model for Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 9202–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porzycka-Strzelczyk, S.; Rotter, P.; Strzelczyk, J. Automatic Detection of Subsidence Troughs in SAR Interferograms Based on Circular Gabor Filters. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczak, M.; Bała, J. Application of the Hough Transform for subsidence troughs detection in SAR images. In Proceedings of the SGEM Conference Proceedings, Albena, Bulgaria, 29 June–5 July 2017; Volume 21, pp. 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Deng, K.; Fan, H.; Lei, S.; Yan, S.; Wang, L. An Improved Adaptive Template Size Pixel-Tracking Method for Monitoring Large-Gradient Mining Subsidence. J. Sens. 2017, 2017, 3059159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, P.; Muron, W. Automatic Detection of Subsidence Troughs in SAR Interferograms based on convolutional neutral networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bała, J.; Dwornik, M.; Franczyk, A. Automatic subsidence troughs detection in SAR interferograms using circlet transform. Sensors 2021, 21, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwornik, M.; Bała, J.; Franczyk, A. Application of a New Semi-Automatic Algorithm for the Detection of Subsidence Areas in SAR Images on the Example of the Upper Silesian Coal Basin. Energies 2021, 14, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadeusiewicz, R. Neural networks in mining sciences-general overview and some representative examples. Arch. Min. Sci. 2015, 60, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurkiewicz, E.; Tomecka-Suchoń, S.; Tadeusiewicz, R. Application of neural network enhanced ground-penetrating radar to localization of burial sites. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2016, 30, 844–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y. Target classification using the deep convolutional networks for SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4806–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Boser, B.; Denker, J.; Henderson, D.; Howard, R.; Hubbard, W.; Jackel, L. Backpropagation Applied to Handwritten Zip Code Recognition. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Volume 8689, pp. 818–833. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 11–12 June 2015; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In Proceedings of the ICLR, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Hartwig, M. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), LAs Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 22–25 July 2017; pp. 6517–6525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, J.; Huang, Y.; Huo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yeo, T. SAR automatic target recognition based on multiview deep learning framework. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2196–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T. A survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, C. Basic principles of ROC analysis. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1978, 8, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franczyk, A.; Bała, J.; Dwornik, M. Monitoring Subsidence Area with the Use of Satellite Radar Images and Deep Transfer Learning. Sensors 2022, 22, 7931. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207931
Franczyk A, Bała J, Dwornik M. Monitoring Subsidence Area with the Use of Satellite Radar Images and Deep Transfer Learning. Sensors. 2022; 22(20):7931. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207931
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranczyk, Anna, Justyna Bała, and Maciej Dwornik. 2022. "Monitoring Subsidence Area with the Use of Satellite Radar Images and Deep Transfer Learning" Sensors 22, no. 20: 7931. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207931
APA StyleFranczyk, A., Bała, J., & Dwornik, M. (2022). Monitoring Subsidence Area with the Use of Satellite Radar Images and Deep Transfer Learning. Sensors, 22(20), 7931. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22207931







