Rich Structural Index for Stereoscopic Image Quality Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
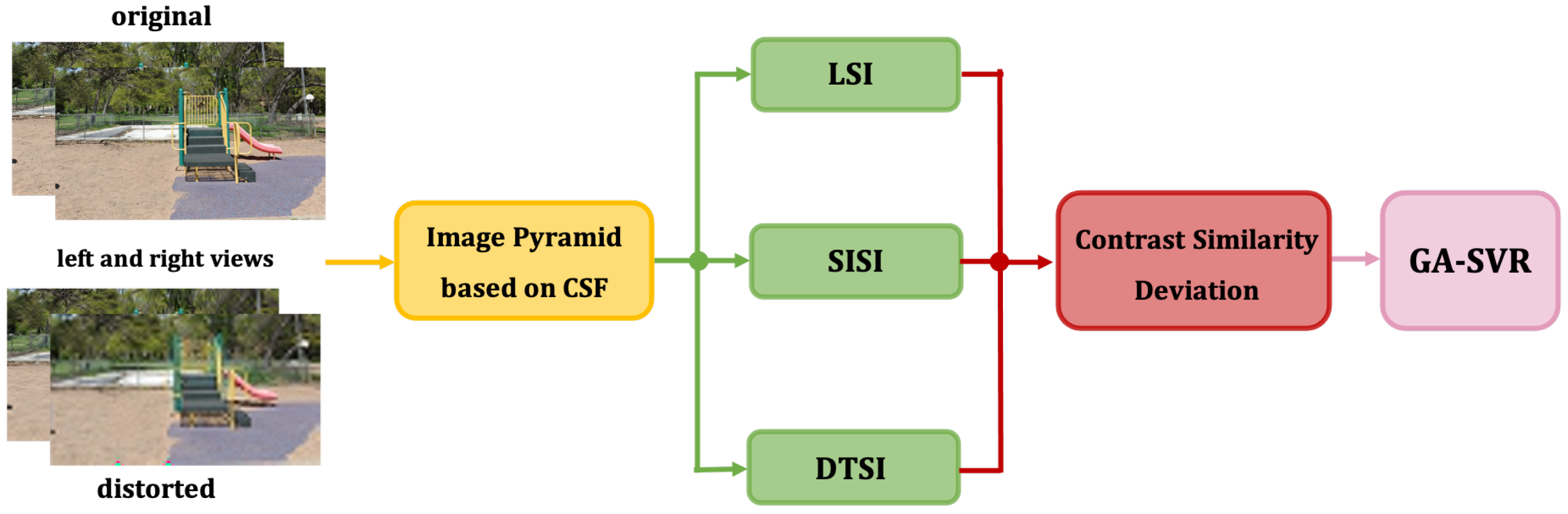
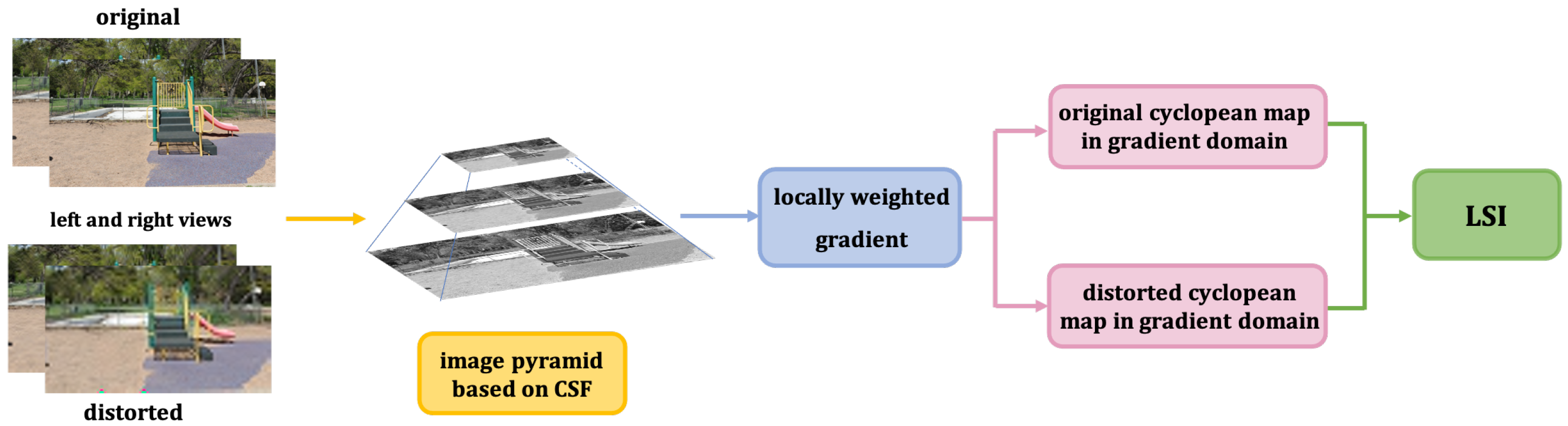
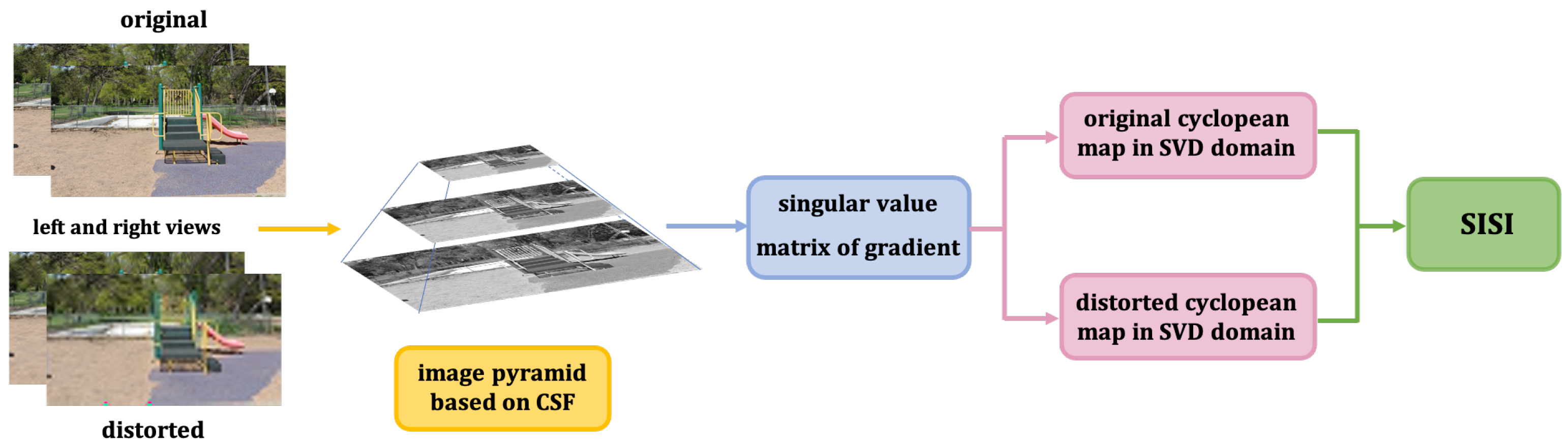
- Considering the image edge texture structure and internal hierarchical structure, we propose local Luminance and Structural Index (LSI) and the Sharpness and Intrinsic Structural Index (SISI) introducing image pyramid and cyclopean map to express the binocular perception characteristics of image information at different viewing distances;
- Binocular parallax is the most important physiological basis for human beings, which can reflect depth perception information. Towards this end, we advance Depth Texture Structural Index (DTSI) which combines the disparity map and the cross-mapping of gradient with sensitive factors to build a model extracting depth information closer to human visual subjective perception.
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Image Pyramid Based on CSF (IPC)
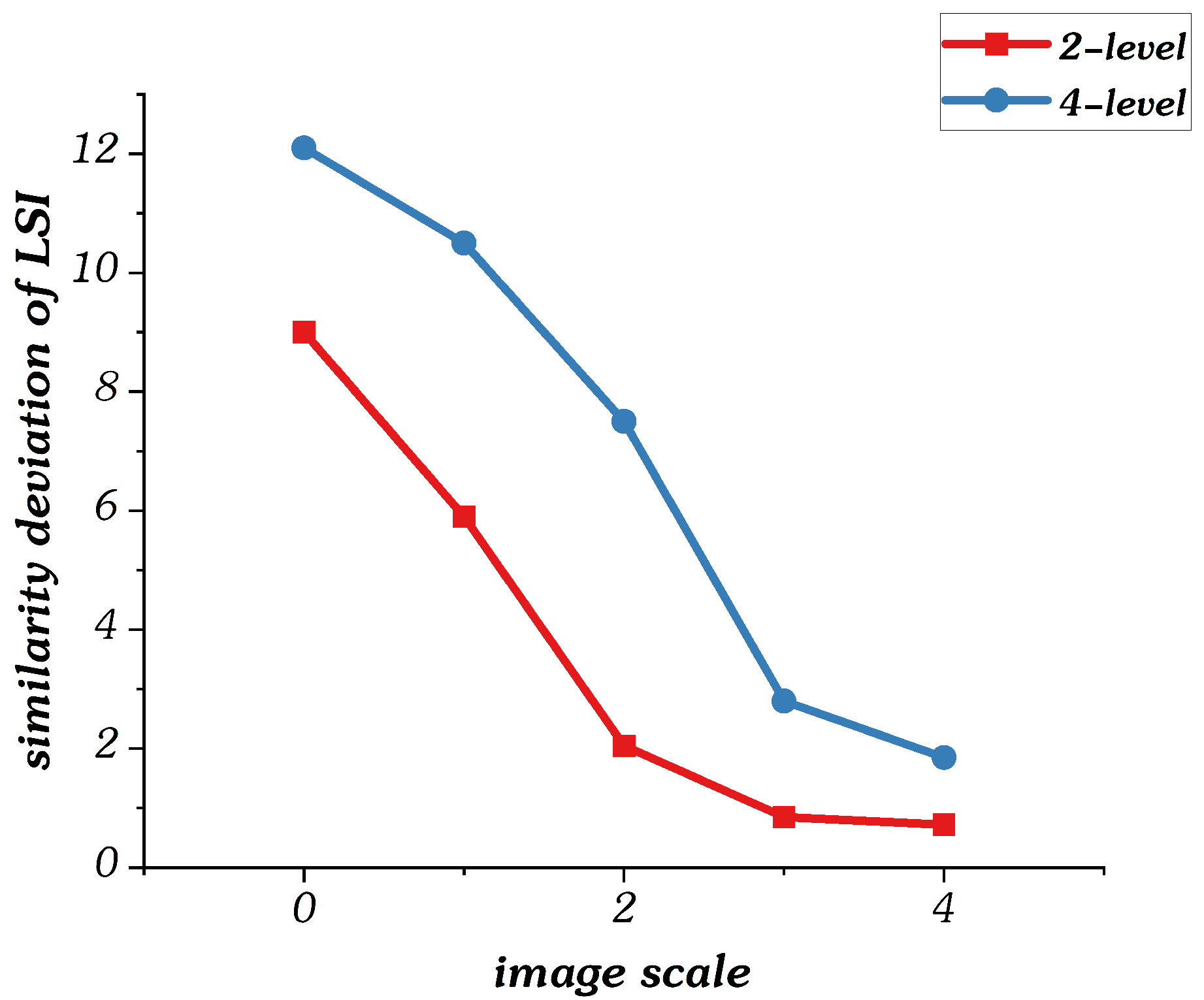
3.1.1. Image Pyramid
3.1.2. Contrast Sensitivity Function (CSF)
3.2. Rich Structural Indexes (RSI)
3.2.1. Local Luminance and Structural Index (LSI)
3.2.2. The Sharpness and Intrinsic Structural Index (SISI)
3.2.3. Depth Texture Structural Index (DTSI)
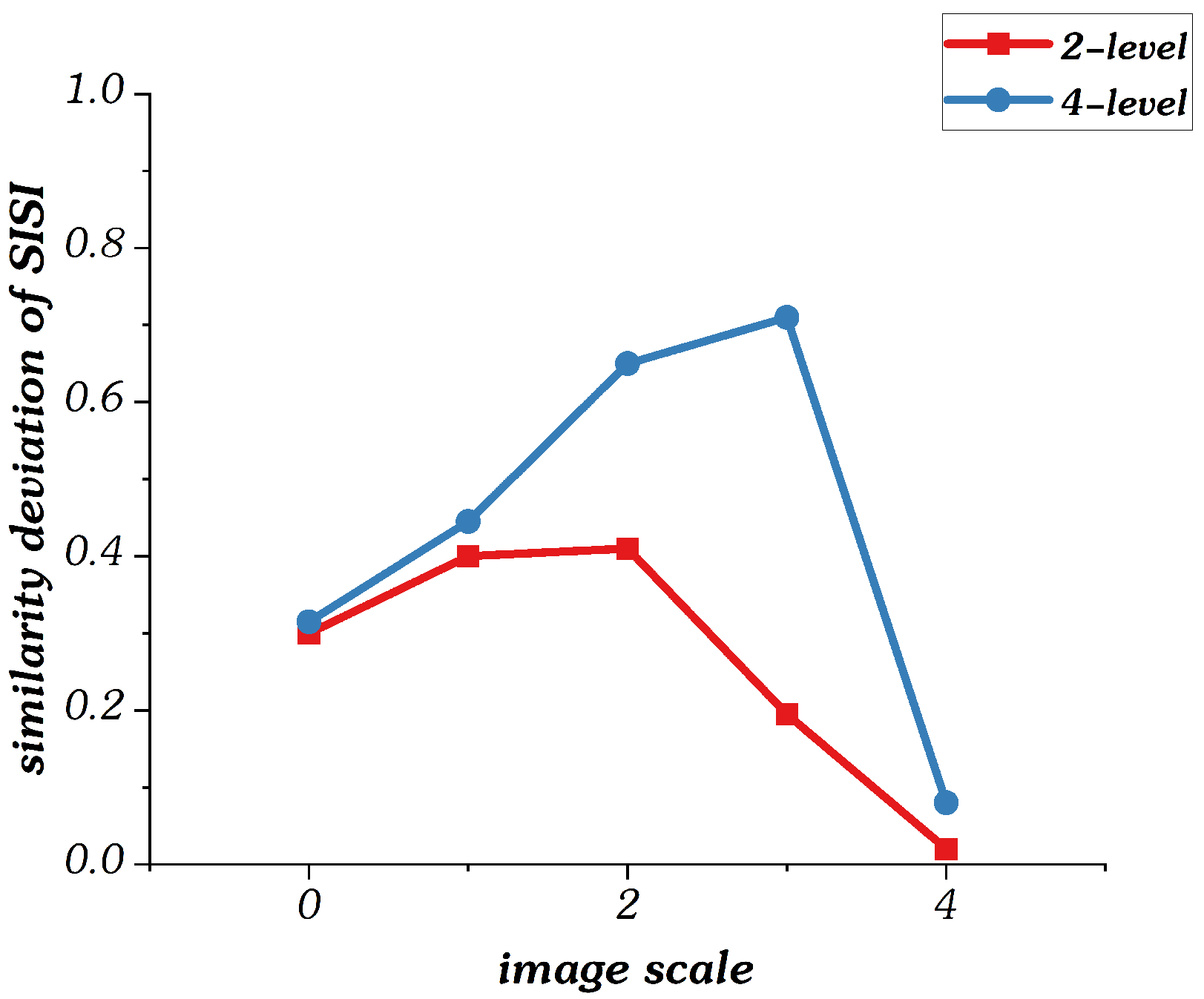
3.3. Contrast Similarity Deviation
3.4. Final Quality Assessment
- 1.
- The penalty factor c which reflects the degree of penalty of the algorithm on the sample data beyond the pipeline and representing the radial basis function in the SVR are coded to generate the initial population.
- 2.
- The new population is obtained by random cross selection, single point crossover, and mutation with probability 0.7. Then, we calculate the fitness of new population and select the highest fitness.
- 3.
- Judge whether the highest fitness satisfies the stopping condition. If so, determine it as the optimal parameter combination and apply it to SVR. If not, return to step 2 and start the calculation again.
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Databases
4.2. Overall Performance Comparison
4.3. Single Distortion Performance Comparison
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Gao, Z.; Chu, R. New stereo shooting evaluation metric based on stereoscopic distortion and subjective perception. Opt. Rev. 2015, 3, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lin, W.; Shi, G.; Li, L.; Fang, Y. Orientation selectivity based visual pattern for reduced-reference image quality assessment. Inf. Sci. 2016, 251, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 4, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, E.; Chandler, D. Most apparent distortion: Full-reference image quality assessment and the role of strategy. J. Electron. Imaging 2010, 1, 10–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Simoncelli, E.; Bovik, A. Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the Thrity-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 9–12 November 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1298–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.; Lin, W. Image Quality Assessment Based on Gradient Similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 4, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Xia, W.; Lin, W. No-Reference and Robust Image Sharpness Evaluation Based on Multiscale Spatial and Spectral Features. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2017, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, J. Objective Quality Assessment Method Of Stereo Images. In Proceedings of the 2009 3DTV Conference: The True Vision—Capture, Transmission and Display of 3D Video, Potsdam, Germany, 4–6 May 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, F.; Lin, W.; Gu, S.; Jiang, G.; Srikanthan, T. Perceptual Full-Reference Quality Assessment of Stereoscopic Images by Considering Binocular Visual Characteristics. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Fu, C.; Ji, L.; Tang, K.; Zhou, M. Feature selection and parameter optimization for support vector machines: A new approach based on genetic algorithm with feature chromosomes. Expert Syst. Appl. Int. J. 2011, 38, 5197–5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalouf, A.; Larabi, M. Cyclop: A stereo color image quality assessment metric. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–27 May 2011; pp. 1161–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Su, C.; Kwon, D. Full-reference quality assessment of stereopairs accounting for rivalry. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2013, 9, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fezza, S.; Larabi, M. Stereoscopic 3d image quality assessment based on cyclopean view and depth map. In Proceedings of the IEEE Fourth International Conference on Consumer Electronics—Berlin (ICCE-Berlin), Berlin, Germany, 7–10 September 2014; pp. 335–339. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Yang, J.; Lu, W.; Meng, Q.; Song, Z. Quality index for stereoscopic images by jointly evaluating cyclopean amplitude and cyclopean phase. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2016, 1, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Lu, W.; Meng, Q.; Lv, Z.; Zhao, D.; Gao, Z. Quality assessment metric of stereo images considering cyclopean integration and visual saliency. Inf. Sci. 2016, 373, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.; Channappayya, S. Sparsity based stereoscopic image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the 50th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 6–9 November 2016; pp. 1858–1862. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Q.; Duan, F.; Shao, F. 3d visual attention for stereoscopic image quality assessment. JSW 2014, 7, 1841–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Meng, Q.; Lv, Z.; Song, A.; Gao, Z. Stereoscopic image quality assessment method based on binocular combination saliency model. Signal Process. 2016, 125, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.; Shen, X.; Geng, X.; An, P. Combining visual saliency and binocular energy for stereoscopic image quality assessment. In Proceedings of the International Forum of Digital TV and Wireless Multimedia Communication, Shanghai, China, 9–10 November 2016; pp. 104–114. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.; Channappayya, S. Estimating Depth-Salient Edges and Its Application to Stereoscopic Image Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 12, 5892–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qu, C. Learning structure of stereoscopic image for no-reference quality assessment with convolutional neural network. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 59, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yu, L. Binocular responses for no-reference 3d image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2016, 6, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, K.; Liu, M.; Zhai, G.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W. Quality assessment considering viewing distance and image resolution. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2015, 3, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Jia, H.; Li, B.; Shu, H. Multiscale contrast similarity deviation: An effective and efficient index for perceptual image quality assessment. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2016, 45, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A. Visual detection of spatial contrast patterns: Evaluation of five simple models. Opt. Express 2000, 6, 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agaian, S. Visual morphology. In Proceedings of the IS & T/SPIE’s Symposium on Electronic Imaging Science & Technology, San Jose, CA, USA, 23–29 January 1999; pp. 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Panetta, K.; Agaian, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wharton, E. Parameterized logarithmic framework for image enhancement systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Part B (Cybern.) 2011, 41, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Kim, M. A Novel Image Quality Assessment with Globally and Locally Consilient Visual Quality Perception. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 25, 2392–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Kim, M. A novel DCT-based JND model for luminance adaptation effect in DCT frequency. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2013, 20, 893–896. [Google Scholar]
- Mannos, J.; Sakrison, D. The effects of a visual delity criterion of the encoding of images. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1974, 4, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, S. Subroutine for the Generation of a Two Dimensional Human Visual Contrast Sensitivity Function; Technical Report 233203Y; Eastman Kodak: Rochester, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Damera-Venkata, N.; Kite, T.; Geisler, W.; Evans, B.; Bovik, A. Image quality assessment based on a degradation model. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2000, 4, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daly, S. Visible differences predictor: An algorithm for the assessment of image fidelity. In Proceedings of the 1992 Symposium on Electronic Imaging: Science and Technology, San Jose, CA, USA, 9–14 February 1992; Volume 1666, pp. 2–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, A.; Sejnowski, T. The ‘independent components’ of natural scenes are edge filters. Vis. Res. 1997, 23, 3327–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Bovik, A. Gradient magnitude similarity deviation: A highly efficient perceptual image quality index. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 2, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Cai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, W.; Kot, A.; Sun, X. Sparse representation-based image quality index with adaptive sub-dictionaries. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 8, 3775–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Mou, X.; Zhang, D. Fsim: A feature similarity index for image quality assessment. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 8, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narwaria, M.; Lin, W. SVD-based quality metric for image and video using machine learning. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B (Cybern.) 2011, 2, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narwaria, M.; Lin, W. Automatic Parameter Selection for Denoising Algorithms Using a No-Reference Measure of Image Content. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 3116–3132. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, R.; Wilson, H. Binocular vision. Vis. Res. 2011, 7, 754–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Yu, L.; Wu, M. Simulating binocular vision for no-reference 3D visual quality measurement. Opt. Express 2015, 18, 23710–23725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Cormack, L.; Bovik, A. No-Reference quality assessment of natural stereopairs. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2013, 9, 3379–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelli, D.; Bex, P. Measuring contrast sensitivity. Vis. Res. 2013, 90, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peli, E. Contrast in complex images. JOSA A 1990, 10, 2032–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, G.; Hou, C.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, Y. Blind stereoscopic 3D image quality assessment via analysis of naturalness, structure, and binocular asymmetry. Signal Process. 2018, 150, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, Y. No-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment based on saliency-guided binocular feature consolidation. Electron. Lett. 2017, 22, 1468–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Deng, R.; Xie, X.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Krylov, A. No-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment using convolutional neural network for adaptive feature extraction. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 37595–37603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, A.; Bovik, A. Blind image quality assessment: From natural scene statistics to perceptual quality. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 12, 3350–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sim, K.; Gao, X.; Lu, W.; Meng, Q.; Li, B. A blind stereoscopic image quality evaluator with segmented stacked autoencoders considering the whole visual perception route. IEEE Trans. Image Process. Mar. 2019, 3, 1314–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, A.; Su, C.; Mittal, A.; Bovik, A. Subjective evaluation of stereoscopic image quality. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2013, 8, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, K.; Wang, Z. Quality prediction of asymmetrically distorted stereoscopic images from single views. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Chengdu, China, 14–18 July 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Song, R.; Ko, H.; Kuo, C. Mcl-3d: A Database for Stereoscopic Image Quality Assessment Using 2d-Image-Plus-Depth Source. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1405.1403. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Qiu, W.; Wu, M.; Luo, T. Blind quality estimator for 3D images based on binocular combination and extreme learning machine. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 71, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; An, P.; Shen, L.; Li, K. Full-reference quality assessment of stereoscopic images by learning binocular visual properties. Appl. Opt. 2017, 29, 8291–8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, X.; Shen, L.; Li, K.; An, P. A stereoscopic image quality assessment model based on independent component analysis and binocular fusion property. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2017, 52, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; He, M.; Yu, M.; Shao, F.; Peng, Z. Perceptual stereoscopic image quality assessment method with tensor decomposition and manifold learning. IET Image Process. 2018, 5, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Chen, W.; Jiang, G.; Ho, Y. Modeling the perceptual quality of stereoscopic images in the primary visual cortex. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 15706–15716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, F.; Tian, W.; Lin, W.; Jiang, G.; Dai, Q. Toward a blind deep quality evaluator for stereoscopic images based on monocular and binocular interactions. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 5, 2059–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lin, C.; Liu, H.; Pei, S. Blind Stereoscopic Image Quality Assessment Based on Hierarchical Learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 8058–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Q | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLCC | SROCC | RMSE | PLCC | SROCC | RMSE | PLCC | SROCC | RMSE | PLCC | SROCC | RMSE | |
| LIVE Phase-I | 0.9412 | 0.9278 | 5.2598 | 0.9389 | 0.9201 | 5.7892 | 0.8545 | 0.8458 | 8.5975 | 0.9512 | 0.9429 | 5.0028 |
| LIVE Phase-II 3D | 0.9325 | 0.9317 | 5.8256 | 0.9263 | 0.9136 | 5.2715 | 0.7789 | 0.7369 | 10.2548 | 0.9431 | 0.9452 | 4.2859 |
| WaterlooIVC Phase-I | 0.9458 | 0.9389 | 5.0214 | 0.9404 | 0.9321 | 5.5825 | 0.7782 | 0.7654 | 9.8975 | 0.9546 | 0.9478 | 4.2859 |
| MCL | 0.9124 | 0.9147 | 1.2925 | 0.9077 | 0.9101 | 1.2356 | 0.7625 | 0.7855 | 1.5478 | 0.9219 | 0.9259 | 1.0026 |
| LIVE Phase-I | LIVE Phase-II | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLCC | SROCC | RMSE | PLCC | SROCC | RMSE | |
| Jiang [56] | 0.9460 | 0.9378 | 5.3160 | 0.9261 | 0.9257 | 4.2627 |
| Yue [45] | 0.9370 | 0.9140 | 5.6521 | 0.9140 | 0.9060 | 4.4490 |
| Khan [20] | 0.9272 | 0.9163 | - | 0.9323 | 0.9272 | - |
| Shao [57] | 0.9389 | 0.9308 | 5.6459 | 0.9263 | 0.9282 | 4.1996 |
| Geng [55] | 0.9430 | 0.9320 | 5.5140 | 0.9210 | 0.9190 | 5.4001 |
| Ma [54] | 0.9409 | 0.9340 | 5.2110 | 0.9300 | 0.9218 | 4.1232 |
| proposed | 0.9512 | 0.9429 | 5.0028 | 0.9431 | 0.9452 | 4.2859 |
| PLCC | SROCC | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Khan [20] | 0.9344 | 0.9253 | - |
| Ma [54] | 0.9252 | 0.9117 | 5.8766 |
| Yue [45] | 0.9261 | 0.9192 | 4.6101 |
| Yang [49] | 0.9439 | 0.9246 | - |
| Geng [55] | 0.8460 | 0.8101 | 9.4691 |
| Proposed | 0.9546 | 0.9478 | 4.6836 |
| PLCC | SROCC | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zhou [53] | 0.8850 | 0.8520 | 1.1770 |
| Shao [58] | 0.9138 | 0.9040 | 1.0233 |
| Khan [20] | 0.9113 | 0.9058 | - |
| Liu [59] | 0.9044 | 0.9087 | 1.1137 |
| Chen [42] | 0.8278 | 0.8300 | 1.4596 |
| Proposed | 0.9219 | 0.9259 | 1.0026 |
| LIVE Phase-I | LIVE Phase-II | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2K | JPEG | Gblur | WN | FF | JP2K | JPEG | Gblur | WN | FF | |
| Jiang [56] | 0.9408 | 0.6975 | 0.9578 | 0.9516 | 0.8554 | 0.8463 | 0.8771 | 0.9845 | 0.9593 | 0.9601 |
| Yue [45] | 0.9350 | 0.7440 | 0.9710 | 0.9620 | 0.8540 | 0.9860 | 0.8430 | 0.9730 | 0.9860 | 0.9230 |
| Khan [20] | 0.9508 | 0.7110 | 0.9593 | 0.9470 | 0.8583 | 0.9270 | 0.8925 | 0.9778 | 0.9699 | 0.8987 |
| Shao [57] | 0.9366 | 0.6540 | 0.9542 | 0.9441 | 0.8304 | 0.8768 | 0.8506 | 0.9445 | 0.9339 | 0.9330 |
| Geng [55] | 0.9420 | 0.7190 | 0.9620 | 0.9630 | 0.8670 | 0.8510 | 0.8350 | 0.9790 | 0.9490 | 0.9480 |
| Ma [54] | 0.9610 | 0.7746 | 0.9711 | 0.9412 | 0.8941 | 0.9670 | 0.9350 | 0.9384 | 0.9341 | 0.9489 |
| Proposed | 0.9679 | 0.7847 | 0.9787 | 0.9558 | 0.8856 | 0.9327 | 0.9452 | 0.9870 | 0.9707 | 0.9627 |
| LIVE Phase-I | LIVE Phase-II | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2K | JPEG | Gblur | WN | FF | JP2K | JPEG | Gblur | WN | FF | |
| Jiang [56] | 0.9027 | 0.6628 | 0.9361 | 0.9529 | 0.8079 | 0.8497 | 0.8547 | 0.9383 | 0.9563 | 0.9555 |
| Yue [45] | 0.8320 | 0.5950 | 0.8570 | 0.9320 | 0.7790 | 0.9590 | 0.7690 | 0.8680 | 0.9590 | 0.9130 |
| Khan [20] | 0.9074 | 0.6062 | 0.9295 | 0.9386 | 0.8092 | 0.9133 | 0.8670 | 0.8854 | 0.9584 | 0.8646 |
| Shao [57] | 0.9000 | 0.6339 | 0.9242 | 0.9430 | 0.7807 | 0.8747 | 0.8340 | 0.9241 | 0.9325 | 0.9409 |
| Geng [55] | 0.9050 | 0.6530 | 0.9310 | 0.9560 | 0.8160 | 0.8360 | 0.8410 | 0.9210 | 0.9390 | 0.9160 |
| Ma [54] | 0.9140 | 0.6659 | 0.9030 | 0.9037 | 0.8312 | 0.9328 | 0.8968 | 0.8992 | 0.8893 | 0.9167 |
| Proposed | 0.9271 | 0.6758 | 0.9252 | 0.9335 | 0.8156 | 0.9636 | 0.9087 | 0.9398 | 0.9319 | 0.9174 |
| Zhou [53] | Shao [58] | Khan [20] | Liu [59] | Proposed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG | 0.8260 | 0.7016 | 0.9574 | 0.9404 | 0.9432 |
| JP2K | 0.8760 | 0.8571 | 0.9640 | 0.9219 | 0.9725 |
| WN | 0.9140 | 0.6748 | 0.9561 | 0.9135 | 0.9345 |
| Gblur | 0.9340 | 0.9013 | 0.9270 | 0.9479 | 0.9603 |
| Sblur | 0.9410 | 0.8640 | 0.9409 | 0.9530 | 0.9600 |
| Tloss | 0.8910 | 0.5814 | 0.8722 | 0.7618 | 0.8571 |
| Zhou [53] | Shao [58] | Khan [20] | Liu [59] | Proposed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG | 0.7760 | 0.7992 | 0.8877 | 0.8506 | 0.9045 |
| JP2K | 0.8520 | 0.8415 | 0.9317 | 0.9011 | 0.9320 |
| WN | 0.9040 | 0.6404 | 0.9517 | 0.9256 | 0.9273 |
| Gblur | 0.9160 | 0.8993 | 0.9131 | 0.9519 | 0.9504 |
| Sblur | 0.9330 | 0.8532 | 0.9348 | 0.9577 | 0.9617 |
| Tloss | 0.8450 | 0.5674 | 0.8744 | 0.7909 | 0.8818 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Gou, R.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, B.; Shen, Z. Rich Structural Index for Stereoscopic Image Quality Assessment. Sensors 2022, 22, 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22020499
Zhang H, Hu X, Gou R, Zhang L, Zheng B, Shen Z. Rich Structural Index for Stereoscopic Image Quality Assessment. Sensors. 2022; 22(2):499. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22020499
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hua, Xinwen Hu, Ruoyun Gou, Lingjun Zhang, Bolun Zheng, and Zhuonan Shen. 2022. "Rich Structural Index for Stereoscopic Image Quality Assessment" Sensors 22, no. 2: 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22020499
APA StyleZhang, H., Hu, X., Gou, R., Zhang, L., Zheng, B., & Shen, Z. (2022). Rich Structural Index for Stereoscopic Image Quality Assessment. Sensors, 22(2), 499. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22020499






