Pixel-Reasoning-Based Robotics Fine Grasping for Novel Objects with Deep EDINet Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a fine grasping representation model to generate the gripper configuration of parallel-jaw, which can effectively avoid the collision problem for clutter objects. Besides, the adaptive grasping width is fine for deformed or rigid objects in the grasping process;
- It is proposed to use the EDINet network to generate pixel-level gripper configurations to avoid missing potential ground truth grasp poses and reduce calculation time. The EDINet meets the real-time performance within 25 ms and achieves a very good balance in the speed and accuracy of grasping reasoning;
- Our system shows out-performance on the Cornell grasp datasets due to proper network structure, and it has been proven to be effective for novel objects in cluttered scenes. In actual robot grasping, our method has an average grasp success rate of 97.2% in a single-object scene and an average success rate of 93.7% in a cluttered scene. Moreover, our method outperforms the state-of-the-art algorithms in real application;
- Our network uses RGB-D multi-modal data to enhance the diversity and saliency of features so that it is easy to train the model and effectively improve the accuracy and success rate of grasping detection.
2. Related Work
2.1. Robotic Grasping
2.2. Grasping Representation
2.3. Network for Grasping
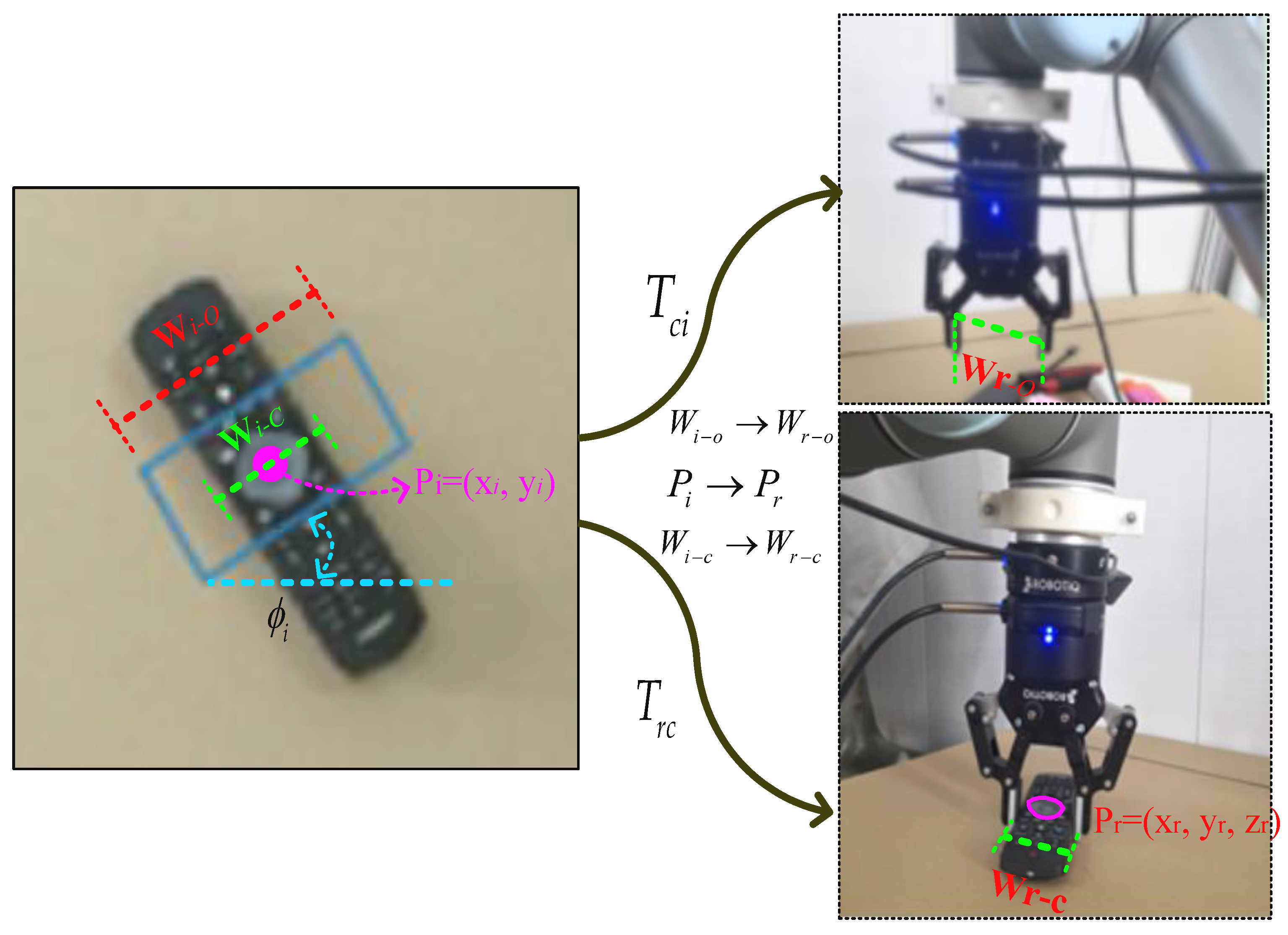
3. Robot Grasp Representation
4. Proposed Methods
4.1. The Robotics Grasping System
4.2. The EDINet Architecture
4.3. Grasping Training
- Grasp confidence: We regard the grasp confidence as a binary label and express it with a score between 0 and 1. The closer it is to 1, the higher the success rate of grasping.
- Grasp width: In order to achieve depth invariance, we set the grasping width and in the range of [0,], and is the maximum width of the gripper. In the training process, we first scale it to [0,1] and then use the camera parameters and the measured depth to calculate the grasp width.
- Grasp Angle: Set the area of the grasp rectangle to and encoding the angle as a vector component on the unit circle produces a value in the range [–1,1] and eliminates the possibility of discontinuity when the angle surrounds . We use to represent the grasp angle.
4.4. Loss Function
4.5. Pixel-Level Grasping Detection
5. Implementation Details
5.1. Training Dataset
5.2. Metrics for Grasp Detection
- (1)
- The rotation angle difference between the predicted grasp rectangle and the ground truth rectangle is less than 30°;
- (2)
- The Jaccard index between the predicted grasping rectangle and the ground truth rectangle is more than 0.25, where the Jacquard index is defined as:
5.3. Test in Datasets
6. Results and Analysis
6.1. Ablation Experiment on Network
6.2. Test Results on the Cornell Grasp Dataset
6.3. Test Results on the Jacquard Dataset
7. Robot Fine Grasping
7.1. Adaptive Closing Width Test
7.2. Grasping with Adaptive Opening Test
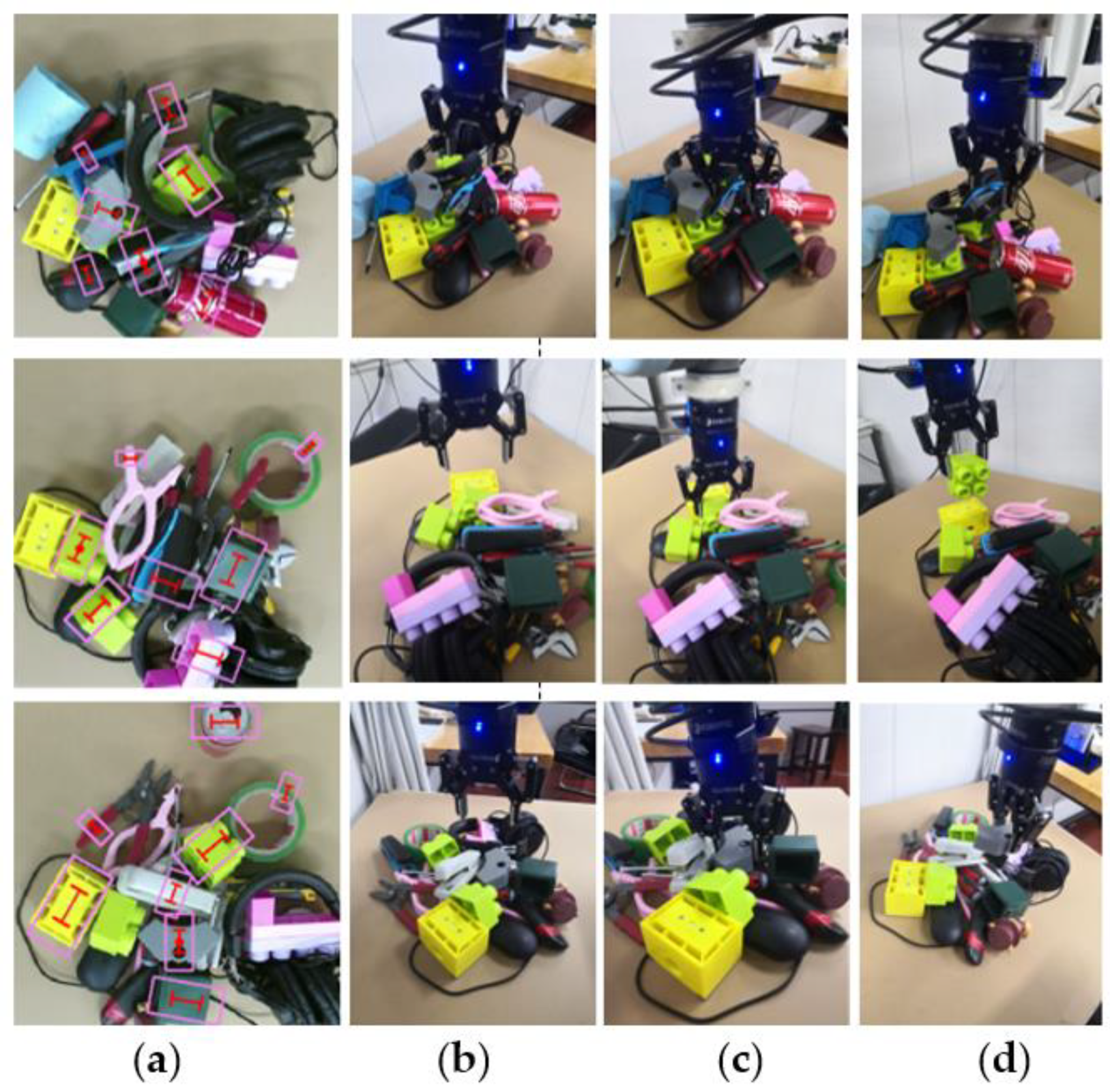
8. Unknown Objects Grasping
8.1. Single Target Grasping Test
8.2. Cluttered Grasping Test
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sergiyenko, O.Y.; Tyrsa, V.V. 3D optical machine vision sensors with intelligent data management for robotic swarm navigation improvement. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 11262–11274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tan, J.; He, H. Magichand: Context-aware dexterous grasping using an anthropomorphic robotic hand. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 9895–9901. [Google Scholar]
- Collodi, L.; Bacciu, D.; Bianchi, M.; Averta, G. Learning with few examples the semantic description of novel human-inspired grasp strategies from RGB data. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 2573–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Quiñonez, J.; Sergiyenko, O.; Hernandez-Balbuena, D.; Rivas-Lopez, M.; Flores-Fuentes, W.; Basaca-Preciado, L. Improve 3D laser scanner measurements accuracy using a FFBP neural network with Widrow-Hoff weight/bias learning function. Opto-Electron. Rev. 2014, 22, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergiyenko, O.Y.; Ivanov, M.V.; Tyrsa, V.; Kartashov, V.M.; Rivas-López, M.; Hernández-Balbuena, D.; Flores-Fuentes, W.; Rodríguez-Quiñonez, J.C.; Nieto-Hipólito, J.I.; Hernandez, W. Data transferring model determination in robotic group. Rob. Autom. Syst. 2016, 83, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Cruz, L.; Gonçalves, N. Deep facial diagnosis: Deep transfer learning from face recognition to facial diagnosis. IEEE Access. 2020, 8, 123649–123661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Yang, M.; Tian, X.; Jiang, N.; Wang, D. A full stage data augmentation method in deep convolutional neural network for natural image classification. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2020, 2020, 4706576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, M.; Fang, H.-S.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, S.; Wang, C.; Lu, C. Rgb matters: Learning 7-dof grasp poses on monocular rgbd images. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 13459–13466. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Ho, D.; Meng, M.Q.-H. High accuracy and efficiency grasp pose detection scheme with dense predictions. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 3604–3610. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Kong, T.; Sun, F.; Liu, H. Object discovery and grasp detection with a shared convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 2038–2043. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Liu, C.; Chang, F.; Li, N.; Li, G. High-performance Pixel-level Grasp Detection based on Adaptive Grasping and Grasp-aware Network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, P.; Ma, Z.; Chen, L. A Context-Free Method for Robust Grasp Detection: Learning to Overcome Contextual Bias. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, X.; Shen, W. A novel robotic grasp detection method based on region proposal networks. Robot. Comput. -Integr. Manuf. 2020, 65, 101963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Song, S.; Yu, K.-T.; Donlon, E.; Hogan, F.R.; Bauza, M.; Ma, D.; Taylor, O.; Liu, M.; Romo, E. Robotic pick-and-place of novel objects in clutter with multi-affordance grasping and cross-domain image matching. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 3750–3757. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Lan, X.; Zhou, X.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, N. Visual manipulation relationship recognition in object-stacking scenes. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 140, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.-S.; Wang, C.; Gou, M.; Lu, C. Graspnet-1billion: A large-scale benchmark for general object grasping. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, Online, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11444–11453. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Akinola, I.; Gupta, A.; Xu, F.; Varley, J.; Watkins-Valls, D.; Allen, P.K. Generative Attention Learning: A “GenerAL” framework for high-performance multi-fingered grasping in clutter. Auton. Robot. 2020, 44, 971–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Hermans, T. Modeling grasp type improves learning-based grasp planning. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundell, J.; Verdoja, F.; Kyrki, V. Ddgc: Generative deep dexterous grasping in clutter. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 6899–6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laili, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ren, L.; Wang, X.; Deen, M.J. Custom Grasping: A Region-Based Robotic Grasping Detection Method in Industrial Cyber-Physical Systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, B.; Huang, D. Double-Dot Network for Antipodal Grasp Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 4654–4661. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Geng, W.; Yu, J.; Zhang, W. A Two-Stream CNN With Simultaneous Detection and Segmentation for Robotic Grasping. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 52, 1167–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, J.; Liang, J.; Niyaz, S.; Laskey, M.; Doan, R.; Liu, X.; Ojea, J.A.; Goldberg, K. Dex-Net 2.0: Deep Learning to Plan Robust Grasps with Synthetic Point Clouds and Analytic Grasp Metrics. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.09312. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Kong, T.; Chu, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, L. Simultaneous Semantic and Collision Learning for 6-DoF Grasp Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 3571–3578. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, D.; Corke, P.; Leitner, J. Closing the loop for robotic grasping: A real-time, generative grasp synthesis approach. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.05172. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Zhai, D.-H.; Xia, Y.; Wu, H.; Liao, J. SE-ResUNet: A Novel Robotic Grasp Detection Method. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 5238–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, I.; Lee, H.; Saxena, A. Deep learning for detecting robotic grasps. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2015, 34, 705–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, F.-J.; Xu, R.; Vela, P.A. Real-world multiobject, multigrasp detection. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 3355–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Depierre, A.; Dellandréa, E.; Chen, L. Optimizing correlated graspability score and grasp regression for better grasp prediction. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.00872. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Cao, H.; Qu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liang, Z. Event-based robotic grasping detection with neuromorphic vision sensor and event-grasping dataset. Front. Neurorobot. 2020, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Moseson, S.; Saxena, A. Efficient grasping from rgbd images: Learning using a new rectangle representation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 3304–3311. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.; Seo, Y.; Shin, D.; Choi, J.; Chun, S.Y. A single multi-task deep neural network with post-processing for object detection with reasoning and robotic grasp detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 7300–7306. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, L.; Gupta, A. Supersizing self-supervision: Learning to grasp from 50k tries and 700 robot hours. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 3406–3413. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, X.; Lan, X.; Li, J.; Tian, Z.; Zheng, N. A real-time robotic grasping approach with oriented anchor box. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 51, 3014–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, U.; Tang, J.; Harrer, S. Densely supervised grasp detector (DSGD). In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; pp. 8085–8093. [Google Scholar]
- Kumra, S.; Kanan, C. Robotic grasp detection using deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 769–776. [Google Scholar]
- Chaurasia, A.; Culurciello, E. Linknet: Exploiting encoder representations for efficient semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 10–13 December 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, D.; Corke, P.; Leitner, J. Learning robust, real-time, reactive robotic grasping. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2020, 39, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainetter, S.; Fraundorfer, F. End-to-end trainable deep neural network for robotic grasp detection and semantic segmentation from rgb. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 13452–13458. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Qu, D.; Xu, F.; Zou, F. Robust robot grasp detection in multimodal fusion. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences, Chengdu, China, 16–17 December 2017; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Lin, J.; Knoll, A. Residual Squeeze-and-Excitation Network with Multi-scale Spatial Pyramid Module for Fast Robotic Grasping Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 13445–13451. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Huang, P.; Meng, Z. Convolutional multi-grasp detection using grasp path for RGBD images. Rob. Autom. Syst. 2019, 113, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lan, X.; Zhang, H.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, N. Fully convolutional grasp detection network with oriented anchor box. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 7223–7230. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Z.; Qu, Y.; Ren, G.; Wang, G.; Guan, Y.; Shi, Z.; Tan, J. Batch Normalization Masked Sparse Autoencoder for Robotic Grasping Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 9614–9619. [Google Scholar]
- Depierre, A.; Dellandréa, E.; Chen, L. Scoring Graspability based on Grasp Regression for Better Grasp Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 4370–4376. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Shang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Cong, S.; Li, Z. Robotic grasping of unknown objects using novel multilevel convolutional neural networks: From parallel gripper to dexterous hand. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Tao, X.; Yuan, L.; Du, Y.; Cong, M. Robotic Objects Detection and Grasping in Clutter based on Cascaded Deep Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Angelova, A. Real-time grasp detection using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 1316–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, U.; Tang, J.; Harrer, S. GraspNet: An Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Real-time Grasp Detection for Low-powered Devices. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 4875–4882. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Sun, F.; Liu, H.; Kong, T.; Fang, B.; Xi, N. A hybrid deep architecture for robotic grasp detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 1609–1614. [Google Scholar]
- Karaoguz, H.; Jensfelt, P. Object detection approach for robot grasp detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 4953–4959. [Google Scholar]
- Kumra, S.; Joshi, S.; Sahin, F. Antipodal robotic grasping using generative residual convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020–24 January 2021; pp. 9626–9633. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, F.-J.; Vela, P.A. Deep grasp: Detection and localization of grasps with deep neural networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.00520. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Lan, X.; Bai, S.; Zhou, X.; Tian, Z.; Zheng, N. Roi-based robotic grasp detection for object overlapping scenes. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 4768–4775. [Google Scholar]
- Depierre, A.; Dellandréa, E.; Chen, L. Jacquard: A large scale dataset for robotic grasp detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 3511–3516. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.; Meng, Z. Edge-dependent efficient grasp rectangle search in robotic grasp detection. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2020, 26, 2922–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Gao, Y. GATER: Learning Grasp-Action-Target Embeddings and Relations for Task-Specific Grasping. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 7, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, F.; Ru, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J. Keypoint-based robotic grasp detection scheme in multi-object scenes. Sensors 2021, 21, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Baseline | Encoder–Decoder | Inception Module | Up-Sampling Module | IW (%) | OW (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| √ | 94.9 | 94.7 | |||
| √ | √ | 96.2 | 95.9 | ||
| √ | √ | √ | 98.3 | 97.3 | |
| √ | √ | √ | √ | 98.9 | 97.7 |
| Authors | Algorithm | Accuracy (%) | Speed (ms) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IW | OW | |||
| Wang et al. [21] | DDNet | 96.1 | 95.5 | |
| Yu et al. [22] | TsGNet | 93.13 | 92.99 | |
| Yu et al. [26] | SE-ResUNet | 98.2 | 97.1 | 25 |
| Park et al. [32] | DNNs | 97.7 | 96.1 | 7 |
| Song et al. [13] | RPN | 96.2 | 95.6 | |
| Asif et al. [35] | DGDG | 97.5 | 111 | |
| Kumra et al. [36] | ResNet-50x2 | 89.2 | 88.9 | 103 |
| Morrison et al. [38] | GG-CNN | 73 | 69 | 19 |
| Ainetter et al. [39] | Det_Seg_refine | 98.2 | 32 | |
| Cao et al. [41] | RSEN | 96.4 | - | - |
| Chen et al. [42] | FCN | 82.8 | 81.9 | |
| Zhou et al. [43] | FCGN, Resnet101 | 97.7 | 96.6 | 117 |
| Shao et al. [44] | SAE+BN+SAE | 95.51 | - | - |
| Depierre et al. [45] | Grasp Regression | 95.2 | - | - |
| Yu et al. [46] | Multilevel CNNs | 95.8 | 96.2 | - |
| Liu et al. [47] | Mask-RCNN Q-Net, Y-Net | 95.2 | - | - |
| Redom et al. [48] | AlexNet | 88.0 | 87.1 | 76 |
| Asif et al. [49] | GraspNet | 90.2 | 90.6 | 24 |
| Guo et al. [50] | ZF-net | 93.2 | 89.1 | - |
| Karaoguz et al. [51] | GPRN | 88.7 | - | 200 |
| Kumra et al. [52] | GR-ConvNet | 97.7 | 96.6 | 20 |
| Chu et al. [53] | FasterRcnn | 96.0 | 96.1 | 120 |
| Zhang et al. [54] | ROI-GD | 93.6 | 93.5 | 40 |
| Ours | EDINet-RGB | 97.8 | 96.6 | 24 |
| EDINet-D | 95.5 | 93.2 | 24 | |
| EDINet-RGBD | 98.9 | 97.7 | 25 | |
| Authors | Splitting | Jaccard Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.20 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.40 | ||
| Song et al. [13] | IW (%) | - | 95.6 | 94.9 | 91.2 | 87.6 |
| Chu et al. [28] | - | 96.0 | 94.9 | 92.1 | 84.7 | |
| Zhou et al. [43] | 98.31 | 97.74 | 96.61 | 95.48 | - | |
| Ours | 99.1 | 98.9 | 98.2 | 97.2 | 96.7 | |
| Song et al. [13] | OW (%) | - | 97.1 | 97.1 | 96.4 | 93.4 |
| Chu et al. [28] | 96.1 | 92.7 | 87.6 | 82.6 | ||
| Zhou et al. [43] | 97.74 | 96.61 | 93.78 | 91.53 | - | |
| Ours | 98.9 | 97.7 | 97.6 | 97.1 | 96.5 | |
| Authors | Algorithm | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Song et al. [13] | RPN | 91.5 |
| Yu et al. [26] | ResUNet | 95.7 |
| Ainetter et al. [39] | Det_Seg_refine | 94.86 |
| Liu et al. [47] | Mask-RCNN Q-Net, Y-Net | 92.1 |
| Depierre et al. [45] | Grasping Regression | 85.74 |
| Morrison et al. [38] | GG-CNN2 | 84 |
| Kumra et al. [52] | GR-ConvNet | 94.6 |
| Depierre et al. [55] | AlexNet | 74.2 |
| Ours | EDINet-RGB | 95.5 |
| EDINet-D | 94.9 | |
| EDINet-RGBD | 96.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, C.; Miao, C.; Zhong, X.; Zhong, X.; Hu, H.; Liu, Q. Pixel-Reasoning-Based Robotics Fine Grasping for Novel Objects with Deep EDINet Structure. Sensors 2022, 22, 4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22114283
Shi C, Miao C, Zhong X, Zhong X, Hu H, Liu Q. Pixel-Reasoning-Based Robotics Fine Grasping for Novel Objects with Deep EDINet Structure. Sensors. 2022; 22(11):4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22114283
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Chaoquan, Chunxiao Miao, Xungao Zhong, Xunyu Zhong, Huosheng Hu, and Qiang Liu. 2022. "Pixel-Reasoning-Based Robotics Fine Grasping for Novel Objects with Deep EDINet Structure" Sensors 22, no. 11: 4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22114283
APA StyleShi, C., Miao, C., Zhong, X., Zhong, X., Hu, H., & Liu, Q. (2022). Pixel-Reasoning-Based Robotics Fine Grasping for Novel Objects with Deep EDINet Structure. Sensors, 22(11), 4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/s22114283






