A Novel GBSM for Non-Stationary V2V Channels Allowing 3D Velocity Variations
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Works
1.2. Main Contributions
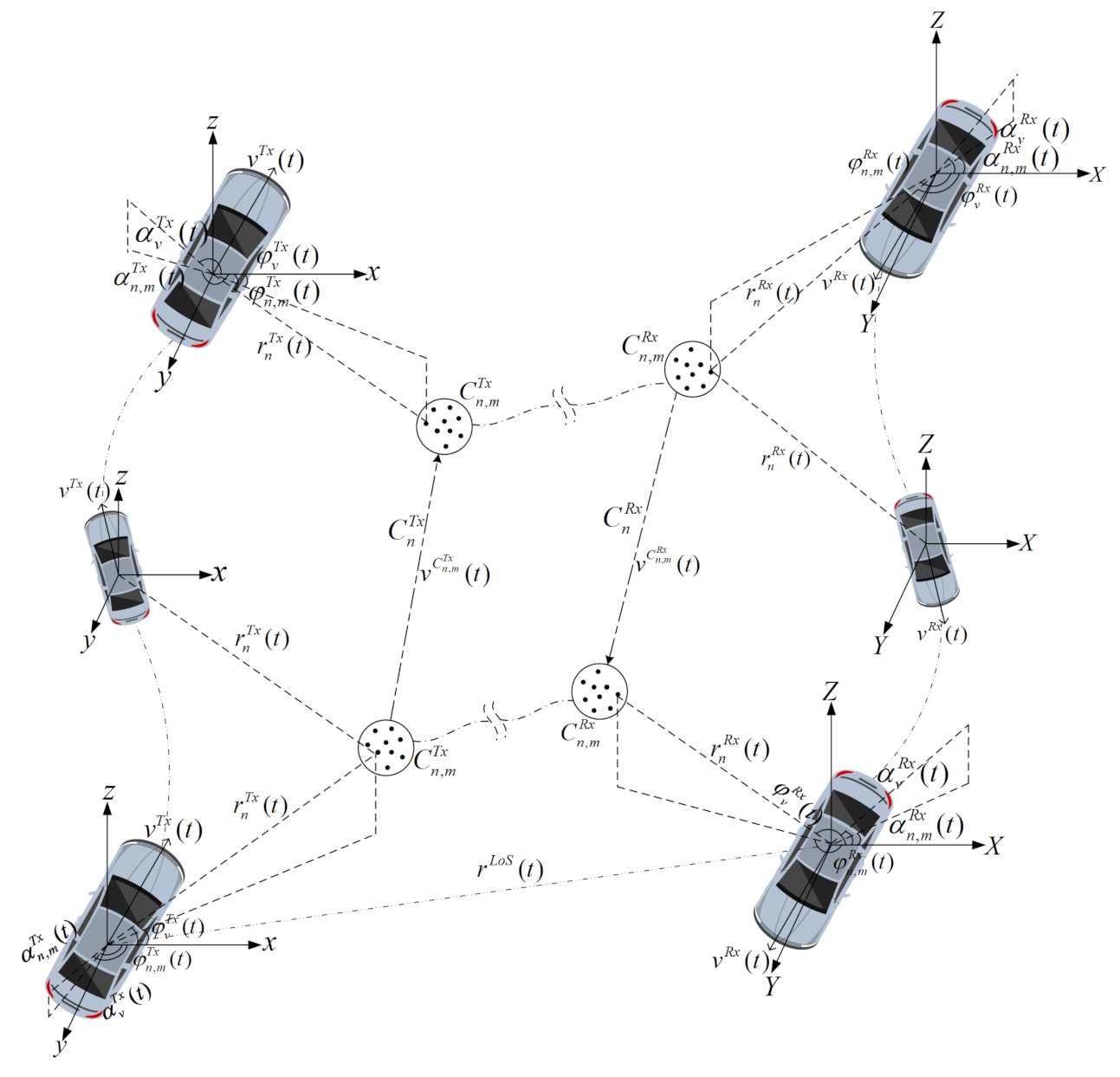
2. A GBSM for Non-Stationary V2V Channels
3. Proposed V2V Channel Model
4. Time-Variant Parameter Computations
4.1. Time-Variant Distances
4.2. Time-Variant AoAs and AoDs
4.3. Time-Variant Path Delays and Powers
5. Statistical Properties for the Proposed Model
5.1. Time-Variant PDF
5.2. Time-Variant ACF
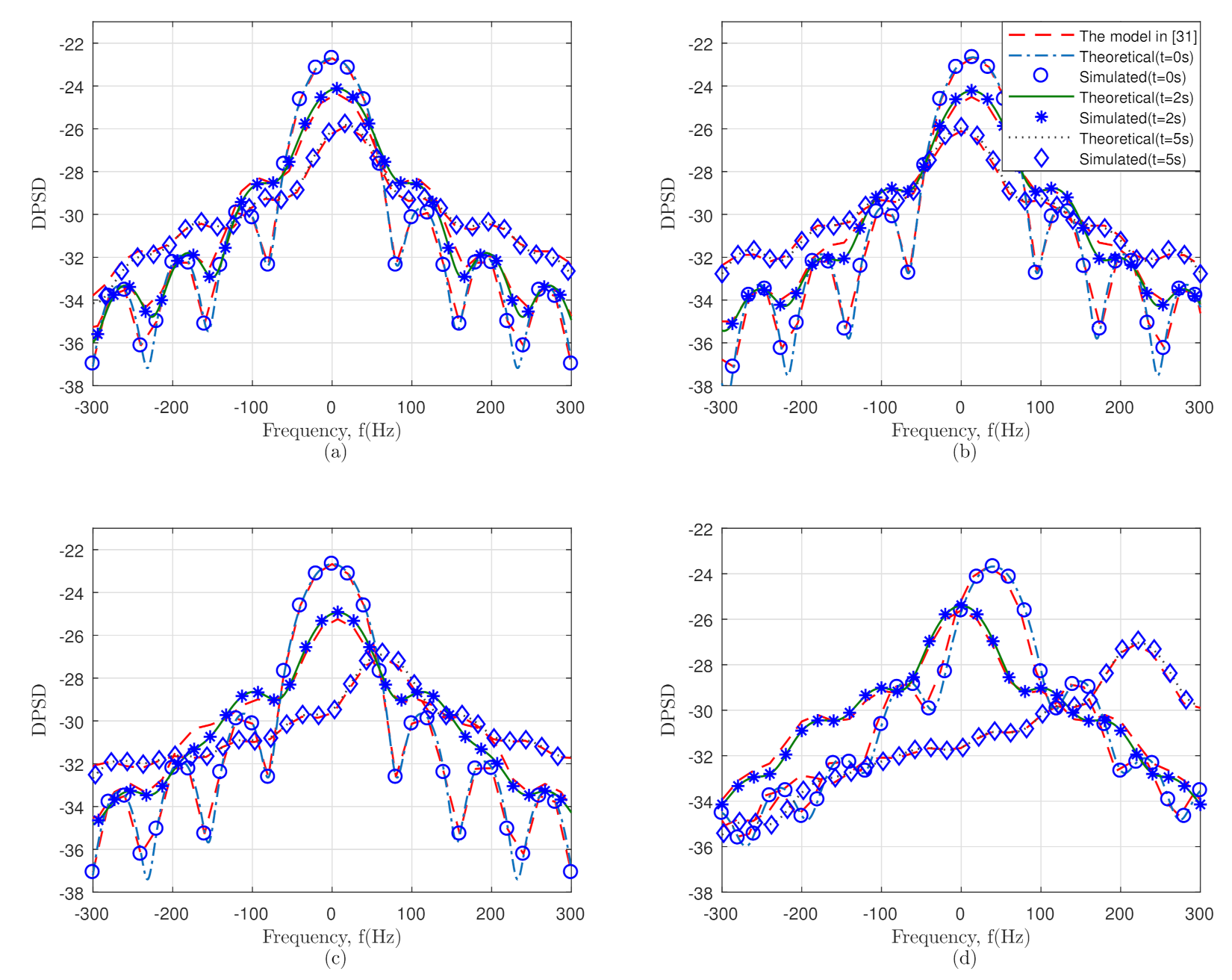
5.3. Time-Variant DPSD
6. Simulation and Analysis of the Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, R.; Ai, B.; Zhong, Z.; Schneider, C.; Dupleich, D.A.; Wang, G.; Thomae, R.S.; Boban, M.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y. Propagation Channels of 5G Millimeter-Wave Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communications: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2020, 15, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Liang, L.; Shen, X.; Li, G.Y. Vehicular Communications: A Network Layer Perspective. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 1064–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wymeersch, H.; Seco-Granados, G.; Destino, G.; Dardari, D.; Tufvesson, F. 5G mmWave Positioning for Vehicular Networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.X.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; You, X.; Hao, Y. 6G Wireless Channel Measurements and Models: Trends and Challenges. IEEE Veh. Tech. Mag. 2020, 15, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Chaudhry, R.; Kaiwartya, O.; Kumar, N.; Ahmed, S.H. Green Computing in Software Defined Social Internet of Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intel. Trans. Syst. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasana, R.; Kumar, S.; Kaiwartya, O.; Kharel, R.; Lloret, J.; Aslam, N.; Wang, T. Fuzzy-Based Channel Selection for Location Oriented Services in Multichannel VCPS Environments. IEEE Int. Things J. 2018, 5, 4642–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.X.; Bian, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M. A survey of 5G channel measurements and models. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 3142–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, C.X.; Aggoune, M.; Alwakeel, M.M.; You, X.H. A general 3-D non-stationary 5G wireless channel model. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2018, 66, 3065–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamungkas, W.; Suryani, T.; Wirawan, W.; Affandi, A. Power Spectral Density of V2V Communication System in the Presence of Moving Scatterers. Int. J. Intel. Eng. Syst. 2019, 12, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, K.; Ai, B.; Nicolas, M.L.; Geise, R.; Möller, A.; Zhong, Z.; Kürner, K. On the influence of scattering from traffic signs in vehicle-to-x communications. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 5835–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhoul, G.; Mani, F.; D’Errico, R.; Oestges, C. On the modeling of time correlation functions for mobile-to-mobile fading channels in indoor environments. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2017, 16, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Renaudin, O.; Kolmonen, V.M.; Haneda, K.; Zhong, Z.; Ai, B.; Hubert, S.; Oestges, C. Vehicle-to-vehicle radio channel characterization in crossroad scenarios. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 5850–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Ai, B.; Stüber, G.L.; Zhong, Z. Mobility Model-Based Non-Stationary Mobile-to-Mobile Channel Modeling. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 4388–4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, L.; Dang, J. A Non-Stationary Geometry-Based Scattering Vehicle-to-Vehicle MIMO Channel Model. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 1510–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzold, M.; Hajri, N.; Youssef, N. Analysis of the level-crossing rate and average duration of fades of WSSUS channels. In Proceedings of the 2017 11th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), Paris, France, 19–24 March 2017; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Eldowek, B.M.; El-atty, S.M.A.; El-Rabaie, E.S.; El-Samie, F.E.A. 3D non-stationary vehicle-to-vehicle MIMO channel model for 5G millimeter-wave communications. Digit. Signal Process. 2019, 95, 102580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, L.; Zheng, X. A geometry-based non-stationary MIMO channel model for vehicular communications. China Commun. 2018, 15, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutirrez, C.A.; Gutirrez-Mena, J.T.; Luna-Rivera, J.M.; Campos-Delgado, D.U.; Velzquez, R.; Pätzold, M. Geometry-based statistical modeling of non-WSSUS mobile-to-mobile Rayleigh fading channels. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Wang, C.X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, M.; Huang, J.; Aggoune, E.H.M. A 3D Wideband Non-Stationary Multi-Mobility Model for Vehicle-to-Vehicle MIMO Channels. IEEE Acc. 2019, 7, 32562–32577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Dang, J.; Wu, L. A General 3D Non-Stationary Wideband Twin-Cluster Channel Model for 5G V2V Tunnel Communication Environments. IEEE Acc. 2019, 7, 137744–137751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Xu, R.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, P. 3-D MIMO: How much does it meet our expectations observed from channel measurements. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 35, 1887–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, L.; Dang, J. Novel 3D irregular-shaped geometry-based channel modeling for semi-ellipsoid vehicle-to-vehicle scattering environments. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2018, 7, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liang, X.; Li, S.; Ai, B. Two-cylinder and multi-ring GBSMSM for realizing and modeling of vehicle-to-vehicle wideband MIMO channels. IEEE Trans. Intel. Transp. Syst. 2016, 17, 2787–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, M.; Liu, M.; Xu, X. A novel 3D non- stationary channel model based on the von mises-fisher scattering distribution. Mobile Inf. Syst. 2016, 2016, 2161460. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, H.; Fu, Y.; Wang, C.X.; Tan, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Q. A novel 3D non-stationary wireless MIMO channel simulator and hardware emulator. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 66, 3865–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhani, A.; Stüber, G.L.; Pätzold, M. A random trajectory approach for the development of nonstationary channel models capturing different scales of fading. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 2–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Tan, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, C.X.; Li, W. A novel 3D non-stationary vehicle-to- vehicle channel model and its spatial-temporal correlation properties. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 43633–43643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, C.X.; Xu, D.; Bian, J.; Chen, X.; Zhong, W. Temporal correlations for a nonstationary vehicle-to-vehicle channel model allowing velocity variations. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2019, 23, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahech, W.; Patzold, M.; Gutierrez, C.A.; Youssef, N. A nonstationary mobile-to-mobile channel model allowing for velocity and trajectory variations of the mobile stations. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 1987–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, C.A.; Patzold, M.; Dahech, W.; Youssef, N. A non-WSSUS mobile-to-mobile channel model assuming velocity variations of the mobile stations. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–22 March 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Q.; Zhong, W.; Xu, D.; Bai, F. A novel segment-based model for non-stationary vehicle-to-vehicle channels with velocity variations. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 133442–133451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhong, W. A general 3D nonstationary vehicle-to-vehicle channel model allowing 3D arbitrary trajectory and 3D-shaped antenna array. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2019, 2019, 8708762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinilä, J.; Kyösti, P.; Hentilä, L.; Jämsä, T.; Suikkanen, E.; Heino, P.; Kunnari, E.; Narandzic, M. CP5-026 WINNERC D5.3 V1.0 WINNERC Final Channel Models [Online]. 2010. Available online: http://projects.celticinitiative.org/winner+/ (accessed on 25 February 2021).
- Patzold, M. Mobile Fading Channels; John Wiley Sons: Chichester, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
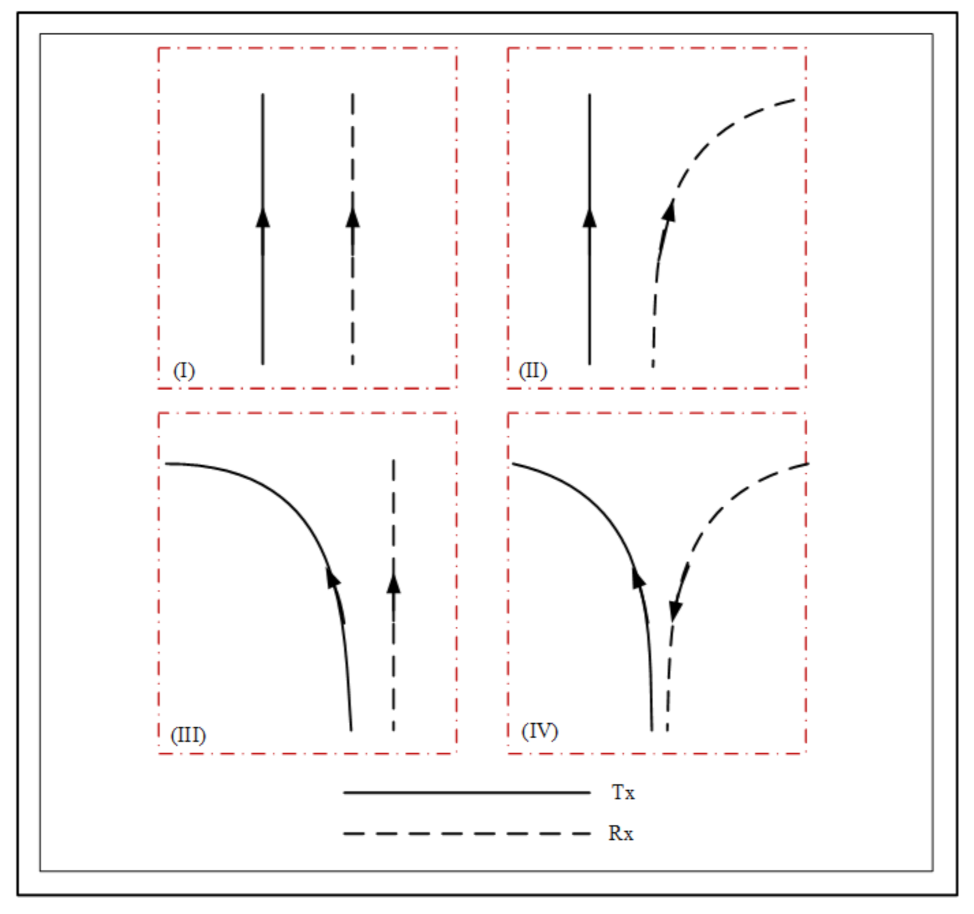


| Scenarios | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.6,0.8 (ms) | 0.8,0.6 (ms) | ||
| II | 0.5,0.6 (ms) | 0.8,1 (ms) | ||
| III | 0.9,1 (ms) | 1,0.8 (ms) | ||
| IV | 1,0.7 (ms) | 0.7,1 (ms ) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, N.; Hua, B.; Zhu, Q.; Mao, K.; Bao, J. A Novel GBSM for Non-Stationary V2V Channels Allowing 3D Velocity Variations. Sensors 2021, 21, 3271. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21093271
Ahmed N, Hua B, Zhu Q, Mao K, Bao J. A Novel GBSM for Non-Stationary V2V Channels Allowing 3D Velocity Variations. Sensors. 2021; 21(9):3271. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21093271
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Naeem, Boyu Hua, Qiuming Zhu, Kai Mao, and Junwei Bao. 2021. "A Novel GBSM for Non-Stationary V2V Channels Allowing 3D Velocity Variations" Sensors 21, no. 9: 3271. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21093271
APA StyleAhmed, N., Hua, B., Zhu, Q., Mao, K., & Bao, J. (2021). A Novel GBSM for Non-Stationary V2V Channels Allowing 3D Velocity Variations. Sensors, 21(9), 3271. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21093271







