Comparison of Self-Reported and Device-Based Measured Physical Activity Using Measures of Stability, Reliability, and Validity in Adults and Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
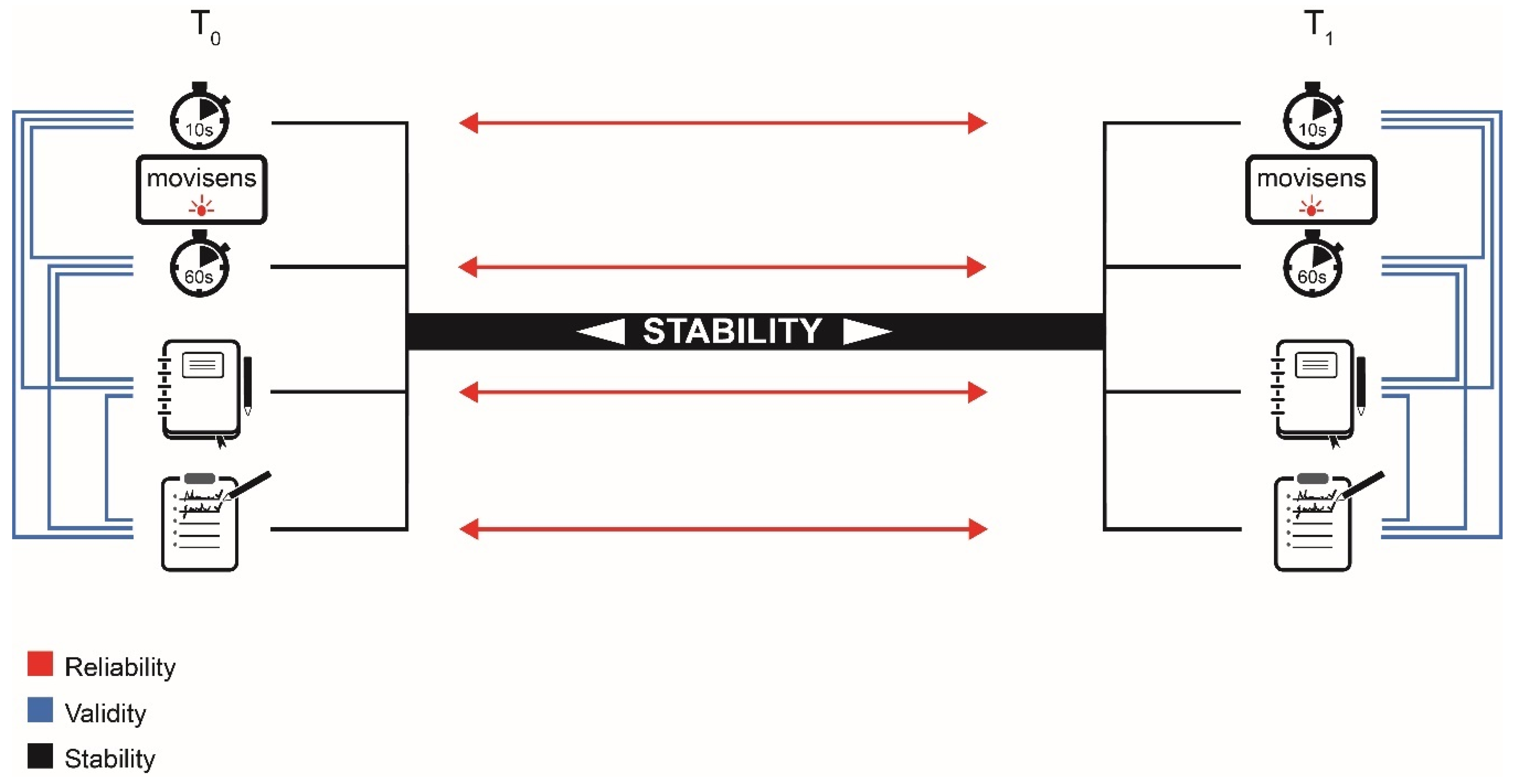
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedure
2.2. Measurements
2.2.1. Accelerometer
2.2.2. Diary
2.2.3. Questionnaire
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Physical Activity Outcomes
3.2.1. Stability between the Differences of the Parameters at the Two Measurement Weeks
3.2.2. Test-Retest Reliability
3.2.3. Validity
4. Discussion
4.1. Quality Criteria
4.1.1. Stability
4.1.2. Reliability
4.1.3. Validity
4.2. General Discussion
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, I.-M.; Shiroma, E.J.; Lobelo, F.; Puska, P.; Blair, S.N.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable diseases worldwide: An analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy. Lancet 2012, 380, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, H.W.; Craig, C.L.; Lambert, E.V.; Inoue, S.; Alkandari, J.R.; Leetongin, G.; Kahlmeier, S. The pandemic of physical inactivity: Global action for public health. Lancet 2012, 380, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Lawson, K.D.; Kolbe-Alexander, T.L.; Finkelstein, E.A.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; van Mechelen, W.; Pratt, M. The economic burden of physical inactivity: A global analysis of major non-communicable diseases. Lancet 2016, 388, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skender, S.; Ose, J.; Chang-Claude, J.; Paskow, M.; Brühmann, B.; Siegel, E.M.; Steindorf, K.; Ulrich, C.M. Accelerometry and physical activity questionnaires—A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hukkanen, H.; Husu, P.; Sievänen, H.; Tokola, K.; Vähä-Ypyä, H.; Valkeinen, H.; Mäki-Opas, T.; Suni, J.H.; Vasankari, T. Aerobic physical activity assessed with accelerometer, diary, questionnaire, and interview in a Finnish population sample. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 2196–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrstad, S.M.; Hansen, B.H.; Holme, I.M.; Anderssen, S.A. Comparison of self-reported versus accelerometer-measured physical activity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagstromer, M.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Oja, P.; Sjostrom, M. Comparison of a Subjective and an Objective Measure of Physical Activity in a Population Sample. J. Phys. Act. Health 2010, 7, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hees, V. How to Measure PA Guideline Adherence? Accelting. Available online: https://accelting.com/updates/how-to-measure-pa-guideline-adherence/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Hardeman, W.; Houghton, J.; Lane, K.; Jones, A.; Naughton, F. A systematic review of just-in-time adaptive interventions (JITAIs) to promote physical activity. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2019, 16, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, T.; Bull, F.C. Development of the World Health Organization Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ). J. Public Health 2006, 14, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, F.C.; Maslin, T.S.; Armstrong, T. Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ): Nine Country Reliability and Validity Study. J. Phys. Act. Health 2009, 6, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, S.D.; Heumann, K.J.; der Ananian, C.A.; Ainsworth, B.E. Validity and Reliability of the Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ). Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2013, 17, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunton, G.F. Ecological Momentary Assessment in Physical Activity Research. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2017, 45, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, M.C.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Andersen, L.B.; Foster, C.; Hagströmer, M.; Jaunig, J.; Kelly, P.; Kohl, H.W., III; Matthews, C.E.; Oja, P.; et al. Physical activity self-reports: Past or future? Br. J. Sports Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troiano, R.P.; Stamatakis, E.; Bull, F.C. How can global physical activity surveillance adapt to evolving physical activity guidelines? Needs, challenges and future directions. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasopoulou, P.; Tubic, M.; Schmidt, S.; Neumann, R.; Woll, A.; Härtel, S. Validation and comparison of two methods to assess human energy expenditure during free-living activities. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, E.; Huang, B.-H.; Maher, C.; Thøgersen-Ntoumani, C.; Stathi, A.; Dempsey, P.C.; Johnson, N.; Holtermann, A.; Chau, J.Y.; Sherrington, C.; et al. Untapping the Health Enhancing Potential of Vigorous Intermittent Lifestyle Physical Activity (VILPA): Rationale, Scoping Review, and a 4-Pillar Research Framework. Sports Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burchartz, A.; Anedda, B.; Auerswald, T.; Giurgiu, M.; Hill, H.; Ketelhut, S.; Kolb, S.; Mall, C.; Manz, K.; Nigg, C.R.; et al. Assessing physical behavior through accelerometry—State of the science, best practices and future directions. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2020, 49, 101703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feehan, L.M.; Geldman, J.; Sayre, E.C.; Park, C.; Ezzat, A.M.; Yoo, J.Y.; Hamilton, C.B.; Li, L.C. Accuracy of Fitbit Devices: Systematic Review and Narrative Syntheses of Quantitative Data. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2018, 6, e10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwardson, C.L.; Gorely, T. Epoch length and its effect on physical activity intensity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migueles, J.H.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Tudor-Locke, C.; Löf, M.; Esteban-Cornejo, I.; Molina-Garcia, P.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Rodriguez-Ayllon, M.; Garcia-Marmol, E.; Ekelund, U.; et al. Comparability of published cut-points for the assessment of physical activity: Implications for data harmonization. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orme, M.; Wijndaele, K.; Sharp, S.J.; Westgate, K.; Ekelund, U.; Brage, S. Combined influence of epoch length, cut-point and bout duration on accelerometry-derived physical activity. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, M.B.E.; Robson, P.J.; Wallace, J.M.W.; McKinley, M.C. How active are we? Levels of routine physical activity in children and adults. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 681–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slootmaker, S.M.; Schuit, A.J.; Chinapaw, M.J.; Seidell, J.C.; van Mechelen, W. Disagreement in physical activity assessed by accelerometer and self-report in subgroups of age, gender, education and weight status. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2009, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, P. Reliability, Validity, and Methodological Response to the Assessment of Physical Activity via Self-Report. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2000, 71, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirad, J.R.; Forsyth, A.; Oakes, M.J.; Schmitz, K.H. Accelerometer Test-Retest Reliability by Data Processing Algorithms: Results from the Twin Cities Walking Study. J. Phys. Act. Health 2011, 8, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Williams, E.; Klesges, R.C.; Hanson, C.L.; Eck, L.H. A prospective study of the reliability and convergent validity of three physical activity measures in a field research trial. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1989, 42, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivière, F.; Widad, F.Z.; Speyer, E.; Erpelding, M.-L.; Escalon, H.; Vuillemin, A. Reliability and validity of the French version of the global physical activity questionnaire. J. Sport Health Sci. 2018, 7, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pols, M.A.; Peeters, P.H.; Ocke, M.C.; Slimani, N.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Collette, H.J. Estimation of Reproducibility and Relative Validity of the Questions Included in the EPIC Physical Activity Questionnaire. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 26, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pols, M.A.; Peeters, P.H.; Ocké, M.C.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Slimani, N.; Kemper, H.C.; Collette, H.J. Relative Validity and Repeatability of a New Questionnaire on Physical Activity. Prev. Med. 1997, 26, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, O.T.H.; Nguyen, N.D.; van der Ploeg, H.P.; Dibley, M.J.; Bauman, A.E. Test-Retest Repeatability and Relative Validity of the Global Physical Activity Questionnaire in a Developing Country Context. J. Phys. Act. Health 2009, 6, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cust, A.E.; Smith, B.J.; Chau, J.Y.; van der Ploeg, H.P.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Armstrong, B.K.; Bauman, A.E. Validity and repeatability of the EPIC physical activity questionnaire: A validation study using accelerometers as an objective measure. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2008, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubans, D.R.; Sylva, K.; Osborn, Z. Convergent Validity and Test–Retest Reliability of the Oxford Physical Activity Questionnaire for Secondary School Students. Behav. Chang. 2008, 25, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunsch, K.; Eckert, T.; Fiedler, J.; Cleven, L.; Niermann, C.; Reiterer, H.; Renner, B.; Woll, A. Effects of a Collective Family-Based Mobile Health Intervention Called "SMARTFAMILY" on Promoting Physical Activity and Healthy Eating: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2020, 9, e20534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochaska, J.J.; Sallis, J.F.; Long, B. A Physical Activity Screening Measure for Use with Adolescents in Primary Care. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2001, 155, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottenbacher, J. Difference between Move 2, Move 3 and Move 4. Sensor 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Anastasopoulou, P.; Härtel, S.; Hey, S. A Comparison of Two Commercial Activity Monitors for Measuring Step Counts During Different Everyday Life Walking Activities. Int. J. Sports Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Härtel, S.; Gnam, J.-P.; Löffler, S.; Bös, K. Estimation of energy expenditure using accelerometers and activity-based energy models—Validation of a new device. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barouni, A.; Ottenbacher, J.; Schneider, J.; Feige, B.; Riemann, D.; Herlan, A.; El Hardouz, D.; McLennan, D. Ambulatory sleep scoring using accelerometers-distinguishing between nonwear and sleep/wake states. Peer. J. 2020, 8, e8284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäder, U.; Martin, B.W.; Schutz, Y.; Marti, B. Validity of four short physical activity questionnaires in middle-aged persons. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downloadable Questionnaires—International Physical Activity Questionnaire. Available online: https://sites.google.com/site/theipaq/questionnaire_links (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- IPAQ Research Committee. Guidelines for Data Processing and Analysis of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ)-Short and Long Forms. Available online: https://docs.google.com/viewer?a=v&pid=sites&srcid=ZGVmYXVsdGRvbWFpbnx0aGVpcGFxfGd4OjE0NDgxMDk3NDU1YWRlZTM (accessed on 7 January 2021).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wickam, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, M.; Poggiali, D.; Whitaker, K.; Marshall, T.; Rhys, K.; Rogier, A. Rainclud plots: A multi-platform tool for robust datavisualization: [version 1; peer review: 2 approved]. Wellcome Open Res. 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxime Hervé. RVAideMemoire: Testing and Plotting Procedures for Biostatistics. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=RVAideMemoire. (accessed on 7 January 2021).
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobi, D.; Charles, M.-A.; Tafflet, M.; Lommez, A.; Borys, J.-M.; Oppert, J.-M. Relationships of self-reported physical activity domains with accelerometry recordings in French adults. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 24, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toftager, M.; Kirstensen, P.L.; Oliver, M.; Duncan, S.; Christiansen, L.B.; Boyle, E.; Brønd, J.C.; Troelsen, J. Accelerometer data reduction in adolescents: Effects on sample retention and bias. Int.J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colley, R.; Gorber, S.C.; Tremblay, M.S. Quality control and data reduction procedures for accelerometry-derived measures of physical activity. Health Reports 2010, 21, 63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giurgiu, M.; Bussmann, J.B.J.; Hill, H.; Anedda, B.; Kronenwett, M.; Koch, E.D.; Ebner-Priemer, U.W.; Reichert, M. Validating Accelerometers for the Assessment of Body Position and Sedentary Behavior. J. Meas. Phys. Behav. 2020, 3, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuster, R.P.; Grooten, W.J.A.; Blom, V.; Baumgartner, D.; Hagströmer, M.; Ekblom, Ö. Is Sitting Always Inactive and Standing Always Active? A Simultaneous Free-Living activPal and ActiGraph Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, A.V.; Dawkins, N.P.; Maylor, B.; Edwardson, C.L.; Fairclough, S.J.; Davies, M.J.; Harrington, D.M.; Khunti, K.; Yates, T. Enhancing the value of accelerometer-assessed physical activity: Meaningful visual comparisons of data-driven translational accelerometer metrics. Sports Med. Open 2019, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tang, W.; Chen, G.; Lu, Y.; Feng, C.; Tu, X.M. Correlation and agreement: Overview and clarification of competing concepts and measures. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 2016, 28, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giavarina, D. Understanding Bland Altman analysis. Biochem. Med. 2015, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiedler, J.; Eckert, T.; Wunsch, K.; Woll, A. Key facets to build up eHealth and mHealth interventions to enhance physical activity, sedentary behavior and nutrition in healthy subjects—An umbrella review. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichert, M.; Giurgiu, M.; Koch, E.; Wieland, L.M.; Lautenbach, S.; Neubauer, A.B.; von Haaren-Mack, B.; Schilling, R.; Timm, I.; Notthoff, N.; et al. Ambulatory Assessment for Physical Activity Research: State of the Science, Best Practices and Future Directions. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2020, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Adults | Children | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean (SD) | N | Mean (SD) | |
| Gender (m/f) | 11/21 | - | 15/17 | - |
| Age (y) | 31 | 47.90 (4.44) | 32 | 13.22 (2.94) |
| Height (cm) | 31 | 170.42 (8,52) | 31 | 162.68 (17.61) |
| Weight (kg) | 31 | 72.74 (13.27) | 29 | 51.10 (14.10) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 31 | 24.97 (3.62) | 29 | 18.96 (2.94) |
| Adults | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | T0 Mean (SD) [Min-Max] | T1 Mean (SD) [Min-Max] | T1-T0 Mean (SD) Difference [%] | rs (p-Value) [CI] | |
| MPA (min/wk) | |||||
| Acc 10–Acc 60 | 28 | 206.47 (74.33) [122.50–456.40] | 181.40 (102.78) [−207.67–364.00] | −25.06 (107.39) [−12.93%] | 0.604 (0.001 *) [0.242–0.842] |
| Acc 10–Diary | 25 | 394.80 (533.57) [−1513.00–1152.20] | 398.29 (514.08) [−1196.60–1566.83] | 3.49 (70.37) [1.41%] | 0.579 (0.002 *) [0.111–0.879] |
| Acc 10- IPAQ | 25 | −195.42 (764.58) [−2262.00–873.00] | −125.04 (730.91) [−2744.00–631.50] | 70.37 (854.72) [43.92%] | 0.613 (0.001 *) [0.268–0.841] |
| Acc 60–Diary | 25 | 185.97 (528.88) [−1839.00–755.00] | 216.77 (488.43) [−1324.80–1208.67] | 30.80 (595.35) [15.30%] | 0.699 (<0.001 *) [0.314–0.890] |
| Acc 60–IPAQ | 25 | −393.48 (779.17) [−2558.00–654.00] | −303.05 (769.65) [−2978.00–622.83] | −107.63 (852.18) [25.97%] | 0.598 (0.001 *) [0.266–0.828] |
| Diary–IPAQ | 24 | −607.17 (858.53) [−3224.00–480.00] | −466.08 (743.78) [−2640.00–750.00] | −141.08 (1061.75) [26.29%] | 0.072 (0.737) [−0.431–0.603] |
| VPA (min/wk) | |||||
| Acc 10–Acc 60 | 28 | 15.39 (11.79) [−16.00–43.00] | 23.37 (31.34) [1.00–176.17] | 7.98 (32.51) [41.18%] | 0.569 (0.002 *) [0.162–0.858] |
| Acc 10–Diary | 25 | 22.74 (87.04) [−222.00–204.00] | 35.50 (67.60) [−119.67–228.67] | 12.75 (99.56) [43.82%] | 0.197 (0.344) [−0.249–0.558] |
| Acc 10–IPAQ | 26 | −79.57 (292.69) [−1417.00–129.00] | −117.10 (281.61) [−942.50–228.67] | −37.53 (266.22) [38.17%] | 0.279 (0.167) [−0.113–0.625] |
| Acc 60–Diary | 25 | 6.93 (86.72) [−239.00–193.00] | 10.86 (52.11) [−130.17–157.00] | 3.93 (89.12) [44.18%] | 0.155 (0.459) [−0.266–0.558] |
| Acc 60–IPAQ | 26 | −94.96 (292.49) [−1432.00–118.00] | −140.26 (275.82) [−957.67–52.50] | −60.67 (262.90) [38.52%] | 0.142 (0.490) [−0.233–0.509] |
| Diary–IPAQ | 25 | −99.44 (289.09) [−1440.00–120.00] | −152.92 (292.10) [−960.00–17.00] | −53.48 (261.13) [42.38%] | 0.219 (0.293) [−0.221–0.625] |
| Children | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | T0 Mean (SD) [Min–Max] | T1 Mean (SD) [Min–Max] | T1-T0 Mean (SD) difference [%] | rs (p-Value) [CI] | |
| MPA (min/wk) | |||||
| Acc 10–Acc 60 | 24 | 78.77 (48.73) [−16.33–171.50] | 61.10 (54.36) [−69.00–177.00] | −17.67 (37.36) [25.27%] | 0.785 (<0.001 *) [0.548–0.920] |
| Acc 10–Diary | 23 | 376.80 (348.08) [−470.00–1037.83] | 342.78 (326.38) [−272–979.00] | −34.02 (402.33) [9.46%] | 0.363 (0.090) [−0.152–0.806] |
| Acc 60–Diary | 23 | 299.96 (364.70) [−538.00–1027.33] | 283.99 (331.10) [−300.75–967.00] | −15.97 (380.57) [5.47%] | 0.383 (0.072) [−0.083–0.754] |
| VPA (min/wk) | |||||
| Acc 10–Acc 60 | 24 | 29.43 (19.36) [9.33–102.67] | 25.57 (21.25) [5.60–105.00] | −3.86 (12.81) [14.04%] | 0.448 (0.028 *) [0.010–0.762] |
| Acc 10–Diary | 23 | −37.24 (174.17) [−541.25–295.17] | −16.02 (157.83) [−550.67–131.83] | 21.23 (207.55) [79.68%] | 0.417 (0.049 *) [−0.053–0.786] |
| Acc 60–Diary | 23 | −67.17 (167.10) [−564.00–234.50] | −40.83 (152.54) [−560.00–105.00] | 26.35 (203.06) [48.78%] | 0.275 (0.205) [−0.227–0.659] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fiedler, J.; Eckert, T.; Burchartz, A.; Woll, A.; Wunsch, K. Comparison of Self-Reported and Device-Based Measured Physical Activity Using Measures of Stability, Reliability, and Validity in Adults and Children. Sensors 2021, 21, 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082672
Fiedler J, Eckert T, Burchartz A, Woll A, Wunsch K. Comparison of Self-Reported and Device-Based Measured Physical Activity Using Measures of Stability, Reliability, and Validity in Adults and Children. Sensors. 2021; 21(8):2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082672
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiedler, Janis, Tobias Eckert, Alexander Burchartz, Alexander Woll, and Kathrin Wunsch. 2021. "Comparison of Self-Reported and Device-Based Measured Physical Activity Using Measures of Stability, Reliability, and Validity in Adults and Children" Sensors 21, no. 8: 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082672
APA StyleFiedler, J., Eckert, T., Burchartz, A., Woll, A., & Wunsch, K. (2021). Comparison of Self-Reported and Device-Based Measured Physical Activity Using Measures of Stability, Reliability, and Validity in Adults and Children. Sensors, 21(8), 2672. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21082672








