Cerium(IV) and Iron(III) Oxides Nanoparticles Based Voltammetric Sensor for the Sensitive and Selective Determination of Lipoic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Sensor Creation
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
2.5. Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Analysis
2.6. Coulometric Determination
2.7. Statistical Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
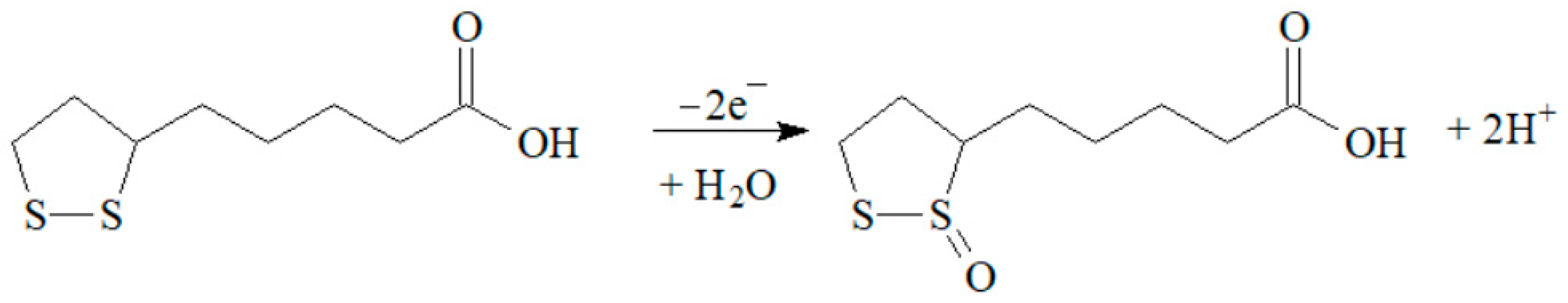
3.1. Voltammetric Characteristics of Lipoic Acid
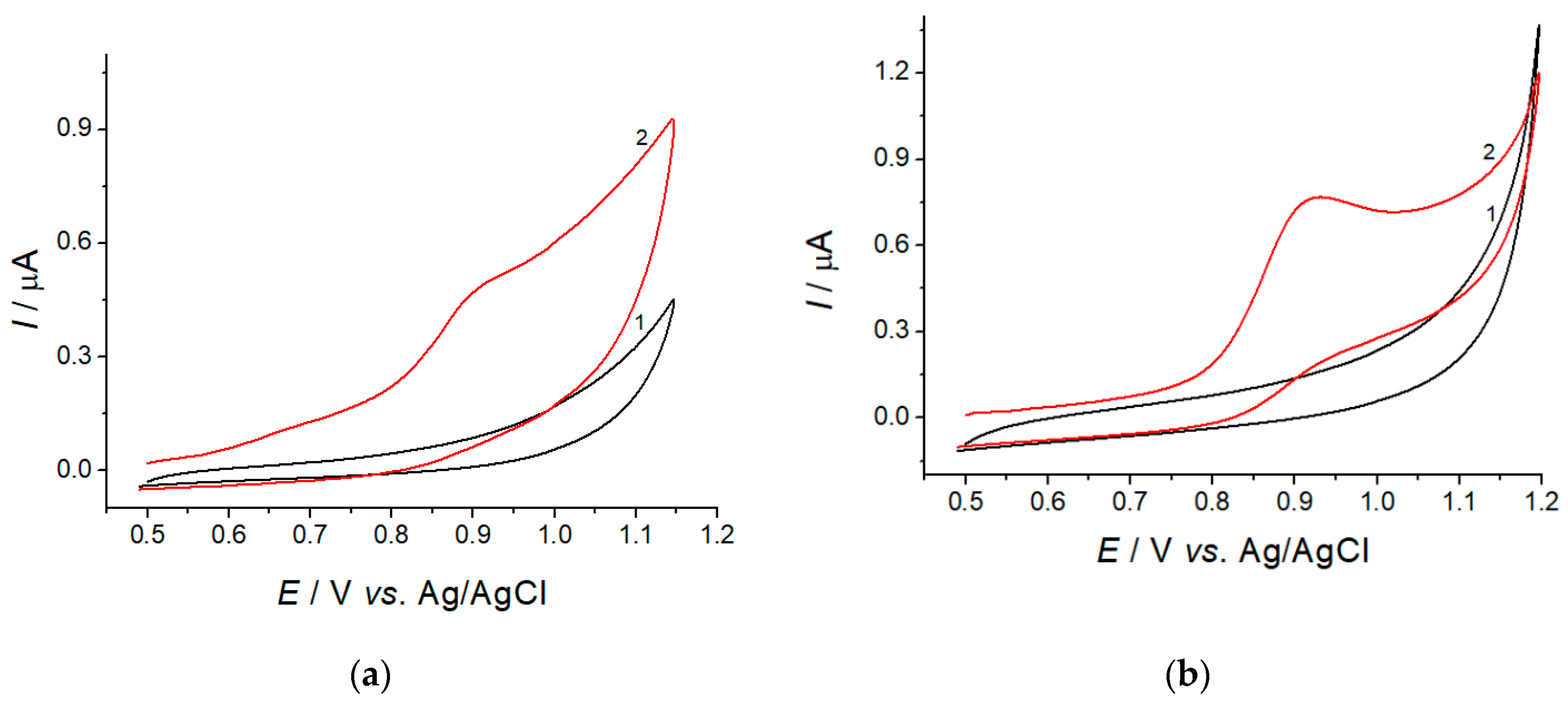
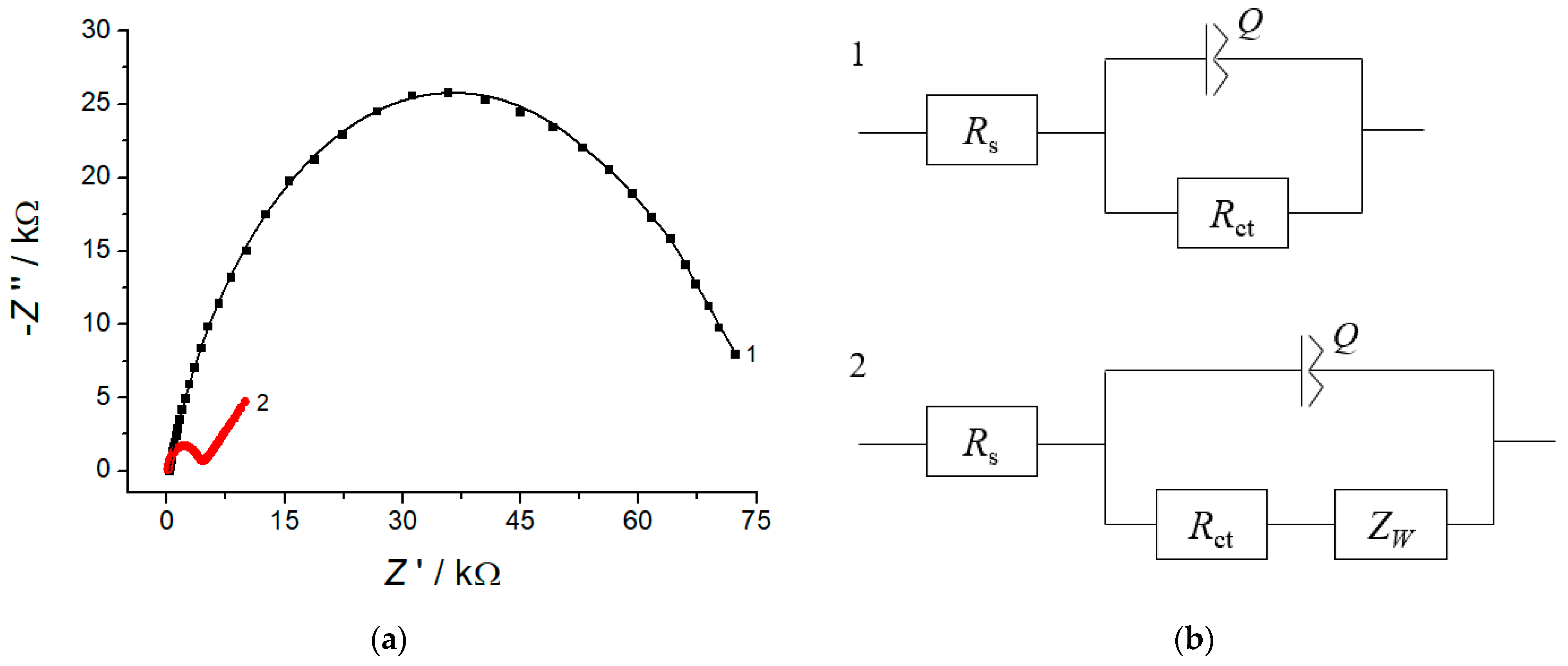
3.2. SEM and Electrochemical Characterization of the Electrodes
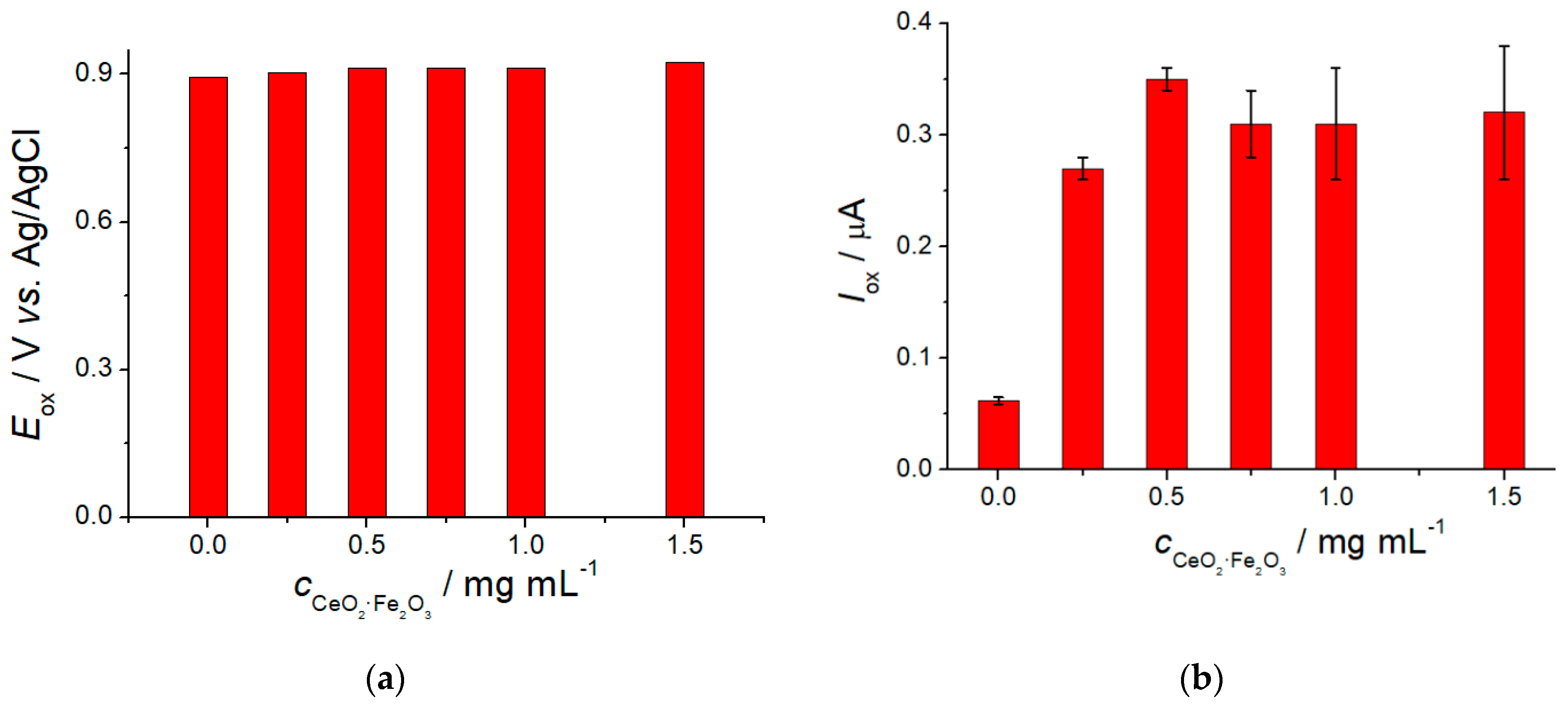
3.3. Electrooxidaton of Lipoic Acid at the CeO2·Fe2O3 NPs/GCE
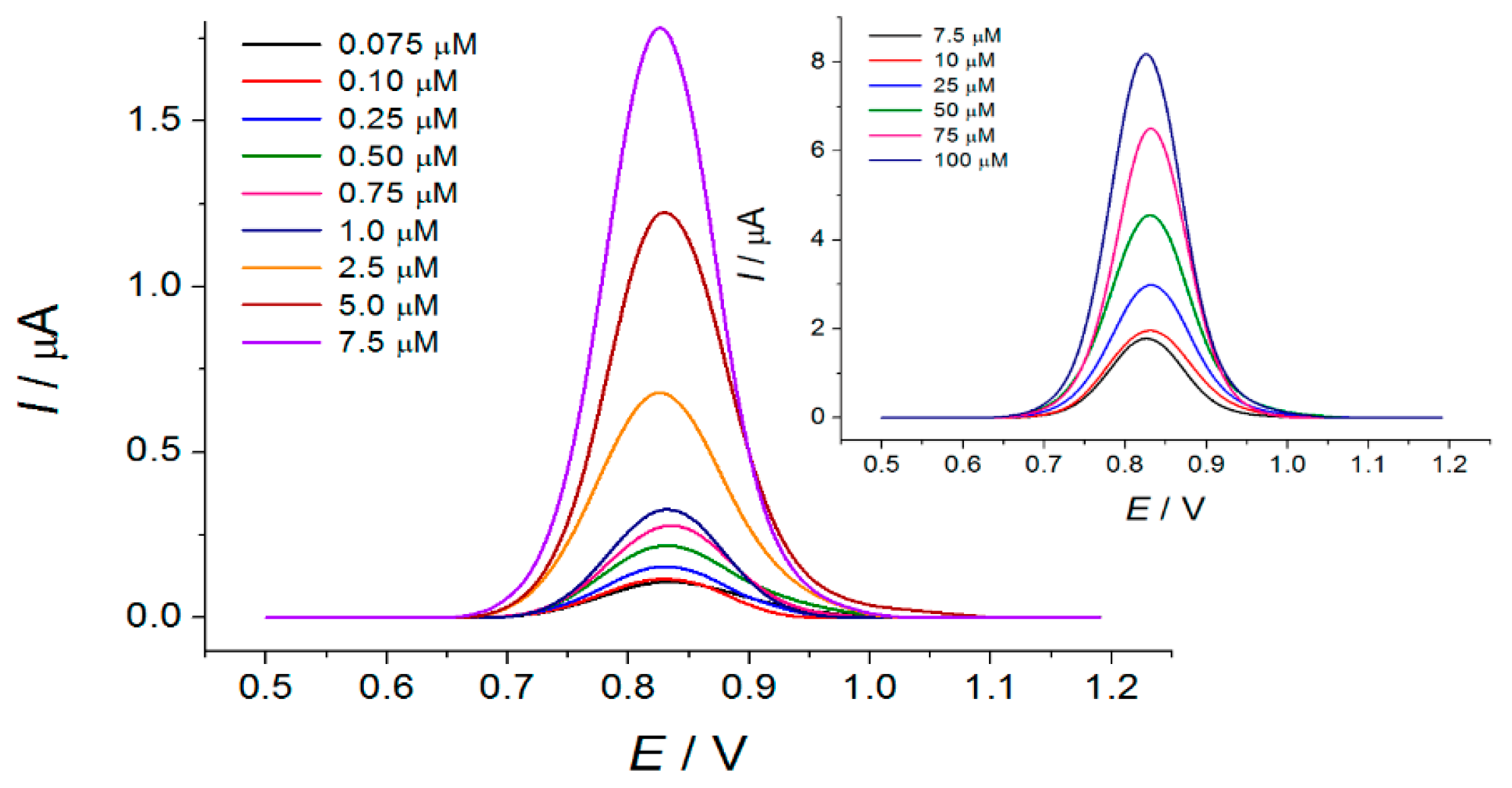
3.4. Lipoic Acid Quantification Using CeO2·Fe2O3 NPs Based Sensor
3.4.1. Selectivity Study
3.4.2. Application to Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorąca, A.; Huk-Kolega, H.; Piechota, A.; Kleniewska, P.; Ciejka, E.; Skibska, B. Lipoic acid—Biological activity and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Rep. 2011, 63, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbidi, S.; Badran, M.; Laher, I. Diabetes and alpha lipoic acid. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derosa, G.; D’Angelo, A.; Romano, D.; Maffioli, P. A Clinical trial about a food supplement containing α-lipoic acid on oxidative stress markers in type 2 diabetic patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.J.; Frei, B. Alpha-lipoic acid inhibits TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappa B activation and adhesion molecule expression in human aortic endothelial cells. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2423–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, M.; Lete, C.; Manolescu, B.N.; Lupu, S. Electrochemical determination of α-lipoic acid in human serum at platinum electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 729, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyatdinova, G.K.; Budnikov, G.K.; Pogorel’tsev, V.I. Electrochemical determination of lipoic acid. J. Anal. Chem. 2004, 59, 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corduneanu, O.; Garnett, M.; Brett, A.M.O. Anodic oxidation of α-lipoic acid at a glassy carbon electrode and its determination in dietary supplements. Anal. Lett. 2007, 40, 1763–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorupa, A.; Michalkiewicz, S. Voltammetric determination of α-lipoic acid using carbon fiber microelectrode in acetic acid—Acetonitrile solutions. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 1581–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanković, D.M.; Mehmeti, E.; Kalcher, K. Development of sensitive analytical approach for the quantification of α-Lipoic acid using boron doped diamond electrode. Anal Sci. 2016, 32, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skorupa, A.; Michalkiewicz, S.; Jakubczyk, M. Highly sensitive determination of α-lipoic acid in pharmaceuticals on a boron-doped diamond electrode. Open Chem. 2021, 19, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyatdinova, G.K.; Grigor’eva, L.V.; Budnikov, G.K. Electrochemical determination of unithiol and lipoic acid at electrodes modified with carbon nanotubes. J. Anal. Chem. 2009, 64, 185–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.P.M.; dos Santos Pereira, L.N.; da Silva, I.S.; Tanaka, S.M.C.N.; Tanaka, A.A.; Angnes, L. Determination of α-lipoic acid on a pyrolytic graphite electrode modified with cobalt phthalocyanine. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 2138–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Pereira, L.N.; da Silva, I.S.; Araújo, T.P.; Tanaka, A.A.; Angnes, L. Fast quantification of α-lipoic acid in biological samples and dietary supplements using batch injection analysis with amperometric detection. Talanta 2016, 154, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güngör, Ö.; Kiliç, B.; Karasürmeli, T.S.; Özcan, İ.; Köytepe, S. Voltammetric determination of alpha lipoic acid using chitosan-based polyurethane membrane electrode. Measurement 2021, 182, 109752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, S.T.; Hassine, C.B.A.; Burç, M.; Güngör, Ö. Voltammetric determination of α-lipoic acid using poly(vanillin) modified platinum electrode. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 2020, 12, 857–869. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, M.P.; del Rio, R.; del Valle, M.A.; Faundez, M.; Armijo, F. Use of fluorine-doped tin oxide electrodes for lipoic acid determination in dietary supplements. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2012, 668, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyatdinova, G.; Antonova, T.; Vorobev, V.; Osin, Y.; Budnikov, H. Selective voltammetric determination of α-lipoic acid on the electrode modified with SnO2 nanoparticles and cetyltriphenylphosphonium bromide. Monatsh. Chem. 2019, 150, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenkitamorn, K.; Chaiyo, S.; Chailapakul, O.; Siangproh, W. Low-cost and disposable sensors for the simultaneous determination of coenzyme Q10 and α-lipoic acid using manganese (IV) oxide-modified screen-printed graphene electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2018, 1004, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petković, B.B.; Ognjanović, M.; Antić, B.; Avdin, V.V.; Manojlović, D.D.; Đurić, S.V.; Stanković, D.M. Easily Prepared Co3O4 doped porous carbon material decorated with single-wall carbon nanotubes applied in voltammetric sensing of antioxidant α-lipoic acid. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, R.; Ranganathan, P.; Chen, S.-M.; Rwei, S.-P. f-MWCNTs-PIN/Ti2O3 nanocomposite: Preparation, characterization and nanomolar detection of α -lipoic acid in vegetables. Sens. Actuat. B 2018, 255, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, E.; Spadaro, S.; Corsaro, C.; Neri, G.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, F.; Lavanya, N.; Sekar, C.; Donato, N.; Neri, G. Metal-oxide based nanomaterials: Synthesis, characterization and their applications in electrical and electrochemical sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnihotri, A.S.; Varghese, A.; Nidhin, M. Transition metal oxides in electrochemical and bio sensing: A state-of-art review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 4, 100072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyatdinova, G.; Ziganshina, E.; Nguyen Cong, P.; Budnikov, H. Voltammetric determination of thymol in oregano using CeO2-modified electrode in Brij®® 35 micellar medium. Food Anal. Meth. 2017, 10, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyatdinova, G.; Ziganshina, E.; Romashkina, S.; Budnikov, H. Highly sensitive amperometric sensor for eugenol quantification based on CeO2 nanoparticles and surfactants. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyatdinova, G.K.; Zakharova, S.P.; Ziganshina, E.R.; Budnikov, H.C. Voltammetric determination of flavonoids in medicinal plant materials using electrodes modified by cerium dioxide nanoparticles and surfactants. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 74, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyatdinova, G.K.; Antonova, T.S.; Mubarakova, L.R.; Budnikov, H.C. An amperometric sensor based on tin dioxide and cetylpyridinium bromide nanoparticles for the determination of vanillin. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 73, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyatdinova, G.; Yakupova, E.; Davletshin, R. Voltammetric determination of hesperidin on the electrode modified with SnO2 nanoparticles and surfactants. Electroanalysis 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pwavodi, P.C.; Ozyurt, V.H.; Asir, S.; Ozsoz, M. Electrochemical sensor for determination of various phenolic compounds in wine samples using Fe3O4 nanoparticles modified carbon paste electrode. Micromachines 2021, 12, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikere, C.; Faisal, N.H.; Lin, P.K.T.; Fernandez, C. Zinc oxide nanoparticles modified-carbon paste electrode used for the electrochemical determination of gallic acid. J. Phys. Conf. Series 2019, 1310, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinay, M.M.; Nayaka, Y.A. Iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanoparticles modified carbon paste electrode as an advanced material for electrochemical investigation of paracetamol and dopamine. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2019, 4, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayemi, O.E.; Adekunle, A.S.; Ebenso, E.E. Electrochemical determination of serotonin in urine samples based on metal oxide nanoparticles/MWCNT on modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2017, 13, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Baião, V.; Tomé, L.I.N.; Brett, C.M.A. Iron oxide nanoparticle and multiwalled carbon nanotube modified glassy carbon electrodes. application to levodopa detection. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 1342–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zuo, J.; Hou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Huang, C. Preparation of electrochemical sensor based on zinc oxide nanoparticles for simultaneous determination of AA, DA, and UA. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 592538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho, R.C.; Betts, A.J.; Cassidy, J.F. Diclofenac determination using CeO2 nanoparticle modified screen-printed electrodes—A study of background correction. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramu, J.; Mahanthappa, M.; Yellappa, S.; Chandrasekhar, K.B. γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode for the sensitive detection of folic acid. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanabaratti, R.M.; Tuwar, S.M.; Nandibewoor, S.T.; Gowda, J.I. Fabrication and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode for sensitive determination of paracetamol. Chem. Data Collect. 2020, 30, 100540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.S.; Shetti, N.P.; Nayak, D.S.; Revankar, R.S. Fabrication of multi-walled carbon nanotubes and ZnO nanoparticles composite electrode as a sensor for paracetamol. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 18, 1124–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Janaj, A.A.; Shetti, N.P.; Malode, S.J.; Bukkitgar, S.D.; Kulkarni, R.M. TiO2 nanoparticles modified sensor for theophylline drug. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 18, 606–612. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, N.; Alam, M.; Wahab, R.; Ahmad, J.; Ubaidullah, M.; Ansari, A.A.; Alotaibi, N.M. Synthesis of NiO-CeO2 nanocomposite for electrochemical sensing of perilous 4-nitrophenol. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 17643–17653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Alam, M.M.; Asiri, A.M. Potential application of mixed metal oxide nanoparticle-embedded glassy carbon electrode as a selective 1,4-dioxane chemical sensor probe by an electrochemical approach. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 42050–42061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.-N.; Kang, T.-F.; Zhang, J.-J.; Lua, L.-P.; Cheng, S.-Y. Fe3O4@ZrO2 magnetic nanoparticles as a new electrode material for sensitive determination of organophosphorus agents. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 5053–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Umar, A.; Kumar, A.; Chaudhary, G.R.; Singh, S.; Mehta, S.K. Synthesis of CeO2-ZnO nanoellipsoids as potential scaffold for the efficient detection of 4-nitrophenol. Sens. Actuat. B 2014, 202, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001; 864p. [Google Scholar]
- Arul, N.S.; Mangalaraj, D.; Ramachandran, R.; Grace, A.N.; Han, J.I. Fabrication of CeO2/Fe2O3 composite nanospindles for enhanced visible light driven photocatalysts and supercapacitor electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 15248–15258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, C.V.; Garnett, M. Electrochemical behavior of the super antioxidant, α-lipoic acid. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 3607–3630. [Google Scholar]
- Velasco, J.G. Determination of standard rate constants for electrochemical irreversible processes from linear sweep voltammograms. Electroanalysis 1997, 9, 880–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sensor | Detection Mode | Detection Potential | Limit of Detection/µM | Linear Dynamic Range/µM | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-walled carbon nanotubes/GCE | LSW 1 | 0.81 | 19 | 26–180 and 210–780 | [11] |
| Cobalt phthalocyanine/Pyrolytic graphite electrode | DPV 2 | 0.8 | 0.0034 | 0.499–19.6 | [12] |
| BIA with AD 3 | 0.9 | 0.015 | 1.3–100 | [13] | |
| Chitosan-based polyurethane/Gold electrode | DPV | 0.87 | 4.931 | 5–200 | [14] |
| Poly(vanillin)/Platinum electrode | AdASWV 4 | 0.88 | 25 | 30–2000 | [15] |
| Fluorine-doped SnO2 electrode | SWV | 0.95 | 3.68 | 5–500 | [16] |
| SnO2 nanoparticles in cetyltriphenylphosphonium bromide/GCE | DPV | 0.843 | 0.13 | 0.50–50 and 50–400 | [17] |
| MnO2/Screen-printed graphene electrode | SWASV 5 | 0.65 | 0.42 | 1.4–120 | [18] |
| Co3O4 nanoparticles–single-walled carbon nanotubes–carbon paste electrode | SWV | 0.87 | 0.37 | 2–100 | [19] |
| Carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotubes–polyindole–Ti2O3/GCE | AdADPV 6 | 0.9 | 0.012 | 0.39–115.8 | [20] |
| Electrode | Rs/Ω | Rct/kΩ | Q/µΩ−1 | n | W/µΩ−1 | Χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCE | 245 ± 5 | 72 ± 3 | 3.7 ± 0.2 | 0.789 | - | 0.03 |
| CeO2·Fe2O3 NPs/GCE | 92 ± 1 | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 0.448 ± 0.009 | 0.883 | 236 ± 12 | 0.02 |
| Added/µg | Found/µg | RSD/% | R/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0620 | 0.061 ± 0.002 | 1.6 | 98 ± 2 |
| 0.620 | 0.63 ± 0.01 | 1.8 | 101 ± 2 |
| 6.20 | 6.17 ± 0.04 | 0.46 | 99.5 ± 0.6 |
| 20.6 | 20.6 ± 0.2 | 0.49 | 100 ± 1 |
| 82.5 | 82.5 ± 0.7 | 0.65 | 100.0 ± 0.8 |
| Sample Type | № | Labelled Amount/mg, mg mL−1,* | Found/mg, mg mL−1,* | RSD/% | Found by Coulometry/mg, mg mL−1,* | RSD/% | t-Test 1 | F-Test 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tablets | 1 | 25 | 25.0 ± 0.5 | 1.5 | 25.0 ± 0.4 | 1.4 | 0.0890 | 1.07 |
| 2 | 600 | 611 ± 19 | 2.5 | 612 ± 12 | 1.6 | 0.173 | 2.65 | |
| Concentrate for the infusion preparation | 3 | 30 * | 29.5 ± 0.6 * | 1.5 | 29.6 ± 0.3 * | 0.70 | 0.183 | 4.58 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziyatdinova, G.; Gimadutdinova, L. Cerium(IV) and Iron(III) Oxides Nanoparticles Based Voltammetric Sensor for the Sensitive and Selective Determination of Lipoic Acid. Sensors 2021, 21, 7639. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227639
Ziyatdinova G, Gimadutdinova L. Cerium(IV) and Iron(III) Oxides Nanoparticles Based Voltammetric Sensor for the Sensitive and Selective Determination of Lipoic Acid. Sensors. 2021; 21(22):7639. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227639
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiyatdinova, Guzel, and Liliya Gimadutdinova. 2021. "Cerium(IV) and Iron(III) Oxides Nanoparticles Based Voltammetric Sensor for the Sensitive and Selective Determination of Lipoic Acid" Sensors 21, no. 22: 7639. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227639
APA StyleZiyatdinova, G., & Gimadutdinova, L. (2021). Cerium(IV) and Iron(III) Oxides Nanoparticles Based Voltammetric Sensor for the Sensitive and Selective Determination of Lipoic Acid. Sensors, 21(22), 7639. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21227639







