Abstract
The place of public key cryptography (PKC) in guaranteeing the security of wireless networks under human-centered IoT environments cannot be overemphasized. PKC uses the idea of paired keys that are mathematically dependent but independent in practice. In PKC, each communicating party needs the public key and the authorized digital certificate of the other party to achieve encryption and decryption. In this circumstance, a directory is required to store the public keys of the participating parties. However, the design of such a directory can be cost-prohibitive and time-consuming. Recently, identity-based encryption (IBE) schemes have been introduced to address the vast limitations of PKC schemes. In a typical IBE system, a third-party server can distribute the public credentials to all parties involved in the system. Thus, the private key can be harvested from the arbitrary public key. As a result, the sender could use the public key of the receiver to encrypt the message, and the receiver could use the extracted private key to decrypt the message. In order to improve systems security, new IBE schemes are solely desired. However, the complexity and cost of designing an entirely new IBE technique remain. In order to address this problem, this paper presents a provably secure IBE transformation model for PKC using conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps under the human-centered IoT environment. In particular, we offer a robust and secure IBE transformation model and provide extensive performance analysis and security proofs of the model. Finally, we demonstrate the superiority of the proposed IBE transformation model over the existing IBE schemes. Overall, results indicate that the proposed scheme posed excellent security capabilities compared to the preliminary IBE-based schemes.
1. Introduction
Human-centered Internet of Things (IoT) enables seamless processing of electronic transactions, healthcare information systems, efficient operation of intelligent devices, and more [1]. However, the design of modern human-centered IoTs poses several opportunities to be harnessed and several challenges that need to be addressed appropriately. Currently, several massive devices are incorporated into human-centric IoT systems, thereby enabling the exchange of user information over public communication channels [2]. However, the problem of preserving user confidentiality and privacy over such channels remains. Thus, there is a need for an efficient and reliable security mechanism, based on chaotic frameworks, to guarantee secure information exchange via the deployment of lightweight security schemes for application in human-centered IoT environments.
Additionally, the IoT has brought dramatic changes in modern society, leading to significant improvements in our daily interactions with the natural environment [3,4,5]. In the human-centered IoT environment, billions of smart devices are interconnected to communicate with each other wirelessly [6]. In an active wireless network, smart devices orchestrate user data collection, analysis, and user data sharing in real-time [7]. Due to the complexity of the wireless network infrastructure, its vulnerability to several malicious and adversarial attacks becomes an issue that requires urgent attention. In order to address this problem, there is a need to provide the requisite authentication and confidentiality based conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps (CCCM) [8] for sensitive user data before transmission over public wireless channels, which is the motivation for the current study.
In recent years, research in chaotic maps and their applications within cryptography has acquired significant attention. Chaotic frameworks display features that appear to be fundamentally analogous to those needed by certain cryptographic primitives. In practice, Chebyshev chaotic maps play significant roles in increasing the security of cryptographic schemes and decreasing the communication overhead compared to pairing, elliptic curve, etc. For instance, the work of [8] is based on extended chaotic maps, whereas our proposed work is based on conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps.
Chebyshev polynomial and conformable calculus have been used in the design of the proposed IBE scheme. Conformable calculus plays a significant role in increasing the security of cryptographic schemes compared to cryptographic schemes based on chaotic maps, enabling the selection of arbitrary rational numbers . Here, the foe cannot calculate the arbitrary rational number via guessing the security of the system. Additionally, the proposed scheme requires minimum communication cost compared to the scheme reported in [8].
1.1. Contribution
This paper presents a provably secure IBE transformation model under the human-centered IoT contexts. The model can convert a conformable Chebyshev chaotic map-based PKC into secure IBE utilizing a conformable Chebyshev chaotic map without requiring the creation of a new framework. In particular, our novel approach includes a key generation stage (KGS) with extraordinarily low processing computation complexity. Furthermore, the original conformable Chebyshev chaotic map in the PKC does not need to be adjusted using our new model. By converting a conformable Chebyshev chaotic map-based PKC into an IBE using a conformable Chebyshev chaotic map, our new model provides the same level of suitability and client-friendliness as the original conformable Chebyshev chaotic map-based PKC. In this case, individual users can choose their names or network addresses as their identifiers. As a result, public-key confirmation seems quite natural and straightforward.
Interestingly, there is no need for an extensive public key database under the proposed architecture. Furthermore, we present a reductionist security investigation against the selective identity adaptive chosen ciphertext attack (IND-sID-CCA) in the ROM. In particular, the key contributions of the paper are outlined as follows:
- ■
- We provide a provably secure IBE transformation model under the human-centered IoT contexts comprising a KGS with extremely low processing computation complexity;
- ■
- We show that the presented transformation procedure is accomplished by interpreting a well-designed and secure conformable Chebyshev chaotic map-based scheme into an equally robust ID-based cryptosystem under human-centered IoT environments;
- ■
- We demonstrate that our new model provides the same level of suitability and client-friendliness compared to the original conformable Chebyshev chaotic map-based PKC;
- ■
- We show that there is no need for an extensive public key database under the new architecture;
- ■
- We test the proposed ID-based system against IND-sID-CCA in the ROM by employing the reductionist method.
1.2. Paper Organization
The following is how the rest of the article is structured. The related works are summarized in Section 2. In Section 3, some background materials on conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps are presented. In Section 4, we describe our IBE transformation model for PKC in human-centered IoT contexts. An example of how the suggested framework operates is also provided to help demonstrate its viability. After that, in Section 5, the security analysis and prospects of the new IBE transformation model are examined. The projected model is compared to several other related models in terms of efficiency and performance. Finally, in Section 6, the conclusion to the paper is drawn.
2. Related Works
In the existing literature, several public-key cryptographic (PKC) and signature-based schemes have been proposed to provide seamless and secure communications of critical user data [9]. However, smart devices require lightweight operations to guarantee extensive security requirements. In recent years, digital signatures have been proposed to guarantee the authenticity and confidentiality of user information. However, the problem of building a robust public-key database to generate millions of public-key certificates remains uncharacterized. Consequently, several schemes have been projected to address this problem in IoT-based systems.
Real-world security and IoT-based solutions are susceptible to various attacks that pose severe security and privacy issues. Recently, intrusion detection systems (IDSs) have been deployed in [3] to address these issues. In particular, the work proposed software-defined IDS-based distributed cloud architecture to secure an IoT platform. The results showed impressive security against tested attacks. The work in [10] suggested a password-enabled lightweight authentication protocol, smart card, and biometric identification. The scheme achieved mutual authentication among users with increased nonrepudiation.
In [4], multi-level decomposition feedback provided an evaluation model for user information security. Four novel indicators were used to supervise the performance of the evaluation model better, and simulation results show the suitability of the proposed model for the security of IoT systems. Similarly, a new scheme based on secure architecture for energy-efficient IoT in edge infrastructure was proposed [11]. Blockchain-enabled distributed network is used at the fog layer for security and privacy. Performance evaluation of the scheme showed superior features to the existing schemes. In [5], a multi-level key exchange and encryption protocol for IoT was proposed. The work presents a secret key generation technique and a new authentication protocol for enhanced security.
In 1984, Shamir [12] introduced an identity-based cryptosystem (IBC) that needs no certificates to secure critical user information over public channels. The Cocks IBE scheme [13], which encrypts the plaintext into ciphertext, is another encryption algorithm worth mentioning in this paper. However, the performance of this algorithm depends on the computational processing time of integer factorization, which is cumbersome to resolve in practice.
Furthermore, the Boneh–Boyen IBE scheme [14] is a special IBE scheme used to encrypt the identity of the users in a well-defined security system. Additionally, Boneh and Franklin [15,16] presented a provably secure and implementable IBC scheme that uses pairing. However, the scheme has a high computation processing time, which poses a significant limitation. Recently, Sakai–Kasahara [17] reported a bilinear pairing-based IBE scheme faster than the Boneh and Franklin scheme. It is worth mentioning that the Sakai–Kasahara scheme shows superior security features to the Boneh and Franklin scheme as it does not use modular exponentiation. However, the scheme possesses computationally intensive characteristics, which limits its usefulness in lightweight IoT-centered environments.
It is immensely gratifying to note that the emergence of the pairing-based IBC scheme has opened a new frontier of research in the public key cryptography domain [18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Therefore, the current undertaking aimed at a provably secure IBE transformation model for PKC using conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps under human-centered IoT environments is not out of place.
In human-centered IoT environments, application-specific signatures have been advanced [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. In particular, the work in [25] proposed a signature scheme that does not use the random oracle. In [26], optimized security schemes that enable message signature independent of online computation were presented. Furthermore, Guo et al. [27] extended the scheme in [26] to accommodate online computational leakage resilience. In work due to Yao and Zhao [28], signature schemes were designed specially for low-power applications. Additionally, signature schemes have been reported for wireless sensor networks [29,30]. Also, Zheng et al. [31] have reported signatures that use lattice. Furthermore, Addobea et al. [32] put up a certificateless signature scheme for medical devices. However, most of the signature schemes are based on pairing, and such IBS constructions require complex pairing operations in groups, which poses substantial computational costs.
In recent times, IoT smart devices have been integrated with sensors to facilitate user data sharing in public wireless channels. However, sensors are designed with limited storage and computing resources. Therefore, lightweight and energy-saving schemes are highly coveted to guarantee the authentication and confidentiality of IoT-based systems. Toward this end, Even et al. [33] introduced a special-purpose signature, which finds practical applications in lightweight devices. Liu et al. [21] suggested an efficient, provably secure IBS technique that uses multi-time usage of offline storage. In [34], an IBS scheme derived from Hohenberger’s RSA signature [35] was examined, highlighting its flaws. Similarly, the concept of certificateless cryptography [9] was employed by Liu et al. [36] to present an identity-based signature scheme that does not require pairing.
Recently, Meshram et al. [37] presented a provably secure scheme using extended chaotic maps. Guo et al. [38] also provided an extended signature technique and applied it to IBE. In Guo et al.’s scheme, lightweight computations are performed in the online encryption phase, while the offline encryption phase carries out computationally intensive tasks. In related work, Liu and Zhou [39] reported an efficient IBE scheme with short ciphertexts and claimed its superiority over the preliminary schemes.
The encryption and decryption phases of the scheme demonstrated by Liu and Zhou have significant improvements in computational costs compared to the scheme reported in [30]. Additionally, an identity-based key encapsulation scheme with security against chosen-ciphertext attacks was presented in [40]. Selvi et al. [41] identified some flaws in the scheme proposed in [39] and improved the scheme to achieve CCA security. Towards this end, an ordinary IBE scheme was converted to an online/offline IBE scheme by Lai et al. [42]. Similarly, the authors in [43] reported an IBE scheme for lightweight devices, and the work in [44] extended the technique of online/offline to attribute-based encryption.
In recent times, the work in [45] presented a new one-dimensional chaotic map based on a simple iterative mathematical equation. Intel I7-7700HQ processor with 16 GB RAM powers the experimentation environment. The proposed map shows a simple structure, a high chaotic behaviour, an infinite chaotic range, and is suitable for the design of chaos-based cryptographic systems. The scheme also offers a better security level and a higher encryption speed. In recent times, chaotic techniques have been found in diverse fields, like cryptosystems and image encryption. In particular, the work in [46] presents a novel method for digital image encryption. The simulation and theoretical analysis of the scheme indicate that this scheme is suitable for actual image encryption.
Recently, a robust elliptic curve–based image encryption and authentication model for grayscale and colour images have been presented [47]. The model uses the secure elliptic curve Diffie–Hellman key exchange to compute a shared session key with the enhanced ElGamal encoding scheme. The model shows low computational costs with minimized point multiplication operations and resilience against chosen-plaintext, known-plaintext, and occlusion attacks. Similarly, a new image encryption scheme based on chaotic hybrid maps is presented in [48]. The scheme employs both the confusion phase to scramble the location of pixels and the diffusion phase for consecutively changing the content of pixels. The scheme shows more comprehensive chaotic behaviour with excellent encryption and decryption processing time.
The work in [49] proposes a new fractional one-dimensional chaotic map with a sizeable chaotic space. The proposed scheme has a simple structure and high chaotic characteristics. The proposed map was also used in the design of a novel real-time image encryption scheme. Simulation tests and experimentation prove that the method has high performance and is highly efficient. A novel video watermarking scheme using a two-dimensional complex chaotic map is presented in [50]. The simulation results showed that the scheme has good visual quality using standard criteria. The scheme was also tested using geometric and non-geometric attacks and offered robust security against all tested attacks.
Given the preceding literature, the IBS signcryption, capable of encryption and signature, has been well investigated [21,51,52]. Although IBE schemes have been studied for several decades, to the authors’ best knowledge, there is no provably secure IBE transformation model for PKC using conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps, especially under human-centered IoT environments. However, encryption and decryption or signature and verification processes require large real numbers, which incur substantial computational overhead. In order to address this problem, this paper proposes a provably secure IBE transformation model for public-key cryptography leveraging conformable Chebyshev chaotic constructions. In particular, the model is designed to generate security credentials for verification and signature processes at a minimal computational cost. It is immensely gratifying that the proposed scheme does not use extensive operations to process encryption and decryption. Additionally, the scheme is protected under adaptive chosen message attack in the random oracle model (ROM). A brief comparison of related works with our proposed work is given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparison of related works with our proposed work.
3. Background and Materials
This segment reviews the various underlying concepts relating to the work, before delving into the current investigation on the IBE transformation model for PKC using conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps under the human-centered IoT environments. First, a short-lived Chebyshev chaotic map implementation is presented. This is followed by a Chebyshev polynomial, conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps, using the minimal method. A list of symbols used in the paper is given in Table 2.

Table 2.
List of mathematical symbols and their meanings.
3.1. Chebyshev Chaotic Polynomials
Chebyshev sequential polynomials (CSP) operatory is examined (see [53]). CSP is a -degree polynomial in the variation. Let be the arrangement, and be an integer. CSP reported the following in general:
Under these circumstances, the functional and are represented as and .
The chaotic and semi-group features of CSP are fundamental [37,54,55,56,57].
The chaotic feature: The CSP map is defined as with degree , is a chaotic map accompanying with the (invariant density) functional for the positive Lyapunov exponent .
- (1)
- Semi-group feature: A semi-possession group must meet the following criteria:
Zhang [58] demonstrated that the semi-group assets preserve the interval, which may be used to improve the property as tracks:
where and is a large and safe prime. As a result, the property is:
Furthermore, the semi-group property is preserved. It is worth mentioning that extended Chebyshev polynomials commute in the presence of confirmation.
For Chebyshev polynomials (CP), there are two assessments that evaluate handling in polynomial time:
- (1)
- Given two and , the objective of the discrete log (DL) is to invent an integer with the ultimate aim .
- (2)
- The goal of the Diffie–Hellman problem (DHP) is to calculate the element using three elements: , , and .
3.2. Conformable Chebyshev Chaotic Maps (CCCM)
The conformable calculus (CC) was previously referred to as the conformable fractional calculus (CFC) [59]. However, it places a strain on the established fractional calculus properties (derivatives of non-integer power). In essence, CC is in charge of future planning. The proposed work is founded on conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps. This implies that the development of the proposed IBE scheme depends on Chebyshev polynomial and conformable calculus. Notably, conformable calculus plays a significant role in enhancing the security of cryptographic schemes, compared to cryptographic schemes based on the chaotic map, due to the selection of arbitrary rational numbers . That being said, the foe cannot calculate the arbitrary rational number by guessing the security of the proposed IBE scheme.
Assume is a fractional (arbitrary) number in the range of 0 to 1. If, and only if, is the self-operator and is the typical difference operational, the operator is conformable differential. is unambiguously conformable for differentiable utility if, and only if, = .
To explain the performance of a proportional-differentiation controller that adheres to the error function, Anderson et al. [59] suggested a novel formulation of CC derived from control theory. The structure of the instruction is as follows.
where the and functions reach the limits
Definition 1.
CC has in the following documentation ifϵ [0, 1] is true.
To obtain the overhead description, we shall deliberate and , or where is the name of the function’s conformable differential operator. As a result, the function’s fractional tuning connections with its derivative, , are always reliable.
The resulting structure is obtained by using the concept of CC to express the polynomial :
Since , then has the subsequent formal relationship (1)
The Formula (1) can be substituted with (2)
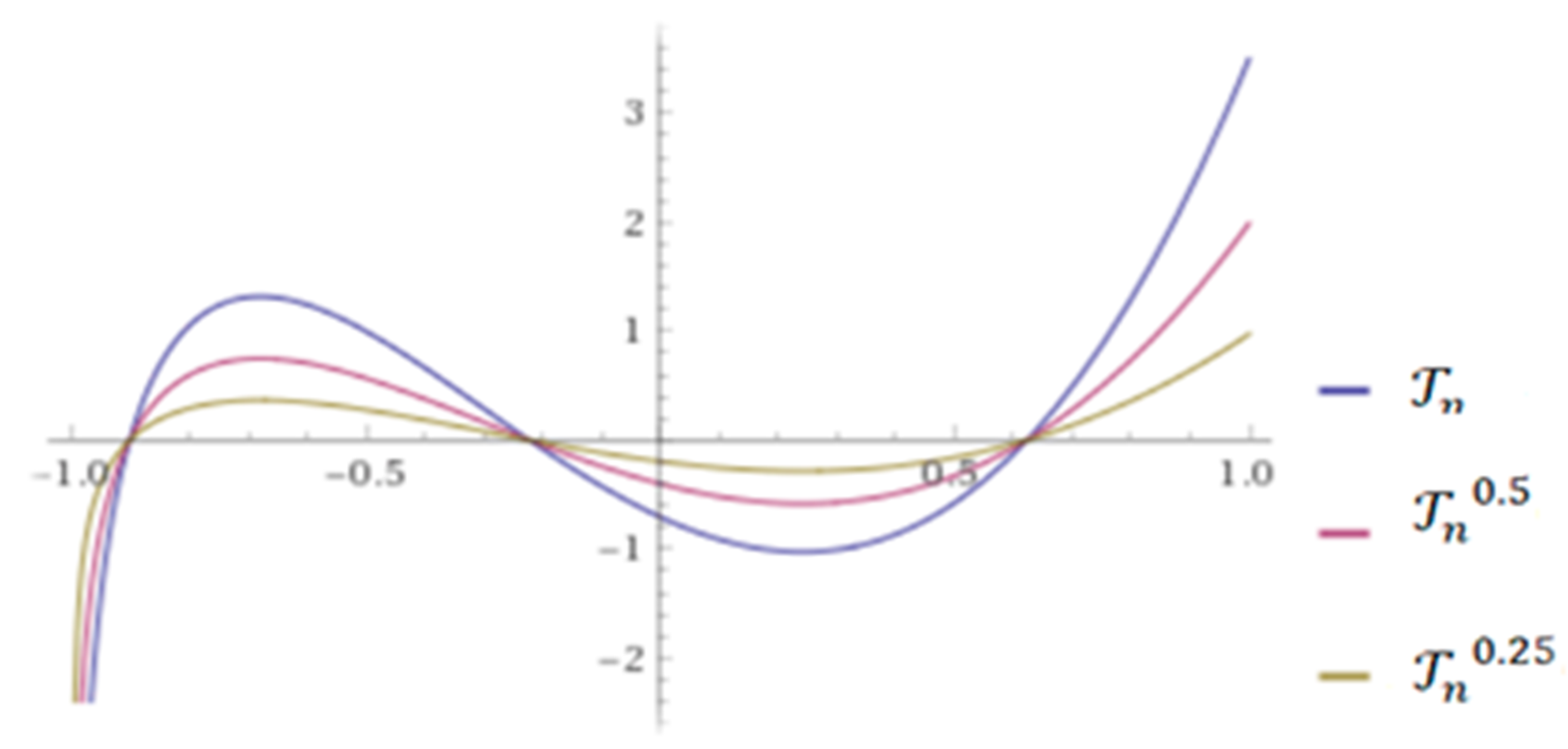
where -times. Equation (2) defines the Conformable Chebyshev Polynomials (CCP) and a few numerical examples of CCP are shown in Figure 1 [60].
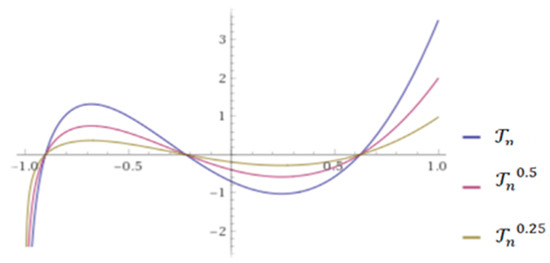
Figure 1.
CCP for different values of with .
Properties of CCCM: The following are two intriguing characteristics of the CCCM:
Definition 2.
(Chaotic properties of CCCM). Under the chaotic property, the CCCM satisfies recurrent relations [8], i.e.,
Definition 3.
(Semi-group properties of CCCM). The semi-group properties look for CCCMs located on the interval (−∞, ∞) [8], i.e.,.
It is worth noting that we obtain the original instance from [43] when we use .
At this time, we should mention that the DL and CCP assignments are roughly DHP.
4. Proposed IBE Transformation Model for PKC under Human-Centered IoT Environments
We will now show our novel concept for converting a conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps-based cryptosystem into an IBE scheme under human-centered IoT environments. Please pay close attention to our essential KGS, since this is where the actual difference is made. Conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps-based cryptosystems can be easily turned into IBE schemes by effectively articulating private keys.
4.1. Setup Phase
- Private Key Generator (PKG) selects any к users who refuse to work together. The minimum bit size of the user’s identity is then determined by the security limitation. Now, let be a huge prime, s. t. and let be a subgroup of the multiplicative group with prime order where is an order prime generator, and is a random rational number. Suppose that 𝑣 and and 𝑣 are the public key and secret key of PKG.
- PKG chooses private info at random, where and the consistent public info , where .
- Each user has a distinct -bit identity , where , .
- Express the hash function
4.2. Key Generation Phase
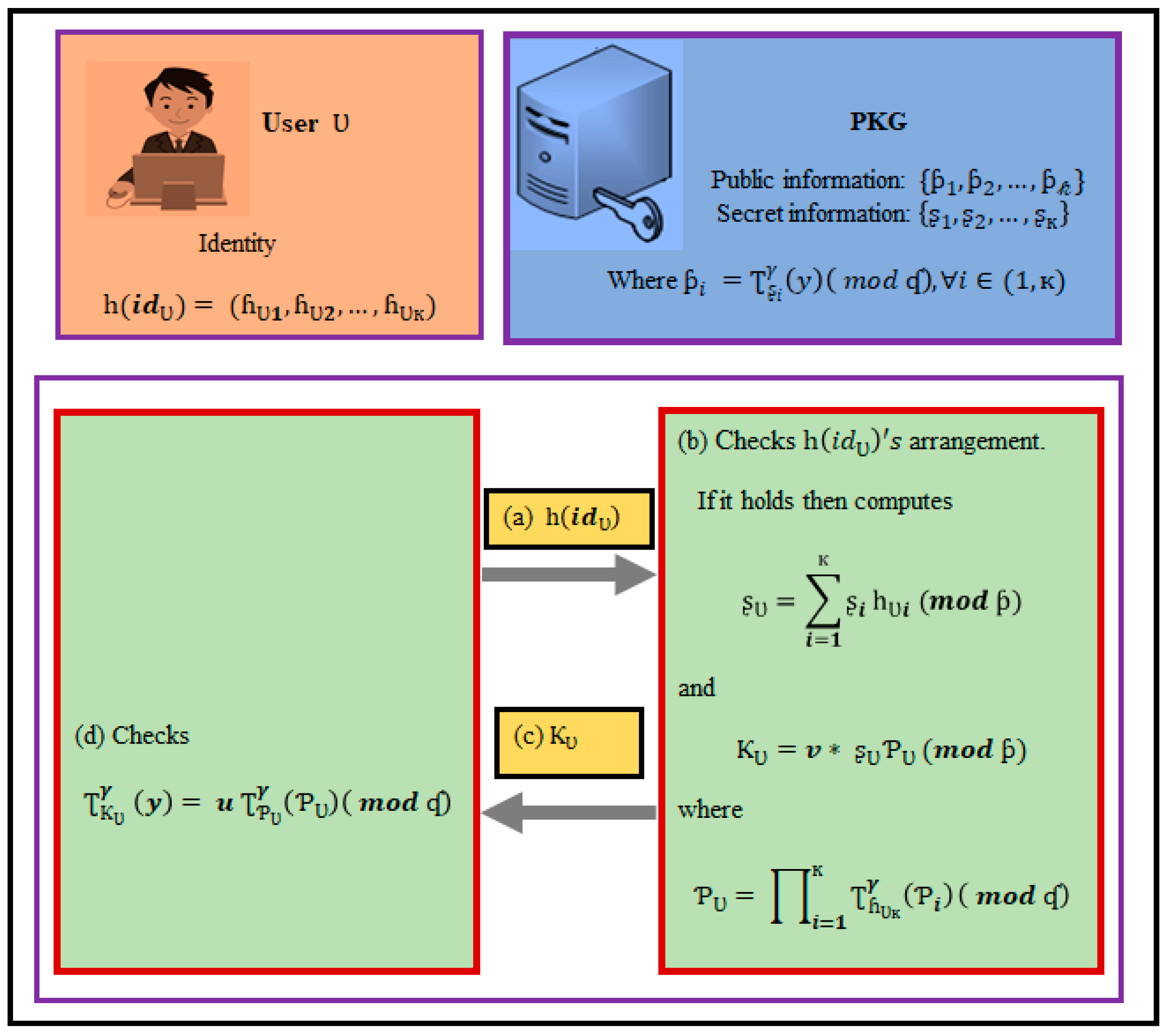
Suppose that, for the sake of argument, that a user wishes to begin the procedure. The private key is then generated using PKG and the key generation phase. The generation of the private key is depicted in Figure 2.
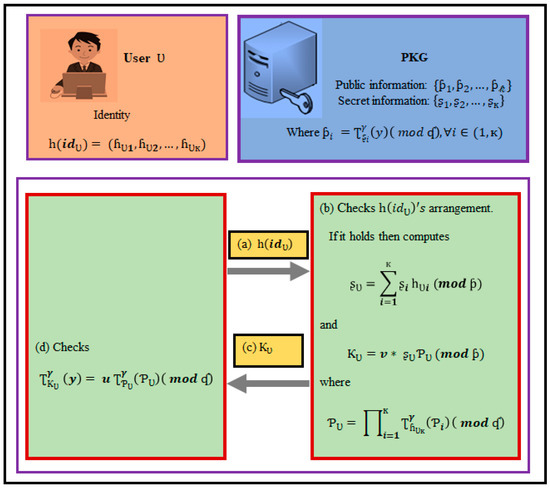
Figure 2.
Private Key Generation (PKG) under the IoT environments.
- A user gives PKG her/his hashed identification , where , .
- PKG examines whether an identity follows a given pattern. At that point, the identity is verified, PKG uses its secret information to compute .
- 3.
- PKG secretly transmits to as ’s private key.
- 4.
- checks whether the condition holds, where can be deduced from public data without any disagreement.
The accuracy of the given equation can be demonstrated in the following manner:
Note:. (Setup phase 3.1 point 3)
4.3. IBE Transformation Model for PKC
A conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps-based cryptographic system can be easily converted to an ID-based cryptographic system using the key generation procedure under human-centered IoT environments. Given a large prime number such that convoyed by a parameter , the conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps-based system (CCCMS) can be demarcated as , where , , and are public and secret keys, respectively. The projected ID-based encryption transformation procedure under human-centered IoT environments is described as follows:
- a.
- Describe the formation of the identity
Users just use their identities as their public keys, which is the most important characteristic of an ID-based cryptography approach under human-centered IoT environments. As a result, the first step is to see if the identity corresponds to a preset formation.
- b.
- Calculate the private key according to the instructions provided by the key generation (KG) process
A user , for example, will get their public keys as a result of the key generating process. Consequently, in the proposed technique, both and will be made public. Anyone can quickly determine the corresponding public assessment of in such a design by computing:
, where
As a result, the projected transformation procedure converts conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps-based cryptosystems into conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps-based ID-based encryption schemes, where is preserved as a private key and is the consistent public key.
Our new model may convert any conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps-based cryptosystem into an ID-based encryption method because the user’s identity is the only key involved in the transformation procedure.
4.4. Verification of the Transformation Mechanism
We show how our new mechanism works under the human-centered IoT environments in this segment. Now, let us iterate that our signature system is built on conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps. Let be the text want to sign, be the private key of , and be the corresponding public key of . The signature system based on conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps can be formulated as: with the key pair (KP) and an arbitrary private integer , and as a random rational number.
, where and
The verification is formulated as follows for and :
The accuracy of the preceding equation can be verified as follows:
To summarize our approach, we use conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps to create a novel ID-based signature scheme:
- Describe the identity prearrangement for as .
- For example, during the key generation step, will receive their secret value. Now is translated into an ID-based encryption model as , where is determined by Equation (3), and is determined by Equation (4). In these lines, the original signature structure based on conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps can be rewritten as , where and .
The verification is described as follows for a given and :
By employing conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps, we can surely implant the logic of ID-based cryptography into novel signature approaches, such as the ElGamal signature [54] and discrete log-based signature procedures [55].
5. Security Examination and Performance Investigation
In this section, we present the security examination and performance investigation of the proposed IBE transformation model. In particular, the security examination is given in Section 5.1, and the performance investigation is given in Section 5.2.
5.1. Security Examination
The chosen-ciphertext attack (IND-CCA) [56,57] is a typical security test against which a public key cryptography system must be tested. By proposing IND-ID-CCA, Boneh and Franklin [16] strengthened chosen-ciphertext security for the IBC techniques, where a gets to choose an objective public key to attack adaptively, even if it is not the challenger’s overall identity. Certainly, IND-ID-CCA is currently the most stringent security necessity on an IBC system, as it provides the adversary with the greatest ease and capability to attack. Canetti et al. [61] then described another security concept for IBC systems, in which the adversary must send an initial signal indicating that it will attack. This type of attack is known as IND-sID-CCA. IND-CCA and IND-sID-CCA are now specified as follows:
Definition 4.
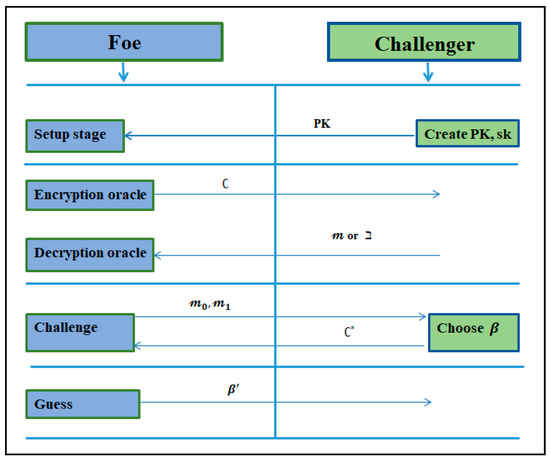
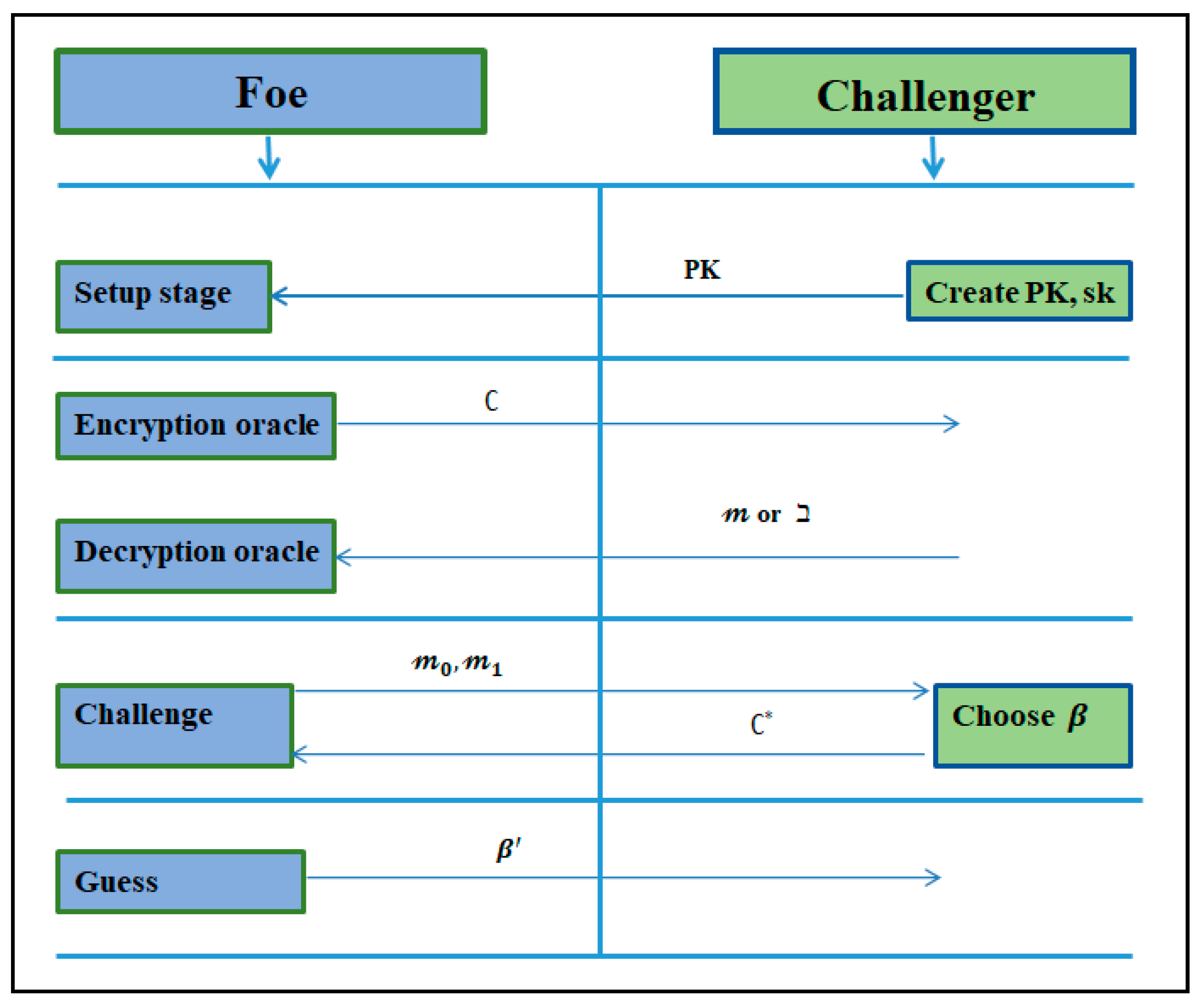
A PKC procedure is said to be IND-CCA secure ifno probabilistic polynomial time (PPT), foehas a non-negligible advantage [56,57], as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Illustrative representation of IND-CCA.
Definition 5.
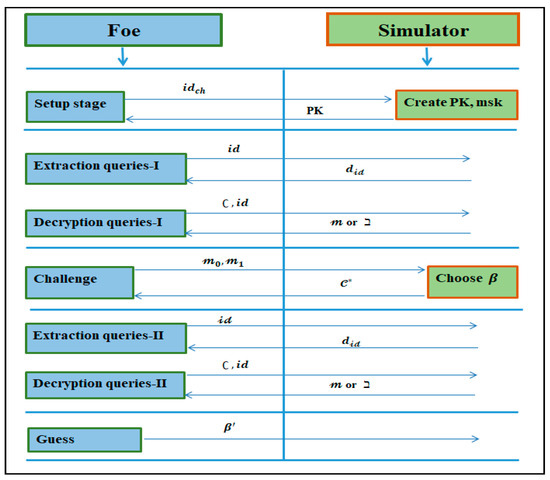
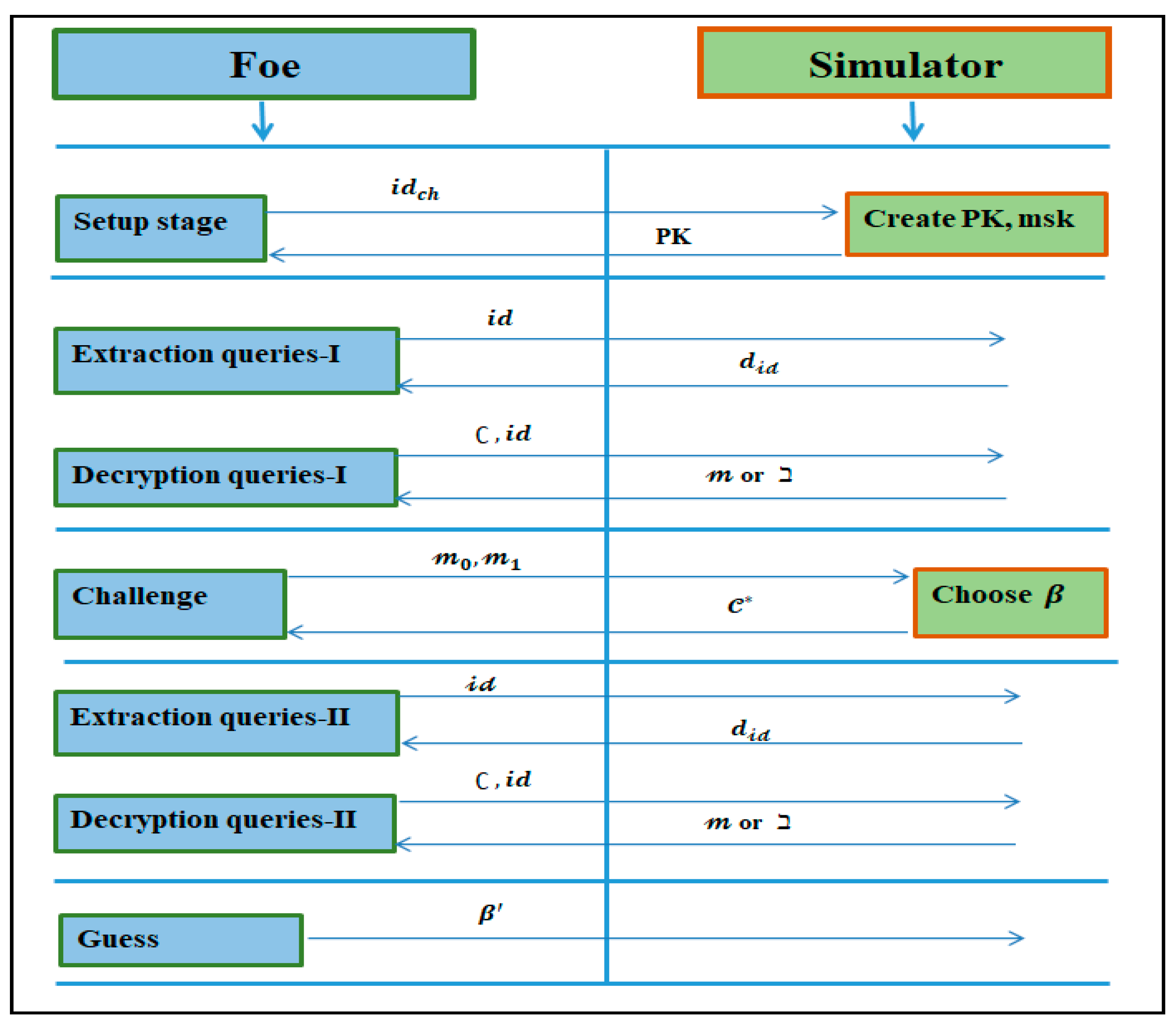
An IBE procedureis said to be IND-sID-CCA secure ifno PPT foehas a non-negligible advantage [61], as demonstrated in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
Illustrative representation of IND--CCA.
Now, let us examine the security of the proposed new approach. Our goal is to carry out the following tests: (1) To demonstrate that the presented transformation procedure is accomplished by interpreting a well-designed and secure conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps-based scheme into an equally robust IBE under the human-centered IoT environments. (2) To test the ID-based system against IND-sID-CCA proposed by Canetti et al. [61] in the ROM, we employed a reductionist method. On the assumption that the inputted PKC employing conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps is IND-CCA secure, the findings showed that our suggested approach is IND-sID-CCA secure.
Theorem 1.
Letbe a random oracle. If the original conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps cryptosystem is IND-CCA secure, the recommended ID-based cryptosystem employing conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps is IND-sID-CCA secure. Assume an IND-sID-CCA foe Ƒ with advantage ϵ(к), which opposes the ID-based cryptosystem based on conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps. Then, in contrast to the cryptosystem utilizing conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps, there exists an IND-CCA adversary with an advantage of at least. It has antimeexecution time.
Proof.
In an IND-CCA game, the basic premise of the validation is to create an IND-CCA foe to get an advantage over the PKC utilizing conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps. □
The IND-CCA challenger constructs and that satisfies . The challenger gives PK to the , then launches an IND-CCA attack with the help of as follows:
Initialization phase: The produces an identity that it wishes to be contested.
Setup phase: The challenger begins the method of setup. The scheme parameters have now been supplied to the foe. It protects itself by keeping the master key.
-queries: In order to respond to an -inquiry, it is appropriate to maintain a list of tuples , which we refer to as a list . The list is empty at the start. When asks for at a specific moment, it replies as follows: If the enquiry appears on in the tuple , then reacts with .
- Else, if is true, it generates an arbitrary and processes , otherwise sets and . mu is a special notation in this case.
- adds the tuple to and returns to .
Step 1 extraction queries: When asks for the private key for , it calls the above process, which returns , where is the equivalent entry in . Because , the genuine private key for maybe recovered. The extraction enquiry will be dismissed.
Step 1 decryption queries: Let be the ciphertext of the conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps-based PKC, and be a decryption investigation supplied by . responds to the question in the following way:
- If is true. Then the -inquiry method is executed to make the connecting tuple on . Then it uses to respond to the decryption question.
- If is true, and the decryption inquiry is executed by with and the response of the challenger are transferred back to .
Challenge: When determines that Phase 1 is complete, it returns, which it wishes to be challenged on. After that, reacts as follows:
- The challenger receives and from . The challenger responds to the PKC’s s. t. is the encryption of for any coin
- executes the -query method to retrieve so that and responds with a to .
Stage 2 extraction inquiries: Except for the extraction query on, which will be refused, reacts in the same way as in Stage 1.
Stage 2 decryption inquiries: Except for the decryption query, which will be rejected, reacts similarly to Stage 1.
Guess: eventually offers an guess for . As a guess for , foe comes up with .
The responses to -inquiries are identical to what will occur in real-world attacks. In the meantime, in , every response is uniformly and freely spread. The full responses to decryption and SK extraction queries are valid. Thus, the will not abort for the simulation period; particularly, the probability of flawless simulation is 1. Following this, we can assume the foe has fruitfully played the adversary and hurled a true attack. We obtained the result , through the explanation of method , which at least has advantage over the PKC utilizing conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps. This concludes the proof and verifies hypothesis 1.
5.2. Performance Investigation
To highlight the efficacy of our original design, we compare our new IBE transformation model to four earlier strategies presented by [62,63,64,65]. Our evaluation findings are presented using the notations and . We depict the execution time for a group modular exponentiation , a chaotic map operation, one modular inverse operation , a modular multiplication , and a one-way hash function in the decryption and encryption stages. It is worth noting that only the encryption and decryption processes require more processing power than the setup and key generation stages. We examine the stages by comparing the computational expenses of our current IBE transformation model to the works of [62,63,64,65].
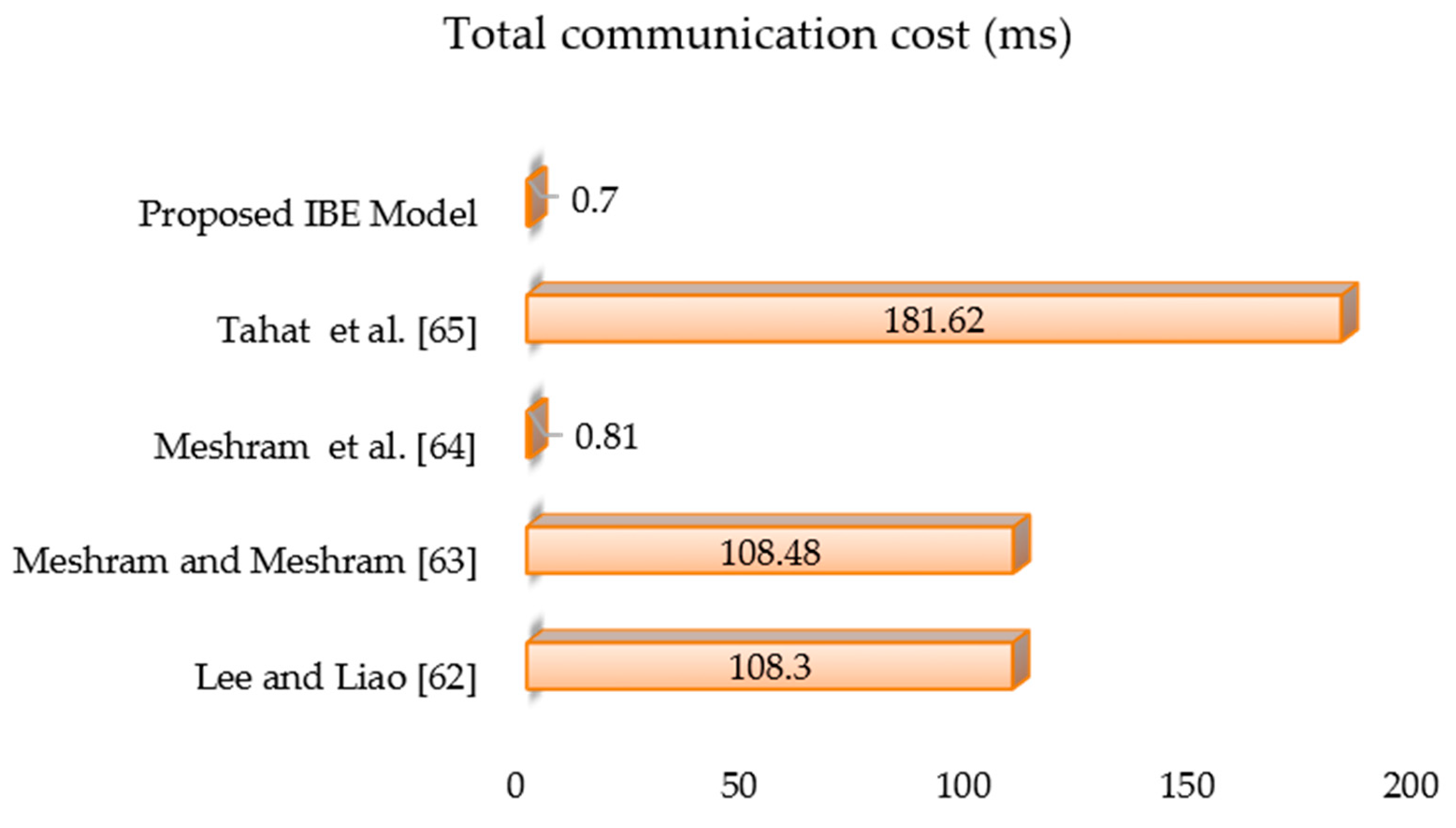
Table 3 lists the functions of the proposed IBE transformation model, and Figure 5 compares the computational costs of relevant models by [62,63,64,65]. Based on the findings of the tests in [6,8,60,66] we arrive at the following computation time statistics with unit hashing time: , and . The order of computational complexity in this method is as follows: . The computation time of the cryptographic primitives was measured using a 32-bit Cortex-M3 microcontroller running at 72 MHz in a simulation hardware environment [67]. A one-way hash function takes 0.06 milliseconds (ms) [8,67] and that [8]. Total communication costs for references by [62,63,64,65], as well as the proposed IBE transformation model, are 108.3 ms, 108.48 ms, 0.81 ms, 181.62 ms, and 0.70 ms, respectively. It should be noted that the transformation model based on extended conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps created in this paper has a lower computing cost than [62,63,64,65] and is probably secure in a random oracle than [62,65]. The work of [64] is based on an extended chaotic map, but the proposed work is based on conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps. In our proposed IBE transformation scheme, the design leverages Chebyshev polynomials and conformable calculus. In particular, conformable calculus helps to significantly increase the security of the cryptographic scheme compared to the cryptographic scheme, which is based on chaotic maps, owing to the selection of arbitrary rational number . As a result, an adversary cannot calculate the arbitrary rational number to break the security of the proposed technique. Also, the proposed scheme requires minimum communication cost when compared to the scheme reported in [64]. We arrive at the following computation time values with unit hashing time based on the experimental results in [6,8,60,66].

Table 3.
Computational cost assessment of proposed IBE transformation model with other models.
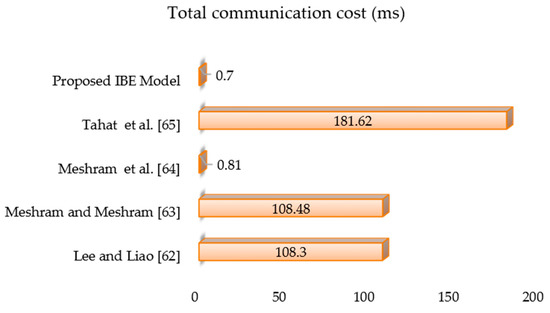
Figure 5.
Total communication cost (ms) analysis of the proposed model with other models.
6. Conclusions
This article has demonstrated how to build a provably secure IBE transformation model for PKC under human-centered IoT environments. The proposed model is designed based on a conformable Chebyshev chaotic map without changing the original PKC configuration. We chose conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps to achieve IBE transformation in avoiding the complexity and cost of inventing an entirely new IBE technique. Specifically, we demonstrated that our new model is secure in the ROM under the IND-sID-CCA. At a relatively low computing cost, this configuration may be easily transmitted to an existing system. Our new model, which combines the strengths of conformable Chebyshev chaotic maps and the IBE, is robust, secure, and poses broad application prospects. Our future work would design and develop a secure identity-based short signature transformation model for a short signature scheme under human-centered IoT environments.
Author Contributions
C.M. and A.L.I. were responsible for the conceptualization of the topic; article gathering and sorting were done by C.M., A.L.I., A.A., A.R.A., S.S.J., and S.K.B.; manuscript writing and original drafting and formal analysis were carried out by C.M. and A.L.I.; writing of reviews and editing was done by A.L.I., A.A., A.R.A., S.S.J. and S.K.B.; C.M. and A.L.I. led the overall research activity. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their gratitude to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through the research groups program under grant number R. G. P. 2/48/42. The work of Agbotiname Lucky Imoize is supported by the Nigerian Petroleum Technology Development Fund (PTDF) and the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD) through the Nigerian–German Postgraduate Program under grant 57473408.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mughal, M.A.; Luo, X.; Ullah, A.; Ullah, S.; Mahmood, Z. A Lightweight Digital Signature Based Security Scheme for Human-Centered Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 31630–31643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Gimekar, A.; Venkatesan, S. An efficient lightweight authentication scheme for human-centered industrial Internet of Things. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2019, e4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicato, J.C.S.; Singh, S.K.; Rathore, S.; Park, J.H. A comprehensive analyses of intrusion detection system for IoT environment. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 16, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Lu, Y.; Gao, H.; Cao, R.; Guo, Z.; Feng, J. Comprehensive information security evaluation model based on multi-level decomposition feedback for IoT. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2020, 65, 683–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poomagal, C.T.; Sathish Kumar, G.A.; Mehta, D. Multi level key exchange and encryption protocol for internet of things (loT). Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2020, 35, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, C.; Ibrahim, R.W.; Obaid, A.J.; Meshram, S.G.; Meshram, A.; Abd El-Latif, A.M. Fractional chaotic maps based short signature scheme under human-centered IoT environments. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 32, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoize, A.L.; Adedeji, O.; Tandiya, N.; Shetty, S. 6G Enabled Smart Infrastructure for Sustainable Society: Opportunities, Challenges, and Research Roadmap. Sensors 2021, 21, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, C.; Ibrahim, R.W.; Obaidat, M.S.; Sadoun, B.; Meshram, S.G.; Tembhurne, J.V. An effective mobile-healthcare emerging emergency medical system using conformable chaotic maps. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 8905–8920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Riyami, S.S.; Paterson, K.G. Certificateless Public Key Cryptography. In Advances in Cryptology—ASIACRYPT 2003; Laih, C.-S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 452–473. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, D.; Yang, Q. A lightweight three-factor user authentication protocol for the information perception of IoT. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2019, 58, 545–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Pan, Y.; Park, J.H. OTS scheme based secure architecture for energy-efficient iot in edge infrastructure. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 66, 2905–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamir, A. Identity-Based Cryptosystems and Signature Schemes. In Advances in Cryptology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1985; pp. 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Cocks, C. A Note on Non-Secret Encryption. Preprint 1973, 1. Available online: https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwiX4PHShvHzAhUgwosBHYoOB5kQFnoECAIQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fcryptocellar.org%2Fcesg%2Fnotense.pdf&usg=AOvVaw3YRaQ5uTslbZnnPuKAX_PB (accessed on 30 October 2021).
- Boneh, D.; Boyen, X. Short signatures without random oracles and the SDH assumption in bilinear groups. J. Cryptol. 2008, 21, 149–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boneh, D.; Franklin, M. Identity-based encryption from the weil pairing. In Advances in Cryptology—CRYPTO 2001; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Boneh, D.; Franklin, M. Identity-Based Encryption from the Weil Pairing. SIAM J. Comput. 2003, 32, 586–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Malone-Lee, J.; Smart, N.P. Efficient ID-KEM based on the Sakai-kasahara key construction. IEE Proc. Inf. Secur. 2006, 153, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Choon, J.C.; Hee Cheon, J. An Identity-Based Signature from Gap Diffie-Hellman Groups. In Public Key Cryptography—PKC 2003; Desmedt, Y.G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 18–30. [Google Scholar]
- Libert, B.; Quisquater, J.-J. Identity Based Undeniable Signatures. In Topics in Cryptology—CT-RSA 2004; Okamoto, T., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 112–125. [Google Scholar]
- Herranz, J. Deterministic Identity-Based Signatures for Partial Aggregation. Comput. J. 2005, 49, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.K.; Baek, J.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Wong, J.W. Efficient online/offline identity-based signature for wireless sensor network. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 2010, 9, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberger, S.; Sahai, A.; Waters, B. Full Domain Hash from (Leveled) Multilinear Maps and Identity-Based Aggregate Signatures. In Advances in Cryptology—CRYPTO 2013; Canetti, R., Garay, J.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 494–512. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.; Weng, J.; Weng, J.; Hou, L. Scalable revocable identity-based signature over lattices in the standard model. Inf. Sci. 2020, 518, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, A.; Ji, Y. RKA Security for Identity-Based Signature Scheme. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 17833–17841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosawa, K.; Schmidt-Samoa, K. New Online/Offline Signature Schemes Without Random Oracles. In Public Key Cryptography—PKC 2006; Yung, M., Dodis, Y., Kiayias, A., Malkin, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 330–346. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.; Mu, Y. Optimal Online/Offline Signature: How to Sign a Message without Online Computation. In Provable Security; Baek, J., Bao, F., Chen, K., Lai, X., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 98–111. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.; Mu, Y.; Susilo, W. Efficient Online/Offline Signatures with Computational Leakage Resilience in Online Phase. In Information Security and Cryptology; Lai, X., Yung, M., Lin, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 455–470. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, A.C.; Zhao, Y. Online/Offline Signatures for Low-Power Devices. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2013, 8, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, J. Provably secure online/off-line identity-based signature scheme for wireless sensor network. Int. J. Netw. Secur. 2014, 16, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Zeng, P.; Choo, K.K.R.; Song, F. An improved online/offline identity-based signature scheme for WSNs. Int. J. Netw. Secur. 2016, 18, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.; Yang, S.-J.; Wu, W.; Shao, J.; Huang, X. A New Design of Online/Offline Signatures Based on Lattice. In Information Security Practice and Experience; Su, C., Kikuchi, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 198–212. [Google Scholar]
- Addobea, A.A.; Hou, J.; Li, Q. MHCOOS: An Offline-Online Certificateless Signature Scheme for M-Health Devices. Secur. Commun. Networks 2020, 2020, 7085623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even, S.; Goldreich, O.; Micali, S. On-line/off-line digital signatures. In Proceedings of the CRYPTO 1989, Lecture Notes on Computer Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989; Volume 2442, pp. 263–275. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, W. An ID-based online/offline signature scheme without random oracles for wireless sensor networks. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2013, 17, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenberger, S.; Waters, B. Short and Stateless Signatures from the RSA Assumption. In Advances in Cryptology—CRYPTO 2009; Halevi, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 654–670. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, H.; Shi, R.; Wang, Y. An Efficient ID-based Online/Offline Signature Scheme without Key Escrow. Int. J. Netw. Secur. 2017, 19, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Meshram, C.; Li, C.-T.; Meshram, S.G. An efficient online/offline ID-based short signature procedure using extended chaotic maps. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Mu, Y.; Chen, Z. Identity-Based Online/Offline Encryption. In Financial Cryptography and Data Security; Tsudik, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 247–261. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.K.; Zhou, J. An Efficient Identity-Based Online/Offline Encryption Scheme. In Applied Cryptography and Network Security; Abdalla, M., Pointcheval, D., Fouque, P.-A., Vergnaud, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 156–167. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, S.S.M.; Liu, J.K.; Zhou, J. Identity-Based Online/Offline Key Encapsulation and Encryption. In Proceedings of the 6th ACM Symposium on Information, Computer and Communications Security, Hong Kong, China, 22–24 March 2011; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Selvi, S.S.D.; Vivek, S.S.; Rangan, C.P. Identity Based Online/Offline Encryption and Signcryption Schemes Revisited. In Security Aspects in Information Technology; Joye, M., Mukhopadhyay, D., Tunstall, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 111–127. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, J.; Mu, Y.; Guo, F.; Susilo, W. Improved Identity-Based Online/Offline Encryption. In Information Security and Privacy; Foo, E., Stebila, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 160–173. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wu, X.; Xie, X. Efficient Identity-Based Offline/Online Encryption Scheme for Lightweight Devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Third International Conference on Data Science in Cyberspace (DSC), Guangzhou, China, 18 June 2018; pp. 569–575. [Google Scholar]
- Hohenberger, S.; Waters, B. Online/Offline Attribute-Based Encryption. In Public-Key Cryptography—PKC 2014; Krawczyk, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 293–310. [Google Scholar]
- Talhaoui, M.Z.; Wang, X.; Midoun, M.A. A new one-dimensional cosine polynomial chaotic map and its use in image encryption. Vis. Comput. 2021, 37, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourasad, Y.; Ranjbarzadeh, R.; Mardani, A. A New Algorithm for Digital Image Encryption Based on Chaos Theory. Entropy 2021, 23, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, P.; Pradhan, C.; Gao, X.-Z.; Roy, D.S.; Barik, R.K. Image Encryption and Authentication With Elliptic Curve Cryptography and Multidimensional Chaotic Maps. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 76191–76204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjabbar Kari, A.; Habibizad Navin, A.; Bidgoli, A.M.; Mirnia, M. A new image encryption scheme based on hybrid chaotic maps. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 2753–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talhaoui, M.Z.; Wang, X. A new fractional one dimensional chaotic map and its application in high-speed image encryption. Inf. Sci. 2021, 550, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayubi, P.; Jafari Barani, M.; Yousefi Valandar, M.; Yosefnezhad Irani, B.; Sedagheh Maskan Sadigh, R. A new chaotic complex map for robust video watermarking. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 1237–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Mu, Y.; Guo, F. Efficient identity-based online/offline encryption and signcryption with short ciphertext. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 2017, 16, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Khurram Khan, M.; Alghathbar, K.; Takagi, T. Identity-based online/offline signcryption for low power devices. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2012, 35, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.C.; Handscomb, D.C. Chebyshev Polynomials; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- ElGmal, T. A Public key cryptosystem and a signature scheme based on discrete logarithms. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 1995, 31, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujii, S.; Itoh, T. An ID-based cryptosystem based on the discrete logarithm problem. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 1989, 7, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwan, M.S.; Lo, J.W.; Lin, S.C. An efficient user identification scheme based on ID-based cryptosystem. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2004, 26, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiltz, E.; Vahlis, Y. CCA2 secure IBE: Standard model efficiency through authenticated symmetric encryption. In CT-RSA, Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 4964, pp. 221–239. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L. Cryptanalysis of the public key encryption based on multiple chaotic systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2008, 37, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.; Camrud, E.; Ulness, D.J. On the nature of the conformable derivative and its applications to physics. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.02005. [Google Scholar]
- Meshram, C.; Lee, C.C.; Meshram, S.G.; Meshram, A. OOS-SSS: An Efficient Online/Offline Subtree-Based Short Signature Scheme Using Chebyshev Chaotic Maps for Wireless Sensor Network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 80063–80073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canetti, R.; Halevi, S.; Katz, J. A forward-secure public-key encryption scheme. Adv. Cryptol.—Eurocrypt. 2003, 2656, 255–271. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.C.; Liao, K.C. Constructing identity-based cryptosystems for discrete logarithm-based cryptosystems. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2004, 22, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, C.; Meshram, S. An identity-based cryptographic model for discrete logarithm and integer factoring based cryptosystem. Inf. Process. Lett. 2013, 113, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, C.; Lee, C.C.; Meshram, S.G.; Li, C.T. An Efficient ID-based Cryptographic Transformation Model for Extended Chaotic-Map-Based Cryptosystem. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 6937–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahat, N.; Alomari, A.K.; Al–Freedi, A.; Al-Hazaimeh, O.M.; Al–Jamal, M.F. An Efficient Identity-Based Cryptographic Model for Chebyhev Chaotic Map and Integer Factoring Based Cryptosystem. J. Appl. Secur. Res. 2019, 14, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.H.; Kumari, S.; Das, A.K.; Wazid, M.; Odelu, V. Secure anonymous mutual authentication for star two-tier wireless body area networks. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 135, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Yan, R.; Sun, R. Efficient authenticated key exchange protocols for wireless body area networks. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).