Critical Frequency of Self-Heating in a Superelastic Ni-Ti Belleville Spring: Experimental Characterization and Numerical Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Experimental Characterization
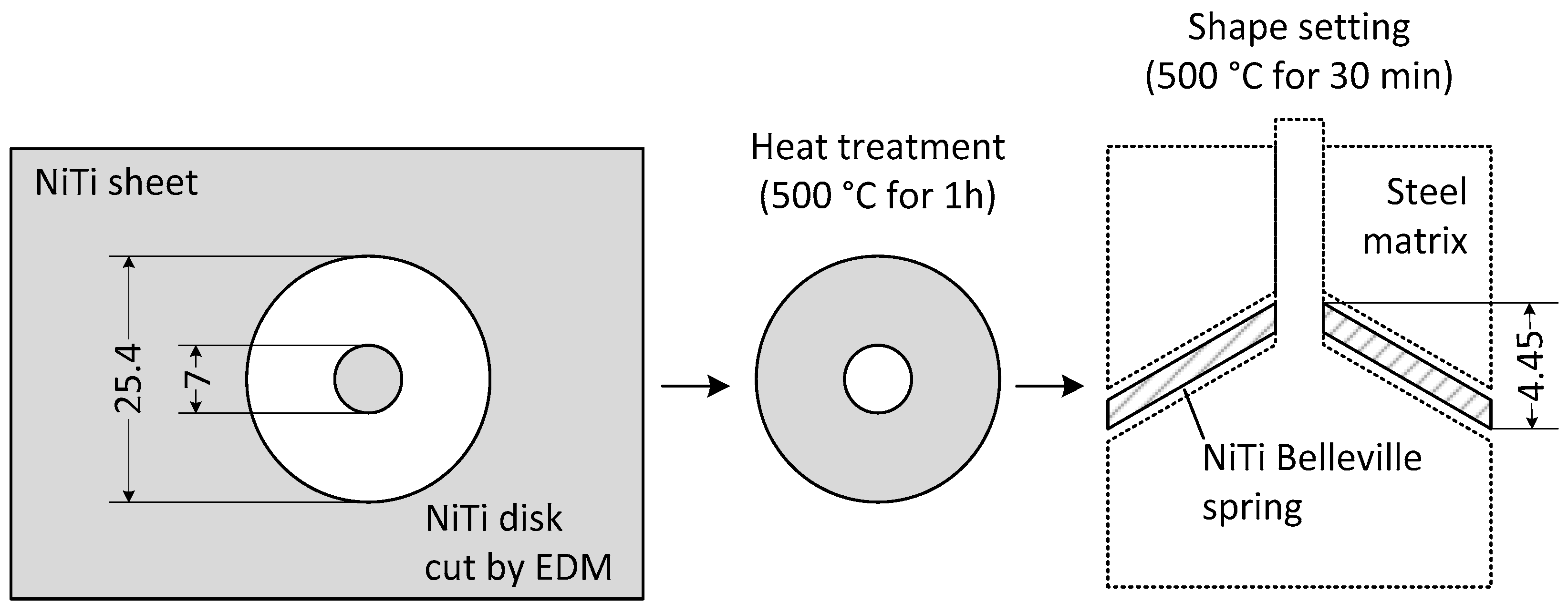
2.1.1. Material and Spring Manufacturing
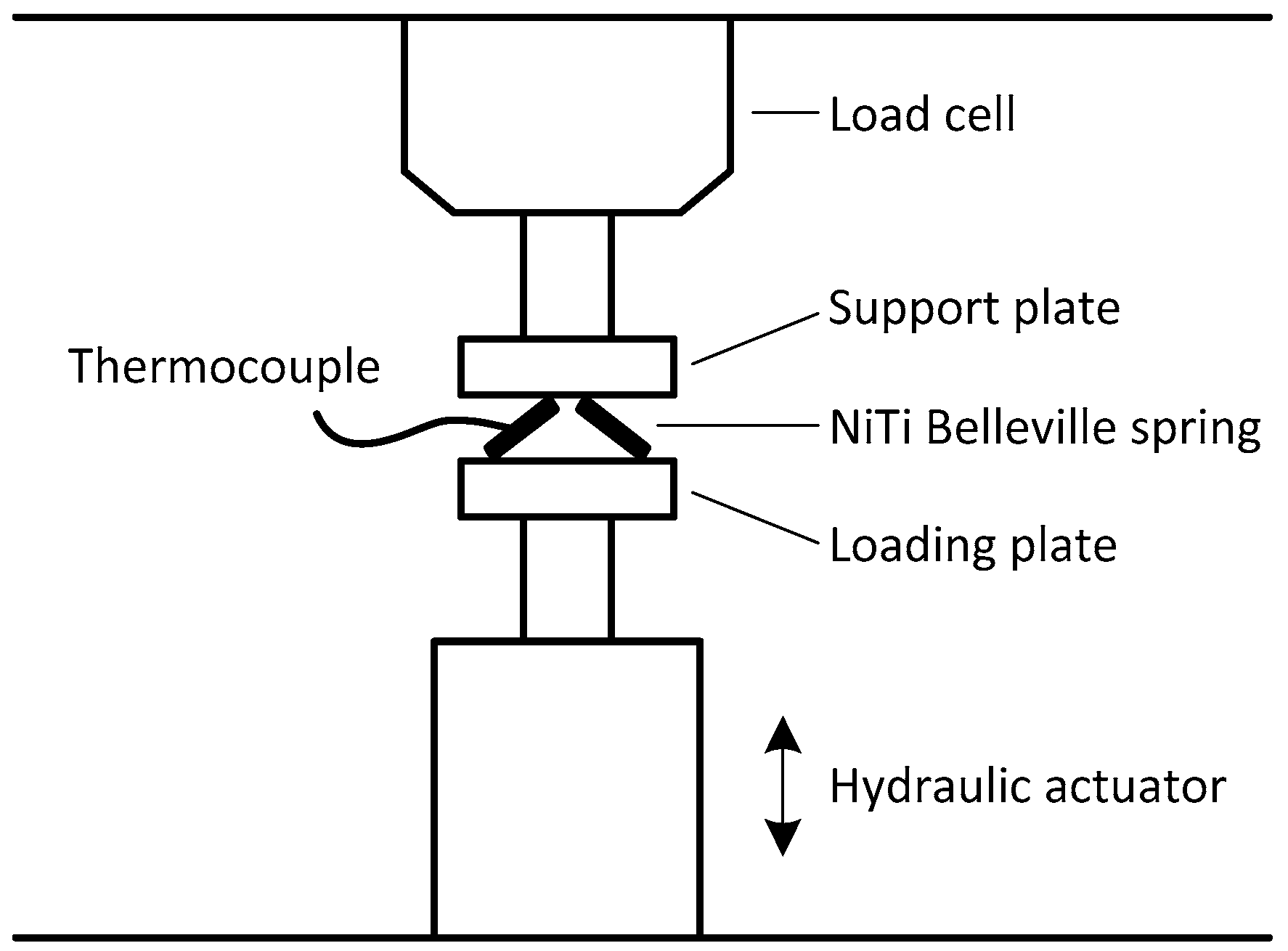
2.1.2. Thermal Characterization of the NiTi Belleville Spring
2.1.3. Mechanical Characterization of the NiTi Belleville Spring
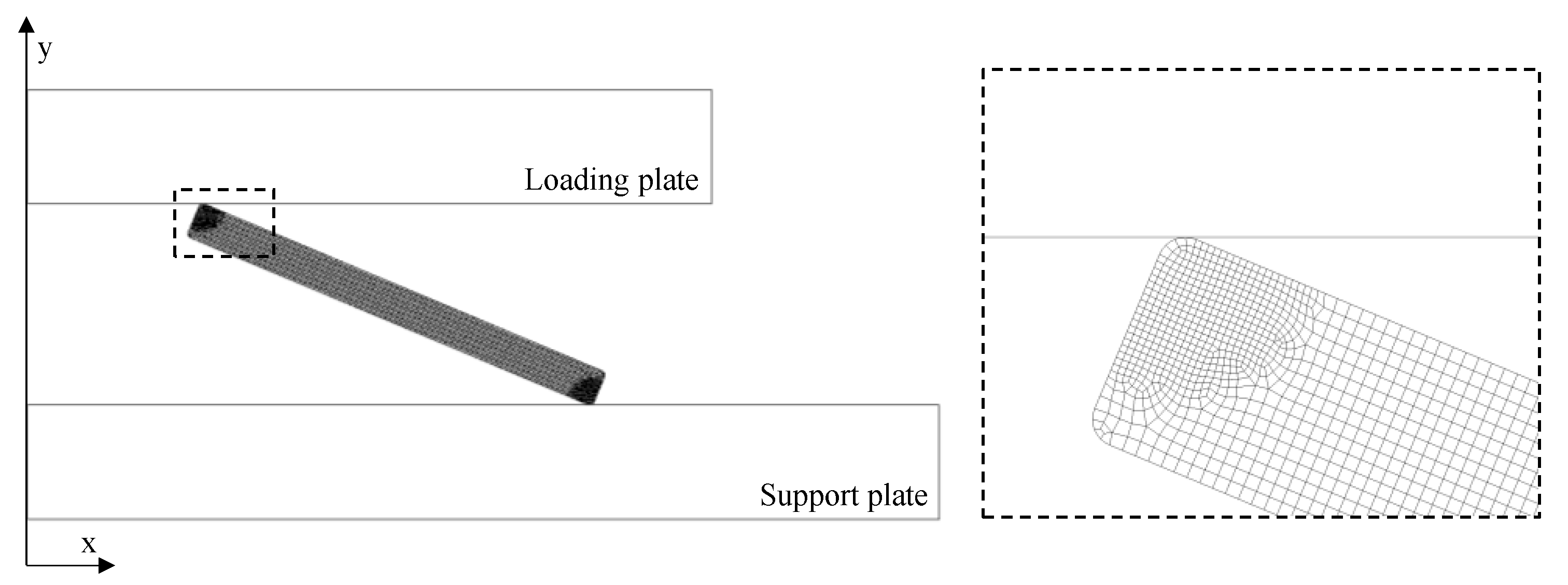
2.2. Numerical Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Analysis
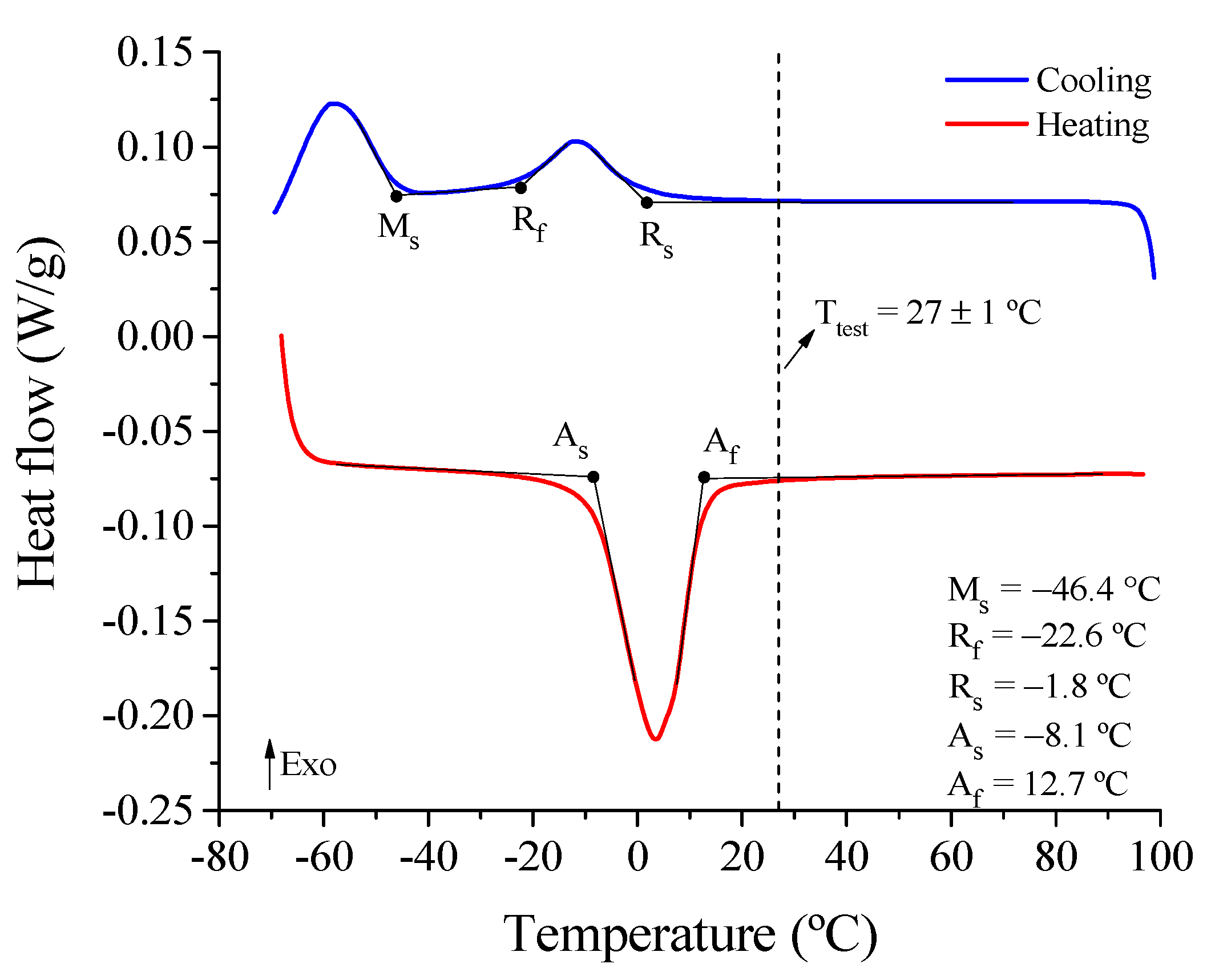
3.1.1. Transformation Temperatures
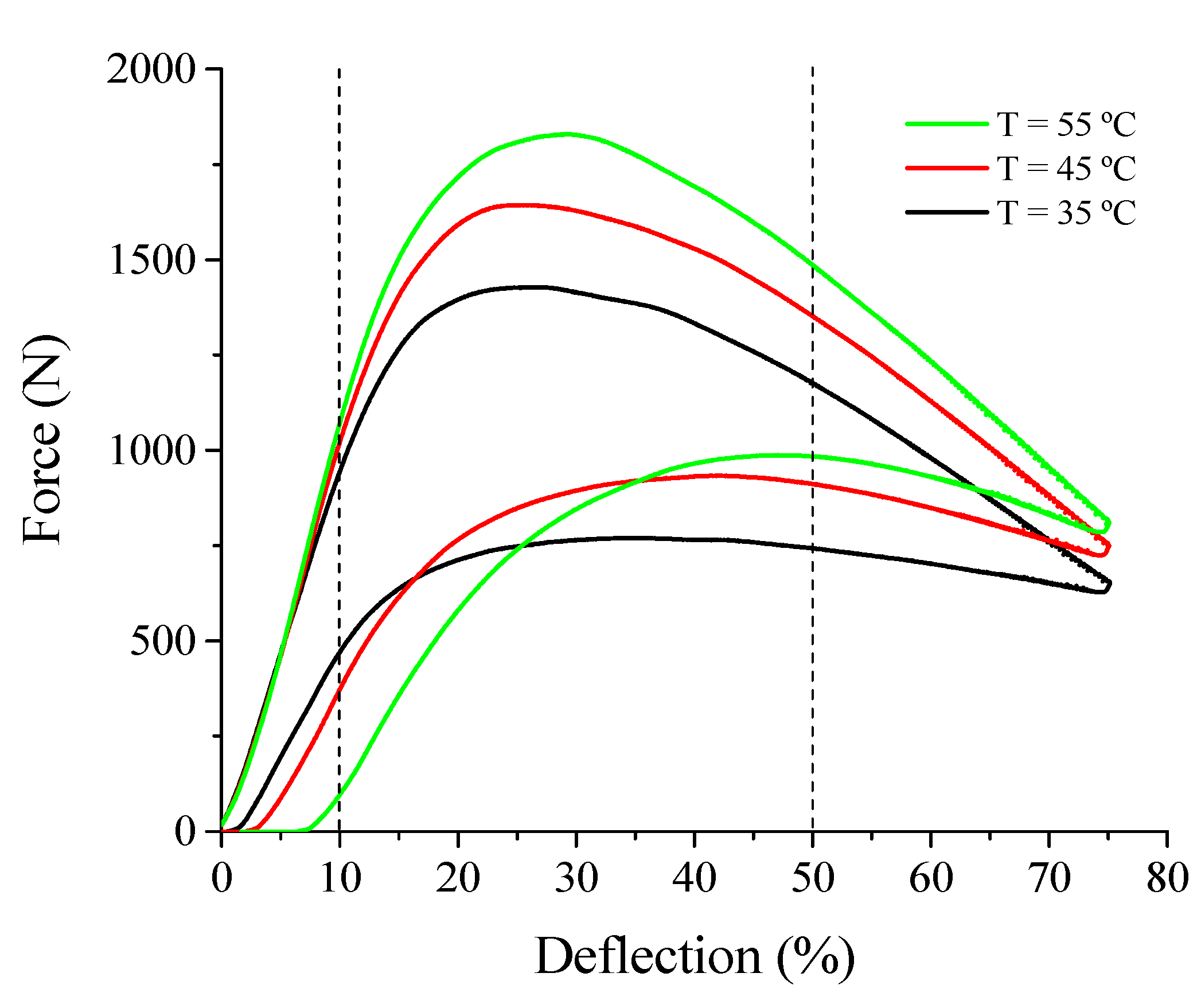
3.1.2. Superelastic Response at Low Loading Frequency
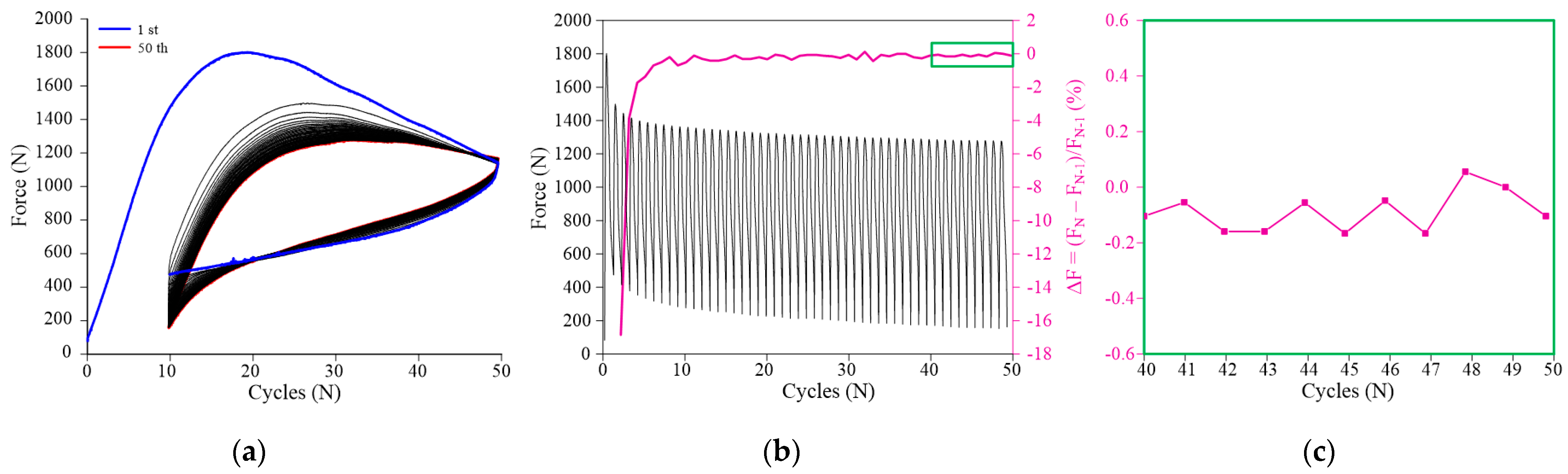
3.1.3. Mechanical Pre-Cycling
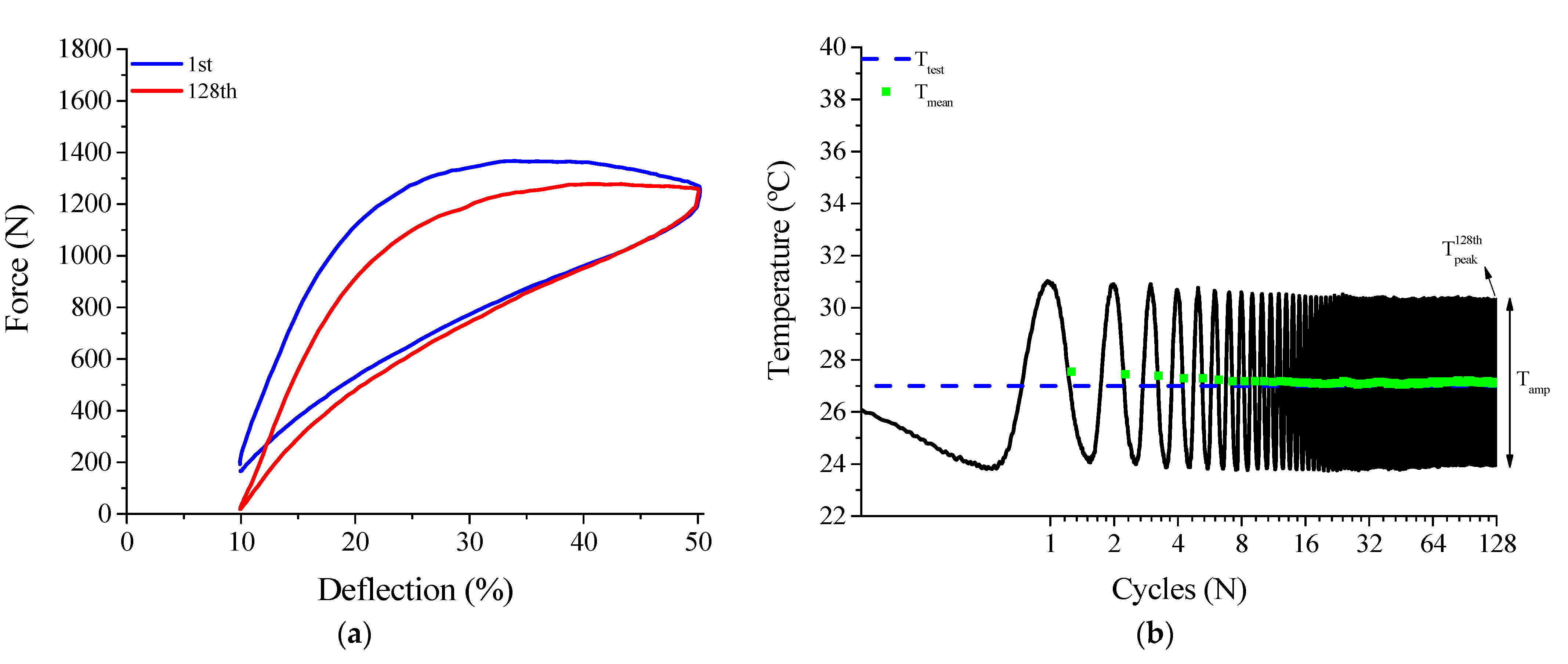
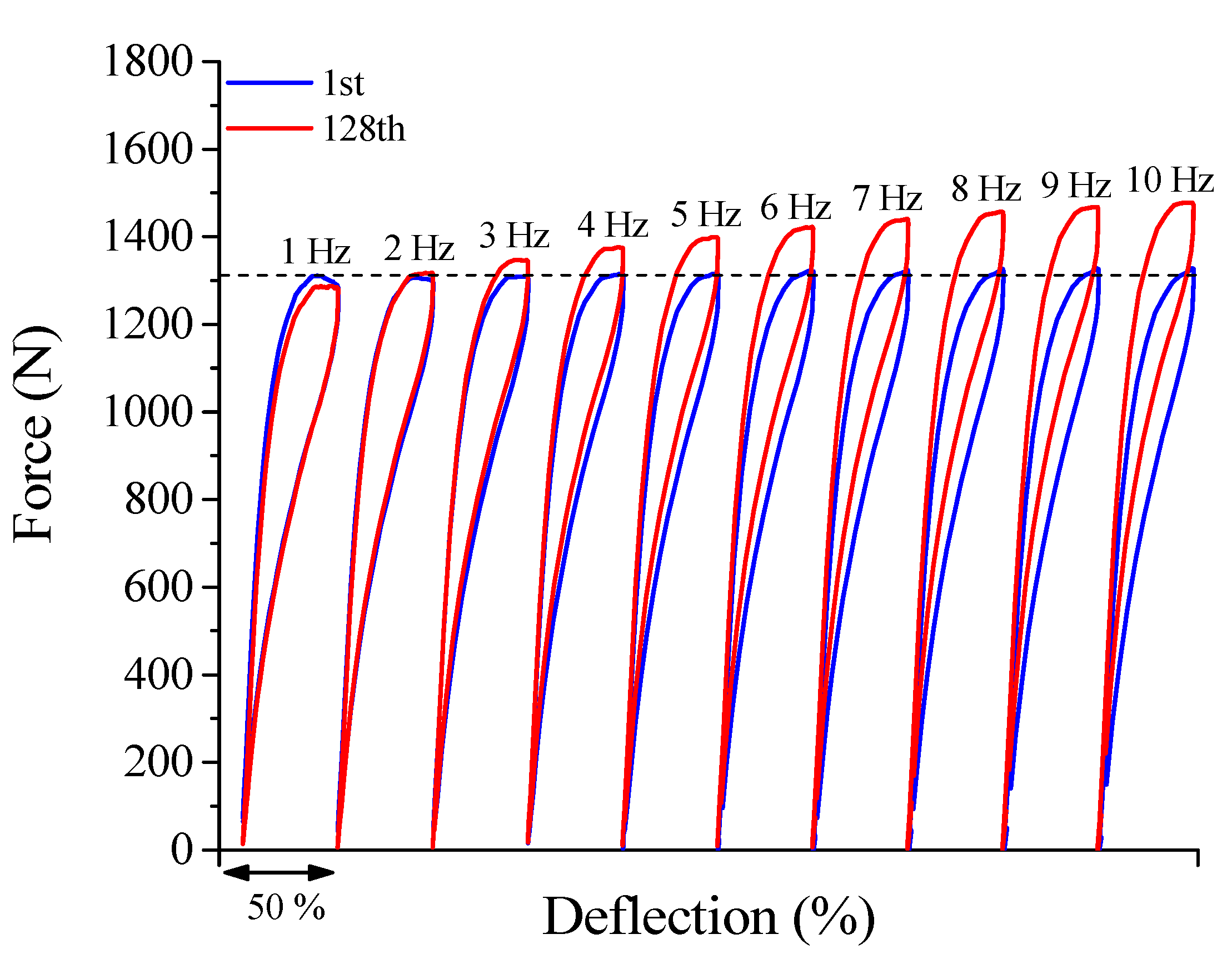
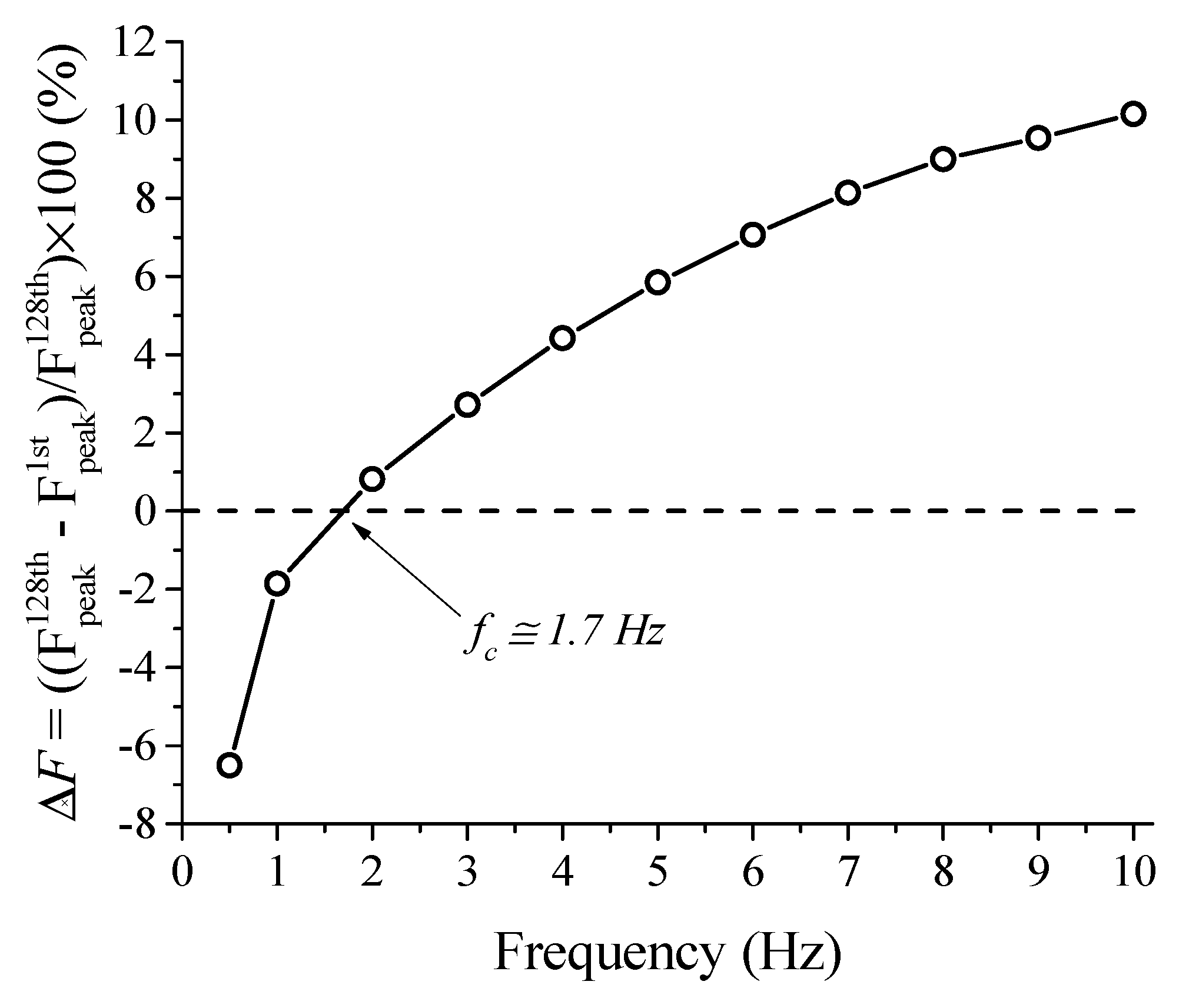
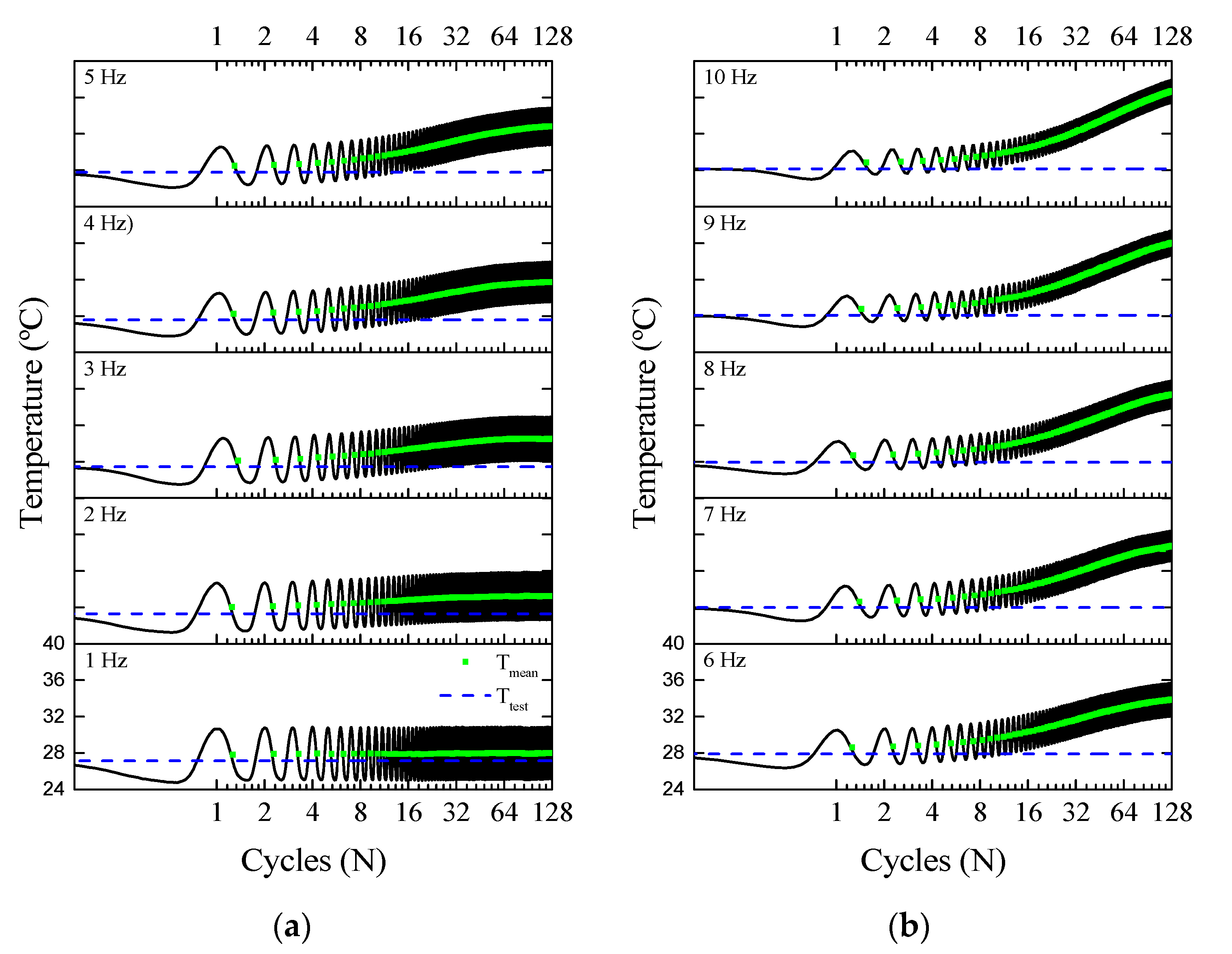
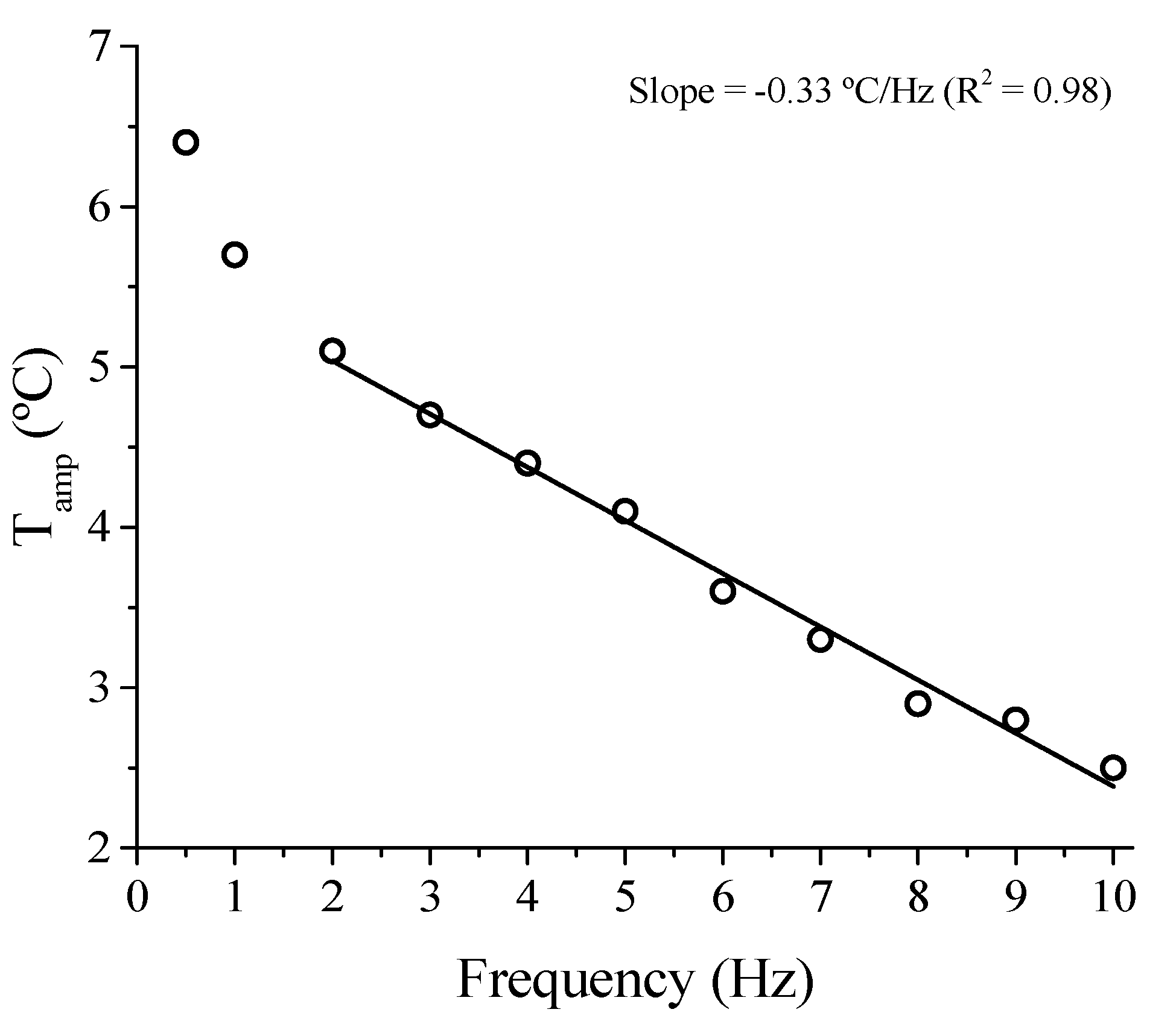
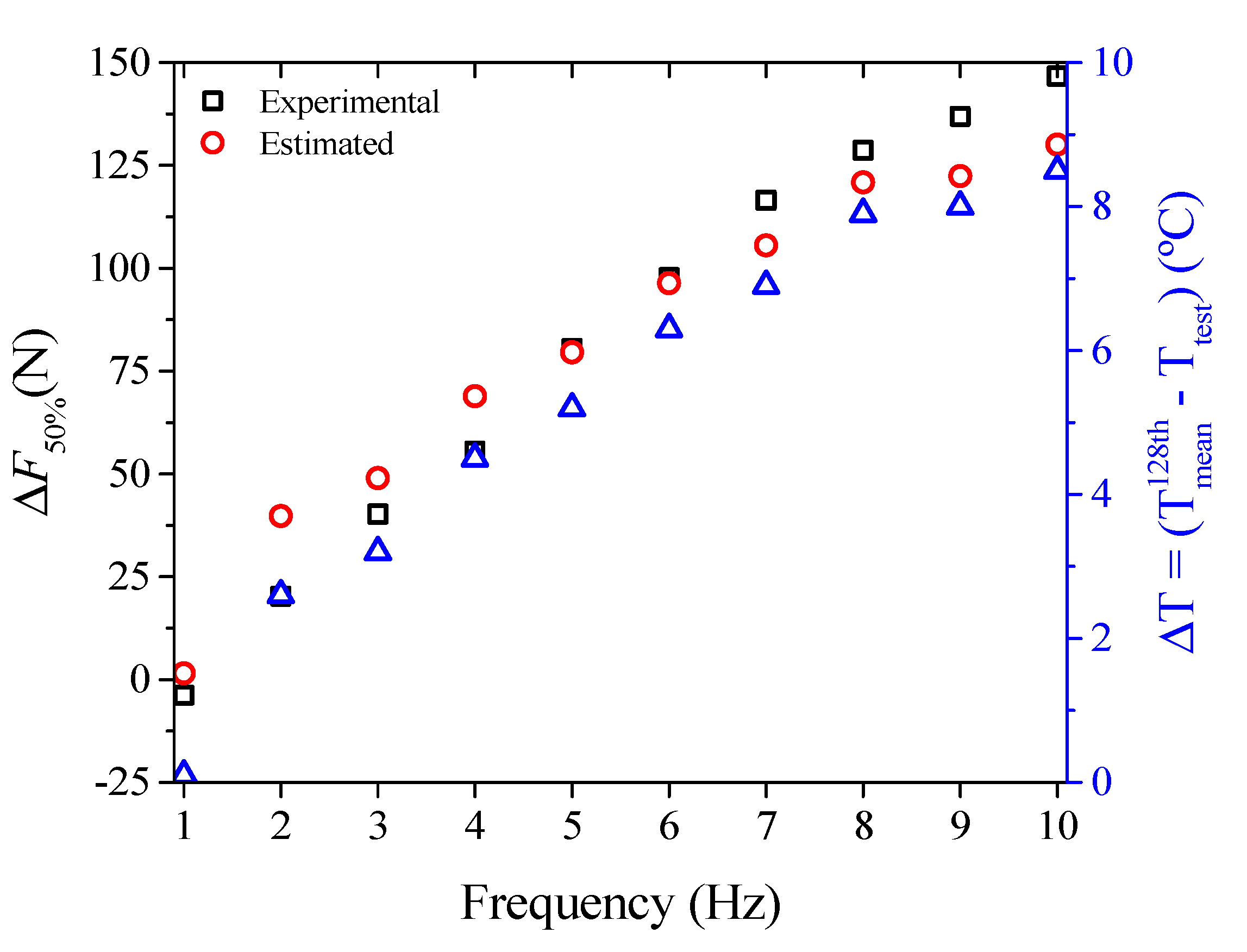
3.1.4. Superelastic Response and Thermomechanical Coupling in the Dynamic Regime
3.1.5. Functional Properties
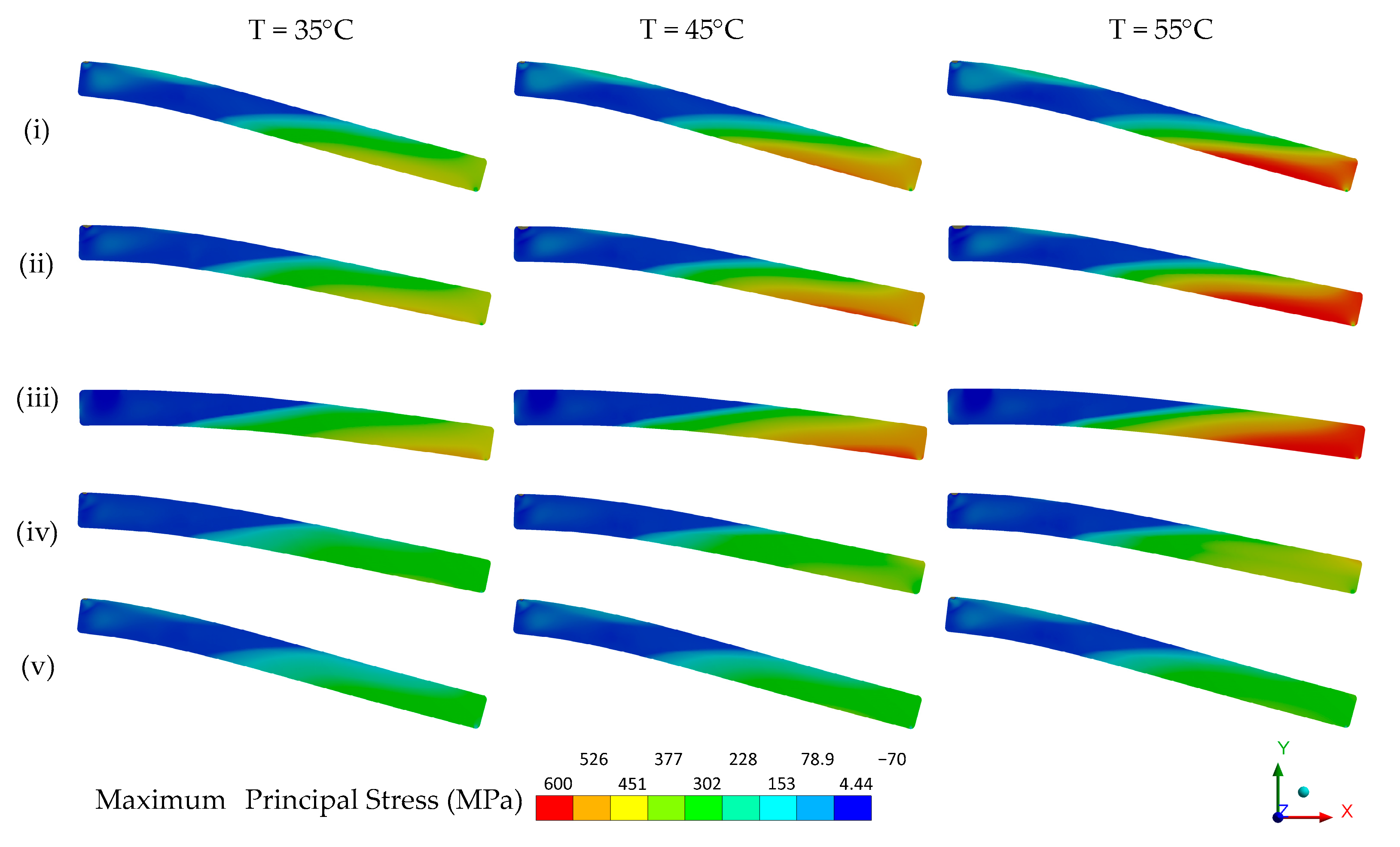
3.2. Numerical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lagoudas, D.C. Shape Memory Alloys: Modeling and Engineering Applications; Lagoudas, D.C., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780387476858. [Google Scholar]
- Duerig, T.W.; Bhattacharya, K. The measurement and interpretation of transformation temperatures in nitinol. In Proceedings of the ASM International—International Conference on Shape Memory and Superelastic Technologies, SMST 2017, San Diego, CA, USA, 15–19 May 2017; pp. 204–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, E.N.D.; Chagnon, G.; de Oliveira, H.M.R.; Favier, D. Anisotropy and Clausius-Clapeyron relation for forward and reverse stress-induced martensitic transformations in polycrystalline NiTi thin walled tubes. Mech. Mater. 2020, 146, 103392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wollants, P.; Roos, J.R.; Delaey, L. Thermally and stress-induced thermoelastic martensitic transformations in the reference frame of equilibrium thermodynamics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1993, 37, 227–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Q.; Yu, C.; Kang, G.; Li, J.; Yan, W. Experimental observations on rate-dependent cyclic deformation of super-elastic NiTi shape memory alloy. Mech. Mater. 2016, 97, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.A.; Kyriakides, S. Thermomechanical aspects of NiTi. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1995, 43, 1243–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemat-Nasser, S.; Choi, J.Y.; Guo, W.G.; Isaacs, J.B. Very high strain-rate response of a NiTi shape-memory alloy. Mech. Mater. 2005, 37, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, P.; Youssef, M.A. Seismic performance of steel moment resisting frames utilizing superelastic shape memory alloys. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2016, 125, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wilkinson, T.; Cho, C. Feasibility study on a self-centering beam-to-column connection by using the superelastic behavior of SMAs. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Zhou, X.; Osofero, A.I.; Shu, Z.; Corradi, M. Superelastic SMA Belleville washers for seismic resisting applications: Experimental study and modelling strategy. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 105013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, C.; Yam, M.C.H.; Chan, T.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Lin, X. A study of hybrid self-centring connections equipped with shape memory alloy washers and bolts. Eng. Struct. 2018, 164, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, R.P.B.; Silva, P.C.S.; Senko, R.; Silva, A.A.; Araújo, C.J. De Methodology for the estimation of material damping as applied to superelastic shape memory alloy mini-springs. Mater. Des. 2019, 161, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.G.; Silva, A.A.; de Araújo, C.J.; Senko, R.; dos Reis, R.P.B. Design and experimental analysis of a smart bearing using shape memory alloy springs. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2020, 31, 1390–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, J.M.; Silva, A.A.; de Araújo, C.J.; Pimentel, R.L.; de Aquino, A.S.; Senko, R.; dos Reis, R.P.B. On the active control of a rotor-bearing system using shape memory alloy actuators: An experimental analysis. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foard, J.H.D.; Rollason, D.; Thite, A.N.; Bell, C. Polymer composite Belleville springs for an automotive application. Compos. Struct. 2019, 221, 110891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patangtalo, W.; Aimmanee, S.; Chutima, S. A unified analysis of isotropic and composite Belleville springs. Thin-Walled Struct. 2016, 109, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramhormozian, S.; Clifton, G.C.; MacRae, G.A.; Davet, G.P.; Khoo, H.H. Experimental studies on Belleville springs use in the sliding hinge joint connection. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 159, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramhormozian, S.; Clifton, G.C.; MacRae, G.A.; Davet, G.P. Stiffness-based approach for Belleville springs use in friction sliding structural connections. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 138, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trochu, F.; Terriault, P. Nonlinear modelling of hysteretic material laws by dual kriging and application. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1998, 151, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgambitterra, E.; Maletta, C.; Furgiuele, F. Modeling and simulation of the thermo-mechanical response of NiTi-based Belleville springs. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2014, 27, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maletta, C.; Filice, L.; Furgiuele, F. NiTi Belleville washers: Design, manufacturing and testing. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Structures 2013, 24, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Liang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Yam, M.C.H.; Sun, R. Rocking bridge piers equipped with shape memory alloy (SMA) washer springs. Eng. Struct. 2020, 214, 110651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yam, M.C.H.; Fang, C.; Lam, A.C.C.; Zhang, Y. Numerical study and practical design of beam-to-column connections with shape memory alloys. J. Constr. Steel Res. Numer. 2015, 104, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speicher, M.; Hodgson, D.E.; DesRoches, R.; Leon, R.T. Shape Memory Alloy Tension/Compression Device for Seismic Retrofit of Buildings. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2009, 18, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Humbeeck, J. Cycling effects, fatigue and degradation of shape memory alloys. J. Phys. IV Proc. 1991, 1, C4-189–C4-197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zotov, N.; Pfund, M.; Polatidis, E.; Mark, A.F.; Mittemeijer, E.J. Change of transformation mechanism during pseudoelastic cycling of NiTi shape memory alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 682, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auricchio, F. A robust integration-algorithm for a finite-strain shape-memory-alloy superelastic model. Int. J. Plast. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budynas, R.G.; Nisbett, J.K. Singley’s Mechanical Engineering Design, 8th ed.; Mc Graw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 0-390-76487-6. [Google Scholar]
- Savi, M.A.; Paiva, A.; de Araujo, C.J.; de Paula, A.S. Shape Memory Alloys. In Dynamics of Smart Systems and Structures: Concepts and Applications; Lopes, V., Jr., Steffen, V., Jr., Savi, M.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 155–188. ISBN 978-3-319-29982-2. [Google Scholar]
- Schnorr Corporation. Handbook for Disc Springs; Schnorr Corporation: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2003; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Speicher, M.S. Cyclic Testing and Assessment of Shape Memory Alloy Recentering Systems; Georgia Institute of Technology: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki, S.; Imai, T.; Igo, Y.; Otsuka, K. Effect of Cyclic Deformation on the Pseudoelasticity Characteristics of Ti-Ni Alloys. Metall. Transactions. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 1986, 17A, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delville, R.; Malard, B.; Pilch, J.; Sittner, P.; Schryvers, D. Transmission electron microscopy investigation of dislocation slip during superelastic cycling of Ni–Ti wires. Int. J. Plast. 2011, 27, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedmák, P.; Šittner, P.; Pilch, J.; Curfs, C. Instability of cyclic superelastic deformation of NiTi investigated by synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Acta Mater. 2015, 94, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


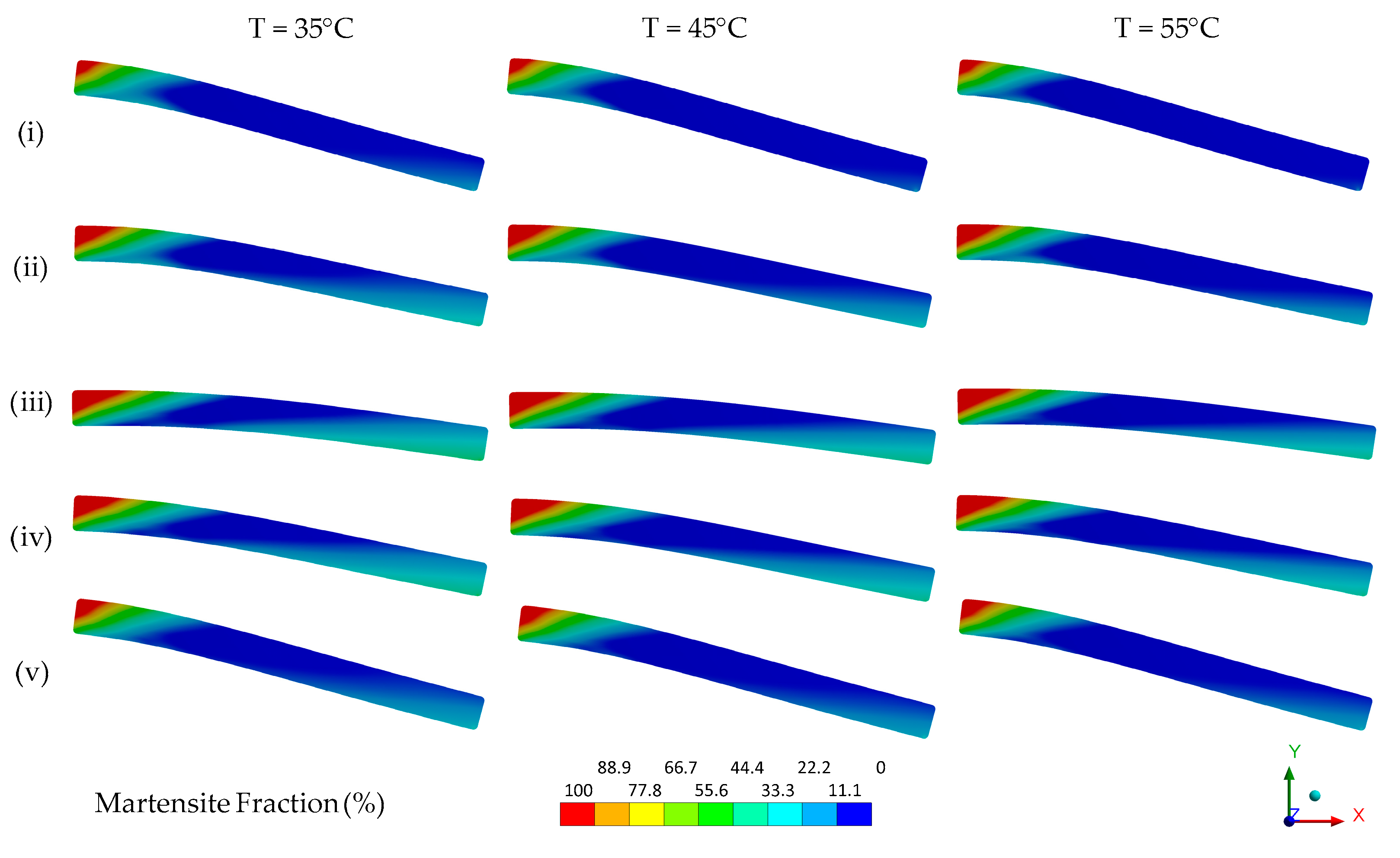

| Body (Material Model) | Material Parameter | Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compression plates (Linear elastic) | E (MPa) | 200,000 | ||
| ν | 0.3 | |||
| NiTi Belleville spring (SMA superelastic) | E (MPa) | 40,000 | ||
| ν | 0.3 | |||
| 35 °C | 45 °C | 55 °C | ||
| (MPa) | 350 | 450 | 525 | |
| (MPa) | 575 | 625 | 650 | |
| (MPa) | 300 | 350 | 375 | |
| (MPa) | 150 | 175 | 200 | |
| (mm/mm) | 0.06 | |||
| α | 0 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Souza, E.F.; da Silva, P.C.S.; Grassi, E.N.D.; de Araújo, C.J.; de Lima, A.G.B. Critical Frequency of Self-Heating in a Superelastic Ni-Ti Belleville Spring: Experimental Characterization and Numerical Simulation. Sensors 2021, 21, 7140. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217140
de Souza EF, da Silva PCS, Grassi END, de Araújo CJ, de Lima AGB. Critical Frequency of Self-Heating in a Superelastic Ni-Ti Belleville Spring: Experimental Characterization and Numerical Simulation. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7140. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217140
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Souza, Emmanuel Ferreira, Paulo César Sales da Silva, Estephanie Nobre Dantas Grassi, Carlos José de Araújo, and Antonio Gilson Barbosa de Lima. 2021. "Critical Frequency of Self-Heating in a Superelastic Ni-Ti Belleville Spring: Experimental Characterization and Numerical Simulation" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7140. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217140
APA Stylede Souza, E. F., da Silva, P. C. S., Grassi, E. N. D., de Araújo, C. J., & de Lima, A. G. B. (2021). Critical Frequency of Self-Heating in a Superelastic Ni-Ti Belleville Spring: Experimental Characterization and Numerical Simulation. Sensors, 21(21), 7140. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217140







