Omnidirectional Fingertip Pressure Sensor Using Hall Effect
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Fabrication of the Fingertip Pressure Sensor
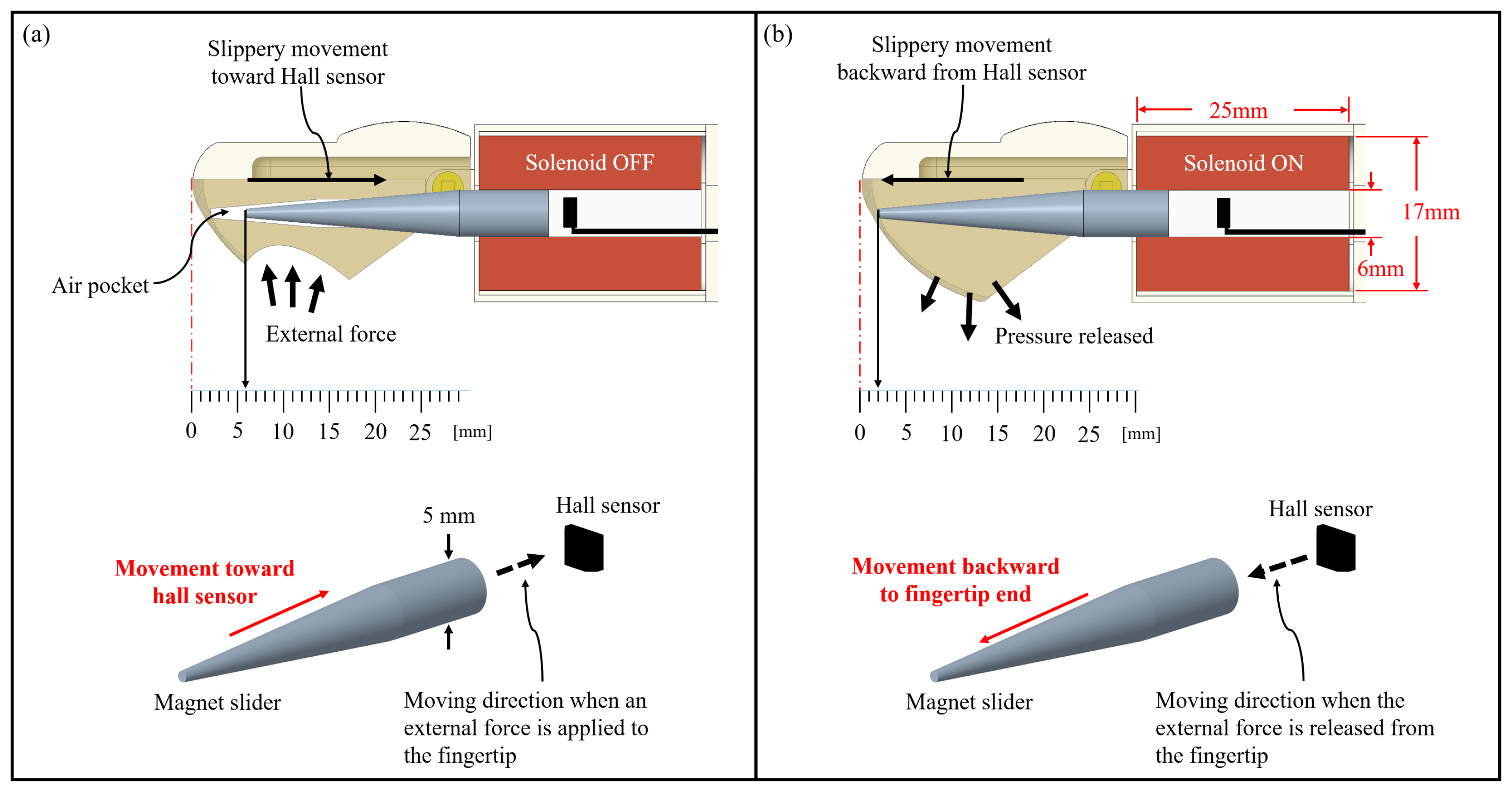
2.2. Pressure Sensing Mechanism
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
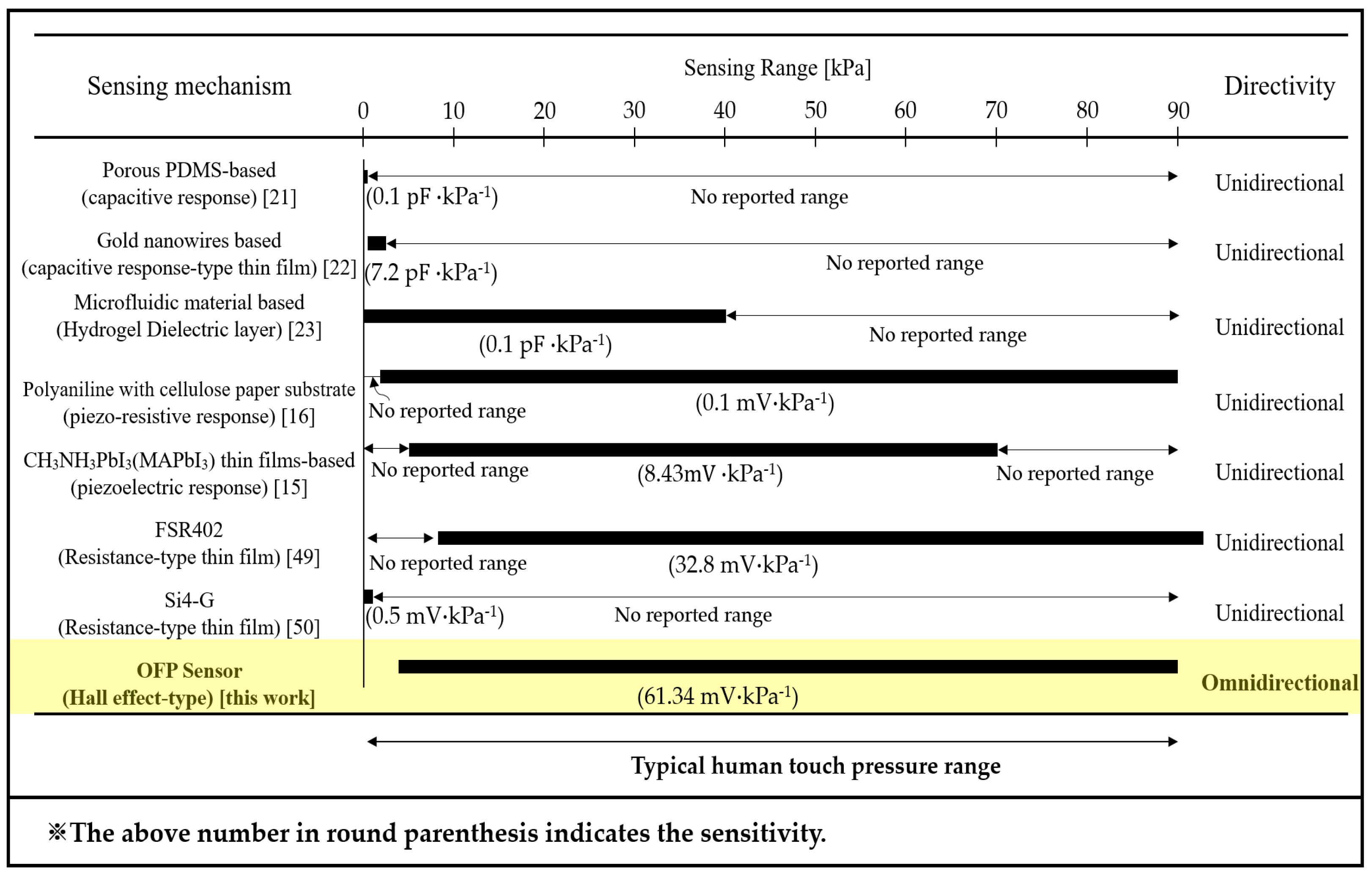
3.1. Performance Comparison of Pressure Sensor Regarding the Sensitivity and Working Range
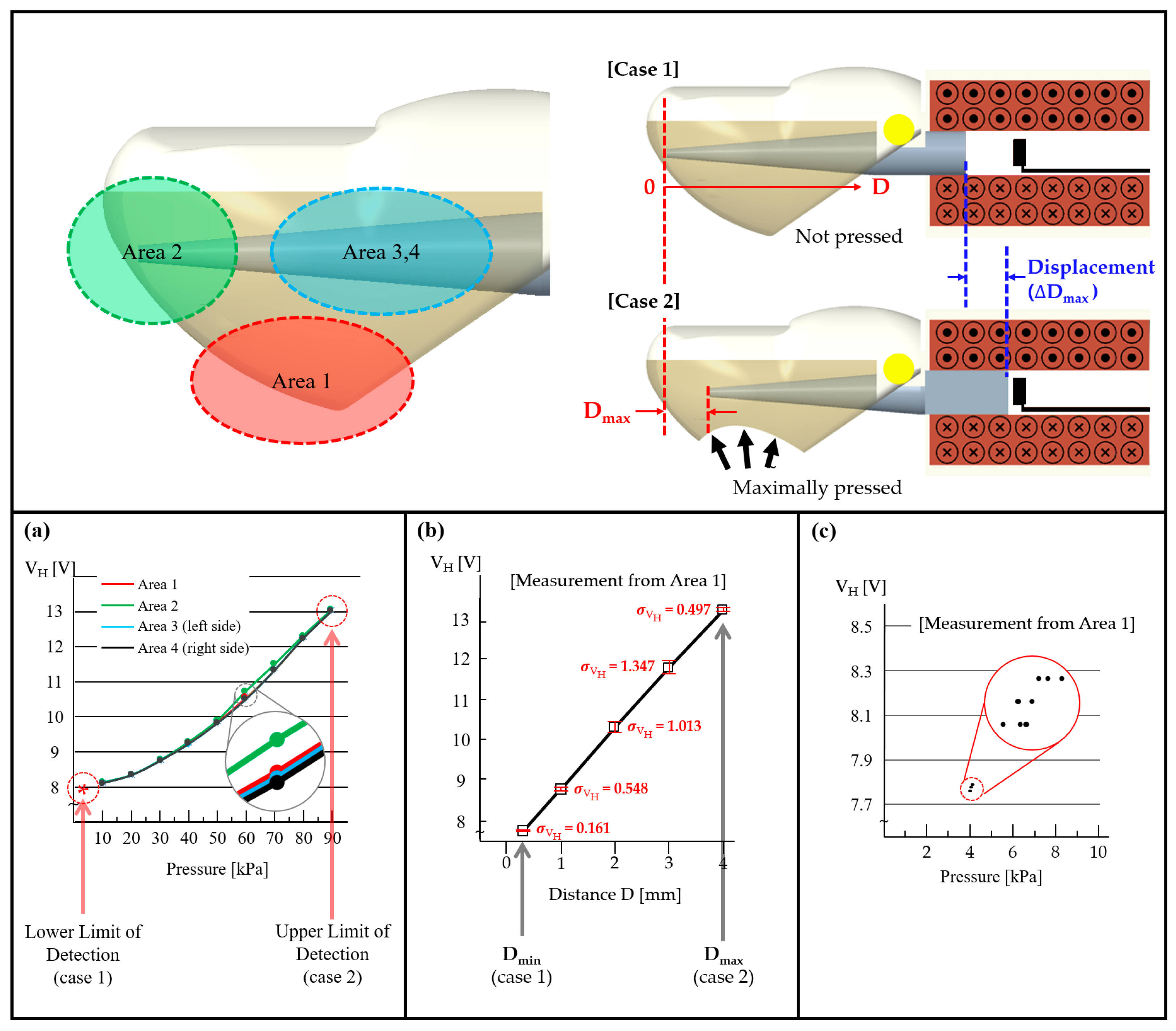
3.2. Pressure rueMeasurement from Various Sides of the Fingertip
3.3. Omnidirectionality and Sensitivity Comparison between OFP and FSR Sensors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Su, Z.; Song, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, X.; Meng, B.; Song, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhang, H. Omnidirectional bending and pressure sensor based on stretchable CNT-PU sponge. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, E.; Lee, H.-B.; Kim, D.-I.; Lee, N.-E. A Solution-Processable, Omnidirectionally Stretchable, and High-Pressure-Sensitive Piezoresistive Device. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, B.H.; Zabeeb, A.; Trung, T.Q.; Wen, L.; Lee, J.D.; Choi, Y.I.; Lee, H.B.; Kim, J.H.; Han, J.G.; Lee, N.E.L. A transparent stretchable sensor for distinguishable detection of touch and pressure by capacitive and piezoresistive signal transduction. NPG Asia Mater. 2019, 11, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, M.; Zhang, X.; Sun, X.; Meng, B.; Liu, W.; Zhang, H. Magnetic-assisted triboelectric nanogenerators as self-powered visualized omnidirectional tilt sensing system. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahrens, J. Auralization of omnidirectional room impulse responses based on the spatial decomposition method and synthetic spatial data. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Takane, E.; Tadakuma, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Konyo, M.; Tadokoro, S. A mechanical approach to realize reflexive omnidirectional bending motion for pneumatic continuum robots. ROBOMECH J. 2016, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean-Leon, E.; Pierce, B.; Bergner, F.; Mittendorfer, P.; Ramirez-Amaro, K.; Burger, W.; Cheng, G. TOMM: Tactile omnidirectional mobile manipulator. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 2441–2447. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, B.; Ehlers, K.; Osterloh, C.; Maehle, E. Smart-E, an Autonomous Omnidirectional Underwater Robot. Paladyn J. Behav. Robot. 2013, 4, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiner, P.; Neef, C.; Shibata, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Asfour, T. An Embedded, Multi-Modal Sensor System for Scalable Robotic and Prosthetic Hand Fingers. Sensors 2019, 20, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, G.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, F.; Xu, W. A smart high accuracy silicon piezoresistive pressure sensor temperature compensation system. Sensors 2014, 14, 12174–12190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, B. Mechanical structural design of a piezoresistive pressure sensor for low-pressure measurement: A computational analysis by increases in the sensor sensitivity. Sensors 2018, 18, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sobolčiak, P.; Tanvir, A.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Krupa, I. Piezoresistive Sensors Based on Electrospun Mats Modified by 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene. Sensors 2019, 19, 4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Persano, L.; Dagdeviren, C.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Girardo, S.; Pisignano, D.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J.A. High performance piezoelectric devices based on aligned arrays of nanofibers of poly(vinylidenefluoride-co-trifluoroethylene). Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, F.G.; Budoya, D.E.; de Almeida, V.A.; Ulson, J.A.C. An experimental study on the effect of temperature on piezoelectric sensors for impedance-based structural health monitoring. Sensors 2014, 14, 1208–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, J.-H.; Choi, H.-J.; Pammi, S.V.N.; Tran, V.D.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Yoon, S.-G. Self-powered pressure and light sensitive bimodal sensors based on long-term stable piezo-photoelectric MAPbI3 thin films. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 2786–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannichankandy, D.; Pataniya, P.M.; Narayan, S.; Patel, V.; Sumesh, C.K.; Patel, K.D.; Solanki, G.K.; Pathak, V.M. Flexible piezo-resistive pressure sensor based on conducting PANI on paper substrate. Synth. Met. 2021, 273, 116697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.W.; Lin, S.F. Wearable Piezoelectric-Based System for Continuous Beat-to-Beat Blood Pressure Measurement. Sensors 2020, 20, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, M.; Yun, K.S. MEMS capacitive pressure sensor monolithically integrated with CMOS readout circuit by using post CMOS processes. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2017, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohli, S.; Saini, A.; Pillai, A.J. MEMs based capacitive pressure sensor simulation for healthcare and biomedical applications. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2013, 4, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar]
- Metzger, C.; Fleisch, E.; Meyer, J.; Dansachmüller, M.; Graz, I.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Keplinger, C.; Schwödiauer, R.; Bauer, S. Flexible-foam-based capacitive sensor arrays for object detection at low cost. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 013506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, C.; Lee, S.D. Low-cost flexible pressure sensor based on dielectric elastomer film with micro-pores. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 240, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Schwalb, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Si, J.; Shirinzadeh, B.; Cheng, W. A wearable and highly sensitive pressure sensor with ultrathin gold nanowires. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, B.; Li, R.; Cao, J.; Brandt, J.D.; Pan, T. Flexible transparent iontronic film for interfacial capacitive pressure sensing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 6055–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Ji, B.; Wei, Y.; Hu, B.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, B. A bio-inspired cilia array as the dielectric layer for flexible capacitive pressure sensors with high sensitivity and a broad detection range. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 27334–27346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerratt, A.P.; Balakrisnan, B.; Penskiy, I.; Bergbreiter, S. Dielectric elastomer actuators fabricated using a micro-molding process. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 055004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Qing, X. A flexible ionic liquid-polyurethane sponge capacitive pressure sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 285, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.; Byun, J.; Seong, N.; Ha, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.; Im, H.; Kim, D.; Hong, Y. Silver nanowire-embedded PDMS with a multiscale structure for a highly sensitive and robust flexible pressure sensor. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6208–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Niu, Z.; Wang, H.; Leow, W.R.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wei, J.; Huo, F.; Chen, X. Microstructured graphene arrays for highly sensitive flexible tactile sensors. Small 2014, 10, 3625–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.-Y.; Lu, J.; Shieh, H.-P.D. Influence of Permittivity on the Sensitivity of Porous Elastomer-Based Capacitive Pressure Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 1870–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhuo, B.; Guo, X. Large Area One-Step Facile Processing of Microstructured Elastomeric Dielectric Film for High Sensitivity and Durable Sensing over Wide Pressure Range. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 20364–20370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-Y.; Keplinger, C.; Whitesides, G.M.; Suo, Z. Ionic skin. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7608–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Choi, B.-G.; Oh, G.-W.; Kim, C.-J.; Jung, Y.-S.; Jang, J.-S.; Joung, K.-Y.; Suh, J.-H.; Kang, I. Piezoresistive Characteristics of Nanocarbon Composite Strain Sensor by Its Longitudinal Pattern Design. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AVNET ABACUS. Pressure Sensors: The Design Engineer’s Guide. 2020. Available online: https://www.avnet.com/wps/portal/abacus/solutions/technologies/sensors/pressure-sensors/core-technologies/capacitive-vs-piezoresistive-vs-piezoelectric/ (accessed on 26 September 2021).
- Hassanli, K.; Kordrostami, Z.; Akbarian, A. MEMS piezoresistive pressure sensor with patterned thinning of diaphragm. Microelectron. Int. 2020, 37, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Nallathambi, A.; Shanmuganantham, T.; Sindhanaiselvi, D. Design and Analysis of MEMS based Piezoresistive Pressure sensor for Sensitivity Enhancement. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 1897–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Huang, B.; Lee, K.K.; Xu, Y. An Intelligent Shoe-Integrated System for Plantar Pressure Measurement. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Kunming, China, 17–20 December 2006; pp. 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Jiang, W.; Lü, Z.; Miran, S.M.; Luo, Z.-Z. Daily activity monitoring and fall detection based on surface electromyography and plantar pressure. Complexity 2020, 2020, 9532067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, G.S.; Barlow, P.; David, S. Review of sensors and sensor integration for the control of a humanoid robot. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Hangzhou, China, 10–12 May 2011; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Xia, Y.; Wu, X.; Kirk, T.V.; Chen, X.D. A low-cost and highly integrated sensing insole for plantar pressure measurement. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2019, 26, 100298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramp, S.; Maccoll, C.; Wallace, R.B. Preliminary Results for Novel Shear Force Sensor using Force Sensitive Resistors. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Dubrovnik, Croatia, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Chen, R.; Merhi, L.-K.; Xiao, Z.; Pousett, B.; Menon, C. Force Myography to Control Robotic Upper Extremity Prostheses: A Feasibility Study. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, S.; Fonseca, J.; Almeida, J.; Carvalho, R.; Pereira, P.; Simoes, R. Embedded Textile Sensing System for Pressure Mapping and Monitoring for the Prevention of Pressure Ulcers. In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2019), Prague, Czech Republic, 22–24 February 2019; pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Qin, M.; Nie, M.; Huang, Q. A MEMS pressure sensor based on Hall effect. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2011 IEEE, Limerick, Ireland, 28–31 October 2011; pp. 218–221. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Jung, C.; Jung, Y.; Moon, H.; Lim, H. Biomimetic skin-type shear sensor. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems (ICCAS), Gyeongju, Korea, 16–19 October 2016; pp. 1331–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.; Damian, D.D.; Shan, W.; Lu, T.; Majidi, C. Soft-matter capacitive sensor for measuring shear and pressure deformation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 3529–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosset, S.; Niklaus, M.; Dubois, P.; Shea, H.R. Mechanical characterization of a dielectric elastomer microactuator with ion-implanted electrodes. Sens. Afctuator A Phys. 2008, 144, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Poll, M.L.; Khodabakhsh, S.; Brewer, P.J.; Shard, A.G.; Ramstedt, M.; Huck, W.T. Surface modification of PDMS via self-organization of vinyl-terminated small molecules. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, C.L.; Westgate, C.R. The Hall Effect and Its Applications; Springer Science+Business Media, LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Datasheet F. S. R. Model 400. Interlink Electronics, Inc. 2010. Available online: http://www.interlinkelectronics.com/datasheets/DatasheetFSR.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2021).
- Microsoft Word—SI4-G-DS-CH-V2.2.docx, Leanstar. 2019. Available online: https://datasheet.lcsc.com/szlcsc/1912122144_L-EANSTAR-SI4-G_C469149.pdf (accessed on 26 September 2021).
- Force Sensing Resistor. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Force-sensing_resistor (accessed on 26 September 2021).
- Velásquez, E.I.G.; Gómez, V.; Paredes-Madrid, L.; Colorado, H.A. Error compensation in force sensing resistors. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2019, 26, 100300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SS49E Datasheet (PDF)—Honeywell Accelerometers, Honeywell. 2012. Available online: https://pdf1.alldatasheet.com/data-sheet-pdf/view/533446/HONEYWELL-ACC/SS49E.html (accessed on 26 September 2021).
- Dewi, S.D.T.; Panatarani, C.; Joni, I.M. Design and development of DC high current sensor using Hall-Effect method. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1712, 030006. [Google Scholar]





| 10 kPa | 20 kPa | 30 kPa | 40 kPa | 50 kPa | 60 kPa | 70 kPa | 80 kPa | 90 kPa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area 1 | 0.058 | 0.000 | 0.166 | 0.113 | 0.079 | 0.223 | 0.137 | 0.227 | 0.056 | 0.118 |
| Area 2 | 0.000 | 0.095 | 0.144 | 0.133 | 0.086 | 0.128 | 0.215 | 0.116 | 0.078 | 0.110 |
| Area 3 | 0.058 | 0.000 | 0.167 | 0.158 | 0.145 | 0.138 | 0.075 | 0.266 | 0.061 | 0.119 |
| Area 4 | 0.058 | 0.000 | 0.163 | 0.157 | 0.107 | 0.162 | 0.125 | 0.301 | 0.081 | 0.128 |
| 0.044 | 0.024 | 0.160 | 0.140 | 0.104 | 0.163 | 0.138 | 0.227 | 0.069 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, M.-J.; Yoo, J.-C. Omnidirectional Fingertip Pressure Sensor Using Hall Effect. Sensors 2021, 21, 7072. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217072
Seo M-J, Yoo J-C. Omnidirectional Fingertip Pressure Sensor Using Hall Effect. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7072. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217072
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Moo-Jung, and Jae-Chern Yoo. 2021. "Omnidirectional Fingertip Pressure Sensor Using Hall Effect" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7072. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217072
APA StyleSeo, M.-J., & Yoo, J.-C. (2021). Omnidirectional Fingertip Pressure Sensor Using Hall Effect. Sensors, 21(21), 7072. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217072






