Intelligent Techniques for Detecting Network Attacks: Review and Research Directions
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Background
- (i)
- What is/are the classification algorithms implemented?
- (ii)
- What is/are the datasets employed for developing the intelligent systems?
- (iii)
- Furthermore, this research article compared the results obtained using different evaluation metrics.
- (i)
- Which algorithm(s) was/were commonly implemented and in which kind of attacks?
- (ii)
- Which dataset(s) is/are considered more reliable based on the results obtained?
2. Network Attacks
2.1. Types of Network Attacks
2.2. Network Attack Detection and Prevention Techniques
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS): Referred to also as network-based IDS (NIDS). This system intensely monitors malicious network activities and notifies officials if an attack is detected with no prevention abilities. Signature-based and anomaly-based detection are the two most prevalent approaches used by IDS to identify threats. Signature-based procedures are applied to detect only known threats, relying on a database containing a list of pre-existing characteristics of known attacks (attacks signatures) to identify suspicious events. The database needs to be continuously updated to include emerging attacks. On the other hand, anomaly-based procedures attempt to differentiate malicious traffic from real traffic based on a change in the network traffic; thus, they can detect unknown threats. Inconsistencies such as high-size traffic, network latency, traffic from uncommon ports, and abnormal system performance, all represent changes in the normal behaviors of the system and can indicate the presence of network attacks.
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS): Known also as intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS). It scans the network continuously for the presence of illegal or rogue control points that are detected on the basis of changes in behavior. The system automatically takes countermeasures to tackle the threats and defend the system. The primary objective of an IDPS is to keep malicious or undesired packets and attacks from causing any harm. IDPS is more effective than IDS as it not only detects threats, but is able to take action against them. There are two types of IDPS: network-based intrusion detection and prevention systems (NIDPS) that analyze the network protocol to identify any suspicious activities and host-based intrusion detection and prevention systems (HIDPS) that are used to monitor host activities for any suspicious events within the host.
3. Intelligent Network Attack Mitigation Techniques
3.1. Problem Domains of the Reviewed Articles
3.1.1. Insider Threat
3.1.2. DDoS Attacks
3.1.3. Phishing Attacks
3.1.4. Zero-Day Attacks
3.1.5. Malware Attacks
3.1.6. Malware Botnet Attacks
3.1.7. Detecting Attacks over IoT Networks
3.1.8. Malicious Traffic Classification
Malicious Traffic in a Cloud Environment
3.1.9. Attacks at DNS Level
3.1.10. Intrusion Detection
3.2. Common Intelligent Algorithms Applied
3.3. Common Datasets Used
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goli, Y.D.; Ambika, R. Network Traffic Classification Techniques-A Review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Techniques, Electronics and Mechanical Systems, CTEMS 2018, Belgaum, India, 21–22 December 2018; pp. 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Jing, X.; Yan, Z.; Pedrycz, W. Network traffic classification for data fusion: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2021, 72, 22–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Hassan, S.A.; Hussain, R.; Hossain, E. Machine Learning for Resource Management in Cellular and IoT Networks: Potentials, Current Solutions, and Open Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 1251–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaikh, M.; Vadivel, R. Cloud computing: Major challenges and counter acts. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Sci. 2018, 9, 742–744. [Google Scholar]
- Goudos, S.K.; Dallas, P.I.; Chatziefthymiou, S.; Kyriazakos, S. A Survey of IoT Key Enabling and Future Technologies: 5G, Mobile IoT, Sematic Web and Applications. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 97, 1645–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, R.U.; Tomar, D.S. Security attacks on wireless networks and their detection techniques. In Emerging Wireless Communication and Network Technologies: Principle, Paradigm and Performance; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 241–270. ISBN 9789811303968. [Google Scholar]
- Azeez, N.A.; Bada, T.M.; Misra, S.; Adewumi, A.; der Vyver, C.; Ahuja, R. Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems: An Updated Review. In Data Management, Analytics and Innovation; Sharma, N., Chakrabarti, A., Balas, V.E., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 685–696. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, I.; Frank, E.; Hall, M.; Pal, C. Data Mining—Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques, 4th ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: Burlington, MA, USA, 2016; ISBN 9780128042915. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning-Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning Series—Deep Learning; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0262035613. [Google Scholar]
- Tuor, A.; Kaplan, S.; Hutchinson, B.; Nichols, N.; Robinson, S. Deep learning for unsupervised insider threat detection in structured cybersecurity data streams. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence for Cyber Security Workshop (AAAI-2017), San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–5 February 2017; pp. 224–234. [Google Scholar]
- Lindauer, B.; Glasser, J.; Rosen, M.; Wallnau, K. Generating test data for insider threat detectors. J. Wirel. Mob. Netw. Ubiquitous Comput. Dependable Appl. 2014, 5, 80–94. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Cao, Y.; Shang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, J.; Fang, B. Insider Threat Detection with Deep Neural Network. In Computational Science—ICCS 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasser, J.; Lindauer, B. Bridging the gap: A pragmatic approach to generating insider threat data. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Security and Privacy Workshops, San Francisco, CA, USA, 23–24 May 2013; pp. 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Niu, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Lu, J.; Liu, Y. An Insider Threat Detection Approach Based on Mouse Dynamics and Deep Learning. Secur. Comm. Netw. 2019, 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fülöp, A.; Kovács, L.; Kurics, T.; Windhager-Pokol, E. GitHub—Balabit/Mouse-Dynamics-Challenge. 2016. Available online: https://github.com/balabit/Mouse-Dynamics-Challenge (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Yuan, X.; Li, C.; Li, X. DeepDefense: Identifying DDoS Attack via Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), Hong Kong, China, 29–31 May 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiravi, A.; Shiravi, H.; Tavallaee, M.; Ghorbani, A.A. Toward developing a systematic approach to generate benchmark datasets for intrusion detection. Comput. Secur. 2012, 31, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, U.J.; Ji, S.H.; Park, J.T.; Lee, M.S.; Park, J.S.; Kim, M.S. DDoS Attack Detection on Bitcoin Ecosystem using Deep-Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 20th Asia-Pacific Network Operations and Management Symposium (APNOMS), Matsue, Japan, 18–20 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasek, M.; Thornton, M.; Moore, T. Replication data for: Empirical analysis of denial-of-service attacks in the bitcoin ecosystem. Harvard Dataverse, V2. Available online: https://dataverse.harvard.edu/dataset.xhtml?persistentId=doi:10.7910/DVN/25541 (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Sabeel, U.; Heydari, S.S.; Mohanka, H.; Bendhaou, Y.; Elgazzar, K.; El-Khatib, K. Evaluation of Deep Learning in Detecting Unknown Network Attacks. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Smart Applications, Communications and Networking (SmartNets), Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt, 17–19 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, M.S.; Le-Khac, N.A.; Dev, S.; Jurcut, A.D. DDoSNet: A Deep-Learning Model for Detecting Network Attacks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 21st International Symposium on "A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks" (WoWMoM), Cork, Ireland, 31 August–3 September 2020; pp. 391–396. [Google Scholar]
- DDoS. Datasets | Research| Canadian Institute for Cybersecurity | UNB. 2019. Available online: https://www.unb.ca/cic/datasets/ddos-2019.html (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Doriguzzi-Corin, R.; Millar, S.; Scott-Hayward, S.; Martinez-Del-Rincon, J.; Siracusa, D. Lucid: A Practical, Lightweight Deep Learning Solution for DDoS Attack Detection. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2020, 17, 876–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahuja, N.; Singal, G.; Mukhopadhyay, D. DLSDN: Deep learning for DDOS attack detection in software defined networking. In Proceedings of the 2021 11th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), Noida, India, 28–29 January 2021; pp. 683–688. [Google Scholar]
- Swab, M. Mendeley Data. J. Can. Health Libr. Assoc. 2016, 37, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.; Li, J.; Wu, C. DeepDDoS: Online DDoS attack detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 9–13 December 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyaz, Q.; Sun, W.; Javaid, A.Y. A Deep Learning Based DDoS Detection System in Software-Defined Networking (SDN). ICST Trans. Secur. Saf. 2017, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pande, S.; Khamparia, A.; Gupta, D.; Thanh, D.N.H. DDOS Detection Using Machine Learning Technique. In Studies in Computational Intelligence; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 921. [Google Scholar]
- University of New Brunswick. NSL-KDD Data Set for Network-Based Intrusion Detection Systems. NSL-KDD Dataset. 2018. Available online: http://www.unb.ca/cic/datasets/nsl.html (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Radivilova, T.; Kirichenko, L.; Ageiev, D.; Bulakh, V. Classification methods of machine learning to detect DDoS attacks. In Proceedings of the 2019 10th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications (IDAACS), Metz, France, 18–21 September 2019; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kasassbeh, M.; Al-Naymat, G.; Al-Hawari, E. Towards Generating Realistic SNMP-MIB Dataset for Network Anomaly Detection. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Secur. 2016, 14, 1162. [Google Scholar]
- De Lima Filho, F.S.; Silveira, F.A.F.; De Medeiros Brito Junior, A.; Vargas-Solar, G.; Silveira, L.F. Smart Detection: An Online Approach for DoS/DDoS Attack Detection Using Machine Learning. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2019, 2019, 1574749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazi, H.H.; Gonzalez, H.; Stakhanova, N.; Ghorbani, A.A. Detecting HTTP-based application layer DoS attacks on web servers in the presence of sampling. Comput. Netw. 2017, 121, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayanand, R.; Devaraj, D.; Kannapiran, B. A Novel Deep Learning Based Intrusion Detection System for Smart Meter Communication Network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Techniques in Control, Optimization and Signal Processing (INCOS), Tamilnadu, India, 11–13 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, R.M.A.; Alsmadi, M.K.; Almarashdeh, I.; Alzaqebah, M. An improved rule induction based denial of service attacks classification model. Comput. Secur. 2020, 99, 102008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, N.; Slay, J. UNSW-NB15: A comprehensive data set for network intrusion detection systems (UNSW-NB15 network data set). In Proceedings of the 2015 Military Communications and Information Systems Conference (MilCIS), Canberra, Australia, 10–12 November 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The CAIDA “DDoS Attack 2007” Dataset—CAIDA. Available online: https://www.caida.org/catalog/datasets/ddos-20070804_dataset/ (accessed on 29 June 2021).
- Robinson, R.R.R.; Thomas, C. Ranking of machine learning algorithms based on the performance in classifying DDoS attacks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Recent Advances in Intelligent Computational Systems (RAICS), Trivandrum, India, 10–12 December 2016; pp. 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettich, S.B. The UCI KDD Archive. Irvine, CA: University of California, Department of Information and Computer Science. 1999. Available online: http://kdd.ics.uci.edu/ (accessed on 12 October 2021).
- Barati, M.; Abdullah, A.; Udzir, N.I.; Mahmod, R.; Mustapha, N. Distributed Denial of Service detection using hybrid machine learning technique. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Biometrics and Security Technologies (ISBAST), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 26–27 August 2014; pp. 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Shim, M.; Choi, E. CNN-Based Network Intrusion Detection against Denial-of-Service Attacks. Electronics 2020, 9, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ur Rehman, S.; Khaliq, M.; Imtiaz, S.I.; Rasool, A.; Shafiq, M.; Javed, A.R.; Jalil, Z.; Bashir, A.K. DIDDOS: An approach for detection and identification of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) cyberattacks using Gated Recurrent Units (GRU). Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 118, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.N.; Sarma, D.; Lima, F.F.; Saha, I.; Ulfath, R.E.; Hossain, S. Phishing attacks detection using machine learning approach. In Proceedings of the 2020 Third International Conference on Smart Systems and Inventive Technology (ICSSIT), Tirunelveli, India, 20–22 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad, R.M.; Thabtah, F.; McCluskey, L. Predicting phishing websites based on self-structuring neural network. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 25, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammad, R.M.A.; McCluske, L.; Thabtah, F. Phishing Websites Data Set. Available online: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/phishing+websites (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Mohammad, R.M.; Thabtah, F.; McCluskey, L. An assessment of features related to phishing websites using an automated technique. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions, London, UK, 10–12 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Thabtah, F.; Mohammad, R.M.; McCluskey, L. A dynamic self-structuring neural network model to combat phishing. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rendall, K.; Nisioti, A.; Mylonas, A. Towards a Multi-Layered Phishing Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Yuan, H.; Liu, W. A stacking model using URL and HTML features for phishing webpage detection. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 94, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, R.; Divakaran, M.; Ng, J.Y.; Chan, Q.Z.; Lu, Y.; Si, Y.; Zhang, F.; Dong, J.S. Phishpedia: A Hybrid Deep Learning Based Approach to Visually Identify Phishing Webpages. In Proceedings of the 30th {USENIX} Security Symposium ({USENIX} Security 21, Online, 11–13 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Butnaru, A.; Mylonas, A.; Pitropakis, N. Towards lightweight url-based phishing detection. Futur. Internet 2021, 13, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Malicious and Benign URLs | Kaggle. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/siddharthkumar25/malicious-and-benign-urls (accessed on 19 October 2021).
- SEO Backlink Checker & Link Building Toolset | Majestic.com. Available online: https://majestic.com/ (accessed on 19 October 2021).
- Rao, R.S.; Vaishnavi, T.; Pais, A.R. PhishDump: A multi-model ensemble based technique for the detection of phishing sites in mobile devices. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2019, 60, 101084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchal, S.; Asokan, N. On Designing and Evaluating Phishing Webpage Detection Techniques for the Real World. 2018. Available online: https://w3techs.com/technologies/ (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Das, A.; Baki, S.; El Assaal, A.; Verma, R.; Dunbar, A. SoK: A Comprehensive Reexamination of Phishing Research From the Security Perspective. IEEE Comm. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 671–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaver, J.M.; Symons, C.T.; Gillen, R.E. A learning system for discriminating variants of malicious network traffic. In Proceedings of the Eighth Annual Cyber Security and Information Intelligence Research Workshop, Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 8–10 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Jabbar, W.A.; Sadiq, A.S.; Patel, H. Deep learning-based classification model for botnet attack detection. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The CTU-13 Dataset. A Labeled Dataset with Botnet, Normal and Background traffic—Stratosphere IPS. Available online: https://www.stratosphereips.org/datasets-ctu13 (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Barut, O.; Grohotolski, M.; Dileo, C.; Luo, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, T. Machine Learning Based Malware Detection on Encrypted Traffic: A Comprehensive Performance Study. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Networking, Systems and Security, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 22–24 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, S.; Parmisano, A.; Jose Erquiaga, M. Stratosphere IoT-23 Dataset: A labeled dataset of Malware and Benign IoT Traffic—Stratosphere IPS. IoT-23: A labeled dataset with malicious and benign IoT network traffic (Version 1.0.0) [Data set]. Zenodo. 2020. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/4743746#.YXeyAhyEZPY (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Marín, G.; Casas, P.; Capdehourat, G. DeepMAL-Deep Learning Models for Malware Traffic Detection and Classification. Data Science – Analytics and Applications; Springer Vieweg: Wiesbaden, Germnay, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, M.; Zeng, X.; Ye, X.; Sheng, Y. Malware traffic classification using convolutional neural network for representation learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), Da Nang, Vietnam, 11–13 January 2017; pp. 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Song, Y.; Cheong, Y.G. Classification of attack types for intrusion detection systems using a machine learning algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Fourth International Conference on Big Data Computing Service and Applications (BigDataService), Bamberg, Germany, 26–29 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Takakura, H.; Okabe, Y.; Eto, M.; Inoue, D.; Nakao, K. Statistical analysis of honeypot data and building of Kyoto 2006+ dataset for NIDS evaluation. In Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Building Analysis Datasets and Gathering Experience Returns for Security, BADGERS 2011, Salzburg, Austria, 10 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- David, O.E.; Netanyahu, N.S. DeepSign: Deep learning for automatic malware signature generation and classification. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Killarney, Ireland, 12–17 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Shi, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, W. Enhancing machine learning based malware detection model by reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Communication and Network Security, Qingdao, China, 2–4 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, H.S.; Roth, P. EMBER: An Open Dataset for Training Static PE Malware Machine Learning Models. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.04637. [Google Scholar]
- Letteri, I.; Penna, G.; Di Vita, L.; Grifa, M.T. MTA-KDD’19: A Dataset for Malware Traffic Detection. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/IvanLetteri/MTA-KDD-19 (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Letteri, I.; Di Cecco, A.; Della Penna, G. Dataset Optimization Strategies for MalwareTraffic Detection. 2020. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2009.11347 (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Ramos, K.S.H.; Monge, M.A.S.; Vidal, J.M. Benchmark-based reference model for evaluating botnet detection tools driven by traffic-flow analytics. Sensors 2020, 20, 4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenazi, A.; Traore, I.; Ganame, K.; Woungang, I. Holistic Model for HTTP Botnet Detection Based on DNS Traffic Analysis. Adv. Artif. Intell. 2017, 10618, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pektaş, A.; Acarman, T. Deep learning to detect botnet via network flow summaries. Neural Comput. Appl. 2019, 31, 8021–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Al-Haija, Q.; Zein-Sabatto, S. An Efficient Deep-Learning-Based Detection and Classification System for Cyber-Attacks in IoT Communication Networks. Electronics 2020, 9, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Abbas, S.; Rehman, A.; Saeed, Y.; Zeb, A.; Uddin, M.I.; Nasser, N.; Ali, A. A Machine Learning Approach for Blockchain-Based Smart Home Networks Security. IEEE Netw. 2021, 35, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Naeem, H.; Jabbar, S.; Khalid, S.; Latif, M.A.; Al-Turjman, F.; Mostarda, L. Cyber security threats detection in internet of things using deep learning approach. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 124379–124389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub—Jur1cek/gcj-Dataset: Collected Solutions from Google Code Jam Programming Competition (2008–2020). Available online: https://github.com/Jur1cek/gcj-dataset (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Tama, B.A.; Rhee, K.-H. Attack classification analysis of IoT network via deep learning approach. Res. Briefs Inf. Commun. Technol. Evol. 2017, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, M.; Wunderlich, S.; Grüdl, D.; Landes, D.; Hotho, A. Flow-Based Benchmark Data Sets for Intrusion Detection. In Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Cyber Warfare and Security. ACPI, Dublin, Ireland, 29–30 June 2017; pp. 361–369. [Google Scholar]
- Vilela, D.W.F.L.; Ferreira, E.T.; Shinoda, A.A.; De Souza Araujo, N.V.; De Oliveira, R.; Nascimento, V.E. A dataset for evaluating intrusion detection systems in IEEE 802.11 wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Colombian Conference on Communications and Computing (COLCOM), Bogota, Colombia, 4–6 June 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrashdi, I.; Alqazzaz, A.; Aloufi, E.; Alharthi, R.; Zohdy, M.; Ming, H. AD-IoT: Anomaly detection of IoT cyberattacks in smart city using machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 9th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference, CCWC 2019, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 7–9 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.T.; Liu, J.C.; Kristiani, E.; Liu, M.L.; You, I.; Pau, G. NetFlow Monitoring and Cyberattack Detection Using Deep Learning with Ceph. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 7842–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Der Chou, L.; Tseng, C.W.; Lai, M.S.; Chen, W.Y.; Chen, K.C.; Yen, C.K.; Ou, T.F.; Tsai, W.H.; Chiu, Y.H. Classification of Malicious Traffic Using TensorFlow Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Korea, 17–19 October 2018; pp. 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, V.; Choraś, M.; Pawlicki, M.; Kozik, R. A deep learning ensemble for network anomaly and cyber-attack detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasevicius, R.; Venckauskas, A.; Grigaliunas, S.; Toldinas, J.; Morkevicius, N.; Aleliunas, T.; Smuikys, P. Litnet-2020: An annotated real-world network flow dataset for network intrusion detection. Electronics 2020, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overview—EvalAI. Available online: https://eval.ai/web/challenges/challenge-page/526/overview (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Sun, R.; Yang, B.; Peng, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Jing, S. Traffic classification using probabilistic neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2010 Sixth International Conference on Natural Computation, Yantai, China, 10–12 August 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, K.; Cheng, A.; Chew, H.G.; Lim, C.C. Deep learning for classifying malicious network traffic. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2018, 11154 LNAI, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liang, G.; Li, B.; Wen, G.; Gao, T. A deep-learning- and reinforcement-learning-based system for encrypted network malicious traffic detection. Electron. Lett. 2021, 57, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ray, S.; Subramanyan, P.; Malik, S. Malware detection using machine learning based analysis of virtual memory access patterns. In Proceedings of the Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Lausanne, Switzerland, 27–31 March; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- De Lucia, M.J.; Cotton, C. Detection of Encrypted Malicious Network Traffic using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 2019—2019 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), Norfolk, VA, USA, 12–14 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, S. Malware Capture Facility Project. Available online: https://stratosphereips.org (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- PcapPlusPlus—A multiplatform C++ library for capturing, parsing and crafting of network packets. Available online: https://pcapplusplus.github.io/ (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- Shafiq, M.; Yu, X.; Bashir, A.K.; Chaudhry, H.N.; Wang, D. A machine learning approach for feature selection traffic classification using security analysis. J. Supercomput. 2018, 74, 4867–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Curran, K.; Lunney, T. Detection of Virtual Private Network Traffic Using Machine Learning. Int. J. Wirel. Netw. Broadband Technol. 2020, 9, 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Tang, M. Auto Malicious Websites Classification Based on Naive Bayes Classifier. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Aided Education (ICISCAE), Dalian, China, 27–29 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mamun, M.S.I.; Rathore, M.A.; Lashkari, A.H.; Stakhanova, N.; Ghorbani, A.A. Detecting Malicious URLs Using Lexical Analysis. In Formal Methods in Outer Space; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 9955, pp. 467–482. [Google Scholar]
- Ongun, T.; Sakharaov, T.; Boboila, S.; Oprea, A.; Eliassi-Rad, T. On Designing Machine Learning Models for Malicious Network Traffic Classification. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.04846. [Google Scholar]
- Alshammari, A.; Aldribi, A. Apply machine learning techniques to detect malicious network traffic in cloud computing. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldribi, A.; Traoré, I.; Moa, B.; Nwamuo, O. Hypervisor-based cloud intrusion detection through online multivariate statistical change tracking. Comput. Secur. 2020, 88, 101646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, K.; Kumar, R.; Mohanty, D.; Bera, P. Robust Adaptive Cloud Intrusion Detection System Using Advanced Deep Reinforcement Learning; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12586, ISBN 9783030666255. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, M.; Hu, J.; Slay, J. Evaluating host-based anomaly detection systems: Application of the one-class SVM algorithm to ADFA-LD. In Proceedings of the 2014 11th International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD), Xiamen, China, 19–21 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Creech, G.; Hu, J. Generation of a new IDS test dataset: Time to retire the KDD collection. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Shanghai, China, 7–10 April 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhoenshoven, F.; Napoles, G.; Falcon, R.; Vanhoof, K.; Koppen, M. Detecting malicious URLs using machine learning techniques. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Athens, Greece, 6–9 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Saul, L.K.; Savage, S.; Voelker, G.M. Identifying suspicious URLs: An application of large-scale online learning. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–18 June 2009; p. 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, G.; Tian, S.; Pei, X. Malicious URL detection based on a parallel neural joint model. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 9464–9472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Mahmoud, Q.H. A Scheme for Generating a Dataset for Anomalous Activity Detection in IoT Networks. In Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12109, pp. 508–520. [Google Scholar]
- Maniriho, P.; Niyigaba, E.; Bizimana, Z.; Twiringiyimana, V.; Mahoro, L.J.; Ahmad, T. Anomaly-based Intrusion Detection Approach for IoT Networks Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer Engineering, Network, and Intelligent Multimedia (CENIM), Surabaya, Indonesia, 17–18 November 2020; pp. 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Qaddoura, R.; Al-Zoubi, A.M.; Almomani, I.; Faris, H. A multi-stage classification approach for iot intrusion detection based on clustering with oversampling. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaddoura, R.; Al-Zoubi, A.M.; Faris, H.; Almomani, I. A multi-layer classification approach for intrusion detection in iot networks based on deep learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Roy, P.K. Detecting Malicious DNS over HTTPS Traffic Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Innovation and Intelligence for Informatics, Computing and Technologies (3ICT), Sakheer, Bahrain, 20–21 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Qi, X.; Liu, J.; Han, H. Design and implementation of traditional DNS protocol. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Technology, Electronics and Communication (ICCTEC), Dalian, China, 19–21 December 2017; pp. 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub—Ahlashkari/DoHLyzer: DoHlyzer Is a DNS over HTTPS (DoH) Traffic Flow Generator and Analyzer for Anomaly Detection and Characterization. Available online: https://github.com/ahlashkari/DoHlyzer (accessed on 9 October 2021).
- Al-Qatf, M.; Lasheng, Y.; Al-Habib, M.; Al-Sabahi, K. Deep Learning Approach Combining Sparse Autoencoder with SVM for Network Intrusion Detection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 52843–52856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyaz, Q.; Sun, W.; Javaid, A.Y.; Alam, M. A deep learning approach for network intrusion detection system. EAI Int. Conf. Bio-inspired Inf. Commun. Technol. 2016, 3, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Ruan, F.; Yin, L.; Chen, X.; Zhai, L.; Liu, F. A Deep Learning Approach for Network Intrusion Detection Based on NSL-KDD Dataset. In Proceedings of 2019 IEEE 13th International Conference on Anti-counterfeiting, Security, and Identification (ASID), Xiamen, China, 25–27 October 2019; pp. 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Guo, H. LuNet: A Deep Neural Network for Network Intrusion Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Xiamen, China, 6–9 December 2019; pp. 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Mehedi Hasan, M.; Pal, B.; Mijanur Rahman Howlader, M. A Neural Network Based Approach To Network Intrusion Detection And Analyzing Different Backpropagation Algorithm Training Approaches. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Telecommunication Engineering, Cox’s Bazar, Banglades, 7–9 February 2019; 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippmann, R.P.; Fried, D.J.; Graf, I.; Haines, J.W.; Kendall, K.R.; McClung, D.; Weber, D.; Webster, S.E.; Wyschogrod, D.; Cunningham, R.K.; et al. Evaluating intrusion detection systems: The 1998 DARPA off-line intrusion detection evaluation. In Proceedings of the DARPA Information Survivability Conference and Exposition. DISCEX’00, Hilton Head, SC, USA, 25–27 January 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- S, D.K.; B, R.B.; Professor, A. An Artificial Neural Network based Intrusion Detection System and Classification of Attacks. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2013, 3, 1959–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Abuadlla, Y.; Kvascev, G.; Gajin, S.; Jovanovic, Z. Flow-based anomaly intrusion detection system using two neural network stages. Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst. 2014, 11, 601–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrawashdeh, K.; Purdy, C. Toward an online anomaly intrusion detection system based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2016 15th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Anaheim, CA, USA, 18–20 December 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraj Al-Janabi, S.T.; Saeed, H.A. A neural network based anomaly intrusion detection system. In Proceedings of the 2011 Developments in E-systems Engineering, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 6–8 December 2011; pp. 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belavagi, M.C.; Muniyal, B. Performance Evaluation of Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms for Intrusion Detection. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 89, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almseidin, M.; Alzubi, M.; Kovacs, S.; Alkasassbeh, M. Evaluation of machine learning algorithms for intrusion detection system. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Intelligent Systems and Informatics (SISY), Subotica, Serbia, 14–16 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, S.; Bhowal, A. Comparative analysis of machine learning algorithms along with classifiers for network intrusion detection. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Smart Technologies and Management for Computing, Communication, Controls, Energy and Materials (ICSTM), Avadi, India, 6–8 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sumaiya Thaseen, I.; Poorva, B.; Ushasree, P.S. Network Intrusion Detection using Machine Learning Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Emerging Trends in Information Technology and Engineering (ic-ETITE), Vellore, India, 24–25 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Churcher, A.; Ullah, R.; Ahmad, J.; Ur Rehman, S.; Masood, F.; Gogate, M.; Alqahtani, F.; Nour, B.; Buchanan, W.J. An experimental analysis of attack classification using machine learning in IoT networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroniotis, N.; Moustafa, N.; Sitnikova, E.; Turnbull, B. Towards the development of realistic botnet dataset in the Internet of Things for network forensic analytics: Bot-IoT dataset. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 100, 779–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halimaa, A.A.; Sundarakantham, K. Machine learning based intrusion detection system. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI), Tirunelveli, India, 23–25 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanem, K.; Aparicio-Navarro, F.J.; Kyriakopoulos, K.G.; Lambotharan, S.; Chambers, J.A. Support Vector Machine for Network Intrusion and Cyber-Attack Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 Sensor Signal Processing for Defence Conference (SSPD), London, UK, 6–7 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, T.; Rais, H.B.M. Machine learning algorithms in context of intrusion detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCOINS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 15–17 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Alsubaie, F.; Al-Akhras, M.; Alzahrani, H.A. Using Machine Learning for Intrusion Detection System in Wireless Body Area Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 First International Conference of Smart Systems and Emerging Technologies (SMARTTECH), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 3–5 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Almomani, I.; Al-Kasasbeh, B.; Al-Akhras, M. WSN-DS: A Dataset for Intrusion Detection Systems in Wireless Sensor Networks. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 4731953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, I.; Basheri, M.; Iqbal, M.J.; Rahim, A. Performance Comparison of Support Vector Machine, Random Forest, and Extreme Learning Machine for Intrusion Detection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 33789–33795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amira, A.S.; Hanafi, S.E.O.; Hassanien, A.E. Comparison of classification techniques applied for network intrusion detection and classification. J. Appl. Log. 2017, 24, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, P.; Borah, B.; Bhattacharyya, D.K. Network anomaly identification using supervised classifier. Informatica 2013, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, P.; Bhuyan, M.H.; Bhattacharyya, D.K.; Kalita, J.K. Packet and Flow Based Network Intrusion Dataset. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2012, 306, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanapongsakorn, N.; Sangkatsanee, P.; Srakaew, S.; Charnsripinyo, C. Classifying network attack types with machine learning approach. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Networked Computing, INC2011, Gumi, Korea, 26–28 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, M.; Wang, J.; Chen, B. Flexible Machine Learning-Based Cyberattack Detection Using Spatiotemporal Patterns for Distribution Systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 1805–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Viinikainen, A.; Hamalainen, T. Evaluation of ensemble machine learning methods in mobile threat detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th International Conference for Internet Technology and Secured Transactions (ICITST), Cambridge, UK, 11–14 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tahir, H.M.; Hasan, W.; Said, A.; Zakar, N.H.; Katuk, N.; Kabir, N.F.; Omar, M.H.; Yahya, N.I. Hybrid Machine Learning Technique for Intrusion Detection System. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computing and Informatics (ICOCI) 2015, Istanbul, Turkey, 11–13 August 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.K.; Pandey, P.; Tiwari, S.K.; Sisodia, M.S. An improved network intrusion detection technique based on k-means clustering via Naïve bayes classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE-International Conference On Advances In Engineering, Science And Management (ICAESM-2012), Nagapattinam, India, 30–31 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lehnert, K.; Friedrich, E. Machine Learning Classification of Malicious Network Traffic. 2012. Available online: http://cs229.stanford.edu/proj2008/LehnertFriedrich-MachineLearningClassificationOfMaliciousNetworkTraffic.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Mohammad, R.M.A.; Alsmadi, M.K. Intrusion detection using Highest Wins feature selection algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 9805–9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.; Lee, B.; Fallon, S.; Jacob, P. Host Based Intrusion Detection System with Combined CNN/RNN Model. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 11329, pp. 149–158. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, K.K.; Hoang, D.T.; Niyato, D.; Wang, P.; Nguyen, D.; Dutkiewicz, E. Cyberattack detection in mobile cloud computing: A deep learning approach. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Netw. Conf. WCNC 2018, 2018, 8376973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tama, B.A.; Comuzzi, M.; Rhee, K.H. TSE-IDS: A Two-Stage Classifier Ensemble for Intelligent Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection System. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 94497–94507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, E.; Long, J.; Liu, Q.; Cui, J.; Chen, W. TR-IDS: Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection through Text-Convolutional Neural Network and Random Forest. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2018, 2018, 4943509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nisioti, A.; Mylonas, A.; Yoo, P.D.; Katos, V. From intrusion detection to attacker attribution: A comprehensive survey of unsupervised methods. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 3369–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.; McGrew, D. Machine learning for encrypted malware traffic classification: Accounting for noisy labels and non-stationarity. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Halifax, NS, Canada, 13–17 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, Z. Non-iterative and Fast Deep Learning: Multilayer Extreme Learning Machines. J. Franklin Inst. 2020, 357, 8925–8955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Saul, L.K.; Savage, S.; Voelker, G.M. Beyond blacklists: Learning to detect malicious web sites from suspicious URLs. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Paris, France, 28 June–1 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Find Open Datasets and Machine Learning Projects | Kaggle. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- UCI Machine Learning Repository, Center for Machine Learning and Intelligent Systems. Available online: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/index.php (accessed on 19 October 2021).

| Attack Name | Description | Attack by (Packets, Tools, etc.) |
|---|---|---|
| Active Attacks | ||
| Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks | ||
| Jamming Attack | By using the channel that they are communicating on, it prohibits other nodes from accessing it to connect. | Radio frequency noise. |
| Flooding | A DoS attack in which a server receives many connection requests but does not reply to complete the handshake. (ICMP Flood, SYN Flood, HTTP Flood). | Unbound number of requests without acknowledgment of packet after receiving it. |
| Smurf Attack | A network layer DDoS attack caused due to the network tools misconfiguration. | Source IP fooling victim IP. |
| Teardrop Attack | A DoS attack that bombards a network with many Internet Protocol (IP) data fragments, then the network is unable to recombine the fragments back into their original packets. | Sending fragmented packets to the target machine. |
| Man in the Middle Attacks | ||
| Ransomware | A form of malware that infiltrates and encrypts important files and systems, preventing a person from accessing their own data. | B0r0nt0k (encryption ransomware), Mado (malicious program) |
| Session Hijacking | To obtain unauthorized access to the Web Server, the Session Hijacking attack disrupts the session token by stealing or guessing a valid session token (e.g., predictable session token). | Malicious JavaScript Codes, XSS, Session Sniffing. |
| Passive Attacks | ||
| Active Reconnaissance | An intruder is engaged in targeting the system to acquire information about vulnerabilities (e.g., port scanning). | Nmap, Metasploit. |
| Passive Reconnaissance | Gathering information about computers and networks without actively engaging with them (e.g., eavesdropping, OS fingerprinting). | Wireshark, Shodan. |
| Traffic Analysis | A method to gather and monitor wireless frames, packets, or messages to drive information for communication patterns. | Sniffing tools. |
| War Driving | Mapping the wireless access points with wireless networks with vulnerabilities in moving cars. | iStumbler, Global Positioning System (GPS), antenna, Wifiphisher. |
| Bitcoin Attack | ||
| Zero Access | An attack that has an unknown pattern or aims to exploit a potentially serious software security vulnerability that the developer or security personnel are not aware of. | Undiscovered vulnerabilities (hardest to detect). |
| Account Attacks | ||
| Credential Stuffing | A kind of cyber-attack in which attackers break into a system using a list of compromised user credentials. (e.g., dictionary attack). | Bots for automation, fake IP addresses. |
| Account Takeover | Account Takeover is like identity theft where a criminal gets unauthorized access to another person’s account (e.g., phishing, call center fraud). | Obtaining compromised credentials. |
| Account Lockout | An attacker who does not have access to genuine website users’ credentials yet nevertheless does harm to them by taking advantage of security mechanisms (e.g., brute force attack). | Locking a huge number of user accounts. |
| Security Breaches | ||
| Vulnerability Scanning | A continuous automated process of finding security flaws in websites on a network to exploit threaten and attack those websites. | Bots that look for security issues and match them to known vulnerabilities in a database. |
| API Abuse | API Abuse is defined as unauthorized or unlawful access to a server’s API via mobile or desktop applications. | Stealing application codes for valuable intellectual property. |
| Authors | Year | Problem Domain | Dataset | Techniques | Results (Evaluation Metrics) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Churcher et al. [128] | 2021 | IDS | Bot-IoT | KNN, SVM, DT, NB, RF, LR, ANN | Binary class: Accuracy (RF-99%) Multi-class: Accuracy (KNN-99%) |
| Yang et al. [89] | 2021 | Malicious Traffic | CTU-13 | ResNet + DQN + DCGAN | Accuracy-99.94% |
| Tuor et al. [10] | 2021 | Insider Threat | CERT v6.2 | SVM, isolation forest, DNN, RNN | Recall (DNN, RNN, isolation forest-100%) |
| Marin et al. [62] | 2021 | Malware Attack | USTCTFC2016 | DeepMAL-using CNN layers | Accuracy (Rbot-99.9%, Neris-63.5%, Virut-54.7%) |
| Ahuja et al. [24] | 2021 | DDoS | Private Dataset | CNN, RNN, LSTM, CNN-LSTM, SVC-SOM, SAE-MLP | Accuracy (SAE-MLP-99.75%) |
| Yuan et al. [106] | 2021 | Malicious Traffic | Private Dataset | Neural Network, RNN | Accuracy (CapsNet, IndRNN = 99.78%) |
| Alshammari et al. [99] | 2021 | Malicious Traffic | ISOT CID | DT, KNN, RF, NB, SVM, NNet | Cross val: Accuracy (RF, DT, KNN-100%) Spit val: Accuracy (RF, DT-100%) |
| Mohammad and Alsmadi [145] | 2021 | IDS | NSL-KDD10 UCI benchmark datasets | NB and C4.5 using HW | Reduced features give similar results Accuracy (C4.5-93.90%) |
| Qaddoura et al. [109] | 2021 | Common IoT attacks | IoT 20 | SLFN | SLFN + SVM-SMOTE: ratio-0.9, k value-3 for k-means++ |
| Qaddoura et al. [110] | 2021 | Common IoT attacks | IoT 20 | LSTM, SLFN | G-mean (LSTM + SLFN-78%) |
| Maniriho et al. [108] | 2021 | Common IoT attacks | IoT 20 | RF | DoS: Accuracy-99.95% MITM: Accuracy-99.9761% Scan: Accuracy-99.96% |
| Butnaru et al. [51] | 2021 | Phishing Attacks | Public Dataset from Kaggle & PhishTank | RF, MLP, SVM, NB, DT | Accuracy (RF-99.29%) |
| Lin et al. [50] | 2021 | Phishing Attacks | Private Dataset | Neural Network (Phishpedia) | Accuracy (Phishpedia-99.2%) |
| Rehman et al. [42] | 2021 | DDoS | CICDDoS2019 | GRU, RNN, NB, SMO | Accuracy (GRU-99.94%) |
| Wang et al. [96] | 2020 | Malicious Traffic | ISCX 2016 | NB | Accuracy (NB-90%) |
| Miller et al. [95] | 2020 | Malicious Traffic | Wireshark Network Captures | Neural Network | Accuracy (NNet-93.71%) |
| Thaseen et al. [127] | 2020 | IDS | Wireshark Network Captures | NB, SVM, RF, KNN | Accuracy (RF-99.81%) |
| Alam et al. [43] | 2020 | Phishing Attacks | Phishing dataset from Kaggle | RF, DT | Accuracy (RF-97%) |
| Barut et al. [60] | 2020 | Malware Traffic | Dataset from Stratosphere IPS, CICIDS2017 | NB, C4.5, DT, RF, SVM, AdaBoost | Accuracy, DR (RF-99.996%), FAR (RF-2.97%) |
| Pande et al. [28] | 2020 | DDoS | NSL-KDD | RF, SVM, Clustering, Neural Networks | Accuracy (RF-99.76%) |
| Cui et al. [140] | 2020 | IDS | Network Captures | BC | TPR (BC-98.75%) |
| Alsubaie et al. [133] | 2020 | IDS | WSN-DS | J.48 form of DT, ANN | Accuracy (J.48-99.66%) |
| Dutta et al. [84] | 2020 | Malicious Traffic | IoT-23, LITNET-2020, and NetML-2020 | ensemble of DNN, LSTM, DSAE | Accuracy-99.7% |
| Al-Haija et al. [74] | 2020 | Common IoT attacks | NSL-KDD | CNN | Binary class: Accuracy-99.3% Multiclass: Accuracy-98.2% |
| Khan et al. [75] | 2020 | Common IoT attacks | NSL-KDD | ELM | Accuracy-93.91% |
| Elsayed et al. [21] | 2020 | DDoS | CICDDoS2019 | AE with RNN | Accuracy-99% |
| Yuan et al. [12] | 2020 | Insider Threat | CERT v4.2 | LSTM + CNN | AUC-0.9449 |
| Ahmed et al. [58] | 2020 | Zero-day attacks | CTU-13 | ANN | Accuracy (ANN-99.6%) |
| Doriguzzi-Corin et al. [23] | 2020 | DDoS | ISCX2012, CICIDS2017, CICIDS2018, UNB201X | CNN | CSECIC2018: Accuracy-98.88% ISCX2012: Accuracy-99.87% CIC2017: Accuracy-99.67% UNB201X: Accuracy-99.46% |
| Yang et al. [82] | 2020 | Malicious Traffic | Network Captures | RNN | Accuracy (RNN-98%) |
| Ramos et al. [71] | 2020 | Botnet Attacks | ISOT-HTTP, CSE-CICIDS2018 | RF, DT, SVM, NB, KNN | CIC-IDS2018: Accuracy (RF, DT-99.99%) ISOT-HTTP: Accuracy (DT-99.90%) |
| Sethi et al. [101] | 2020 | Malicious Traffic | ISOT CID, NSL-KDD | DDQN | ISOT CID: Accuracy-96.87% NSL-KDD: Accuracy-83.40% |
| Singh et al. [111] | 2020 | Malicious DoH Traffic (at DNS level) | CIRA-CIC-DoHBrw-2020 | GB, NB, RF, KNN, LR | Accuracy (RF, GB-100%) |
| Mohammad et al. [35] | 2020 | DDoS | UNSW-NB15, UCI datasets | Improved Rule Induction (IRI) | F Score (IRI-93.90%) |
| Letteri et al. [70] | 2020 | Malware Attack | MTA KDD 19 | MLP using AE optimization or RRw optimization | Accuracy (MLP with RRw opt.-99.60%) |
| Rendall et al. [48] | 2020 | Phishing Attack | Private Dataset | SVM, NB, DT, MLP | Accuracy (MLP, DT-86%) |
| Kim et al. [41] | 2020 | DDoS | KDD-99, CICIDS2018 | CNN, RNN | Accuracy (CNN-99% or more) |
| Alrashdi et al. [81] | 2019 | Common IoT attacks | UNSW-NB15 | RF | Accuracy (ML-99.34%) |
| Chawla et al. [146] | 2019 | IDS | ADFA | RNN, CNN | Time Taken (CNN-GRU 10× faster than LSTM) |
| Halimaa et al. [130] | 2019 | IDS | NSL-KDD | SVM, and NB. | Accuracy (SVM-93.95%) |
| Ongun et al. [98] | 2019 | Malicious Traffic | CTU-13 | LR, RF, and GB | AUC (RF-99%) |
| De Lucia et al. [91] | 2019 | Malicious Traffic | Datasets from Stratosphereips.org | SVM and CNN | F-Score (SVM-0.9997) |
| Filho et al. [32] | 2019 | DDoS | CICDoS2017, CICIDS2017, CICIDS2018 | RF, LR, AdaBoost, Stochastic Gradient Descent, DT, and Perceptron | Accuracy (RF-96%) |
| Radivilova et al. [30] | 2019 | DDoS | SNMP-MIB | RF | Accuracy (RF-0.9) |
| Zhang et al. [116] | 2019 | IDS | NSL-KDD | AE | F-Score-76.47% Recall-79.47% |
| Vijayanand et al. [34] | 2019 | DDoS | CICIDS2017 | SVM, Multi-Layer Deep Networks | Accuracy (MLDN-99.99%) |
| Hu et al. [14] | 2019 | Insider Threat | Private Dataset | CNN | FAR-2.94% FRR-2.28% |
| Ullah et al. [76] | 2019 | Common IoT attacks | Private Dataset | CNN | Accuracy (CNN-97.46%) |
| Baek et al. [18] | 2019 | DDoS | Private Dataset | MLP | Accuracy (MLP-50%) |
| Shi et al. [26] | 2019 | DDoS | CICIDS2017 | LSTM | Accuracy (LSTM-99%) |
| Sabeel et al. [20] | 2019 | DDoS | CICIDS2017 | DNN, LSTM | TPR (DNN-99.8%) TPR (LSTM-99.9%) |
| Wu et al. [117] | 2019 | IDS | UNSW-NB15, NSL-KDD | CNN, RNN | Binary Class: Accuracy-99.24% Multiclass: Accuracy-99.05% |
| Tama et al. [148] | 2019 | IDS | NSL-KDD, UNSW-NB15 | rotation forest + bagging | UNSW-NB15: Accuracy-91.27% NSL-KDD: Accuracy-85.8% |
| Rao et al. [54] | 2019 | Phishing Attacks | Private Dataset | LSTM + SVM | Accuracy (LSTM + SVM-97.3%) |
| Min et al. [149] | 2018 | IDS | ISCX2012 | RF, SVM, NN, CNN | Accuracy (RF-99.13%) |
| Pektas et al. [73] | 2018 | Botnet Attacks | ISOT HTTP, CTU-13 | MLP + LSTM | ISOT: F score-98.8% CTU: F score-99.1% |
| Ahmad et al. [135] | 2018 | IDS | NSL-KDD | SVM, RF, ELM | Accuracy (ELM-99.5%) |
| Shafiq et al. [94] | 2018 | Malicious Traffic | HIT Trace 1 captures NIMS dataset | BayesNet, NB, AdaBoost, Bagging, PART, C4.5, RF, Random Tree, Sequential Minimal Optimization, oneR, Hoeffding | HIT: Accuracy (PART-97.88%) NIMS: Accuracy (RF-100%) |
| Park et al. [64] | 2018 | Malware Traffic | Kyoto 2006+ | RF | F-Score (RF-99%) |
| Chou et al. [83] | 2018 | Malicious Traffic | NSL-KDD | NNET | Accuracy (NNet-97.65%) |
| Nguyen et al. [147] | 2018 | IDS | UNSW-NB15, KDD-99, NSL-KDD | NNET | Accuracy (KDD-99-97.11%) |
| Al-Qatf et al. [114] | 2018 | IDS | NSL-KDD | SVM, STL | Binary: (Accuracy-84.96%) Multiclass (Accuracy-80.48%) |
| Millar et al. [88] | 2018 | Malicious Traffic | UNSW-NB15 | NNET | F-Score (Flow image-94.2%) |
| Wu et al. [67] | 2018 | Malware Traffic | EMBER | DQN, SARSA, Double DQN | Accuracy (DQN-93.5%) |
| Li et al. [49] | 2018 | Phishing Attacks | 50K-PD, 50K-IPD | GBDT + XGBoost + LightGBM | 50K-PD: Accuracy-97.3% 50K-IPD: Accuracy-98.6% |
| Vanhoenshoven et al. [104] | 2017 | Malicious Traffic | Malicious URLs | KNN, RF, SVM, DT, NB, MLP | Accuracy (RF-97%) |
| Kumar et al. [141] | 2017 | IDS | Wireshark Network Captures | ensemble of RF, PART and JRIP | Accuracy-98.2% |
| Anderson et al. [151] | 2017 | Malware Traffic | Captured TLS encrypted sessions | Linear Regression, l1/l2-LR, DT, RF ensemble, SVM, MLP | Accuracy (LR-99.92%) |
| Almseidin et al. [125] | 2017 | IDS | KDD-99 | J.48, RF, Random Tree, Decision Table, NB, Bayes Network, MLP | Accuracy (RF-93.77%) |
| Ghanem et al. [131] | 2017 | IDS | Five datasets gathered from an IEEE 802.11 and a private dataset | SVM | DR, OSR (on all datasets-100%) |
| Xu et al. [90] | 2017 | Malicious Traffic | Network Capture | RF, LR | Kernet: DR(RF-100%) User-level: DR(RF-99%) |
| Tama et al. [78] | 2017 | Common IoT attacks | CIDDS-001, UNSW-NB15, GPRS-WEP, GPRS-WPA2 | DNN | CIDDS-001: Accuracy-94.17% UNSW-NB15: Accuracy-99.99% GPRS-WEP: Accuracy-82.89% GPRS-WPA2: Accuracy-94% |
| Yuan et al. [16] | 2017 | DDoS | ISCX 2012 | RNN | Error Rate (RNN-2.103%) |
| Amira et al. [136] | 2017 | IDS | NSL-KDD | NB, DT, NBTree, BFTree, J.48, RFT, MLP | Accuracy (MLP-98.54%) |
| Niyaz et al. [27] | 2017 | DDoS | Network Capture | SAE | Accuracy (SAE-95.65%) |
| Belavagi et al. [124] | 2016 | IDS | NSL-KDD | LR, SVM, NB, RF | Accuracy-(RF-99%) |
| Mehmood et al. [132] | 2016 | IDS | KDD-99 | SVM, NB, J.48, Decision Table | Accuracy (J.48-–99%) |
| Alrawashdeh et al. [122] | 2016 | IDS | KDD-99 | RBM, DBN, DBN + LR | Accuracy (DBN + LR-97.9%) |
| Robinson et al. [38] | 2016 | DDoS | CAIDA conficker, CAIDA DoS, KDD-99 | NB, RF, MLP, voting, BayesNet, IBK, J.48 | Accuracy (RF-100%) |
| Thabtah et al. [47] | 2016 | Phishing | Datasets from UCI | NNet | Accuracy-93.06% |
| Tahir et al. [142] | 2015 | IDS | NSL-KDD | hybrid of K-means Clustering and SVM | DR-96.26% |
| Choudhury et al. [126] | 2015 | IDS | NSL-KDD | BayesNet, LR, IBK, J.48, PART, JRip, Random Tree, RF, REPTree, boosting, bagging, and blending | Accuracy (RF-91.523%) |
| Niyaz et al. [115] | 2015 | IDS | NSL-KDD | STL with AE | Accuracy (STL-98%) |
| David et al. [66] | 2015 | Malware Attacks | Private Dataset | DBN | Accuracy (DBN-98.6%) |
| Barati et al. [40] | 2015 | DDoS | CAIDA USCD 2007 | GA + MLP | AUC-0.9991 |
| Abuadlla et al. [121] | 2014 | IDS | Network Capture | NNET, RBFN | Accuracy-99.4% |
| Xie et al. [102] | 2014 | Malicious Traffic | ADFA | SVM | Accuracy (70%), FPR (20% when k = 5) |
| Mohammad et al. [44] | 2014 | Phishing Attacks | Private Dataset | ANN | Accuracy (testing set-92.18%) |
| Beaver et al. [57] | 2013 | Zero-day Attacks | KDD-99 | AdaBoost | Accuracy (AdaBoost-94%) |
| Devikrishna et al. [120] | 2013 | IDS | KDD-99 | ANN | Successfully detected and classified attacks |
| Lehnert et al. [144] | 2012 | IDS | KDD-99 | SVM, Clustering, NNET | Error Rate (SVM-2.79%) |
| Sharma et al. [143] | 2012 | IDS | KDD-99 | K-means clustering via NB | DR-99% |
| Gogoi et al. [137] | 2012 | IDS | TUIDS, NSL-KDD, KDD-99 | Clustering | TUIDS Packet level: accuracy = 99.42%. KDD: accuracy = 92.39%. NSL-KDD: accuracy = 98.34% |
| Hasan et al. [118] | 2012 | IDS | DARPA 1998 | NNET | Accuracy (NNet-92%) |
| Wattanapongsakorn et al. [139] | 2011 | IDS | Network Capture | DT, Bayesian, Ripple Rule Back Propagation Neural Network | DR (DT-95.5%) |
| Al-Janabi et al. [123] | 2011 | IDS | KDD-99 | ANN | DR (ANN-91%) |
| Sun et al. [87] | 2010 | Malicious Traffic | Network Capture | SVM, RBFNN, PNN | Accuracy (PNN-88.18%) |
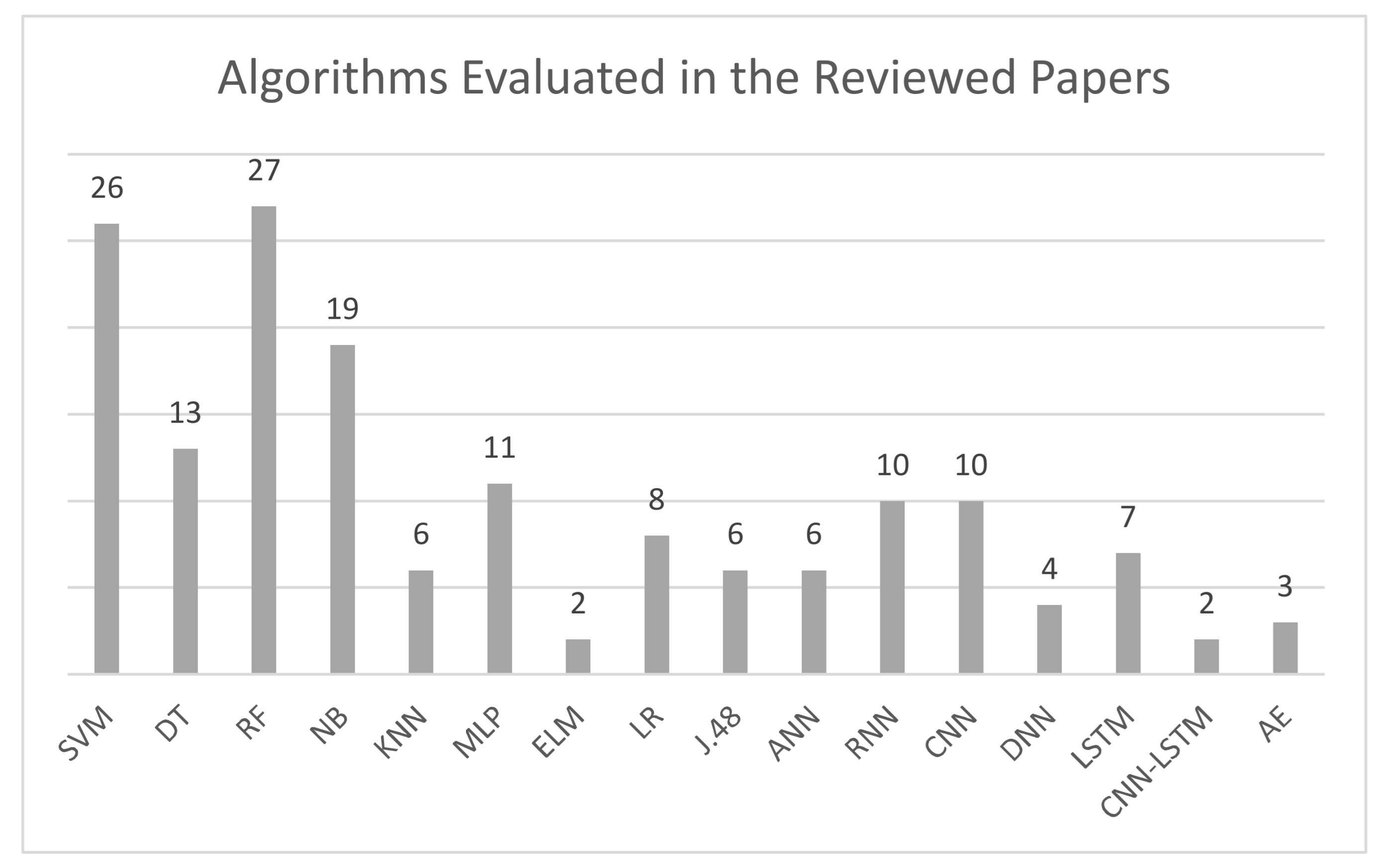
| Algorithm | Papers That Applied It | No. of Articles | Problem Domains | Performance (Highest Accuracy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | [10,28,34,42,48,51,54,60,71,87,91,99,102,104,124,127,128,130,131,132,135,142,144,149,151] | 26 | Insider Threat, DDoS, Malware, Botnet, Malicious Traffic, IDS, Phishing | 93.95% (IDS) |
| DT | [32,43,48,51,60,71,99,104,128,132,136,139,151] | 13 | Insider Threat, DDoS, Phishing, Malware, Botnet, Malicious Traffic, IDS | 100% (Malicious Traffic) |
| RF | [28,30,32,38,43,51,60,64,71,81,90,94,98,99,104,108,111, 124,125,126,127,128,135,136,148,149,151] | 27 | DDoS, Phishing, Malware, Botnet, IoT Network, Malicious Traffic, DNS Level Attack, IDS | 100% (Malicious Traffic, DDoS) |
| NB | [38,42,48,51,60,71,94,99,104,111,124,125,127,128,130, 132,136,143,145] | 19 | DDoS, Malware, Botnet, Malicious Traffic, DNS Level Attack, IDS, Phishing | 90% (Malicious Traffic) |
| KNN | [71,99,104,111,127,128] | 6 | Botnet, Malicious Traffic, DNS Level Attack, IDS | 100% (Malicious Traffic) |
| MLP | [18,34,38,40,48,51,73,104,125,151] | 11 | DDoS, Malware, Botnet, Malicious Traffic, IDS, Phishing | 99.60% (Malware) |
| ELM | [75,135] | 2 | IDS | 99.5% (IDS) |
| LR | [32,90,98,111,124,126,128,151] | 8 | DDoS, Malware, Malicious Traffic, DNS Level Attack, IDS | 99.92% (Malware) |
| J.48 | [38,125,126,132,133,136] | 6 | DDoS, IDS | 99.66% (IDS) |
| ANN | [44,58,120,123,128,133] | 6 | Phishing, Zero-Day, IDS | 99.6% (Zero-Day) |
| RNN | [10,16,21,24,41,42,82,106,117,146] | 10 | Insider Threat, DDoS, Malicious Traffic, IDS | 100% (Insider Threat) |
| CNN | [23,24,41,62,74,76,91,117,146,149] | 10 | Insider Threat, DDoS, Malware, IoT Network, Malicious Traffic, IDS | 99% (DDoS) |
| DNN | [10,20,78,84] | 4 | Insider Threat, DDoS, IoT Network, Malicious Traffic | 99.99% (IoT Network) |
| LSTM | [20,24,26,54,73,84,110] | 7 | DDoS, Botnet, IoT Network, Malicious Traffic, Phishing | 99% (DDoS) |
| CNN-LSTM | [12,24] | 2 | Insider Threat, DDoS | 99.48% (DDoS) |
| AE | [21,115,116] | 3 | DDoS, IDS | 99% (DDoS) |
| Dataset | Articles | Number | Last Time Dataset Used | Publicly Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DARPA-1998 | [118] | 1 | 2012 | [119] |
| KDD-99 | [38,41,57,120,122,123,125,132,137,143,144,147] | 12 | 2018 | [39] |
| NSL-KDD | [28,74,75,83,101,114,115,116,117,124,126,130,135,136,137,142,145,147,148] | 19 | 2021 | [29] |
| UNSW-NB15 | [35,78,81,88,117,147,148] | 7 | 2020 | [36] |
| CICIDS-2017 or 2018 | [20,23,26,32,34,41,60,71] | 8 | 2020 | [17] |
| CTU-13 | [58,73,89,98] | 4 | 2021 | [59] |
| IoTID 20 | [108,109,110] | 3 | 2021 | [107] |
| Kyoto 2006+ | [64] | 1 | 2018 | [65] |
| CERT v6 or v4 | [10,12] | 2 | 2021 | [11,13] |
| SNMP-MIB | [30] | 1 | 2019 | [31] |
| ISCX 2012 or 2016 | [16,23,96,149] | 4 | 2020 | [17,97] |
| ADFA | [102,146] | 2 | 2019 | [103] |
| CAIDA | [38,40] | 2 | 2016 | [37] |
| ISOT CID | [99,101] | 2 | 2021 | [100] |
| ISOT HTTP | [71,73] | 2 | 2020 | [72] |
| Malicious URLs Dataset | [104] | 1 | 2021 | [105] |
| EMBER | [67] | 1 | 2018 | [68] |
| CICDDoS2019 or CICDoS2017 | [21,32,42] | 3 | 2020 | [22,33] |
| USTCTFC2016 | [62] | 1 | 2016 | [63] |
| GPRS WPA2/WEP | [78] | 1 | 2017 | [80] |
| MTA KDD 19 | [70] | 1 | 2020 | [69] |
| LITNET-2020 | [84] | 1 | 2020 | [85] |
| CIRA-CIC-DoHBrw-2020 | [111] | 1 | 2020 | [112] |
| Bot-IoT | [128] | 1 | 2019 | [129] |
| Kaggle Datasets | [43,51] | 2 | 2021 | [52,154] |
| UCI Datasets | [35,47,145] | 3 | 2021 | [155] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljabri, M.; Aljameel, S.S.; Mohammad, R.M.A.; Almotiri, S.H.; Mirza, S.; Anis, F.M.; Aboulnour, M.; Alomari, D.M.; Alhamed, D.H.; Altamimi, H.S. Intelligent Techniques for Detecting Network Attacks: Review and Research Directions. Sensors 2021, 21, 7070. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217070
Aljabri M, Aljameel SS, Mohammad RMA, Almotiri SH, Mirza S, Anis FM, Aboulnour M, Alomari DM, Alhamed DH, Altamimi HS. Intelligent Techniques for Detecting Network Attacks: Review and Research Directions. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7070. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217070
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljabri, Malak, Sumayh S. Aljameel, Rami Mustafa A. Mohammad, Sultan H. Almotiri, Samiha Mirza, Fatima M. Anis, Menna Aboulnour, Dorieh M. Alomari, Dina H. Alhamed, and Hanan S. Altamimi. 2021. "Intelligent Techniques for Detecting Network Attacks: Review and Research Directions" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7070. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217070
APA StyleAljabri, M., Aljameel, S. S., Mohammad, R. M. A., Almotiri, S. H., Mirza, S., Anis, F. M., Aboulnour, M., Alomari, D. M., Alhamed, D. H., & Altamimi, H. S. (2021). Intelligent Techniques for Detecting Network Attacks: Review and Research Directions. Sensors, 21(21), 7070. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217070






