Rapid Detection of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Using Microwave Immunosensor Cavity Resonator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
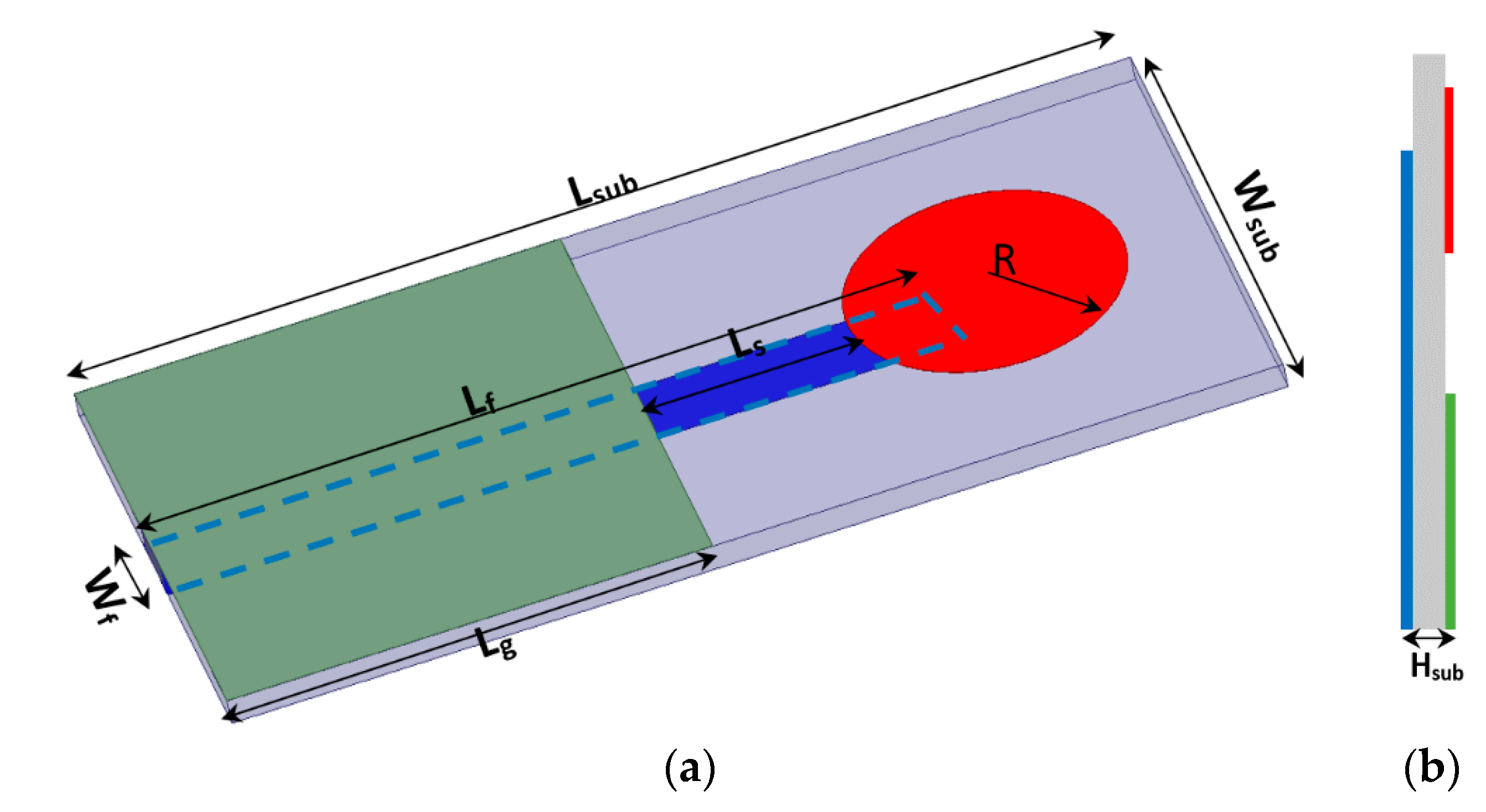
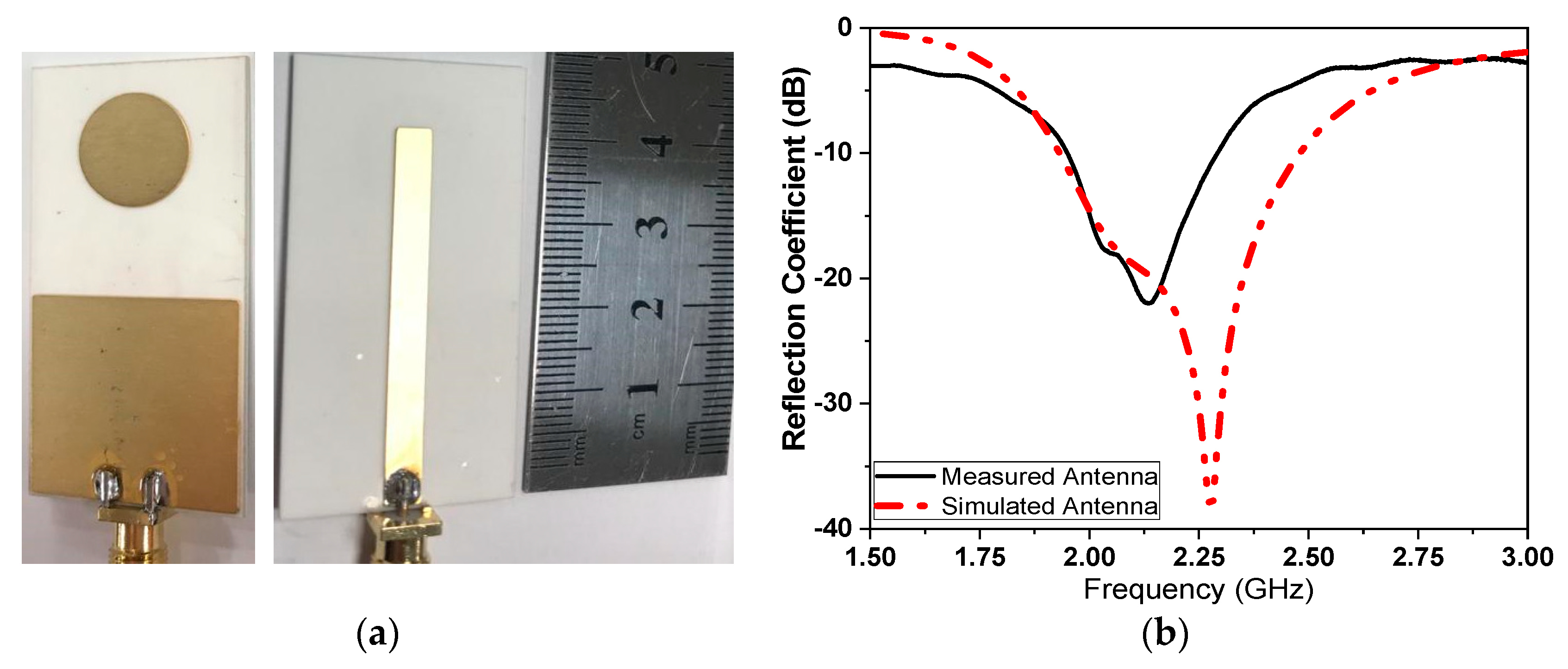
2. Sensor Design and Layouts
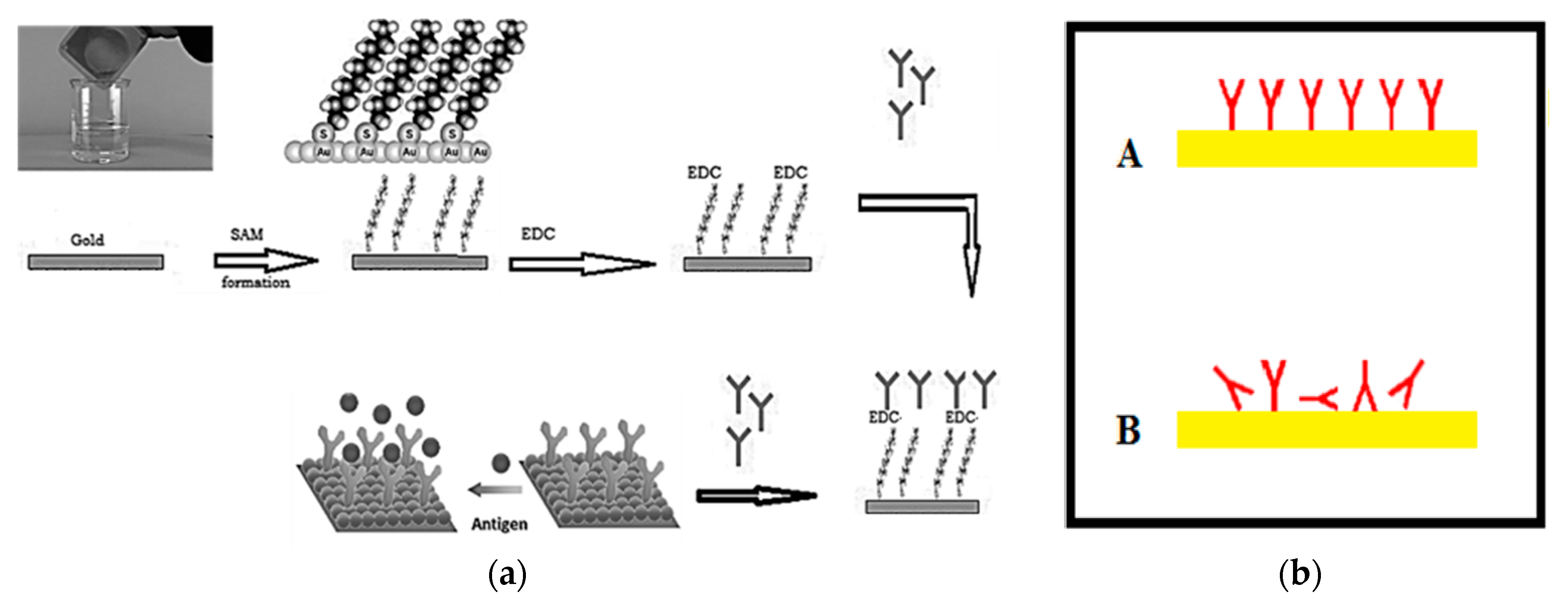
3. Addressable Immobilization of Corona Virus
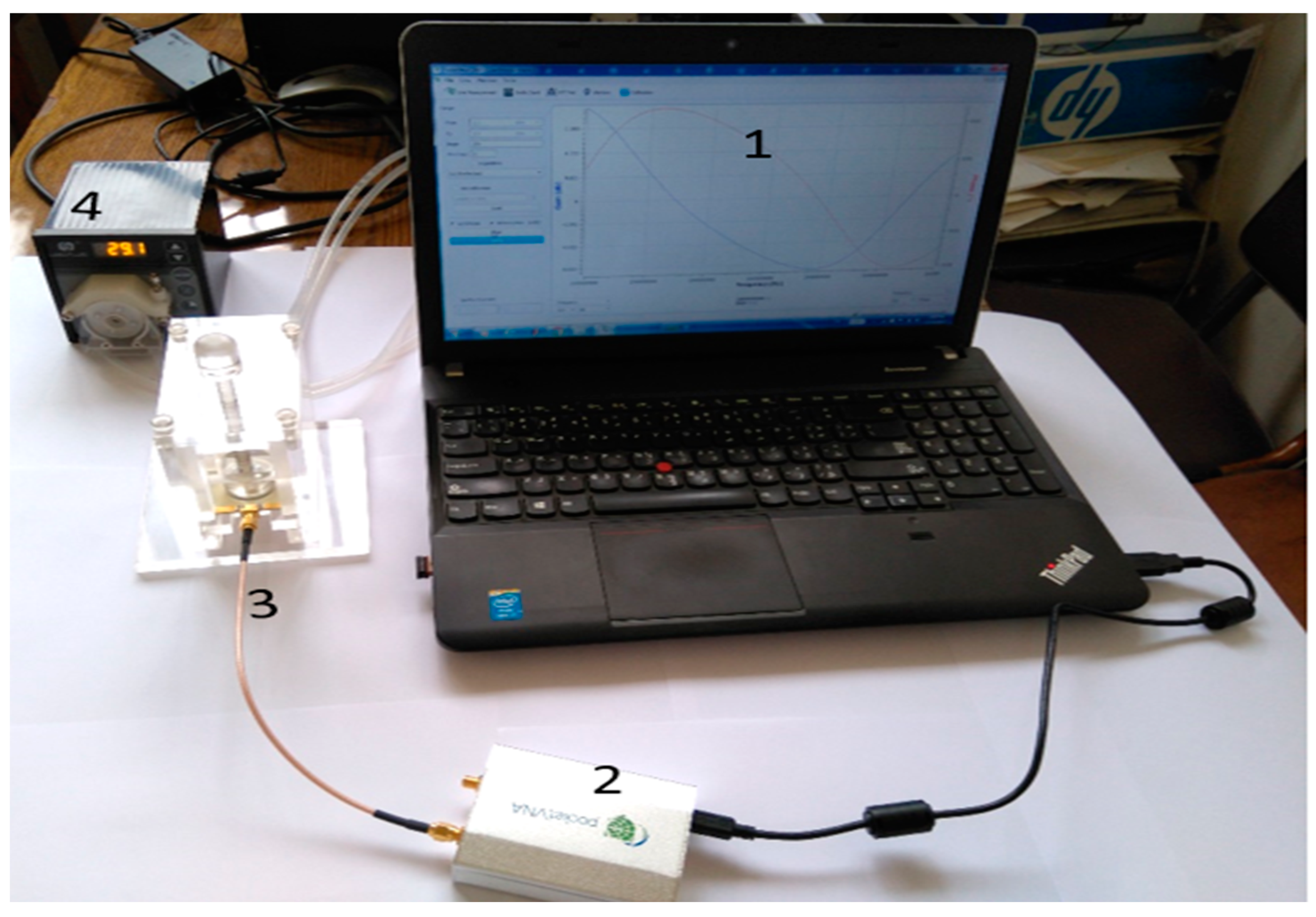
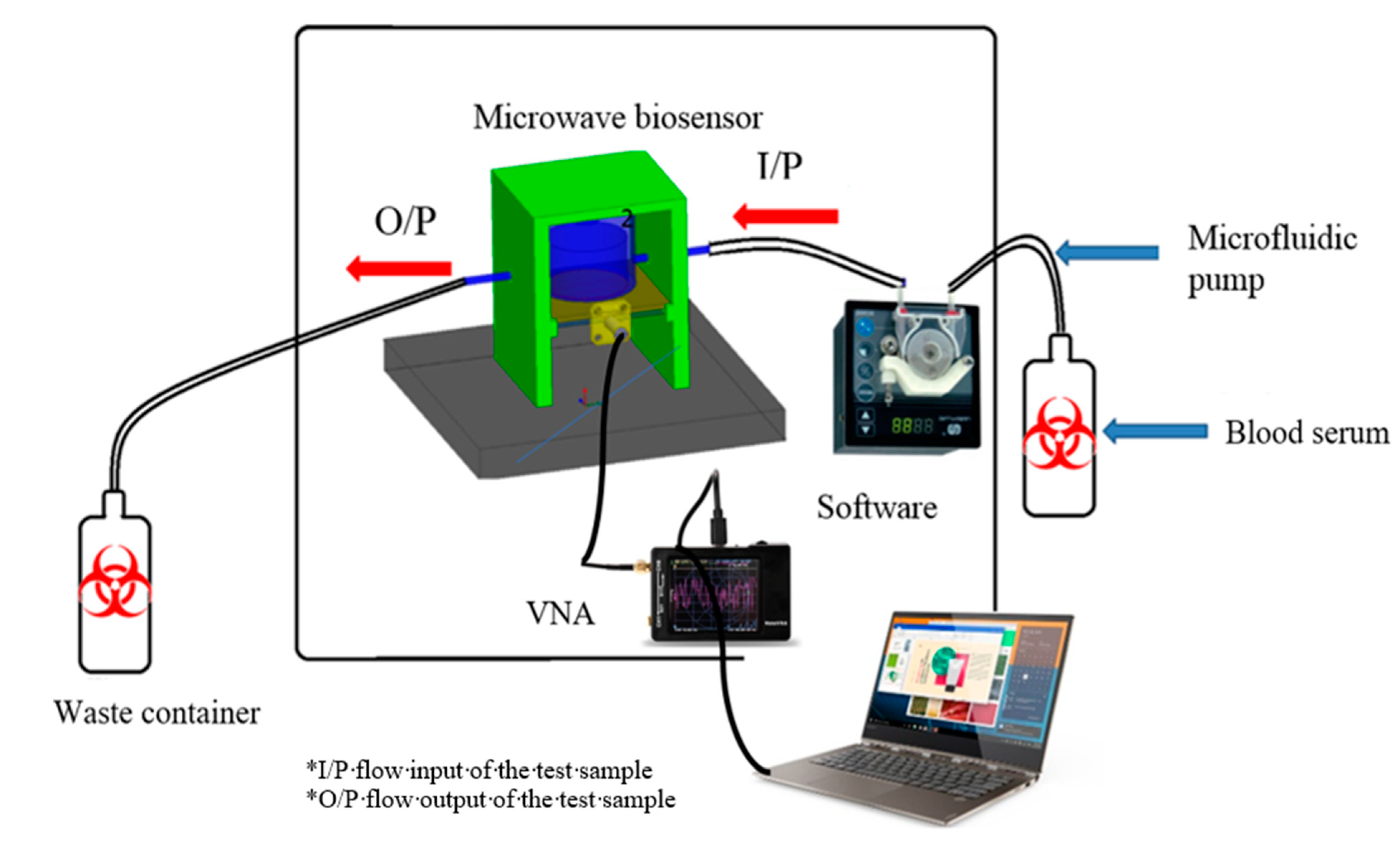
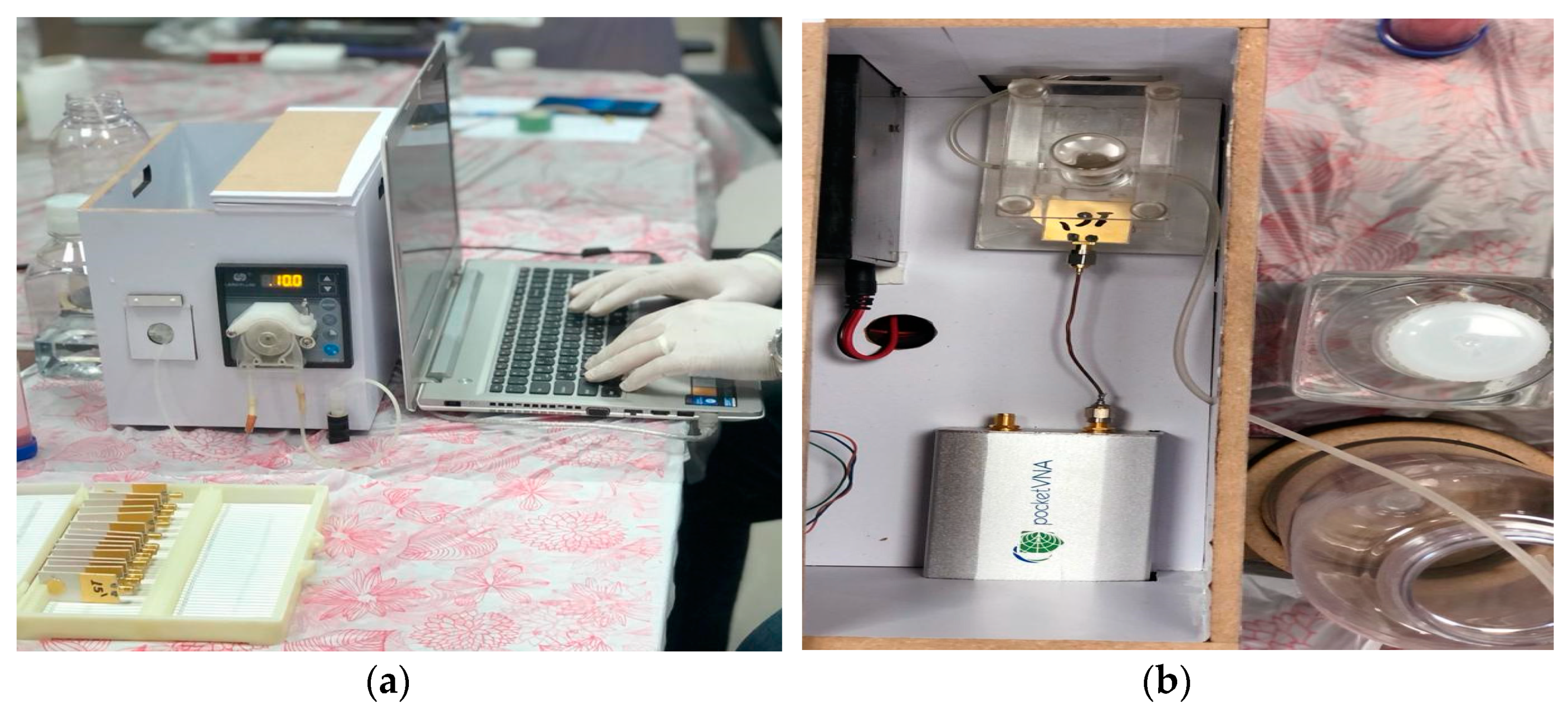
4. System Integration and Assembly
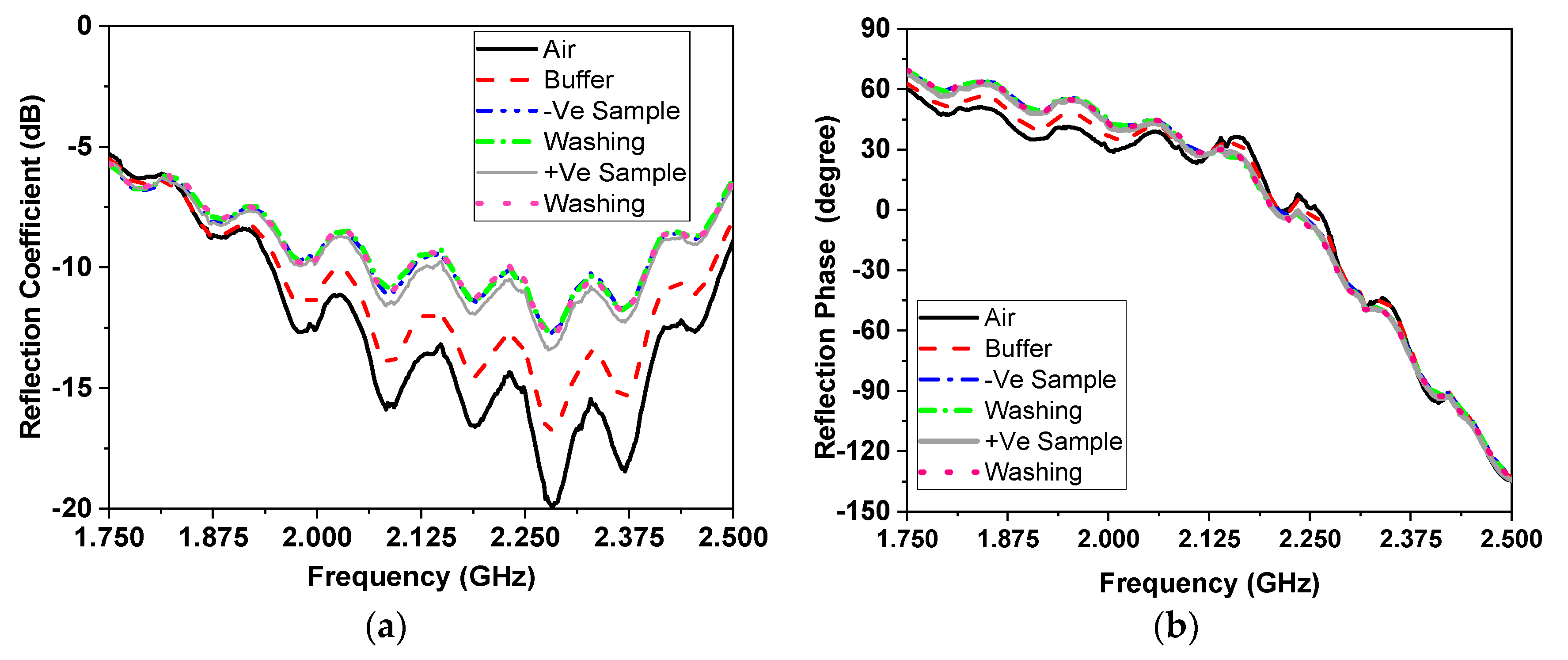
5. Coronavirus Samples Measured Results
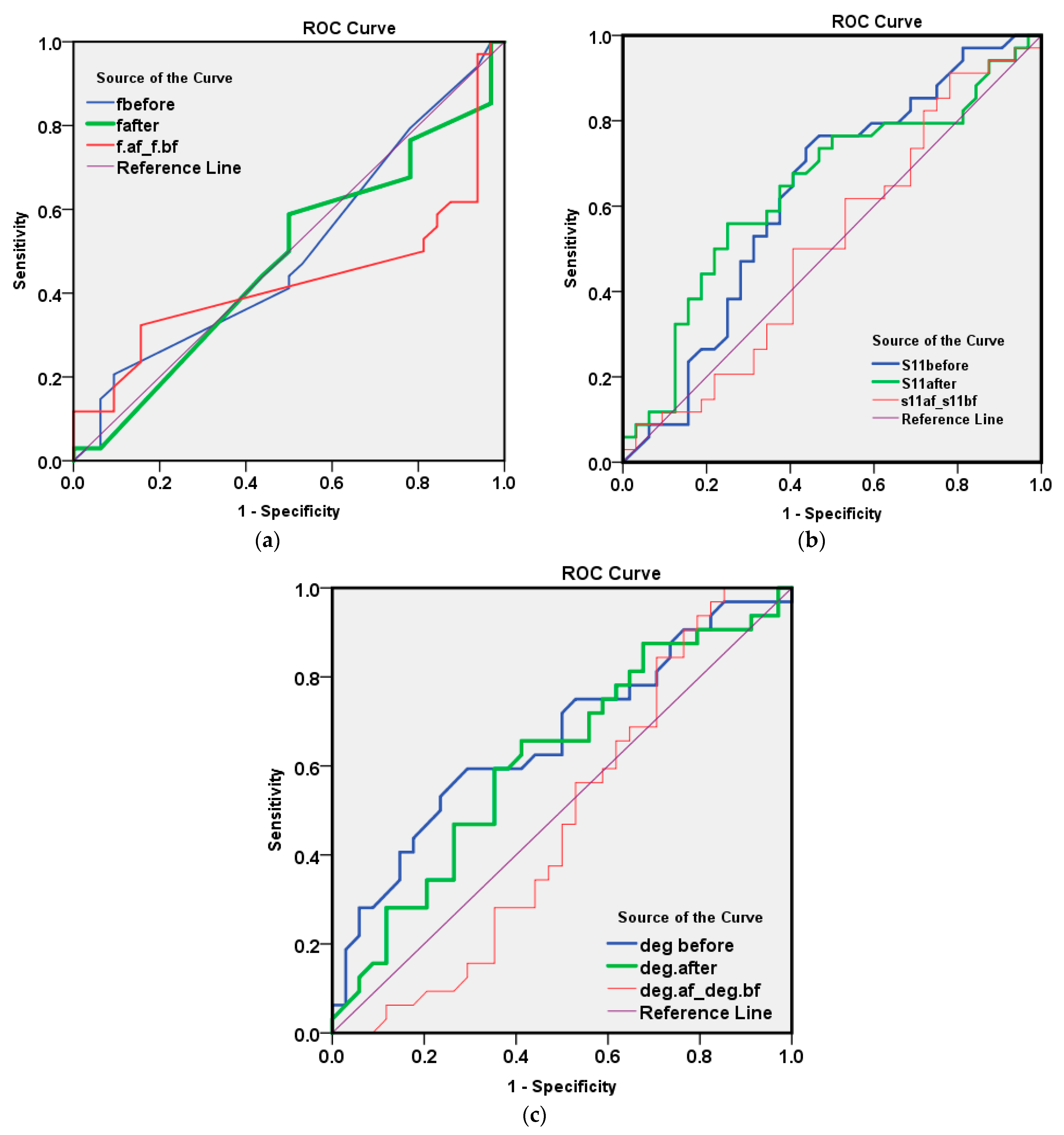
6. Statistical Analysis and Software Packages
- 1-
- Resonance frequency (GHz)
- 2-
- Magnitude of reflection coefficient S11 (dB)
- 3-
- Phase of reflection coefficient S11 (°)
- 1-
- Sensitivity: the probability of the test producing +ve results if the patient is infected
- 2-
- Specificity: the probability of the test producing −ve results if the patient is not infected
- 3-
- Predictive value of positive test: the probability that the patient will have an infection if the test result is positive
- 4-
- Predictive value of negative test: the probability that the patient will not have an infection if the test result is negative
- 5-
- Total accuracy: the combined discriminatory results of the test for both true positive and true negative results
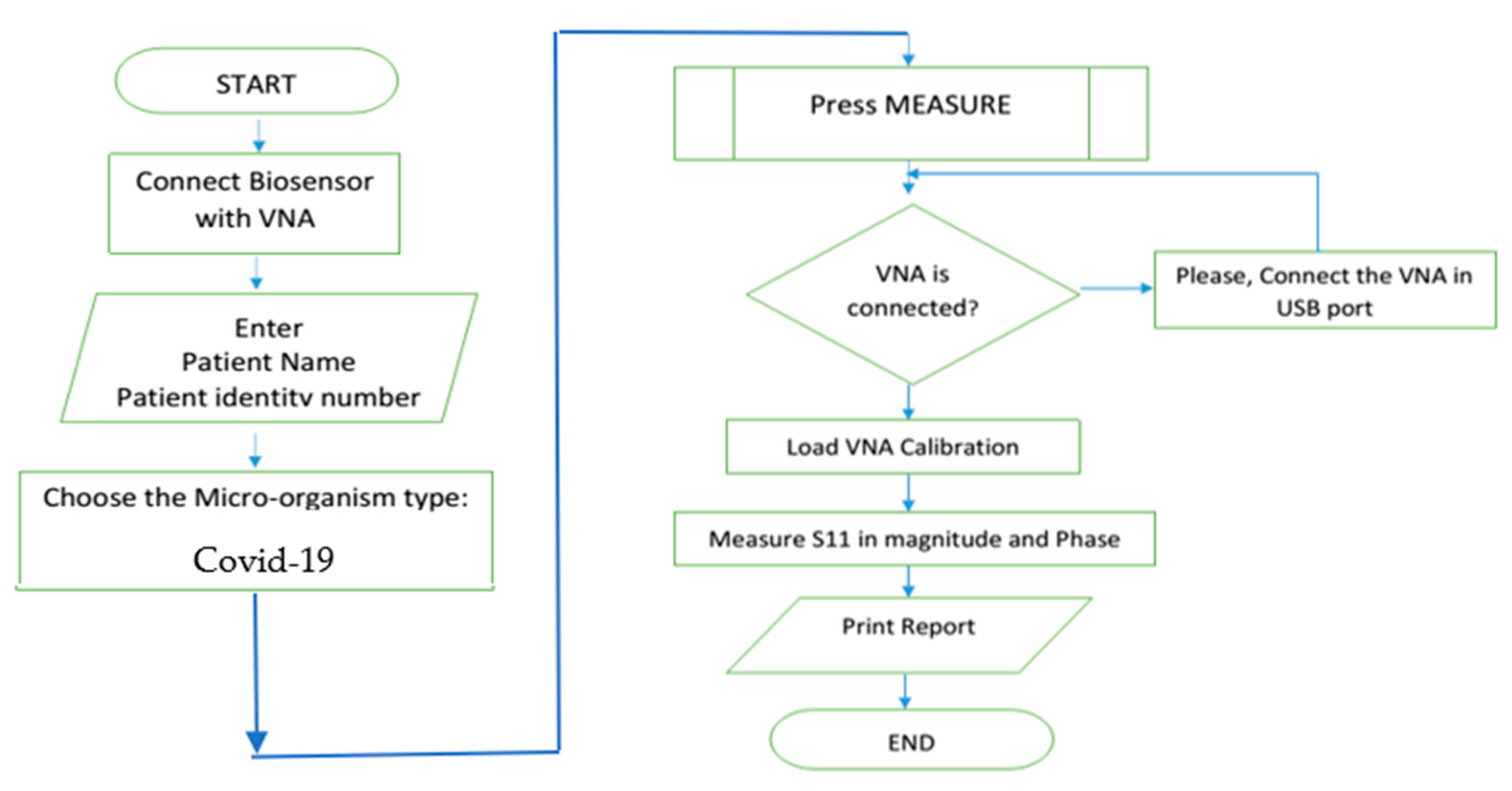
7. Measured Samples and Measurement Methods
7.1. Results of Measured Resonating Frequency
7.2. Results of Measured Reflection Coefficient Amplitude
7.3. Results of Measured of Reflection Coefficient Phase in Degrees
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2021. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Fu, L.W.; Wang, B.Y.; Yuan, T.W.; Chen, X.T.; Ao, Y.L.; Fitzpatrick, T.; Li, P.Y.; Zhou, Y.G.; Lin, Y.F.; Duan, Q.B.; et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.W.; Hu, B.; Zhu, F.F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.B.; Xiang, H.; Cheng, Z.S.; Xiong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Dong, X.; Cao, Y.Y.; Yuan, Y.D.; Yang, Y.B.; Yan, Y.Q.; Akdis, C.A.; Gao, Y.D. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy 2020, 75, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, B.E.; Ong, S.W.X.; Kalimuddin Slow, J.G.; Tan, S.Y.; Loh, J.; Ng, O.T.; Marimuthu, K.; Ang, L.W.; Mak, T.M.; Lau, S.K.; et al. Novel coronavirus outbreak research team, epidemiologic features and clinical course of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Singapore. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, F.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, Z.K.; Cao, L.B.; Wang, C.L.; Wu, J.B.; Du, Q.F. Laboratory testing techniques for SARS-CoV-2. J. South. Med. Univ. 2020, 40, 164–167. [Google Scholar]
- Giovannini, G.; Haick, H.; Garoli, D. Detecting COVID-19 from Breath: A Game Changer for a Big Challenge. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Babka, A.M.; Kearney, B.J.; Radoshitzky, S.R.; Kuhn, J.H.; Zeng, X.K. Molecular detection of SARS-CoV-2 in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimens. JCI Insight 2020, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, D.; Ramadan, S.; Li, Y.; Klein, N. Facile biosensors for rapid detection of COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 170, 112673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abid, S.A.; Muneer, A.A.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.; Sattar, A.A.; Beshbishy, A.M.; Batiha, G.E.-S.; Hetta, H.F. Biosensors as a future diagnostic approach for COVID-19. Life Sci. 2021, 273, 119117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Du, R.H.; Li, B.; Zheng, X.S.; Yang, X.L.; Hu, B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Xiao, G.F.; Yan, B.; Shi, Z.L.; et al. Molecular and serological investigation of 2019-nCoV infected patients: Implication of multiple shedding routes. Emerg. Microb. Infect. 2020, 9, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mobed, A.; Shafigh, E.S. Biosensors promising bio-device for pandemic screening “COVID-19”. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 106094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojsoska, B.; Larsen, S.; Olsen, D.A.; Madsen, J.S.; Brandslund, I.; Alatraktchi, F.A. Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Detection Using Electrochemical Immunosensor. Sensors 2021, 21, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikash, B.C.; Mishra, R.R.; Thatoi, H. Recent biotechnological tools for diagnosis of corona virus disease: A review. Biotechnol. Prog. 2021, 37, e3078. [Google Scholar]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandeil, A.; Gomaa, M.R.; El Taweel, A.; Mostafa, A.; Shehata, M.; Kayed, A.E.; Omnia, K.; Yassmin, M.; Sara, H.; Mina, N.; et al. Common childhood vaccines do not elicit a cross-reactive antibody response against SARS-CoV-2. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Srivastava, N.; Mishra, P.; Malhotra, B.D. Prospects of nanomaterials-enabled biosensors for COVID-19 detection. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsheakh, D.; Ismail, M.; Elsadek, H.; Abdallah, E.; Moghannem, S.A.M.; Elmazny, W.N. Bacterial detection by using micro immunosensing biomedical cavity resonator. In Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), London, UK, 9–13 April 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Acevedo-Osorio, G.; Reyes-Vera, E.; Lobato-Morales, H. Dual-Band Microstrip Resonant Sensor for Dielectric Measurement of Liquid Materials. IEEE Sensors J. 2020, 20, 13371–13378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Nadaraja, A.V.; Luckasavitch, K.; Jain, M.C.; Roberts, D.J.; Zarifi, M.H. A Label-Free, Non-Intrusive, and Rapid Monitoring of Bacterial Growth on Solid Medium Using Microwave Biosensor. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2019, 14, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, M.I.; Da Mota, A.F.; Pepino, V.M.; Carmo, J.P.; Borges, B.H.V. Multi-purpose Microwave Biosensor Based on Signal Encoding Technique and Microfluidics for Improved Sensitivity. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 4571–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.C.; Nadaraja, A.V.; Mohammadi, S.; Vizcaino, B.M.; Zarifi, M.H. Passive Microwave Biosensor for Real-Time Monitoring of Subsurface Bacterial Growth. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2021, 15, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheakh, D.; Elsadek, H.; Abdallah, E.; Atteya, S.; Lmazny, W.N.E. Novel rapid detection of different viruses in blood using microimmuno-sensor. In Proceedings of the 2013 7th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Gothenburg, Sweden, 8–12 April 2013; pp. 1128–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Elsheakh, D.M.; Elsadek, H.A.; Abdallah, E.A.; Atteya, S.; Lmazny, W.N.E. Rapid detection of blood entero-viruses using microstrip antenna bio-sensor. In Proceedings of the 2013 European Microwave Conference, Nuremberg, Germany, 6–10 October 2013; pp. 878–880. [Google Scholar]
- Taha, B.; Al Mashhadany, Y.; Mokhtar, M.H.; Bin Zan, M.D.; Arsad, N. An Analysis Review of Detection Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Based on Biosensor Application. Sensors 2020, 20, 6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, W.; Abbasi, Q.H.; Dashtipour, K.; Ansari, S.; Shah, S.A.; Khalid, A.; Imran, M.A. A Review of the State of the Art in Non-Contact Sensing for COVID-19. Sensors 2020, 20, 5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, A.; Kim, S.-H.; Park, J.Y.; Lim, S. Microfluidic Biosensor Based on Microwave Substrate-Integrated Waveguide Cavity Resonator. J. Sensors 2018, 2018, 1324145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehrotra, P.; Chatterjee, B.; Sen, S. EM-Wave Biosensors: A Review of RF, Microwave, mm-Wave and Optical Sensing. Sensors 2019, 19, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Costa, J.P.D.C.; Bastos, W.B.; Da Costa, P.I.; Zaghete, M.A.; Longo, E.; Carmo, J.P. Portable Laboratory Platform With Electrochemical Biosensors for Immunodiagnostic of Hepatitis C Virus. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 10701–10709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antiochia, R. Nanobiosensors as new diagnostic tools for SARS, MERS and COVID-19: From past to perspectives. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Wang, M.; Ang, I.Y.H.; Lewis, R.F.; Chen, J.I.P.; Gutierrez, R.A.; Gwee, S.X.W.; Chua, P.E.Y.; Yang, Q.; Ng, X.Y.; et al. Potential rapid diagnostics, vaccine and therapeutics for 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV): A systematic review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales-Narváez, E.; Dincer, C. The impact of biosensing in a pandemic outbreak: COVID-19. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 163, 112274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zeng, N.; Wang, N. Sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, associated confidence interval and ROC analysis with practical SAS® implementations. In Proceedings of the NESUG Proceedings: Health Care and Life Sciences, Baltimore, MD, USA, 14–17 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
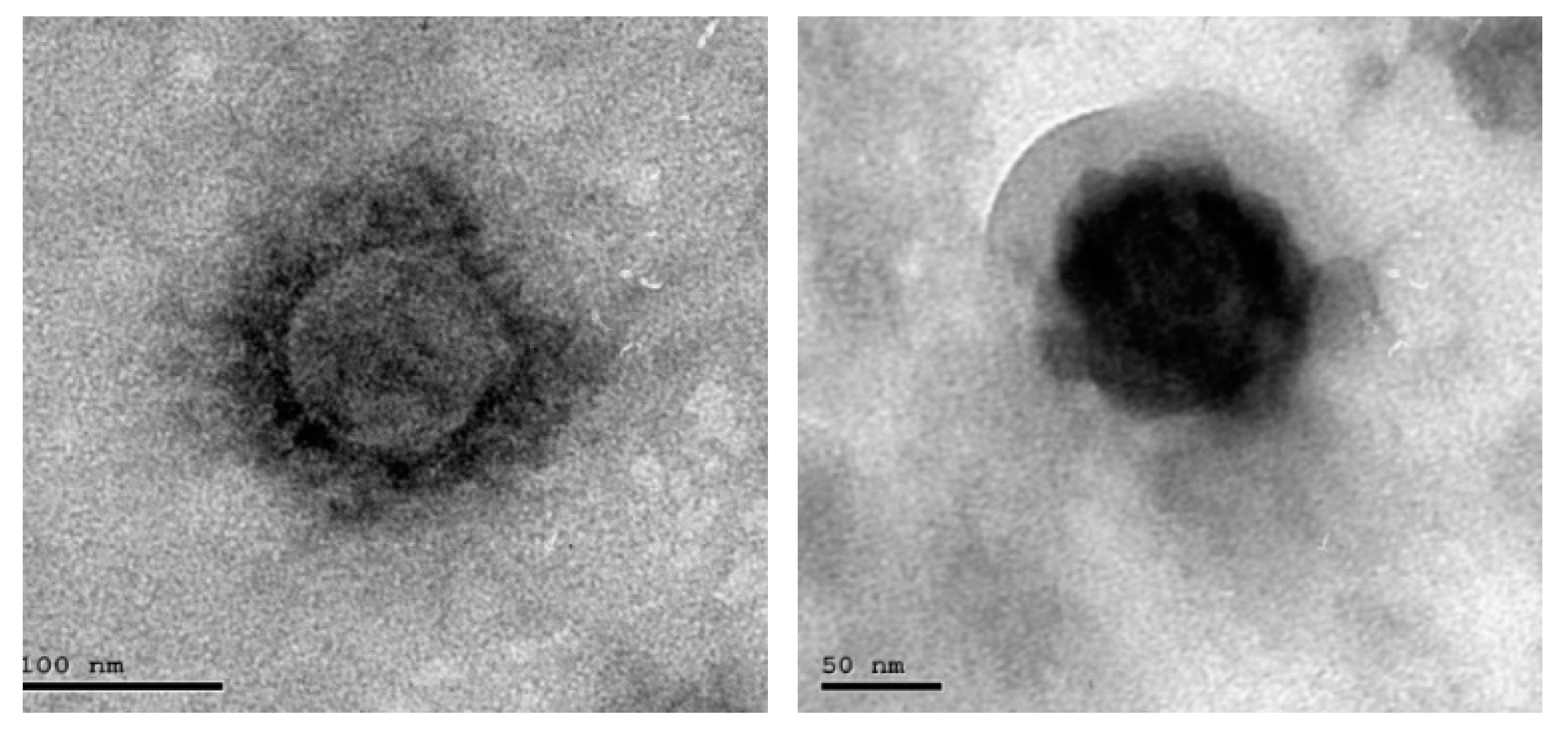

| Diagnostic Tech. | Detection | Type of Sample | Laboratory/Point of Care Test | Advantage | Disadvantage | Size | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RT-PCR | Viral RNA | Nasopharyngeal swab, sputum, stool | Laboratory based | Specific detection and time saving | Low viral load gives false negative results. | large | [14] |
| Serology | Antibody/antigen | Blood | Laboratory based/point of care | Less complex than molecular tests | The antibodies may react with other pathogens in addition, giving false negative results for low viral loading. | large | [15] |
| ELISA | Antibody | Blood | Laboratory based | Simple and cheap laboratory technique, important for vaccine | ELISA tests have not been matured yet. | medium | [16] |
| MCR Proposed | Antibody/antigen | Blood | Laboratory based | Moderate price and fast results | May give a false negative when the virus concentration is low. | small | [18] |
| Lg | Lf | Lsub | R | Wsub | Tan δ | Wf | Ls | Hsub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 42 | 50 | 6.5 | 25 | 0.0035 | 3 | 10 | 1.28 |
| COVID-19 | Reflection Coefficient | Phase | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serial | fbefore (GHz) | fafter (GHz) | S11before (dB) | S11after (dB) | deg before (°) | deg after (°) |
| 1 | 2.285 | 2.285 | −12.44985 | −12.0007 | −26.25539 | −25.62203 |
| 2 | 2.285 | 2.2775 | −12.0007 | −12.12683 | −25.62203 | −20.1454 |
| 3 | 2.285 | 2.285 | −10.85233 | −10.84041 | −16.72242 | −17.47174 |
| 4 | 2.285 | 2.37 | −10.85233 | −10.67627 | −16.72242 | −67.83884 |
| 5 | 2.285 | 2.285 | −12.14496 | −11.82519 | −23.64535 | −25.88884 |
| 6 | 2.285 | 2.275 | −11.82519 | −11.7540 | −25.88884 | −17.6381 |
| 7 | 2.285 | 2.285 | −16.03847 | −15.6323 | −19.85438 | −21.78697 |
| 8 | 2.285 | 2.29 | −15.63235 | −15.3149 | −21.78697 | −26.52782 |
| 9 | 2.285 | 2.285 | −11.39496 | −11.2455 | −15.00481 | −16.92356 |
| 10 | 2.285 | 2.2825 | −11.24558 | −10.9067 | −16.92356 | −16.62737 |
| 11 | 2.285 | 2.285 | −11.93321 | −11.9472 | −24.97691 | −22.87379 |
| 12 | 2.285 | 2.29 | −11.94724 | −11.7377 | −22.87379 | −27.84187 |
| 13 | 2.285 | 2.2875 | −12.61087 | −11.9033 | −24.24766 | −28.77753 |
| 14 | 2.2875 | 2.2825 | −11.90339 | −11.8353 | −28.77753 | −11.92937 |
| Frequency | Percent | |
|---|---|---|
| −ve COVID-19 | 32 | 48.5 |
| +ve COVID-19 | 34 | 51.5 |
| Total | 66 | 100.0 |
| Test Result Variable(s) | Area | Std. Error | Asymptotic Sig. | Asymptotic 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| fbefore | 0.501 | 0.072 | 0.985 | 0.360 | 0.642 |
| fafter | 0.480 | 0.072 | 0.783 | 0.340 | 0.621 |
| fafter-fbefore | 0.430 | 0.074 | 0.330 | 0.284 | 0.576 |
| Test Result Variable(s) | Area | Std. Error | Asymptotic Sig. | Asymptotic 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| S11before | 0.626 | 0.070 | 0.079 | 0.488 | 0.764 |
| S11after | 0.640 | 0.069 | 0.051 | 0.504 | 0.776 |
| S11after-S11before | 0.511 | 0.072 | 0.878 | 0.369 | 0.653 |
| Sensitivity (<−12.5) | Specificity (>−12.5) | PPV | NPV | Total Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S11 after value cutoff = −12.5 | 22/34 (64.7%) | 20/32 (62.5%) | 22/34 (64.7%) | 20/32 (62.5%) | 44/66 (63.6%) |
| Test Result Variable(s) | Area | Std. Error | Asymptotic Sig. | Asymptotic 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| deg before | 0.662 | 0.068 | 0.024 | 0.529 | 0.794 |
| deg after | 0.615 | 0.070 | 0.109 | 0.478 | 0.752 |
| deg after-deg before | 0.474 | 0.073 | 0.719 | 0.332 | 0.617 |
| Sensitivity (<−20.0) | Specificity (>−20.0) | PPV | NPV | Total Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| deg before value cutoff = −20.0 | 17/34 (50%) | 23/32 (71.9%) | 17/26 (65.4%) | 23/40 (57.5%) | 40/66 (60.6%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elsheakh, D.M.; Ahmed, M.I.; Elashry, G.M.; Moghannem, S.M.; Elsadek, H.A.; Elmazny, W.N.; Alieldin, N.H.; Abdallah, E.A. Rapid Detection of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Using Microwave Immunosensor Cavity Resonator. Sensors 2021, 21, 7021. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217021
Elsheakh DM, Ahmed MI, Elashry GM, Moghannem SM, Elsadek HA, Elmazny WN, Alieldin NH, Abdallah EA. Rapid Detection of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Using Microwave Immunosensor Cavity Resonator. Sensors. 2021; 21(21):7021. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217021
Chicago/Turabian StyleElsheakh, Dalia M., Mohamed I. Ahmed, Gomaa M. Elashry, Saad M. Moghannem, Hala A. Elsadek, Waleed N. Elmazny, Nelly H. Alieldin, and Esmat A. Abdallah. 2021. "Rapid Detection of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Using Microwave Immunosensor Cavity Resonator" Sensors 21, no. 21: 7021. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217021
APA StyleElsheakh, D. M., Ahmed, M. I., Elashry, G. M., Moghannem, S. M., Elsadek, H. A., Elmazny, W. N., Alieldin, N. H., & Abdallah, E. A. (2021). Rapid Detection of Coronavirus (COVID-19) Using Microwave Immunosensor Cavity Resonator. Sensors, 21(21), 7021. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21217021








