ZnO Thin Films Growth Optimization for Piezoelectric Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
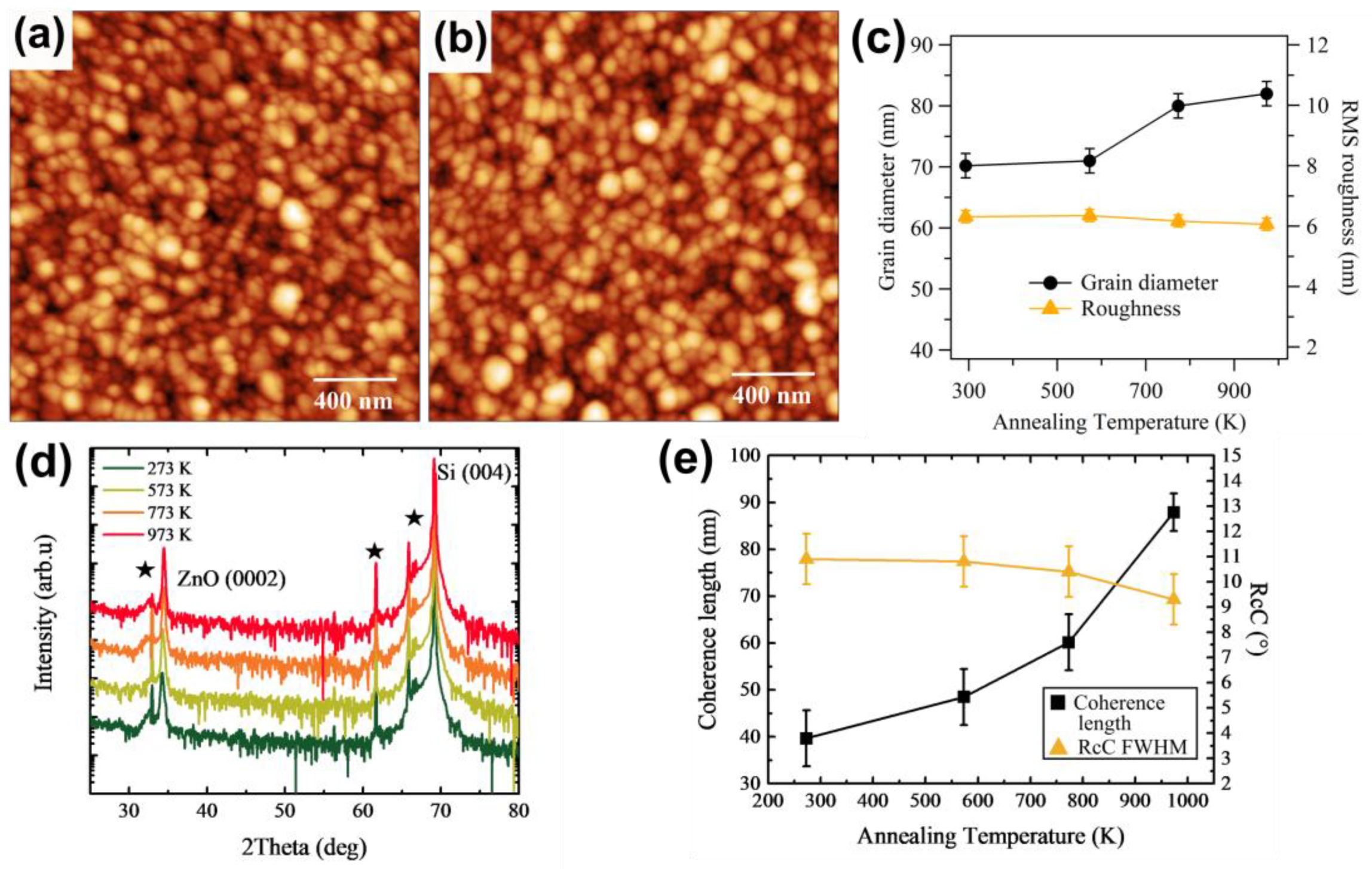
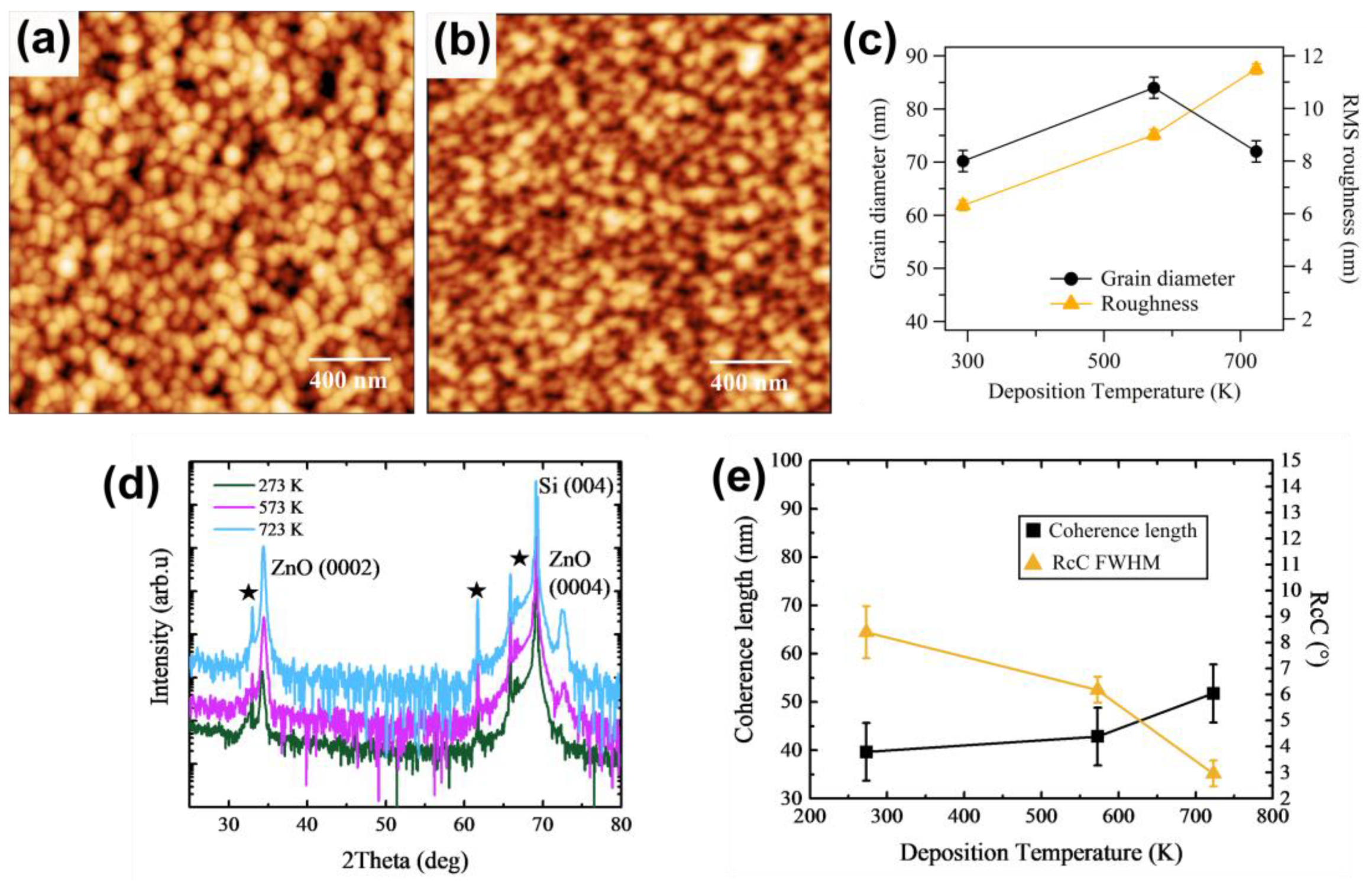
3.1. Temperature Optimization
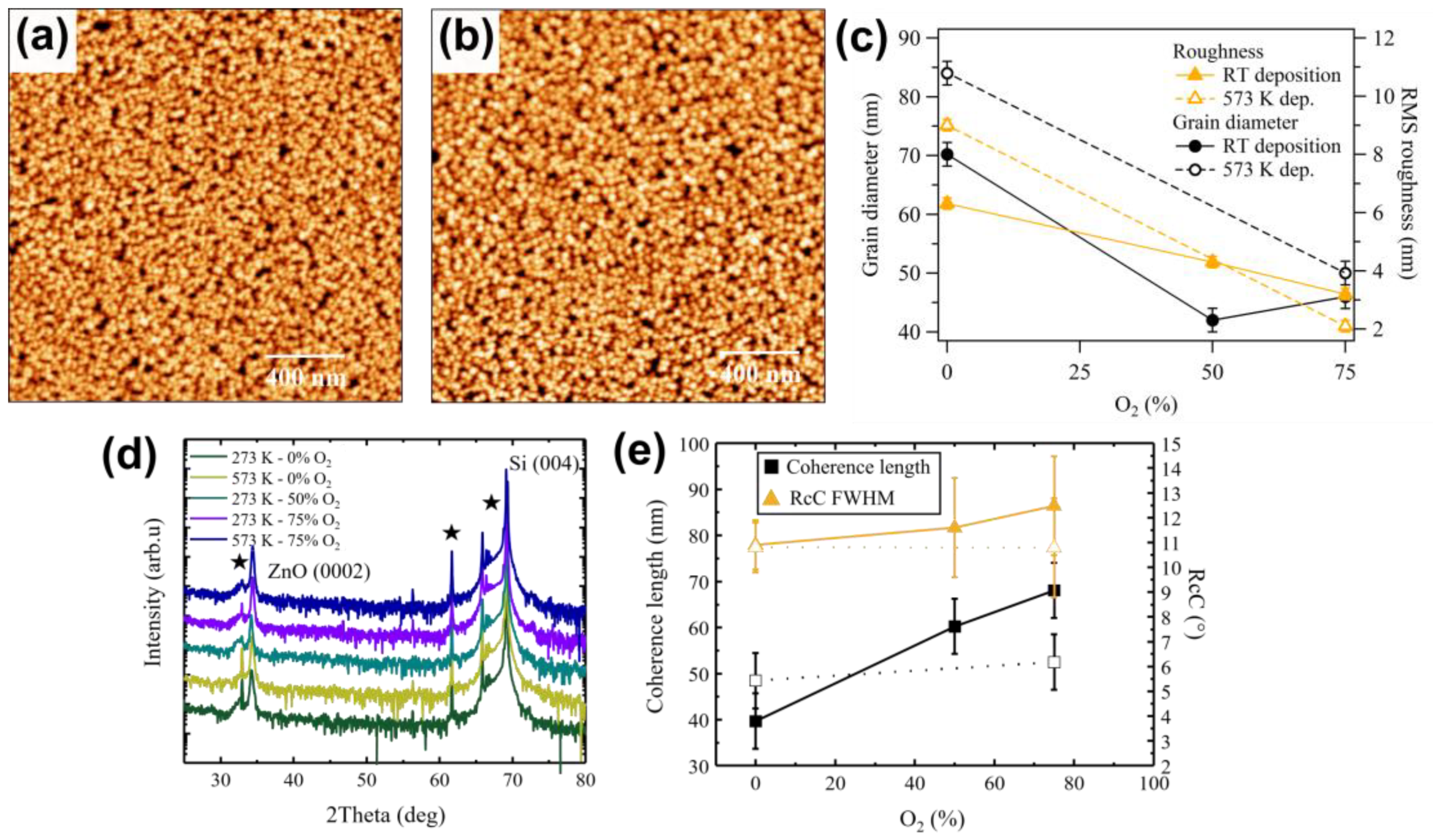
3.2. Role of Oxygen in Sputtering Gas
3.3. Deposition on Metal Electrodes
3.4. Piezoelectric Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ozgur, U.; Hofstetter, D.; Morkoc, H. ZnO Devices and Applications: A Review of Current Status and Future Prospects. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borysiewicz, M.A. ZnO as a Functional Material, a Review. Crystals 2019, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozgur, U.; Alivov, Y.I.; Liu, C.; Teke, A.; Reshchikov, M.A.; Dogan, S.; Avrutin, V.; Cho, S.J.; Morkoc, H. A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 98, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.L. Nanostructures of zinc oxide. Mater. Today 2004, 7, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhati, V.S.; Hojamberdiev, M.; Kumar, M. Enhanced sensing performance of ZnO nanostructures-based gas sensors: A review. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Umar, A.; Bhasin, K.K.; Baskoutas, S. Chemical Sensing Applications of ZnO Nanomaterials. Materials 2018, 11, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elhosni, M.; Elmazria, O.; Petit-Watelot, S.; Bouvot, L.; Zhgoon, S.; Talbi, A.; Hehn, M.; Aissa, K.A.; Hage-Ali, S.; Lacour, D.; et al. Magnetic field SAW sensors based on magnetostrictive-piezoelectric layered structures: FEM modeling and experimental validation. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2016, 240, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.B.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.G.; Hwang, C.S.; Hong, S.H.; Shin, Y.H.; Lee, N.H. Deposition of ZnO thin films by magnetron sputtering for a film bulk acoustic resonator. Thin Solid Films 2003, 435, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhou, X.Y.; Pang, G.K.H.; Zhang, T.; Liu, W.L.; Cheng, J.G.; Song, Z.T.; Feng, S.L.; Lai, L.H.; Chen, J.Z.; et al. ZnO-based film bulk acoustic resonator for high sensitivity biosensor applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 143503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savarimuthu, K.; Sankararajan, R.; Govindaraj, R.; Narendhiran, S. A comparative study on a flexible ZnO-based nano-generator using Schottky and p-n junction contact for energy harvesting applications. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 16022–16029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tlemcani, T.S.; Justeau, C.; Nadaud, K.; Alquier, D.; Poulin-Vittrant, G. Fabrication of Piezoelectric ZnO Nanowires Energy Harvester on Flexible Substrate Coated with Various Seed Layer Structures. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Khassaf, H.; Alpay, S.P. Strain engineering of piezoelectric properties of strontium titanate thin films. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 5978–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christman, J.A.; Woolcott, R.R.; Kingon, A.I.; Nemanich, R.J. Piezoelectric measurements with atomic force microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 3851–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Ali, T.; Pilz, J.; Schaffner, P.; Kratzer, M.; Teichert, C.; Stadlober, B.; Coclite, A.M. Piezoelectric Properties of Zinc Oxide Thin Films Grown by Plasma-Enhanced Atomic Layer Deposition. Phys. Status Solidi A-Appl. Mater. Sci. 2020, 217, 2000319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Farrera, B.; Velasquez-Garcia, L.F. Ultrathin Ceramic Piezoelectric Films via Room-Temperature Electrospray Deposition of ZnO Nanoparticles for Printed GHz Devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 29167–29176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.C.; Song, C.; Wang, X.H.; Zeng, F.; Pan, F. Giant piezoelectric d(33) coefficient in ferroelectric vanadium doped ZnO films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 012907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.Q.; Li, D.N.; Li, J.H.; Wang, C.H. Structure and piezoelectricity properties of V-doped ZnO thin films fabricated by sol-gel method. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 829, 154483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ion, V.; Craciun, F.; Scarisoreanu, N.D.; Moldovan, A.; Andrei, A.; Birjega, R.; Ghica, C.; Di Pietrantonio, F.; Cannata, D.; Benetti, M.; et al. Impact of thickness variation on structural, dielectric and piezoelectric properties of (Ba, Ca) (Ti, Zr)O-3 epitaxial thin films. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polewczyk, V.; Vinai, G.; Motti, F.; Dal Zilio, S.; Capaldo, P.; Sygletou, M.; Benedetti, S.; Rossi, G.; Torelli, P. Original design of a patterned multiferroic heterostructure for electrical control of the magnetic shape anisotropy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 507, 166816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zviagin, A.S.; Chernozem, R.V.; Surmeneva, M.A.; Pyeon, M.; Frank, M.; Ludwig, T.; Tutacz, P.; Ivanov, Y.F.; Mathur, S.; Surmenev, R.A. Enhanced piezoelectric response of hybrid biodegradable 3D poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) scaffolds coated with hydrothermally deposited ZnO for biomedical applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 117, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Bhatti, K.A.; Qindeel, R.; Alonizan, N.; Althobaiti, H.S. Characterizations of multilayer ZnO thin films deposited by sol-gel spin coating technique. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, H.; Roh, Y. Deposition of ZnO thin films by the ultrasonic spray pyrolysis technique. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1-Regul. Pap. Short Notes Rev. Pap. 2001, 40, 2423–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.G.; Ye, Z.Z.; Zeng, Y.J.; Zhu, L.P.; Wang, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, B.H.; Liang, Q.L. Structural, optical, and electrical properties of (Zn,Al)O films over a wide range of compositions. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 073714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmer, K. Magnetron sputtering of transparent conductive zinc oxide: Relation between the sputtering parameters and the electronic properties. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 2000, 33, R17–R32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triboulet, R.; Perriere, J. Epitaxial growth of ZnO films. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 2003, 47, 65–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtomo, A.; Tsukazaki, A. Pulsed laser deposition of thin films and superlattices based on ZnO. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2005, 20, S1–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opel, M.; Geprags, S.; Althammer, M.; Brenninger, T.; Gross, R. Laser molecular beam epitaxy of ZnO thin films and heterostructures. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 034002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenti, I.; Benedetti, S.; Di Bona, A.; Lollobrigida, V.; Perucchi, A.; Di Pietro, P.; Lupi, S.; Valeri, S.; Torelli, P. Electrical, optical, and electronic properties of Al:ZnO films in a wide doping range. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 165304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, S.; Valenti, I.; di Bona, A.; Vinai, G.; Castan-Guerrero, C.; Valeri, S.; Catellani, A.; Ruini, A.; Torelli, P.; Calzolari, A. Spectroscopic identification of the chemical interplay between defects and dopants in Al-doped ZnO. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 29364–29371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, W.R.; Prasad, M. Piezoelectric MEMS based acoustic sensors: A review. Sens. Actuators A-Phys. 2020, 301, 111756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trolier-McKinstry, S.; Muralt, P. Thin film piezoelectrics for MEMS. J. Electroceramics 2004, 12, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Joung, Y.H. Influence of substrate temperature on the optical and piezoelectric properties of ZnO thin films deposited by rf magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 7330–7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Guler, Z.; Jackson, N. Development and characterization of confocal sputtered piezoelectric zinc oxide thin film. Vacuum 2021, 184, 109930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, L.P.; Alkaisi, M.M.; Miller, P.; Reeves, R.J.; Markwitz, A. Comparison of DC and RF sputtered zinc oxide films with post-annealing and dry etching and effect on crystal composition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1-Regul. Pap. Brief Commun. Rev. Pap. 2005, 44, 7555–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurenti, M.; Stassi, S.; Lorenzoni, M.; Fontana, M.; Canavese, G.; Cauda, V.; Pirri, C.F. Evaluation of the piezoelectric properties and voltage generation of flexible zinc oxide thin films. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 215704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Mouis, M.; Ardila, G. Unveiling the Influence of Surface Fermi Level Pinning on the Piezoelectric Response of Semiconducting Nanowires. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 4, 1700299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Haimeur, A.; Slassi, A.; Pershin, A.; Cornil, D.; Makha, M.; Blanco, E.; Dominguez, M.; Bakkali, H. Reducing p-type Schottky contact barrier in metal/ZnO heterostructure through Ni-doping. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 545, 149023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, J.K.; Billah, M.M.; Jang, J. Triple-Stack ZnO/AlZnO/YZnO Heterojunction Oxide Thin-Film Transistors by Spray Pyrolysis for High Mobility and Excellent Stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 37340–37352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Seo, B.C.; Park, H.D.; Yoon, G. Film bulk acoustic resonator fabrication for radio frequency filter applications. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part 1-Regul. Pap. Brief Commun. Rev. Pap. 2000, 39, 4115–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Kao, K.S. Two-step sputtered ZnO piezoelectric films for film bulk acoustic resonators. Appl. Phys. A-Mater. Sci. Process. 2007, 89, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.P.; Dai, W.; Xu, S.; Li, X.W.; Gao, C.Y.; Chen, X.M.; Yang, B.H. Local Piezoelectric Properties and Polarity Distribution of ZnO Films Deposited at Different Substrate Temperatures. J. Electron. Mater. 2015, 44, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, F.K.; Liu, G.X.; Shin, B.C.; Lee, W.J. Annealing Effects of ZnO Thin Films Deposited on Si (100) by Using Pulsed Laser Deposition. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2009, 54, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Kim, J.S. Study on the c-axis preferred orientation of ZnO film on various metal electrodes. Ultramicroscopy 2008, 108, 1288–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Emanetoglu, N.W.; Chen, Y. Chapter 13—ZnO Piezoelectric Devices. In Zinc Oxide Bulk, Thin Films and Nanostructures; Jagadish, C., Pearton, S., Eds.; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 443–489. [Google Scholar]
- Gardeniers, J.G.E.; Rittersma, Z.M.; Burger, G.J. Preferred orientation and piezoelectricity in sputtered ZnO films. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 83, 7844–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamohara, T.; Akiyama, M.; Kuwano, N. Influence of polar distribution on piezoelectric response of aluminum nitride thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 093506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Nayak, M.M.; Rajanna, K. Effect of post-deposition annealing on transverse piezoelectric coefficient and vibration sensing performance of ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 296, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janotti, A.; Van de Walle, C.G. Fundamentals of zinc oxide as a semiconductor. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2009, 72, 126501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albertsson, J.; Abrahams, S.C.; Kvick, A. Atomic Displacement, Anharmonic Thermal Vibration, Expansivity and Pyroelectric Coefficient Thermal Dependences in ZnO. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B-Struct. Sci. 1989, 45, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, W.; Horwat, D.; Pigeat, P.; Miska, P.; Migot, S.; Soldera, F.; Boulet, P.; Mucklich, F. Near-room temperature single-domain epitaxy of reactively sputtered ZnO films. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 235107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, R.; Gupta, V.; Tan, H.H.; Sreenivas, K.; Jagadish, C. Origin of stress in radio frequency magnetron sputtered zinc oxide thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 064905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klug, H.P.; Alexander, L.E. X-ray Diffraction Procedures for Polycrystalline and Amorphous Materials; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Hala, M.; Kato, H.; Algasinger, M.; Inoue, Y.; Rey, G.; Werner, F.; Schubbert, C.; Dalibor, T.; Siebentritt, S. Improved environmental stability of highly conductive nominally undoped ZnO layers suitable for n-type windows in thin film solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 161, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandepol, F.C.M.; Blom, F.R.; Popma, T.J.A. R.f. planar magnetron sputtered ZnO films I: Structural properties. Thin Solid Films 1991, 204, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Water, W.; Chu, S.Y. Physical and structural properties of ZnO sputtered films. Mater. Lett. 2002, 55, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, K.Y.; Gupta, M.K.; Majumder, S.; Kim, S.W. Self-Compensated Insulating ZnO-Based Piezoelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6949–6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, T.; Hirohashi, M. Influence of oxygen partial pressure on transparency and conductivity of RF sputtered Al-doped ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2000, 157, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kado, T. Structure of Ti films deposited on MgO(001) substrates. Surf. Sci. 2000, 454, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.H.; Baik, S.; Kim, S.S. Change of growth orientation in Pt films epitaxially grown on MgO(001) substrates by sputtering. J. Mater. Res. 2002, 17, 2334–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Mansingh, A. ISAF XI’98: Proc. XI IEEE Symp. on Applications of Ferroelectrics; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Montreux, Switzerland, 1998; p. 113. [Google Scholar]
- Bdikin, I.K.; Gracio, J.; Ayouchi, R.; Schwarz, R.; Kholkin, A.L. Local piezoelectric properties of ZnO thin films prepared by RF-plasma-assisted pulsed-laser deposition method. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 235703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
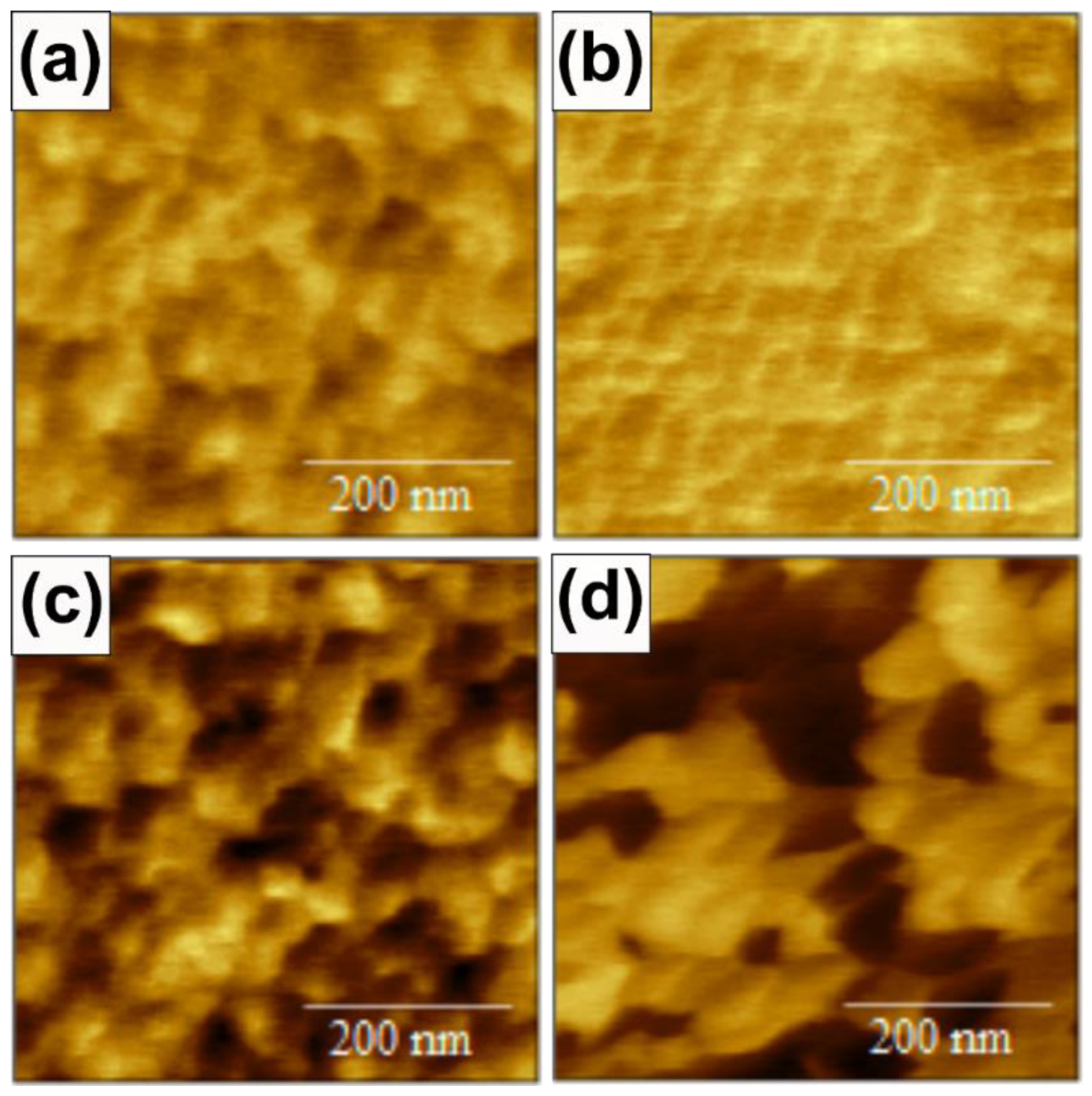
| Bottom Electrode | Deposition Conditions | RMS Roughness (nm) | Grain Diameter (nm) | Bragg Peak (°) | Coherence Length (nm) | RcC of the (0002) Bragg Peak (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt | 273 K | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 49 ± 3 | 34.21 ± 0.02 | 30 ± 4 | >20 |
| Annealed 773 K | 3.5 ± 0.3 | 54 ± 3 | 34.34 ± 0.02 | 42 ± 3 | >20 | |
| 573 K | 6.0 ± 0.2 | 55 ± 5 | 34.31 ± 0.02 | 33 ± 4 | >20 | |
| Annealed 773 K | 4.5 ± 0.4 | 70 ± 5 | 34.39 ± 0.02 | 104 ± 2 | >20 | |
| Ti | 273 K | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 39 ± 4 | 34.28 ± 0.02 | 39 ± 3 | 16 ± 2 |
| Annealed 773 K | 15.2 ± 1 | 130 ± 8 | 34.37 ± 0.02 | 102 ± 2 | 7 ± 2 | |
| 573 K | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 43 ± 3 | 34.33 ± 0.02 | 80 ± 2 | 3 ± 1 | |
| Annealed 773 K | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 44 ± 2 | 34.39 ± 0.02 | 115 ± 2 | 3 ± 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Polewczyk, V.; Magrin Maffei, R.; Vinai, G.; Lo Cicero, M.; Prato, S.; Capaldo, P.; Dal Zilio, S.; di Bona, A.; Paolicelli, G.; Mescola, A.; et al. ZnO Thin Films Growth Optimization for Piezoelectric Application. Sensors 2021, 21, 6114. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186114
Polewczyk V, Magrin Maffei R, Vinai G, Lo Cicero M, Prato S, Capaldo P, Dal Zilio S, di Bona A, Paolicelli G, Mescola A, et al. ZnO Thin Films Growth Optimization for Piezoelectric Application. Sensors. 2021; 21(18):6114. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186114
Chicago/Turabian StylePolewczyk, Vincent, Riccardo Magrin Maffei, Giovanni Vinai, Matteo Lo Cicero, Stefano Prato, Pietro Capaldo, Simone Dal Zilio, Alessandro di Bona, Guido Paolicelli, Andrea Mescola, and et al. 2021. "ZnO Thin Films Growth Optimization for Piezoelectric Application" Sensors 21, no. 18: 6114. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186114
APA StylePolewczyk, V., Magrin Maffei, R., Vinai, G., Lo Cicero, M., Prato, S., Capaldo, P., Dal Zilio, S., di Bona, A., Paolicelli, G., Mescola, A., D’Addato, S., Torelli, P., & Benedetti, S. (2021). ZnO Thin Films Growth Optimization for Piezoelectric Application. Sensors, 21(18), 6114. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21186114








