Validity Evaluation of an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) in Gait Analysis Using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
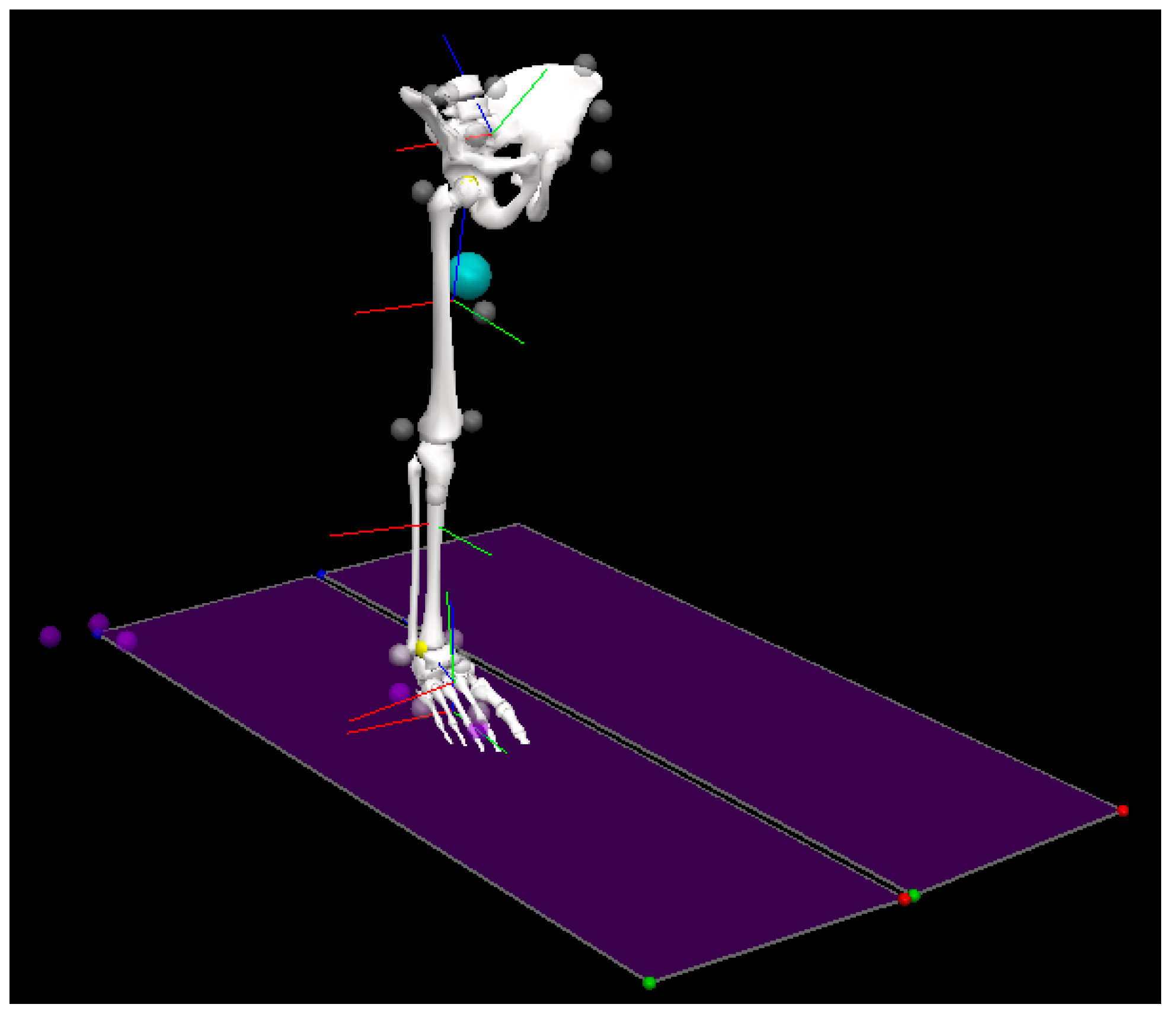
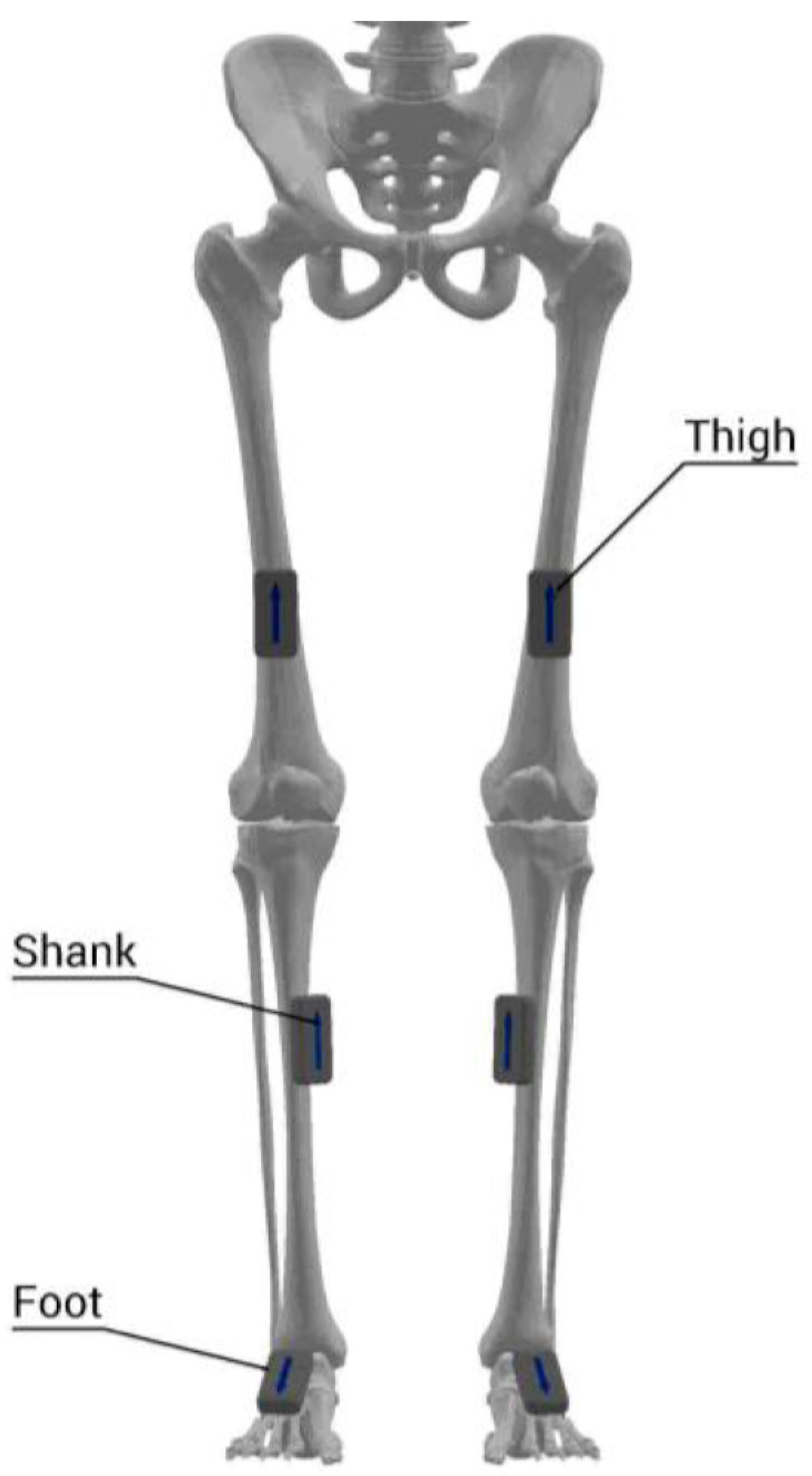
2.2. Procedure and Data Collection
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
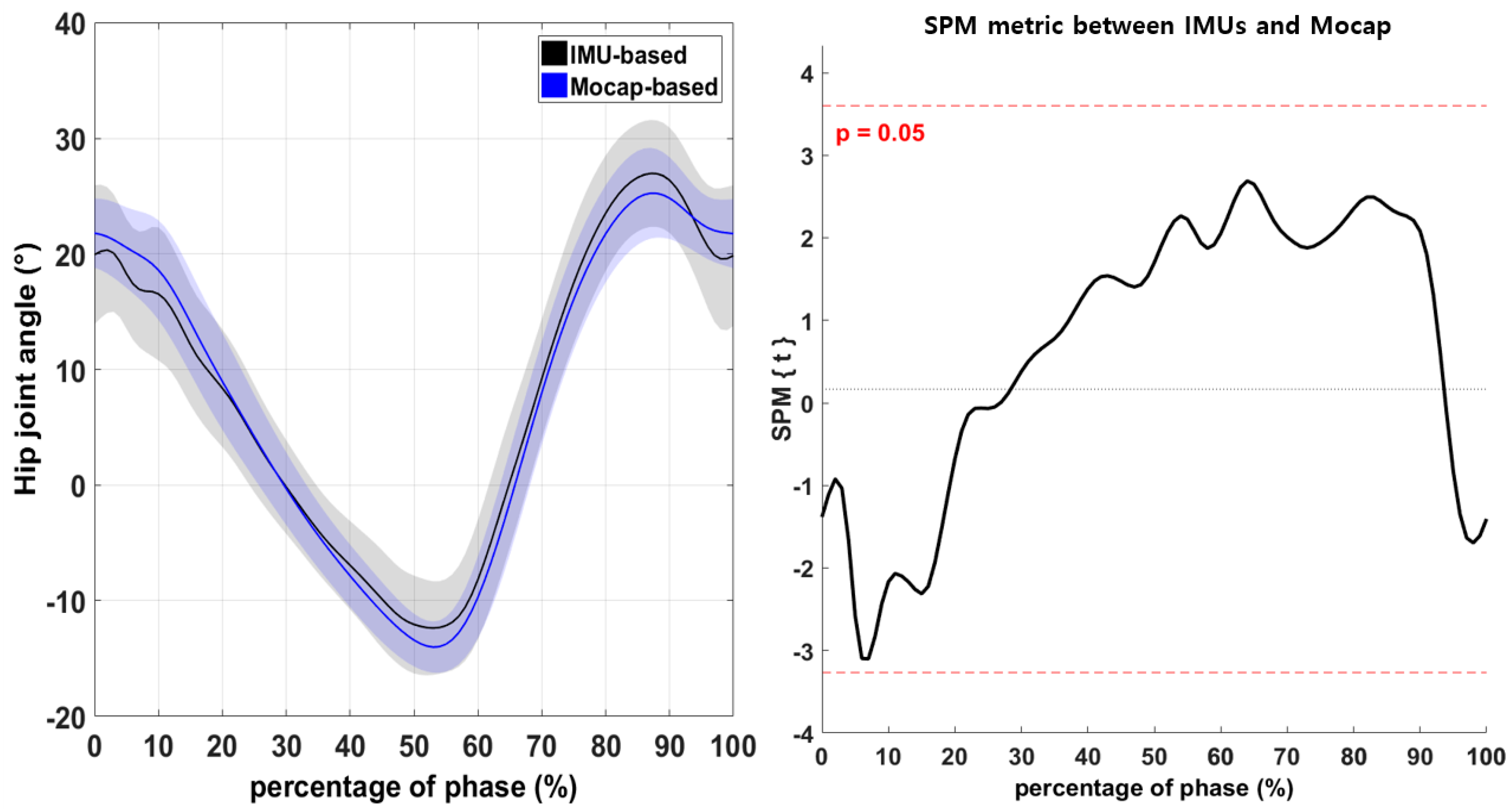
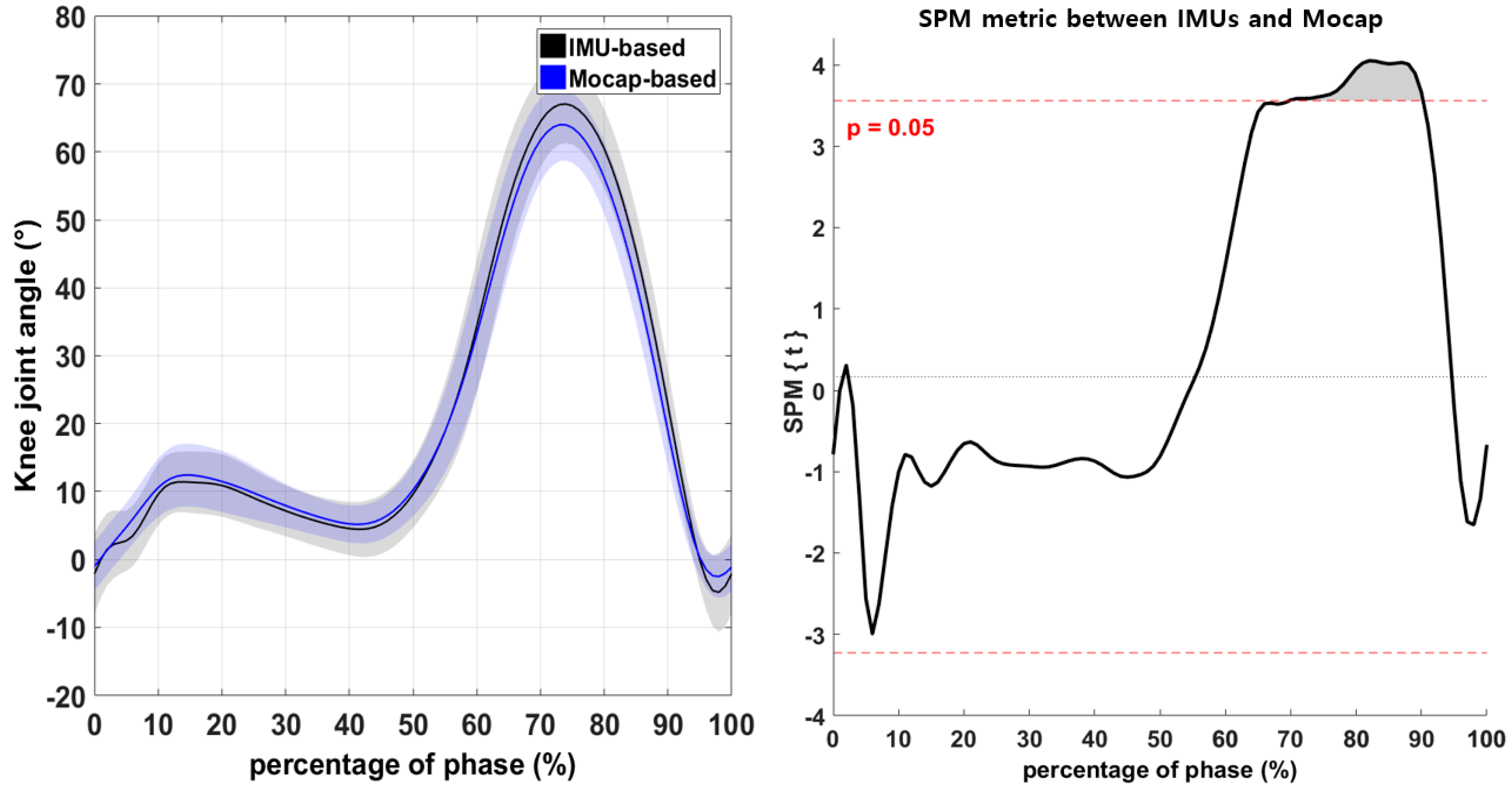
3.1. Discrete Variables of the Lower-Extremity Joints during Walking
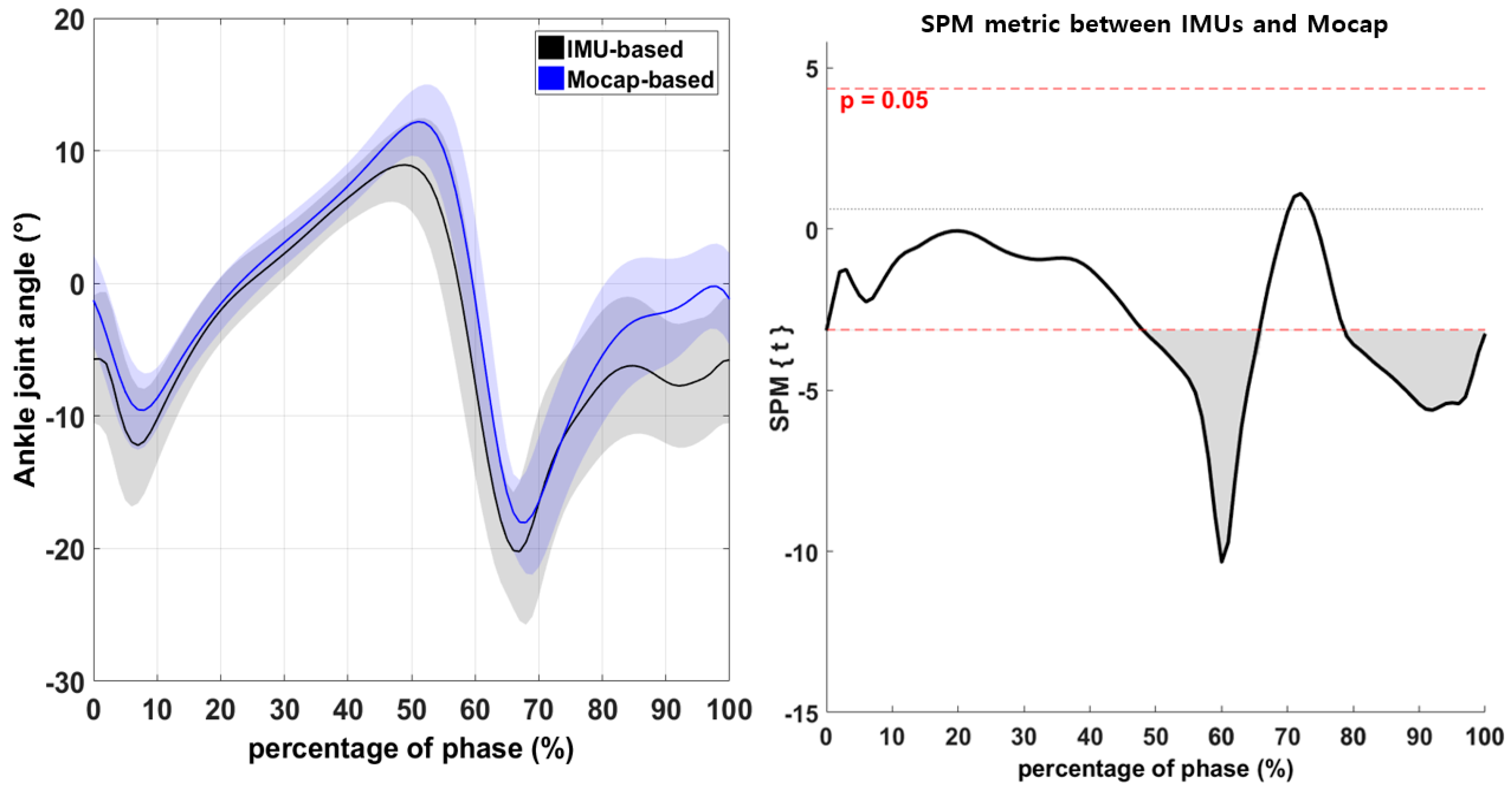
3.2. Continuous Variables of the Lower-Extremity Joints during Walking
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.; Lach, J.; Lo, B.; Yang, G.Z. Toward Pervasive Gait Analysis With Wearable Sensors: A Systematic Review. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 1521–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R. Gait analysis methods in rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2006, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancillao, A. Analysis and measurement of human motion: Modern protocols and clinical considerations. J. Rob. Mech. Eng. Res. 2016, 1, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.Y.; Wong, M.S.; Lo, K.H. Clinical applications of sensors for human posture and movement analysis: A review. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2007, 31, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebel, K.; Boissy, P.; Hamel, M.; Duval, C. Inertial measures of motion for clinical biomechanics: Comparative assessment of accuracy under controlled conditions—Effect of velocity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, C.; Salvia, P.; Lubansu, A.; Feipel, V.; Aminian, K. A wearable inertial system to assess the cervical spine mobility: Comparison with an optoelectronic-based motion capture evaluation. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Noort, J.C.; Ferrari, A.; Cutti, A.G.; Becher, J.G.; Harlaar, J. Gait analysis in children with cerebral palsy via inertial and magnetic sensors. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2013, 51, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayagoitia, R.E.; Nene, A.V.; Veltink, P.H. Accelerometer and rate gyroscope measurement of kinematics: An inexpensive alternative to optical motion analysis systems. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amri, M.; Nicholas, K.; Button, K.; Sparkes, V.; Sheeran, L.; Davies, J.L. Inertial measurement units for clinical movement analysis: Reliability and concurrent validity. Sensors 2018, 18, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berner, K.; Cockcroft, J.; Morris, L.D.; Louw, Q. Concurrent validity and within-session reliability of gait kinematics measured using an inertial motion capture system with repeated calibration. J. Bodyw. Mov. Therapies 2020, 24, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picerno, P. 25 years of lower limb joint kinematics by using inertial and magnetic sensors: A review of methodological approaches. Gait Posture 2017, 51, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusca, M.; Negrini, F.; Perego, P.; Magoni, L.; Molteni, F.; Andreoni, G. Validation of a wearable IMU system for gait analysis: Protocol and application to a new system. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iosa, M.; Picerno, P.; Paolucci, S.; Morone, G. Wearable inertial sensors for human movement analysis. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2016, 13, 641–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Chiari, L.; Holmstrom, L.; Salarian, A.; Horak, F.B. Validity and reliability of an IMU-based method to detect APAs prior to gait initiation. Gait Posture 2016, 43, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abyarjoo, F.; Barreto, A.; Cofino, J.; Ortega, F.R. Implementing a sensor fusion algorithm for 3D orientation detection with inertial/magnetic sensors. In Innovations and Advances in Computing, Informatics, Systems Sciences, Networking and Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Kok, M.; Schön, T.B. Magnetometer calibration using inertial sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 5679–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, A.M. Kalman-filter-based orientation determination using inertial/magnetic sensors: Observability analysis and performance evaluation. Sensors 2011, 11, 9182–9206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Abbas, J. Comparison of Angle Measurements between Vicon and MyoMotion Systems; Arizona State University: Tempe, AZ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, H.; Hou, B.; Lin, Z.; Guo, M. Modeling and Compensation of Random Drift of MEMS Gyroscopes Based on Least Squares Support Vector Machine Optimized by Chaotic Particle Swarm Optimization. Sensors 2017, 17, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teufl, W.; Miezal, M.; Taetz, B.; Fröhlich, M.; Bleser, G. Validity, test-retest reliability and long-term stability of magnetometer free inertial sensor based 3D joint kinematics. Sensors 2018, 18, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolink, S.; Naisas, H.; Senden, R.; Essers, H.; Heyligers, I.; Meijer, K.; Grimm, B. Validity of an inertial measurement unit to assess pelvic orientation angles during gait, sit–stand transfers and step-up transfers: Comparison with an optoelectronic motion capture system. Med. Eng. Phys. 2016, 38, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, P.; Dawes, H.; Collett, J.; Howells, K. IMU: Inertial sensing of vertical CoM movement. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 1578–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafer, J.F.; Provenzano, S.G.; Kern, K.L.; Agresta, C.E.; Grant, J.A.; Zernicke, R.F. Measuring markers of aging and knee osteoarthritis gait using inertial measurement units. J. Biomech. 2020, 99, 109567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brice, S.M.; Phillips, E.J.; Millett, E.L.; Hunter, A.; Philippa, B. Comparing inertial measurement units and marker-based biomechanical models during dynamic rotation of the torso. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2020, 20, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beange, K.H.; Chan, A.D.; Beaudette, S.M.; Graham, R.B. Concurrent validity of a wearable IMU for objective assessments of functional movement quality and control of the lumbar spine. J. Biomech. 2019, 97, 109356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poitras, I.; Dupuis, F.; Bielmann, M.; Campeau-Lecours, A.; Mercier, C.; Bouyer, L.J.; Roy, J.-S. Validity and reliability of wearable sensors for joint angle estimation: A systematic review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sole, G.; Pataky, T.; Tengman, E.; Hager, C. Analysis of three-dimensional knee kinematics during stair descent two decades post-ACL rupture—Data revisited using statistical parametric mapping. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2017, 32, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pataky, T.C.; Robinson, M.A.; Vanrenterghem, J. Vector field statistical analysis of kinematic and force trajectories. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 2394–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K.J.; Holmes, A.P.; Poline, J.B.; Grasby, P.J.; Williams, S.C.; Frackowiak, R.S.; Turner, R. Analysis of fMRI time-series revisited. Neuroimage 1995, 2, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Santago, A.C., II; Vidt, M.E.; Saul, K.R. Analysis of effects of loading and postural demands on upper limb reaching in older adults using statistical parametric mapping. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 2806–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataky, T.C. One-dimensional statistical parametric mapping in Python. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 15, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.A.; Vanrenterghem, J.; Pataky, T.C. Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) for alpha-based statistical analyses of multi-muscle EMG time-series. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2015, 25, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrien, B.; Goossens, M.; Baeyens, J.-P. Statistical parametric mapping of biomechanical one-dimensional data with Bayesian inference. Int. Biomech. 2019, 6, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.; Killeen, T.; Easthope, C.S.; Curt, A.; Bolliger, M.; Linnebank, M.; Zörner, B.; Filli, L. Familiarization with treadmill walking: How much is enough? Sci. Rep. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, D.A. Biomechanics and Motor Control of Human Movement; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tylkowski, C.M.; Simon, S.R.; Mansour, J.M. The Frank Stinchfield Award Paper. Internal rotation gait in spastic cerebral palsy. Hip 1982, 89–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Siegler, S.; Allard, P.; Kirtley, C.; Leardini, A.; Rosenbaum, D.; Whittle, M.; D’Lima, D.D.; Cristofolini, L.; Witte, H.; et al. ISB recommendation on definitions of joint coordinate system of various joints for the reporting of human joint motion—Part I: Ankle, hip, and spine. International Society of Biomechanics. J. Biomech. 2002, 35, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NORAXON. Available online: https://www.noraxon.com/noraxon-download/imu-technology-overview/ (accessed on 21 May 2021).
- Eerdekens, M.; Peerlinck, K.; Staes, F.; Hermans, C.; Lobet, S.; Deschamps, K. The biomechanical behaviour of ankle and foot joints during walking with shoes in patients with haemophilia. Haemophilia 2020, 26, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.; Burnfield, J.M. Gait analysis: Normal and pathological function. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 1993, 35, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta-Vargas, A.I.; Galán-Mercant, A.; Williams, J.M. The use of inertial sensors system for human motion analysis. Phys. Ther. Rev. 2010, 15, 462–473. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, G.; Sheret, I.; McMillan, L.; Siliverdis, K.; Sha, N.; Hodgins, D.; Kenney, L.; Howard, D. Inertial sensor-based knee flexion/extension angle estimation. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 2678–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebel, K.; Boissy, P.; Nguyen, H.; Duval, C. Inertial measurement systems for segments and joints kinematics assessment: Towards an understanding of the variations in sensors accuracy. Biomed. Eng. Online 2017, 16, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramia, C.; Torricelli, D.; Schmid, M.; Munoz-Gonzalez, A.; Gonzalez-Vargas, J.; Grandas, F.; Pons, J.L. IMU-based classification of Parkinson’s disease from gait: A sensitivity analysis on sensor location and feature selection. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, M.; Beato, M.; McErlain-Naylor, S.A. Inter-unit reliability of IMU Step metrics using IMeasureU Blue Trident inertial measurement units for running-based team sport tasks. J. Sports Sci. 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| (Unit: deg) | Variable | System | Mean ± SD | t (p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip-joint angle (+ flexion / − extension) | Max | IMU | 27.18 ± 4.66 | 1.88 (0.09) |
| Mocap | 25.70 ± 3.85 | |||
| Min | IMU | −12.97 ± 3.83 | 1.83 (0.10) | |
| Mocap | −14.41 ± 2.23 | |||
| ROM | IMU | 39.89 ± 3.81 | 0.01 (1.00) | |
| Mocap | 39.88 ± 3.22 | |||
| Knee-joint angle (+ flexion /− extension) | Max | IMU | 67.66 ± 5.79 | 3.29 (0.01) * |
| Mocap | 64.58 ± 5.21 | |||
| Min | IMU | −5.66 ± 5.79 | −1.84 (0.10) | |
| Mocap | −3.18 ± 3.11 | |||
| ROM | IMU | 72.67 ± 5.34 | 7.07 (0.01) * | |
| Mocap | 67.20 ± 4.66 | |||
| Ankle-joint angle (+ dorsi flexion /− plantar flexion) | Max | IMU | 9.63 ± 2.90 | −5.33 (0.01) * |
| Mocap | 12.66 ± 2.71 | |||
| Min | IMU | −23.16 ± 5.09 | −5.20 (0.01) * | |
| Mocap | −19.44 ± 3.79 | |||
| ROM | IMU | 31.84 ± 5.75 | 0.15 (0.89) | |
| Mocap | 31.71 ± 4.97 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Yoon, S. Validity Evaluation of an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) in Gait Analysis Using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM). Sensors 2021, 21, 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113667
Park S, Yoon S. Validity Evaluation of an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) in Gait Analysis Using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM). Sensors. 2021; 21(11):3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113667
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sangheon, and Sukhoon Yoon. 2021. "Validity Evaluation of an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) in Gait Analysis Using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM)" Sensors 21, no. 11: 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113667
APA StylePark, S., & Yoon, S. (2021). Validity Evaluation of an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) in Gait Analysis Using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM). Sensors, 21(11), 3667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21113667







