Robust Species Distribution Mapping of Crop Mixtures Using Color Images and Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material
2.1. Plot Trial Sites
2.1.1. Biomass Samples in Plot Trials
2.1.2. Image Acquisition in Plot Trials
2.1.3. Image Preprocessing
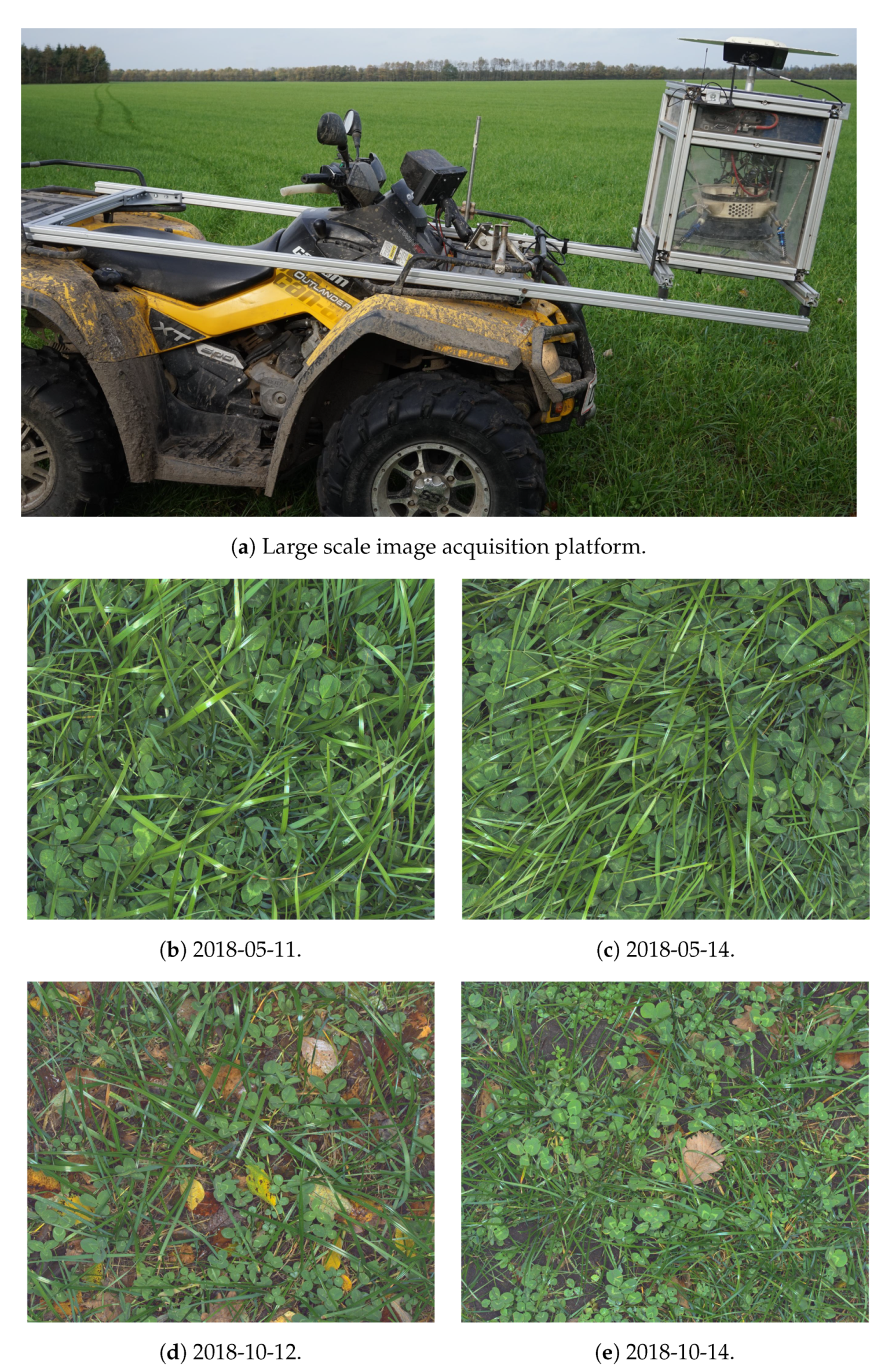
2.2. Large Scale Image Acquisition in Farmed Fields
2.2.1. ATV-Mounted Image Acquisition Platform
2.2.2. Sampling Strategy
2.2.3. Image Preprocessing
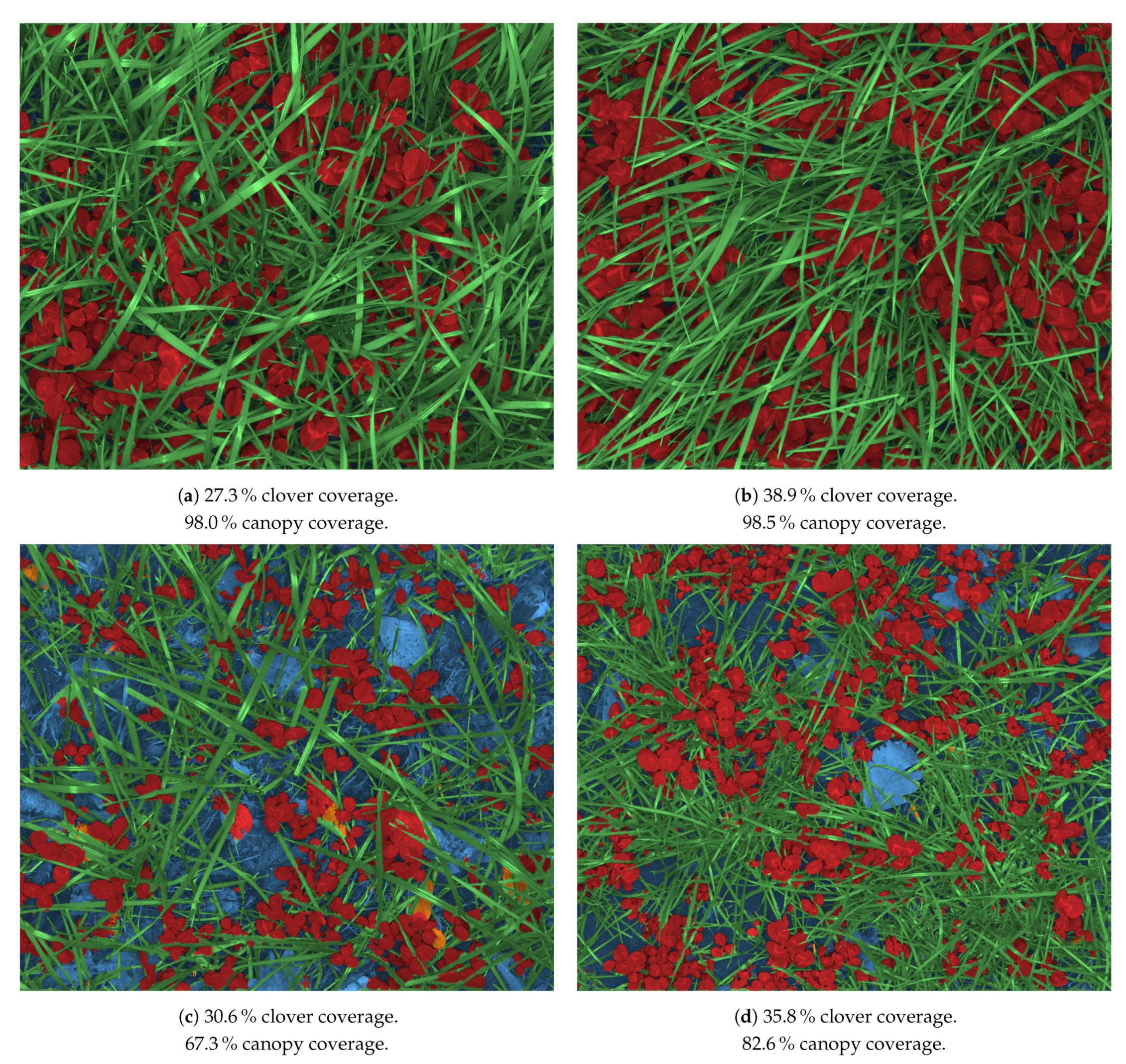
2.3. Synthetic Image Dataset with Hierarchical Labels
2.4. Image Annotation
3. Methods
3.1. Data-Driven Canopy Image Segmentation
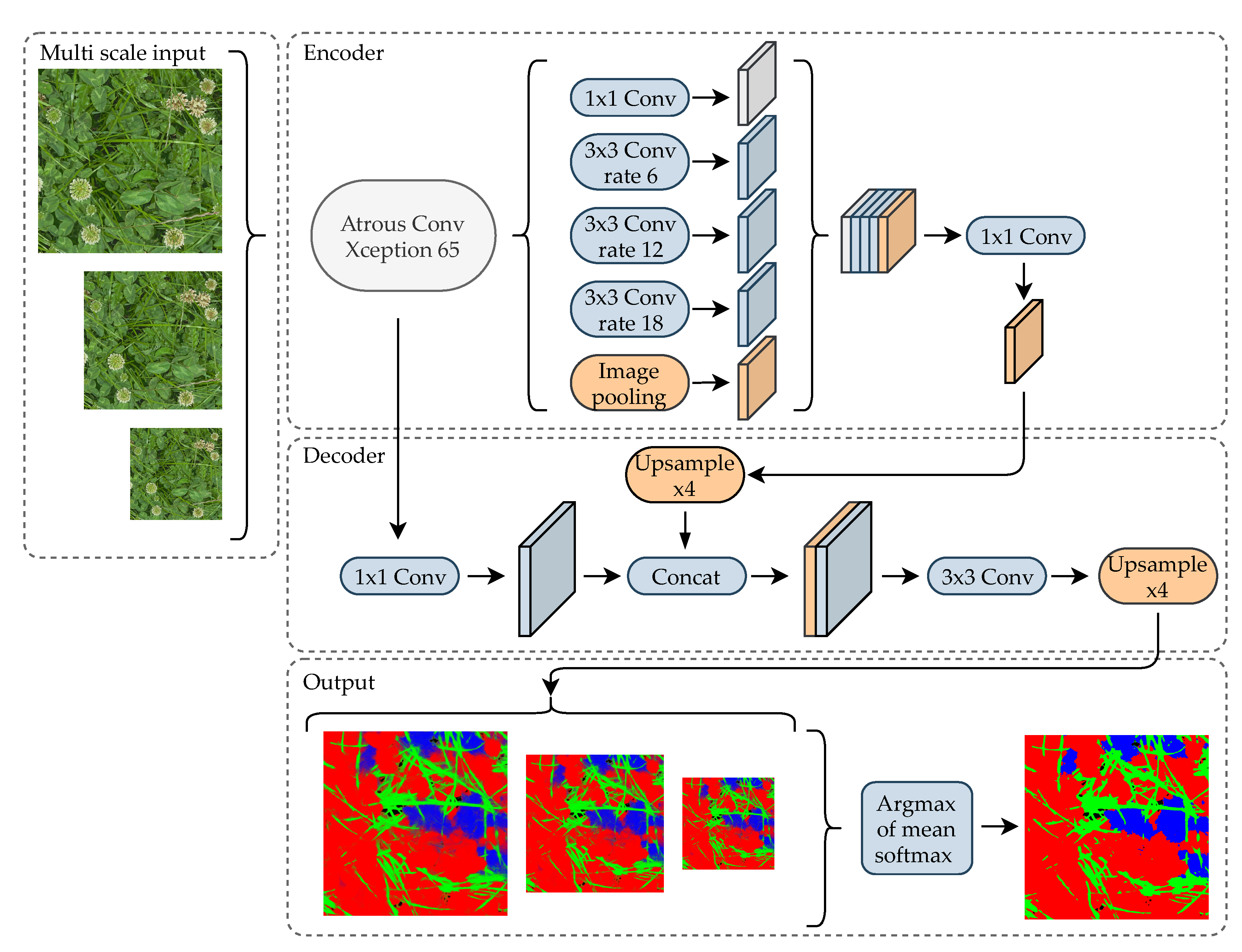
3.2. Neural Network Architecture
3.3. Training Procedure
3.3.1. Sub-Class Weights
3.3.2. Aggressive Image Augmentation
3.3.3. Style Transfer Augmentation to Create Weather Condition Invariance
3.4. Validation in Large Scale Mapping
4. Results
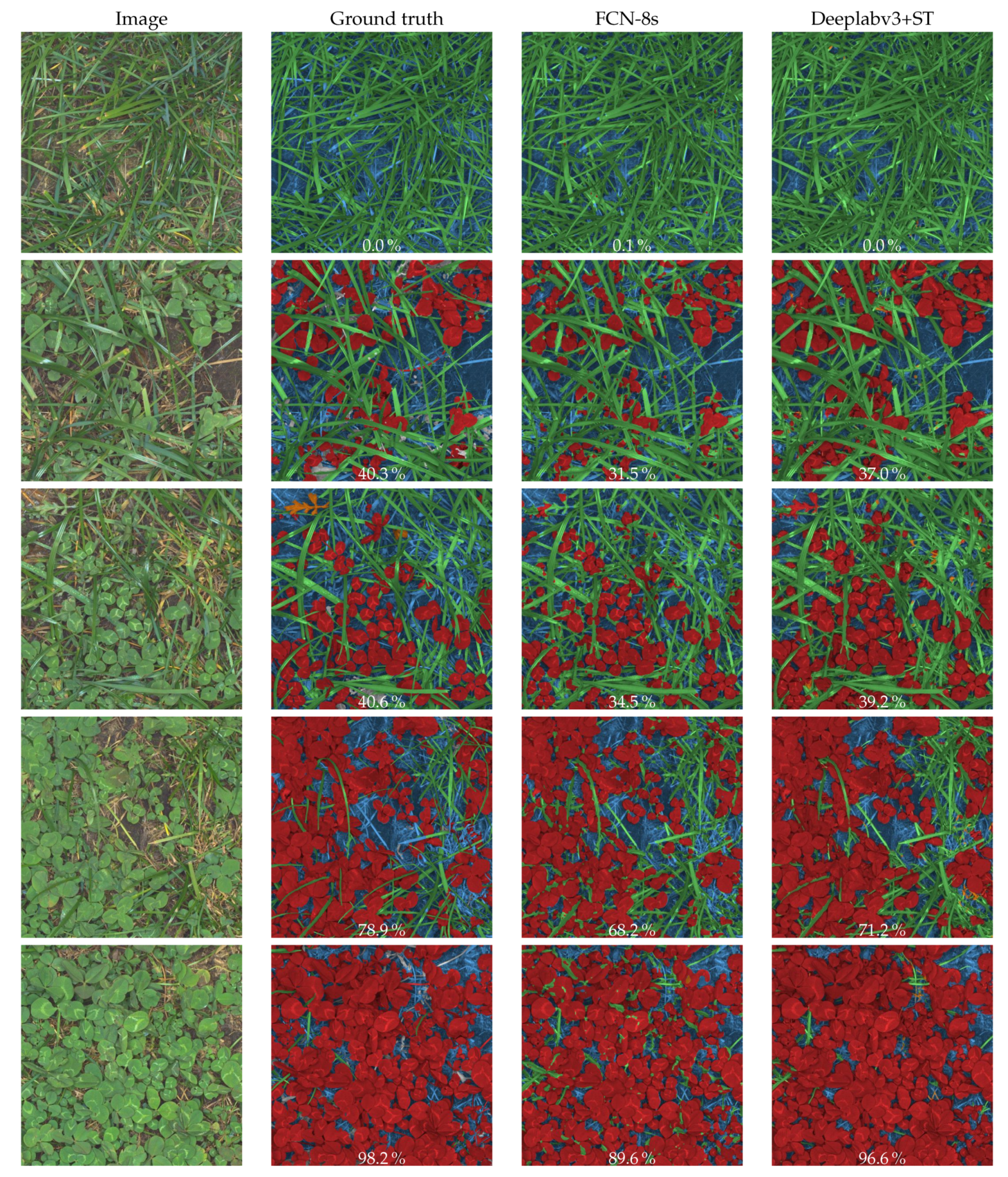
4.1. Semantic Segmentation
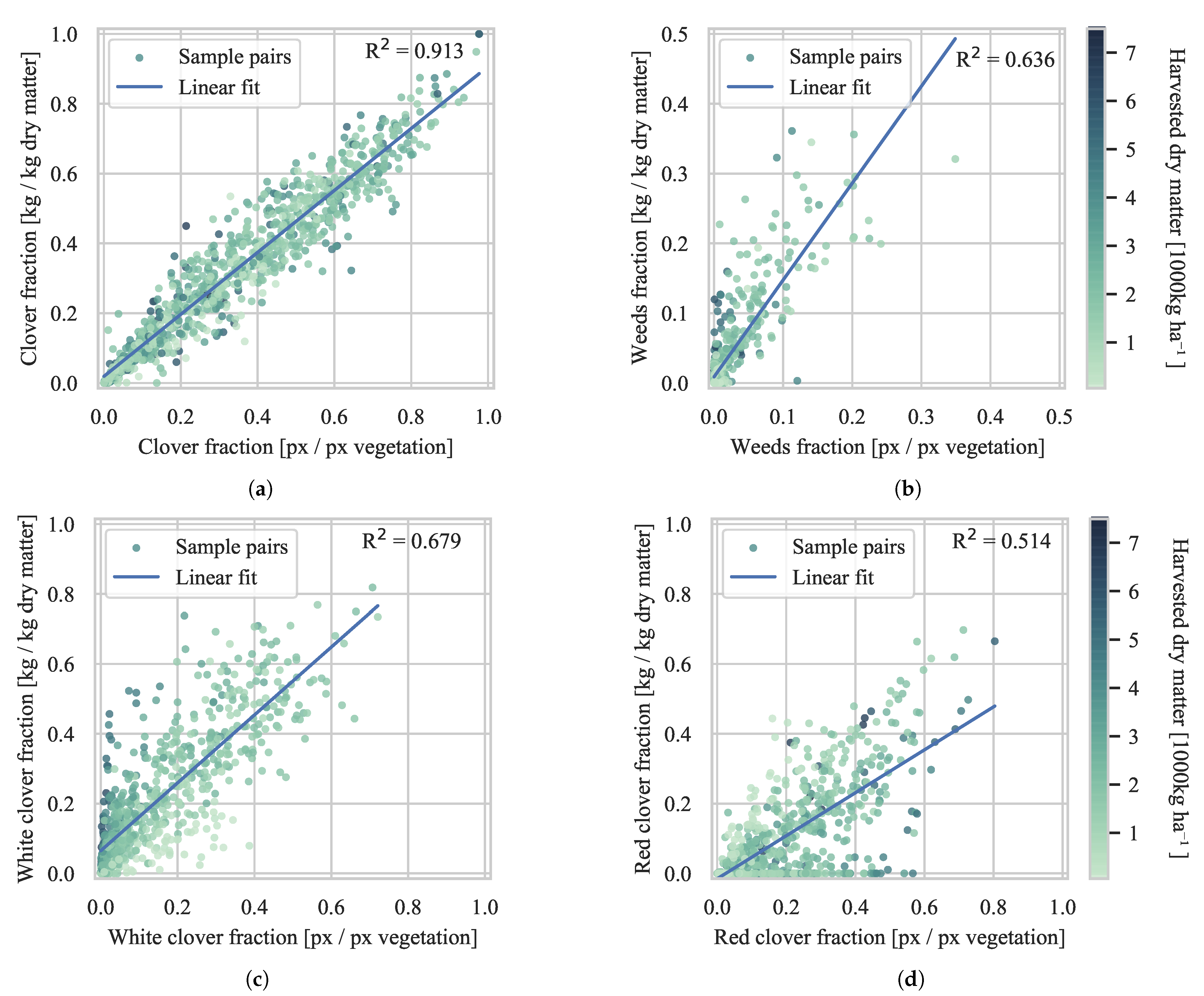
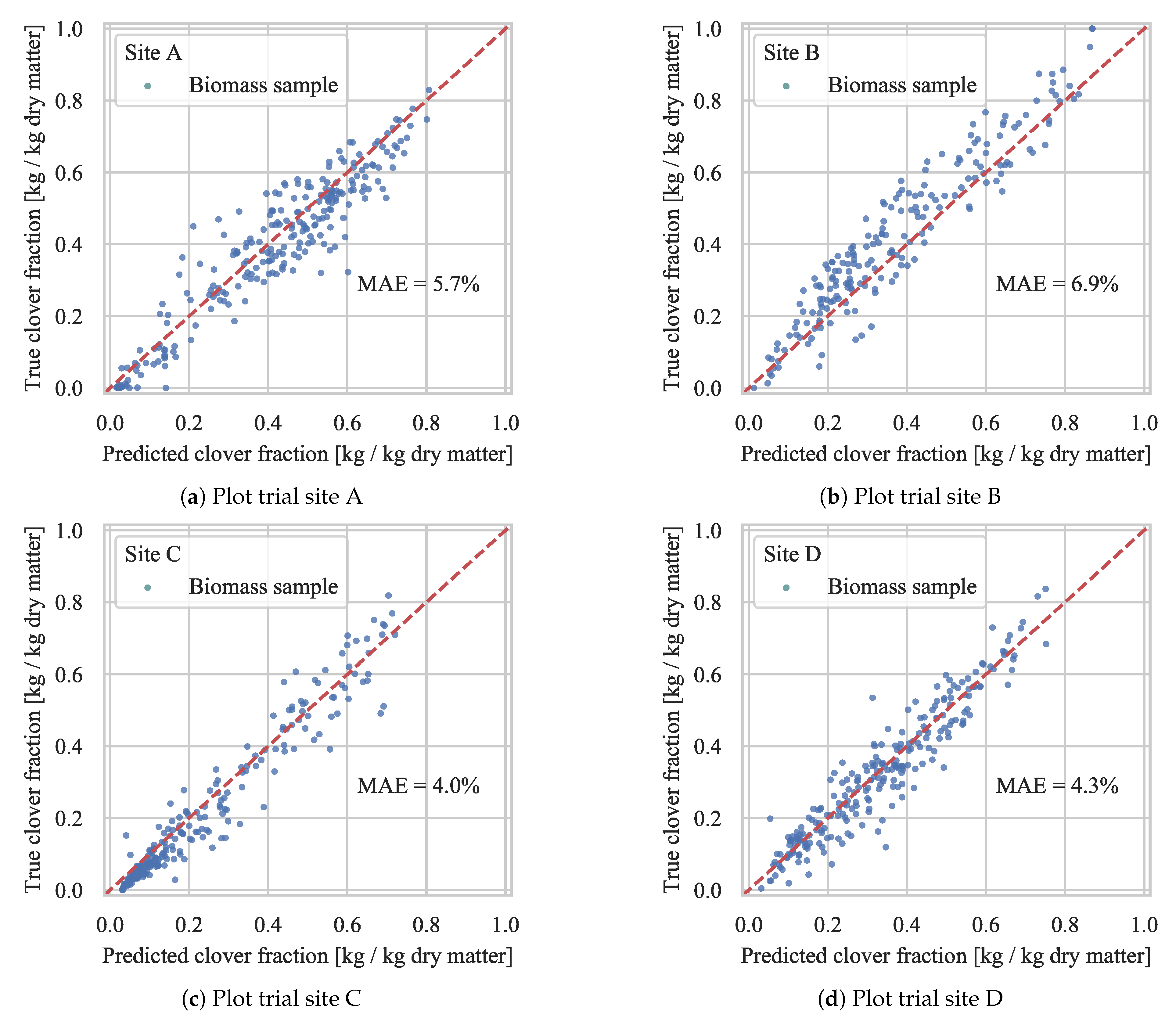
4.2. Biomass Composition Prediction
4.2.1. Evaluation of Generalization
4.2.2. Comparison with Previous Studies
4.2.3. Test Set Validation
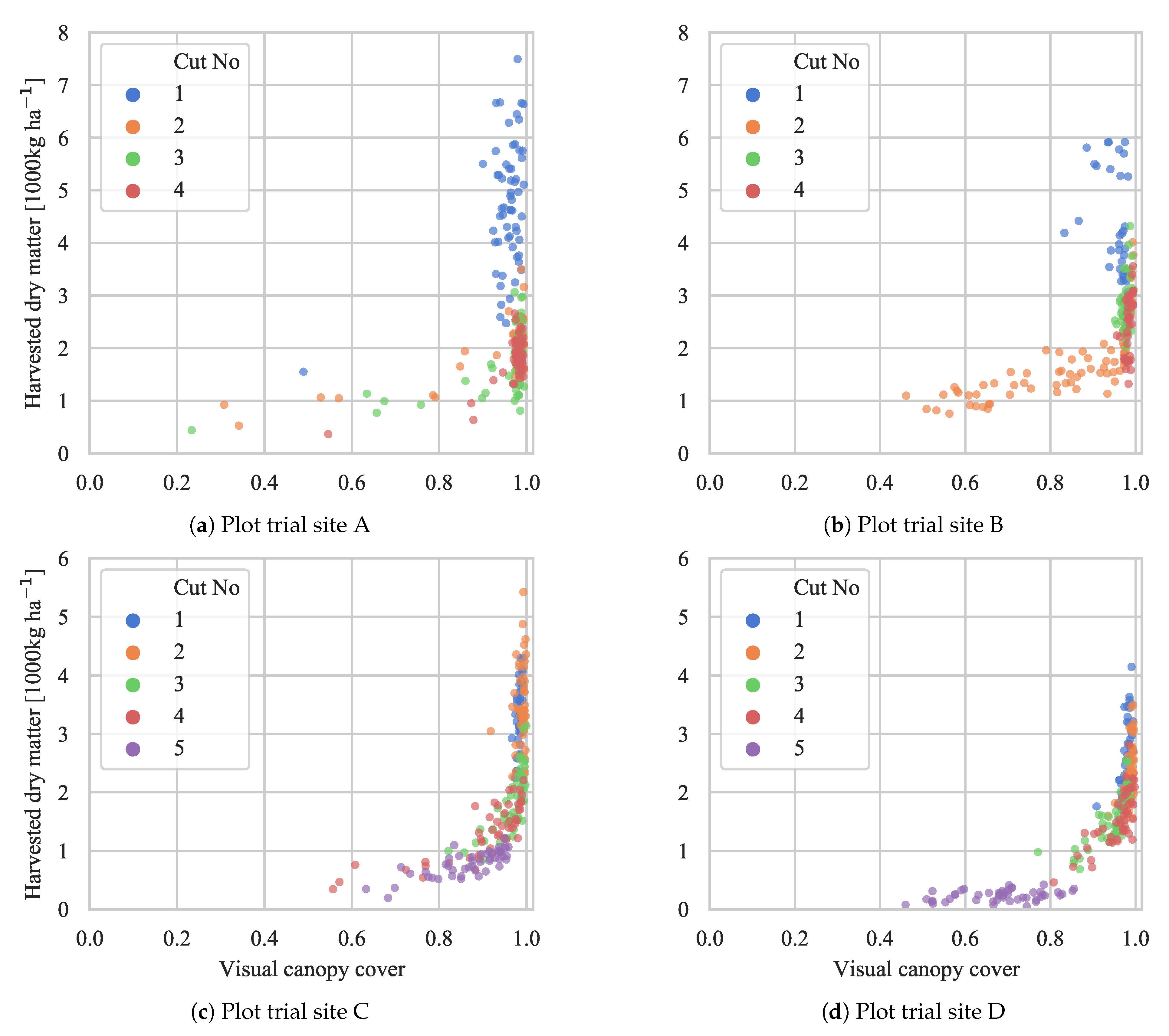
4.3. Biomass Yield Prediction
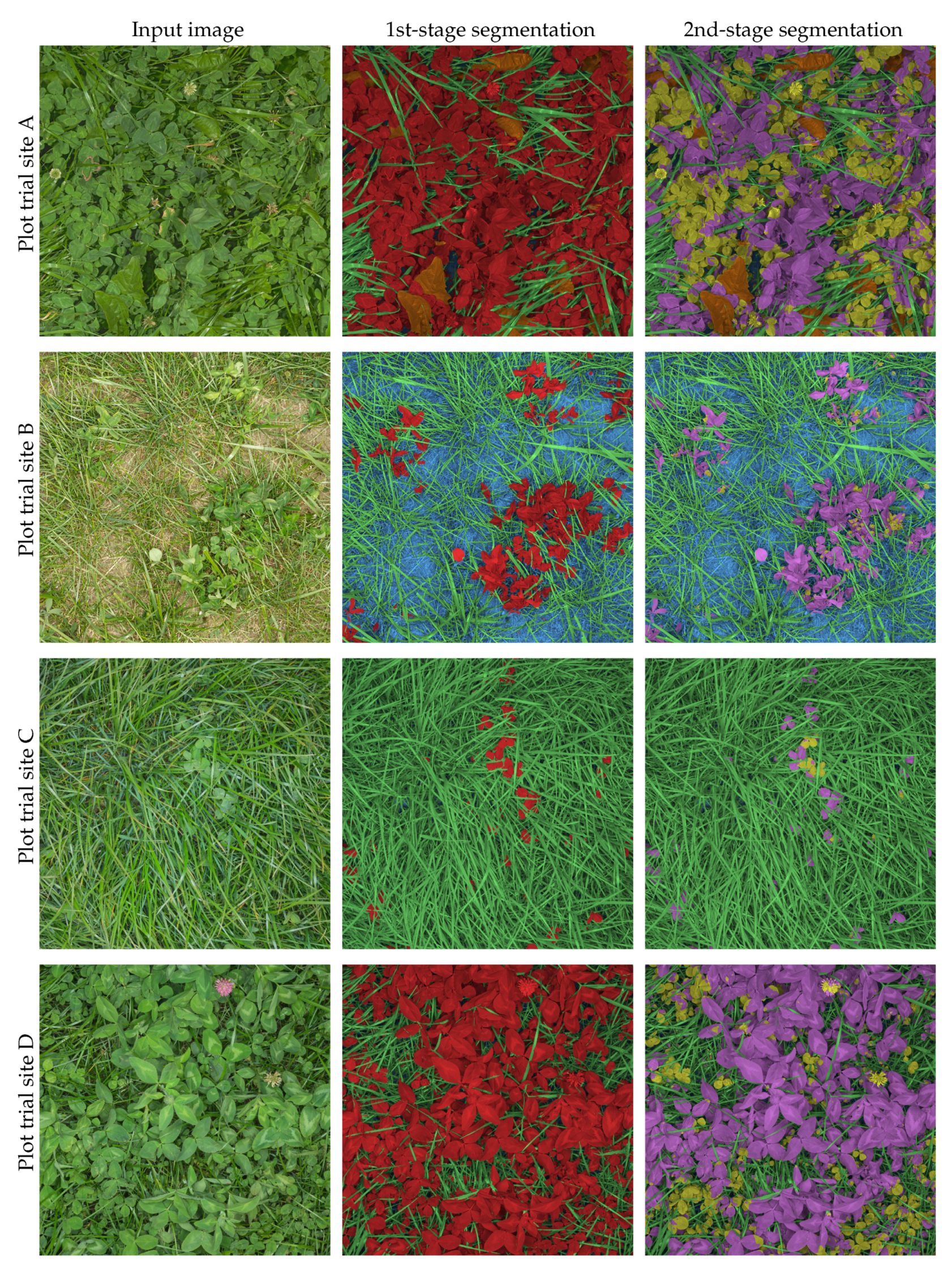
4.4. Large Scale Mixed Crop Mapping
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eriksen, J.; Frandsen, T.; Knudsen, L.; Skovsen, S.; Nyholm Jørgensen, R.; Steen, K.; Green, O.; Rasmussen, J. Nitrogen fertilization of grass-clover leys. Improving Sown Grasslands Through Breeding and Management. In Proceedings of the Grassland Science in Europe, Zürich, Switzerland, 24–27 June 2019; pp. 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, C.J.; Fourie, J.; Hsiao, J.; Irie, K.; Heslop, A.; Hilditch, A.; Hagedorn, M.; Jessep, B.; Gebbie, S.; Ghamkhar, K. Assessment of Mixed Sward Using Context Sensitive Convolutional Neural Networks. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skovsen, S.; Dyrmann, M.; Mortensen, A.K.; Steen, K.A.; Green, O.; Eriksen, J.; Gislum, R.; Jørgensen, R.N.; Karstoft, H. Estimation of the Botanical Composition of Clover-Grass Leys from RGB Images Using Data Simulation and Fully Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems—Volume 1; NIPS’12; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Bonesmo, H.; Kaspersen, K.; Kjersti Bakken, A. Evaluating an image analysis system for mapping white clover pastures. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. Soil Plant Sci. 2004, 54, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himstedt, M.; Fricke, T.; Wachendorf, M. Determining the Contribution of Legumes in Legume–Grass Mixtures Using Digital Image Analysis. Crop Sci. 2009, 49, 1910–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himstedt, M.; Fricke, T.; Wachendorf, M. The Relationship between Coverage and Dry Matter Contribution of Forage Legumes in Binary Legume—Grass Mixtures. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 2186–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himstedt, M.; Fricke, T.; Wachendorf, M. The Benefit of Color Information in Digital Image Analysis for the Estimation of Legume Contribution in Legume–Grass Mixtures. Crop Sci. 2012, 52, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, A.; Karstoft, H.; Søegaard, K.; Gislum, R.; Jørgensen, R. Preliminary Results of Clover and Grass Coverage and Total Dry Matter Estimation in Clover-Grass Crops Using Image Analysis. J. Imaging 2017, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayburn, E.B. Measuring Legume Content in Pastures Using Digital Photographs. Forage Grazinglands 2014, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovsen, S.; Dyrmann, M.; Eriksen, J.; Gislum, R.; Karstoft, H.; Jørgensen, R.N. Predicting Dry Matter Composition of Grass Clover Leys Using Data Simulation and Camera-Based Segmentation of Field Canopies into White Clover, Red Clover, Grass and Weeds. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Precision Agriculture, Montreal, QC, Canada, 24–27 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bakken, A.K.; Bonesmo, H.; Pedersen, B. Spatial and temporal abundance of interacting populations of white clover and grass species as assessed by image analyses. Dataset Pap. Sci. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovsen, S.; Laursen, M.; Gislum, R.; Eriksen, J.; Dyrmann, M.; Mortensen, A.; Farkhani, S.; Karstoft, H.; Jensen, N.; Jørgensen, R. Species distribution mapping of grass clover leys using images for targeted nitrogen fertilization. In Precision Agriculture ’19; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2019; Chapter 79; pp. 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovsen, S.; Dyrmann, M.; Mortensen, A.K.; Laursen, M.S.; Gislum, R.; Eriksen, J.; Farkhani, S.; Karstoft, H.; Jorgensen, R.N. The GrassClover Image Dataset for Semantic and Hierarchical Species Understanding in Agriculture. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 5–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Quigley, M.; Conley, K.; Gerkey, B.P.; Faust, J.; Foote, T.; Leibs, J.; Wheeler, R.; Ng, A.Y. ROS: An open-source Robot Operating System. In Proceedings of the ICRA Workshop on Open Source Software, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Malvar, R.; He, L.w.; Cutler, R. High-Quality Linear Interpolation for Demosaicing of Bayer-Patterned Color Images. In International Conference of Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing; International Conference of Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing, Ed.; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- McRoberts, K.C.; Benson, B.M.; Mudrak, E.L.; Parsons, D.; Cherney, D.J. Application of local binary patterns in digital images to estimate botanical composition in mixed alfalfa—Grass fields. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 123, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 833–851. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google Deeplab Github Repository. Available online: https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/research/deeplab (accessed on 31 July 2020).
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. (IJCV) 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2014; Fleet, D., Pajdla, T., Schiele, B., Tuytelaars, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Xing, W.; Lu, D. GLStyleNet: Higher Quality Style Transfer Combining Global and Local Pyramid Features. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.07260v1. [Google Scholar]
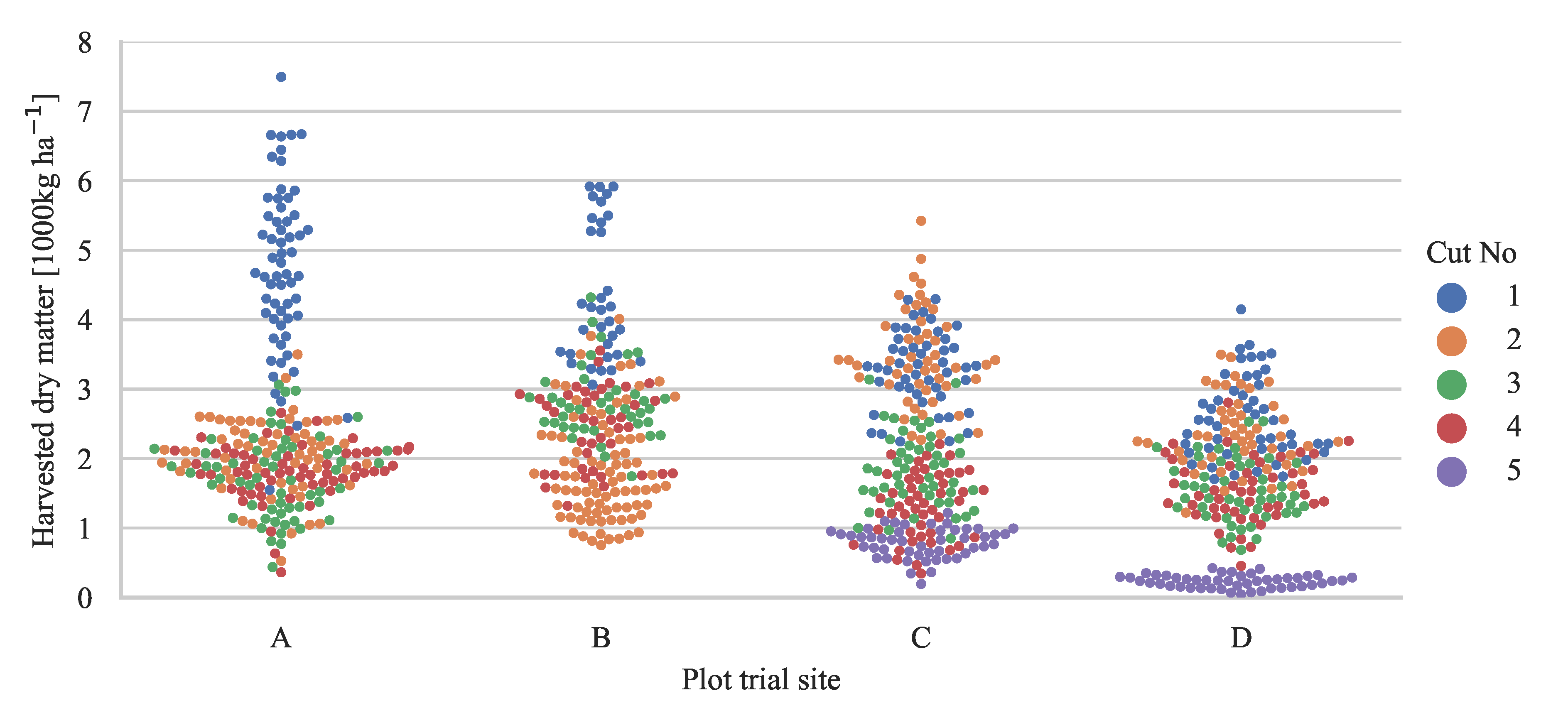





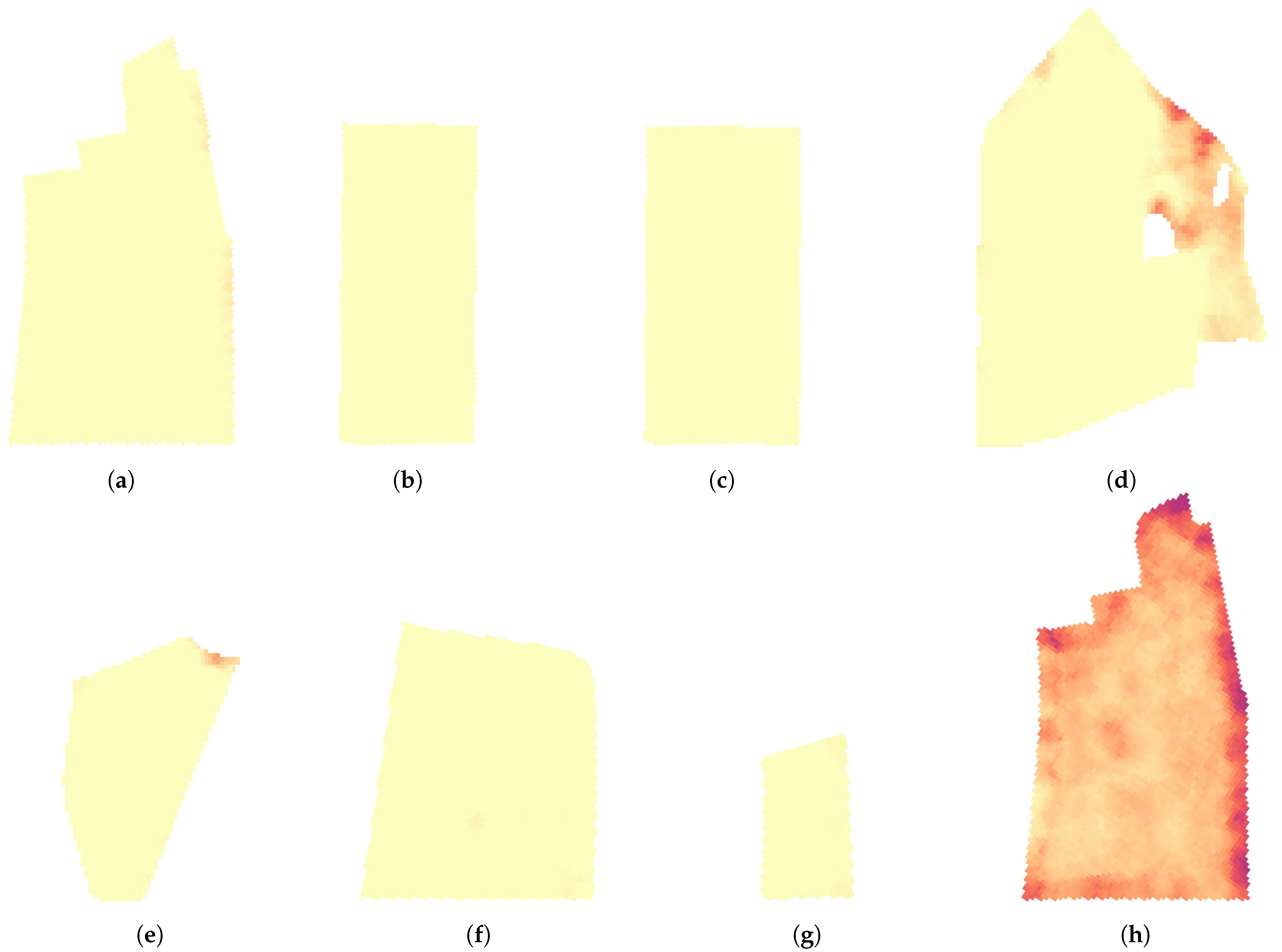
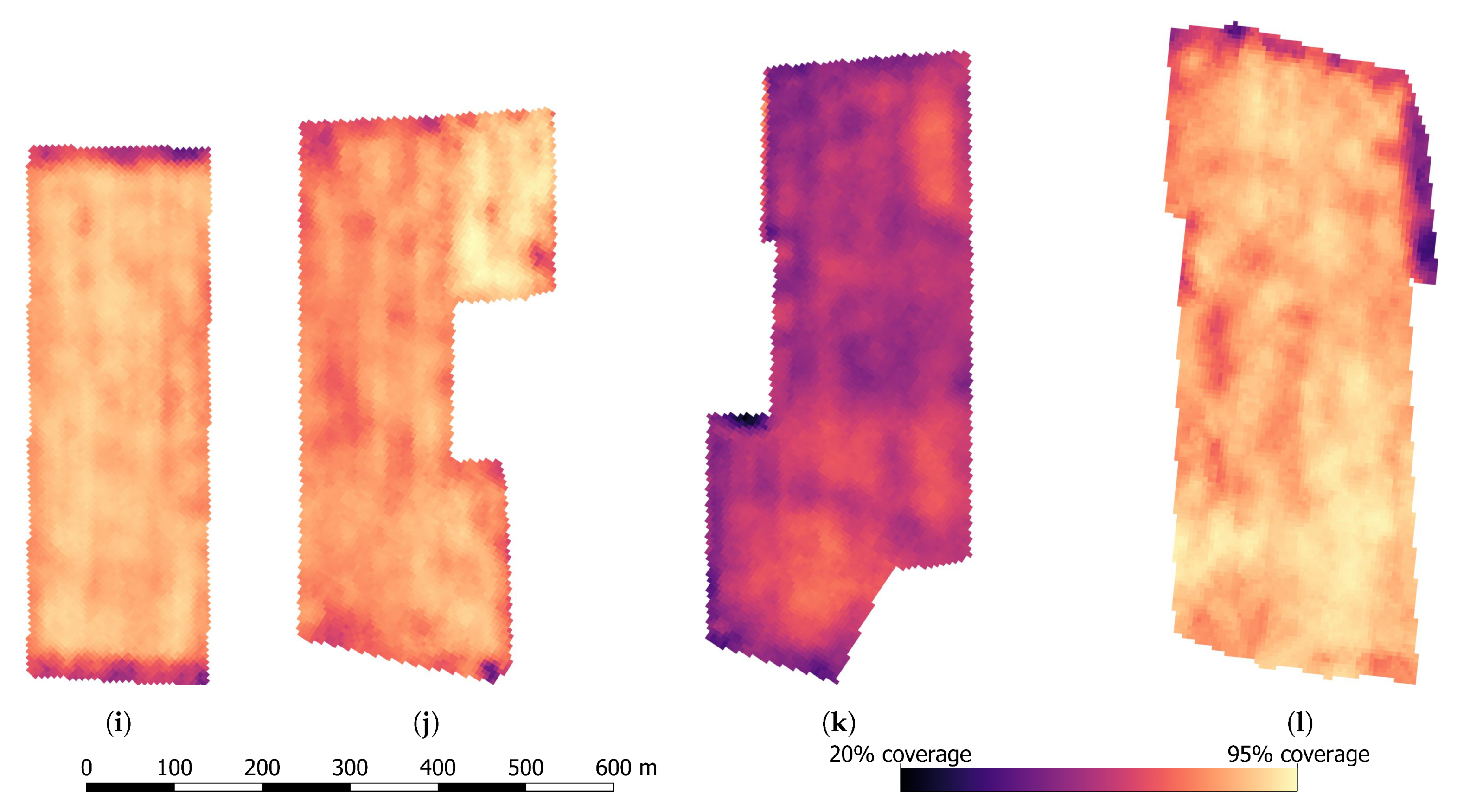
| Plot Trial Site | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seeded plant species | ||||
| Lolium perenne | ✓ | (✓) | ✓ | ✓ |
| × Festulolium | (✓) | ✓ | ||
| Trifolium repens | ✓ | (✓) | ✓ | ✓ |
| Trifolium pratense | ✓ | (✓) | ✓ | |
| Herbicides | ✓ | |||
| Soil type | Loamy sand | Sandy loam | Loamy sand | Coarse sand |
| Cuts per season | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 |
| No. of plots at site | 60 | >200 | 48 | 48 |
| Years since plot establishment | 1–4 | 1–2 | 2 | 2 |
| Sample years | 2017 | 2017–18 | 2019 | 2019 |
| Acquisition weather conditions | ||||
| Sunny | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Rain | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Morning dew | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Location | ||||
| Latitude | 56.4957 | 55.3397 | 55.5370 | 56.1702 |
| Longitude | 9.5693 | 12.3808 | 8.4952 | 8.7816 |
| Camera system samples | ||||
| Nikon D810A + LED flash | 179 | 83 | ||
| Sony a7 + ring flash | 60 | 113 | 180 | 240 |
| Sony a7 + speedlight flash | 60 | |||
| Total number of biomass samples | 239 | 196 | 240 | 240 |
| Farm | Field | Area [ha] | Acquisition Time [mm:ss] | Images | Density [Images ha−1] | Speed [ha hour −1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| May 2018 | ||||||
| A | 1 | 11.3 | 44:35 | 2223 | 197 | 15.3 |
| A | 2 | 18.6 | 67:01 | 3398 | 183 | 16.7 |
| A | 3 | 8.1 | 23:04 | 1188 | 145 | 21.1 |
| A | 4 | 7.1 | 26:50 | 1330 | 185 | 15.9 |
| B | 1 | 14.2 | 49:58 | 2025 | 143 | 17.1 |
| B | 2 | 4.8 | 17:50 | 723 | 148 | 16.1 |
| B | 3 | 9.2 | 40:43 | 1202 | 135 | 13.6 |
| B | 4 | 2.2 | 10:50 | 1202 | 135 | 12.2 |
| Oct 2018 | ||||||
| A | 1 | 11.3 | 34:38 | 1380 | 122 | 19.6 |
| A | 2 | 45.8 | 28:16 | 1422 | 31 | 97.2 |
| A | 3 | 16.9 | 49:25 | 2423 | 143 | 20.5 |
| A | 4 | 14.6 | 46:49 | 2170 | 148 | 18.7 |
| A | 5 | 12.5 | 44:11 | 2163 | 173 | 17.0 |
| C | 1 | 9.4 | 47:06 | 1878 | 200 | 12.0 |
| C | 2 | 20.5 | 78:12 | 3324 | 162 | 15.7 |
| C | 3 | 18.8 | 58:46 | 2999 | 160 | 19.2 |
| Cascaded CNN Models | Intersection over Union [%] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Stage Model | 2nd Stage Model | Mean | Grass | White Clover | Red Clover | Weeds | Soil |
| FCN-8s [16] | FCN-8s [16] | 55.0 | 64.6 | 59.5 | 72.6 | 39.1 | 39.0 |
| DeepLabv3 + ST | DeepLabv3+ | 65.8 | 78.5 | 62.3 | 75.0 | 51.4 | 61.6 |
| DeepLabv3 + ST | FCN-8s [16] | 68.4 | 78.5 | 70.5 | 80.1 | 51.4 | 61.6 |
| Cascaded CNN Models | Relative Biomass R2 [%] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Stage Model | 2nd Stage Model | Total Clover | Grass | White Clover | Red Clover | Weeds |
| FCN-8s [16] | FCN-8s [16] | 84.1 | 87.2 | 61.1 | 53.5 | 46.1 |
| DeepLabv3+ | DeepLabv3+ | 88.6 | 87.3 | 64.8 | 44.9 | 53.8 |
| DeepLabv3 + ST | DeepLabv3+ | 91.3 | 90.5 | 64.4 | 45.8 | 64.6 |
| DeepLabv3 + ST | FCN-8s [16] | 91.3 | 90.5 | 67.9 | 51.4 | 64.6 |
| Relative Clover Biomass R2 [%] | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cut 1 | Cut 2 | Cut 3 | Cut 4 | Cut 5 | All Cuts | ||
| Morph. filt. | Site A | 71.8 | 81.3 | 79.9 | 36.3 | - | 19.1 |
| Site B | 65.6 | 68.1 | 69.9 | 22.5 | - | 64.8 | |
| Site C | 92.7 | 89.2 | 75.5 | 91.5 | 88.9 | 54.8 | |
| Site D | 67.9 | 65.3 | 61.5 | 81.8 | 68.0 | 54.2 | |
| All sites | 36.4 | 26.4 | 59.3 | 58.3 | 76.4 | 36.9 | |
| FCN-8s | Site A | 74.1 | 87.8 | 87.8 | 56.9 | - | 74.4 |
| Site B | 90.7 | 84.3 | 87.3 | 79.6 | - | 84.9 | |
| Site C | 95.0 | 91.2 | 93.4 | 95.3 | 94.8 | 92.8 | |
| Site D | 90.9 | 84.8 | 92.6 | 91.2 | 68.7 | 86.1 | |
| All sites | 88.4 | 79.9 | 89.9 | 86.1 | 79.0 | 84.1 | |
| DeepLabv3+ | Site A | 82.1 | 94.4 | 95.1 | 67.0 | - | 87.8 |
| Site B | 92.5 | 92.6 | 90.6 | 87.6 | - | 90.2 | |
| Site C | 95.5 | 93.4 | 95.4 | 97.5 | 95.6 | 94.6 | |
| Site D | 92.0 | 87.2 | 94.1 | 91.6 | 70.6 | 89.8 | |
| All sites | 91.2 | 90.7 | 92.8 | 91.4 | 85.3 | 91.3 | |
| Method | Data Source | BM Range [1000 kg ha−1] | GSD [mm−1] | No. Samples | No. Cuts | Eval. Sites | Species Mixture | Clover R2 [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Morph. filtering [8] | [8] | < 2.8 | 2 | 24 | 3 | 1 | wc, rg | 85 |
| FCN-8s [2] | [2] | 1.0–3.3 | 2–3 | 70 | 2 | 1 | wc, rg | 79.3 |
| LC-Net [2] | [2] | 1.0–3.3 | 2–3 | 70 | 2 | 1 | wc, rg | 82.5 |
| Morph. filtering [9] | Site C | 0.2–5.4 | 6 | 240 | 5 | 1 | wc, rg | 54.8 |
| FCN-8s [16] | Site C | 0.2–5.4 | 6 | 240 | 5 | 1 | wc, rg | 92.8 |
| DeeplabV3 + ST | Site C | 0.2–5.4 | 6 | 240 | 5 | 1 | wc, rg | 94.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skovsen, S.K.; Laursen, M.S.; Kristensen, R.K.; Rasmussen, J.; Dyrmann, M.; Eriksen, J.; Gislum, R.; Jørgensen, R.N.; Karstoft, H. Robust Species Distribution Mapping of Crop Mixtures Using Color Images and Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors 2021, 21, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010175
Skovsen SK, Laursen MS, Kristensen RK, Rasmussen J, Dyrmann M, Eriksen J, Gislum R, Jørgensen RN, Karstoft H. Robust Species Distribution Mapping of Crop Mixtures Using Color Images and Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors. 2021; 21(1):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010175
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkovsen, Søren Kelstrup, Morten Stigaard Laursen, Rebekka Kjeldgaard Kristensen, Jim Rasmussen, Mads Dyrmann, Jørgen Eriksen, René Gislum, Rasmus Nyholm Jørgensen, and Henrik Karstoft. 2021. "Robust Species Distribution Mapping of Crop Mixtures Using Color Images and Convolutional Neural Networks" Sensors 21, no. 1: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010175
APA StyleSkovsen, S. K., Laursen, M. S., Kristensen, R. K., Rasmussen, J., Dyrmann, M., Eriksen, J., Gislum, R., Jørgensen, R. N., & Karstoft, H. (2021). Robust Species Distribution Mapping of Crop Mixtures Using Color Images and Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors, 21(1), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21010175






