High-Resolution Neural Network for Driver Visual Attention Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Saliency Map Estimation and Visual Attention Prediction in Driving Scene
2.2. Convolutional Neural Networks for Pixel-Wise Prediction
3. Proposed Approach
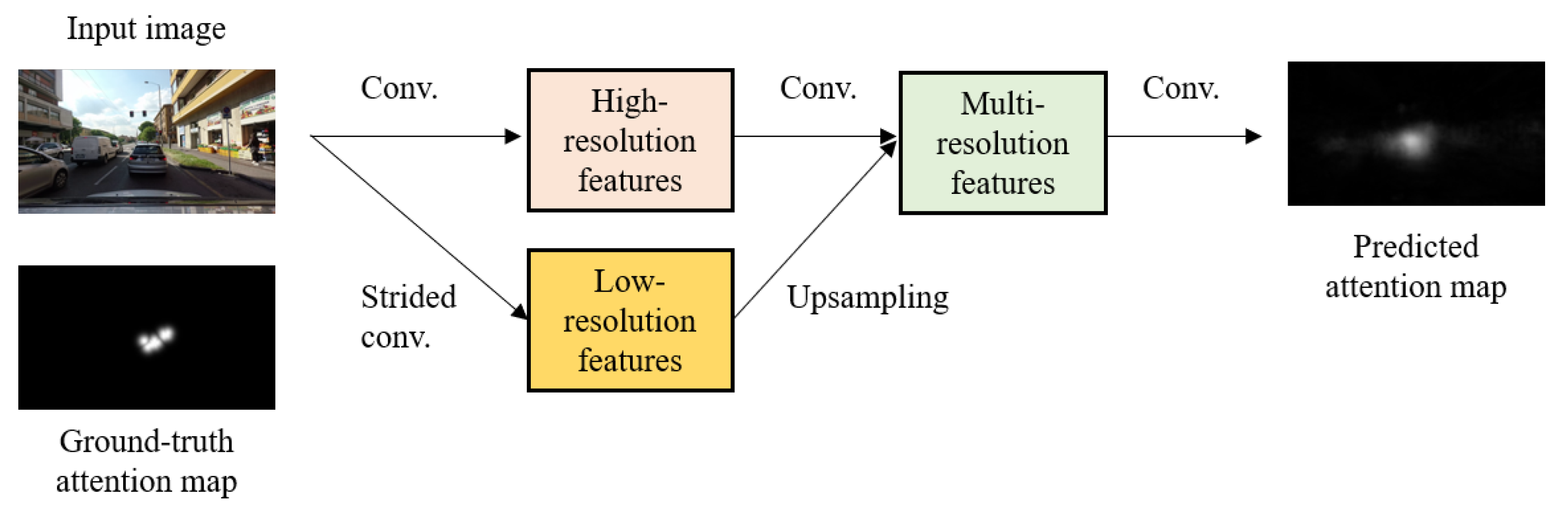
3.1. Key Considerations
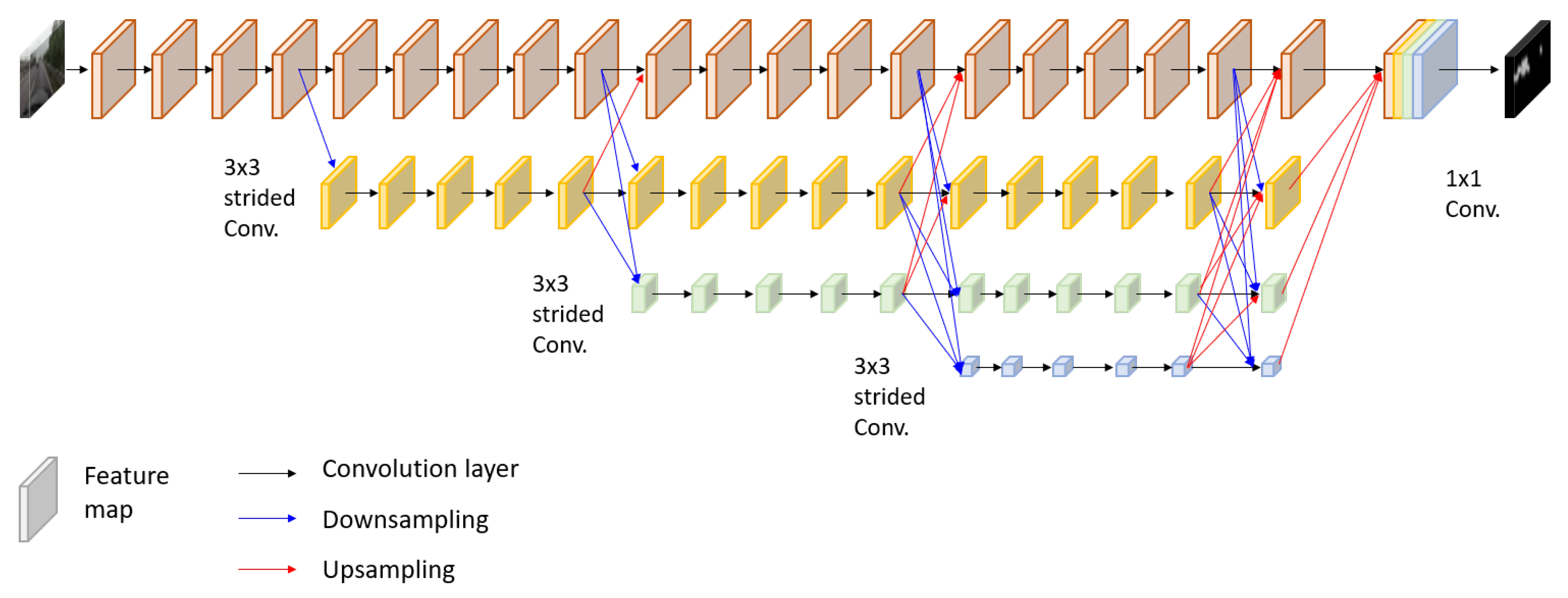
3.2. Model Description
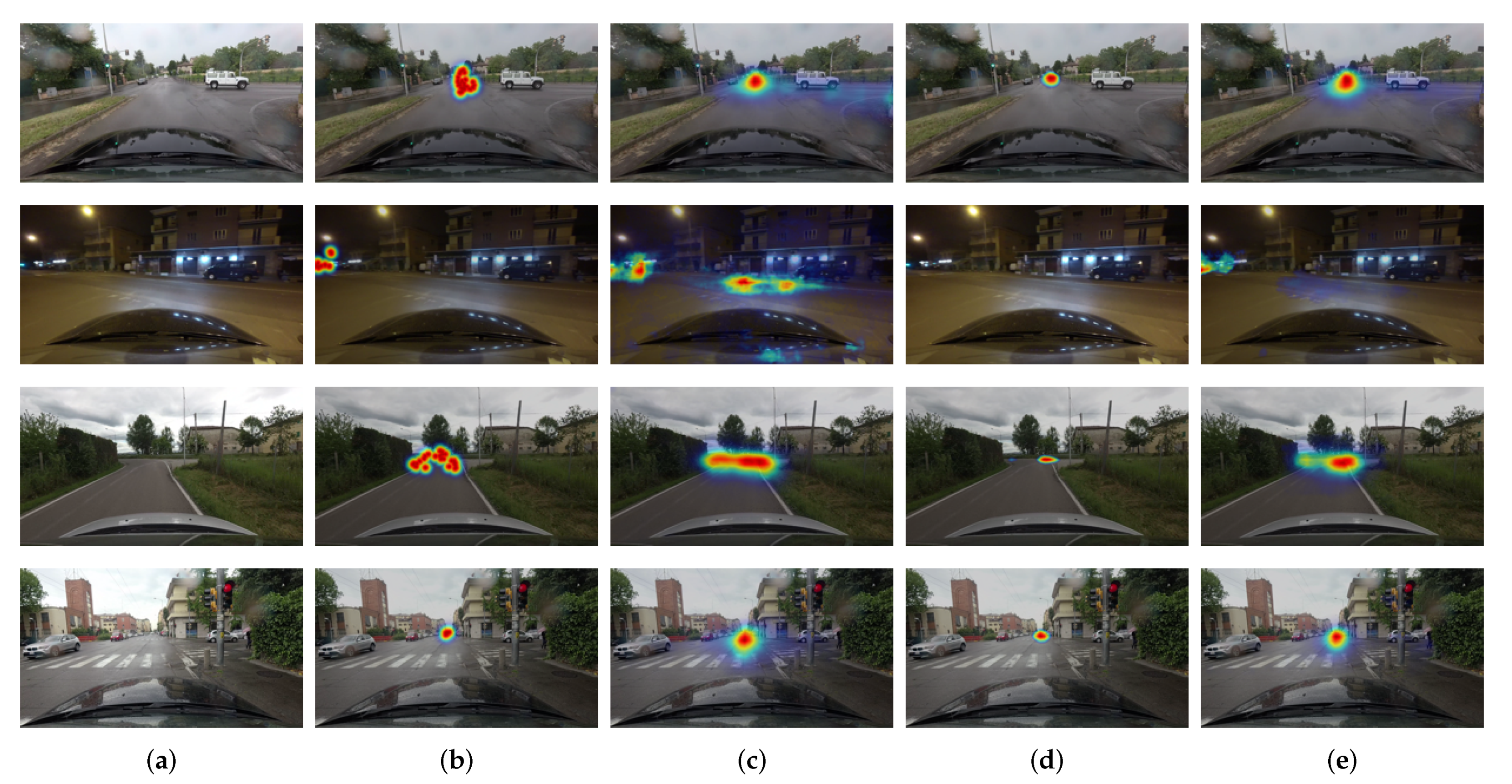
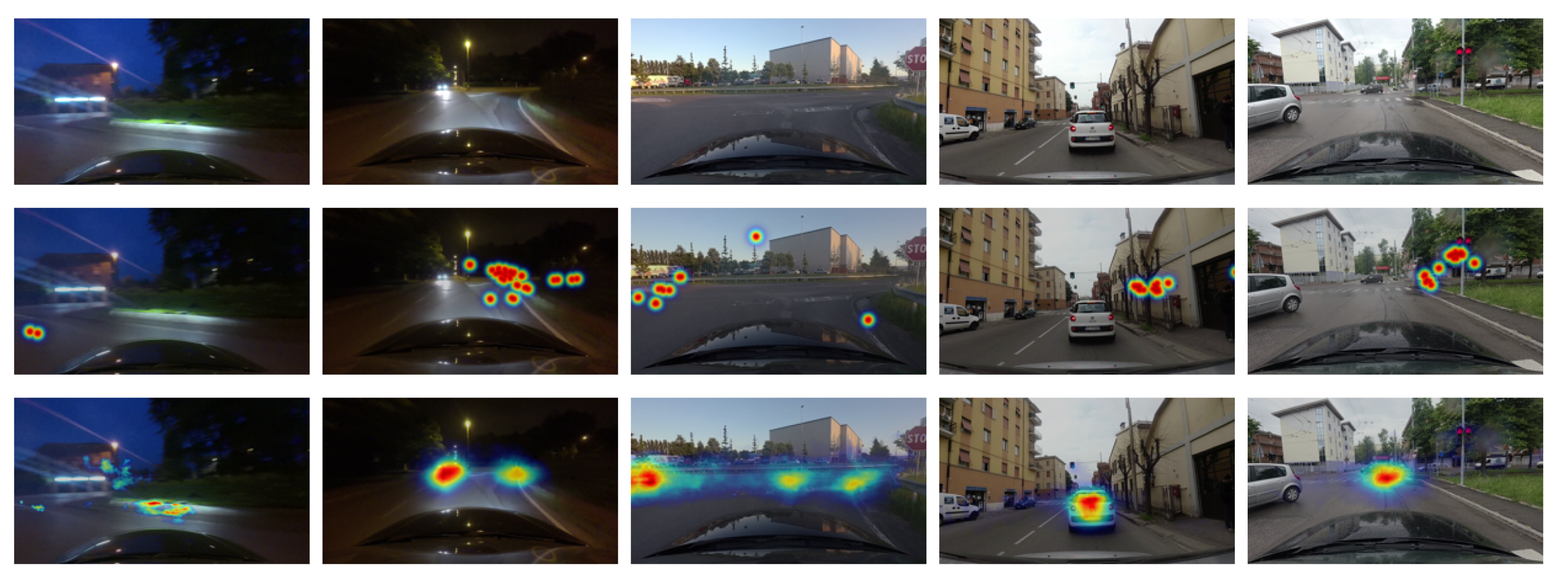
4. Experimental Setup and Results
4.1. Dataset
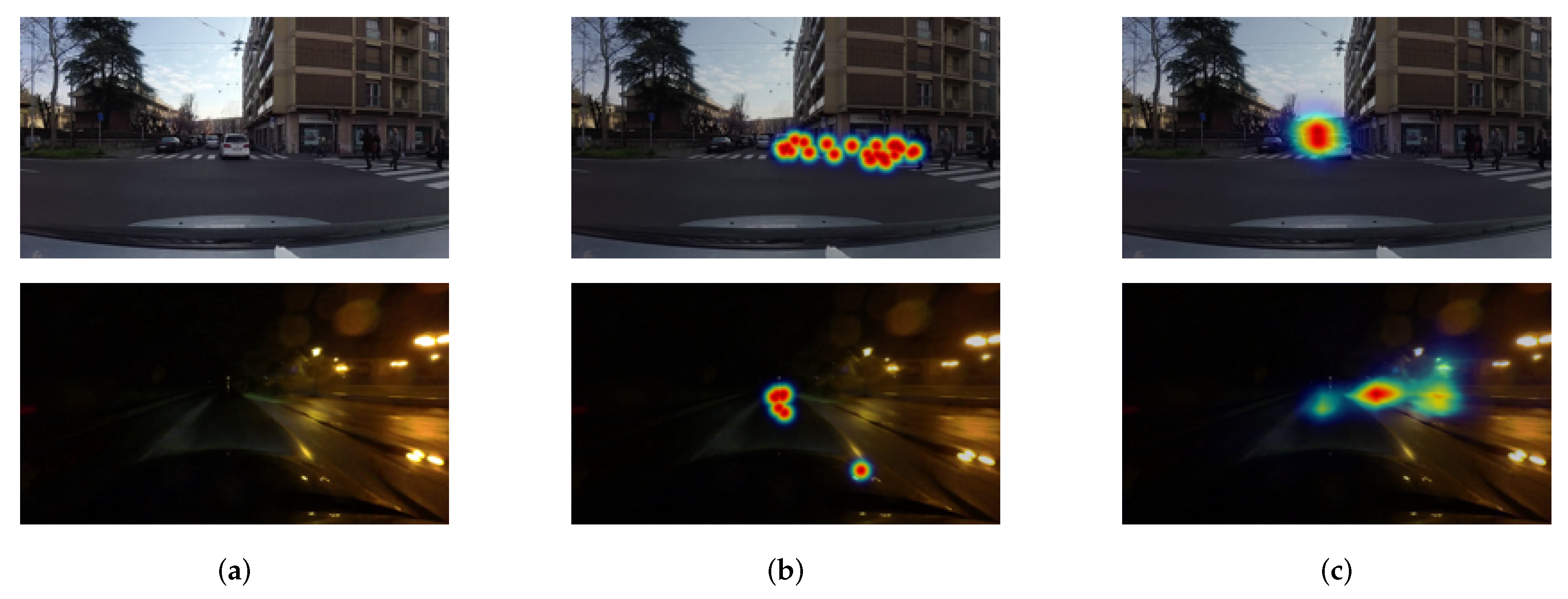
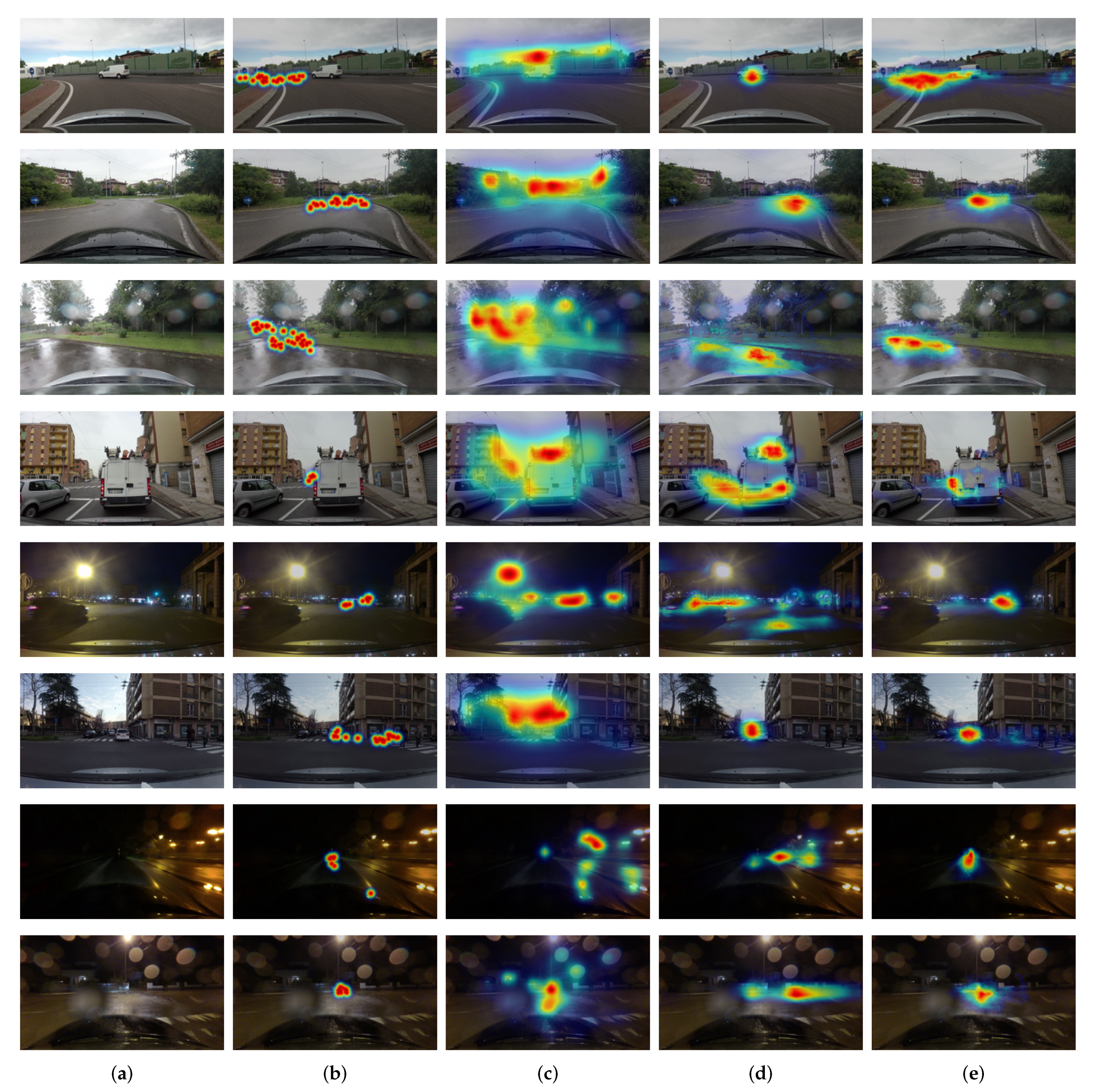
4.2. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADAS | Advanced Driver-Assistance System |
| GBVS | Graph-Base Visual Saliency |
| FCN | Fully Convolutional Network |
| BDD-A | Berkeley DeepDrive Attention |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| RefineNet | Multi-Path Refinement Network |
| ASPP | Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling |
| PSPNet | Pyramid Scene Parsing Network |
| FRRU | Full-Resolution Residual Units |
| ICNet | Image Cascade Network |
| SGD | Stochastic Gradient Descent |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
| NSS | Normalized Scanpath Saliency |
| AUC | Area under ROC Curve |
References
- Ohn-Bar, E.; Trivedi, M.M. Are all objects equal? Deep spatio-temporal importance prediction in driving videos. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 64, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugeault, N.; Bowden, R. How Much of Driving Is Preattentive? IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2015, 64, 5424–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.H.; Bong, J.H.; Park, J.; Park, S. Prediction of driver’s intention of lane change by augmenting sensor information using machine learning techniques. Sensors 2017, 17, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itti, L.; Koch, C. Computational modelling of visual attention. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owsley, C.; McGwin, G., Jr. Vision and driving. Vis. Res. 2010, 50, 2348–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loschky, L.C.; Nuthmann, A.; Fortenbaugh, F.C.; Levi, D.M. Scene perception from central to peripheral vision. J. Vis. 2017, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lumen, A.B.; Lim, R.A.; Orosa, K.; Paralleon, D.; Sedilla, K. Driver Distraction: Determining the Ideal Location of a Navigation Device for Transportation Network Vehicle Services (TNVS) Drivers in Metro Manila. In International Conference on Applied Human Factors and Ergonomics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 554–563. [Google Scholar]
- Valenti, R.; Sebe, N.; Gevers, T. Combining Head Pose and Eye Location Information for Gaze Estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 802–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, L.; Langhans, P.; Lee, J.; Reimer, B. Driver gaze region estimation without use of eye movement. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2016, 31, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawari, A.; Kang, B. A computational framework for driver’s visual attention using a fully convolutional architecture. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 11–14 June 2017; pp. 887–894. [Google Scholar]
- Palazzi, A.; Abati, D.; Solera, F.; Cucchiara, R. Predicting the Driver’s Focus of Attention: The DR (eye) VE Project. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 1720–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, D.; Kim, J.; Nakayama, K.; Zipser, K.; Whitney, D. Predicting driver attention in critical situations. In Asian Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 658–674. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, X.; Huang, S.; Feng, Z.; Wei, Z. Spatial Attention Fusion for Obstacle Detection Using MmWave Radar and Vision Sensor. Sensors 2020, 20, 956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bylinskii, Z.; Judd, T.; Borji, A.; Itti, L.; Durand, F.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. MIT Saliency Benchmark; MIT: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, T.; Durand, F.; Torralba, A. A Benchmark of Computational Models of Saliency to Predict Human Fixations; MIT Technical Report; MIT: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Itti, L.; Koch, C.; Niebur, E. A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1998, 20, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, J.; Koch, C.; Perona, P. Graph-Based Visual Saliency. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS); Schölkopf, B., Platt, J.C., Hoffman, T., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 545–552. [Google Scholar]
- Lethaus, F.; Baumann, M.R.K.; Köster, F.; Lemmer, K. Using Pattern Recognition to Predict Driver Intent. Adaptive and Natural Computing Algorithms; Dobnikar, A., Lotrič, U., Šter, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 140–149. [Google Scholar]
- Tawari, A.; Kang, B. Systems and Methods of a Computational Framework for a Driver’s Visual Attention Using a Fully Convolutional Architecture. US Patent US20180225554A1, 9 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Shelhamer, E.; Long, J.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS); Pereira, F., Burges, C.J.C., Bottou, L., Weinberger, K.Q., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Canny, J. Interpretable learning for self-driving cars by visualizing causal attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2942–2950. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-Scale Context Aggregation by Dilated Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2–4 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W.M., Frangi, A.F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, H.; Hong, S.; Han, B. Learning Deconvolution Network for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1520–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, B.; Cheng, T.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. High-Resolution Representations for Labeling Pixels and Regions. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.04514. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 833–851. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6230–6239. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Milan, A.; Shen, C.; Reid, I. RefineNet: Multi-path Refinement Networks for High-Resolution Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5168–5177. [Google Scholar]
- Pohlen, T.; Hermans, A.; Mathias, M.; Leibe, B. Full-Resolution Residual Networks for Semantic Segmentation in Street Scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3309–3318. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Qi, X.; Shen, X.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. ICNet for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation on High-Resolution Images. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 418–434. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, N.D.; Catton, C.; Janjic, S. A deeper look at saliency: Feature contrast, semantics, and beyond. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 516–524. [Google Scholar]
- Tatler, B.W. The central fixation bias in scene viewing: Selecting an optimal viewing position independently of motor biases and image feature distributions. J. Vis. 2007, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, P.H.; Carmi, R.; Cameron, I.G.; Munoz, D.P.; Itti, L. Quantifying center bias of observers in free viewing of dynamic natural scenes. J. Vis. 2009, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.H. Probability, Statistics, and Random Processes for Engineers; Cl-Engineering: Chon Buri, Thailand, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Leon-Garcia, A. Probability, Statistics, and Random Processes for Electrical Engineering; Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bylinskii, Z.; Judd, T.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A.; Durand, F. What do different evaluation metrics tell us about saliency models? IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 740–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Model | Baseline | Itti [16] | GBVS [17] | Tawari [10] | HWS [12] | Multi-Branch [11] | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average CC |
| Activation Function | Linear | Hyperbolic Tangent | Hard Hyperbolic Tangent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average CC | 0.59 | 0.57 | 0.60 |
| Activation | Linear | Hyperbolic Tangent | Hard hyperbolic Tangent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scene | |||
| Downtown | 0.55 | 0.53 | 0.54 |
| Countryside | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.55 |
| Highway | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.65 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, B.; Lee, Y. High-Resolution Neural Network for Driver Visual Attention Prediction. Sensors 2020, 20, 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072030
Kang B, Lee Y. High-Resolution Neural Network for Driver Visual Attention Prediction. Sensors. 2020; 20(7):2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072030
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Byeongkeun, and Yeejin Lee. 2020. "High-Resolution Neural Network for Driver Visual Attention Prediction" Sensors 20, no. 7: 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072030
APA StyleKang, B., & Lee, Y. (2020). High-Resolution Neural Network for Driver Visual Attention Prediction. Sensors, 20(7), 2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20072030





