Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Voltammetric Sensing of Benzotriazoles in Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Instrumentation and Apparatus
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Data Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Studies
3.2. Study by Differential Pulse Voltammetry
3.3. Determination of Benzotriazole in a Spiked Water Sample
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lapworth, D.J.; Baran, N.; Stuart, M.E.; Ward, R.S. Emerging organic contaminants in groundwater: A review of sources, fate, and occurrence. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, J.C.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Barbosa, M.O.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M. A review on environmental monitoring of water organic pollutants identified by EU guidelines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, S.D.; Kimura, S.Y. Water analysis: Emerging contaminants and current issues. Anal. Chem. 2015, 88, 546–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asimakopoulos, A.; Wang, L.; Thomaidis, N.; Kannan, K. Benzotriazoles and benzothiazoles in human urine from several countries: A perspective on the occurrence, biotransformation, and human exposure. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molins-Delgado, D.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Removal of polar UV stabilizers in biological wastewater treatments and ecotoxicological implications. Chemosphere 2015, 119, S51–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukawa, A.; Molins-Delgado, D.; de Azevedo, J.C.R.; Fernandes, C.V.S.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Sediments as a sink for UV filters and benzotriazoles: The case study of Upper Iguaçu watershed, Curitiba (Brazil). Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2017, R24, 18284–18294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish Environmental Protection Agency. Benzotriazole, and tolyltriazole. In Evaluation of Health Hazards and Proposal of Health-Based Quality Criteria for Soil and Drinking Water, Environmental Project No. 1526; The Danish Environmental Protection Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013; ISBN 978-87-93026-81-0. [Google Scholar]
- Rovira, J.; Domingo, J.L. Human health risks due to exposure to inorganic and organic chemicals from textiles: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 168, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janna, H.; Scrimshaw, M.D.; Williams, R.J.; Churchley, J.; Sumpter, J.P. From dishwasher to tap? Xenobiotic substances benzotriazole and tolyltriazole in the environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3858–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xue, J.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of and exposure to benzotriazoles and benzothiazoles from textiles and infant clothing. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2017, 592, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. NTP (National Toxicology Program), U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Chemical Information Review Document for Phenolic Benzotriazoles. Supporting Nomination for Toxicological Evaluation by the National Toxicology Program Research Triangle Park, NC2011. Available online: http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ (accessed on 25 March 2020).
- Gruden, C.L.; Dow, S.M.; Hernandez, M.T. Fate and toxicity of aircraft deicing fluid additives through anaerobic digestion. Water Environ. Res. 2001, 73, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reemtsma, T.; Miehe, U.; Duennbier, U.; Jekel, M. Polar pollutants in municipal wastewater and the water cycle: Occurrence and removal of benzotriazoles. Water Res. 2010, 44, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Wan, Y.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of benzotriazoles (BTRs) in indoor air from Albany, New York, USA, and its implications for inhalation exposure. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2017, 99, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valls-Cantenys, C.; Scheurer, M.; Iglesias, M.; Sacher, F.; Brauch, H.J.; Salvadó, V. A sensitive multi-residue method for the determination of 35 micropollutants including pharmaceuticals, iodinated contrast media, and pesticides in water. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 6189–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Molins-Delgado, D.; Serra-Roig, M.P.; Kalogianni, E.; Skoulikidis, N.T.; Barceló, D. Personal care products reconnaissance in Evrotas River (Greece): Water-sediment partition and bioaccumulation in fish. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3079–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; De Silva, A.O.; Peart, T.E.; Cook, C.J.; Tetreault, G.R.; Servos, M.R.; Muir, D.C.G. Distribution, partitioning and bioaccumulation of substituted diphenylamine antioxidants and benzotriazole UV stabilizers in an urban creek in Canada. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9089–9097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Peart, T.E.; Cook, C.J.; de Silva, A.O. Simultaneous determination of substituted diphenylamine antioxidants and benzotriazole ultraviolet stabilizers in blood plasma and fish homogenates by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1461, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Kannan, K. Accumulation of 19 environmental phenolic and xenobiotic heterocyclic aromatic compounds in human adipose tissue. Environ. Int. 2015, 78, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Sun, H.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q. Benzotriazoles and benzothiazoles in paired maternal urine and amniotic fluid samples from Tianjin, China. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molins-Delgado, D.; Olmo-Campos, M.M.; Valeta-Juan, G.; Barceló, D.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S. Determination of UV filters residues in human breast milk using turbulent flow chromatography. Environ. Res. 2018, 161, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwell, S.I.; Jordahl, D.M.; Evans, J.E.; May, E.B. Toxicity of aircraft de-icer and anti-icer solutions to aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1995, 14, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, J.S.; Pillard, D.A.; Hernandez, M.T. Comparative measures of the toxicity of component chemicals in aircraft deicing fluid. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000, 19, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancilla, D.A.; Holtkamp, A.; Matassa, L.; Fang, X. Isolation and characterization of Microtox®-active components from aircraft de-icing/anti-icing fluids. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1997, 16, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancilla, D.A.; Martinez, J.; van Aggelen, G.C. Detection of aircraft deicing/anti-icing fluid additives in perched water monitoring well at an international airport. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 3834–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwenberg, J.; Zenker, A.; Baggenstos, M.; Koch, G.; Kazner, C.; Wintgens, T. Comparison of two PAC/UF processes for the removal of micropollutants from wastewater treatment plant effluent: Process performance and removal efficiency. Water Res. 2014, 56, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, H.; Kwee, S. Electroorganic preparations. XXV. Polarography and reduction of benzotriazole and related compounds. Acta Chem. Scand. 1968, 22, 2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, S.U.; Lund, H. Electrochemical reduction of some benzotriazoles in protic and aprotic media. Acta Chem. Scand. B 1988, 42, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokesh, S.V.; Satpati, A.K.; Sherigara, B.S. Electrochemical behavior of 1, 2, 4-triazole and benzotriazole at glassy carbon electrode in acidic media. Open Electrochem. J. 2010, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; Pu, W.; Yang, C. Voltammetric behaviors of an emerging pollutant benzotriazole on multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWNTs)—Nafion modified electrode in various pH mediums. Ionics 2016, 22, 2059–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ababneh, A.N.; Abu-Dalo, M.A.; Horn, C.; Hernandez, M.T. Polarographic determination of benzotriazoles and their sorption behavior on granular activated carbon. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.T.; Li, D.W.; Long, Y.T. Recent developments and applications of screen-printed electrodes in environmental assays—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 734, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunyer, A.; González-Navarro, A.; Serra-Roig, M.P.; Serrano, N.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M. First application of carbon-based screen-printed electrodes for the voltammetric determination of the organic UV filters oxybenzone and octocrylene. Talanta 2019, 196, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, N.; Castilla, O.; Ariño, C.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M. Commercial screen-printed electrodes based on carbon nanomaterials for a fast and cost-effective voltammetric determination of paracetamol, ibuprofen, and caffeine in water samples. Sensors 2019, 19, 4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tromans, D.; Sun, R.H. Anodic polarization behavior of copper in aqueous chloride/benzotriazole solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1991, 138, 3235–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoski, C.G.; Leddy, J.; Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Student Solutions Manual: To accompany Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Bard, A.J., Faulkner, L.R., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Stradyn, Y.P.; Kadysh, V.P.; Giller, S.A. Polarography of heterocyclic compounds. Chem. Heterocycl. Compounds. 1973, 9, 1435–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
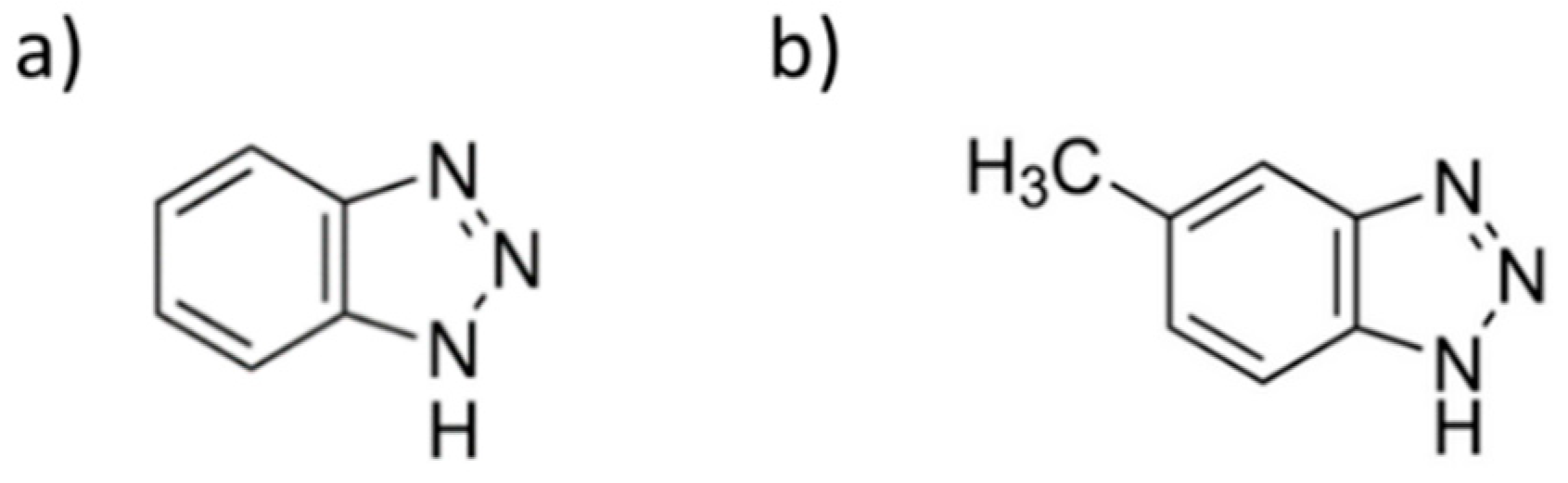
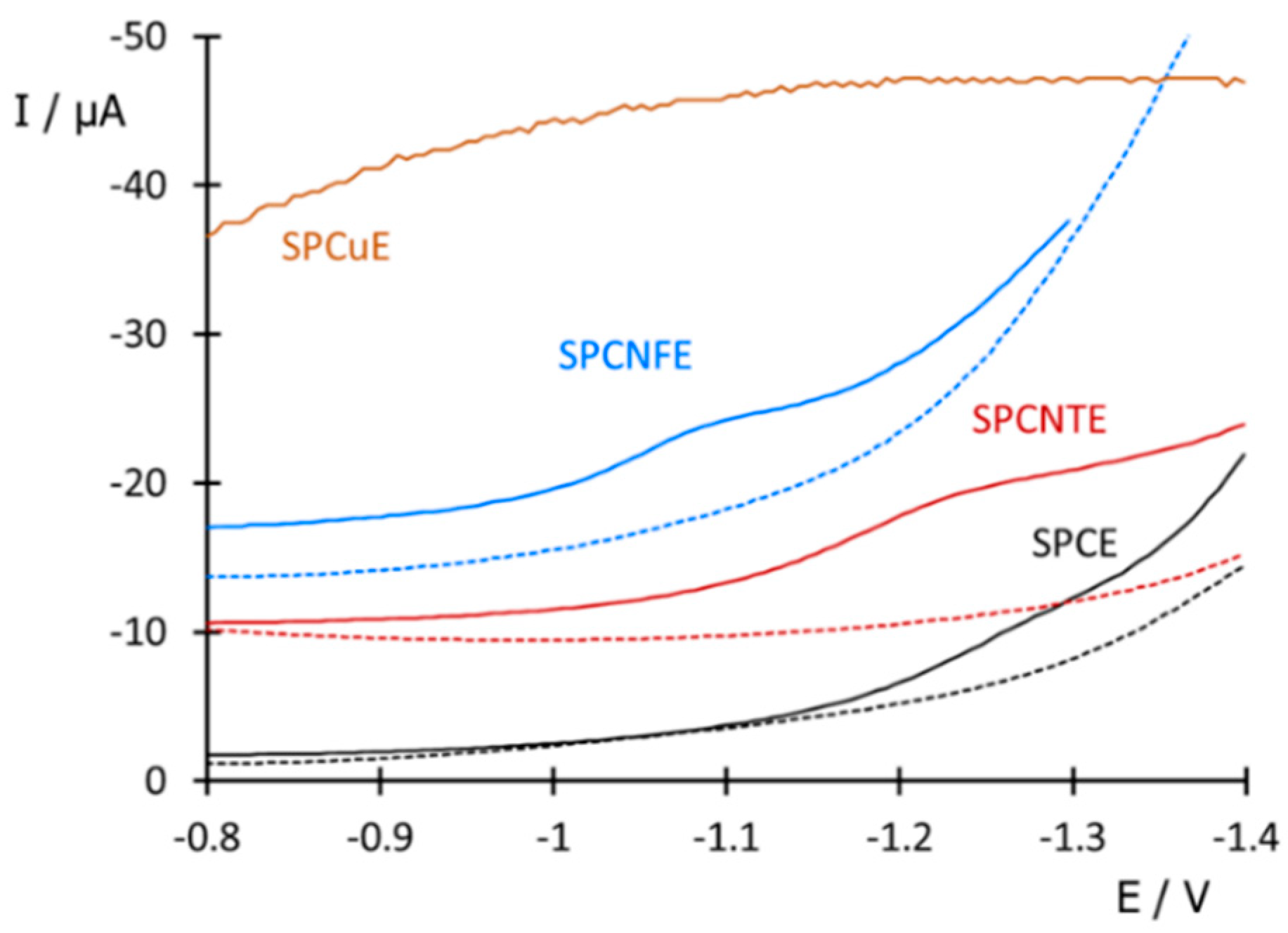
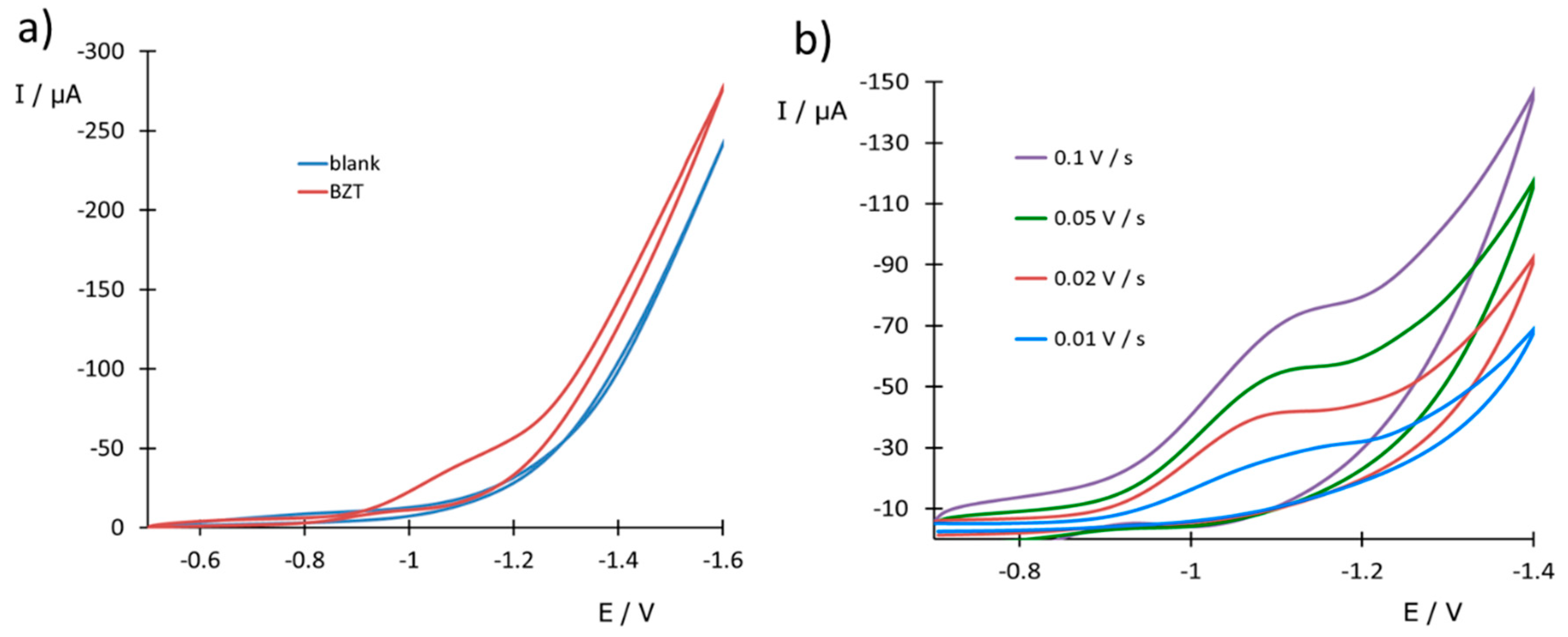

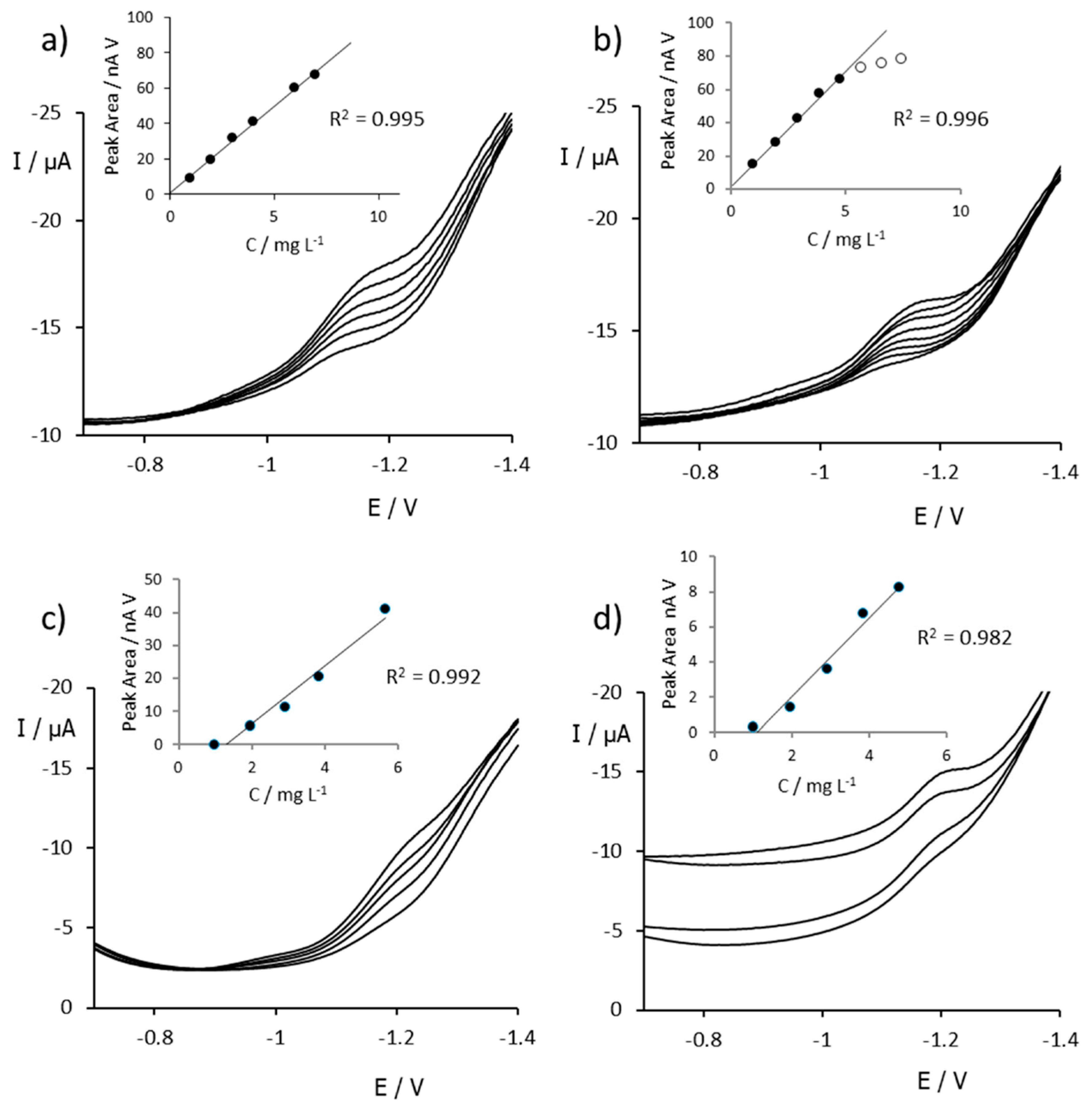

| Electrode /Technique | Analyte | Sensitivity (nA V mg−1 L) | LOD (mg L−1) | LOQ (mg L−1) | Linear Range (mg L−1) | Repeatability (% RSD) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPCNFE/DPV | BZT | 9.8 (0.5) | 0.4 | 1.2 | 1.2–8.0 | 4.3 | This work |
| Me-BZT | 14.6 (0.7) | 0.4 | 1.3 | 1.3–5.0 | 8.0 | This work | |
| SPCNTE/DPV | BZT | 8.7 (0.2) | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.9–6.0 | 6.2 | This work |
| Me-BZT | 11.2 (0.7) | 0.9 | 3.0 | 3.0–5.0 | 13.9 | This work | |
| GCE+CNT +Nafion/SWV | BZT | - | 0.09 | - | 0.4–19.0 | - | [30] |
| SMDE/DPP | Me-BZT | - | 0.05 | - | 0.4–30.0 | [31] |
| R2 | Concentration Spiked (mg L−1) | Concentration Found (mg L−1) | Standard Deviation | Recovery (%) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.990 | 3.0 | 3.3 | 0.1 | 110 | 10 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muschietti, A.; Serrano, N.; Ariño, C.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Díaz-Cruz, J.M. Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Voltammetric Sensing of Benzotriazoles in Water. Sensors 2020, 20, 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20071839
Muschietti A, Serrano N, Ariño C, Díaz-Cruz MS, Díaz-Cruz JM. Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Voltammetric Sensing of Benzotriazoles in Water. Sensors. 2020; 20(7):1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20071839
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuschietti, Alessandra, Núria Serrano, Cristina Ariño, M. Silvia Díaz-Cruz, and José Manuel Díaz-Cruz. 2020. "Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Voltammetric Sensing of Benzotriazoles in Water" Sensors 20, no. 7: 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20071839
APA StyleMuschietti, A., Serrano, N., Ariño, C., Díaz-Cruz, M. S., & Díaz-Cruz, J. M. (2020). Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Voltammetric Sensing of Benzotriazoles in Water. Sensors, 20(7), 1839. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20071839









